Gentics Final
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Sterile Technique
measures taken to prevent the spread of pathogens from the environment to the patient by eliminating all micro-organisms in that environment
Velvet Stamp
A method used to transfer bacteria onto different media by stamping the surface onto the colonies on one plate and stamping again in another to find a missing colonies
"F" Factor
Fertility Factor aka. plasmid. An episome that can copy itself from 1 cell to another & is prone to recombination.
Episome
A genetic element that can exist either as a plasmid or as part of the bacterial chromosome.
Conjugation
The transfer & replication of the F-Factor
TraA
Pilin
TraJ
Transcription factor from TraM & TraY/TraI
TraM
DNA transfer
TraY/TraI
nicks F factor at ori T
TraS/TraT
Exclusion factors
Ori T
Origin of Transfer causes cells to fuse in a mating bridge, directs the separation of the two strands and sends one to the recipient and keeps one in the donor, now both cells have a plasmid.
Ori V
origin of replication
F+ Cell
Bacterial cells that possess a chromosome and F factor
Hfr Cell
a cell with an F factor integrated into its genome
Transduction
phages carry prokaryotic genes from one host cell to another
Electroporation
A technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by applying a brief electrical pulse to a solution containing the cells.
Mapping
Conjugation, Transduction, transformation
Transformation
modification of a cell or bacterium by the uptake and incorporation of foreign DNA
Co-transfer
Transfer of co-transformants at the same time
R
Resistant
S
Susceptible
Eukaryotic Regulation
No operon, gene sparsity, multiple polymerases
Prokaryotic Regulation
Gene dense, Operons, 1 RNA polymerase
GAL4p
the transcriptional activator that binds to GAL gene upstream activator sites (assisted by zinc ion)
activator
A protein that binds to DNA and stimulates transcription of a specific gene by bending the DNA and bringing in polymerase.
Transcriptional Regulators
Activators, Enhancer sequences, Silencer sequences
transcription factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription. (If covering binding sites, transcription is prevented)
Chromosomes Remodeling
Opens up binding sites, Polymerase will push proteins out of the way in order to bind
TAP
Transporter complex (brought closer to TBP via chromosome remodeling)
TBP
TATA-Box Binding Protein (brought closer to TAP via chromosome remodeling)
Methylation
a biochemical process that reduces trasnscription
Silencer Proteins
proteins that bind to the enhancer sequence and block gene transcription. They also compact histones.
CGP Islands
Upstream of genes & recruits proteins to methylate cytosine & remodel chromatin
Imprinting
Includes SNRPN, UBE3A, and Needin. Certain genes are methylated at gametogenesis & methylation occurs differentially in male and female germlines.
Alternative splicing
The splicing of all or some exons resulting in isoforms & different functions/proteins.
control by persistence
Decay of transcripts, RNA interference (RNAi). split into Deadenylation dependent & Deadenylation independent
Deadenylation dependent
Poly A tail is down to 25-60 nucleotides. mRNA cap is lost and exonuclease degrades
Deadenylation independent
Decapped by enzymes & cleaved by endonuclease, then degraded by exonuclease
Autoregulation
Cmyc & similar to prokaryotic auto regulation
cmyc
encodes a cell cycle regulatory protein
Meiosis process
Meiosis I (reductional) ----> Meiosis II (equational)----> Mitosis
Probability calculations
Mathematical methods to determine likelihood of events. Addition Rule, Multiplication rule & allele frequency calculations
Addition rule
Adding mutually exclusive genotypes
Multiplication rule
the probability that two or more independent events is the product of their individual probabilities
chi-squared (x^2)
Sigma {(observed -expected) ^2/expected}
Locus/Loci
anywhere on the genome
genes
Functional loci
genotypes
Combination of alleles
Phenotypes/traits
phenotype is physically expressed; traits are observed characteristics
+
wildtype allele
/
sex-determined trait
Neurospora crassa
bread mold
Apple scab
Venturia inaequalis
Rhizocarpon eupetraeum Ascus
Has a spore called the ascospore
Meiosis I
reductional division
meiosis 2
equational division
Degrees of freedom
Categories -1
Meiosis equation
2n= N + N = 4 N (N + N + N + N)
p-value < 0.05
significant
p-value > 0.05
not significant
Branching Method
breaks down dihybrid cross into two separate monohybrid crosses
Recombination
process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division
Recombination significant factors
Recombination depends on Physical Distance. More space = more recombination
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
self cross
organism crossed with itself
RRYY x rryy
9:3:3:1
Tetrad Analysis
Neurospora Crassa, Apple Scab, Rhizocarpon, Eupetraeum, Ascus
Gametes
sex cells
Independent assortment
One of Mendel's principles; states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
Double recombination
What is this?
