PHYS 1103_Unit 1: Mathematical Introduction and Vectors_C 낱말 카드 | Quizlet
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What defines the SI units of length, mass, and time?
SI units are defined as meters for length, kilograms for mass, and seconds for time. These units are the basis for all measurements in mechanics.
How are dimensions used in physics to verify the correctness of an equation?
In physics, dimensional analysis ensures that the dimensions match on both sides of an equation, confirming its potential correctness.
What is the principle of significant figures in measurement?
Significant figures reflect the precision of a measurement. The rules help ensure that calculations do not imply greater accuracy than the measurements provide.
How do unit conversions work in physics?
Unit conversions in physics involve using conversion factors to change measurements from one unit to another, ensuring that all units in equations are consistent.
Describe how vectors differ from scalar quantities.
Vectors have both magnitude and direction, such as velocity, while scalars have only magnitude, like speed or mass.
What is the process for adding vectors geometrically?
To add vectors geometrically, align the second vector's tail to the first vector's head and draw the resultant from the first vector's tail to the last vector's head.
How do you calculate the components of a vector?
The components of a vector in a rectangular coordinate system are calculated using trigonometry: Ax = A cos(θ) for the x-component, and Ay = A sin(θ) for the y-component.
What does the Pythagorean theorem state in the context of vector components?
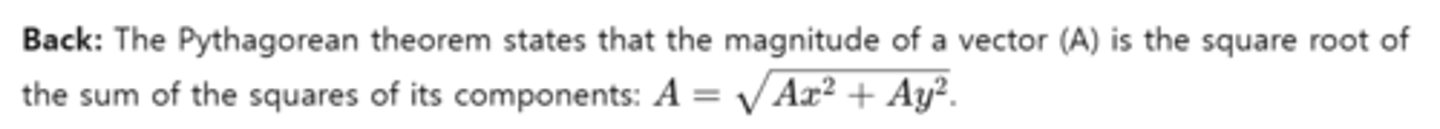
Explain the process of vector subtraction using the concept of vector addition.

Front: How do you determine the direction of a resultant vector using its components?
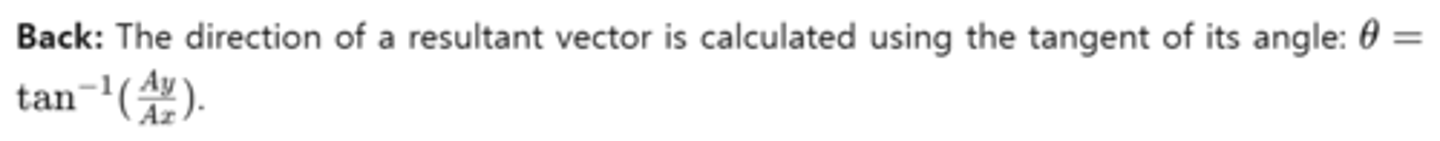
Front: What is the purpose of using dimensional analysis in physics equations?
Back: Dimensional analysis is used to check the consistency of equations, ensuring that all terms match dimensionally, which can confirm or refute their correctness.
Front: What rule do significant figures follow when multiplying or dividing?
Back: When multiplying or dividing, the number of significant figures in the result should match the number in the input with the fewest significant figures.
Front: How do you convert speed from miles per hour to meters per second?
Back: To convert speed from mph to m/s, multiply by approximately 0.447 (since 1 mph ≈ 0.447 m/s).
Front: What distinguishes a vector's magnitude from its components?
Back: A vector's magnitude is the total length or size, calculated from its components using the Pythagorean theorem, independent of its direction.
Front: How does one apply the commutative property to vector addition?

Front: Define scalar multiplication in the context of vectors.
Scalar multiplication involves multiplying a vector by a scalar, changing the vector's magnitude without altering its direction unless the scalar is negative.
How can trigonometry be applied to calculate vector components?
Trigonometry uses the sine and cosine functions to find the y-component (A sin(θ)) and x-component (A cos(θ)) of a vector from its angle θ.
What is the role of the inverse tangent function in determining vector direction?
The inverse tangent function calculates the angle of a vector's direction based on the ratio of its y-component to its x-component.
Explain how unit conversion is applied in physics.
Unit conversion in physics uses specific ratios (conversion factors) to convert measurements between different units, ensuring consistency in equations.
What is an example of a vector subtraction problem in physics?
Subtracting vector B from vector A involves reversing the direction of B and then adding it to A, often visualized by aligning A's tail to B's head and drawing the resultant vector.
What is displacement in physics?
Displacement is the change in position of an object, calculated as the final position minus the initial position, and is a vector quantity.
How is average velocity calculated?
Average velocity is calculated as the displacement divided by the time interval over which the displacement occurred.
What is the difference between average speed and average velocity?
Average speed is a scalar quantity representing the total path length divided by the time interval. Average velocity is a vector quantity and considers the displacement direction.
What is the significance of the direction in the vector quantities like velocity?
The direction in vector quantities like velocity indicates the line of motion and whether the object is moving towards or away from the origin.
Define acceleration in physics.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object, indicating how quickly it speeds up, slows down, or changes direction.
How do you calculate average acceleration?
Average acceleration is calculated as the change in velocity divided by the time over which the change occurs.
What does negative acceleration indicate?
Negative acceleration indicates that the object is slowing down in the direction of motion or speeding up in the opposite direction.
Explain the concept of freely falling objects.
Freely falling objects move under the influence of gravity alone, without any initial propulsion and ignoring air resistance.
What is the value of acceleration due to gravity?

