Sustainable Exam 2
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
bakelite
first fully synthetic plastic
Created to respond to the need of growing electrical industry for insulating wires and other high voltage devices
Combination of phenol and formaldehyde…a type of “resin”
resin
pure polymeric material without any additives
inert
polymers themselves are typically ______
Polyurethanes
Polyacrylonitrile (used in carbon fiber composites) (PAN)
Polyvinyl chloride
Epoxy resins
AcrylonitrileButadiene-styrene(ABS)
rank the toxicity of polymers by synthetic pathway (5)
polyurethanes
which polymer?
ethylene oxide
sterilizes food, sterilizes medical equipment, chemical synthesis
toluene diisocyanate
polyacrylonitrile
which polymer?
used in carbon fiber composites
composite stronger and lighter than steel
common in airplanes
acrylonitrile
polyvinyl chloride
which polymer?
vinyl chloride
used in piping
epoxy resins
endocrine disruptor
bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin
acrylonitrile butadiene-styrene
acrylonitrile, styrene
used in automotive industry
strong plastic
additives
polymer
a material is only called a plastic when it has ______?
otherwise, just a ________.
plasticizers
make plastics more pliable and impact resistant
phthalates
widespread human exposure
bisphenol-A
Used in food packaging as can liners, water tank liners, polycarbonate bottles
Contains (mimics) estrogenic effects in men and women
Studies found lower total testosterone levels in subjects with higher BPA levels and greater frequency of cancers
polybrominated diphenyl ethers
•Fire retardants added to many different resins
•Many plastics can exist as a fuel source
•Limited data on human effects but considered an endocrine disruptor
dioxin
•Considered the world’s most toxic chemical
•Emitted when polybromonated fire retardants are made, mixed with plastics, or during plastic recycling process
•Affects brain development, immune function, cancer risk
alkylphenols
•UV Stabilizers
•Reduce testosterone and estrogen levels, reproductive toxin
•Ex: lignin
anthropocene era
era of earth’s geological history where almost everything is shaped by human activity: forests, lakes, land mass, oceans, atmosphere etc.
When geologists study our age in the future, the presence of plastics may be the greatest indicator of the human activity
30
60
10
____% of all plastic ever produced still in use
____% discarded in landfills or mismanaged environmental leakage
____% recycled or incinerated
asia
n. america
europe
middle east/africa
latin america
highest plastic contributors by country
how plastics degrade
physical/mechanical forces that shear, pulverize, and splinter
chemical: thermal or UV breakdown
biological: biodegradation by microorganisms
1 mm -0 .1 mm
what measurement qualifies as a microplastic?
microplastics
any small particles entering the environment
