KIN223 Exam 2
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Active transport requires
a. an open channel on the surface of the cell
b. a carrier protein on the surface of the cell
c. a receptor within the cell
d. an enzyme within the cell
b. a carrier protein on the surface of the cell
Translation is terminated when a stop codon is presented at the ___ site
a. a
b. p
c. e
d. b
a. a
Translation is the synthesis of
a. mRNA from DNA
b. mRNA from proteins
c. proteins from DNA
d. proteins from mRNA
e. proteins from tRNA
d. proteins from mRNA
When sugar is mixed with water, equilibrium is reached when
a. molecules of sugar stop moving
b. water and sugar molecules are moving at the same speed.
c. the dissolved sugar molecules are evenly distributed throughout the solution
d. there are the same number of water molecules as dissolved sugar molecules
e. two tablespoons of coffee are added
c. the dissolved sugar molecules are evenly distributed throughout the solution
The rate of diffusion is affected by which of the following?
a. temperature
b. size of molecules
c. steepness of the concentration gradient
d. temperature, size of molecules, and steepness of the concentration gradient
e. temperature and size of the molecules only
d. temperature, size of molecules, and steepness of the concentration gradient
Which of the following will pass through a cell membrane most easily?
a. small polar molecules
b. small nonpolar molecules
c. large polar molecules
d. large nonpolar molecules
e. large neutral molecules
b. small nonpolar molecules
Microscopic membrane extensions that extend from the plasma membrane are called
a. cilia
b. microvilli
c. flagella
d. mucus
e. desmosomes
b. microvilli
The lysosome contains ____ enzymes
a. photosynthetic
b. anabolic
c. hydrolytic
d. melancholic
e. alcoholic
c. hydrolytic
The type of epithelium that would best allow for rapid diffusion, osmosis or filtration is ____ epithelium
a. pseudostratified columnar
b. transitional
c. stratified squamous
d. simple squamous
d. simple squamous
A thin extracellular layer upon which an epithelium rests is called a(n)
a. basement membrane
b. apical surface
c. intercellular junction
d. stroma
a. basement membrane
Complete the following multiple-choice questions that describe different connective tissue types:
a. What type of tissue supports epithelium?
b. Which of the following tissues has cells residing in lacunae?
c. Osteocytes are residents of ________ tissue.
d. Tendons and ligaments are primarily made of
e. The structure of the spleen and lymph nodes are composed mainly of
a. loose connective tissue
b. hyaline cartilage
c. bone
d. dense regular connective tissue
e. reticular connective tissue
during childhood, an example of ___ occurs when the liver increases in size as the hepatocytes undergo cell division
a. hyperplasia
b. hypertrophy
c. neoplasia
d. hepatoplasia
a. hyperplasia
From which primary germ layer is the epidermis of the skin derived?
a. endoderm
b. mesoderm
c. ectoderm
d. mesenchyme
e. the epidermis is derived from all three primary germ layers
c. ectoderm
Which feature of a holocrine gland will distinguish it from merocrine and apocrine glands?
a. secretes its product into a duct
b. secretes its product to the outside of an epithelium
d. secretions are released by exocytosis
e. secretions are released by rupture of whole cells
e. secretions are released by rupture of whole cells
Which nerve cell process receives incoming signals and transmits them to the cell body?
