Lecture 26 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Oligonucleotides and Polynucleotides
Oligonucleotides are short (typically 50 nucleotides)
Poly Nucleotides are longer
Properties of Nucleotide Bases
Affect the 3D structure of Nucleic Acids
Aromatic molecules
Most bonds in the ring have partial double bond character (rigidity)
Pyrimidines are planar
Purines have a slight pucker
Solubility of Nucleotides
Hydrophobic and relatively insoluble in pH 7 water
Leads to stacking interactions (van der Waals and dipole dipole)
Charged and more soluble at acidic or alkaline pH values
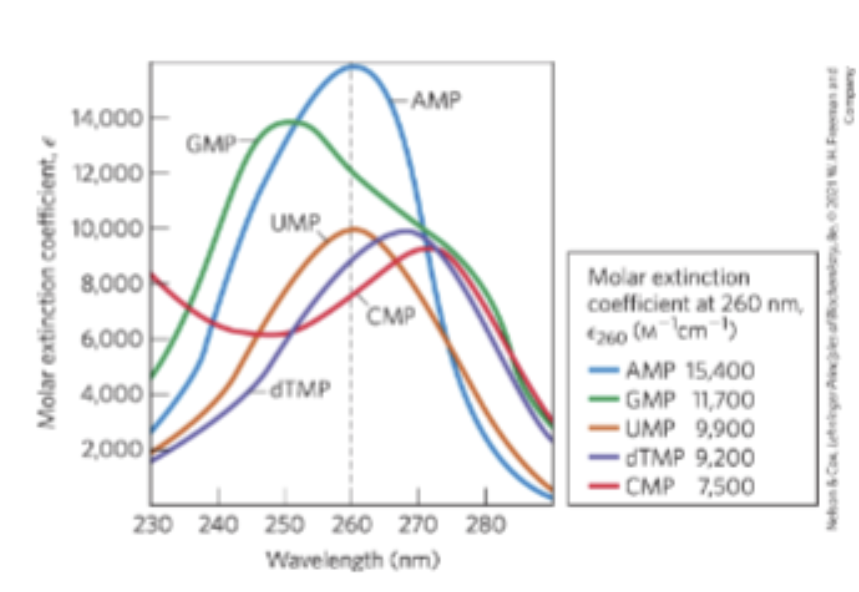
Absorption Spectra of Common Nucleotides
All nucleotide bases absorb UV light
Strong absorption near 260 nm
Base Paring
Permits the duplication of genetic information
Hydrogen bonding patterns between complementary strands of nucleic acids
A bonds to T (or U in RNA) 2 H bonds between
G bonds to C 3 H bonds between
Primary Structure of Nucleic Acid
Covalent structure and nucleotide sequence
Secondary Structure of Nucleic Acid
Regular, stable structure taken up by some or all the nucleotides
Tertiary Structure of Nucleic Acids
Complex folding of large chromosomes or the elaborate folding of tRNA or rRNA structures
Double Helix
DNA is a double helix that stores genetic information
X-ray diffraction pattern revealed DNA molecules are helical
Parallel
3’, 5’ phosphodiester bonds run in the same direction
Antiparallel
3’, 5’ phosphodiester bonds run in opposite directions
Structure of DNA
DNA is read 5’ to 3’
Ultimately confirmed by x-ray analysis
Watson-Crick Model
Offset pairing of the two strands create a major groove (larger, 22 Angstrom wide) and a minor groove (smaller, 12 Angstrom wide)
3 H bonds between G and C
2 H bonds between A and T
Complementary Strands
Double helical DNA strands are complementary
When A occurs on one chain T occurs on the other
Hydrogen bonding does not contribute significantly to stability of the structure
Stabilization of the DNA Double Helix
Metal cations that shield the negative charge of backbone phosphates
Base stacking interactions between successive base pairs
Successive GC or CG are stronger than successive AT or TA
Duplexes with higher GC context are more stable
Replication of DNA
Preexisting or parent strands separate
Each parent stand serves as a template for the biosynthesis of a complementary daughter strand
Different Forms of DNA
Different possible conformations of the deoxyribose
Rotation about the contiguous bonds making up the phosphodeoxyribose backbone
Free rotation about the C1N glycosyl bond
B-Form DNA
The Watson-Crick structure
Most stable for a random sequence DNA molecule under physiological conditions
Right handed, 10.5 base pairs per turn
Alpha Form DNA
Right handed double helix with a wider helix, 11 base pairs per turn and a tilted plane
Favored in solutions devoid of water
Z Form DNA
Left handed helix with 12 base pairs per turn and a backbone with a zig zag appearance
Appears more slender and elongated
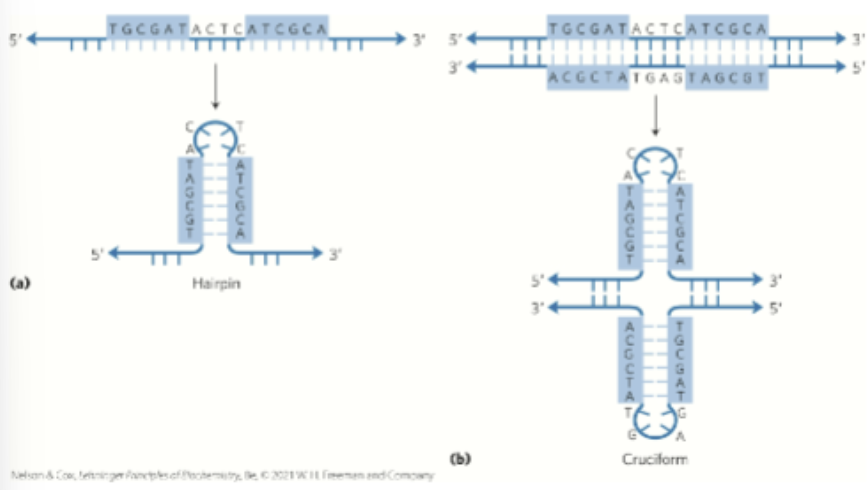
Unusual Structures of DNA
Palindrome and Mirror Repeats
Palindrome
Region of DNA that is identical when read either forward or backward
Applied to regions of DNA with inverted repeats
3’ to 5’ is the same as 5’ to 3’
Mirror Repeat
Sequence when the inverted repeat occurs within each individual strand
5’ TTAGCA ____l____ACGATT 3”
Hairpin and Cruciform Structures
Form from the self complementarity within each strand
Messenger RNA
Code for polypeptide chain
Portion of cellular RNA carrying the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome
Transcription
Process by which mRNA are formed on a DNA template
Monocistronic
Codes for only one polypeptide
Most mRNA in eukaryotes
mRNA has only one gene
Polycistronic
Codes for 2+ different polypeptides
Occurs in bacteria and archaea
mRNA has more than one gene
RNA 3D Structure
Complex but always single stranded
Right-handed helical conformation
Dominated by base stacking interactions
Strongest between two purines
Can base pair with complementary regions of DNA or RNA
Paired strands are anitparrallel
Other Complex 3D Structures of RNA
Structure of complementary RNA strands is an A form right-handed double helix
Breaks caused by mismatched or unmatched bases results in bulges or internal loops
Internal loops form between palindromic sequences
Methylated DNA
Some bases of DNA are methylated
A and C are methylated more frequently than G and T
All known DNA methylases use s-adenosylmethionine as a methyl group donor
In eukaryotes, 5% of cytidine residues are methylated (affects gene expression)