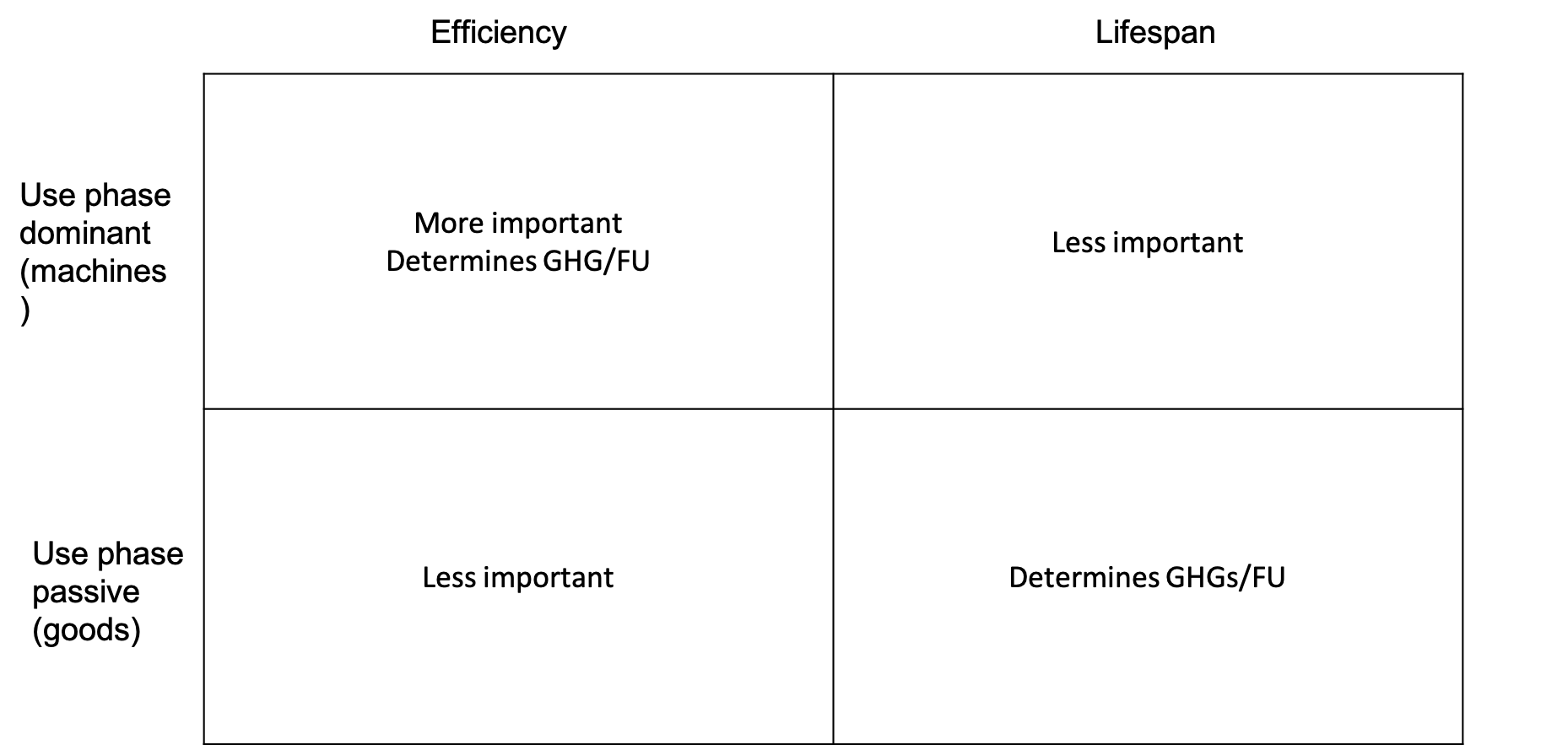
worst scenario (passive)
short lifespan, high manufacturing emissions
worst scenario (dominant)
short lifespan, low efficiency
•because the worst thing you could have is dividing your GHGs by one use
•Best scenario is to have endless uses
•Ex: aluminum
why single use plastics are so bad?
manufacturing
transportation
plastic GHGs come from? (2)
takes more work to convert a natural product like corn into plastic
reason less steps and GHGs with oil to plastic?
issues from plastic waste in waterways
•Blockage / damming of natural water flows
•Become breeding ground for pests / mosquitos
•Source for leaching of toxic chemicals
•Disturbing natural biocycles, nutrient cycles
•MP ingestion and disruption of food chain
•Economic losses to tourism and fishing, economic development
PE
most common polymer type found in fish?
issue of MP pollution on land
disrupts ability of soil to store carbon
nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient cycles disrupted
more GHGs emitted from soil
disrupt natural microbial diversity and affect soil temps
they have increased SA
how are MPs able to absorb nutrients and toxins from the environment?
polymer
large molecule made of repeating units
monomer
individual units that react
dimer
two monomers bonded together
oligomer
several monomers bonded together
polyolefin
what class of polymer?
polypropylene
polyethylene
polystyrene
polyvinyl chloride
polyolefin
•Saturated C-C and C-H bonds with other
functionalization
•Very efficient processing conditions
•Very cheap feedstocks
•Highest produced plastics worldwide
condensation polymers
what class of polymer?
polyethylene terephthalate
polyamide
polycarbonate
polyurethane
condensation polymers
•Higher oxygen and nitrogen content
•Contain reactive bonds that can be used for
biodegradation or chemical recycling
•Many are considered “engineering resins” due to strength, ductility, heat resistance
•More expensive than polyolefins
polyester
reaction of diol and dicarboxylic acid
condensation polymerization
by-products often produced
ex: water
network or gel polymers
crosslinked polymers that contain short side chains (cross links) that connect different polymer chains into a “network”
crosslinked polymers
________ __________ don’t melt, but simply degrade under heat and don’t dissolve into solvents
used as adhesives and binding agents
forming a network from a trifunctional molecule is the reaction of phenol with formaldehyde
bakelite
example of network formation:
thermoplastic
•melts as a response to heat, solidifies upon
cooling
•Heat is able to increase motion of polymer chains until they begin to flow (melt)
•Allows for ease of processing
thermoset
•After the material is cured / synthesized, it will not melt again
•Additional heating results in polymer degradation
•Typically crosslinked polymer systems
thermoplastic
thermoset or thermoplastic?

