Lecture 10: the early embryo and formation of the neural tube
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what is neurulation?
when the notochord induces neuroectoderm to differentiate into the neural plate
fates of the neural plate
wide cranial end-->brain
narrow caudal end-->spinal corod
what is the neural groove?
invagination of neural plate along the central axis around day 18
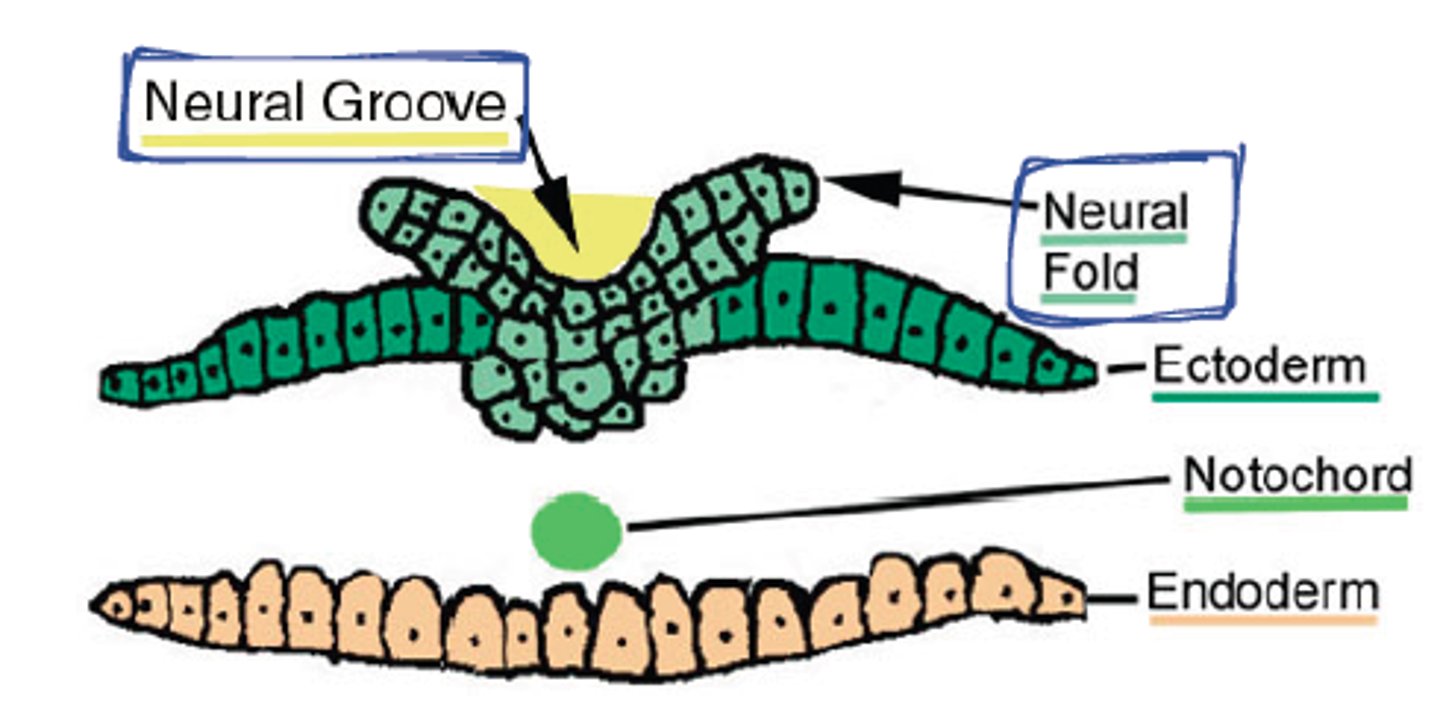
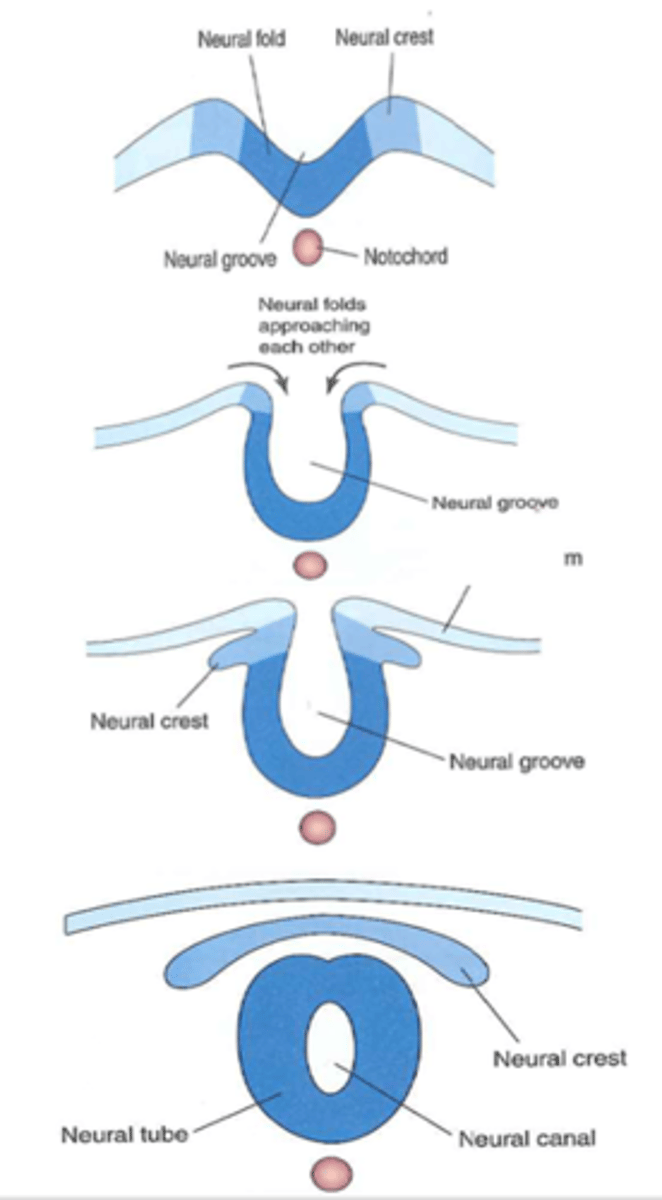
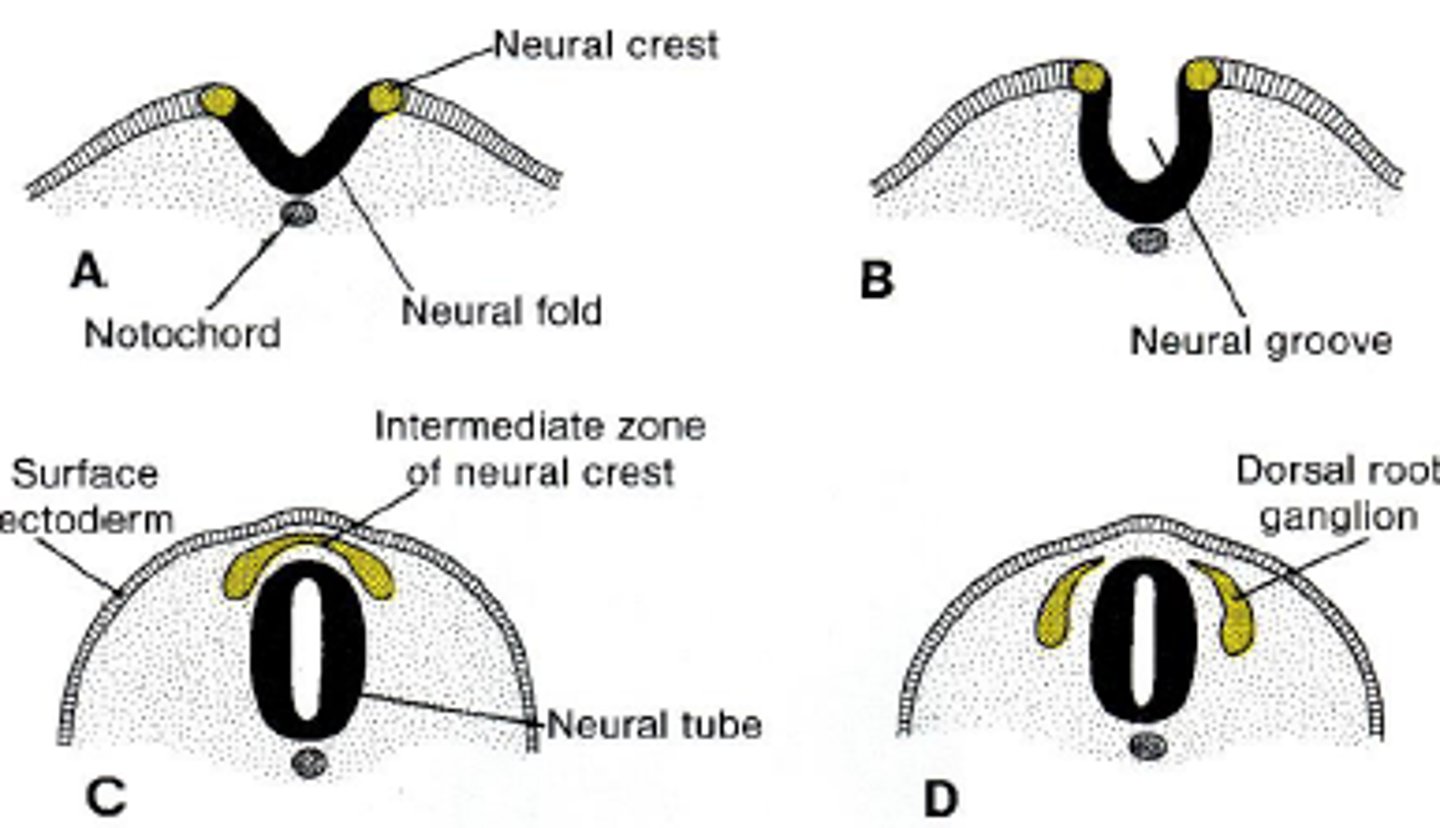
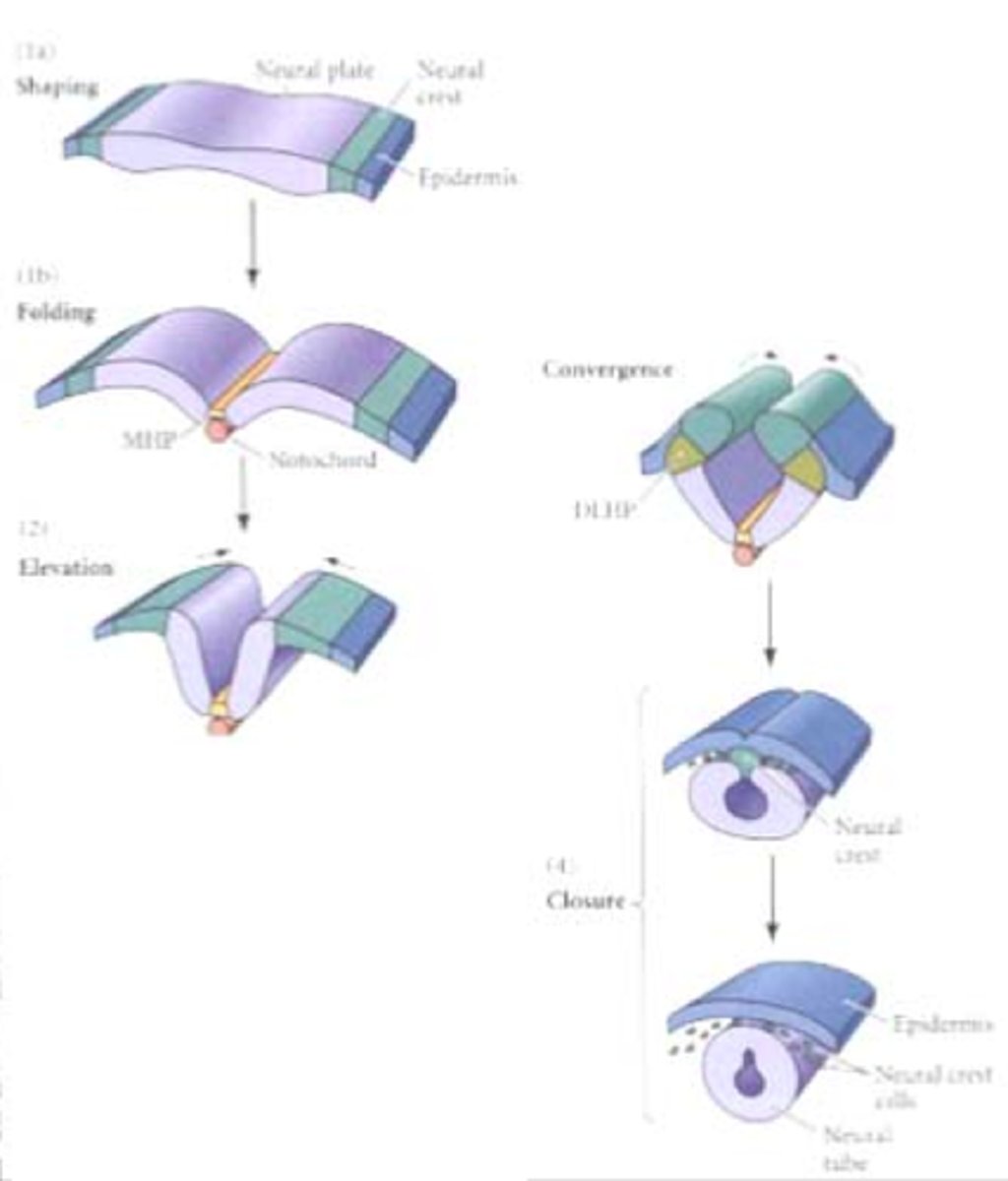
Neural tube formation
Signals from the notochord trigger reorganization of the dorsal ectodermal cells leading the neural tube formation
