PMI Exam 1
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
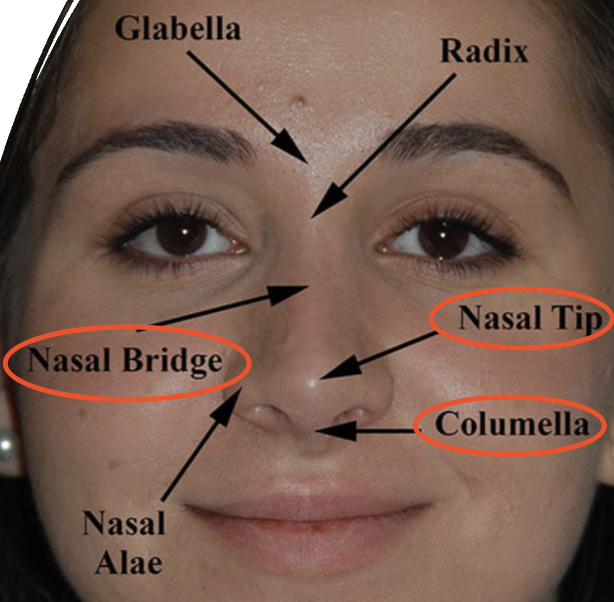
Location of Nasal Bridge, Nasal Tip, and Columella
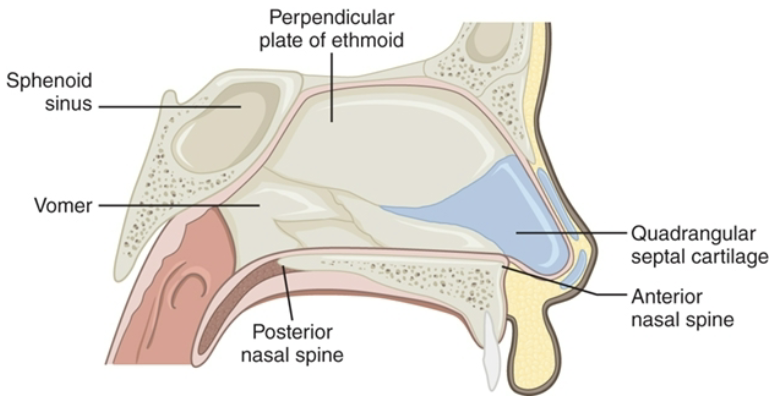
Nasal Septum Anatomy
Quadrangle septal cartilage
Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
Vomer
Vomer
perpendicular structure that fits in median palatine suture groove
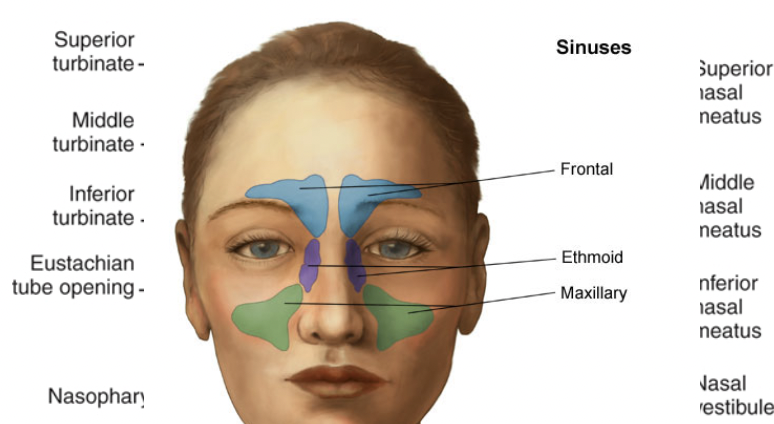
Turbinates and Meatuses
Superior, middle, inferior turbinates: sense of smell (mountains)
Superior, middle, inferior meatuses (valleys)
Paranasal sinuses
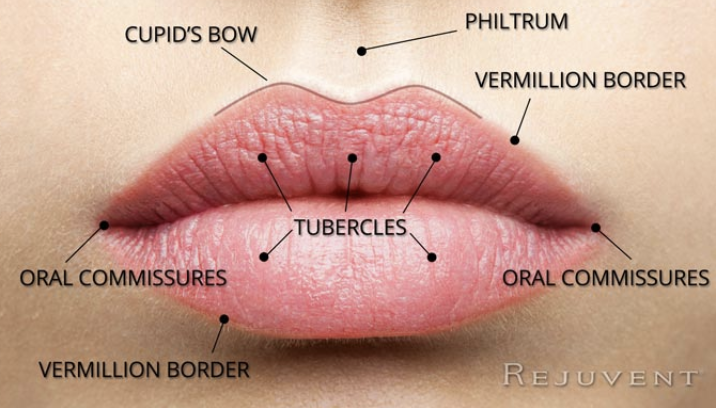
Lip Anatomy
Cupid’s Bow
Philtrum
Vermillion Border
Tubercles
Oral commissures
What is the muscle that surrounds the mouth?