thermoset
thermoset or thermoplastic?

melt processing
•one of the cheapest and most efficient way to use plastics
•Includes mechanical recycling techniques
•Does not often contain by-products
•Includes injection molding, blow molding, thermoforming, and others
•Is largely responsible for the proliferation of plastic containers used in everyday applications
has the lowest melting point of the main polymers, less energy required
why is PE the largest produced polymer from an energy perspective?
crystallinity
Refers to how polymer chains line up on the molecular level and determines many of usable properties of commodity plastics
random- amorphous
Does not contain a definite melting
point but undergoes continual softening
as polymer chains gain more movement
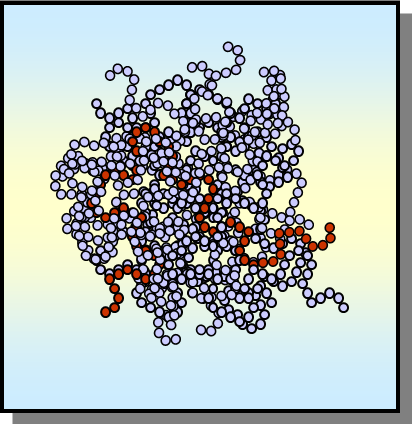
ordered- crystalline
Contains a definite melting point where polymer flow occurs
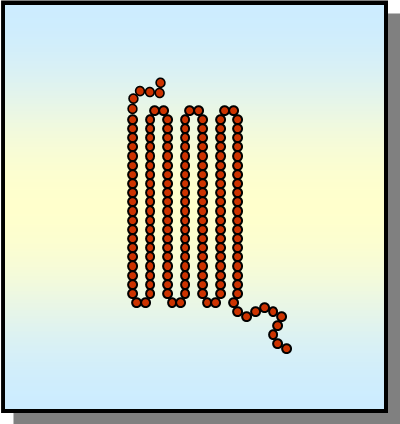
high
high or low crystallinity desired?
high barrier
high
high or low crystallinity desired?
high strength/stiffness
low
high or low crystallinity desired?
toughness (ability to take impact)
low
high or low crystallinity desired?
translucent material
HDPE
which material?
Linear chains pack tightly together and therefore create more dense materials
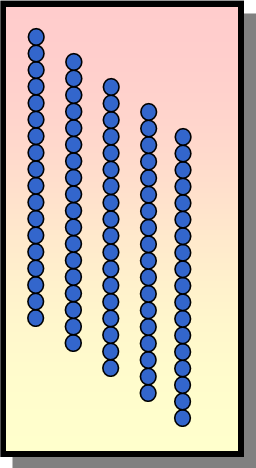
LDPE
which material?
Chains that are branched cannot crystalize do not pack as tightly together and therefore contain more space between the polymer chains
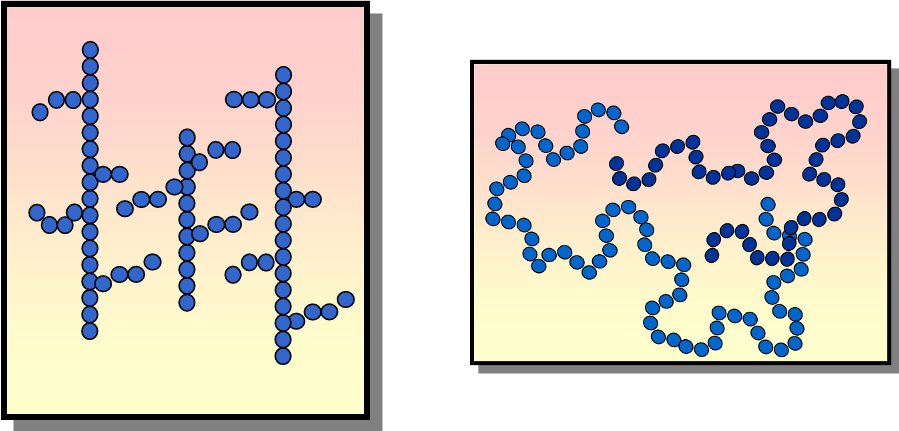
HDPE
HDPE or LDPE?
