BIOL 235 - midterm 1 diagrams
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
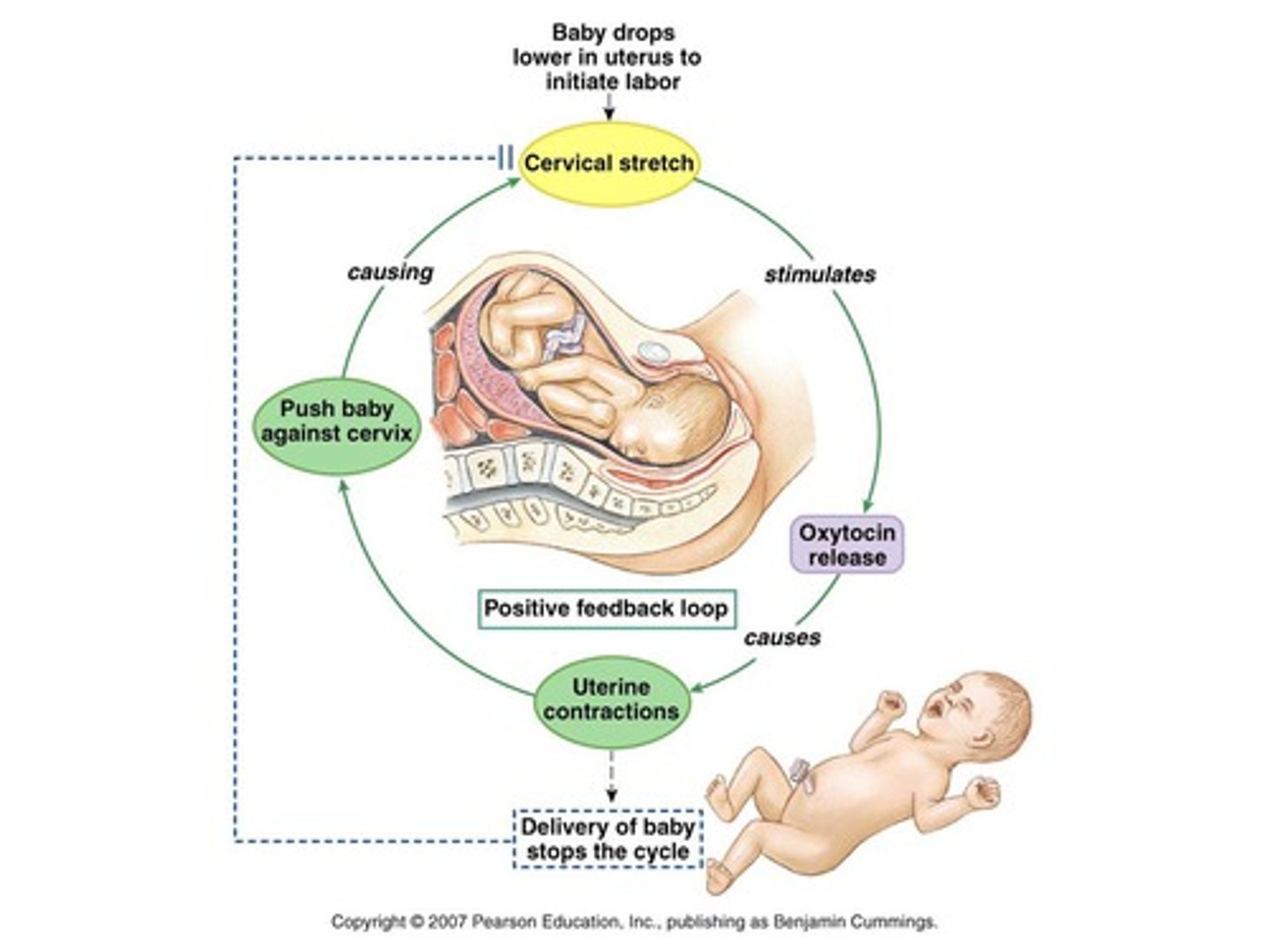
Positive feedback system
if a response enhances the original stimulus
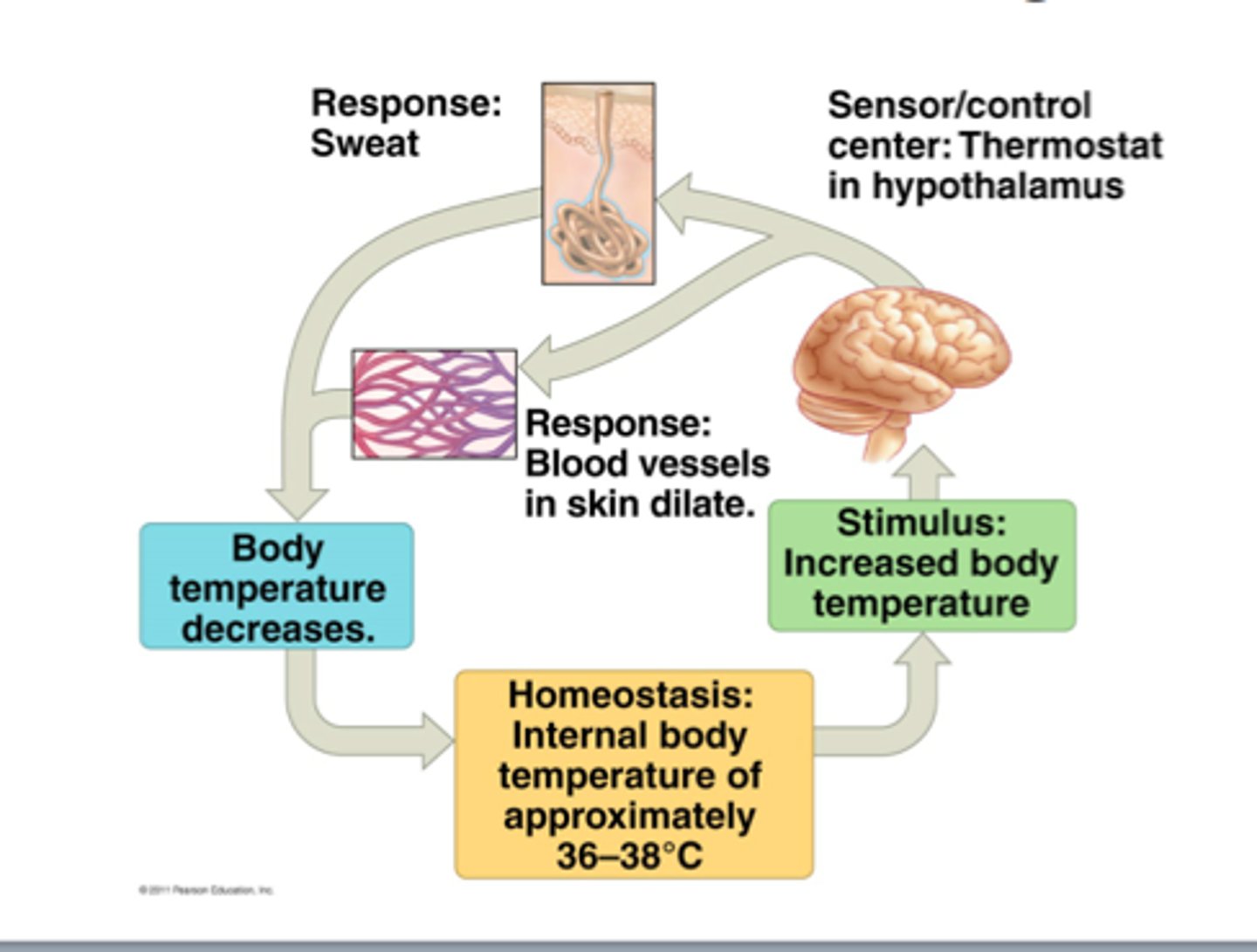
Negative feedback system
if a response reverses the original stimulus
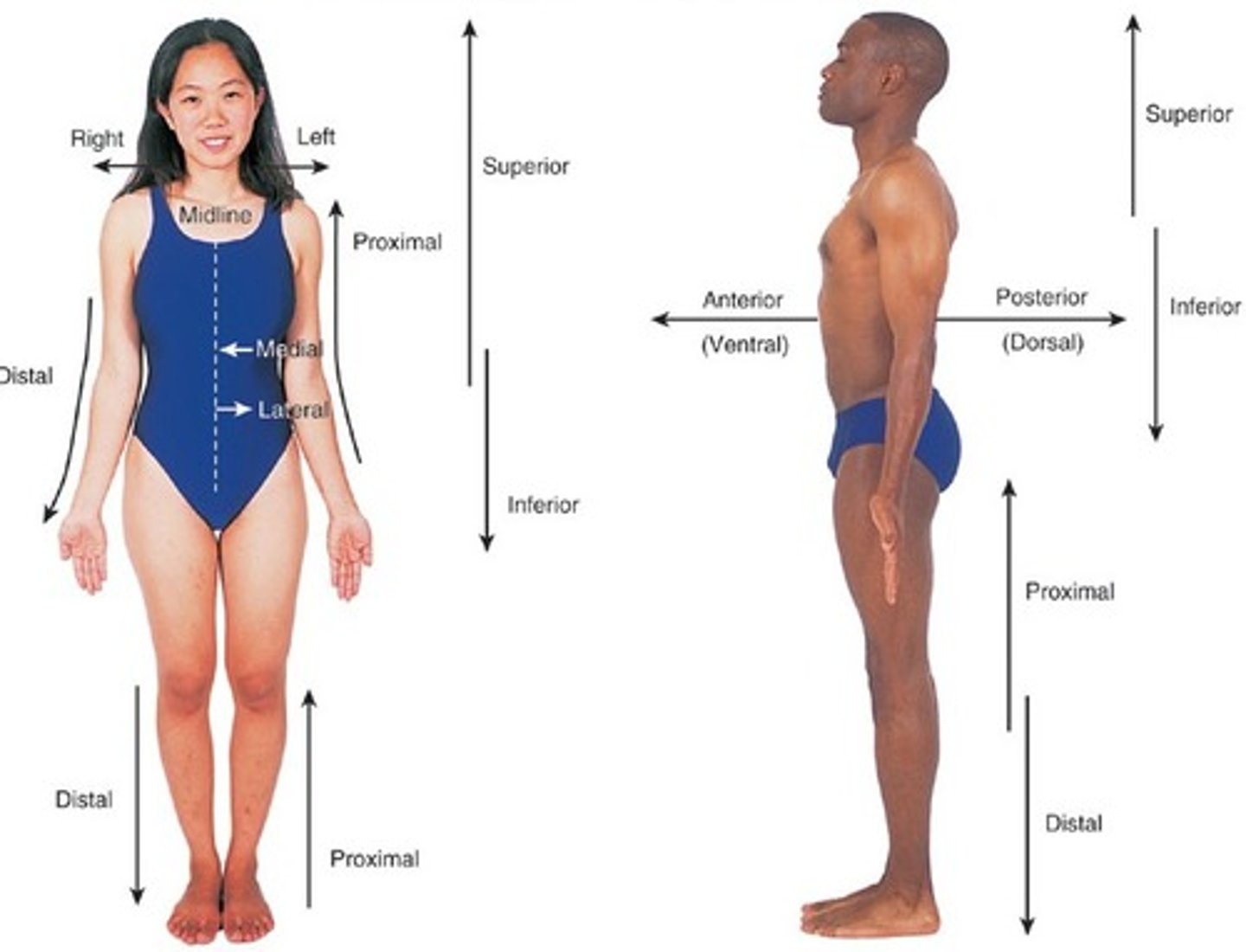
Anatomical position/ directional terms
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
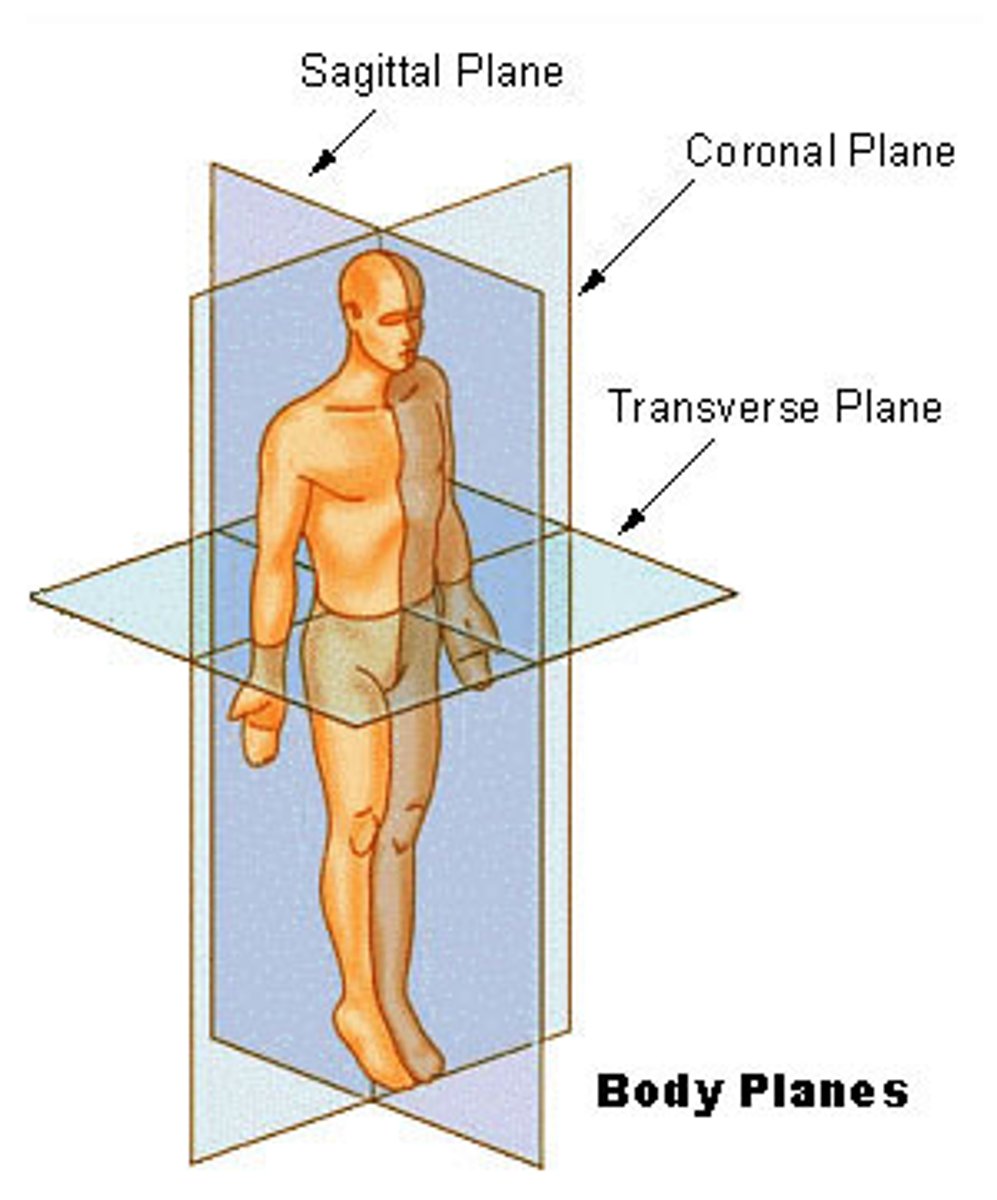
Planes of the body
Dividing the body into planes or flat surfaces is an additional way to describe the body. (useful in CT scans, MRI, etc.)
Sagittal Plane, Midsagittal plane, Frontal plane, Transverse Plane
Body cavities
spaces within the body that contain vital organs
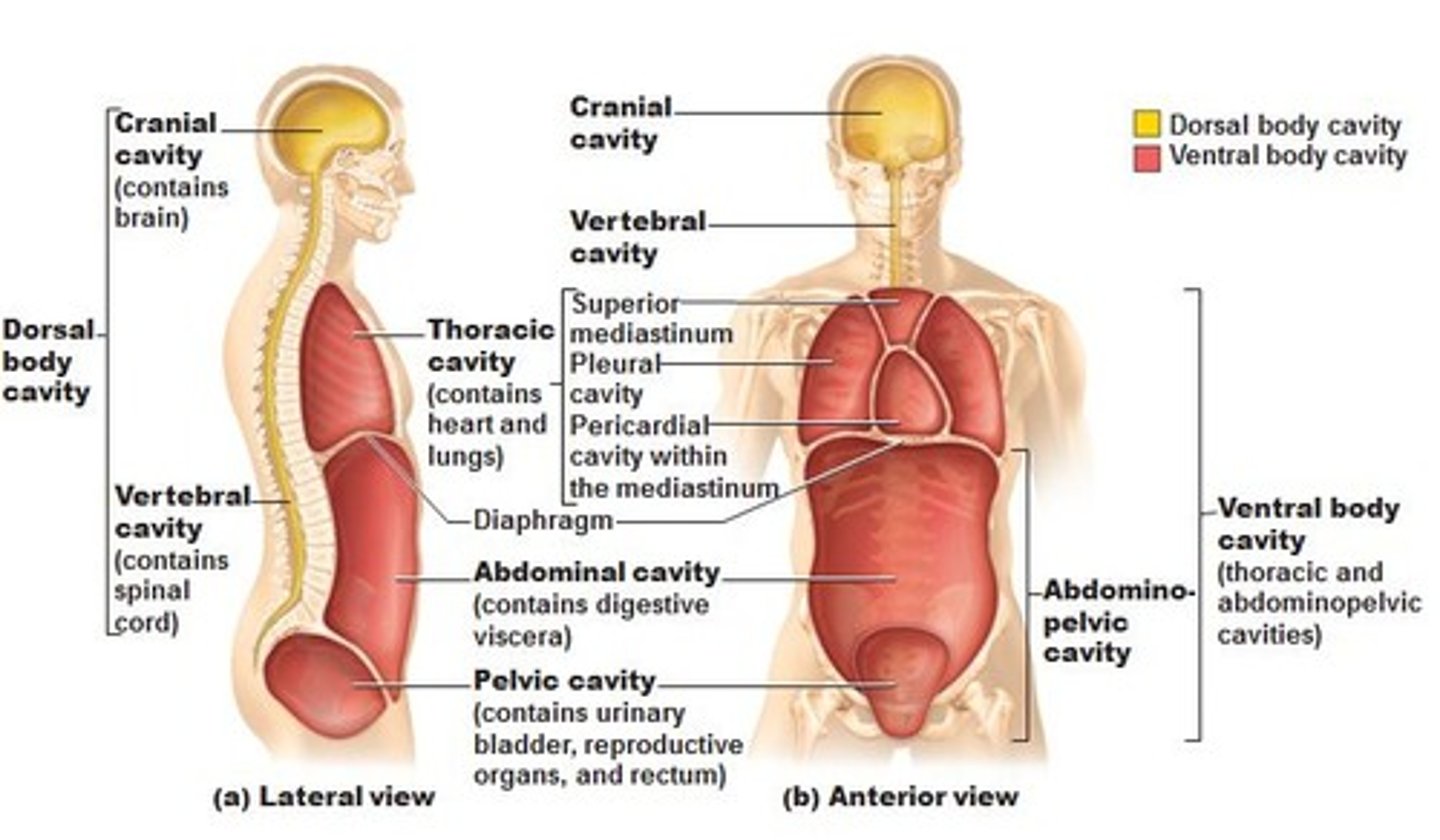
abdominopelvic cavity
contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities
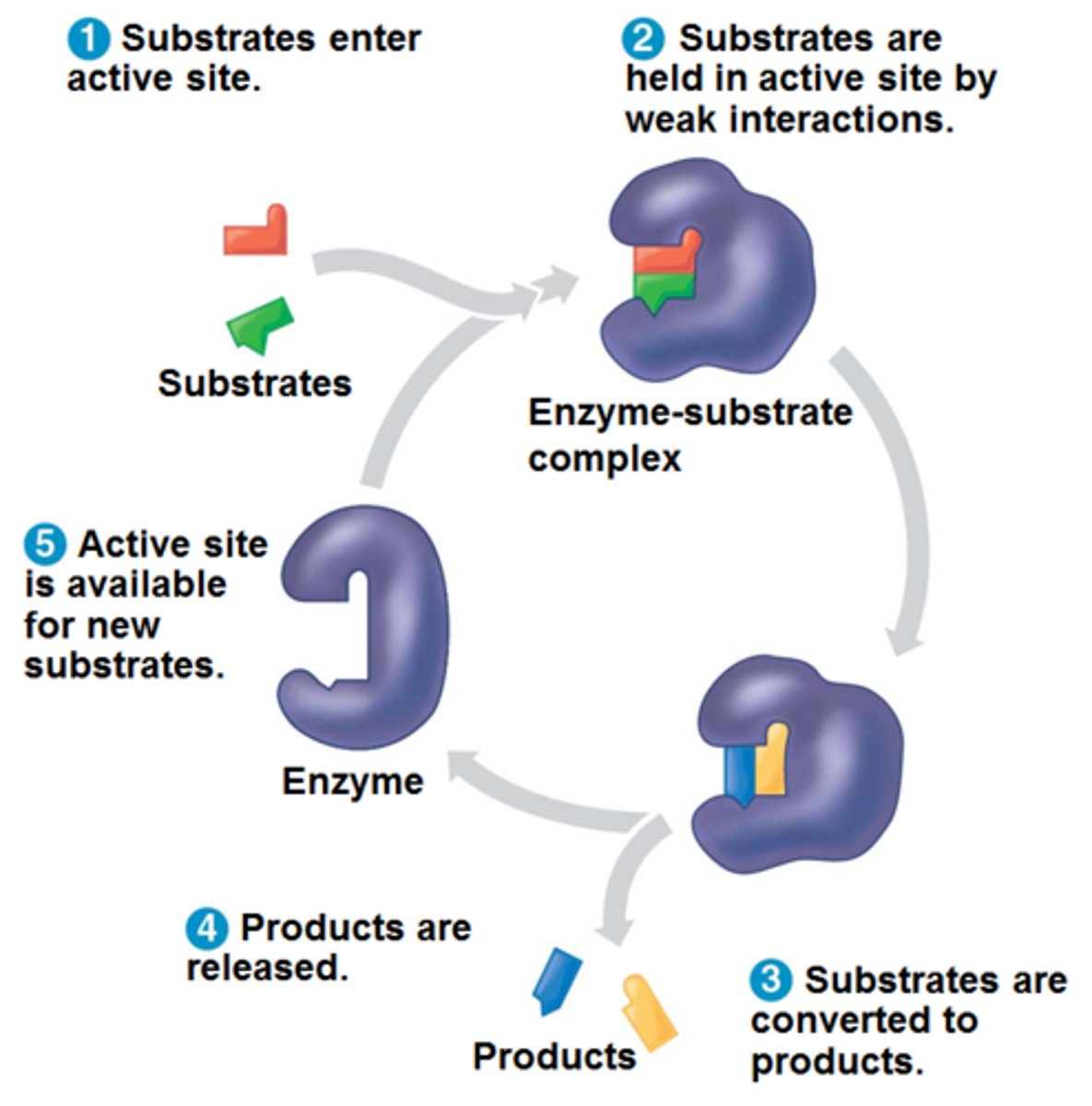
How an enzyme works
1.Substrates are bound to the active site by attractions to amino side chains
2.Shape changes in the active site forces the substrate into a shape that is halfway between the substrate and the product
3. bonds are broken and new bonds are made (make bonds to break bonds)
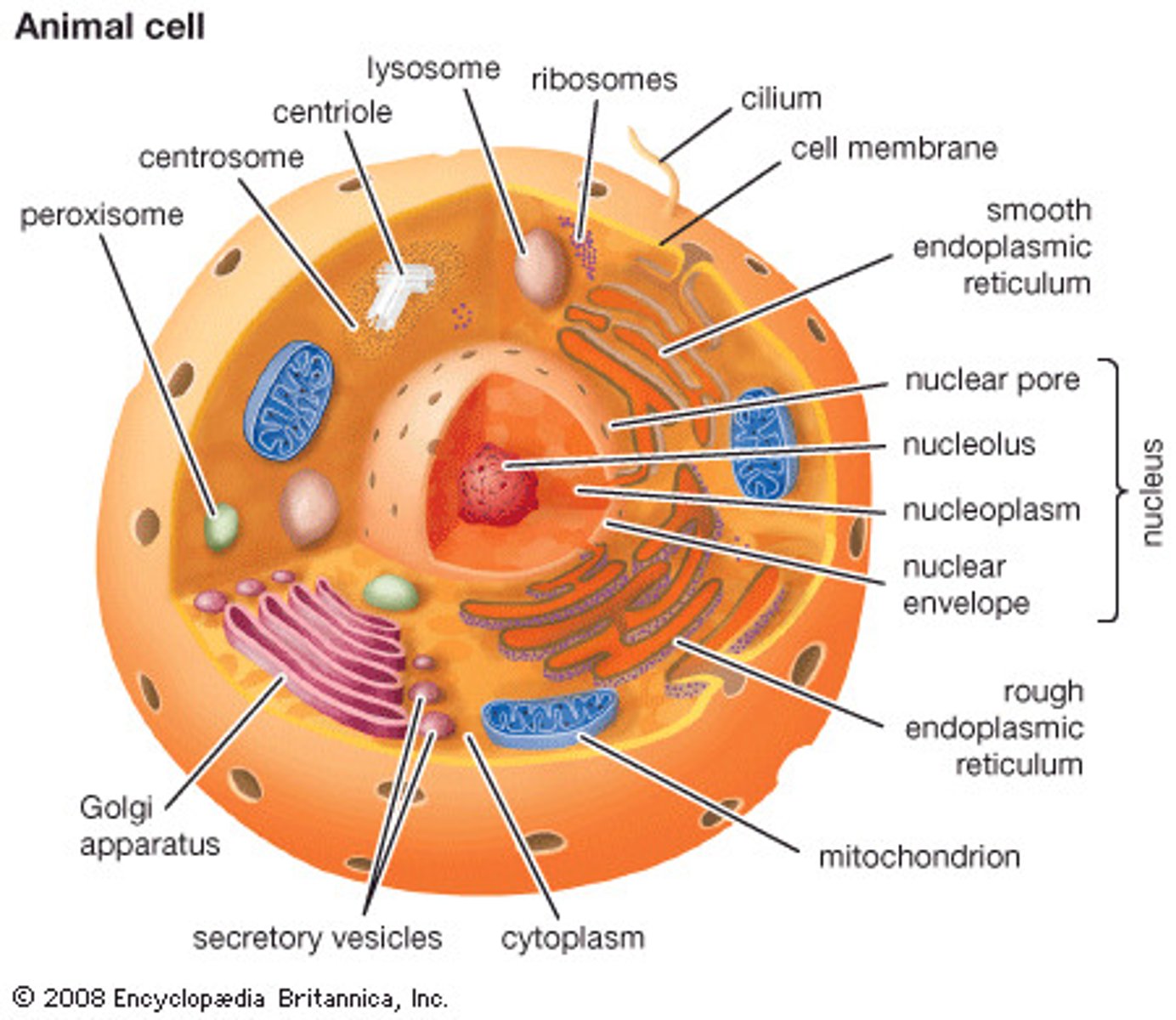
Parts of a cell
Cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplasts, chromatin, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, flagella, golgi complex/apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nucleolus, nucleus, ribosomes, vacuole
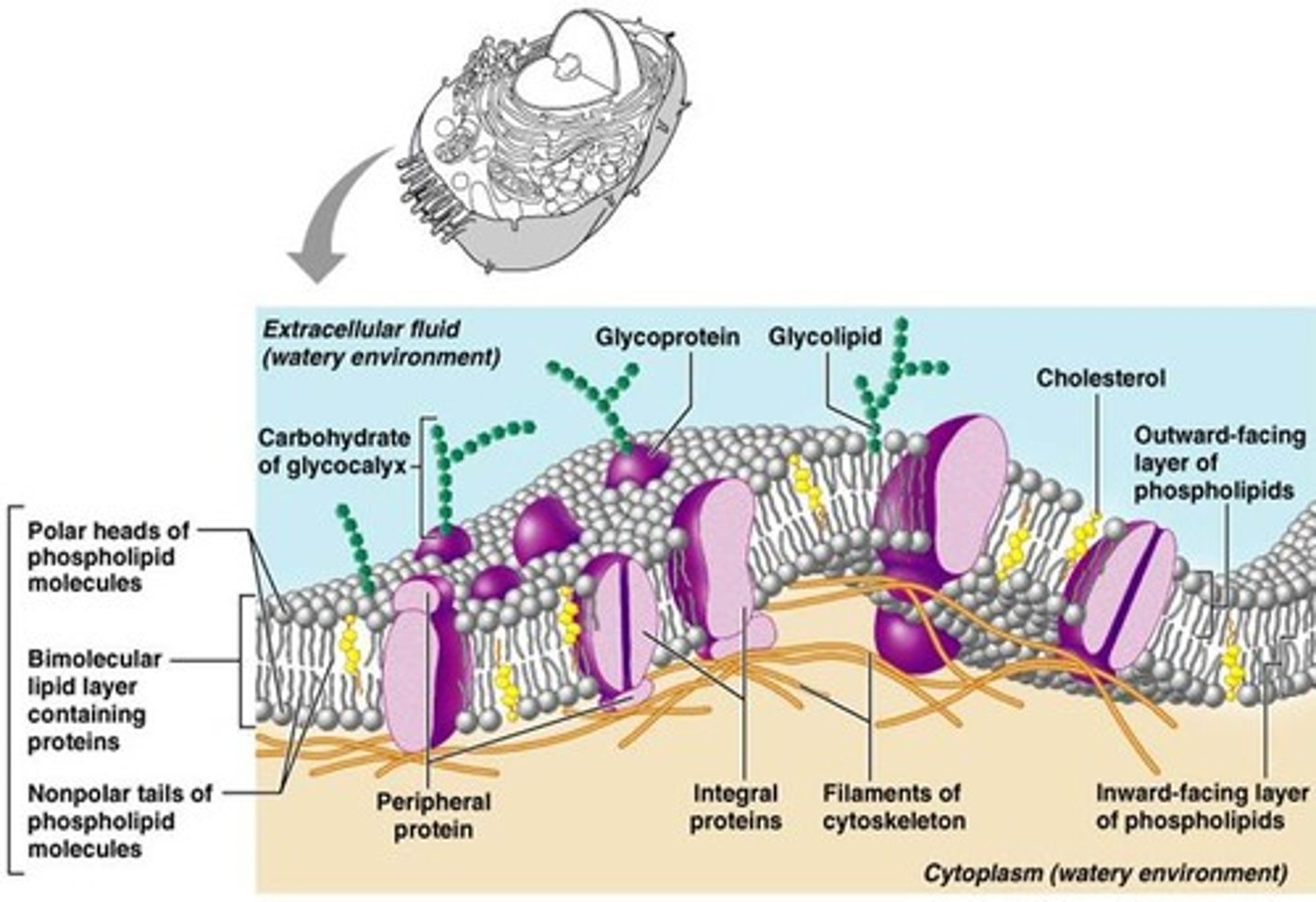
Fluid mosaic model
Structural model of the plasma membrane where molecules are free to move sideways within a lipid bilayer.