Orbicularis oris

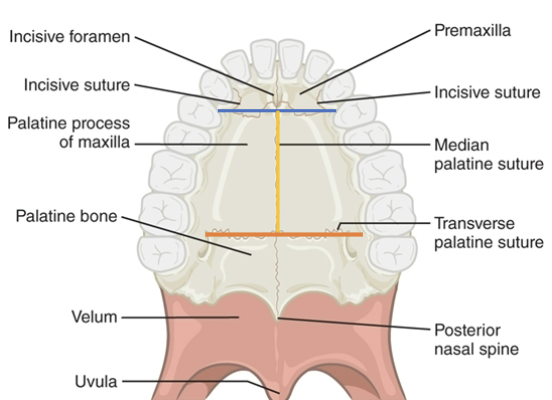
Hard palate anatomy: premaxilla
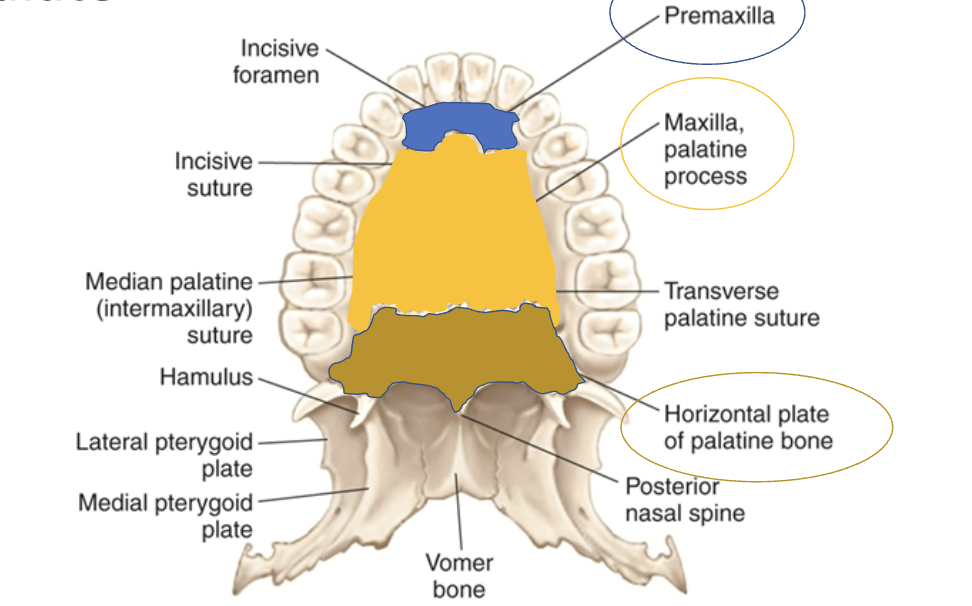

Hard palate anatomy: Maxilla, palatine process

Hard palate anatomy: Horizontal plate of palatine bone
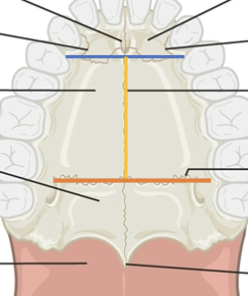
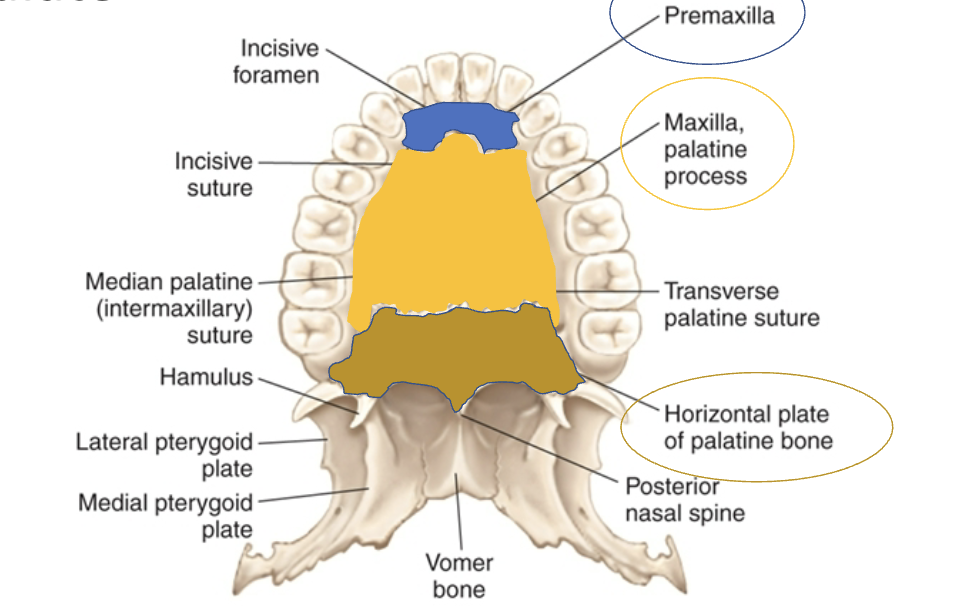
Hard palate suture anatomy: incisive
blue line
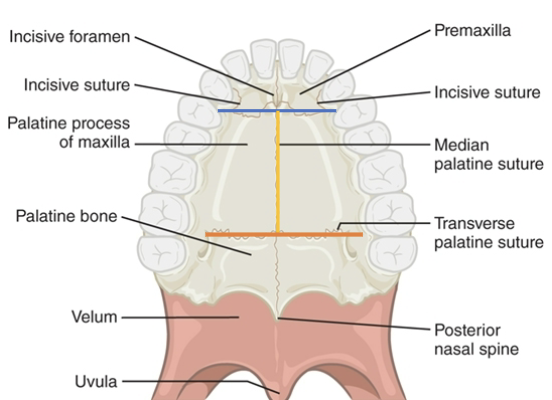
Hard palate suture anatomy: median palatine
yellow line