-neural folds approach each other forming the neural groove
-neural crest forms
-neural tube with a canal breaks off of neural crest
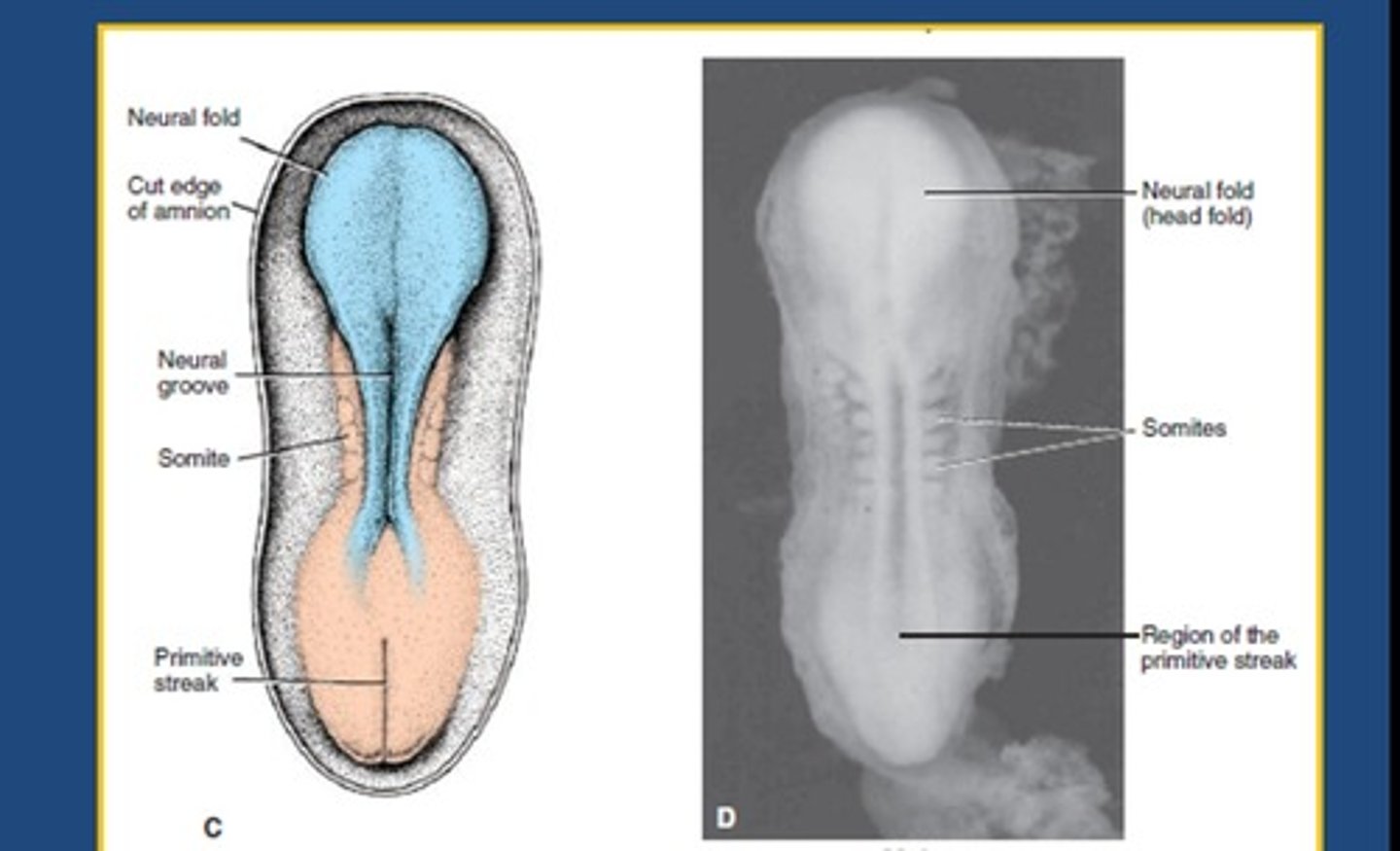
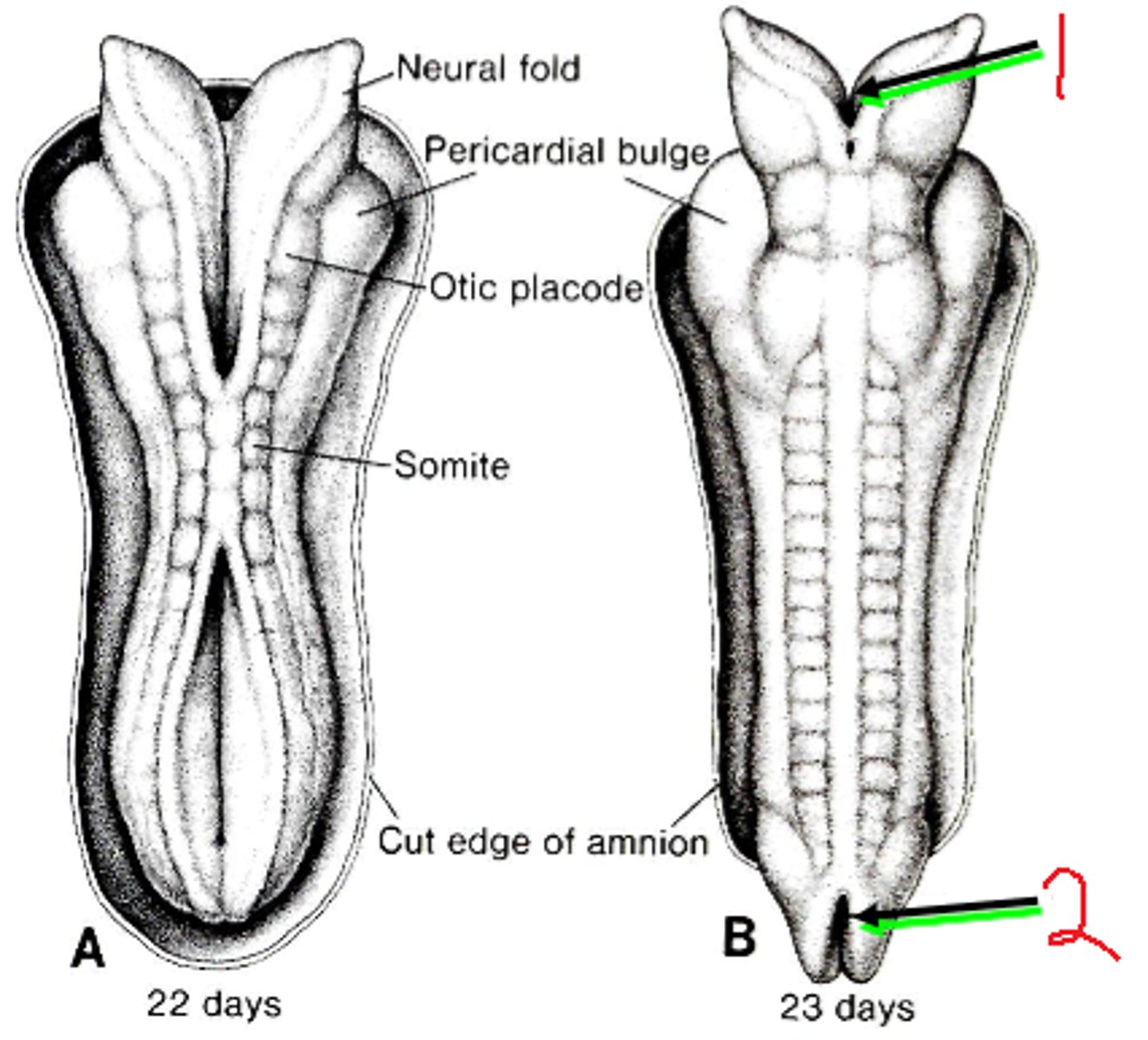
Day 20 of neural tube formation
-fusion of neural tube begins in cervical region
