CHE311 Laboratory Midterm
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Recrystallization
common strategy for the purification of solid materials
typical recrystallization includes
impure compound is dissolved in a hot solvent
as the solvent cools
the solubility of the compound decreases (compound begins to come out of solution- becomes solid)
common recrystallization solvents include
water, ethanol, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and hexanes
why are the crystals rinsed with ice cold solvent
to remove any residual impurities on the surface
The ideal solvent is one in which the compound being purified is
very soluble at high temperatures (fairly insoluble at lower temperatures)
melting point
the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium
Most organic compounds melt over a range of
2-3 °C AND at low enough temperatures that their melting points can be conveniently determined
What are the two reasons that melting points are determined
to help identify an unknown compound & to indicate a compound's purity
pure compounds tend to have
narrow melting ranges
Adding two compounds together, at some composition there is a minimum melting mixture- this minimum is called the
eutectic point
The fact that impure solids have ___________ melting points than pure solids can be used to identify an ___________________.
lower; unknown compound
unknown mixed with known and melting point drops
known and unknown are NOT identical
unknown mixed with known and melting point does not drop
known and unknown are identical
If impurities are present the compound will exhibit a
lower and broader melting point
is melting point alone enough to identify a compound?
no
impurities disrupt
crystal lattice
these disruptions in the crystal lattice lower the amount of
energy required to melt the solid
percent recovery
(mass recovered [purified]/ initial mass[original]) x 100
Digimelt melting point apparatus
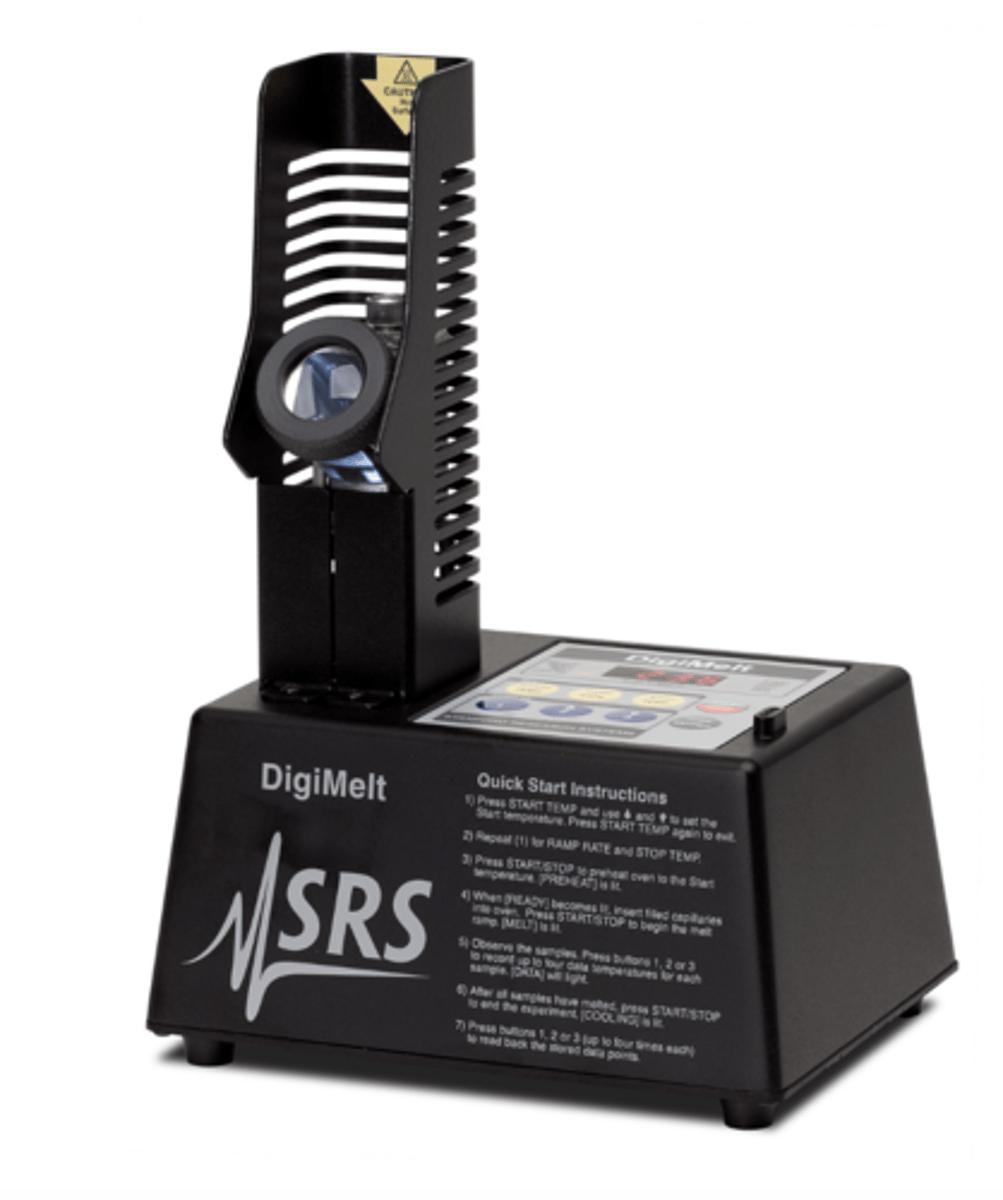