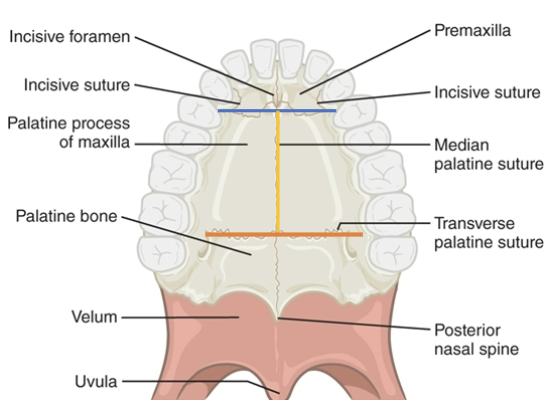
Hard palate suture anatomy: transverse palatine
orange line
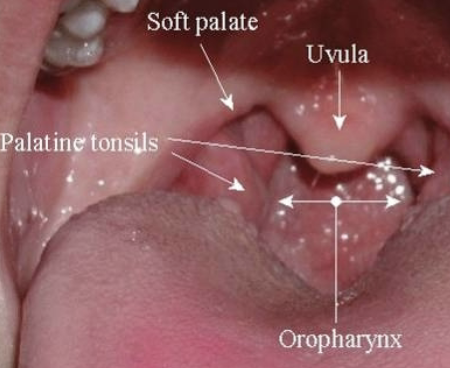
Soft Palate anatomy: uvula
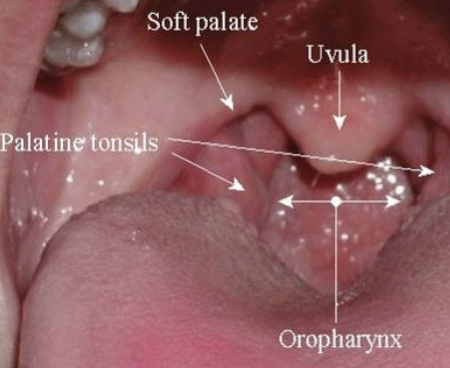
Soft Palate anatomy: palatine tonsils
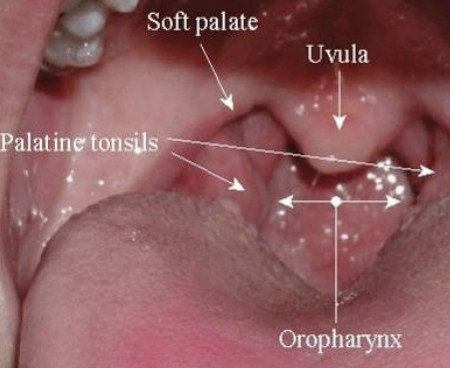
Soft Palate anatomy: oropharynx
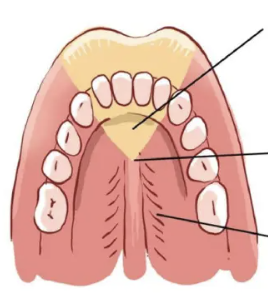
Primary Palate and Secondary Palate Locations
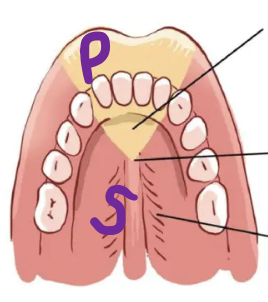