-fusion moves both cranially and caudally
day 25 of neural tube formation
cranial neuropore closes
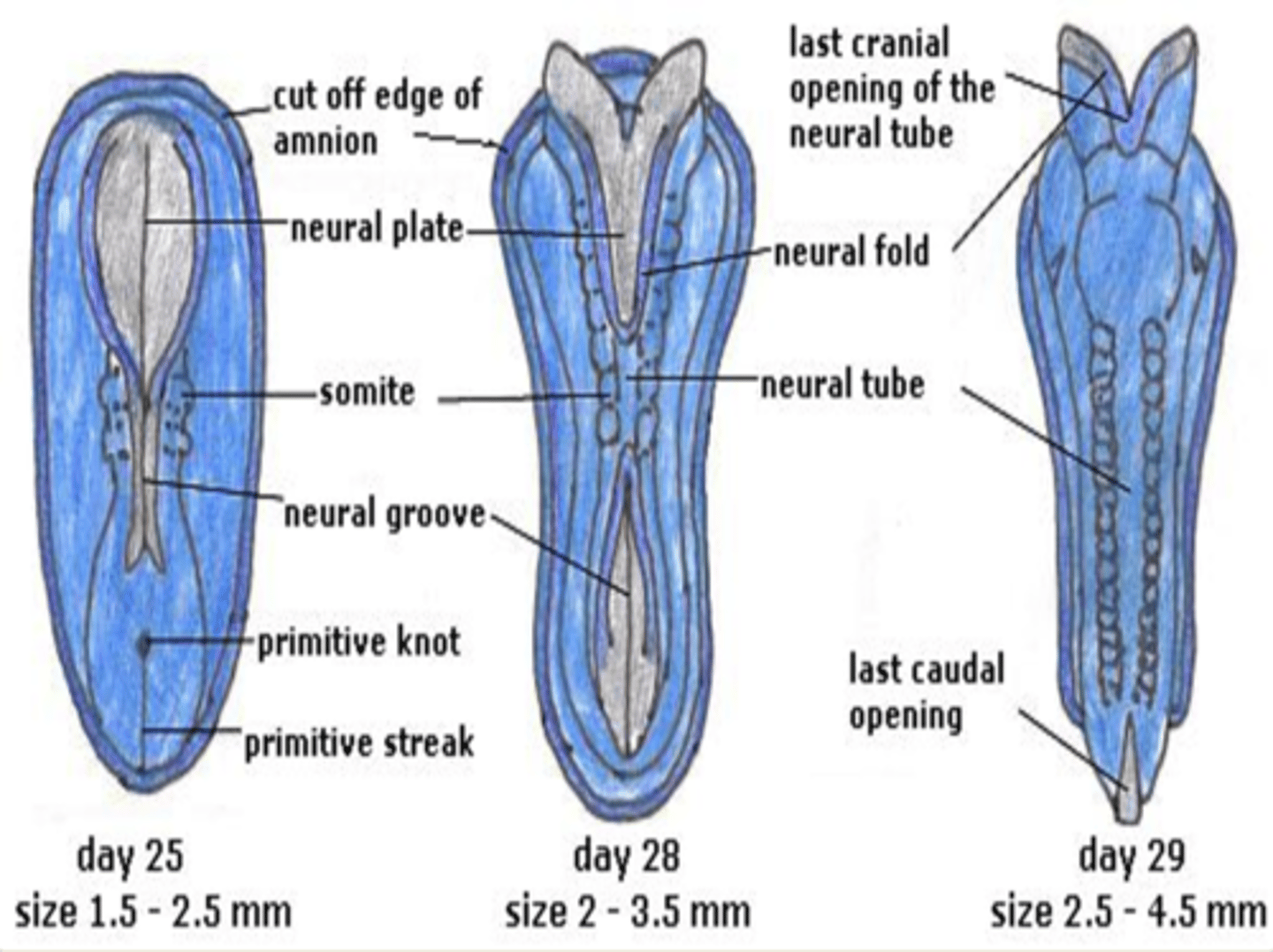
day 27 of neural tube formation
caudal neuropore closes
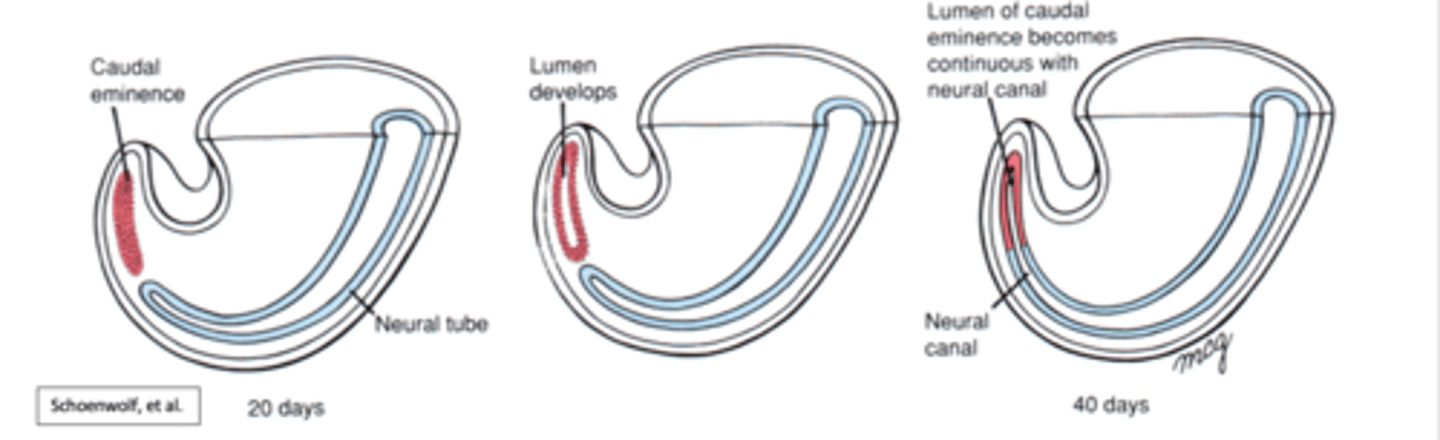
the sacral and coccygeal portions of spinal cord develop from
mesoderm
secondary neurulation
the cells of the neural plate form a cord-like structure that migrates inside the embryo and hollows to form the tube
-at more cranial levles, mesodermal tissue condenses to form caudal eminence
What are neural crest cells?
Appearing at the end of Neurulation, the Neural Crest Cells form from Neurectoderm and can later become Neural Crest Mesenchyme.