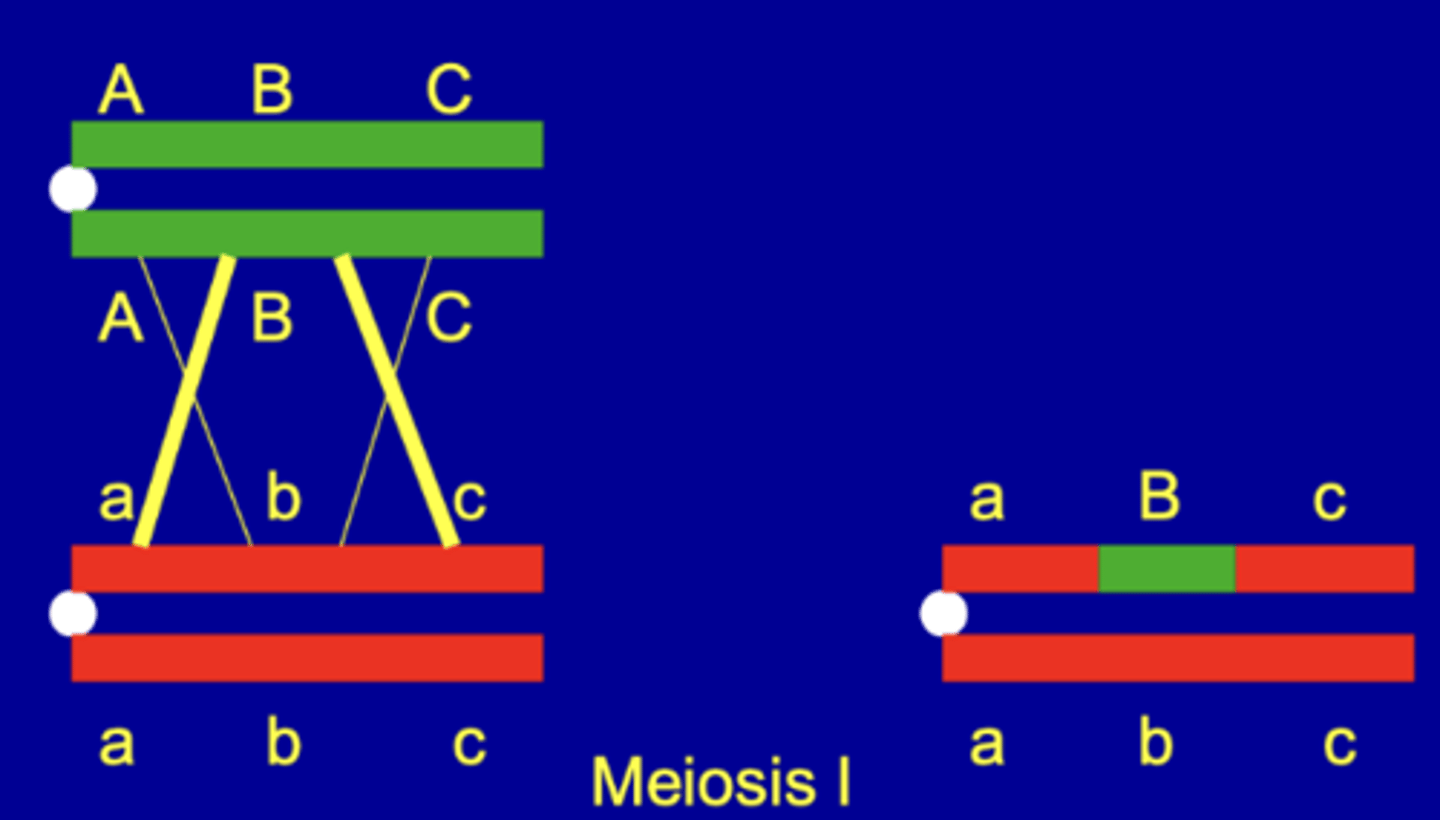
Single Recombination
What is this?