What are the main muscles of the VP valve?
Levator veli palatini
Superior constrictor
Palatopharyngeus
Palatoglossus
Musculus uvulae
Tensor veli palatini
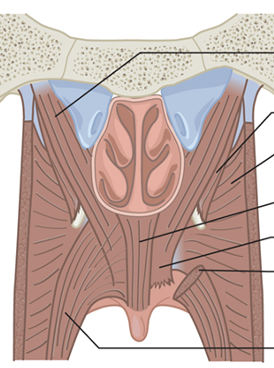
Which muscle is the levator veli palatini?
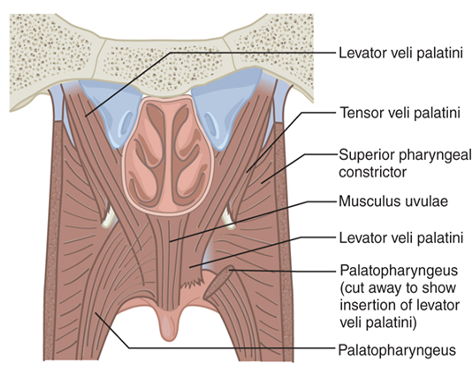
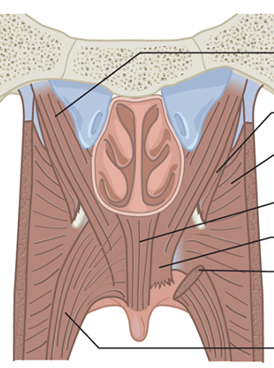
Which muscle is the Superior constrictor?
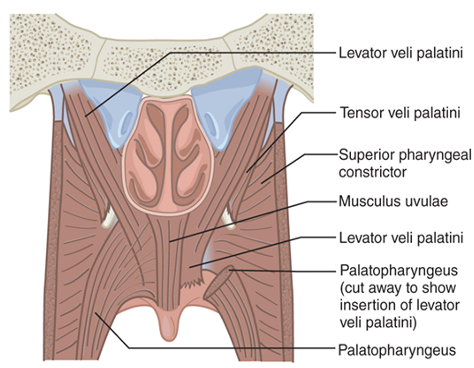
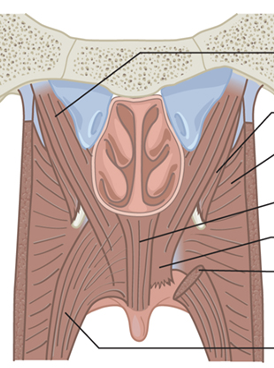
Which muscle is the Palatopharyngeus?