-migrate throughout the entire body
Migration pathways of neural crest cells
-sensory ganglia formation
-autonomic ganglia and enteric nerve plexus formation
-suprarenal medulla formation
-form non neural tissues
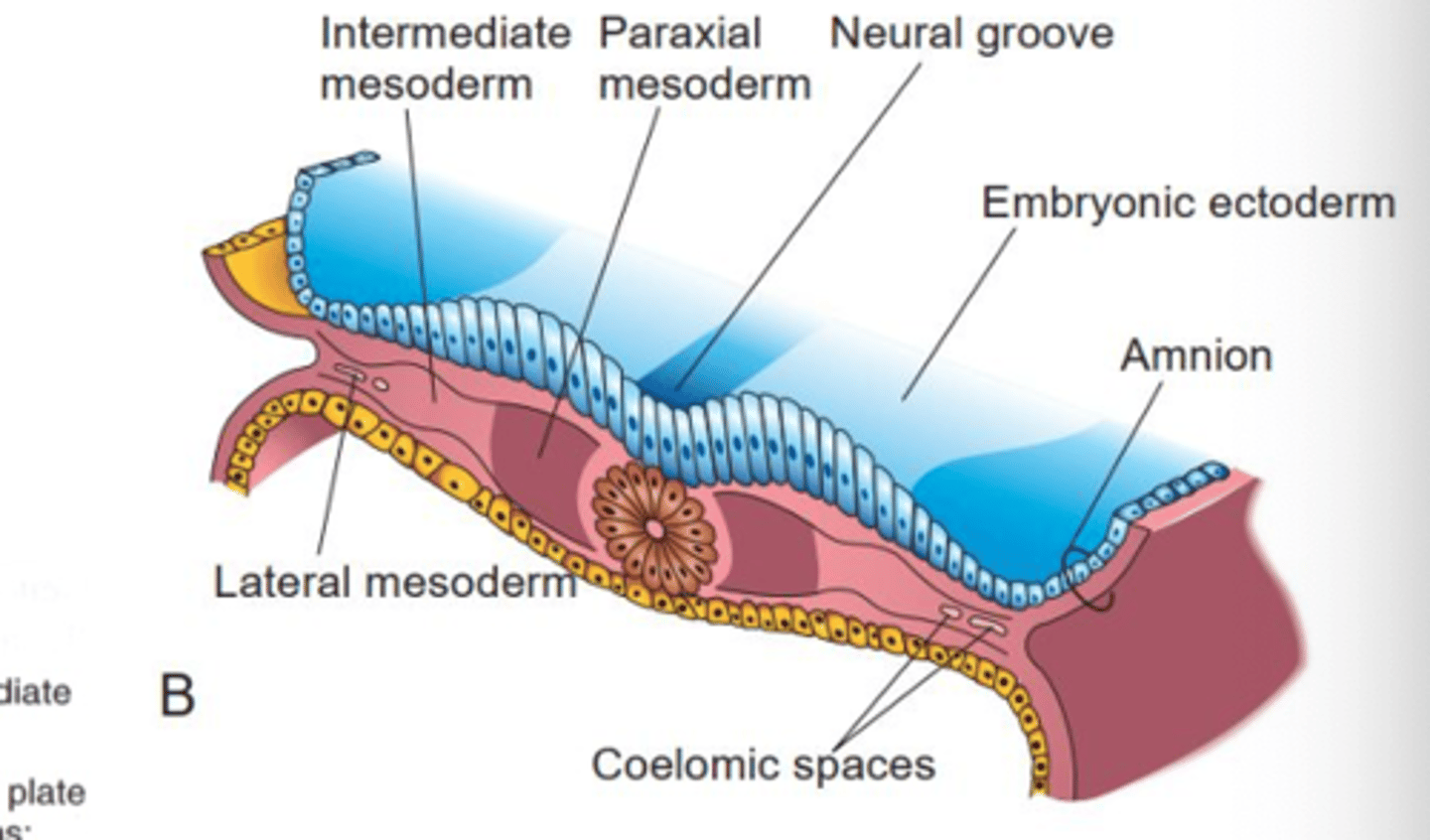
notochord induces mesoderm to differentiate based on
distance!
paraxial, intermediate, and lateral mesoderm
What are somitomeres?
Small derivatives of the paraxial mesoderm resembling paired blocks that ultimately migrate to the pharyngeal arches and to the face.
-will further differentiate into somites
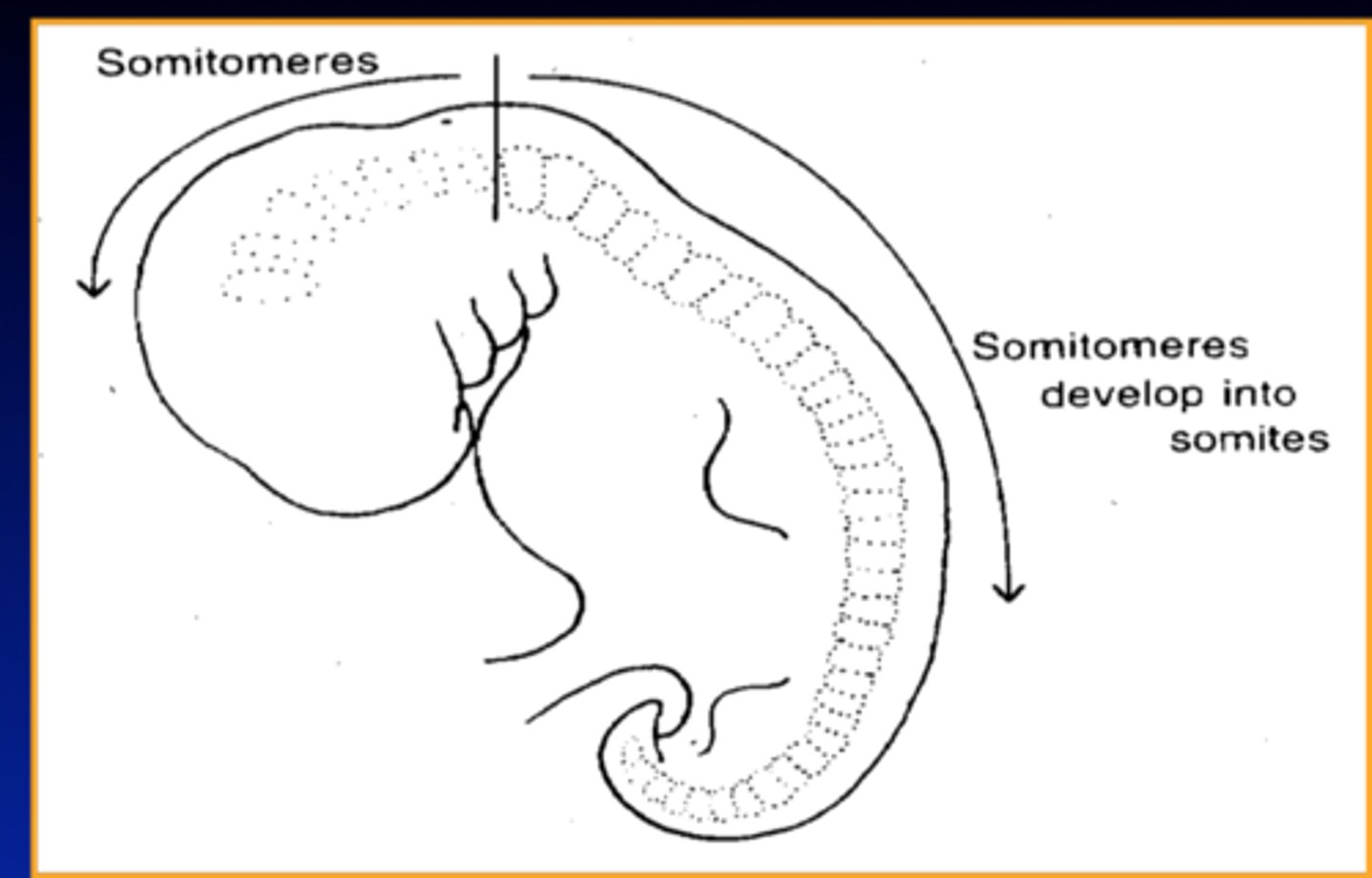
What are somites?