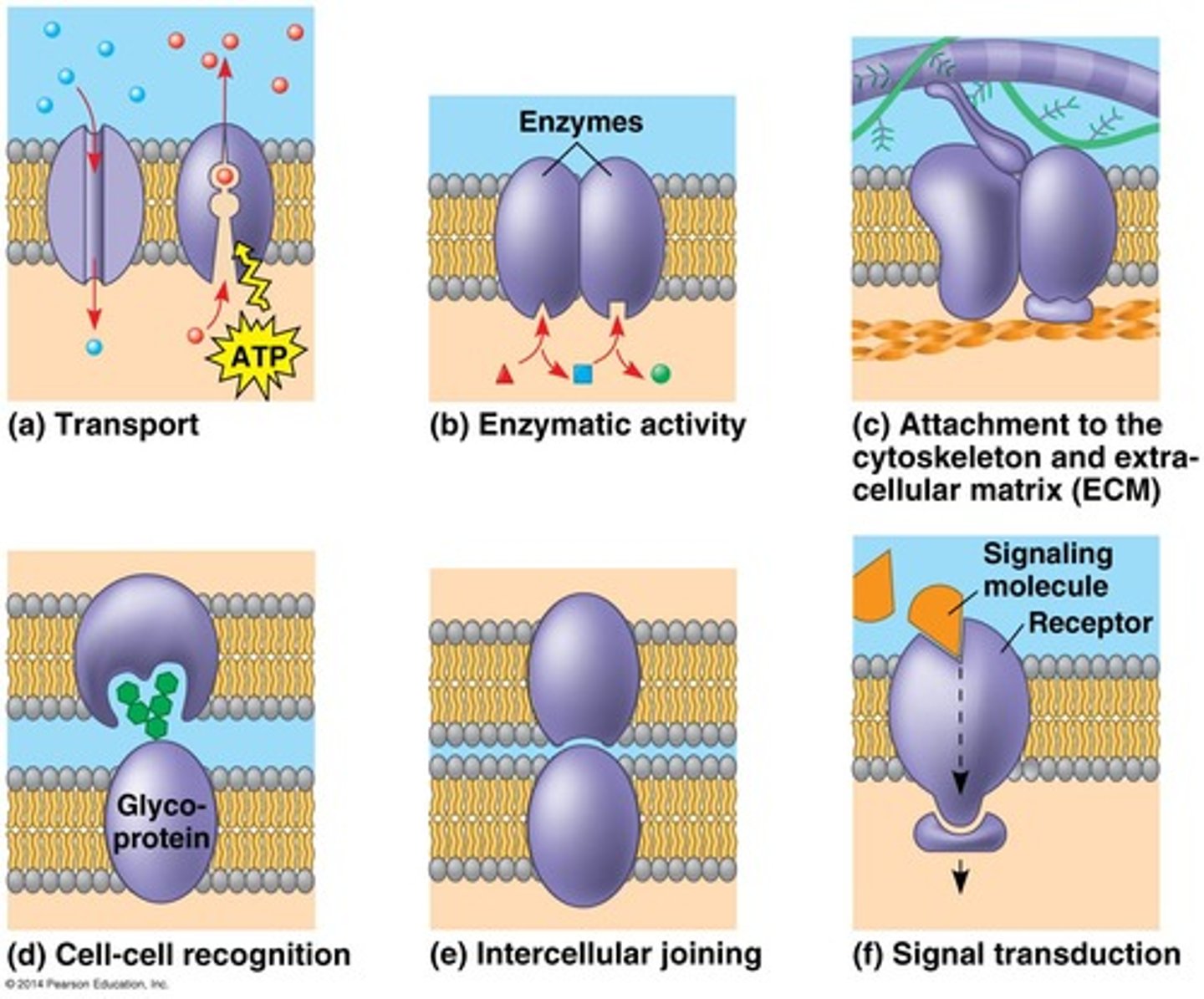
Function of membrane proteins
transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
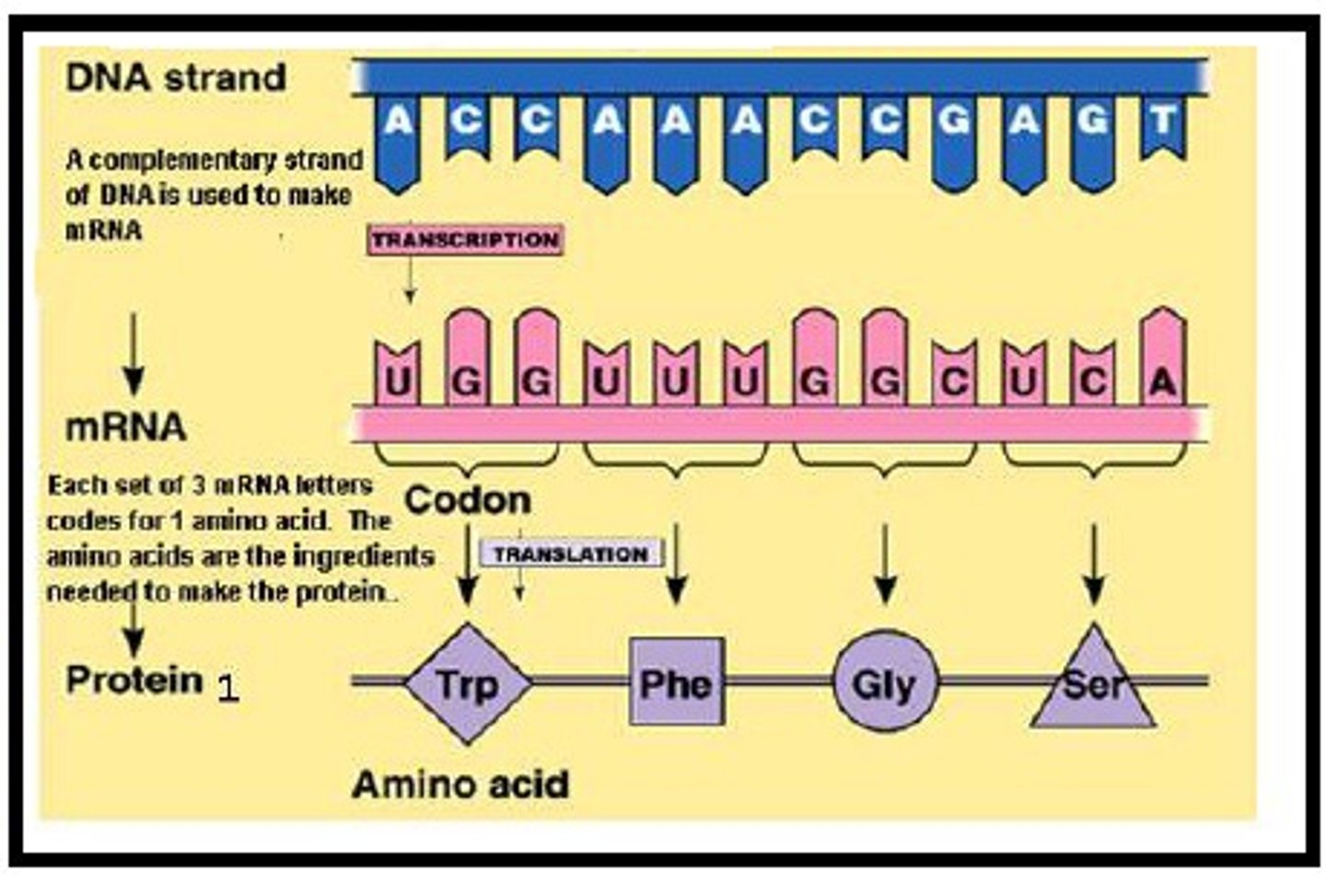
DNA to mRNA
A-U
T-A
C-G
G-C
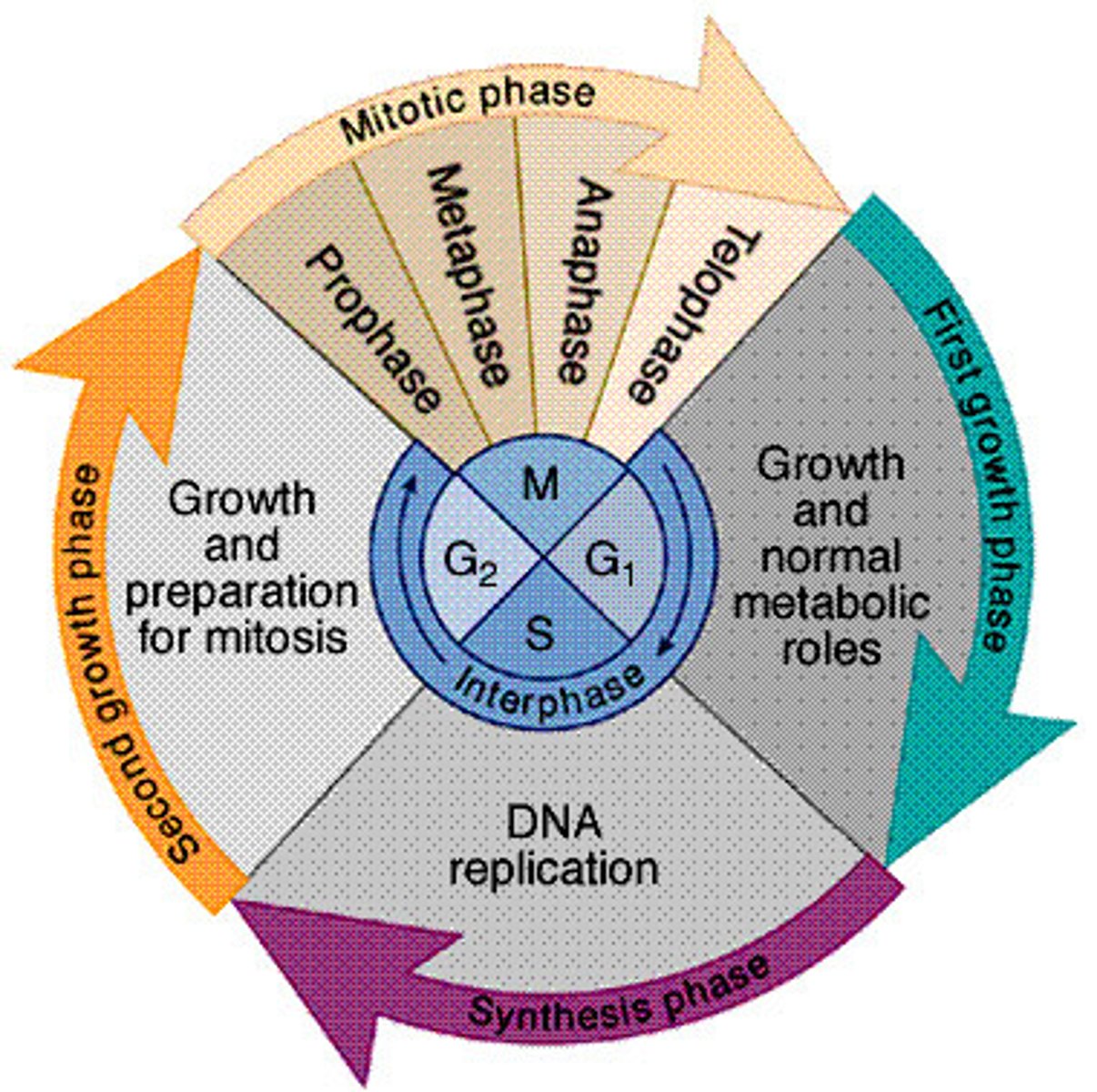
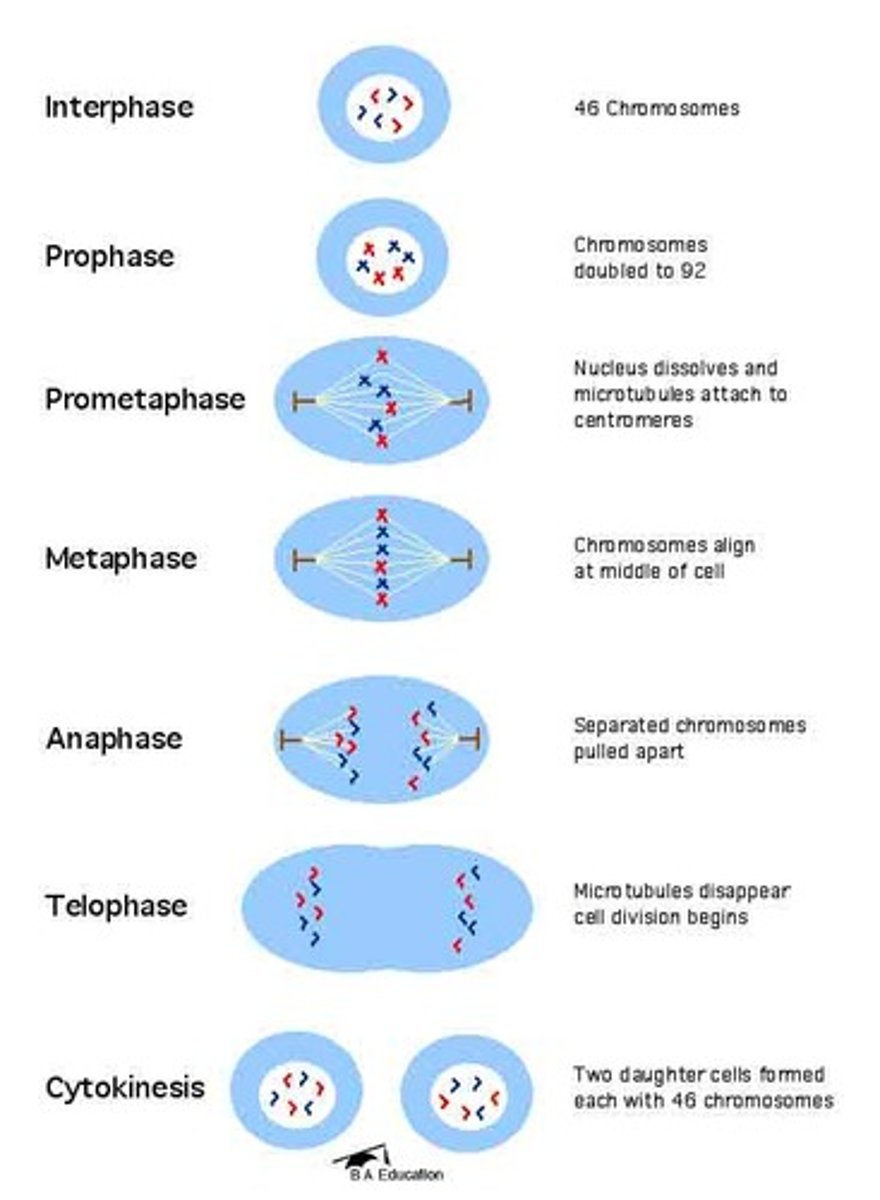
Cell division mitosis
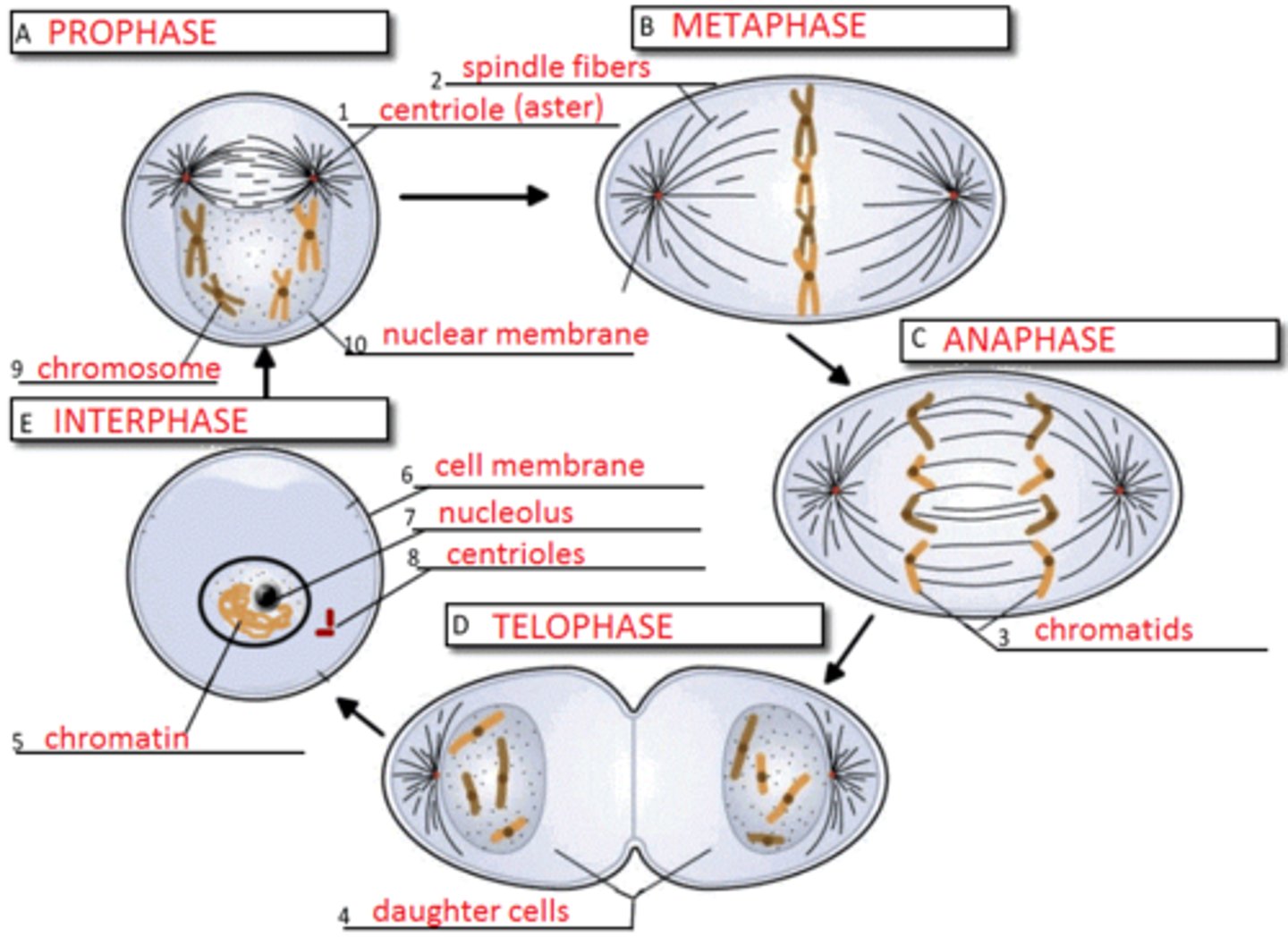
Mitosis reproductive cell division
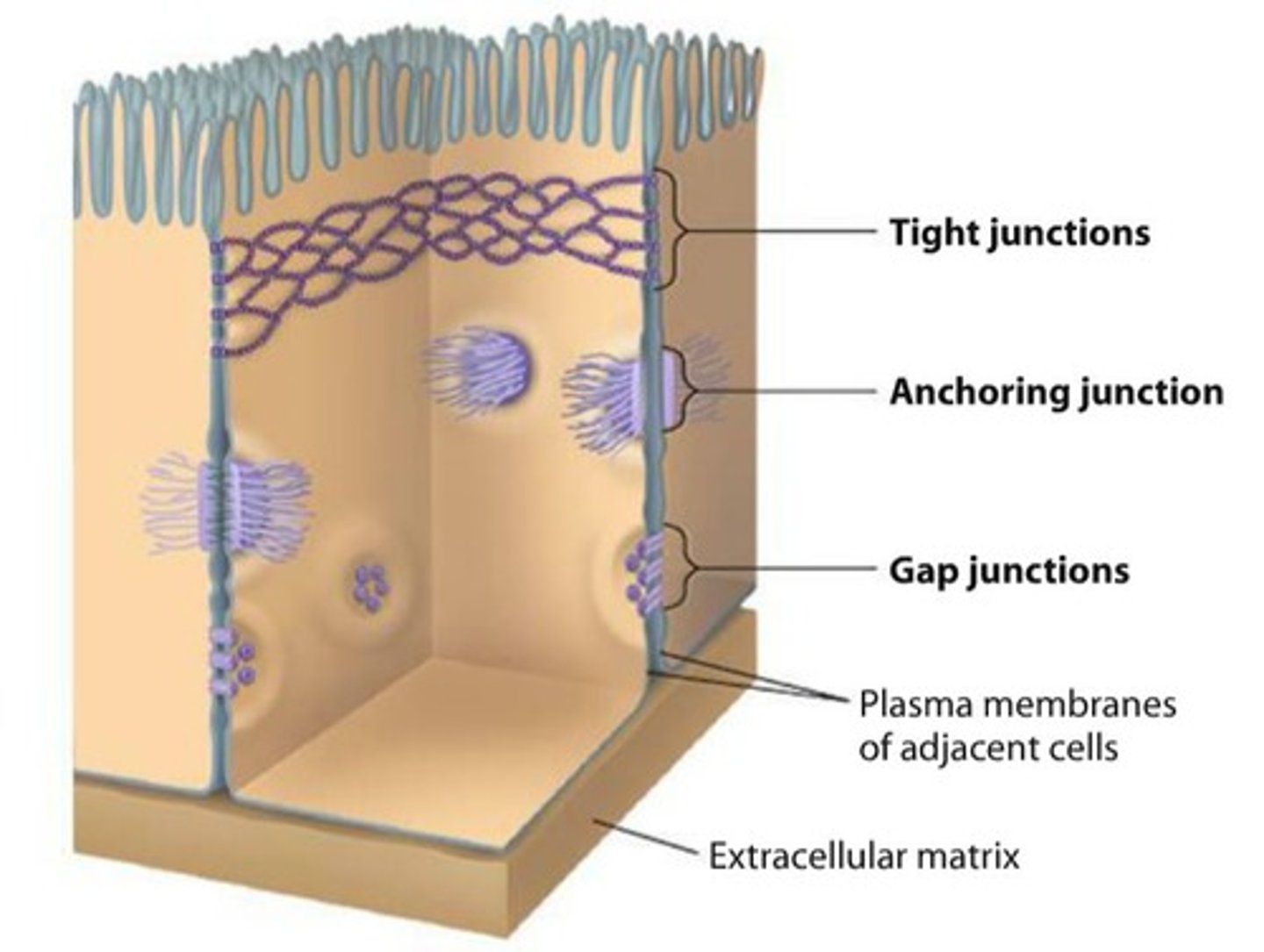
Cell junctions
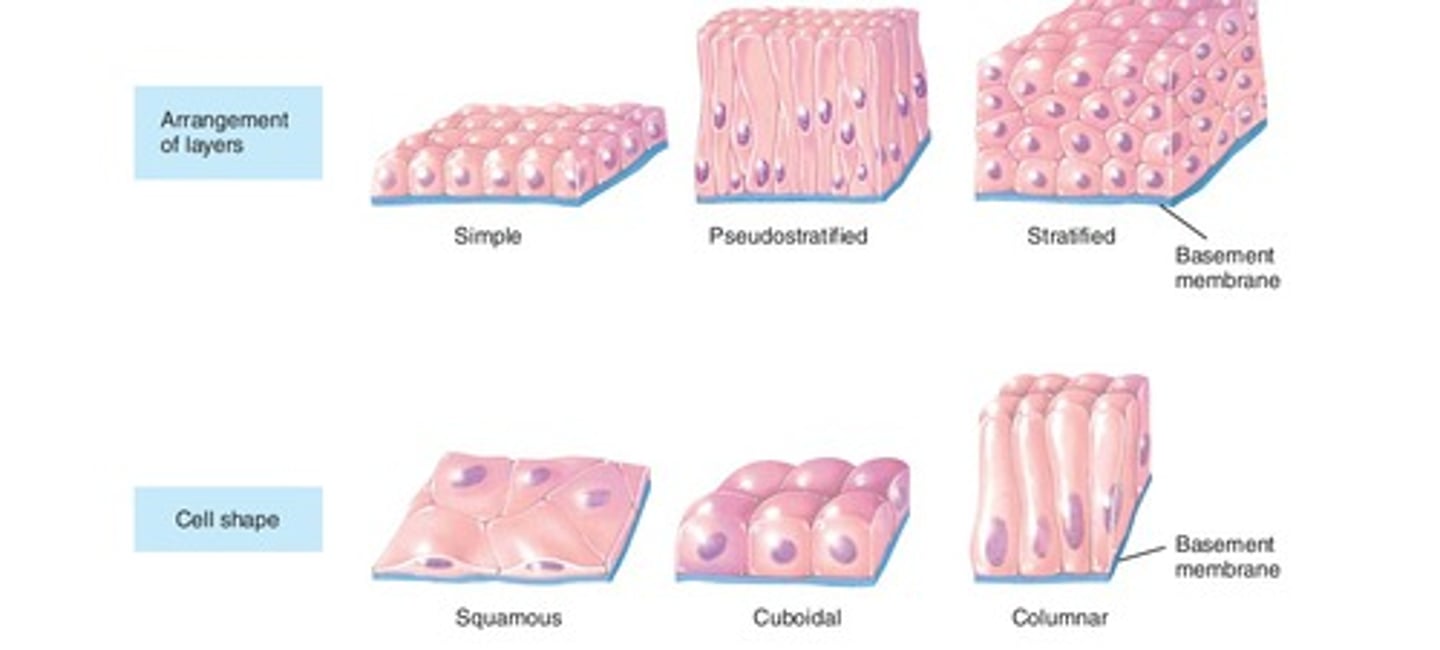
Cell shapes & arrangement of layers