How does constant acceleration affect one-dimensional motion?
In one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration, the object's velocity changes at a constant rate, described by linear equations of motion.
Describe the motion diagram and its purpose.
A motion diagram displays an object's position at successive times, with velocity and acceleration vectors, helping visualize motion characteristics.
What is instantaneous velocity?
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific instant, represented by the slope of the tangent line on a position-time graph.
Explain the relationship between displacement and total path length.
Displacement is the straight-line distance between two points with direction, while total path length is the actual distance traveled, regardless of direction.
How do you determine if velocity is constant from a position-time graph?
Velocity is constant if the position-time graph is a straight line, indicating uniform motion.
What is instantaneous acceleration?
Instantaneous acceleration is the rate of change of velocity at a specific instant, measurable as the slope of a velocity-time graph at that point.
Describe one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration using a real-world example.
A car accelerating uniformly from a stoplight demonstrates one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration, where its velocity increases linearly over time.
How is the direction of acceleration determined in relation to velocity?
Acceleration's direction is the same as velocity when speeding up, and opposite when slowing down.
Define path length in motion.
Path length is the total distance an object travels along its path, irrespective of the direction, unlike displacement.
What does a zero acceleration imply about an object's motion?
Zero acceleration implies that the object is moving at a constant velocity.
How do you calculate the area under a velocity-time graph?
The area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of the object over that time interval.
What defines displacement in two dimensions?
Displacement in two dimensions is the vector difference between the final and initial position vectors, with components in the x and y directions.
How is average velocity in two dimensions calculated?
Average velocity is the displacement vector divided by the time interval, with components in both the x and y directions.
What is the relationship between displacement and average velocity vectors?
The average velocity vector is directed along the displacement vector from the start to end points of the motion.
Describe instantaneous velocity in two dimensions.
Instantaneous velocity is the limit of the average velocity as the time interval approaches zero, tangent to the path of motion.
How is average acceleration calculated in two dimensions?
Back: Average acceleration is the change in velocity vector divided by the time interval, with independent x and y components.
Front: What is the concept of instantaneous acceleration in two dimensions?
Back: Instantaneous acceleration is the rate of change of velocity at any instant, found by taking the limit as the time interval approaches zero.
Front: Explain projectile motion in two dimensions.
Back: Projectile motion involves movement in both horizontal and vertical directions under the influence of gravity alone, forming a parabolic path.
Front: How do the horizontal and vertical motions in projectile motion interact?
Back: Horizontal and vertical motions in projectile motion are independent of each other; horizontal motion has constant velocity, while vertical motion is accelerated due to gravity.
Front: What are the kinematic equations for two-dimensional motion?
Back: There are separate kinematic equations for the x and y directions, incorporating initial velocity components and acceleration.
Front: How does one determine the range of a projectile?
Back: The range is calculated using the horizontal motion equations, considering the constant horizontal velocity and the time of flight.
Front: What is relative velocity in two dimensions?
Back: Relative velocity is the velocity of one object as observed from another moving object, taking into account the motion vectors of both observers.
Front: How does one compute relative velocity?
Back: By subtracting the velocity vector of one object from another, aligning the result with the observer’s frame of reference.
Front: What is the significance of angles in two-dimensional motion equations?
Back: Angles determine the initial velocity components in the x and y directions, affecting the trajectory and range of the motion.
Front: How is average speed different from average velocity in two-dimensional motion?
Back: Average speed is the total path length divided by time, a scalar quantity, while average velocity is vectorial and depends only on the start and end points.
Front: What does it mean if the average acceleration vector changes in two-dimensional motion?
Back: It indicates changes not only in speed but also potentially in the direction of motion.
Front: What are the implications of zero acceleration in a particular direction in two-dimensional motion?
Back: It implies constant velocity in that direction, as seen in the horizontal component of projectile motion under gravity.
Front: What role does the launch angle play in projectile motion?
Back: The launch angle determines the initial velocity components in both directions, affecting the height and range of the trajectory.
Front: How do you calculate the maximum height reached by a projectile?
Back: Using vertical motion equations, set the final vertical velocity to zero and solve for height using the initial velocity and acceleration due to gravity.
Front: How can one calculate the impact angle of a projectile?
Back: By determining the arctangent of the ratio of the vertical to horizontal velocity components just before impact.
Front: What are the conditions for achieving maximum range in projectile motion?
Back: The maximum range is achieved when the launch angle is 45 degrees, assuming no air resistance and uniform gravity.
학습 중 (59)
학습을 시작한 단어들이에요. 화이팅!