segmented blocks of tissue that later differentiate into vertebrae, ribs, and skeletal muscles
-we develop aboout 42-44 pairs, some degenerate
at what week do we form somites?
at day 20 through the end of week 5
what is the segmentation clock
The synchronised molecular feedback loops within groups of cells that regulate the timing of segment formation during development.
-cyclical expression of cell signaling and growth factor genes
signaling in the segmentation clock
-negative feedback loop
-utilizes notch pathway, fibroblsat growth factor and WNT
what inhibits somite production?
high levels of fibroblast growth factor and WNT from segmentation clock
somites are regionally specialized based on
HOX genes
what is HOX gene expression controlled by?
-retinoic acid (synthesized in somites creating a concentration gradient)
-Fgf
-WNT
expression of HOX genes corresponds to
segmentation clock
-HOX genes establish somite identity
what induces somite differentiation?
-notochord secretes sonic hedgehog, inducing somite to differentiate into sclerotome
-sclerotome will form cartilage and bone of vertebral column
how does WNT contribute to somite differentiation?
WNT induces production of PAX3
-delineates dermomyotome from sclerotome, form myotome
-myotome forms epaxial muscles
differentiation of ventrolateral dermomyotome
-responds to WNT and BMP4
-forms ventrolateral cluster of myotomoe cells, hypaxial muscles
embryonic formation of dermatomes and myotomes
neural crest sensory nerve and motor component of spinal nerve linked within somite, continues as the embryo grows
the intermediate mesoderm forms
urogenital ridge, which will form the urinary and reproductive systems
the lateral plate mesoderm splits into
somatic mesoderm and splanchnic mesoderm
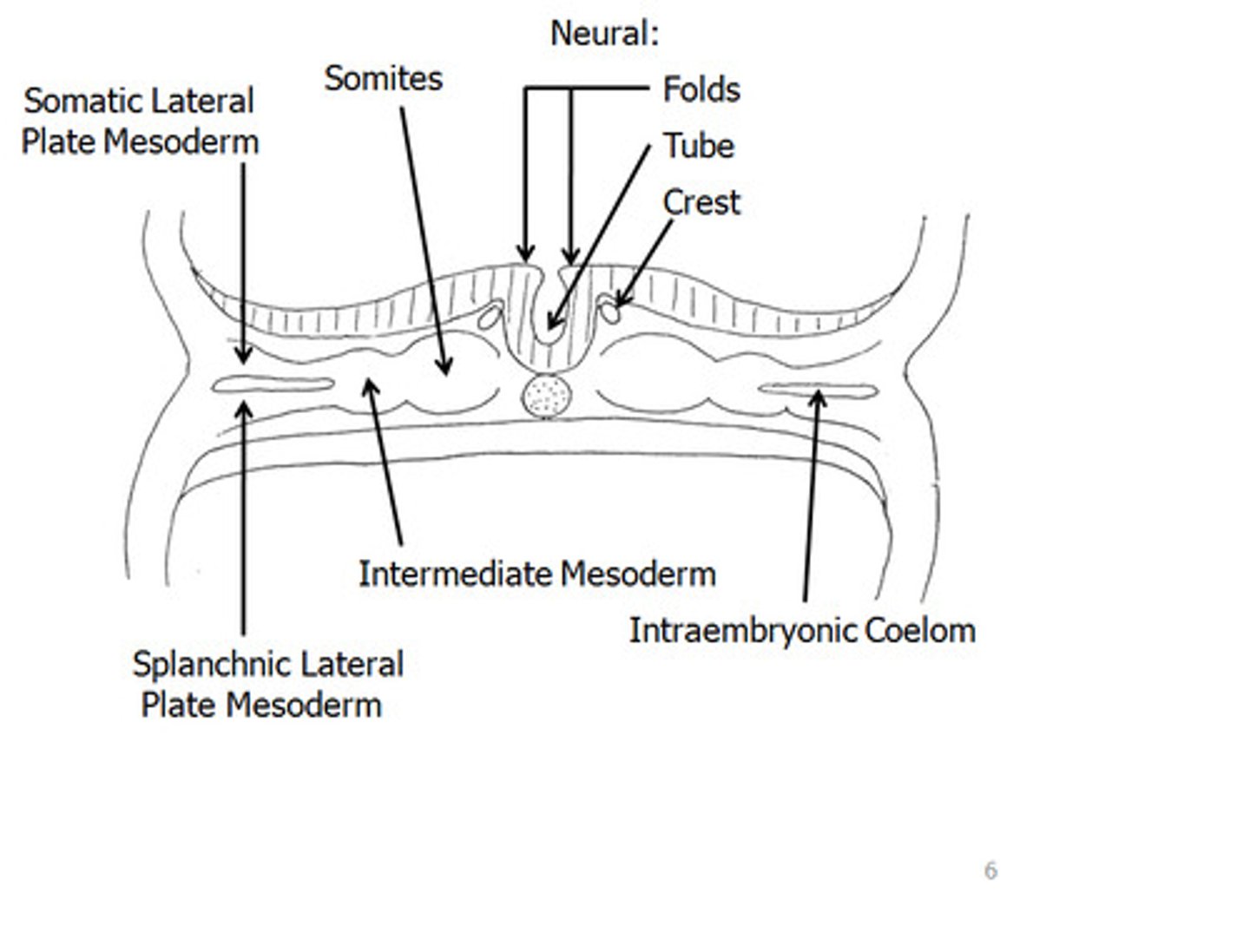
somatic lateral plate mesoderm
-covers the amnion