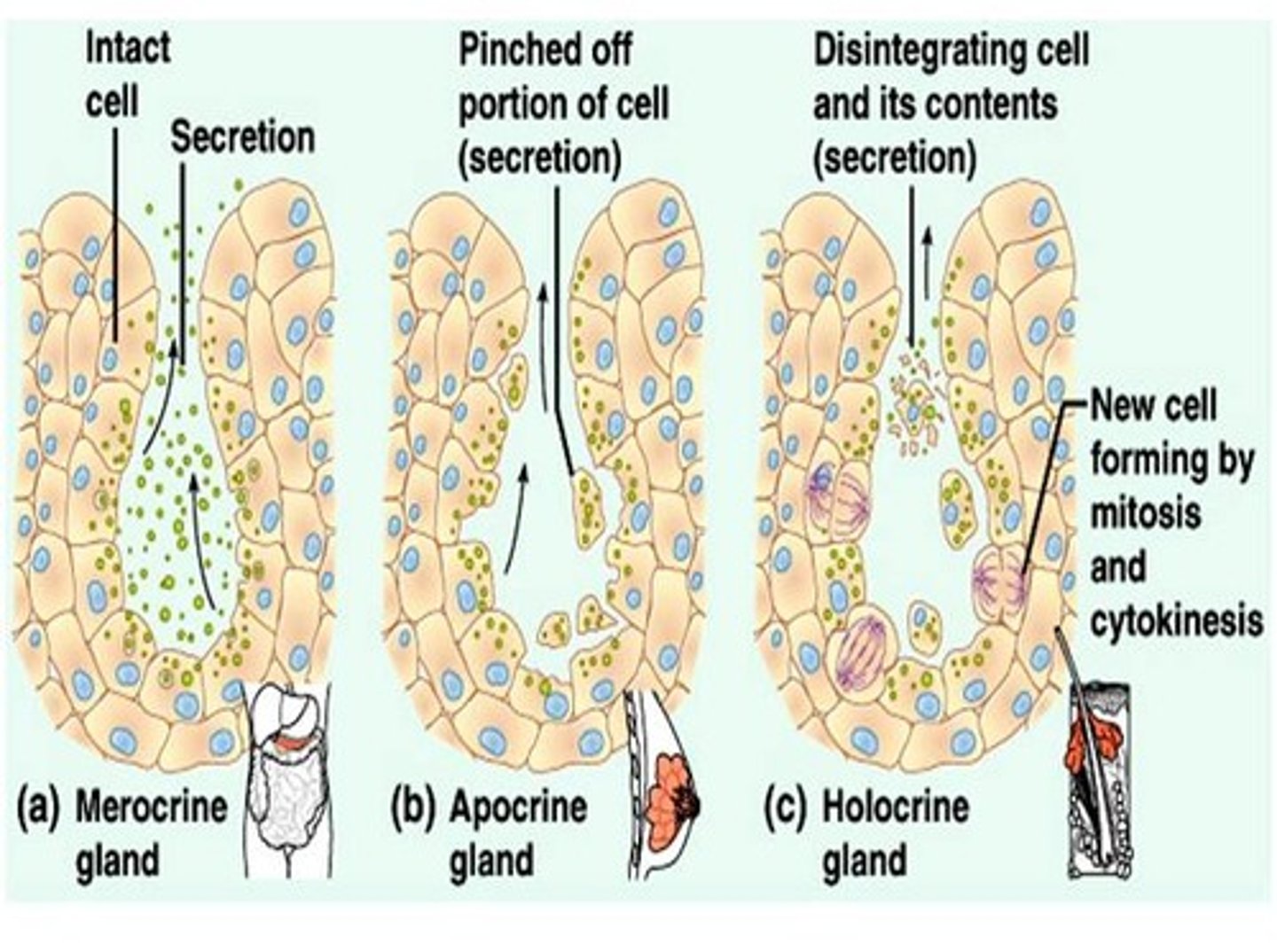
Multicellular exocrine glands
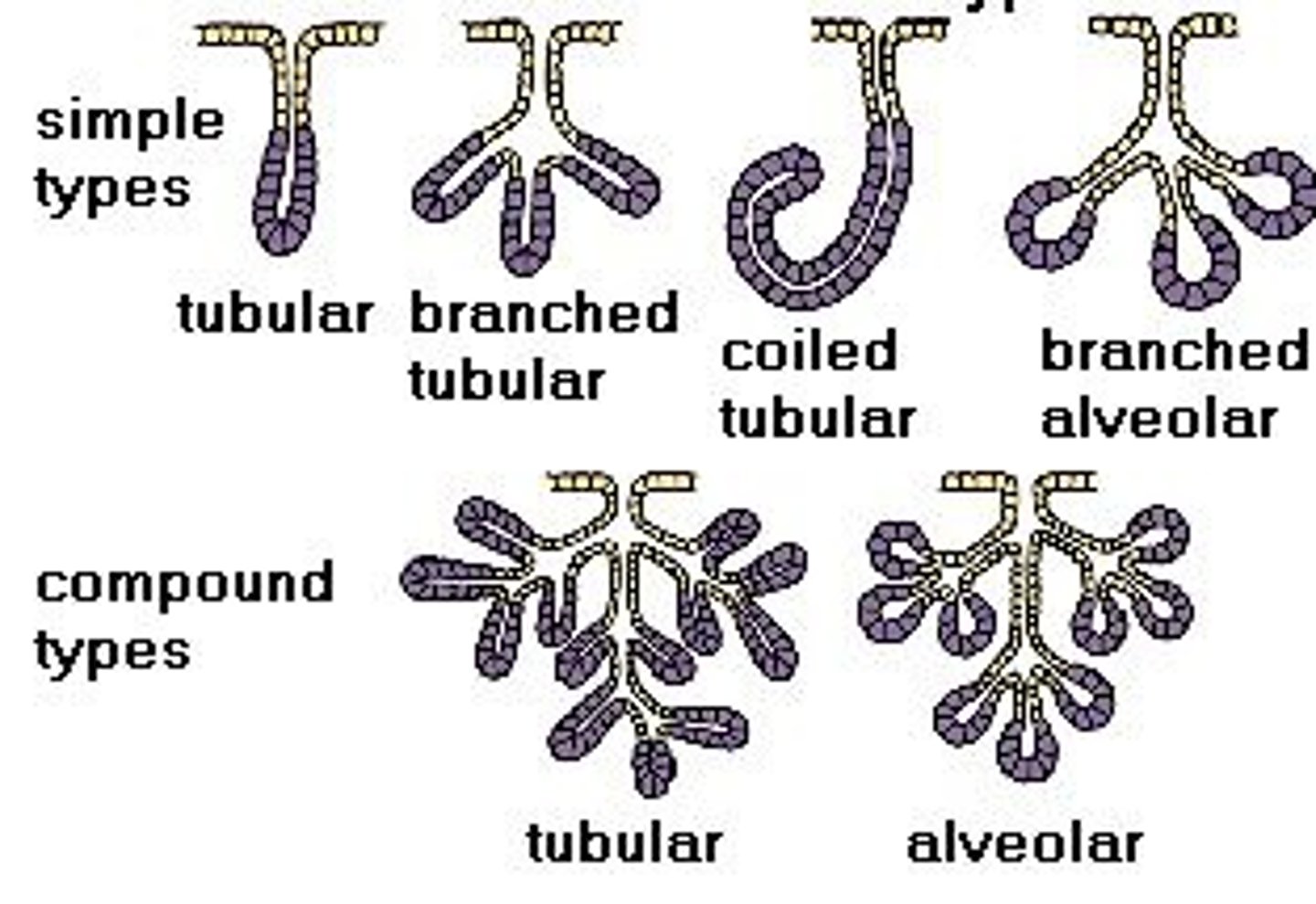
Glands and secretions
- salivary gland
- mammary gland
- sebaceous oil gland
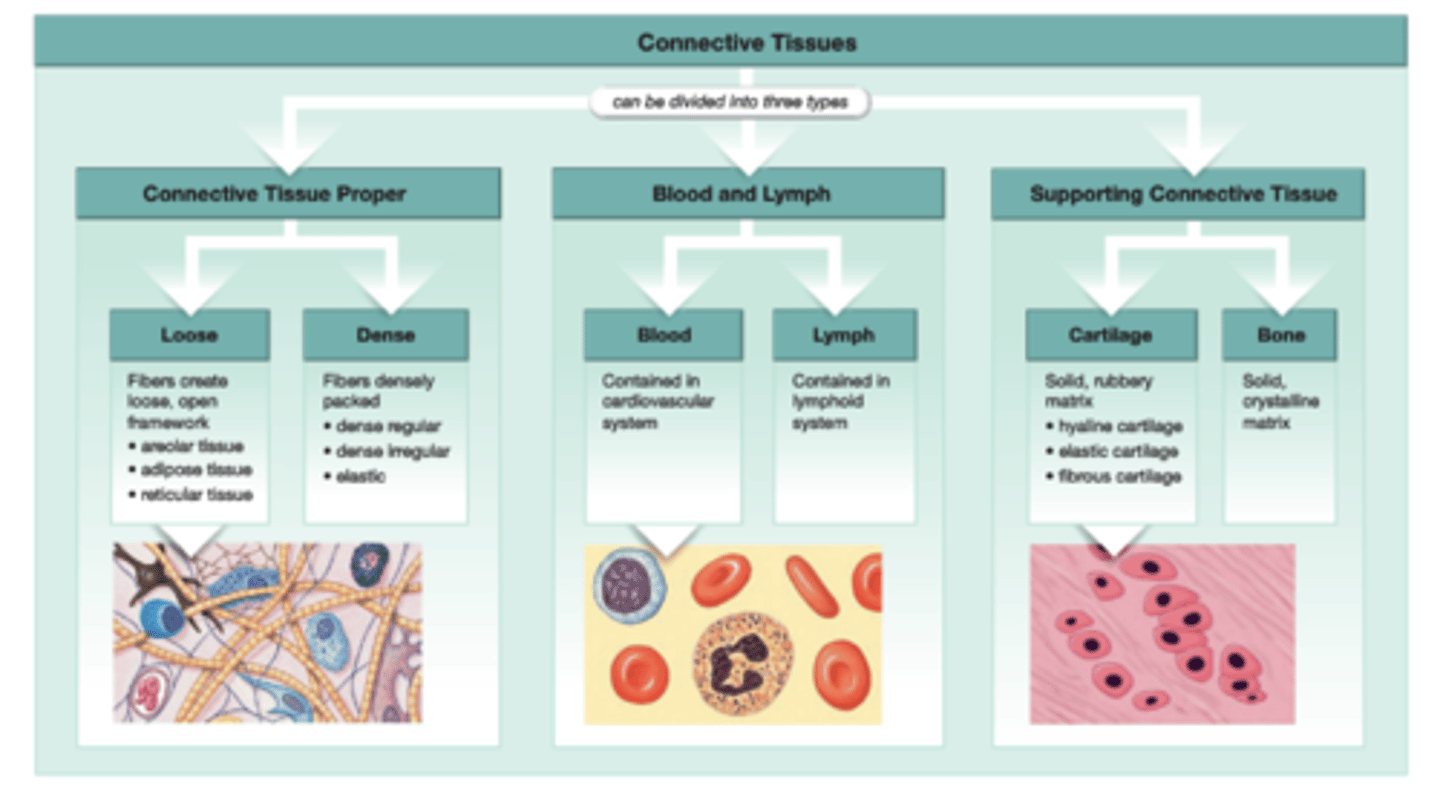
Connective tissues
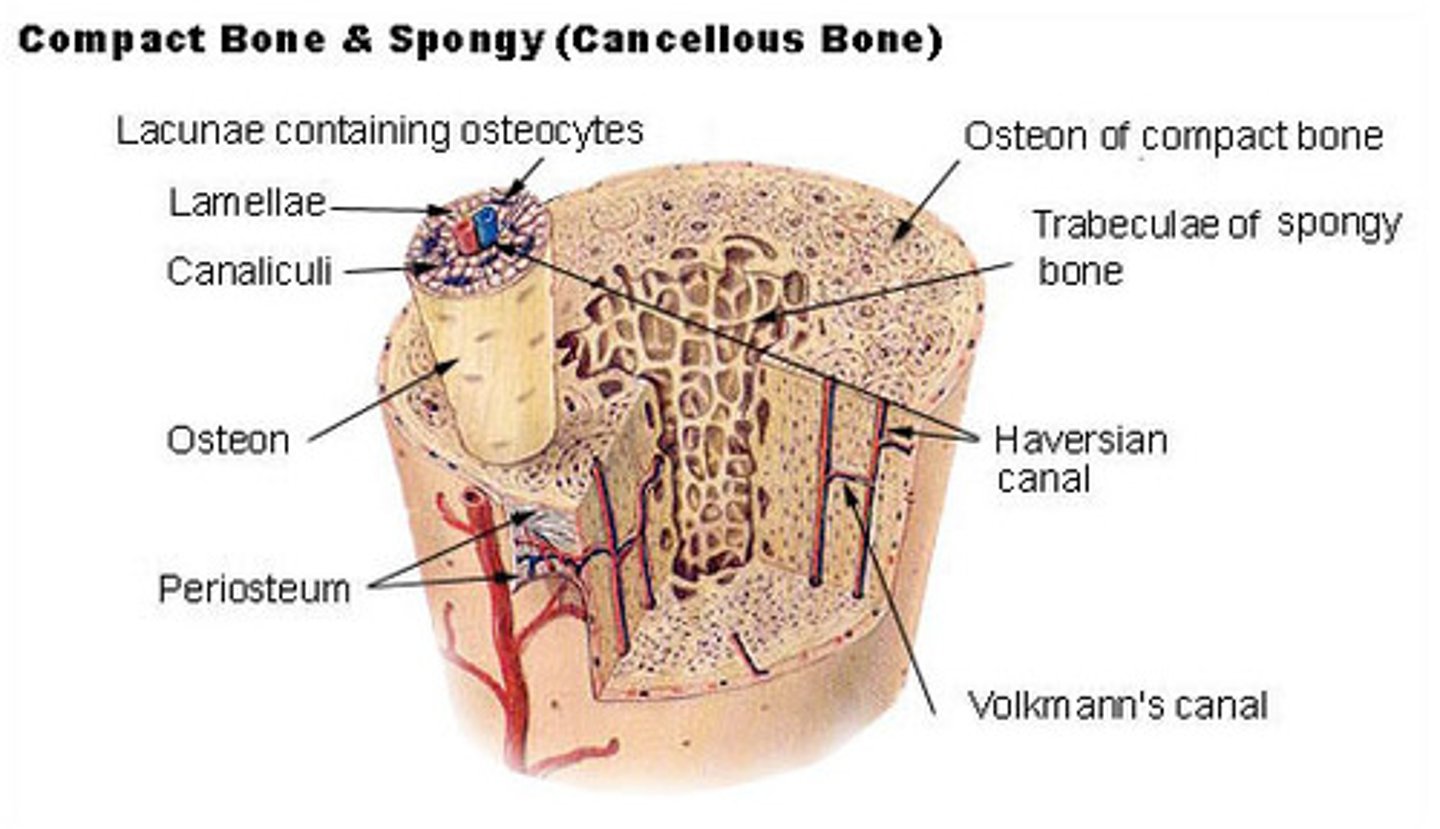
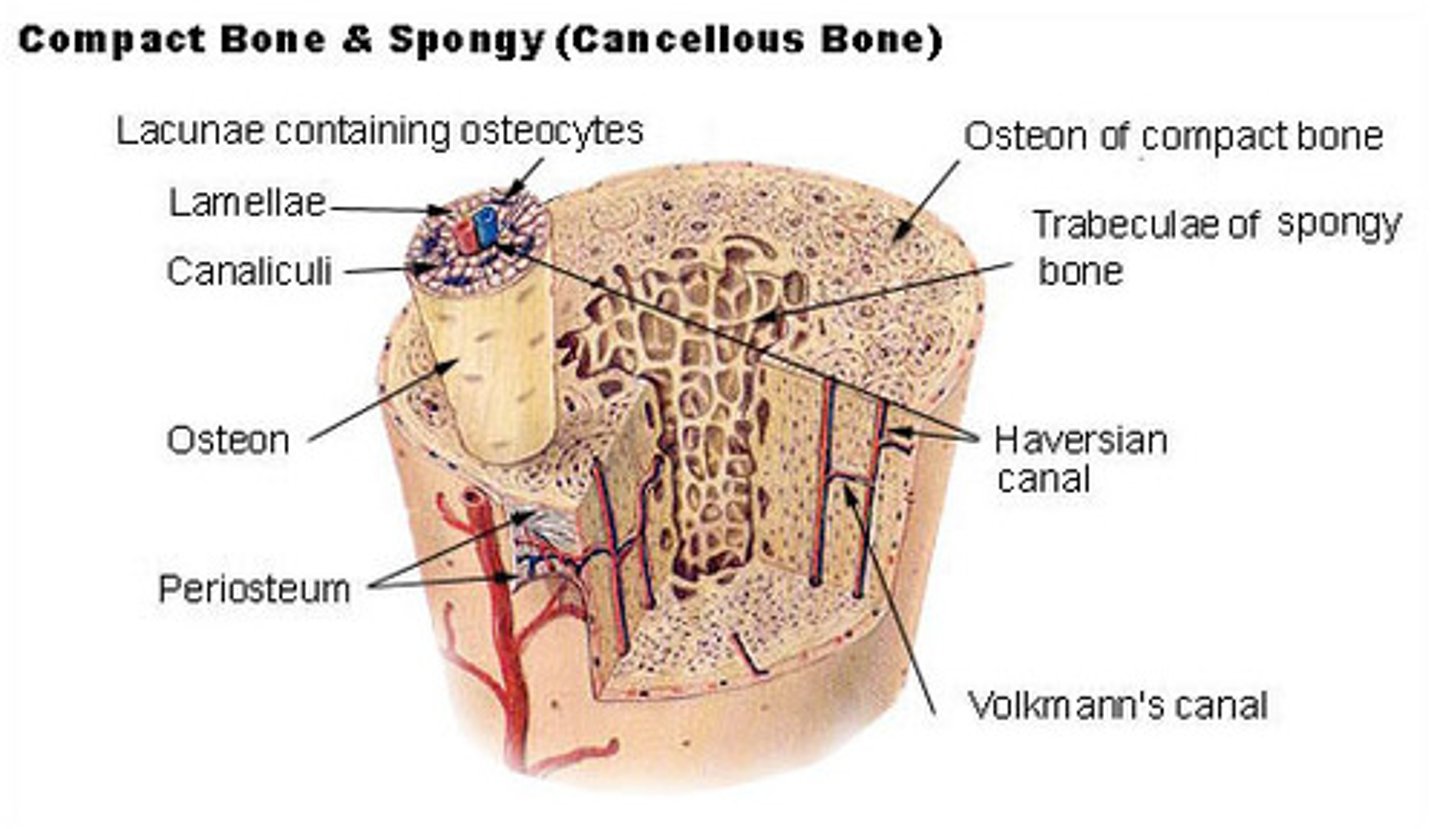
Bone tissue
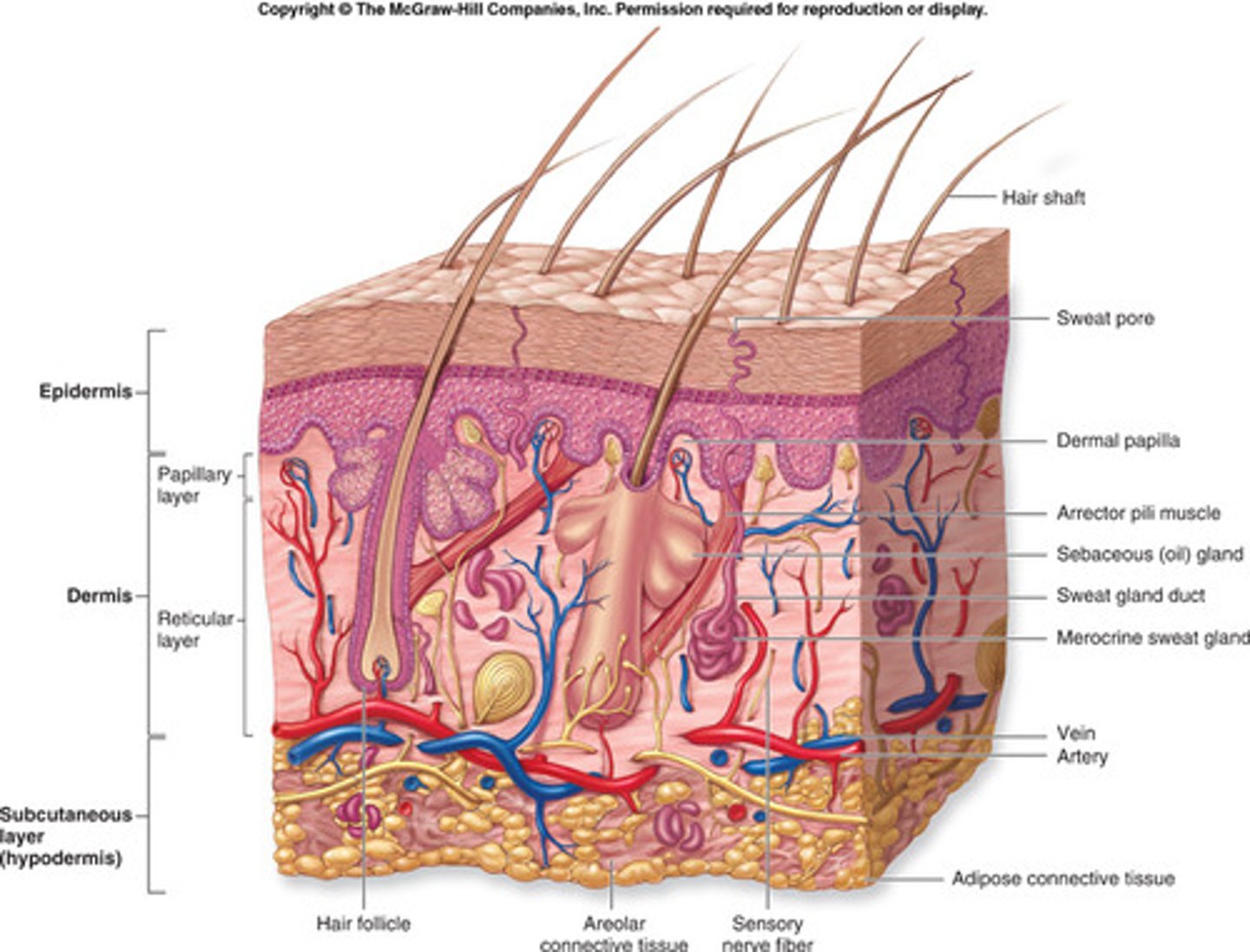
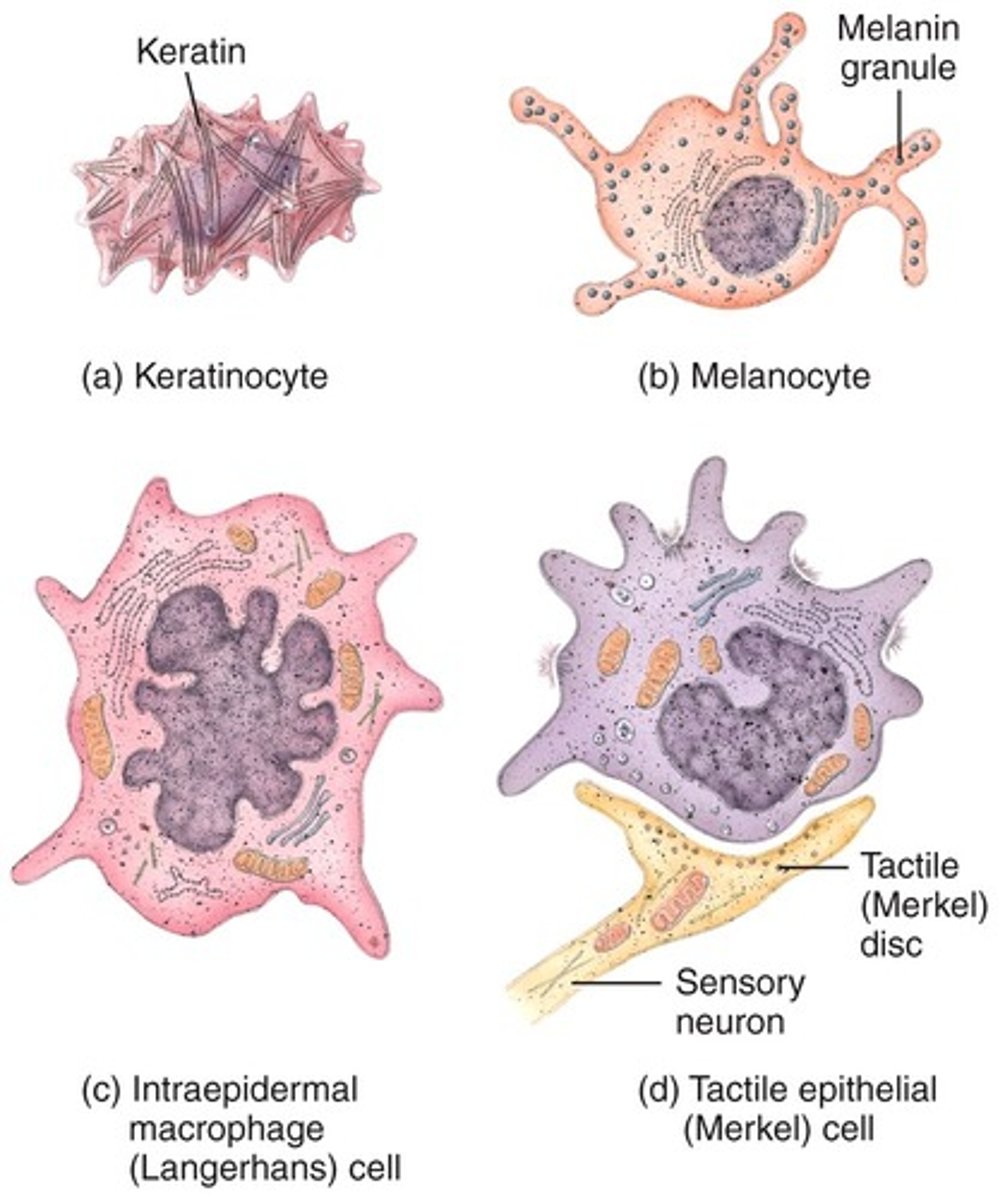
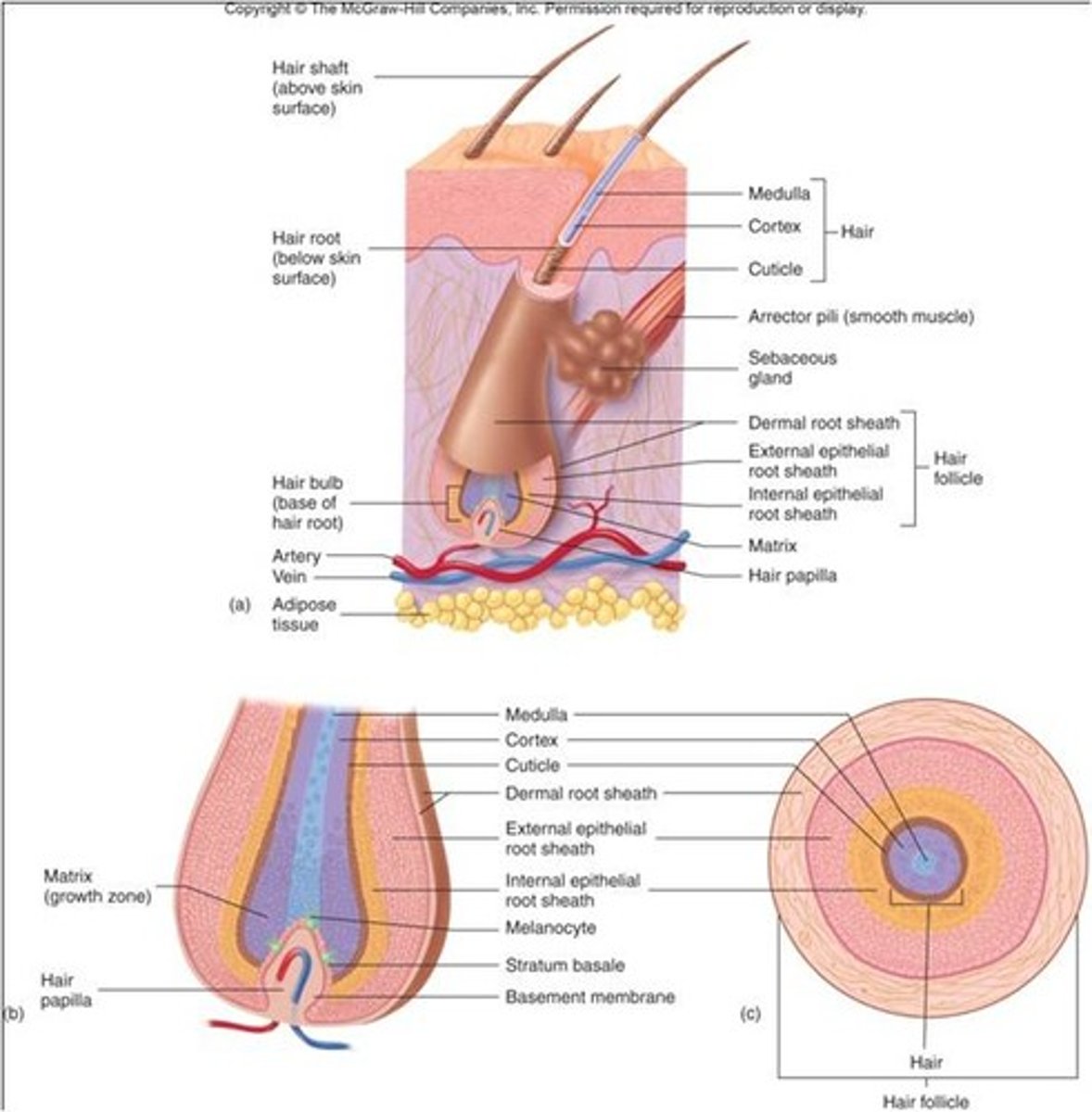
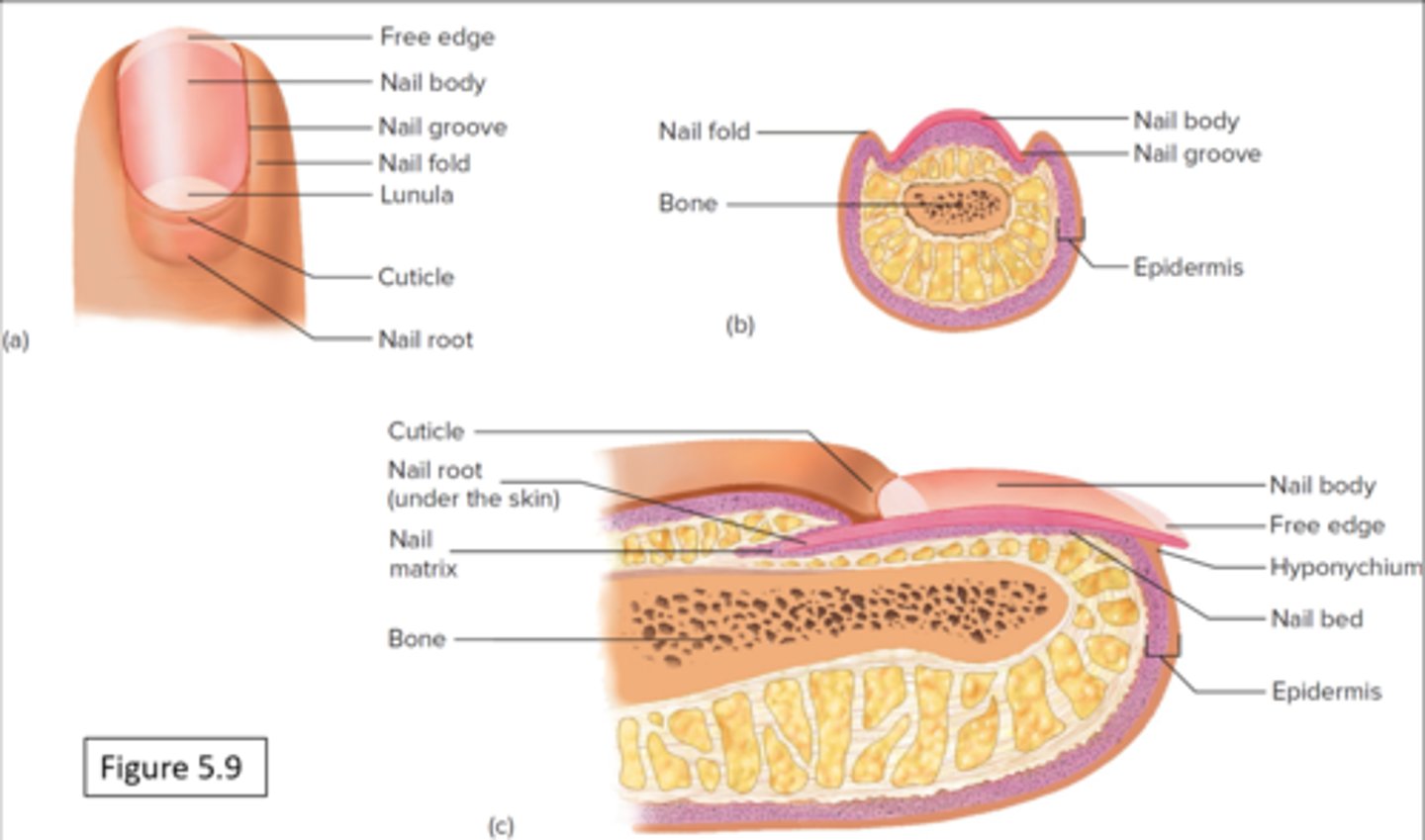