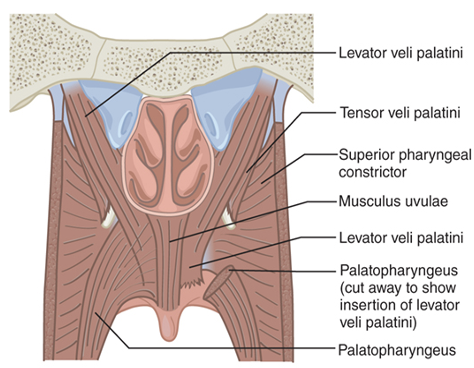
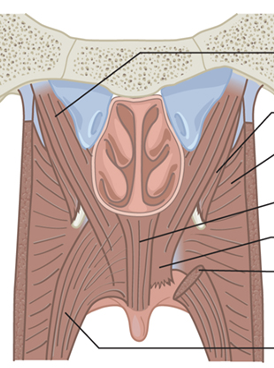
Which muscle is the Palatoglossus?
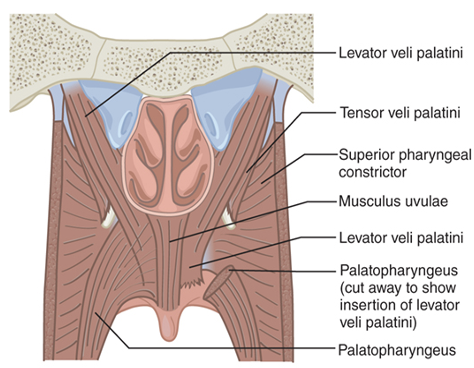
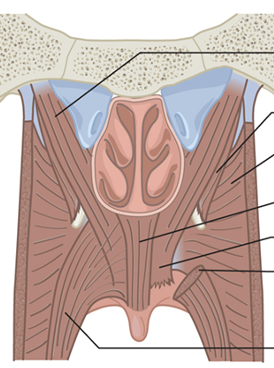
Which muscle is the Musculus uvulae?
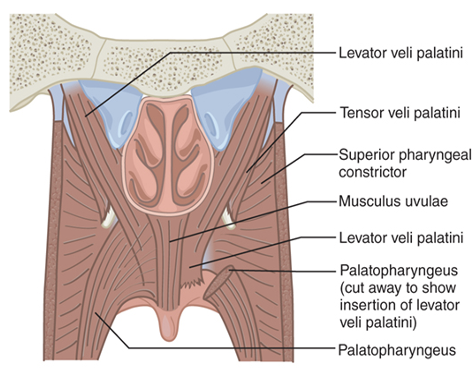
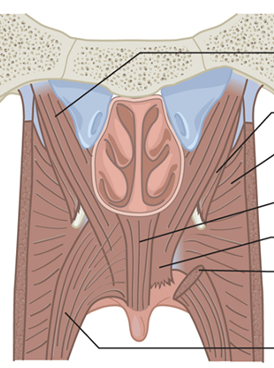
Which muscle is the Tensor veli palatini?
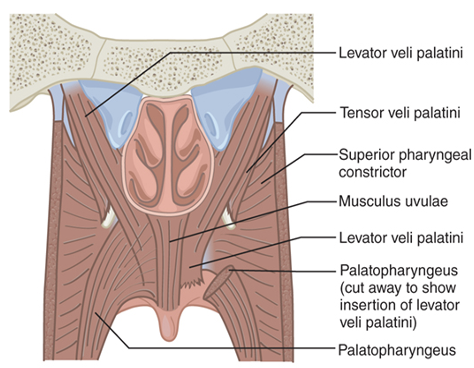
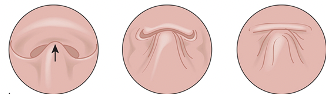
Which VP closure closes velum to posterior pharyngeal wall?
Coronal
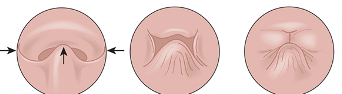
Which VP closure closes using the lateral pharyngeal walls and velum?
Sagittal
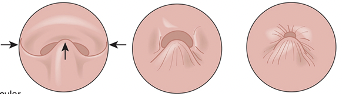
Which VP closure uses all the structures to close?
Circular
Cleft
Abnormal opening or fissure
When does everything fuse together by?
12 weeks
What structures can a cleft affect?