Stronger and more opaque
LDPE: low crystallinity
LLDPE: varying crystallinity
HDPE: high crystallinity
UHMWPE: high strength cases
4 types of PE
increases
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
strength
increases
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
stiffness
decreases
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
toughness
generally decreases
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
optical clarity
Small molecules usually cannot penetrate or diffuse through the crystalline domains, hence “barrier properties”, which make a polymer useful for things like food wrap, increase with degree of crystallinity
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
barrier properties
Similarly, solvent molecules cannot penetrate the crystalline domains, which must be overcome before the polymer will dissolve. Solvent resistance increases with degree of crystallinity
effect with increasing degree of crystallinity:
solubility
chemical feedstocks
polyolefin energy demand comes primarily from _______ __________
electrical requirements
polyolefin GHG emissions come mainly from _______ ________
polyester
which material?
has a more even split for energy demand and chemical feedstocks
less efficient polymer synthesis
higher GHGs than polyolefin
true
T/F: the use phase for polyolefin is insignificant
condensation polymers
•They have other active groups, no longer just a hydrocarbon
•Because of the added groups we get better barrier and mechanical properties
•They have byproducts (even if it’s water)
•Has energy impacts
polyolefins
•long chain hydrocarbon
•Simplest polymer
•Very cheap to produce
•Produced in gas phase
•Use phase not significant
bioplastics
biodegradable plastics
recycled plastics
3 kinds of sustainable plastics
bioplastics
•Made from natural materials
•Some are compostable
•Ex. PLA, PHA, Soy PU, Bio- Polyethylene, Bio-Polyamide, Bio-Polycarbonate
biodegradable plastics
•Engineered to break down faster, but not necessarily into harmless substances
•Ester bonds (biodegrade)
•Can still be made from fossil fuels
•Ex. Starch, Cellulose Acetate, PBAT, PBS, PLA, PHA
recycled plastics
•Starting from processed materials instead of raw materials
•Generally achieves a reduction in energy requirement for second generation materials
Bio-PET
which material?
•Replaces one component in PET synthesis with sugarcane-based ethylene glycol
•No difference in biodegradability from PET
Bio-PE
which material?
•Another product of sugarcane
•Not biodegradable, but recyclable
•Drop-in replacement (chemically identical) to traditional PE
•Applications in HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE packaging
•First made from Brazilian Sugarcane
bc it has a high yield
why is sugarcane used as an alternative?
Bio-PA (nylons)
which material?
•Produced from Castor oil – an industrially produced vegetable oil
•Non-edible oil
•Drop-in replacement to PA 6,10, PA 10,10
•Typically have higher impacts than polyesters
•Require solvents and high temperature for synthesis
non-edible sources for biopolymers
castor bean
jatropha seed
mahua seed
Karanja seed
perilla seed
animal fats
starch
cellulose/lignin
chitosan
tannins/wood resins
polyhydroxyalkanoates (bacteria)
Biobased polycarbonate
which material?
•typically used in clear plastic applications: plexiglass/water bottles, headlights
•Often uses BPA, a biobased version uses glucose-based monomer
•Not biodegradable, similar properties as traditional PC
Bio-PHA?
which material?
•Produced by bacteria and harvested from
intracellular deposits
•Expensive to produce
•Blended with starch and cellulose to improve properties and decrease cost
•About 2 months to decompose in the backyard:
one of very few home compostable plastics
•Uses: food wraps, cups, plates, medical uses (sutures, gauze), coatings
polylactic acid (PLA)
which material?
•Thermoplastic produced through bacterial fermentation
•Less expensive processing than PHA
•First industrially produced bioplastic at scale
•Most widely produced bioplastic
•Brittle and more restrictive in applications
•Degrades 1-6 months in commercial
facilities
•Uses: grocery bags, food packaging, bottles, medical sutures, 3D printing
FALSE
T/F: PLA is industrially compostable and recyclable
over-engineering
a problem brought up by the sustainability community that argues we don’t need our plastics to last 100s of year
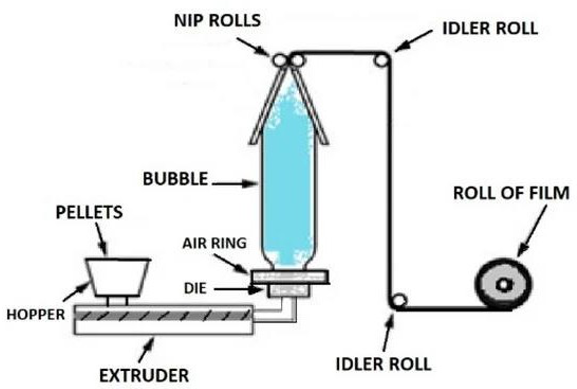
extrusion
blow molding
flexible packaging most often produced through what two processes?