Integumentary system
Cells in the epidermis
Hair (structure)
Nail (structure)
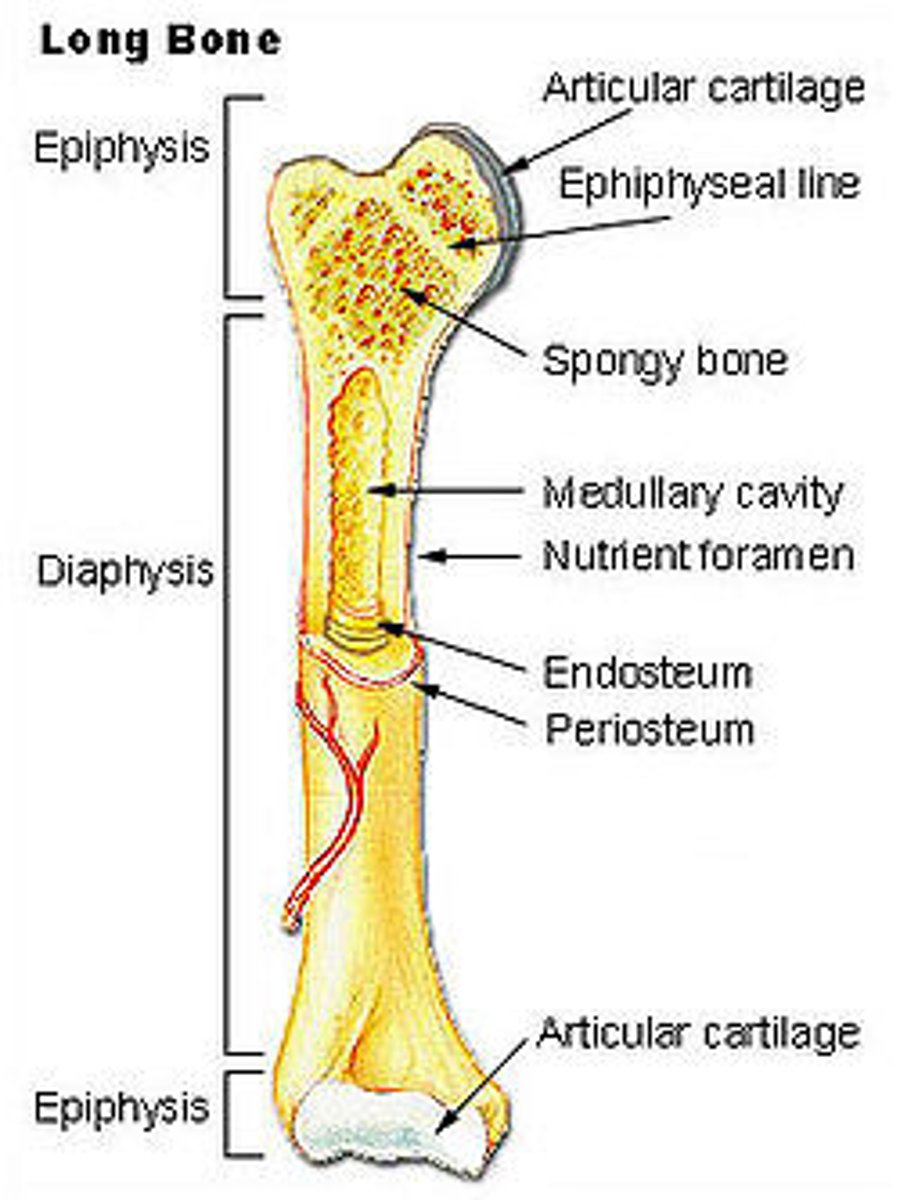
Parts of long bone
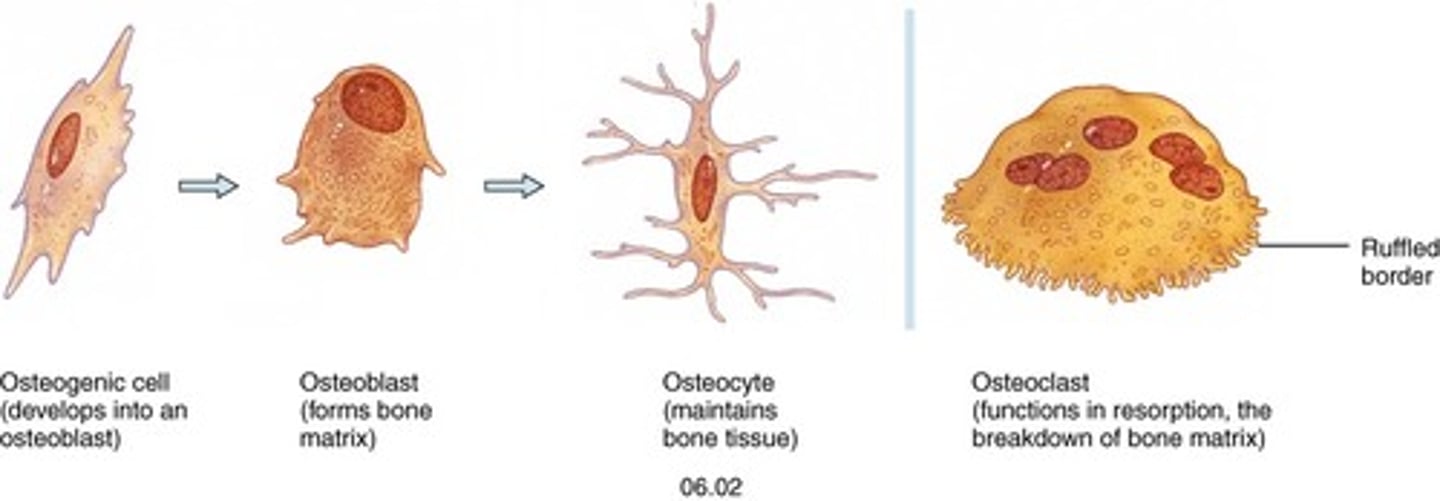
Types of cells in bone tissue
Spongy and compact bone
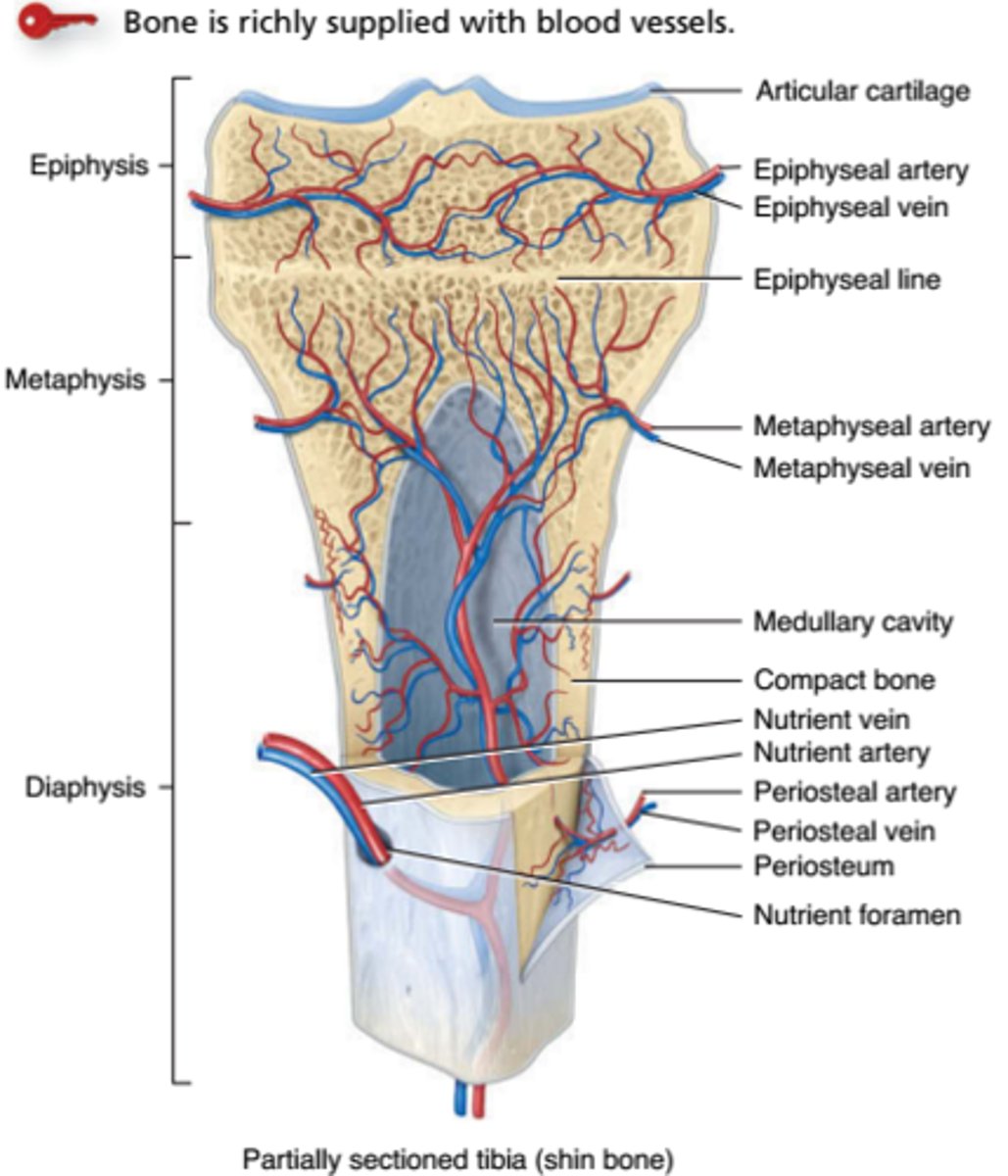
Blood supply of mature long bone
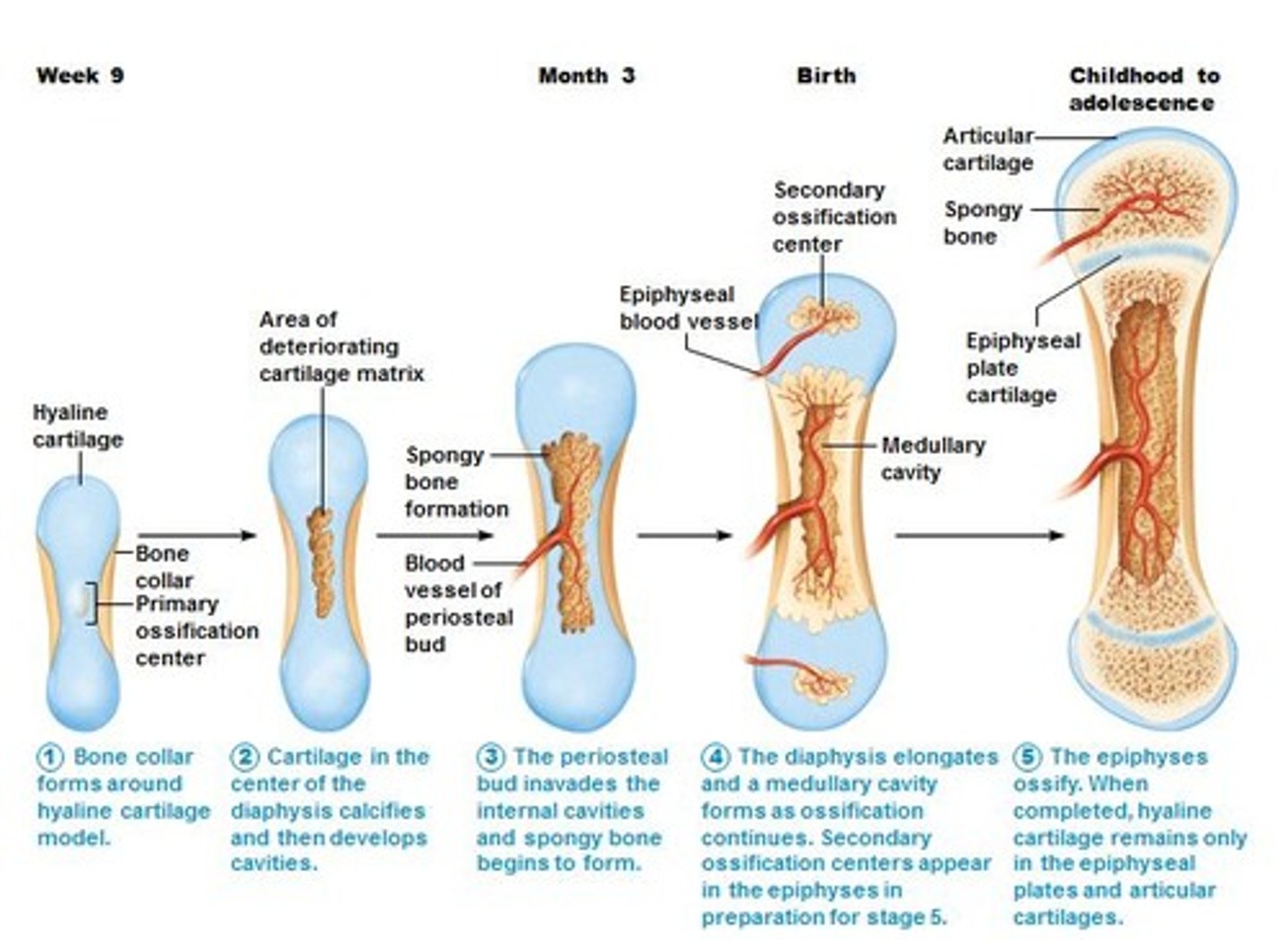
Bone formation
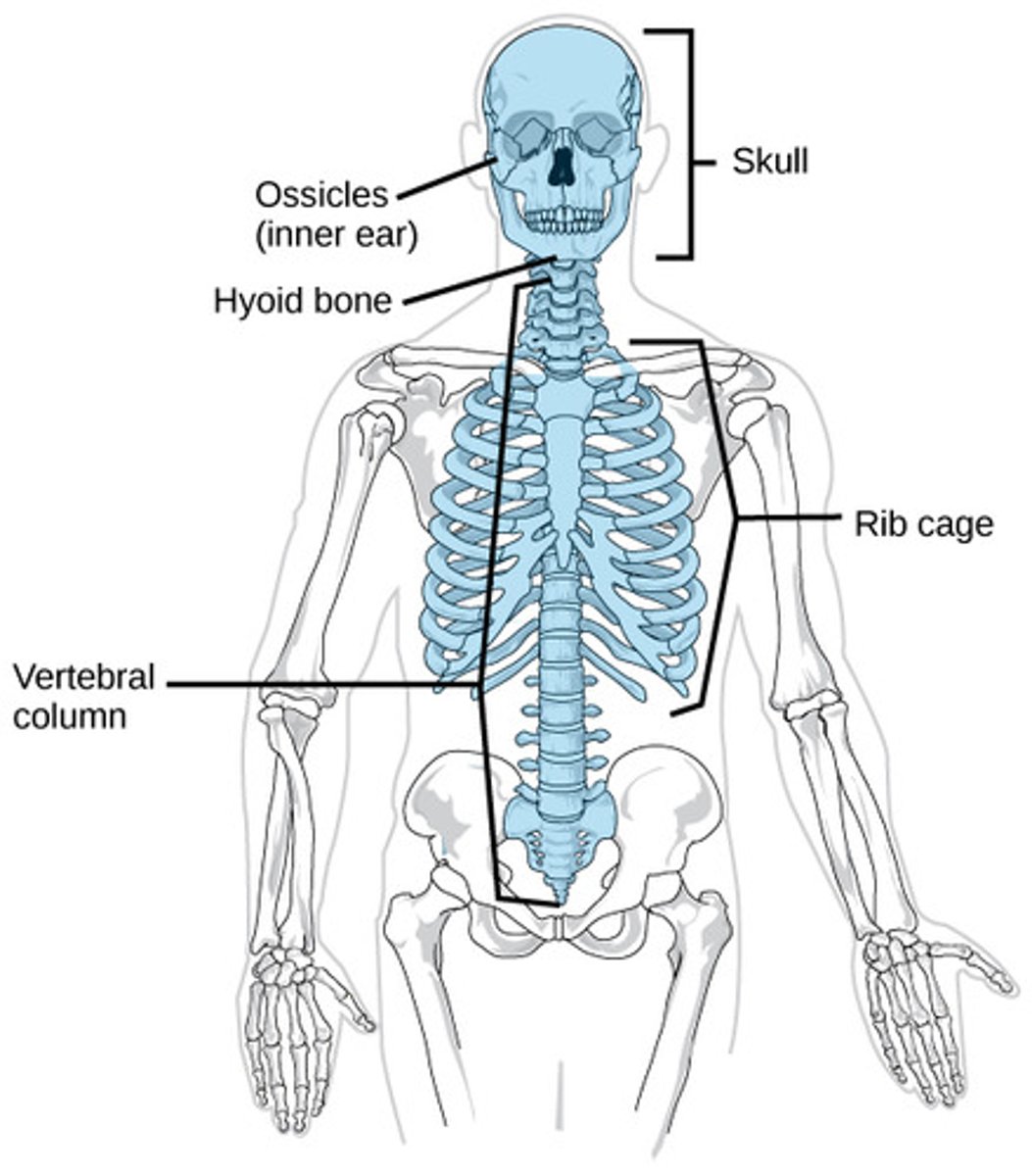
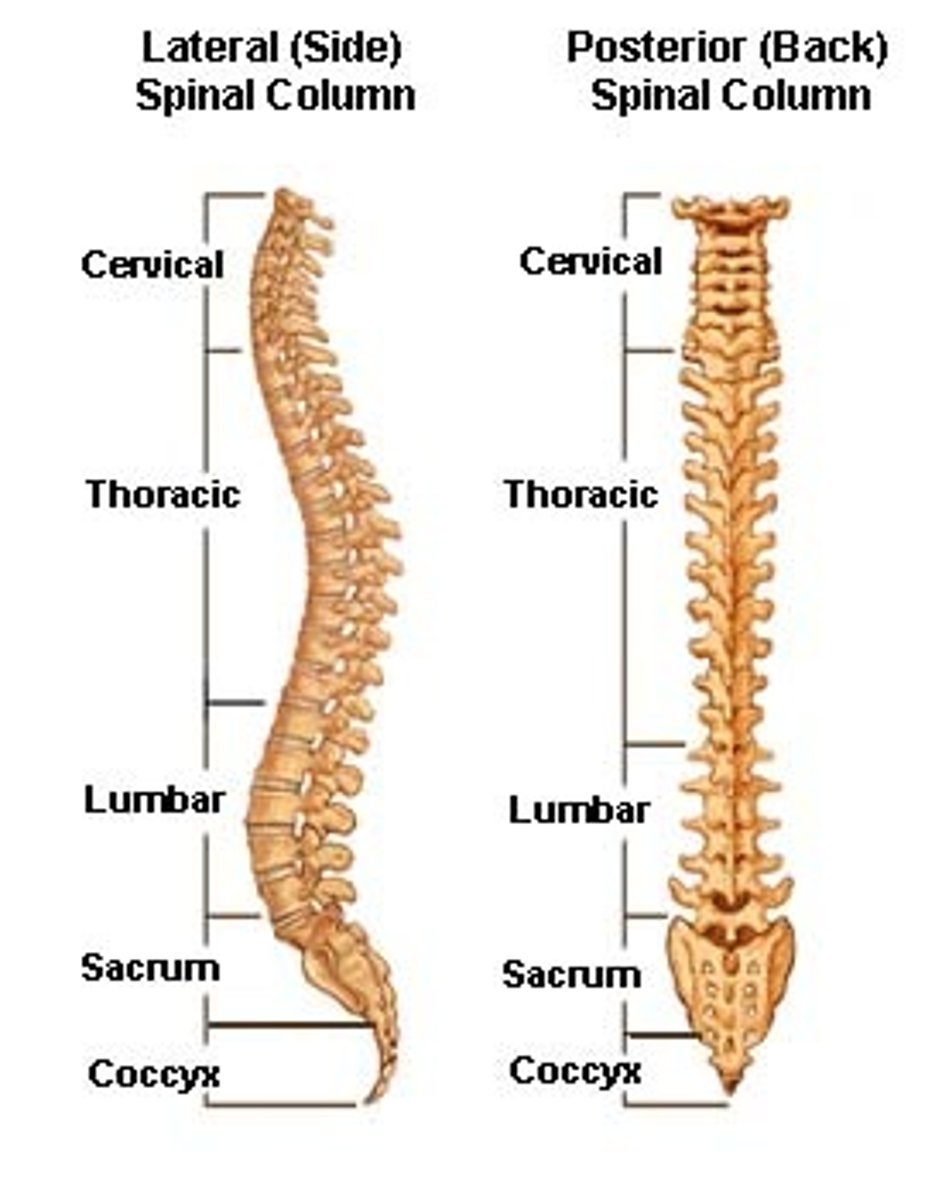
Axial skeleton
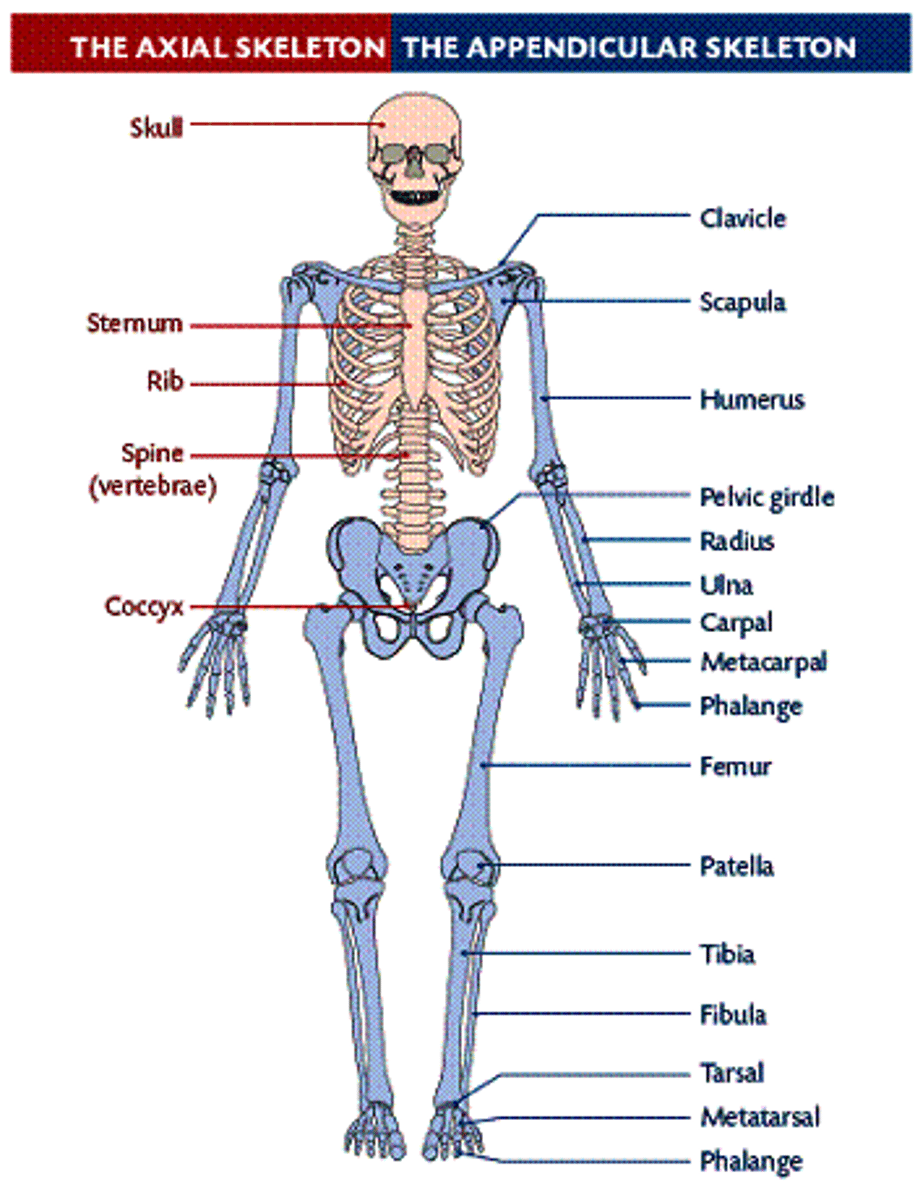