a. dendrite
b. axon
a. dendrite
the type of epithelial tissue that is only one cel-layer tech is called ____; the type of epithelial tissue that is two or more cell-layers thick is called ____
a. stratified; columnar
b. pseudostratified; cuboidal
c. simple; stratified
d. squamous; transitional
c. simple; stratified
Correctly label the following structure of a nail
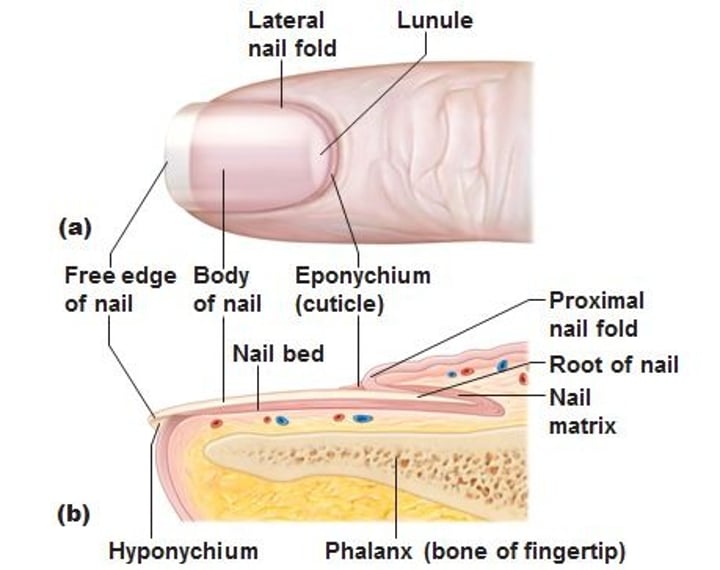
label structures of the integument
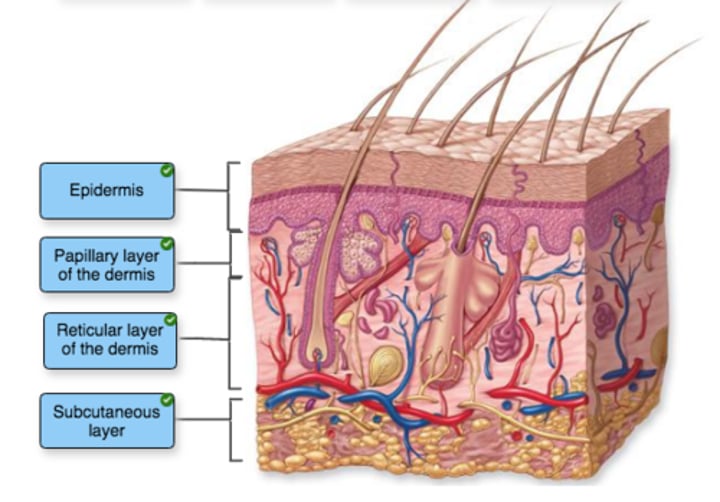
Classify the descriptions based on whether they pertain to thin or thick skin
1. found on the palm of the hands,
2. soles of feet
3. do not contain hair follicles
4. contain all 5 epidermal strata
5. contains sebaceous glands
6. does not include the stratum lucidum
7. contains hair follicles
8. found over most of the body
Thick skin: found on palm of the hands, soles of feet, do not contain hair follicles , and contain all 5 epidermal strata
Thin skin: contains sebaceous glands, does not include the stratum lucidum, contains hair follicles, found over most of the body
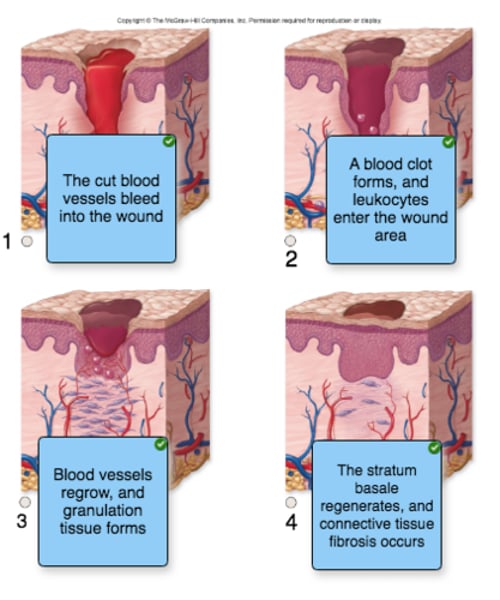
place the events that occur during wound healing into the correct order, using the images as a guide
immune cells found in the epidermis are called
a. epidermal dendritic cells
b. keratinocytes
c. melanocytes
d. adipocytes
a. epidermal dendritic cells
Which of the following are functions of the skin? Check all that apply.
a. Absorption of oils or lipid-soluble chemicals or drugs, such as estrogen or nicotine, through transdermal patches
b. Excretion of sebum that lubricates the skin surface and hair
c. Secretion of the waste product urea during sweating
d. secretion of water and salt during sweating, which plays a role in electrolyte homeostasis
ALL OF THE ABOVE
Which of the following is a true statement regarding sebaceous glands? Check all that apply.