too low a melt-viscosity
why can’t PLA undergo blow molding?
die extrusion
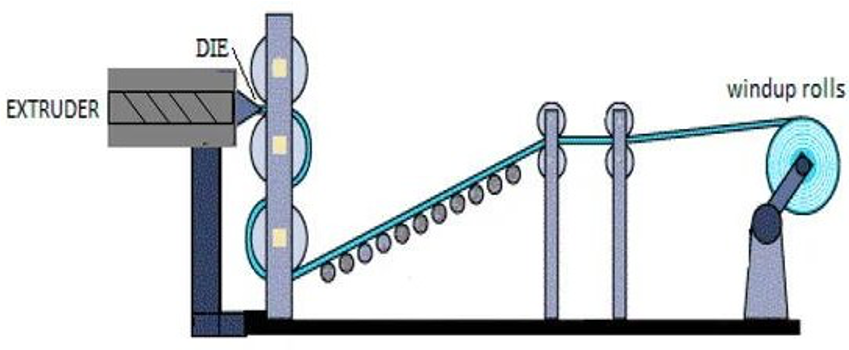
blow molding
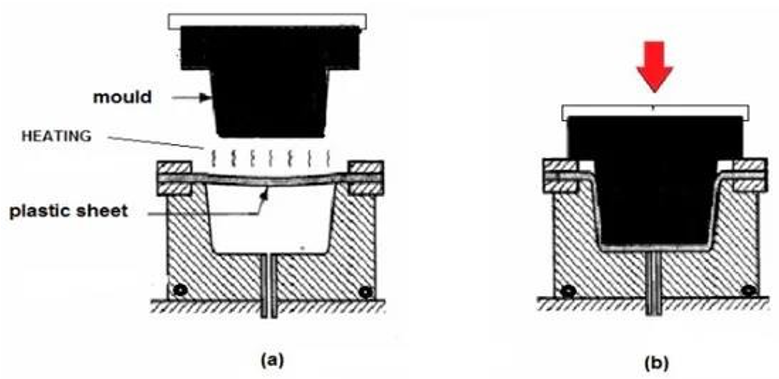
thermoforming
fiber spinning
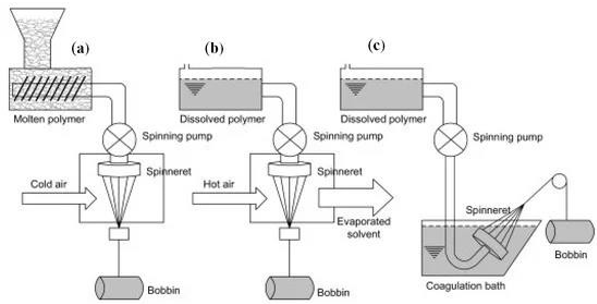
yes
can PLA and PHA both undergo thermoforming?
crystallinity
creating textiles requires high ________
PHA
which material has shown highest promise with fiber spinning?
benefits of using biobased feedstocks
•The same additives are normally needed
•Energy and GHG emissions are normally similar
soy PU foam
•Developed by Ford for automotive seating ~ 30% biomass
•Most toxic component still remains in synthesis: Diisocyanates
•Soy oil replaces petroleum-based polyol
•Can be synthesized at room temperature by mixing a Part A and Part B component
•Can be used in “Foam-in-place” applications
plasticized starch
Can be sourced from corn, wheat, rice, barely, potato, cassava etc.
Blend of amylose and amylopectin: 25/75% respectively
Native starch must be plasticized (is too brittle naturally) to be used in packaging applications
Typically involves heating with water, glycerol, or sorbitol
Then blended with other resins to increase the bio-content, decrease cost, increase biodegradability
for greater insulation properties
why you want a closed cell foam?