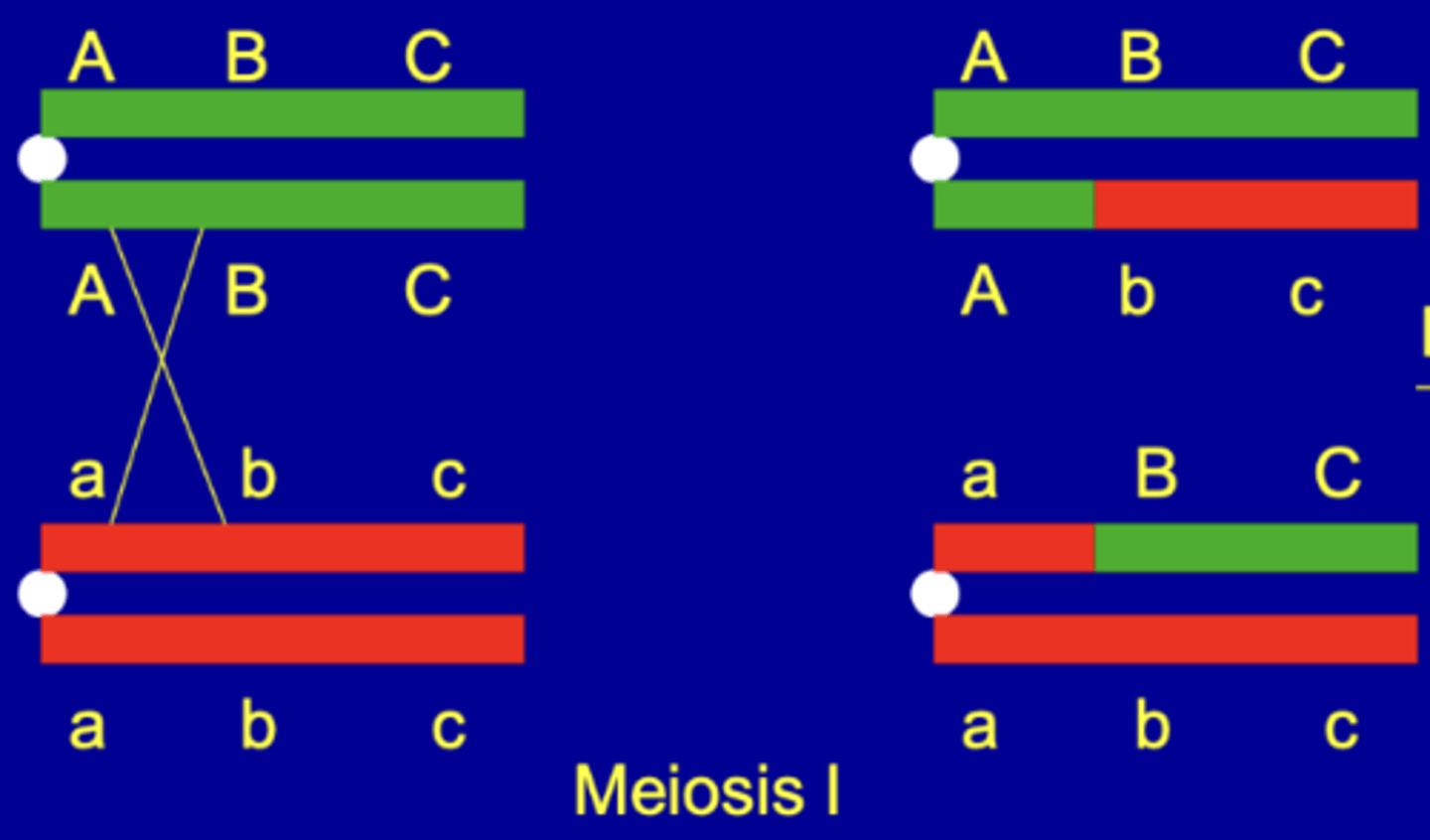
Three Randoms
Random mating, random union of gametes, random genetic drift
Random Mating
Non-directional, Picks a mate from population, non specific genotype
Non-Random mating
Directional & has a preferred mate
Random union of gametes
centered around genotype frequencies, the random selection of alleles into a new generation without regard to genotypes
HWE
Determines the expected frequencies of alleles in a new generation under certain assumptions
HWE Equation
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
HWE assumptions
No Selection, No Mutation, No Migration, Drift, Individuals choose mates at random, Large Population {>500)
Drift
Chance event
Organism Reproduction
Diploid, Sexual reproduction, no overlapping generations
Nature if Variations
Two alleles, Identical frequencies in males & females
Impact on Frequencies
No mutation, no migration, no selection
Mating dynamics
Random mating, large population
Random mating special cases
Multiple alleles, X linked loci
Random mating special cases Equation
(p+q+r)^2 = 1
Triploid
3 sets of chromosomes
Tetraploid
4 sets of chromosomes
Triploid equation
(P+q)^3=1
Tetraploid equation
(P+q)^4=1
Expected for AA
p^2
Expected for aa
q^2
Expected for Aa
(2 x p) q
Df
# of genotypes - # of alleles
HWE History
Created by G.H Hardy & Wilhelm Weinberg
Other authors (CHWE)
W.E. Castle & S.S Chet
Three alleles
p^2 +q^2 +r^2 + 2pq + 2pr +2rq =1
Random mating focuses on
Genotypes
3 multiple choice options
Negative Regulation
The default state of transcription is "on" unless a repressor turns it "off"
Positive Regulation
The default state of transcription is "off" unless a repressor turns it "on"