Lips, Palate, or both
Types of Clefts include:
Isolated vs Combination
Incomplete vs Complete
Unilateral vs Bilateral vs Midline only
Isolated vs Combination meaning
Isolated = cleft lip only or cleft palate only
Combination = both clef lip and palate
Incomplete vs Complete meaning
Incomplete = not full opening, Complete = all the way to incisive foramen
Unilateral vs Bilateral vs Midline only
Unilateral = one side, Bilateral = both sides, Midline = on midline
Where does a primary cleft occur in the mouth?
Front of mouth, structures anterior to incisive foramen: alveolar ridge, lip
Primary Cleft info
Form at 7 weeks
Types: complete/incomplete, unilateral/bilateral
Where does a secondary cleft occur in the mouth?
Back of mouth, structures posterior to incisive foramen: Hard palate, velum, uvula
Secondary Cleft info
Form at 9 weeks
Types: complete/incomplete, midline only
What structures are involved in a Primary cleft?
Cleft of orbicularis oris
Wide, flat nose with spreading nasal ala
Short columella (tissue that divides nostrils)
Abnormal dentition (teeth development)
How does a Primary cleft impact function?
Specific articulation errors
Resonance affected
Feeding issues
What structures are involved in a Secondary cleft?
Absent velar aponeurosis (can’t assist with VP closure)
Altered insertion of the levator velar muscle (interferes w/ VP close)
Abnormalities in nasal septum (breathing issues)
How does a Secondary cleft impact function?
VP insufficiency + hypernasal speech
Feeding problems and nasal regurge
Eustachian tube malfunction
Cleft palate causes are described as?
Multifactorial
What are the multifactorial causes of the cleft palate?
Teratogens: chemical agents that interfere with embryonic development
Environment: lead, radiation, pollution
Drugs and ingested substances
Viruses: rubella, influenza
Maternal nutrition: nutritional deficiencies or obesity with diabetes
Physical interference: crowding in utero that restricts mandibular growth
Syndrome
a pattern of multiple malformations in many individuals which is genetically related
Sequence
series of anomalies that results from a single cause
Association
pattern of multiple malformations in many individuals with no known genetic cause
What causes Pierre Robin Sequence?
Micrognathia
What is micrognathia?
A deformation as a result of physical forces that inhibit mandibular growth in utero
What is the main issue in Pierre Robin Sequence?
mandible does not grow down and forward
tongue remains in superior/posterior position
palatal shelves cannot move into a horizontal position and fuse because of interference
Characteristics of Pierre Robin Sequence?
airway obstruction
tongue in pharyngeal space
negative pressure -> pharyngeal collapse
feeding issues
hearing loss
VP insufficiency
What syndromes/genetic disorders are associated with Pierre Robin?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, Stickler Syndrome, Glossoptosis
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
short fissures
missing philtrum
thin upper lip
micrognathia
ear anomalies
What is Stickler Syndrome?
wide, flat face
myopia
eye abnormalities
hearing loss
skeletal abnormalities
What is Glossoptosis?
Posterior displacement of the tongue in nasopharynx
Facial, Oral, Pharyngeal Anomalies impact?
aesthetics and function
abnormalities of the ear, nose, and throat
affect the quality and intelligibility of speech
Ear abnormalities/malformations include:
External Ear (conductive HL)
Aural atresia
Microtia
Middle Ear (conductive HL)
Absent, hypoplastic ossicles, tympanic membrane
Inner Ear (sensorineural HL)
Malformations in the cochlea, vestibular system, auditory nerve
The external ear abnormalities are?
Aural atresia (absence of external auditory canal)
Microtia (under-developed pinna; small auricle)
The middle ear abnormalities are?
Absent, hypoplastic ossicles, tympanic membrane
Affects transmission of sound
treatment = hearing aids/surgery
The inner ear abnormalities are?
Malformations in the cochlea, vestibular system, auditory nerve
Can be independent of other abnormalities
treatment = hearing aids, cochlear implants
How is the Eustachian tube different in kids than adults?
