R3.2.15 Electrolysis of aqueous solutions
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What happens when aqueous solutions are electrolysed
Water can be oxidized at anode or reduced at cathode
Water half-reactions (reduction/oxidation)
In reduction reaction, twice the volume of hydrogen gas is produced when compared to oxygen gas

Electrolysis of water
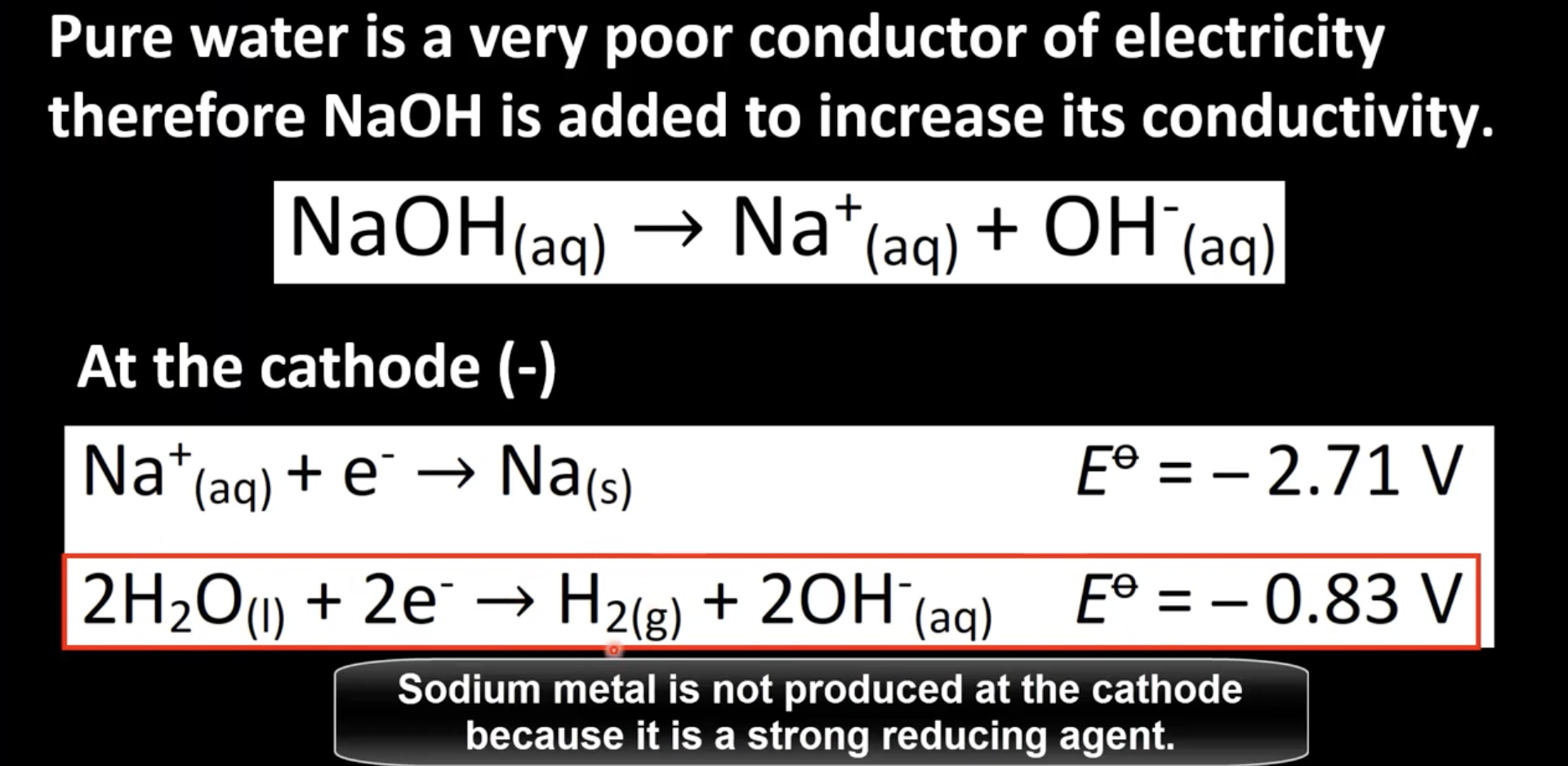
NaOH added to increase pure water’s low conductivity
Water reduced at cathode due to more positive standard electrode potential
Determining half-reaction at cathode
Two possible choices for half-reactions at cathode
Reduction of element with more positive standard electrode potential occurs at cathode
