Cell Structure and Function
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Cell Theory
all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
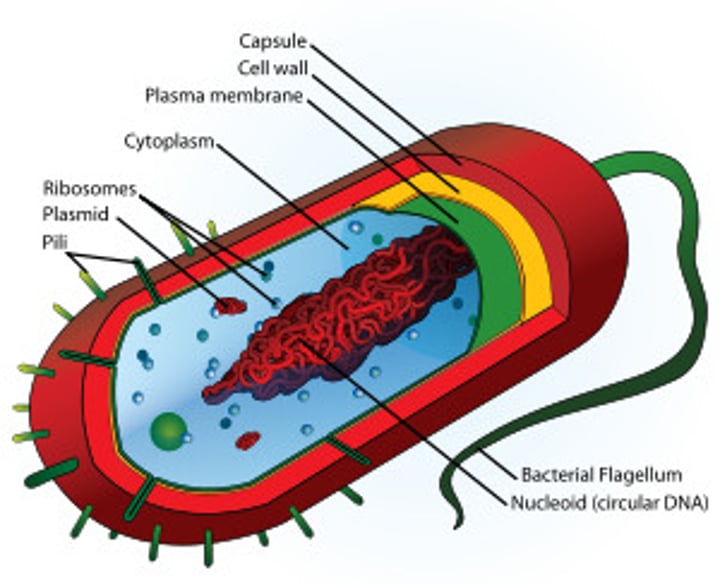
Prokaryote
Bacteria, lacking a nucleus
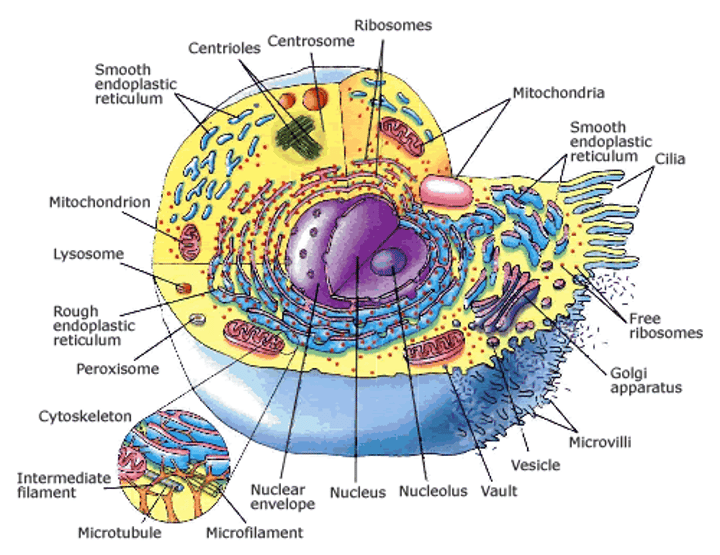
Eukaryote
Plant and animal cells with nuclei and organelles
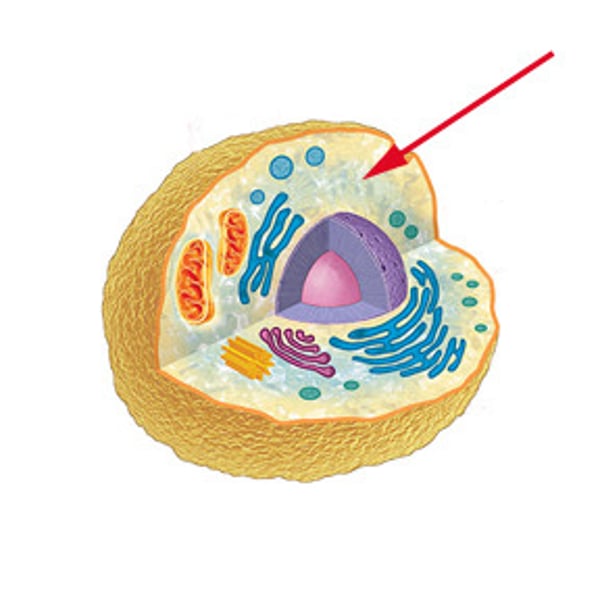
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
Cytoplasm
the portion of the cell outside the nucleus where organelles are suspended
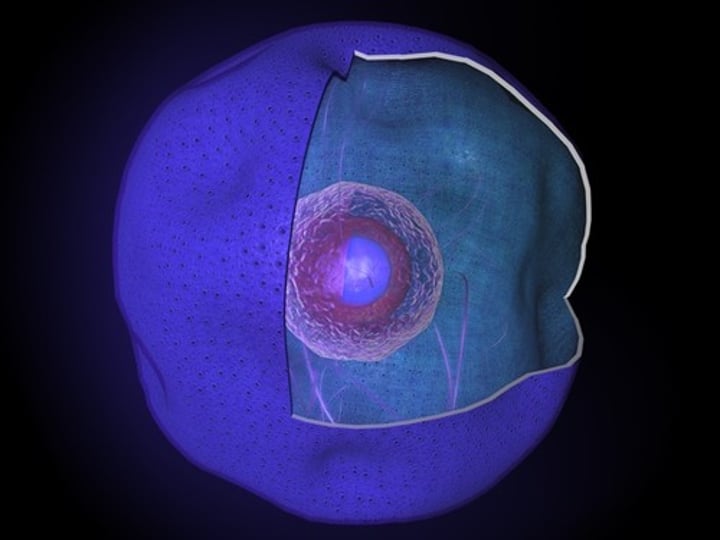
Nucleus
The organelle that contains the DNA and controls the processes of the cell
Ribosome
site of protein synthesis
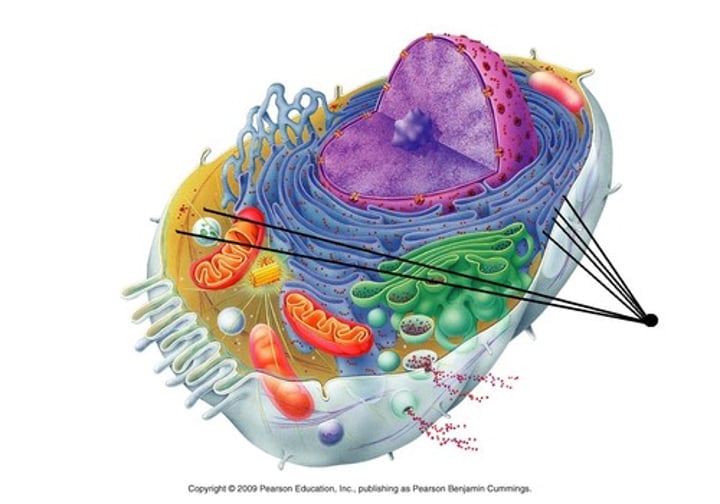
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelle covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
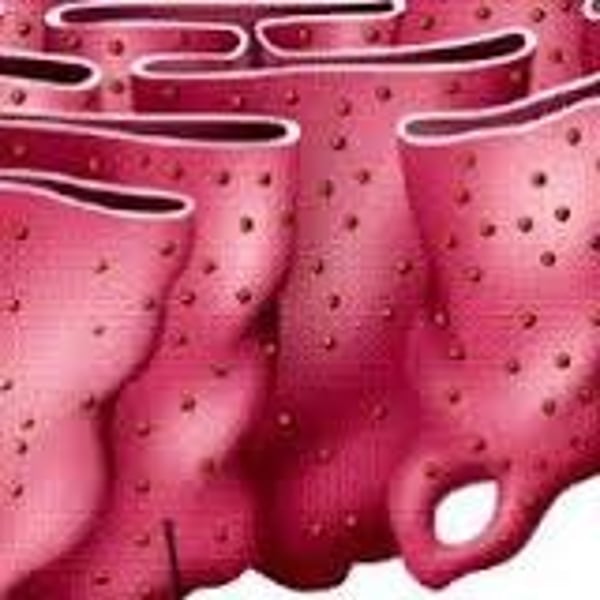