-will form the dermis of the ventrolateral body wall, hypodermis, and skeletal components of limbs
splanchnic lateral plate mesoderm
-covers the yolk sac
-will form smooth muscles and connective tissue of organs and most of heart
neural tube defects
-common congenital anomaly
-defect of cranial neuropore=anencephaly
-defect of caudal neuropore=spina bifida
diagnosing neural tube defects
by visualization prenatally or increase of a-fetoprotein in the CSF
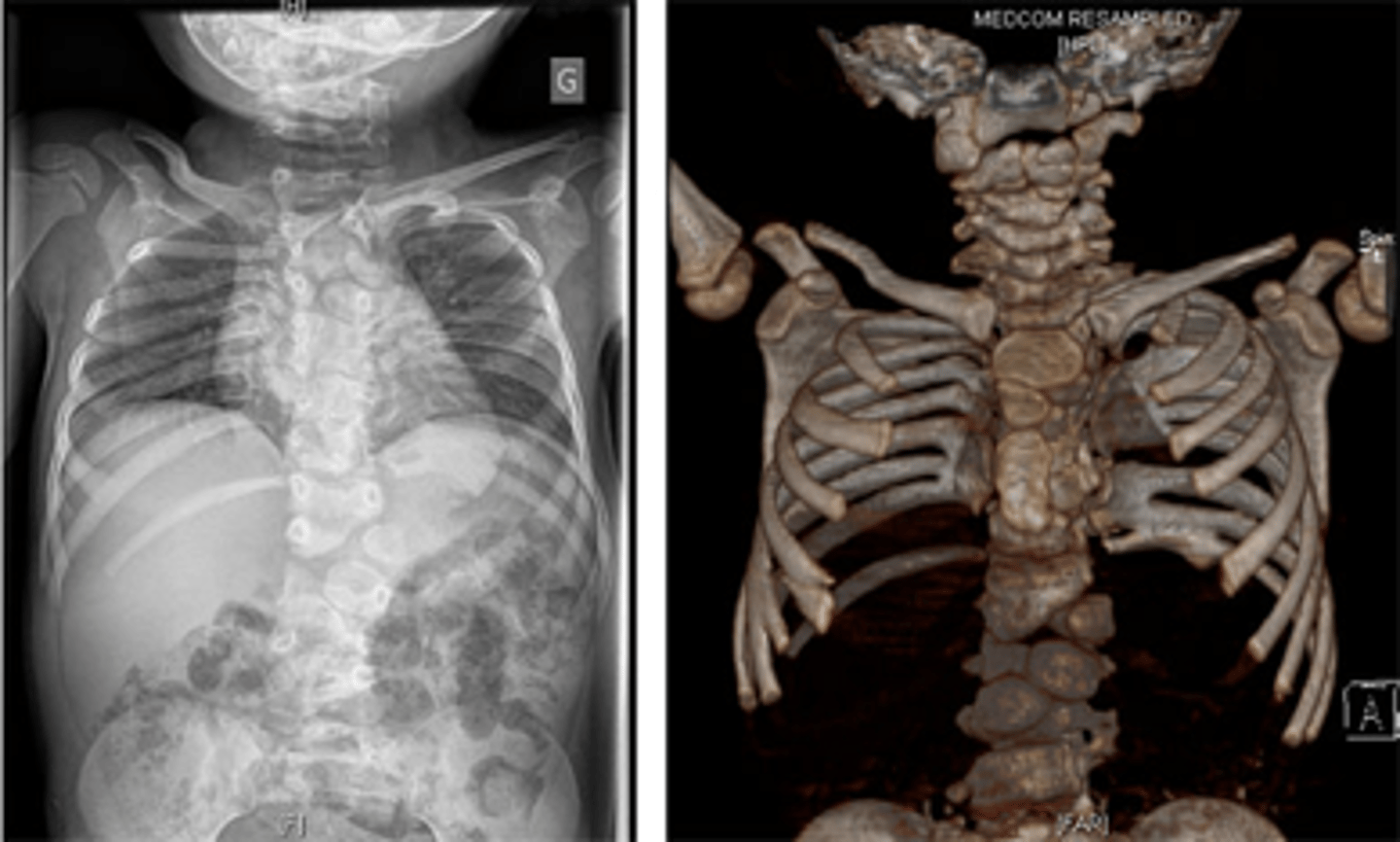
Spondylocostal dysostosis
-rare, heritable disorder
-widespread malformation of the vertebral column and ribs
-mutations in genes that code for proteins in segmentation clock
when is the neural groove formed?
neural plate invaginates along central axis around day 18
non neural tissues derived from neural crest tissue
-pigment cells, pharyngeal arch cartilages
head mesenchyme and connective tissue
-bulbar and conal ridges in heart
HOX gene expression are controlled by
-retinoic acid
-Fgf
-Wnt
what secretes sonic hedgehog?
notochord
how does the neural plate form?
the notochord induces neuroectoderm to differentiate into neural plate
what structures are derived from neural crest tissue?
-sensory and autonomic ganglia
-suprarenal medulla
-pharyngeal arches
lateral mesoderm splits into
somatic and splanchnic mesoderm
what covers the amnion?
parietal lateral mesoderm
what covers the yolk sac?
visceral lateral mesoderm
FGF and WNT in somite formation
-inhibit somite production when concentration is too high
Retinoic Acid (RA) on HOX genes
-controls expression
-creates concentration on either side of somites
Sclerotome (somite)
-from ventrolateral somite, forms cartilage of bone and vertebral column
describe the formation of myotome
-WNT from dorsal neural tube induces production oof PAX3
-delineates dermomyotome from sclerotome-->myotomoe
-forms epaxial muscles