If you successfully removed impurities from your solid, the percent recovery should be less than
100%
Distillation
common technique for the purification of liquids based on differences in boiling point
Separatory funnel

evaporating dish

three-way distillation adaptor
bent distillation adaptor/receiving adaptor

round bottom flasks

magnetic stir bar

graduated cylinder

distillation condenser
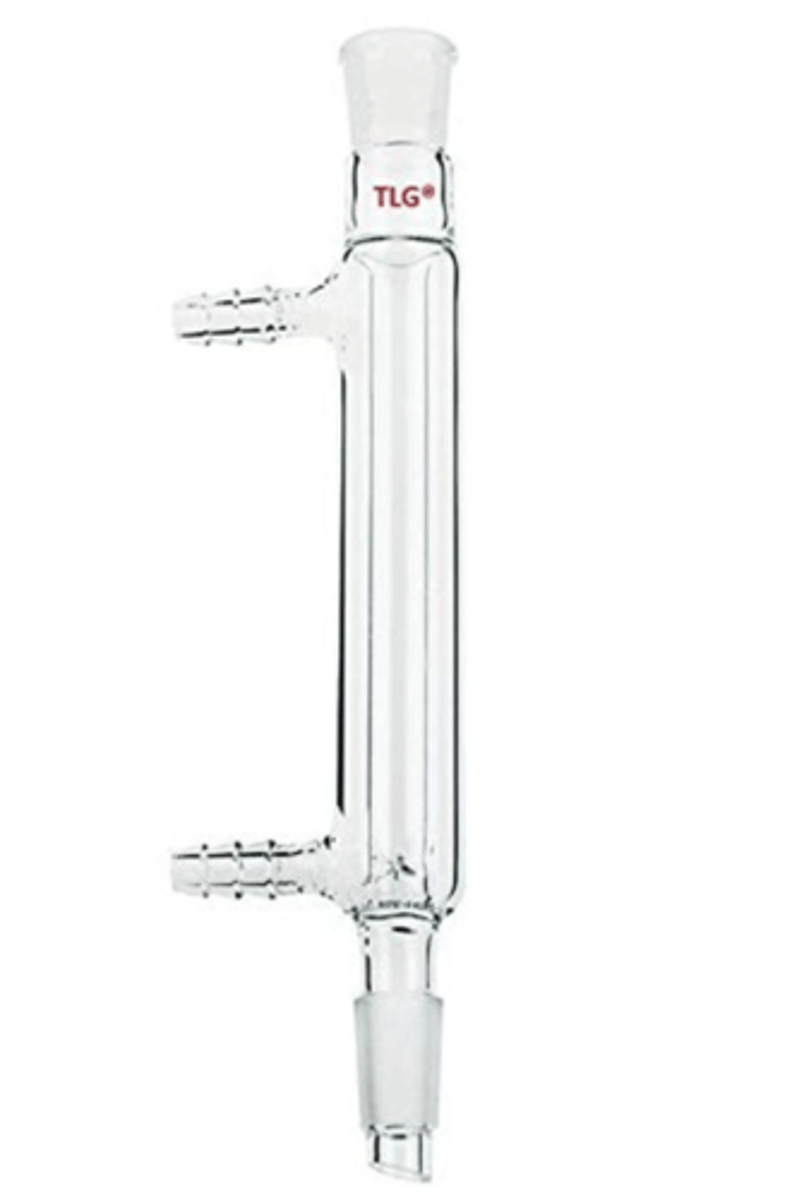

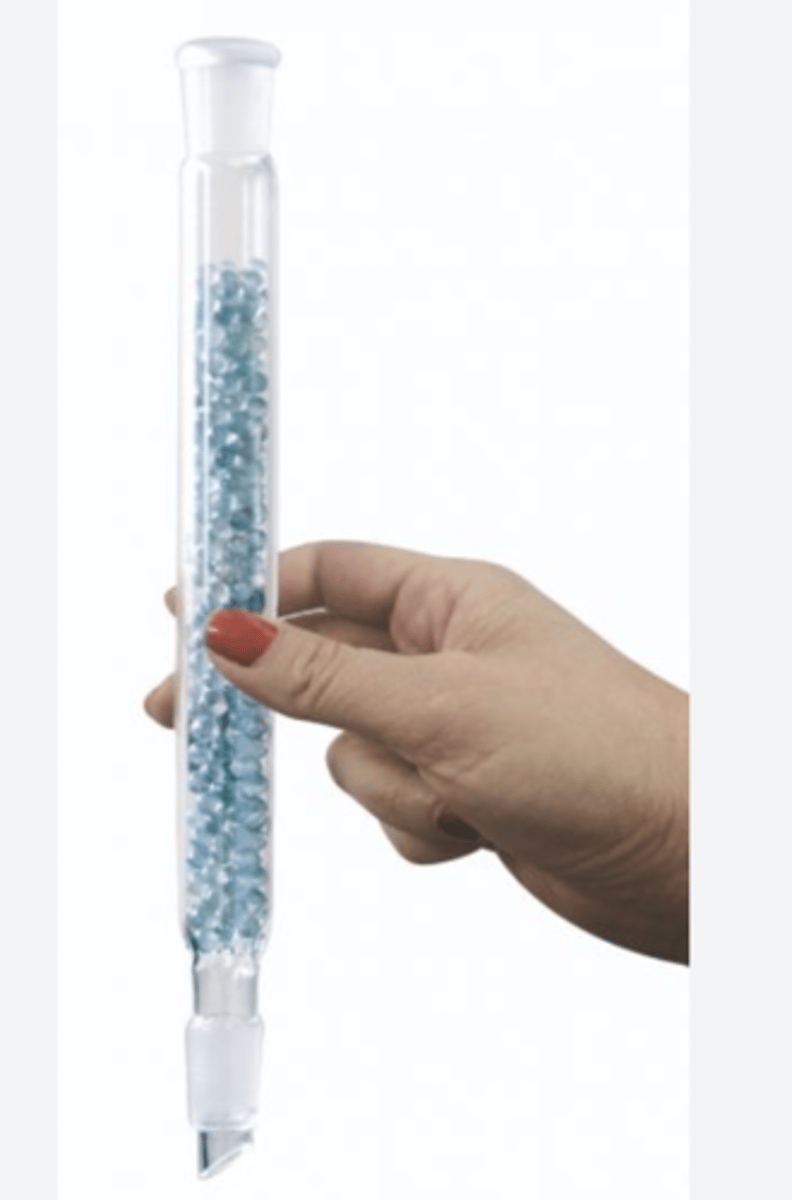
fractionating column

erlenmeyer flask

heating mantle
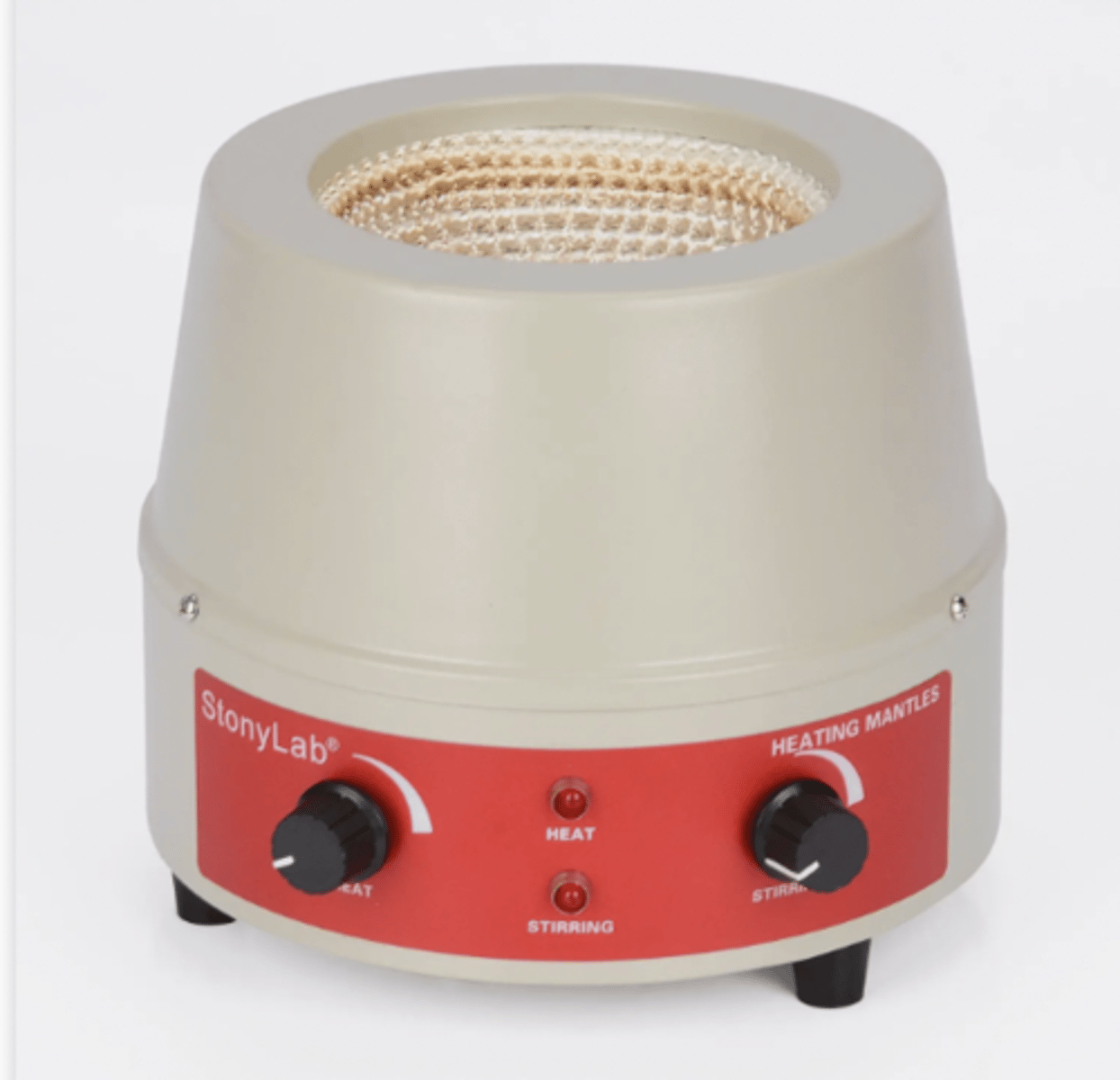

the heating mantle should be plugged into a
voltage controller
analytical balance

balance

rotary evaporator

what is a rotary evaporator used for?
To remove the solvent (similar to vacuum distillation)
convection oven

percent yield
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
dilution
M1V1=M2V2
conversion of mass to volume (or vise versa)
mass (g) = volume (mL) x density (g/mL)
what is the mixed melting point technique?
a small amount of the unknown compound is mixed with the authentic sample, and the melting point of the mixture is measured
if the two compounds are the same, the compound is still pure and
the melting point will stay the same
if the melting point drops
theres an impurity
boiling points of compounds are related to their
vapor pressure
vapor pressure