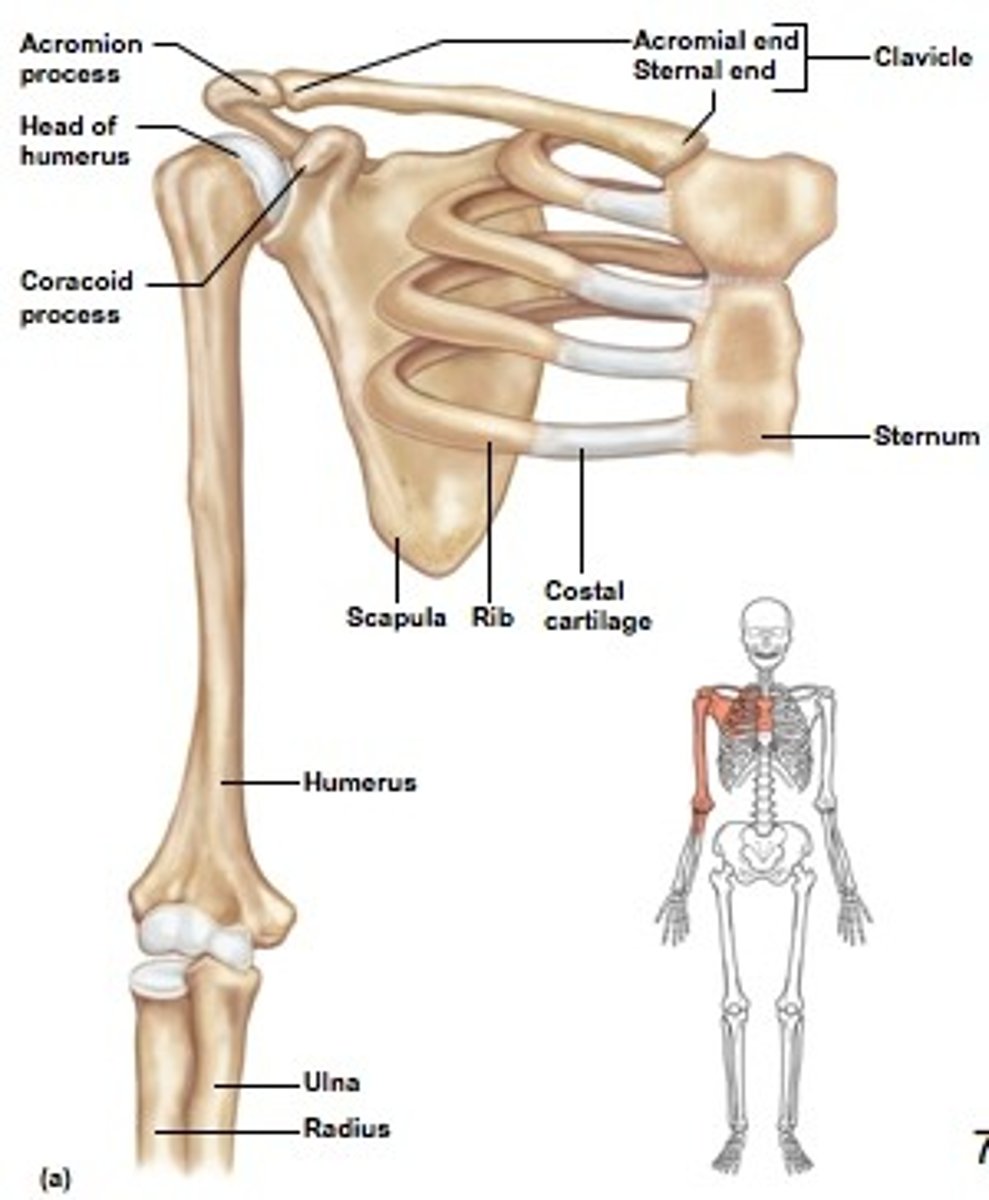
Appendicular skeleton
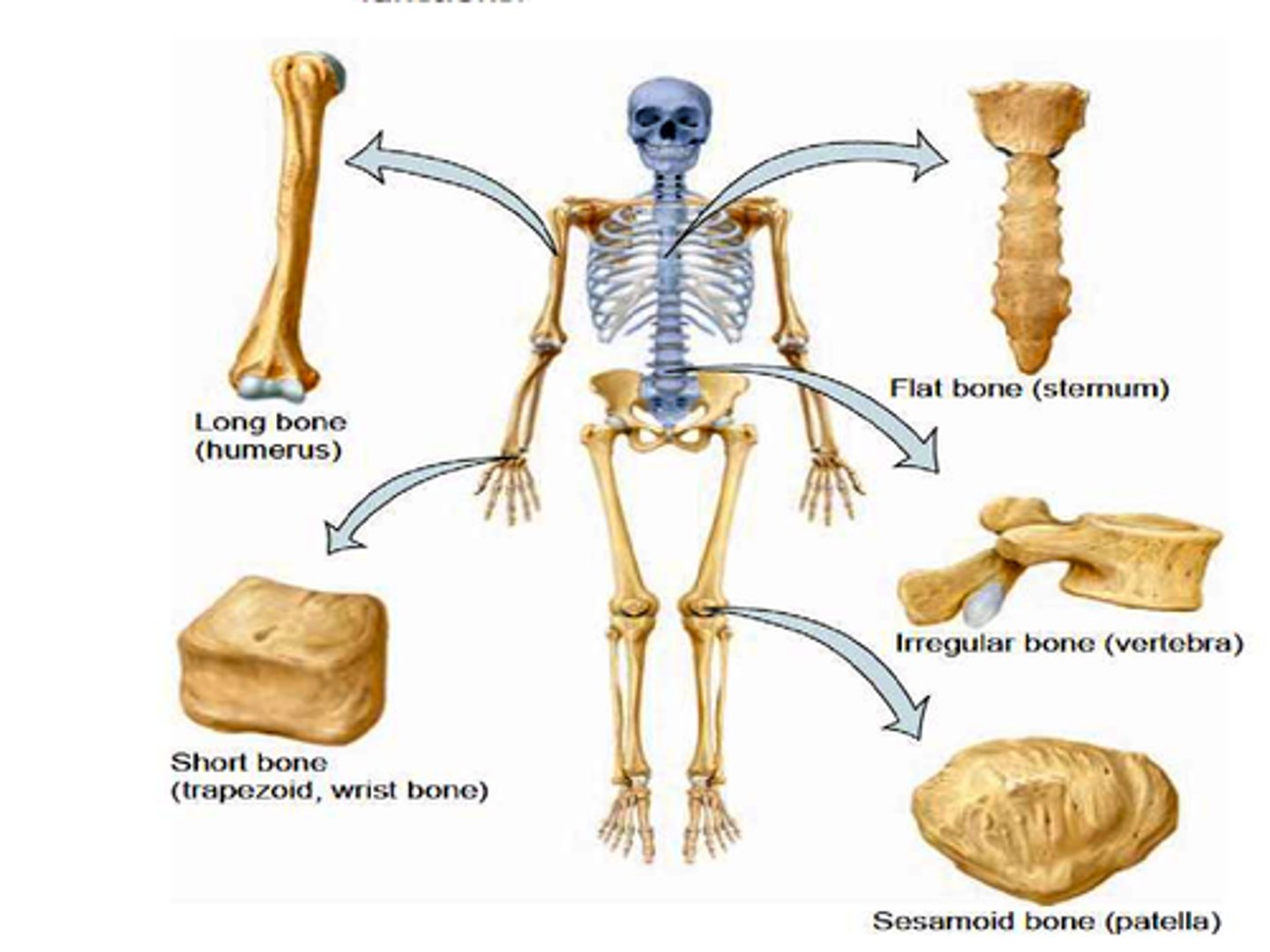
Types of bones
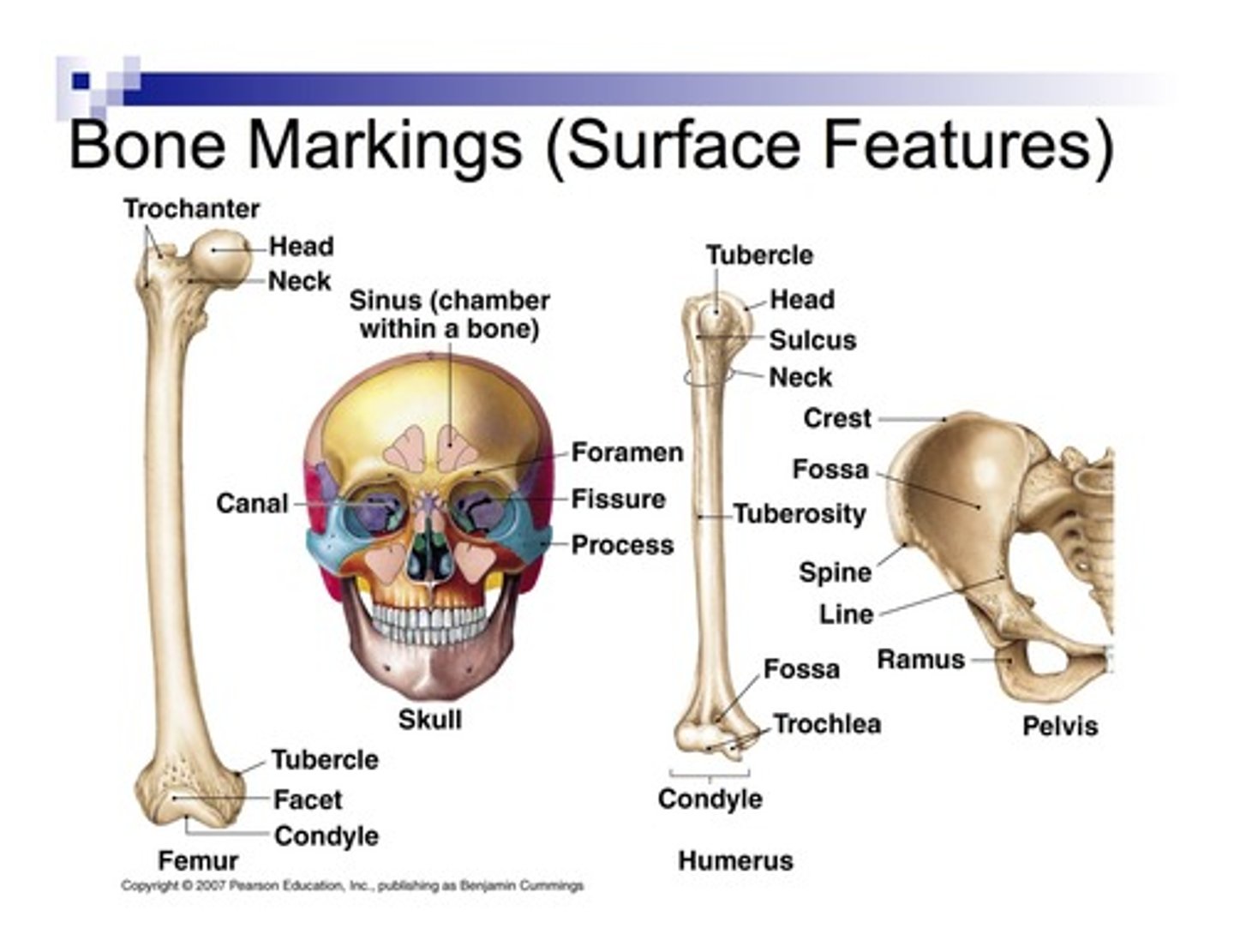
Bone surface markings
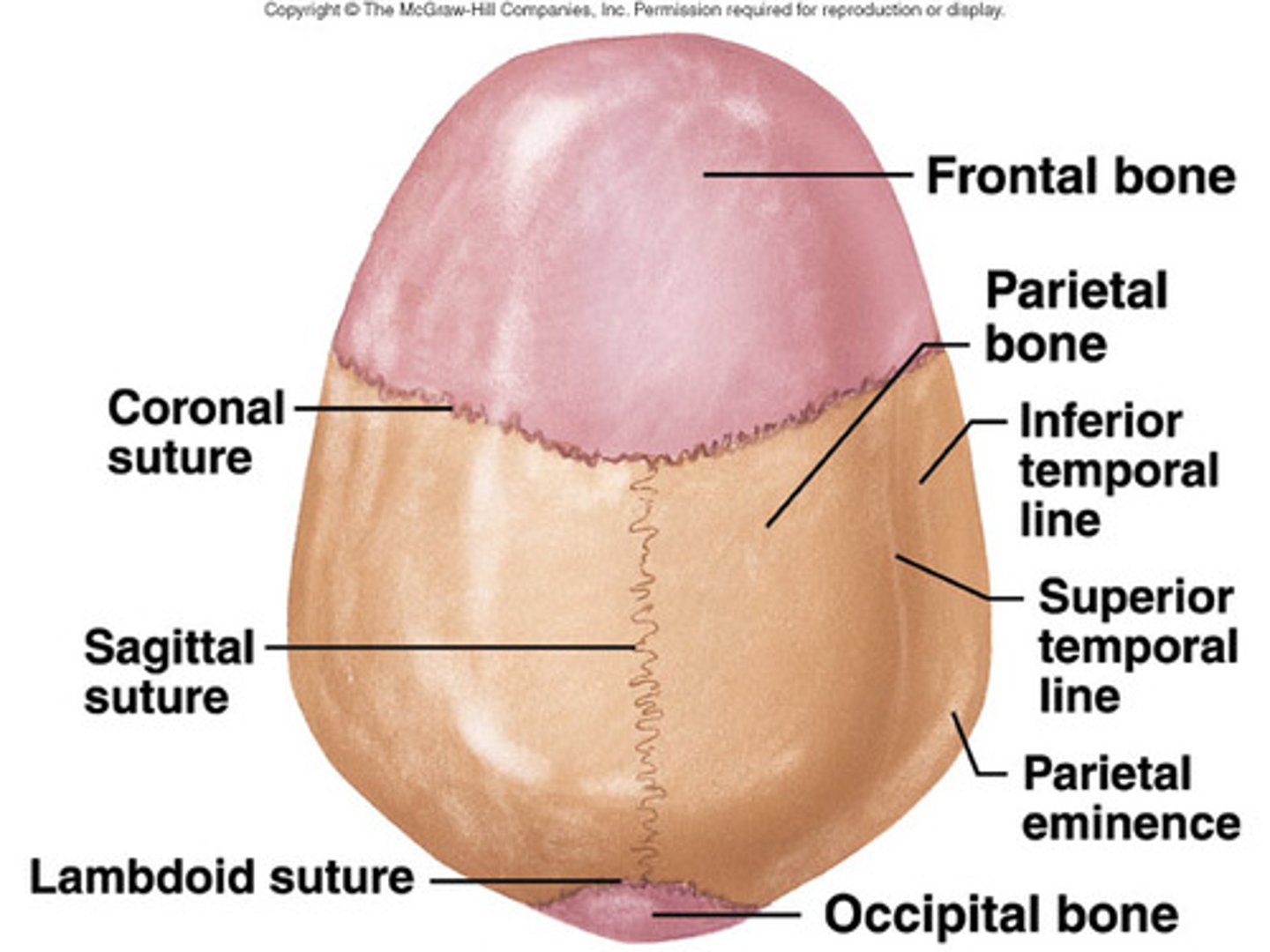
Skull (sutures)
Vertebral column
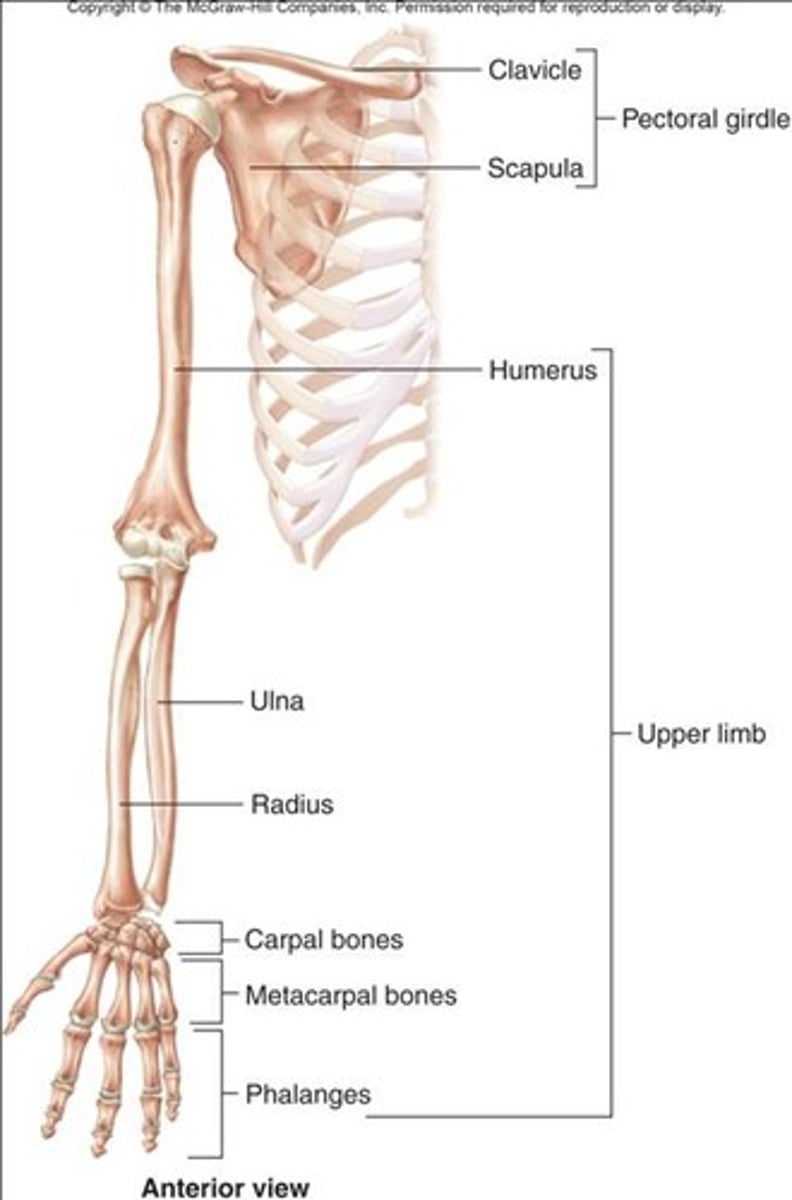
Pectoral girdle
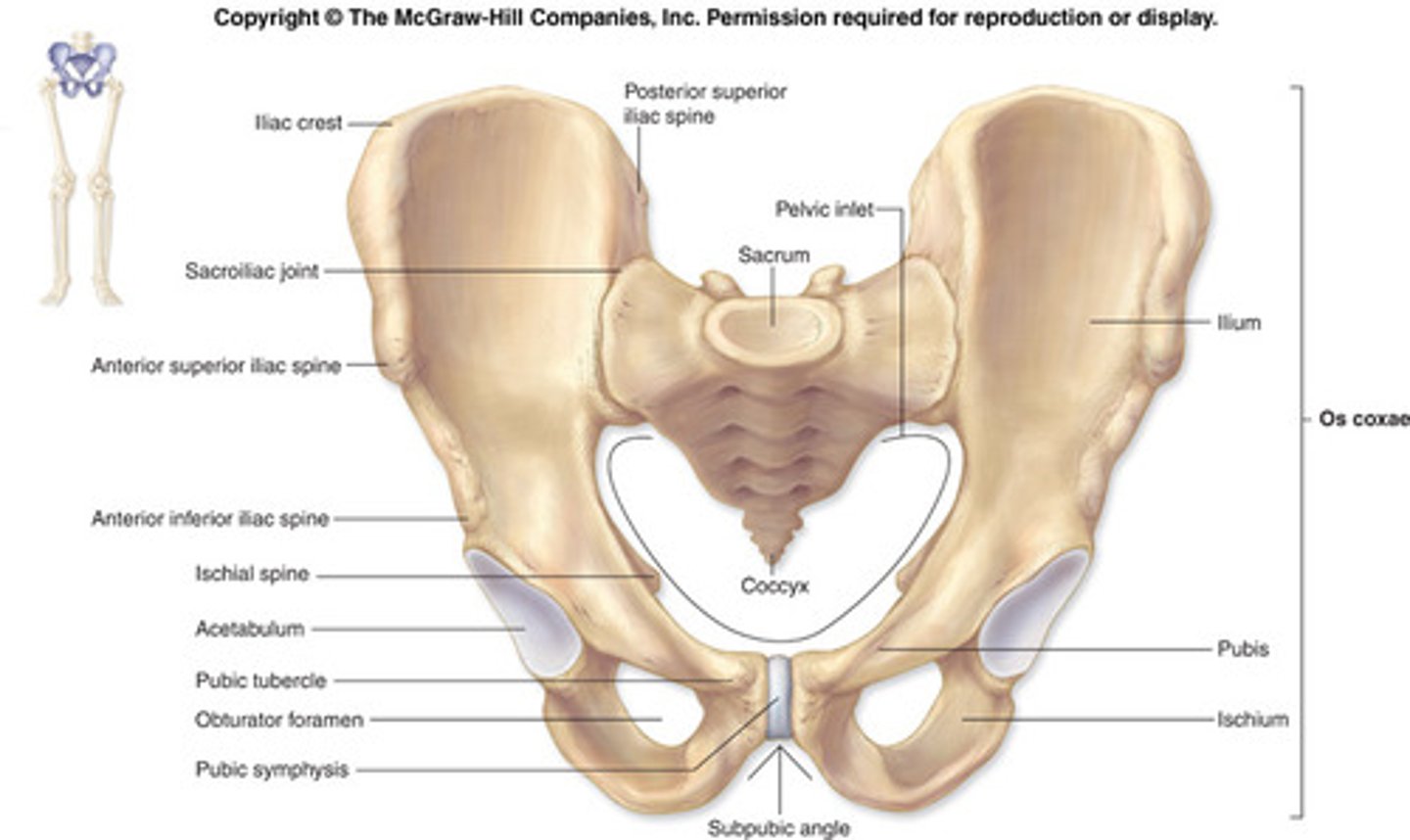
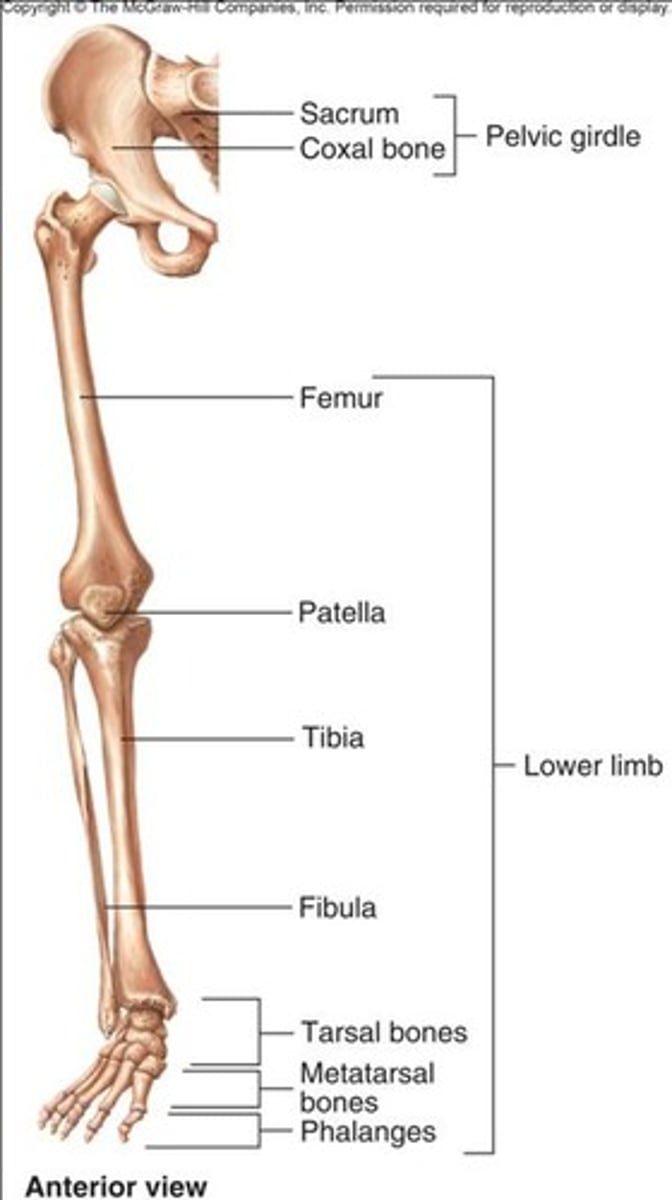
Pelvic girdle
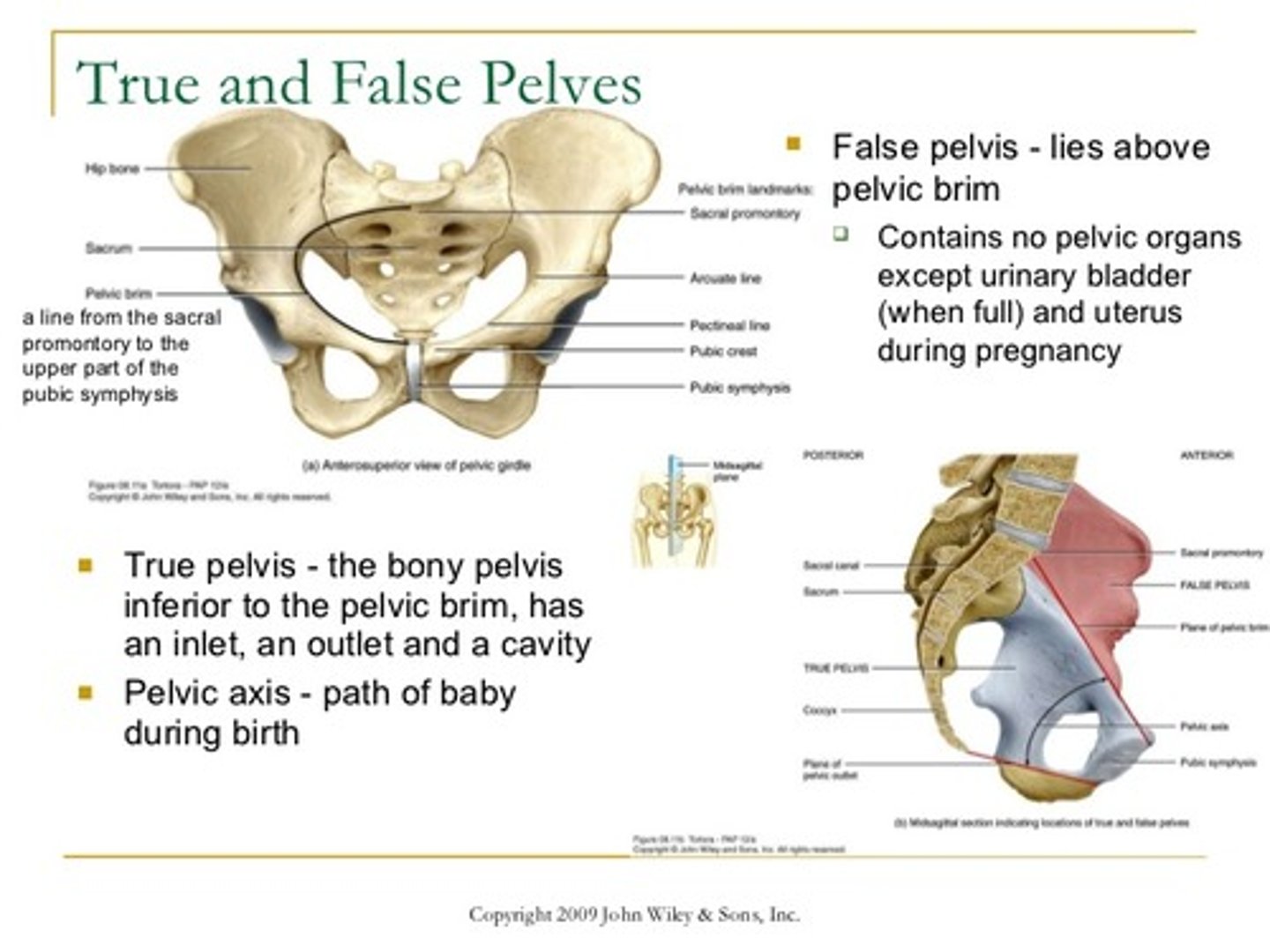
True and false pelvis
Arm bones
