MedChem Sulfonamides
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Antibiotic
A microbial metabolic product that kills or inhibits growth of another microorganism.
penicillins, cephalosporins, vancomycin
Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis
tetracyclines, oxazolidinones, chloramphenicol
Antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis
fluoroquinolones, rifamycins
Antibiotics that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
sulfonamides, isoniazid
Antibiotics classified as antimetabolites
polymyxins, daptomycin
Antibiotics that alter cell membrane function
intrinsic
Term for inherent/natural resistance
acquired
Term for resistance due to alteration of bacterial genome through horizontal and vertical evolution
exclusion
Term to describe resistance due to barrier protection of outer membrane
target modification
Resistance when bacteria changes structure of drug target, reducing sensitivity
efflux
Resistance due to bacteria pumping out drug
enhanced production of the target
Resistance from up-regulated production of key molecules by bacteria
by-pass target
Resistance from bacteria implementing an alternative route to make key molecules
selective
Type of toxicity where an antimicrobial agent is more toxic to a pathogen than to the host
comparative distribution
Differences in distribution of toxicants based on morphology of different organisms
comparative biochemistry
Differences in the presence of metabolic pathways of organisms
comparative cytology
Differences in cell structure and function across organisms
Prontosil
First commercially available antibacterial drug
sulfonamide
Prontosil antibiotic class
dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
MOA of trimethoprim
UTI, burns, ophthalmic infections, rheumatic fever, Crohn’s, UC, AIDS
Uses of sulfonamides
SO2NH2
Sulfonamide structural formula
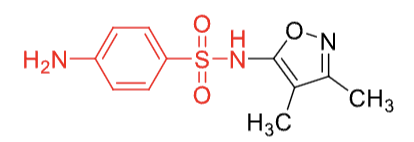
sulfisoxazole
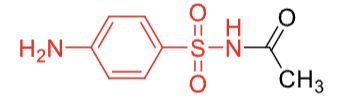
sulfacetamide
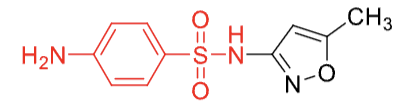
sulfamethoxazole
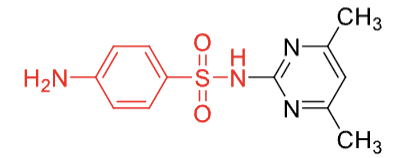
sulfamethazine
urine pH < drug pKa
Why does sulfanilamide cause kidney damage due to crystallization? (think ionization of the acidic drug)
pH= pKa + log (i/u)
Weak ACID Henderson Hasselbalch equation
pH= pKa + log (u/i)
Weak BASE Henderson Hasselbalch equation
%I= (i/u) / (i/u +1) x 100
% ionization formula
acidic
Are sulfonamides acidic or basic
force fluids, raise urine pH, mix or switch sulfonamides
Methods to increase sulfonamide solubility
essential
Folate coenzymes are ____ to life.
dihydrofolic acid
Bacteria and protozoa form what folic acid derivative?
F
T/F Humans can synthesize folic acid.
F
T/F Bacteria utilize folic acid from their host.
cellular impermeability
Why can’t bacteria utilize folic acid from their host?
dihydropteroate synthase
What enzyme is inhibited by sulfonamides?
competitive
What type of inhibition is seen with sulfonamide activity at the enzyme?
PABA
What is the substrate used by microorganisms to form dihydropteroic acid in folic acid biosynthesis?
4-aminobenzoic acid
What is the IUPAC name for PABA?
dihydrofolate reductase
What enzyme is selectively inhibited by trimethoprim?
T
T/F Trimethoprim is selective to the bacterial enzyme, but can still inhibit the human enzyme at high concentration?
dihydrofolic acid
In humans, folic acid is converted to what product by folate reductase?
tetrahydrofolic acid
FAH2 is converted to what product by dihydrofolate reductase?
bacteriostatic
Are sulfonamides bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
bacteriostatic
Term for an antibiotic that prevents the growth and reproduction of bacteria
bactericidal
Term for an antibiotic that kills bacteria
both
Do sulfonamides have gram positive/negative/both activity?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What species are intrinsically resistant to sulfonamides?
PABA
What product has enhanced production during bacterial resistance to sulfonamides?
acquired
Resistance due to R-factor plasmid gene transfer in bacteria is an example of what type of resistance to sulfonamides?
target modification
Alteration of binding affinity to pathway enzymes is an example of what kind of bacterial resistance to sulfonamides?
sulfone
N1 substitution with what molecule will have activity maintained in sulfonamides?
F
T/F Sulfonamide activity will be maintained with N1 disubstitution.
EWG
Will N1 substitution with a EWG or a EDG increase activity in sulfonamides?
6.7-7.4
What is the range of pKa values that have maximum antibacterial effect in sulfonamides?
hypersensitivity
What type of reaction includes Stevens-Johnson syndrome, skin eruptions, allergic myocarditis, photosensitization with sulfonamides?
hematologic
What type of reaction to sulfonamides includes agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia.
crystalluria
What side effect with sulfonamides may occur due to inadequate fluid intake?
free form
Are free form or protein bound fractions active?
increased lipid solubility
What causes an increase in protein binding of sulfonamides?
sulfacetamide sodium, sulfisoxazole diolamine
Sulfonamides used for ophthalmic infections
silver sulfadiazine, mafenide acetate
Sulfonamides used for burn therapy
sulfasalazine
Nonabsorbable sulfonamide used for Crohn’s and IBD