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes lipids
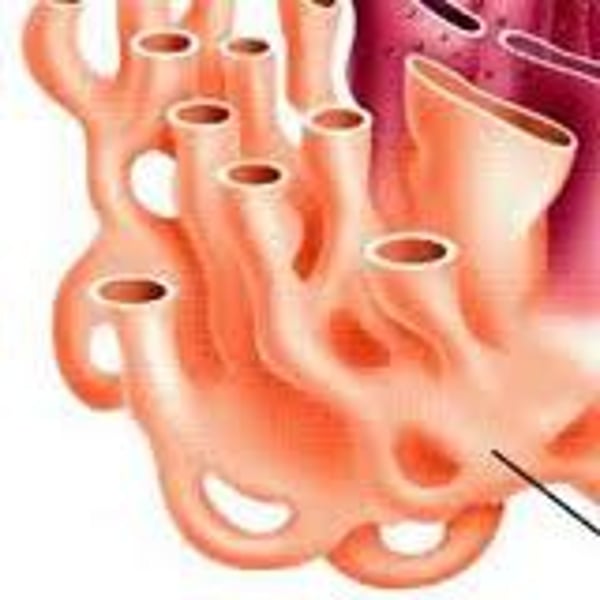
Golgi apparatus
Organelle that modifies and packages proteins for storage or release from the cell

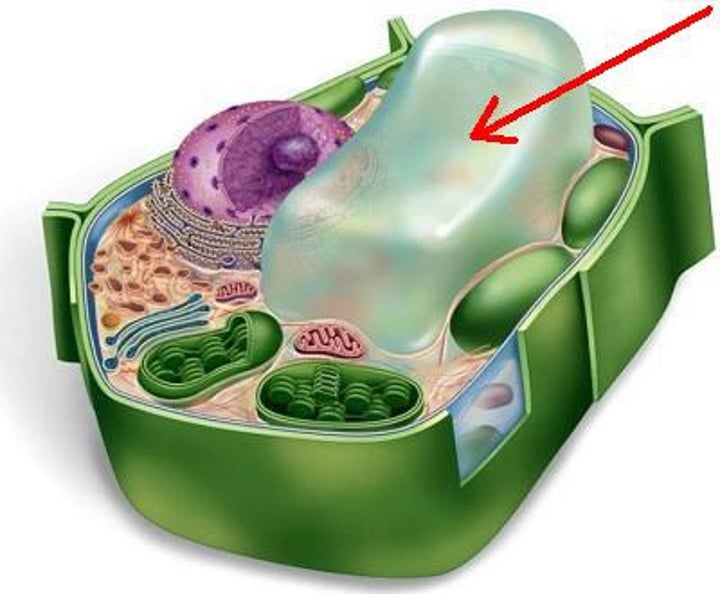
Vacuole
Organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
Vesicle
Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
Lysosomes
Uses chemicals to break down food and worn out cell parts
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
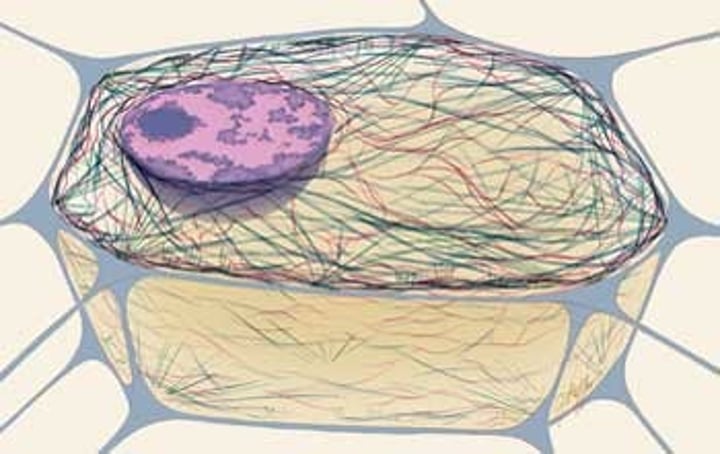
Microfilaments
Fine, threadlike proteins found in the cell's cytoskeleton
Microtubules
Tube-like structure in the cell's cytoskeleton
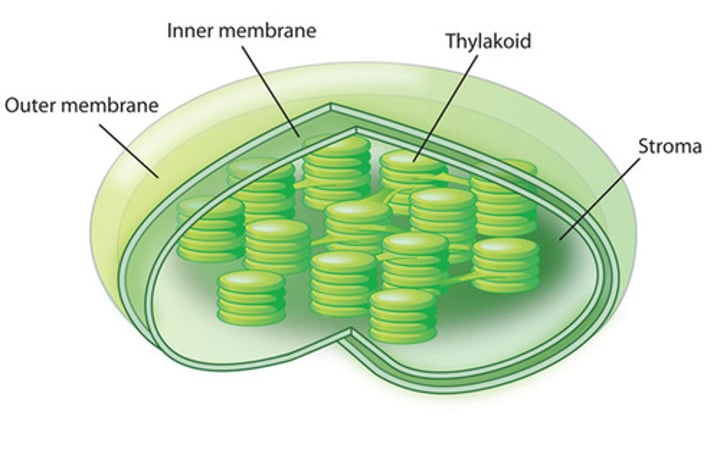
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
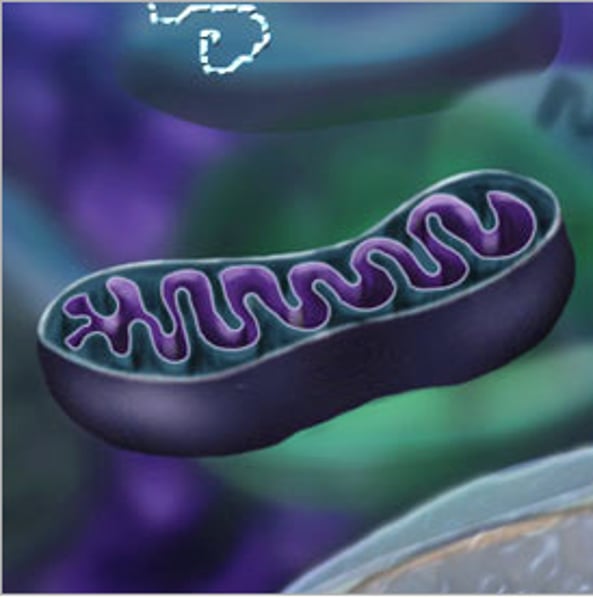
Mitochondria
Convert chemical energy stored in sugars to usable compounds