Kids are less sloped
Tube falls into place after 6
prior: causes middle ear effusion, acute otitis media
Nose Abnormalities include:
Anterior obstruction: due to stenotic nares (narrow), deviated septum, PAS
cause hyponasality
Posterior obstruction: due to choanal stenosis, artesia, enlarged adenoids
cause hyponasality + cul-de-sac resonance
Maxilla Abnormalities include:
Maxillary retrusion/mid-face deficiency
cuases crossbite (class III), air restriction, hyponasality
Upper Lip Abnormalities include:
Short upper lip
caused by cleft palate repair, congenital abnormality
effects: difficulty with bilabials, possible chewing and swallowing
Mouth Abnormalities include:
Macrostomia: large mouth
no affect on speech
Microstomia: small mouth
mumbling speech
Tongue Abnormalities include:
Macroglossia: big tongue; open-mouth posture, airway obstruction
Causes bilabials, labiodentals, frontal and lateral lisps, palatal-dorsal articulation for lingual-alveolar sounds.
Affects resonance since no room in mouth
Microglossia: small tongue
issues if tongue cannot reach alveolar ridge
Lobulated Tongue: extra lobes on tongue
no affect on speech
Ankyloglossia: tongue tie; can’t protrude tongue tip past the edge of the mandibular incisors
Palate Abnormalities include:
Palatal Fistulas: abnormal opening in line of cleft, tongue can push airflow into opening during speech
causes nasal emission regurge in the nostrils, speech-nasality issues, backing sounds
Tonsillar Hypertrophy/enlarged tonsils issues include:
Palatine: causing cul-de-sac resonance, nasal emission, fronting
Adenoid: hyponasality, nasal emission, sleep apnea, conductive HL, facial malocclusion
Lingual: rare; cul-de-sac resonance
Laryngeal Anomalies include:
Laryngomalacia: softening of tissues around larynx; constantly moving
Vocal fold paralysis: unilateral/bilateral
breathy quiet speech
Laryngeal web: soft tissue over VF
noisy speech, breathy voice, hoarsness
Vocal fold nodules: bumps on VF
sound hoarsness
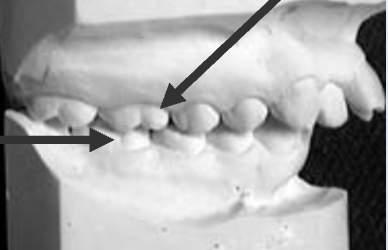
What is Class I occlusion?
Normal; Mesiobuccal cusp of the first maxillary molar fits in the buccal groove
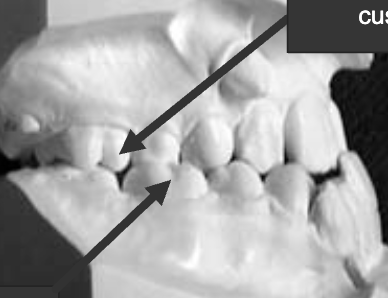
What is Class I malocclusion?
Maxillary and mandibular arch = normal, teeth are misaligned
Speech effect: only if teeth are linguoverted (in the way of tongue tip)
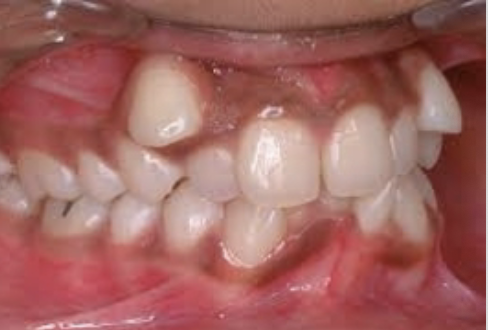
What is Class II malocclusion?
Mandible too far behind maxilla (overbite)
Speech effect: affect anterior sounds, backing of sounds to compensate
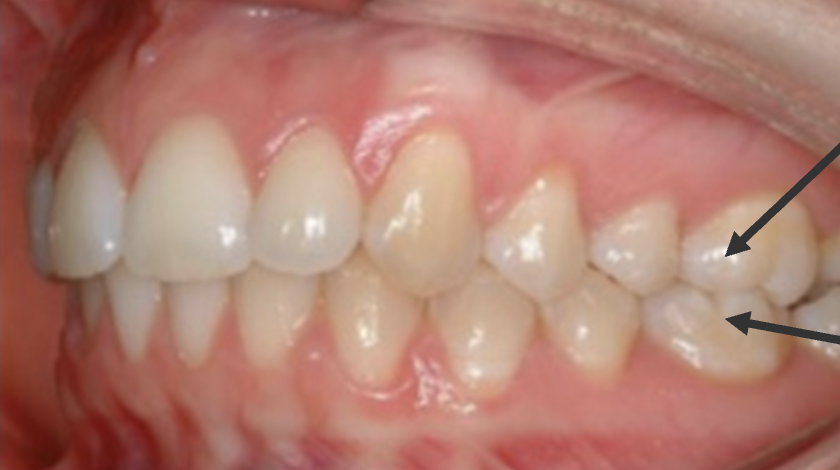
What is Class III malocclusion?