A. Sebaceous glands are a form of sudoriferous gland.
B. Sebaceous glands secrete an oily substance called sebum.
C. Sebaceous glands are modified mammary glands.
D. Sebaceous glands are responsible for the oil that coats the hair on your scalp.
A, B , D
another name for the intracellular fluid is
a. intercellular matrix
b. cisternae
c. cytoplasm
d. cytosol
e. interstitial fluid
d. cytosol
In nutrient glycogen is found stored inside a cell, it is considered a(n)
a. membrane-bound organelle
b. non-membrane-bound organelle
c. inclusion
d. pigment
c. inclusion
Glycolipids are found on the:
a. outer layer of the cell membrane, and they help make the sticky sugar coating on its surface.
b. inside of the cell, where they are a source of high-energy nutrition to power mitochondria
c. middle layer of the cell membrane and they function to transmit solutes through the membrane
d. the inner layer of the cell membrane, and they provide scaffold support to the cell membrane.
a. outer layer of the cell membrane, and they help make the sticky sugar coating on its surface.
proteins that assist the movement of a substance across the membrane are called ____ proteins
a. catalytic
b. cytoskeleton
c. identification
d. intercellular attachment
e. transport
e. transport
Cell shrinking, also known as crenation, occurs when a cell is placed into a(n) _________ solution.
a. exergonic
b. isotonic
c. hypotonic
d. hypertonic
d. hypertonic
Which is a passive transport process?
a. ion pump
b. osmosis
c. receptor-medicated endocytosis
d. pinocytosis
e. phagocytosis
b. osmosis
What is an active transport process?
a. osmosis
b. simple diffusion
c. bulk filtration
d. ion pump
e. facilitated diffusion
d. ion pump
During osmosis, water moves toward the solution with the _________ solute concentration.
a. lesser
b. greater
b. greater
the sodium-potassium pump moves both potassium and sodium down their concentration gradients, from higher to lower concentration.
a. true
b. false
b. false
To maintain a resting membrane
potential, the sodium-potassium pump
a. passively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
b. actively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
c. actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
d. passively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
c. actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
Removal of old organelles is via a process called
a. filtration
b. autophagy
c. autolysis
d. pinocytosis
e. vascularization
b. autophagy
which of the following serve to increase the surface area of a cell for absorption and secretion?
a.microvilli
b. flagella
c. cilia
d. cilia and microvilli
e. cilia and flagella
a. microvilli
Which are the smallest components of the cytoskeleton?
a. centrosomes
b. microfilaments
c. centrioles
d. microtubules
e. intermediate filaments
b. microfilaments
Because they produce ribosome subunits, one would expect to find large numbers of nucleoli in cells that synthesize
a. proteins
b. steroid hormones.
c. pigments.
d. energy sources.
e. solubility-enhancing substances.
a. proteins
Which statement is accurate?
a. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA constitutes a gene; DNA and associated proteins form chromatin.
b. Human cells contain 46 genes; another name for a gene is a nucleosome.
c. Each nucleotide in a gene is bound by hydrogen to the next nucleotide in the sequence; chromatin is a nitrogenous base.
d. DNA is made up entirely of genes; a chromosome is the unwoven form of chromatin.
a. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA constitutes a gene; DNA and associated proteins form chromatin.