the pressure exerted by molecules in the gas phase when the gas phase is in equilibrium with the condensed phase
A substance with a higher vapor pressure is said to be more
volatile
vapor pressure changes with temperature, becoming higher at
higher temperatures
A substance's boiling point is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals
atmospheric pressure
more volatile liquids have
lower boiling points
simple distillation
the sample is boiled and the resultant vapor is immediately collected through a condensing column
simple distillations typically doesn't give good separations unless there is a
large difference in boiling points (>50)
a more effective approach is to use
fractional distillation
what is the only difference between simple and fractional distillation
a vertical fractionating column is added
since the fractionating column is packed with beads, it increases the
surface area
like dissolves
like
Polar solvents will dissolve
polar or ionic molecules.
Nonpolar solvents will dissolve
nonpolar molecules
Solubility of solids increases with
temperature
solubility
a measure of how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of solvent
Quantitatively (solubility)
g/mL
Qualitatively (solubility)
soluble, sparingly soluble, insoluble
A good recrystallization solvent
High solubility at elevated temperatures; slight solubility at room temperature
Simple
for mixtures with large differences in their boiling points, usually greater than 50°C
Fractional
for mixtures with closer boiling points
Steam
for compounds that are immiscible with water
Vacuum
for high boiling mixtures or for air sensitive liquids
simple distillation is also useful for when there is a fairly small
amount of impurity
Although simple distillation seems like a simple task, it rarely
produces a pure distillate
A boiling mixture of liquids gives a mixture of gases, and this gas, when it condenses, produces an impure distillate. Therefore, the goal of simple distillation is to
minimize, rather than eliminate, impurities
Adding vacuum will effectively
lower the boiling point of the compound so as to avoid decomposition issues
To determine the boiling point of a compound under vacuum a ___________ is used
nomograph
vaccum distillation is useful when
Liquid or solid has a high boiling point - normal simple or fractional distillation leads to decomposition
Chromatography is the
separation of a mixture of two or more compounds between two phases, one of which is stationary and the other is mobile
If the compound prefers to adhere to the stationary phase
it will take longerto move through the column
If a compound prefers to stay with the mobile phase
it will move through the column quickly
which solvents mixture was used in lab for distillation?
cyclohexane/toluene