Leg bones
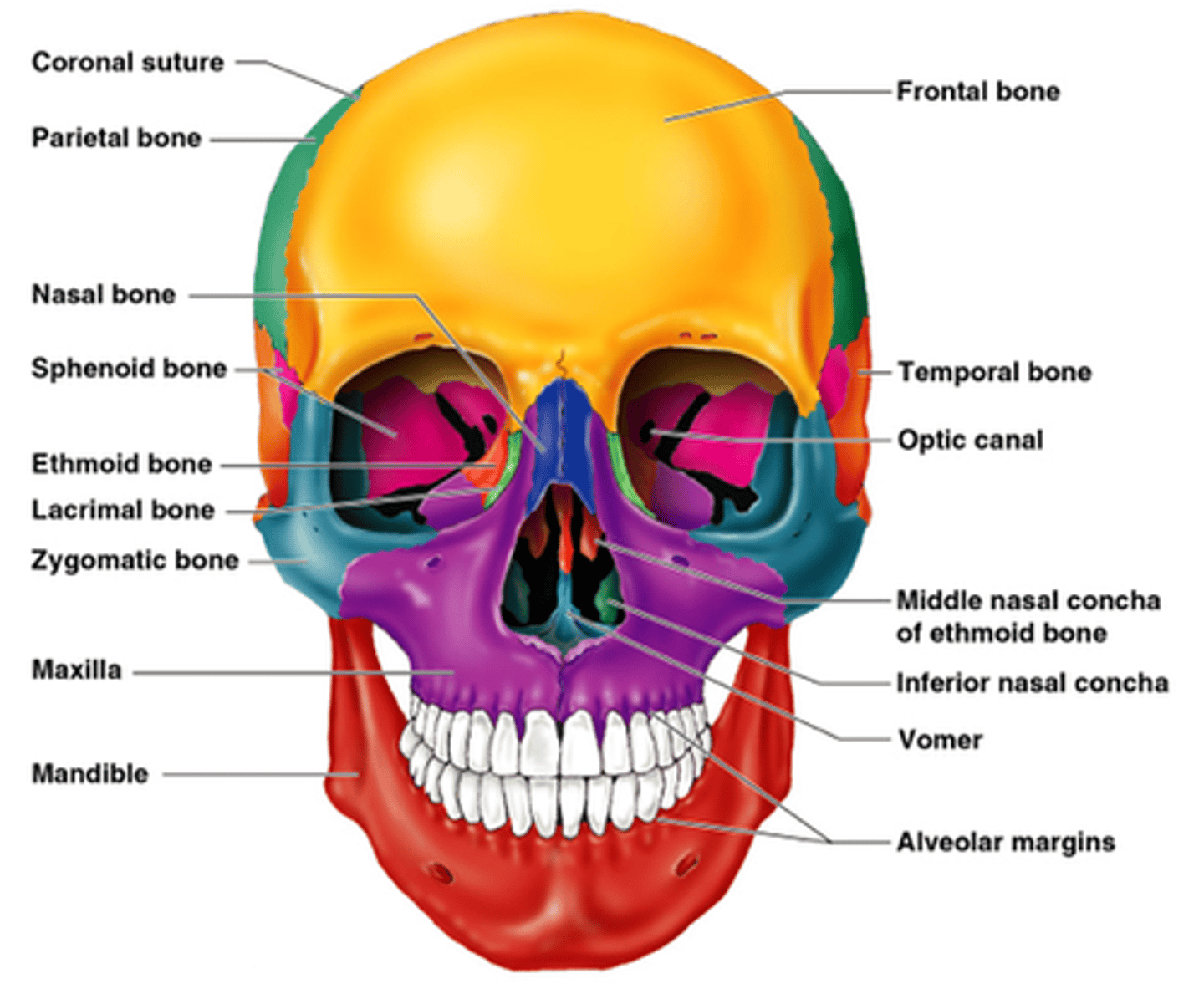
Skull bones
Joints
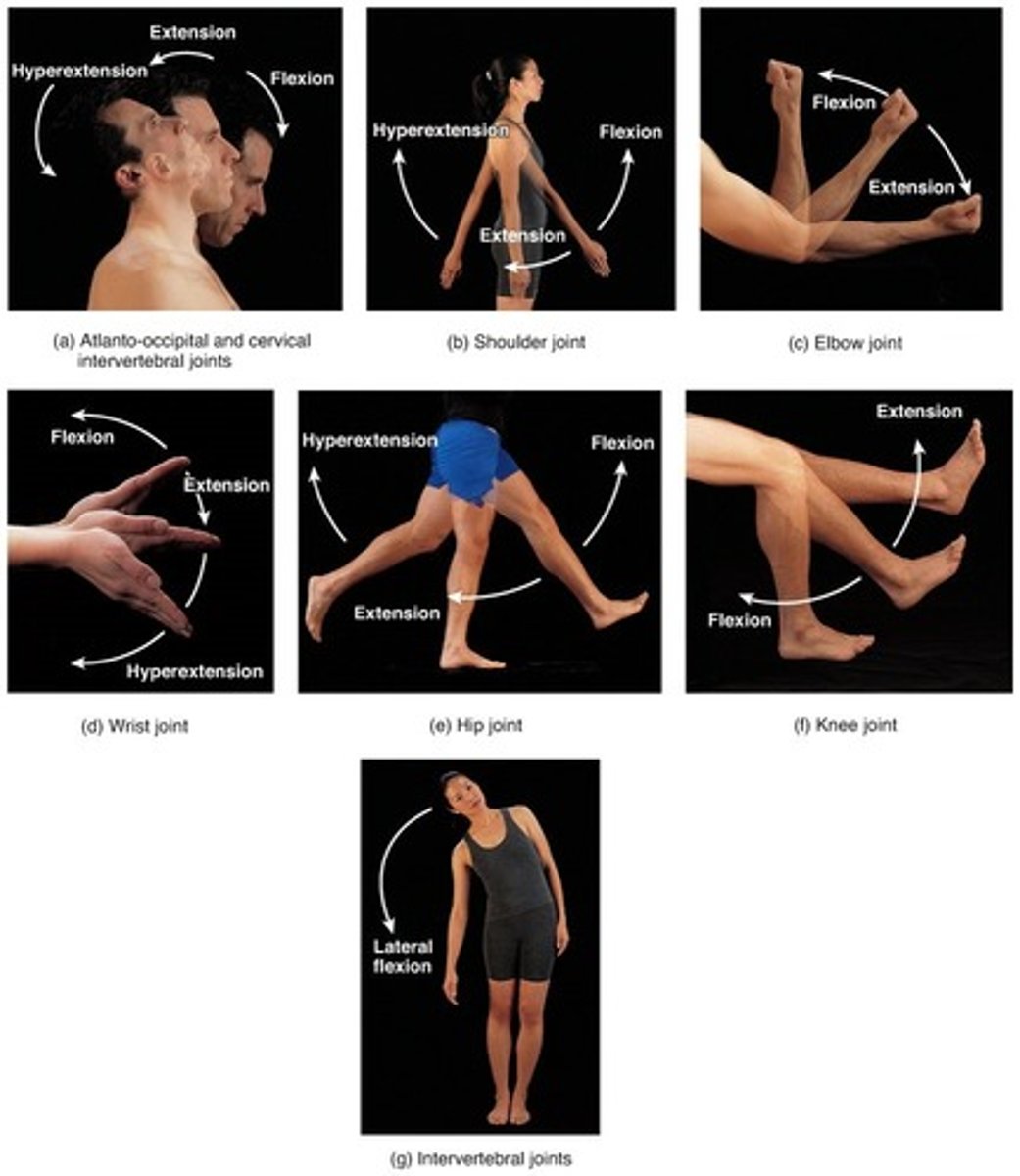
Angular movements
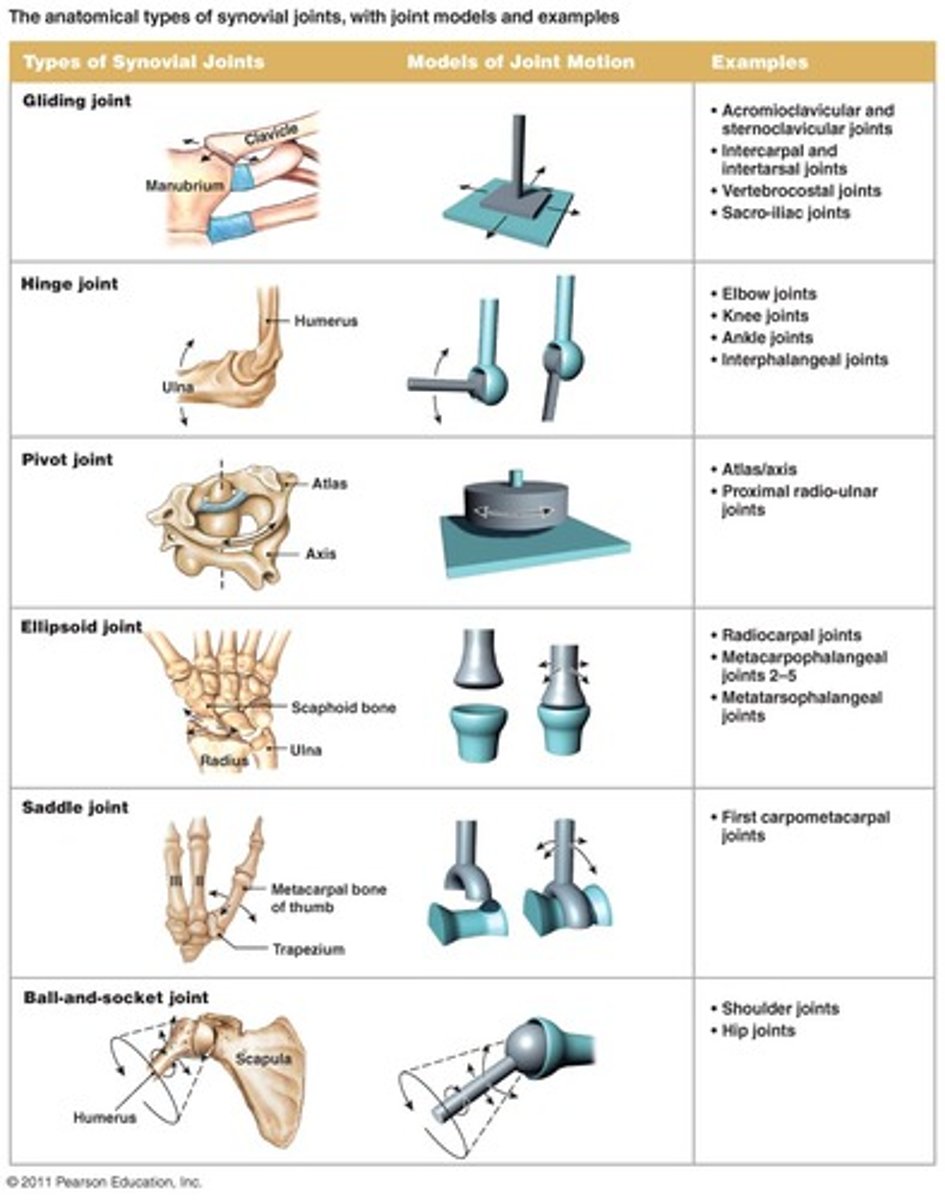
Types of synovial joints
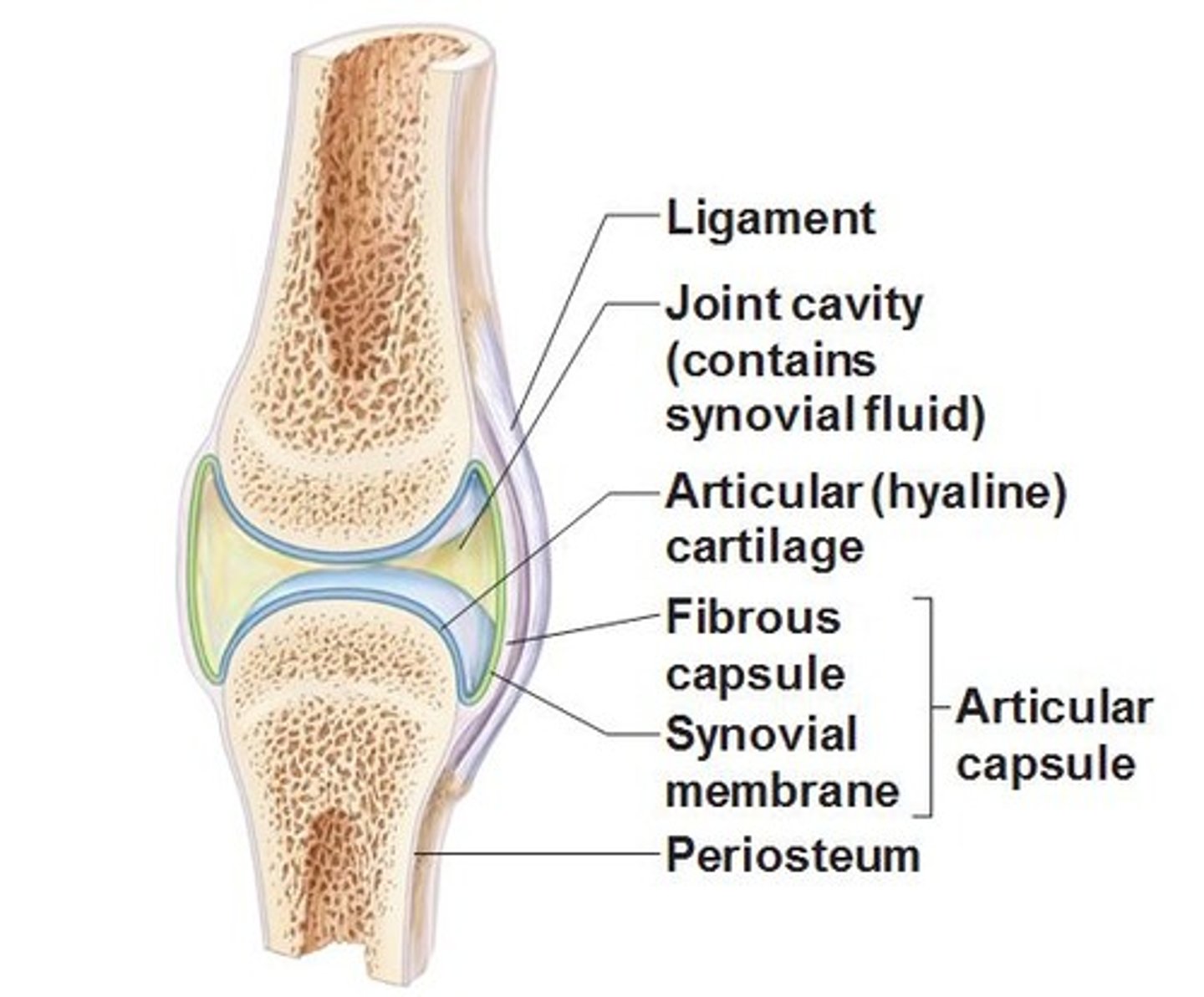
Synovial joints
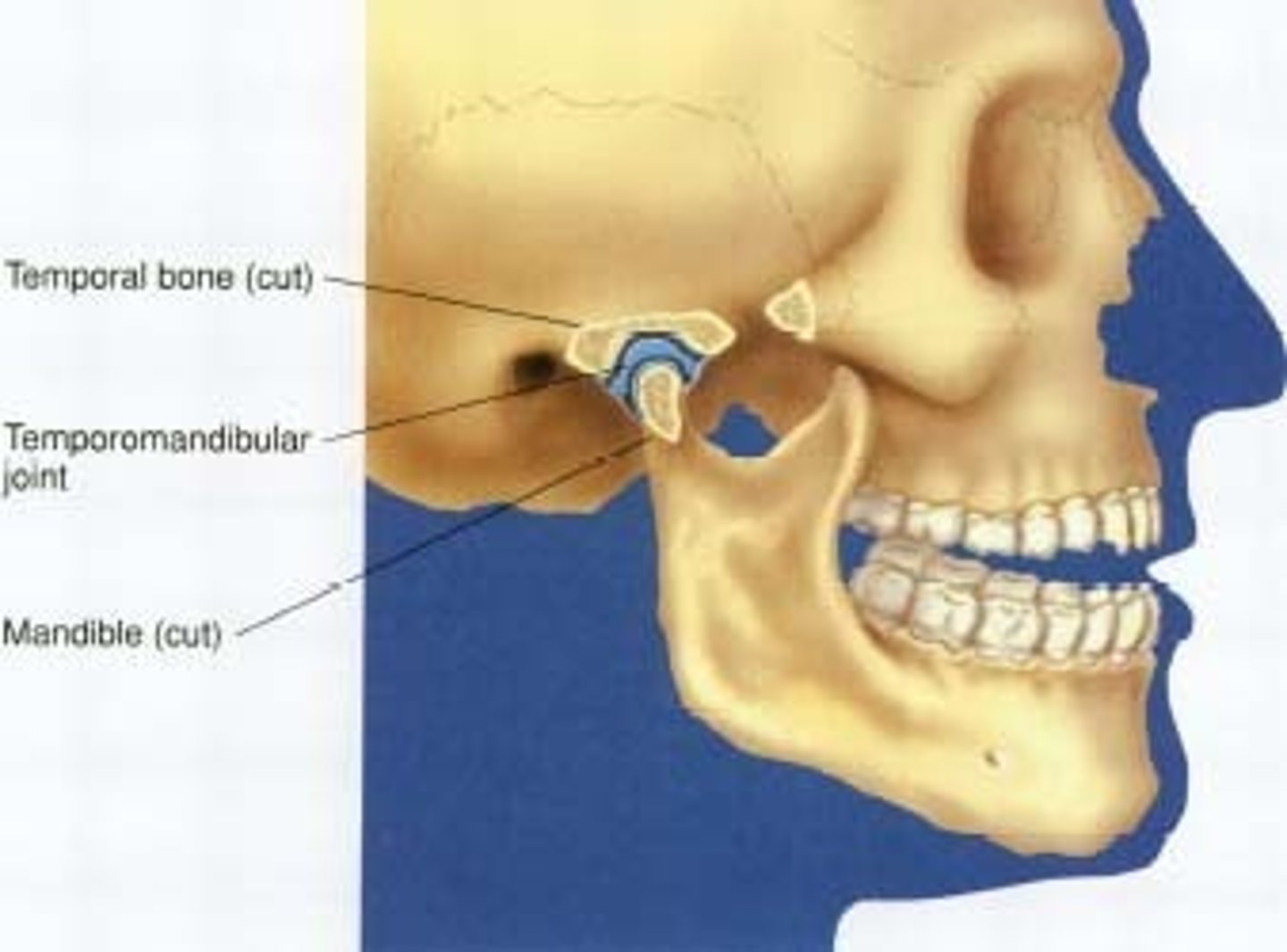
TMJ joint
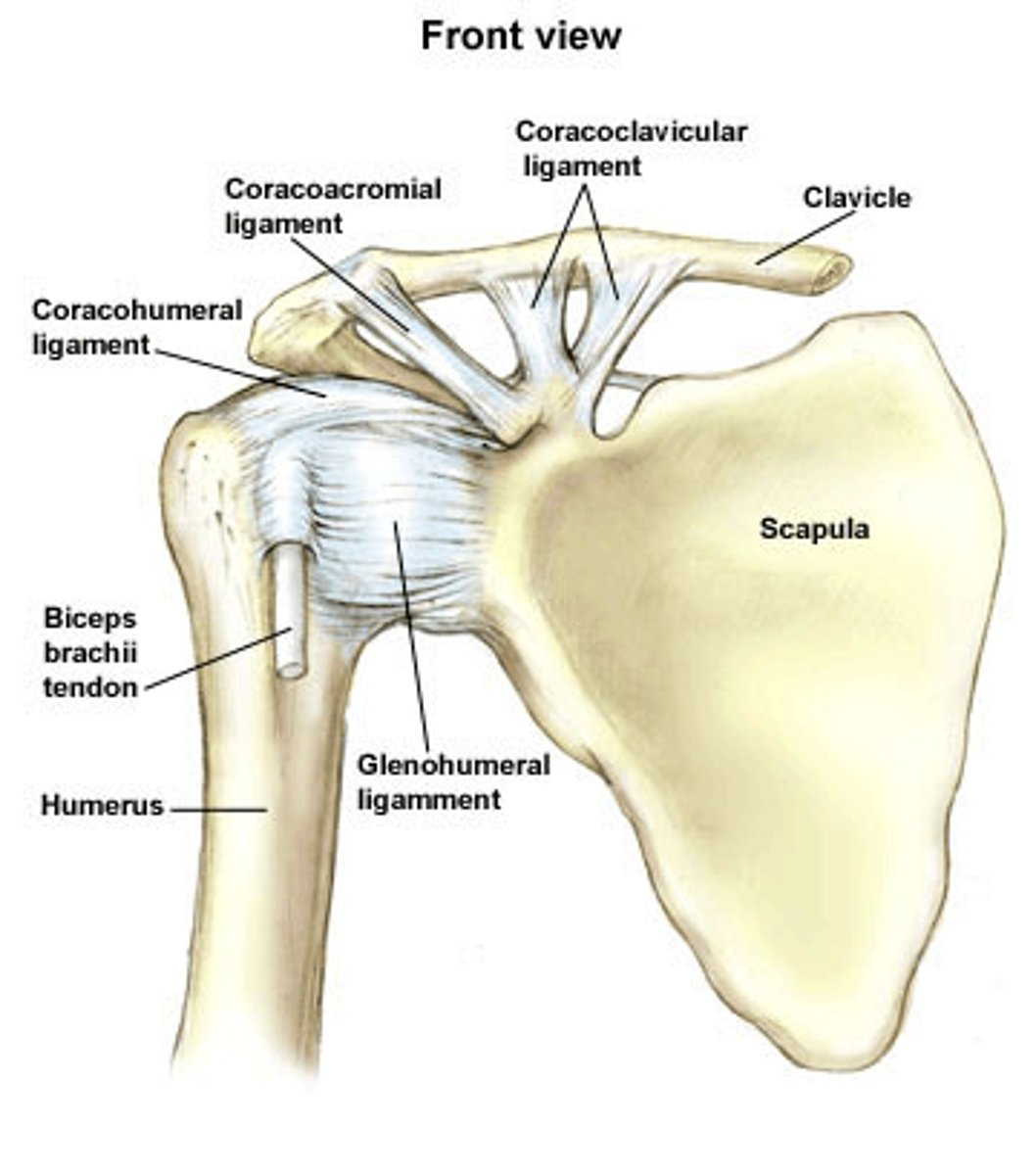
Shoulder joint
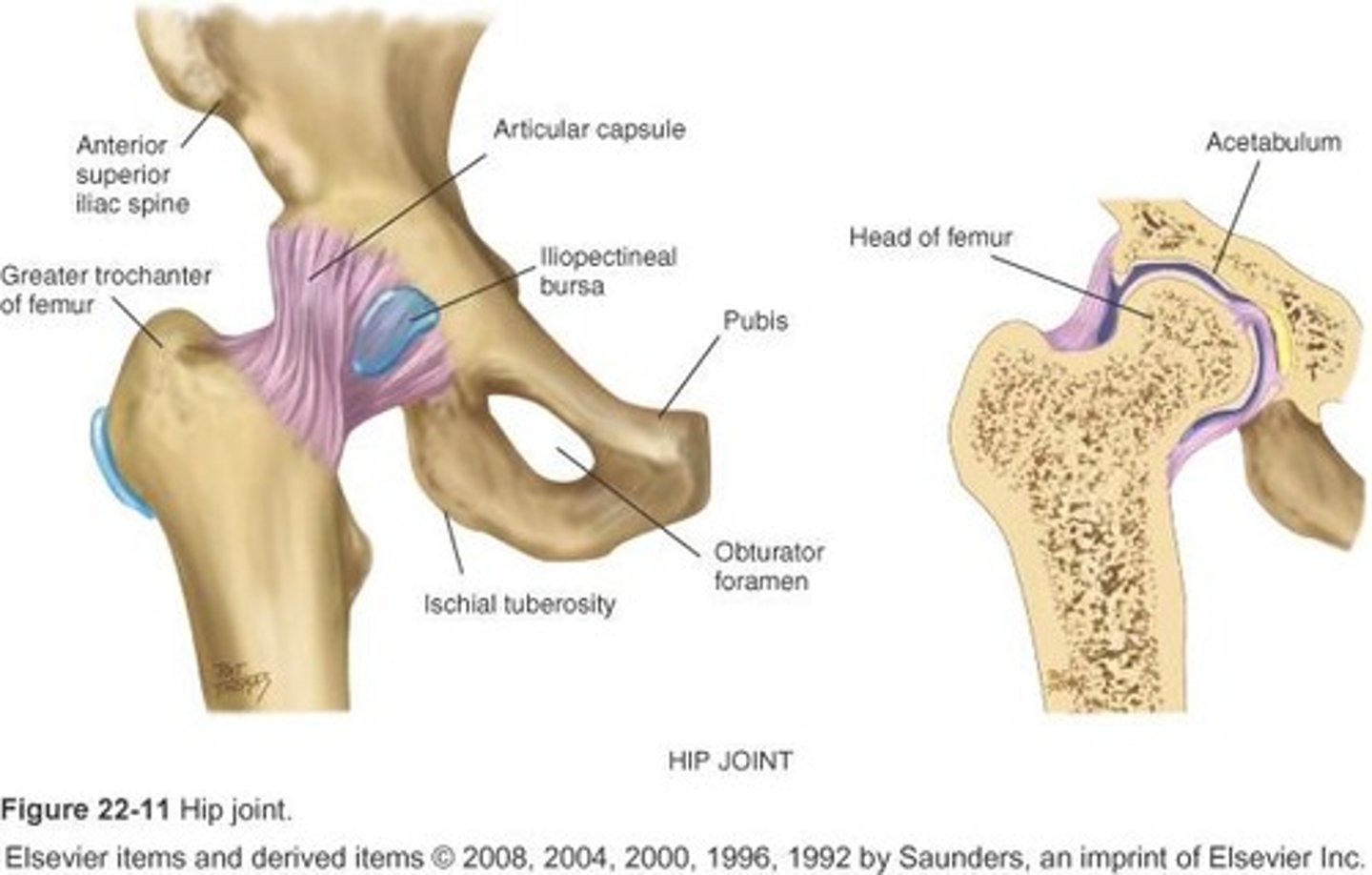
Hip joint
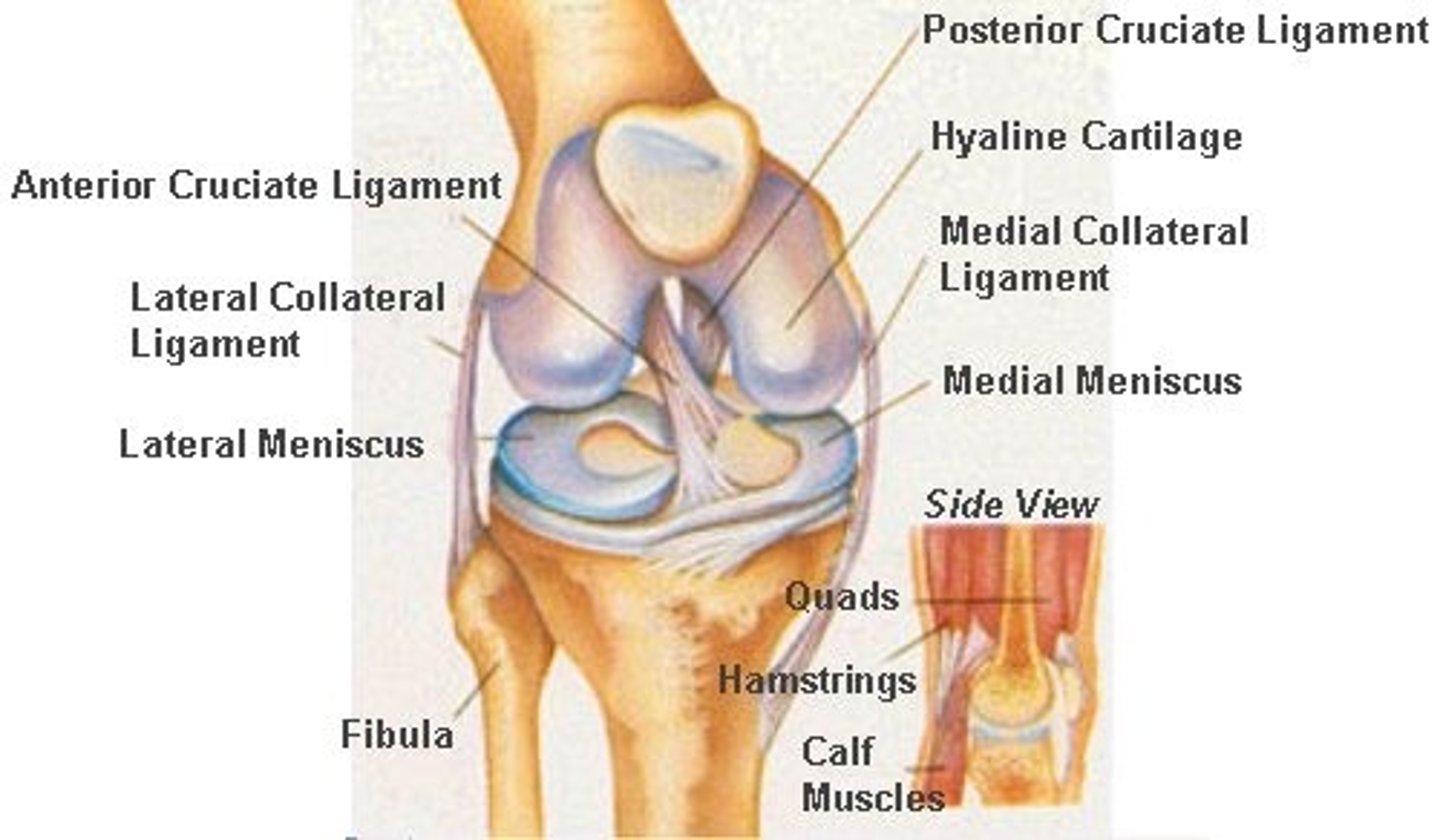
Knee joint
Muscular cells
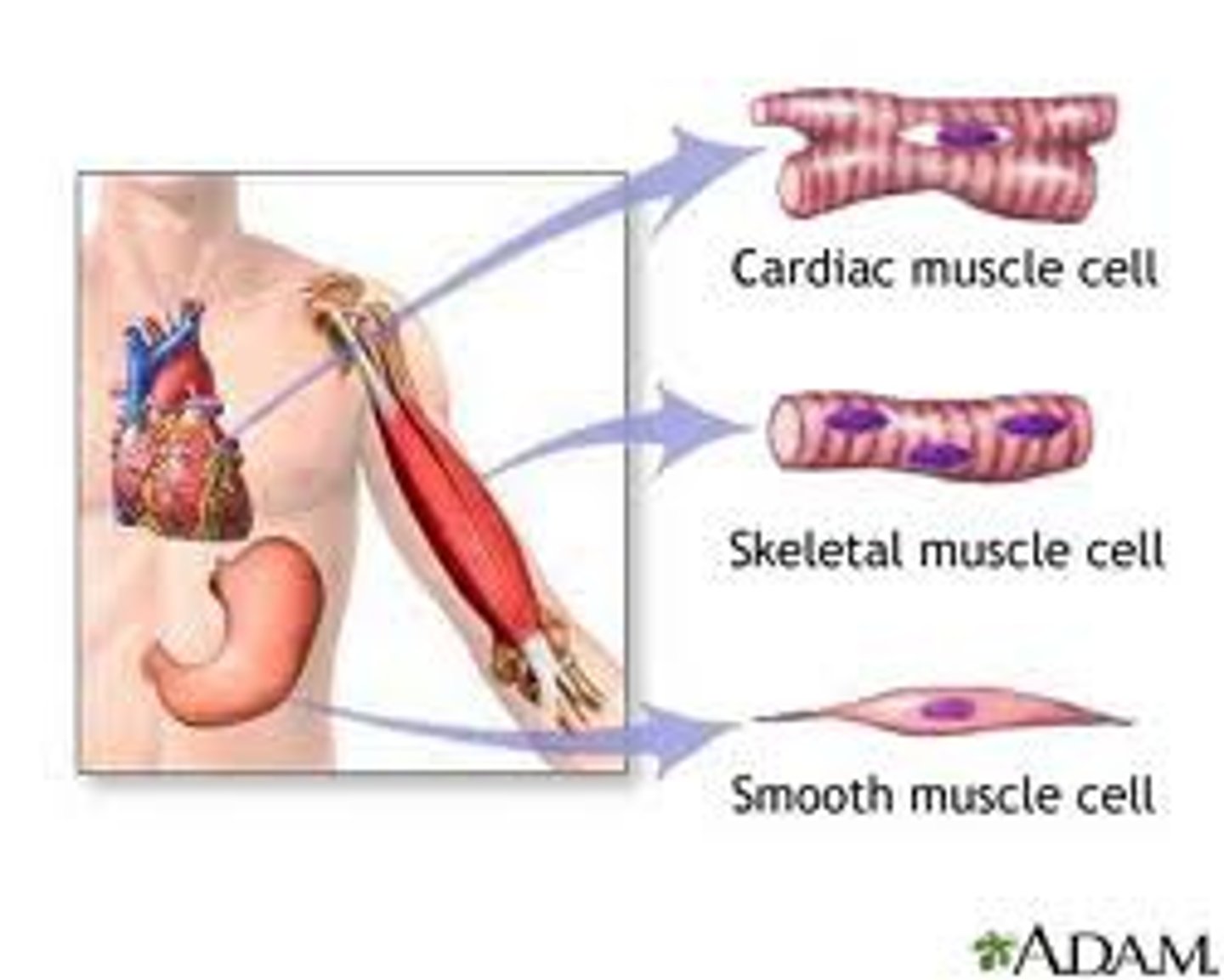