The E site of a ribosome is where
a. the tRNA exits the ribosome
b. the polypeptide elongates
c. new amino acids enter the ribosome
a. the tRNA exits the ribosomes
The term "codon" refers to
a. the part of a rRNA molecule where a new amino acid is added
b. the part of tRNA that is a triplet of bases that forms hydrogen bonds with complementary sequences
c. a three-base sequence of mRNA
d. an amino acid that is coded for by three bases of DNA.
c. a three-base sequence of mRNA
Cytokinesis usually begins before ________ ends.
a. interphase
b. metaphase
c. prophase
d. anaphase
e. telophase
d. anaphase
The lining of the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) is comprised of what epithelium?
a. Simple squamous
b. Simple columnar
c. Stratified squamous
d. Simple cuboidal
e. Transitional
a. simple squamous
Which type of epithelial tissue would be the least protective?
a. Stratified keratinized
b. Simple columnar
c. Simple squamous
d. Transitional
e. Stratified nonkeratinized
c. Simple squamous
Which feature is not characteristic of epithelial tissue?
a. Attachment to a basement membrane
b. Cells connected to each other by intercellular junctions
c. A large amount of extracellular matrix
d. Polarity
e. High regeneration capacity
c. Large amount of extracellular matrix
The type of epithelium that lines the urinary bladder and may include some binucleated cells is called ____________ epithelium.
a. stratified squamous keratinized
b. simple squamous
c. transitional
d. stratified squamous nonkeratinized
e. pseudostratified
c. transitional
Connective tissue proper is divided into two broad categories: loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. This classification is based upon the
a. origin of the tissue type.
b. number of different cells types and their respective arrangement.
c. relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
d. location of the tissue.
e. size of the cells present
c. relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
Where in the body would you expect to find a perichondrium?
a. Covering the heart
b. Covering bones
c. Lining kidney tubules
d. Inside of the brain
e. Covering cartilage
e. Covering cartilage
What feature of your ear accounts for its ability to regain its shape after it has been deformed or compressed?
a. The elastic fibers present in the ear's muscles
b. The elastic fibers present in the ear's cartilage
c. The abundance of reticular fibers forming a dense meshwork
d. The elastic fibers in the ear's skin contract after being stretched
e. The ear's built-in memory based upon its overall size and shape
b. The elastic fibers present in the ear's cartilage
Which primary tissue type would be represented by blood, body fat, ligaments and tendons, dermis of the skin, and the cartilage of some joints?
a. Epithelial tissue
b. Connective tissue
c. Nervous tissue
d. Muscle tissue
e. None of the choices is correct.
b. connective tissue
All connective tissues have three features in common. They are
a. cells, protein fibers, and mucus.
b. cells, a liquid portion, and protein fibers.
c. cells, protein fibers, and ground substance.
d. cells, hormones, and protein fibers.
e. protein fibers, a liquid portion, and ground substance.
c. cells, protein fibers, and ground substance.
The type of muscle that has elongated, multinucleated cells and is under voluntary control is __________ muscle.
a. smooth
b. cardiac
c. skeletal
c. skeletal
A skeletal muscle fiber is
a. a skeletal muscle cell.
b. found only in cardiac muscle.
c. a contractile filament within the osteon of bone.
d. an elongated series of muscles held together by dense connective tissue.
e. a collection of several muscles bound together by a membrane.
a. a skeletal muscle cell.
What type of muscle contains intercalated discs?
a. Cardiac
b. Skeletal
c. Smooth
a. cardiac
Dendrites
a. transmit signals away from the cell body.
b. transmit signals toward the cell body.
c. manufacture proteins to be used by the neuron.
d. use hormones to transmit information.
e. release neurotransmitters.
b. transmit signals toward the cell body.
The nucleus of a neuron is found in its
a. axon.
b. cell body.
c. glioma.
d. dendrite.
b. cell body
The largest of the body membranes, commonly called the skin, is the _______ membrane.
a. mucous
b. cutaneous
c. serous
d. synovial
e. cartilaginous
b. cutaneous
There are four types of body membranes. Select the exception.
a. Synovial
b.Mucous
c. Serous
d. Cartilaginous
e. Cutaneous
d. Cartilaginous
With age, epithelial tissues
a. become more flexible.
b. increase in mass.
c. become thinner.
d. lose resiliency but gain pliability.
e. lose their blood supply.
c. become thinner.
A tissue transplant from one person to another (one who is not genetically identical) is a(n)
a. heterograft.
b. allograft.
c. homograft.
d. autograft.
e. syngenetic graft.
b. allograft.