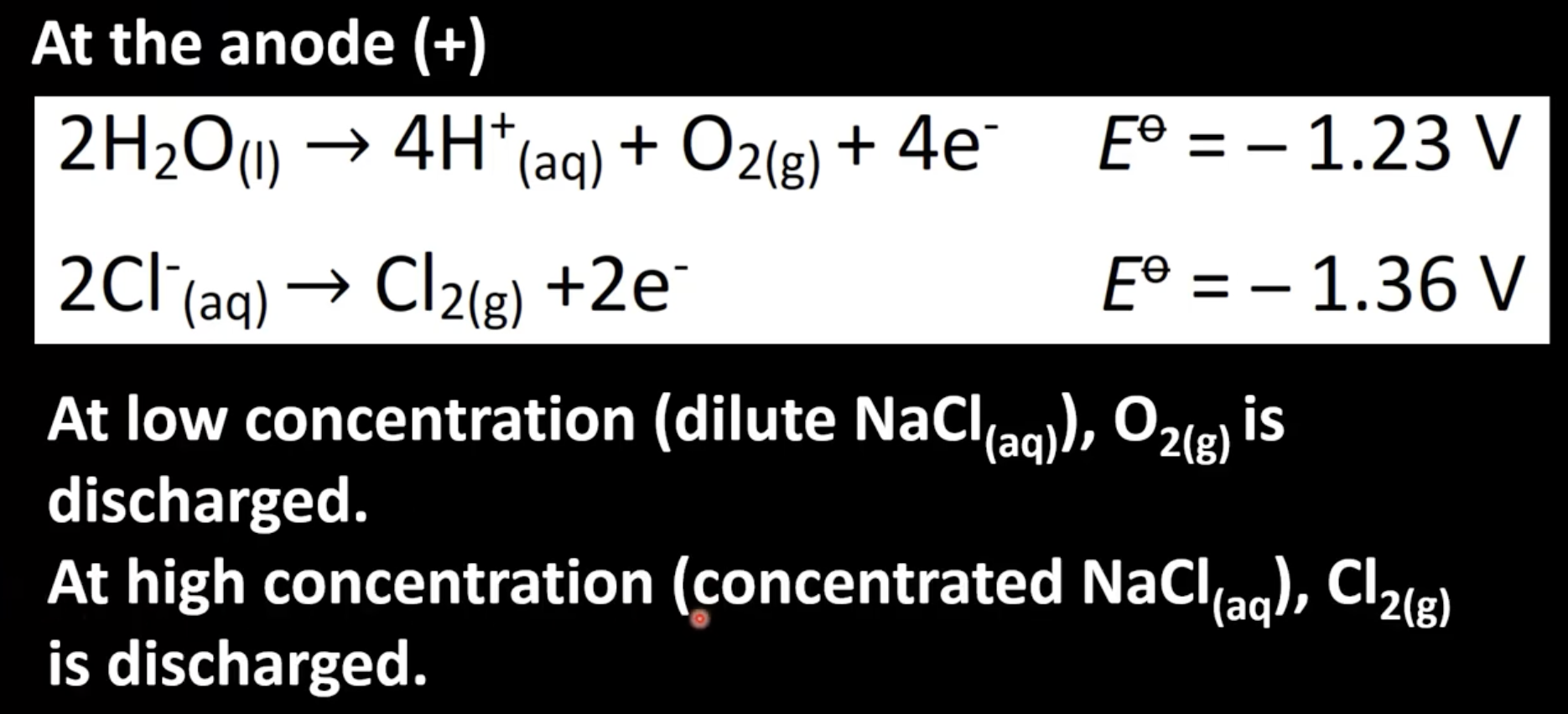
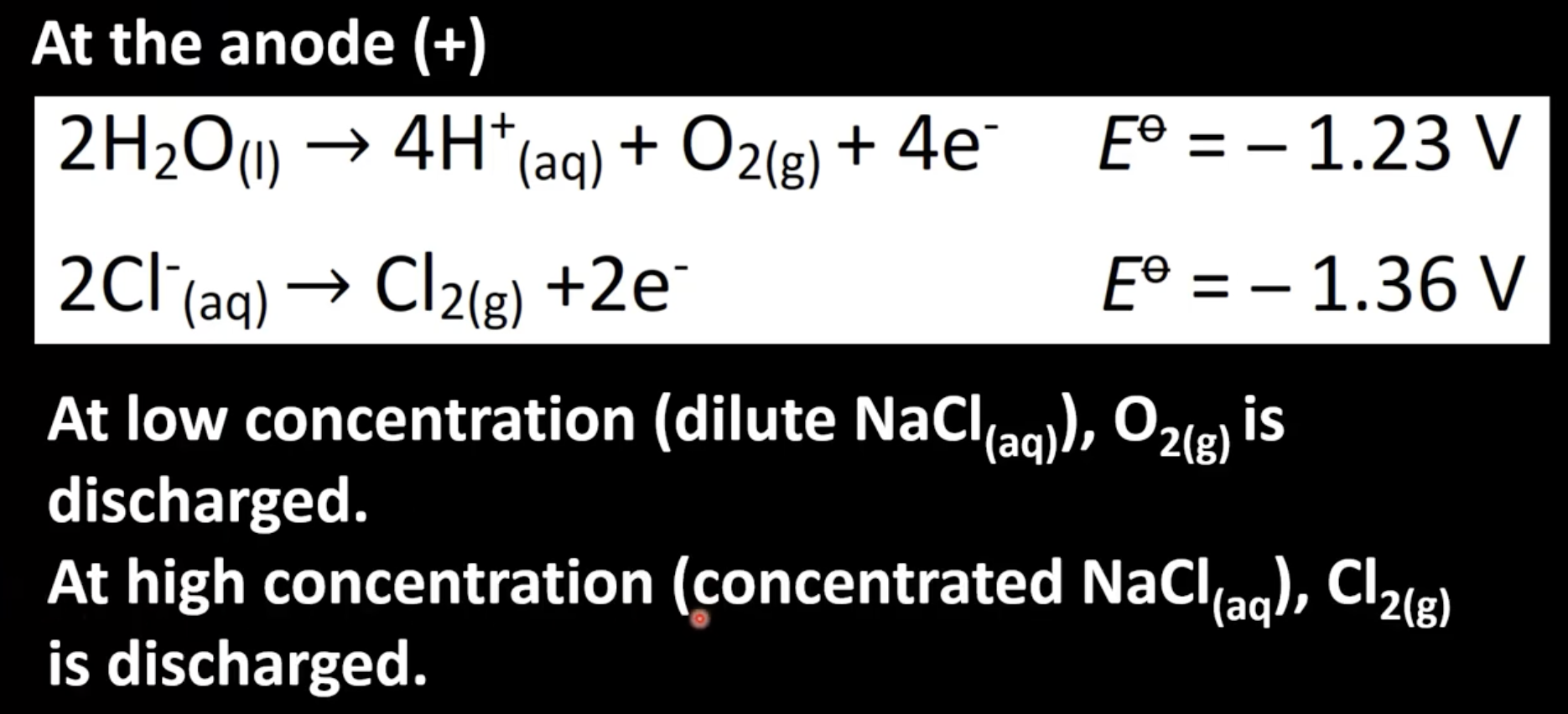
Determining half-reaction at anode
Two possible choices for half-reactions at anode
Oxidation of element with higher concentration occurs at anode
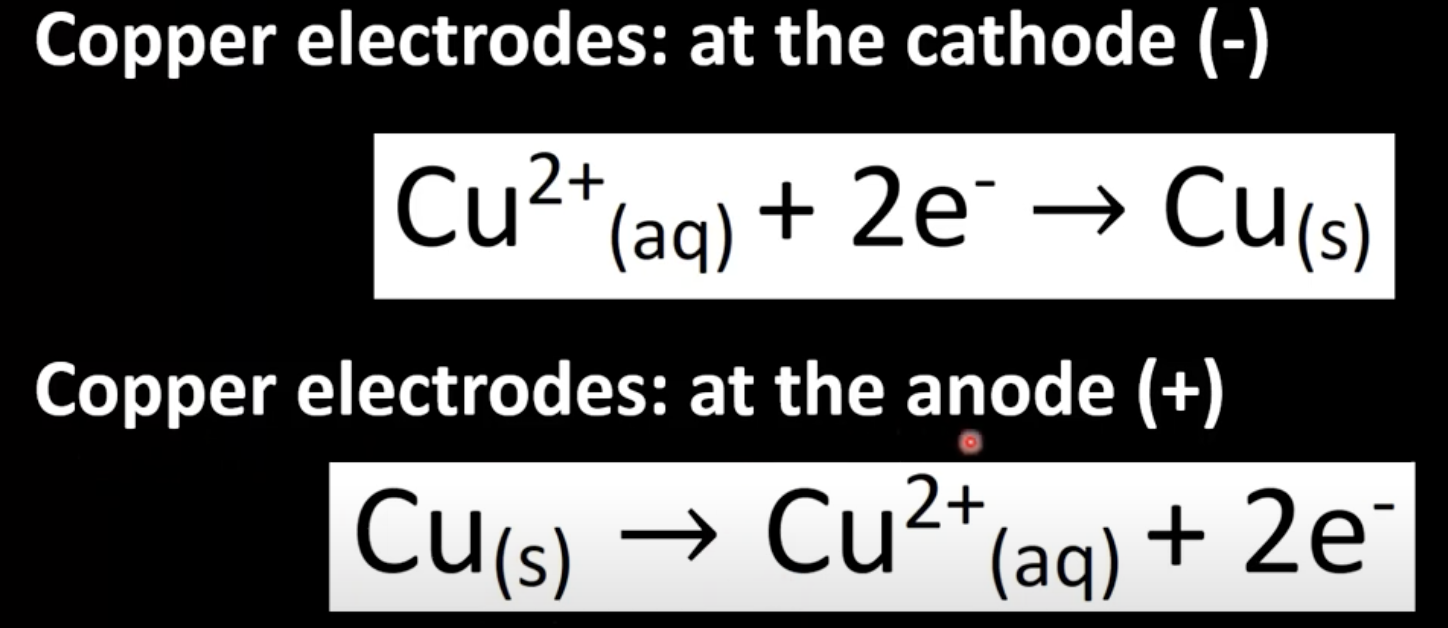
Electrolysis of CuSO4 with copper electrodes
Copper reduced at cathode
Copper oxidized at anode