Muscle tissue (parts)
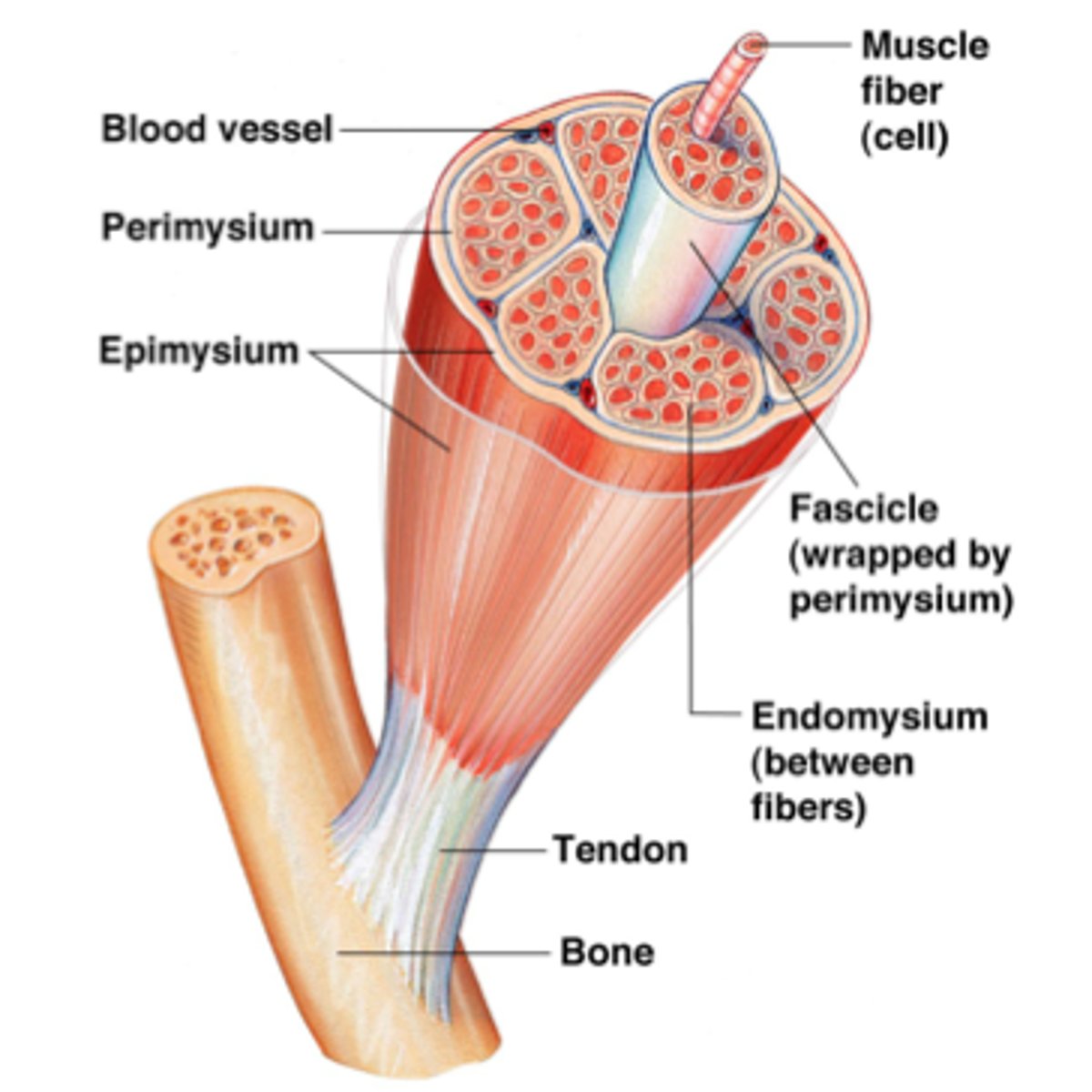
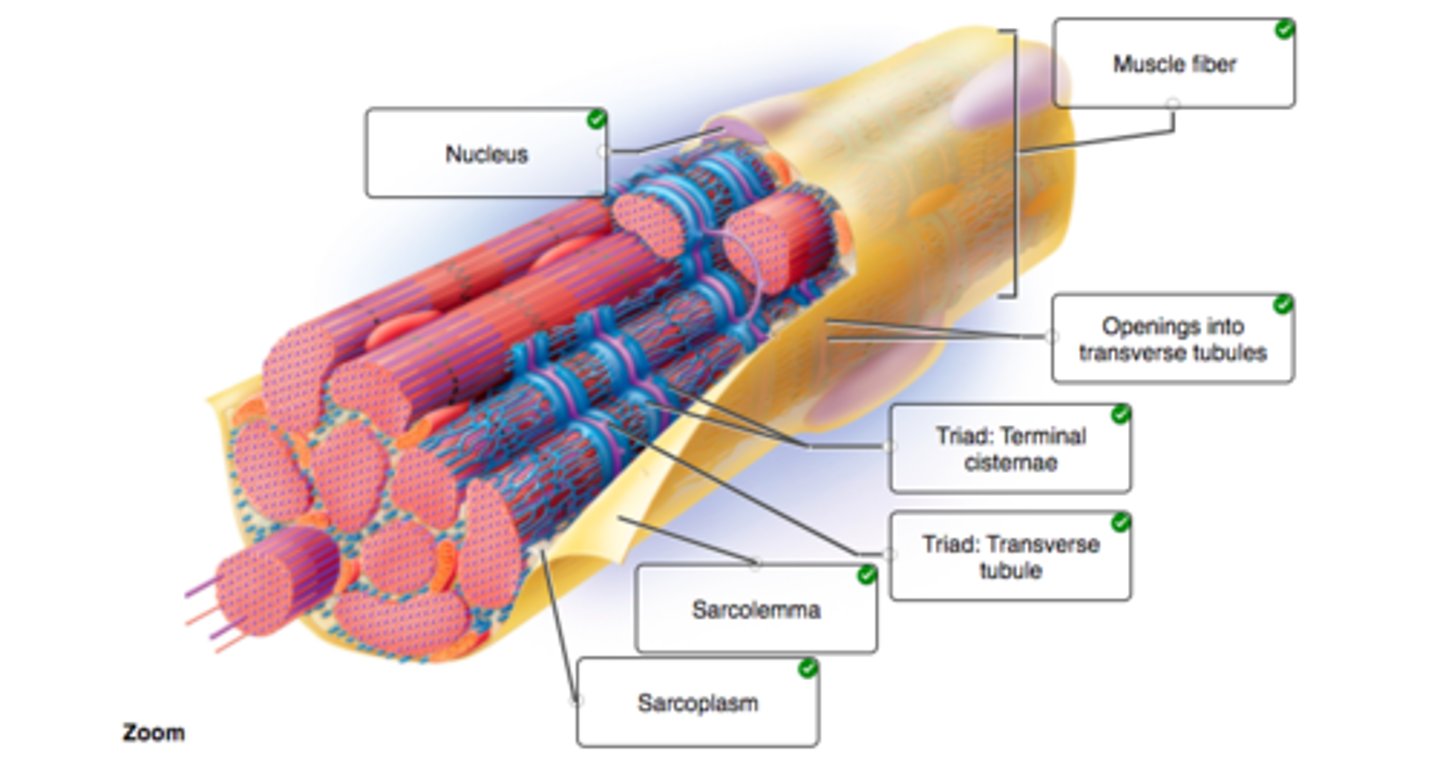
Skeletal muscle (parts)
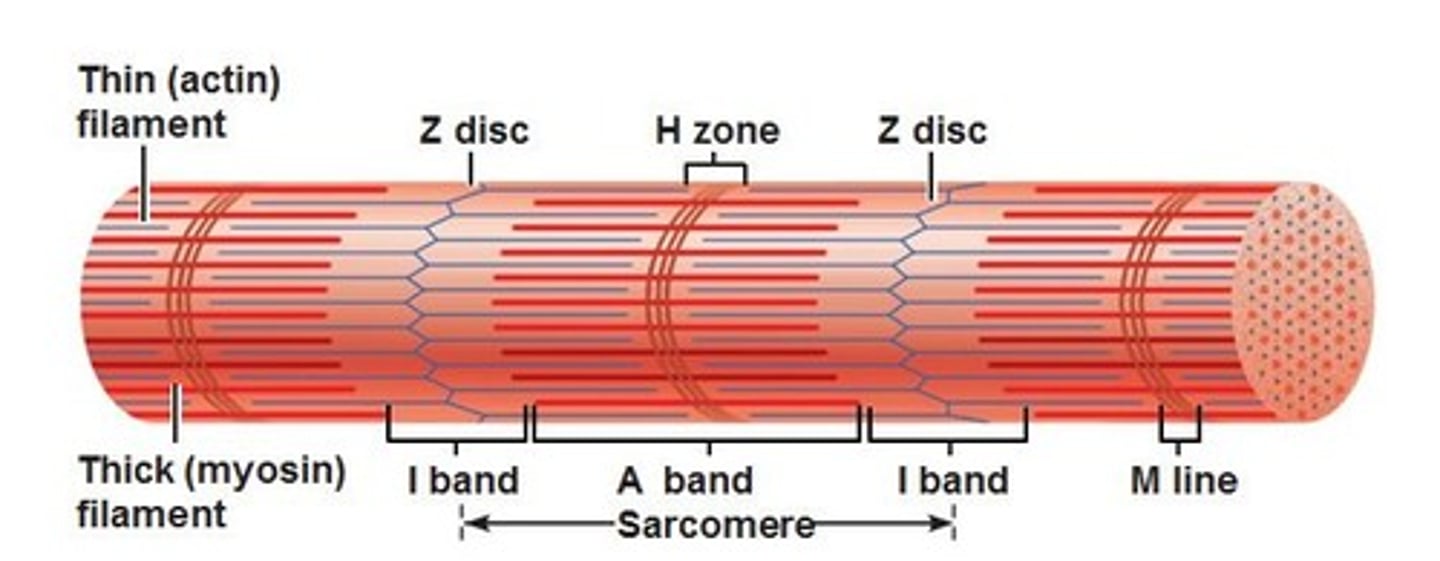
Filaments (with a sarcomere)
Z discs
Narrow, plate-shaped regions of dense material that separate one sarcomere from the next.
A band
Dark, middle part of sarcomere that extends entire length of thick filaments and includes those parts of thin filaments that overlap thick filaments.
I band