When hyperplasia proceeds out of control, a tumor may develop. This condition is termed
a.metaplasia.
b. atrophy.
c. fibrosis.
d. neoplasia.
e. hypertrophy.
d. neoplasia
Which are applicable to the stratum corneum?
a: Most superficial stratum
b: Consists of about 3-5 cell layers
c: Cells are dead
d: Interlocking keratinized cells
e: Cells are anucleate
a, c, d, e
One of the main dangers of burns is
a. respiratory infection, as body defenses are concentrated superficially.
b. hyperthermia, as temperature regulation is very compromised.
c. hypocalcemia, as blood ion levels are dramatically altered.
d. dehydration, as water can escape from the body.
d. dehydration, as water can escape from the body.
Keratinocytes are
a. the most abundant cell type in the epidermis.
b. found throughout all epidermal strata.
c. sometimes alive and sometimes dead, depending on where they are found.
d. able to synthesize the protein keratin.
e. All of the choices are correct.
e. All of the choices are correct.
The hypodermis is rich in adipose, and thus its functions include
a. frequent regeneration, structural support, and defense against infection.
b. maintenance of boundaries and sensation of stimuli.
c. water regulation and vitamin synthesis.
d. organ protection, energy storage, and thermal insulation.
d. organ protection, energy storage, and thermal insulation.
What is the composition of the subcutaneous layer?
a. Areolar connective tissue and adipose connective tissue
b. Areolar connective tissue
c. Dense irregular connective tissue
d. Areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue
e. Adipose connective tissue
a. Areolar connective tissue and adipose connective tissue
Which skin markings usually disappear during childhood?
a. Cavernous hemangiomas
b. Nevi
c. Pili
d. Friction ridges
e. Capillary hemangiomas
e. Capillary hemangiomas
The deeper sublayer of the dermis is the ________ layer, and it is the _______ of the two.
a. reticular, thinner
b. reticular, thicker
c. papillary, thicker
d. papillary, thinner
b. reticular, thicker
In order to retain heat, what occurs in the skin on a cold day?
a.Blood vessels of the epidermis dilate.
b. Blood vessels of the dermis constrict.
c. Blood vessels of the epidermis constrict.
d. Blood vessels of the dermis dilate.
b. Blood vessels of the dermis constrict.
Which of these comprise the nail plate?
a: Free edge
b: Nail folds
c: Eponchyium
d: Nail root
e: Nail body
a, d, e
Which type of hair forms the beard on the face in response to testosterone?
a. Pilus
b. Nonpigmented
c. Vellus
d. Lanugo
e. Terminal
e. terminal
Sebum is a secretion that
a. acts as a pheremone once reproductive maturity is reached.
b. lubricates skin and helps defend against bacteria.
c. maintains water balance through waterproofing the skin.
d. cools the skin and eliminates certain drugs.
b. lubricates skin and helps defend against bacteria.
nails are hard derivatives formed from the stratum ____ of the epidermis
a. granulosum
b. lucidum
c. basale
d. corneum
e. spinosum
d. corneum
The two types of leukocytes that clean up debris underneath the blood clot of a wound are
a. dendritic cells and keratinocytes.
b. keratinocytes and macrophages.
c. Merkel cells and dendritic cells.
d. macrophages and neutrophils.
e. fibroblasts and neutrophils.
d. macrophages and neutrophils.
Sweat and sebaceous glands develop from the
a. stratum corneum.
b. stratum basale of the epidermis.
c. hypodermis.
d. papillary layer of the dermis.
e. reticular layer.
b. stratum basale of the epidermis.
Severe injuries and burns to the skin result in scars that are
a. produced by stratum basale keratinocytes, which effectively bind damaged skin parts together.
b. produced by chondrocytes and made mainly of desmosomes.
c. fully functional regenerations.
d. made by macrophages, which produce a dense granulation tissue.
e. produced by fibroblasts and made mainly of collagen.
e. produced by fibroblasts and made mainly of collagen.