Mandible too far forward (underbite)
Speech effect: lateral distortion, fronting, anterior crossbite
What type of occlusion or malocclusion is this?
Class I occlusion
What type of occlusion or malocclusion is this?
Class I malocclusion
What type of occlusion or malocclusion is this?
Class II malocclusion
What type of occlusion or malocclusion is this?
Class III malocclusion
Speech requires what 2 things?
Sound and airflow
What is sound?
generated from VF vibration
What is airflow?
generated from lungs
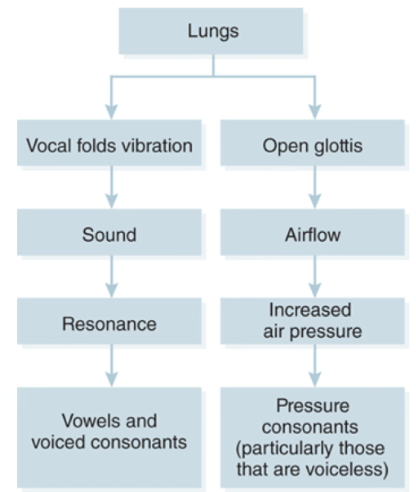
Sound and Airflow chart
What is resonance?
certain frequencies of sound are amplified or strengthened in the vocal tract
What are the two types of resonance?
Oral: resonant quality of sound production in mouth
Nasal: resonant quality of sound in nasal cavity
Normal Resonance occurs when there is?
Balance between oral and nasal = clear, pleasant voice
VP valve function
Size and shape of resonating cavities
Length/volume of phaynx
Size and shape or oral cavity
Shorter/smaller = enhance high freq
Longer/larger = enhance lower freq
Configuration of nasal cavity
Vowels are resonance sounds
What is hypernasality?
too much sound in nasal cavity
usually on vowels/resonant sounds; nasalized voiced plosives, nasal phoneme sub for voiceless phonemes
Causes of hypernasality?
abnormal coupling of oral/nasal cavities
VP open
thin velum
large oronasal fistula
phoneme-specific mislearning
What is hyponasality?
reduction in normal nasal resonance (usually on nasal sounds)
nasal consonants sound similar to their oral cognates
Causes of hyponasality?
blockage in nasal cavity/nasopharynx, common with clefts
What is cul-de-sac resonance?
sound is trapped in nasal cavity
muffled, low volume speech (aka mahomes)
Causes of cul-de-sac resonance?
Oral: sound partially blocked from exiting the oral cavity - microstomia
Nasal: sound partially blocked from exiting nasal cavity - cleft lip/palate
Phayrngeal: sound partially blocked from exiting orophaynx - large palatine tonsils
What is mixed resonance?
any combo of nasality issues
hyper and hypo cannot occur at same time but on certain sounds separately in same person
Causes of mixed resonance?
VPI, obstruction/enlarged tonsils
Hypernasality should be referred to?
Cleft/craniofacial team
Hyponasality and cul-de-sac should be referred to?
ENT
Velopharyngeal disorders include:
VP incompetence
VP insufficiency
VP mislearning
VP incompetence involves
physiology issues / part not moving
What causes VP incompetence?
cranial nerve damage
velar/pharyngeal hypotonia
neurological injury
neuromuscular disease
VP insufficiency involves
anatomy issues
What causes VP insufficiency?
history of cleft palate
deep pharynx
adenoid atrophy
hypertonic tonsils in nasopharynx
latrogenic conditions
Effects of VPI’s on speech?
Hypernasality: phonated sounds in nasal cavity
Nasal emission: leak of airflow into nasal cavity
What is Velopharyngeal mislearning?
Articulation disorder
substitution of a nasal for oral sound