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
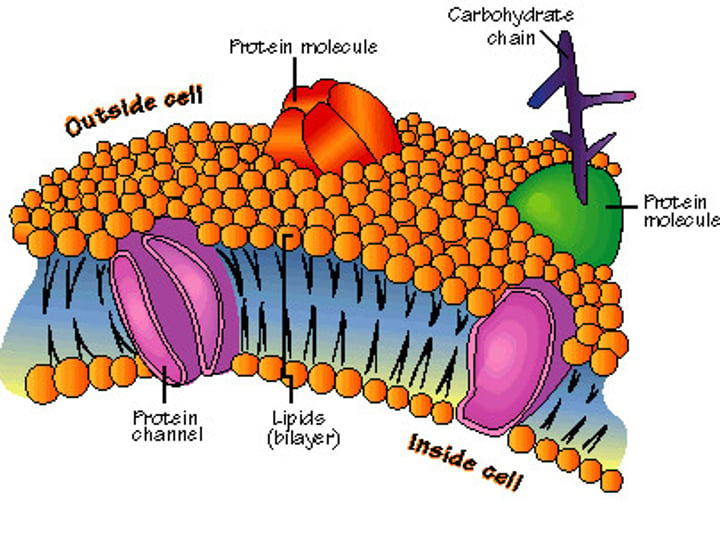
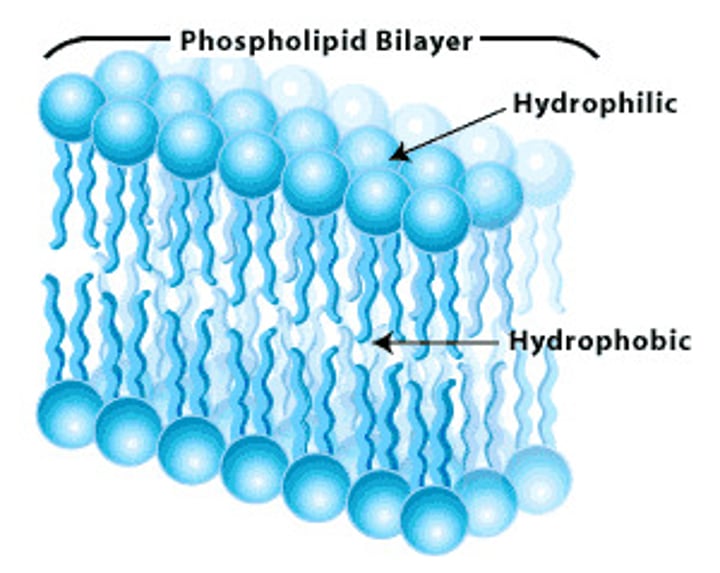
lipid bilayer
makes up cell membrane, hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads
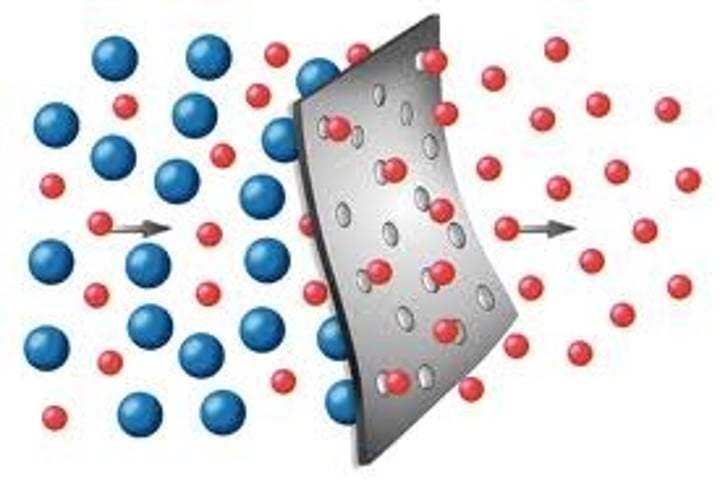
selectively permeable
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
the fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
Passive transport
does not require energy
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Osomosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
isotonic
the concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell
hypertonic
the solution outside the cell has a higher concentration of solutes
hypotonic
the solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of solutes
cytolysis
cell in hypotonic solution bursts
Active transport
movement against concentration gradient requires energy
Endocytosis
the cell takes in large amounts of material
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Cell specialization
the process in which cells develop in different ways to perform different tasks
Cell
basic unit of structure in life
tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
Organ
Groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function
organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Equilibrium
the amount of solute is the same on either side of the membrane
Surface area of a cell
determines the amount of substances that can enter it from the outside environment, and the amount of waste products that can exit to the environment, the cell membrane
Volume of a cell
determines the rate at which materials are used and waste is created
Cell division
Process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells, cells must divide because SA:V limits their size
Interphase
period of growth and DNA replication in the cell cycle between cell divisions
G1 Phase
stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions
S phase
stage of interphase in which DNA replication
G2 phase
stage of interphase in which the cell prepares for mitosis
mitosis
Cell cycle phase in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells
cytokinesis
completes the process of cell division
Cyclin
a protein that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
Van Leeuwenhoek
First to see organisms under a microscope
Virchow
Proposed that all cells come from other cells
Schleiden
concluded that all plants are made of cells
Schwann
concluded that all animals are made of cells
Aquaporins
channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water