Lighter, less dense area of sarcomere that contains remainder of thin filaments but no thick filaments. A Z disc passes through center of each I band.
H zone
Narrow region in center of each A band that contains thick filaments but no thin filaments.
M line
Region in center of H zone that contains proteins that hold thick filaments together at center of sarcomere.
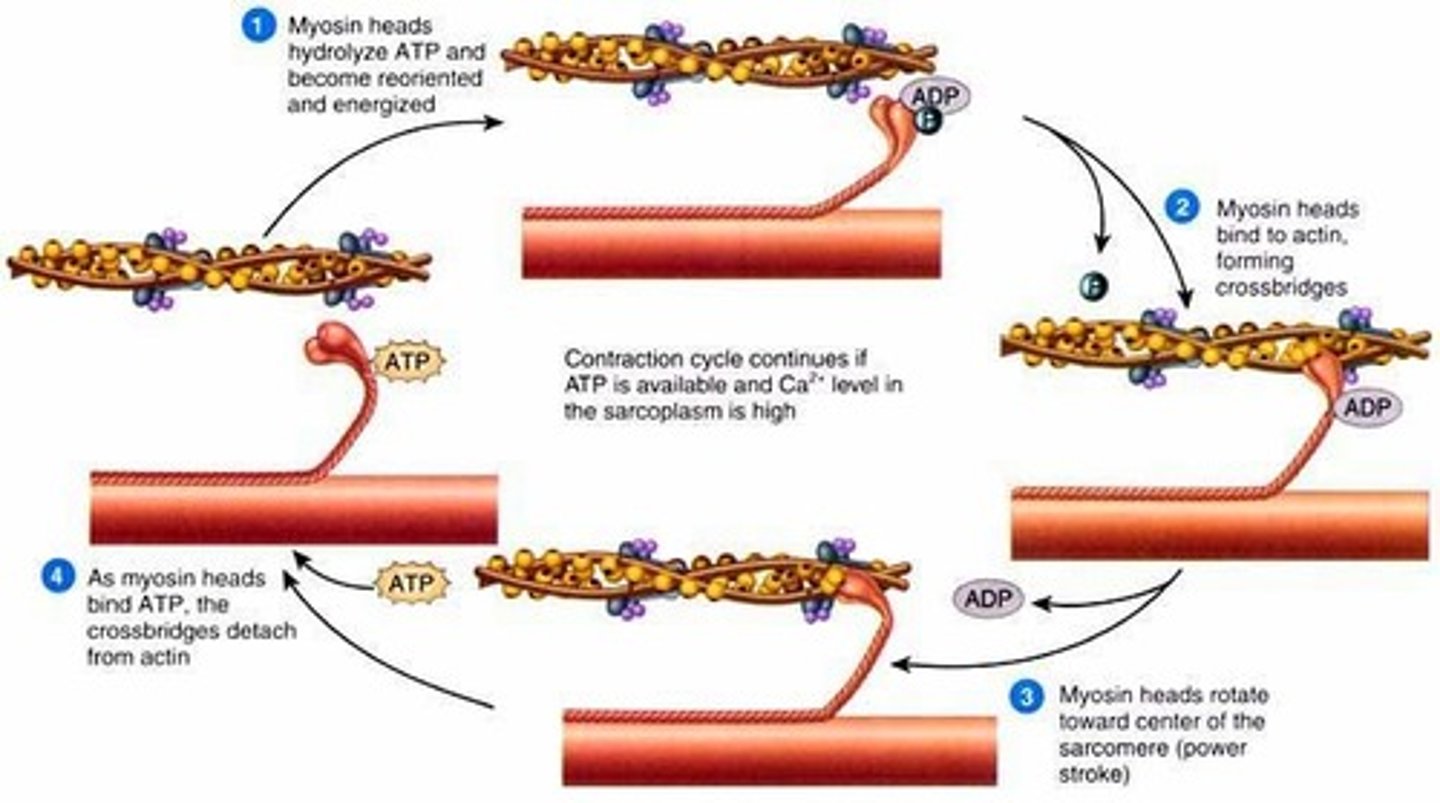
Sliding filaments (muscle contraction)

Contraction cycle
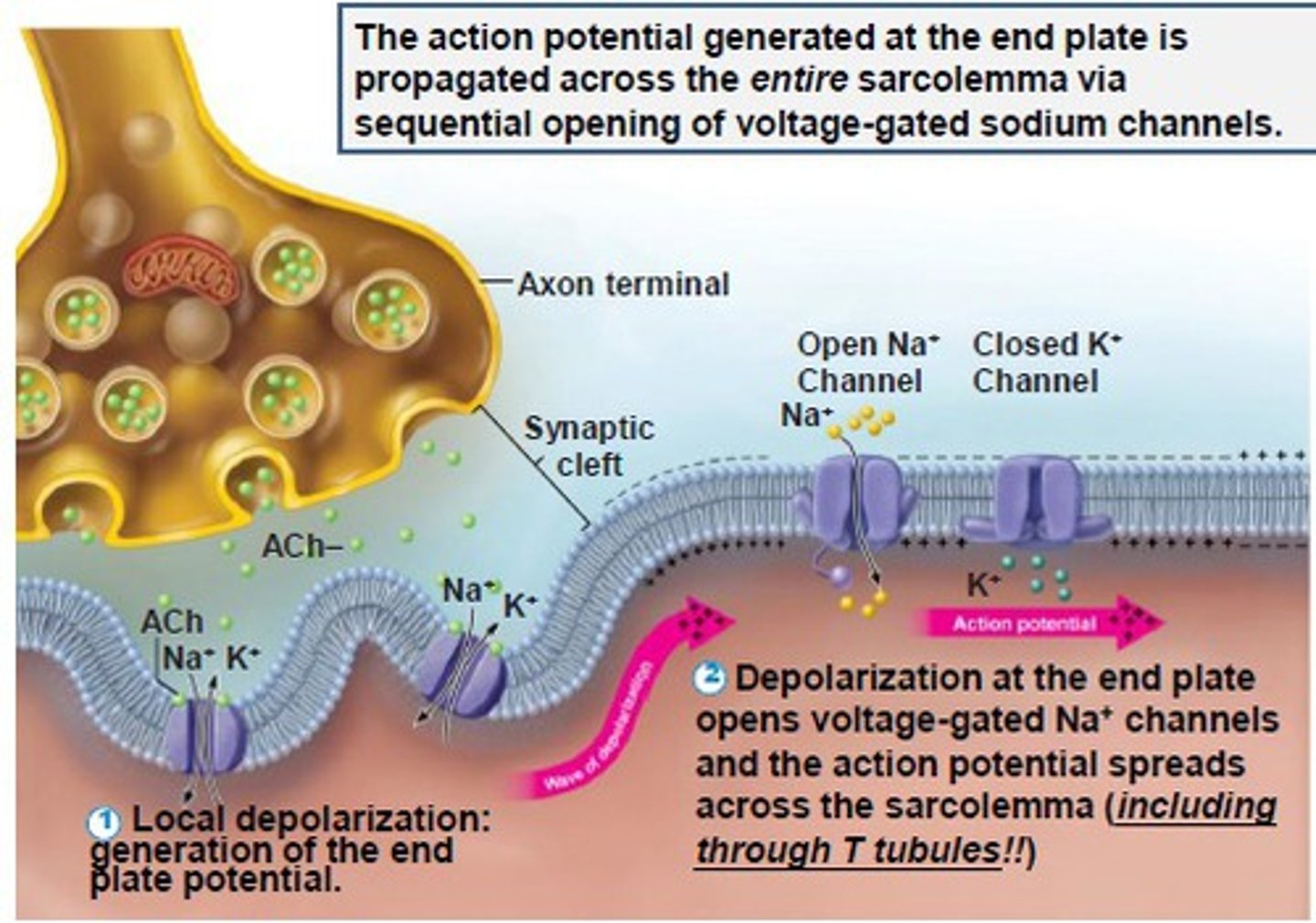
Neuromuscular junction
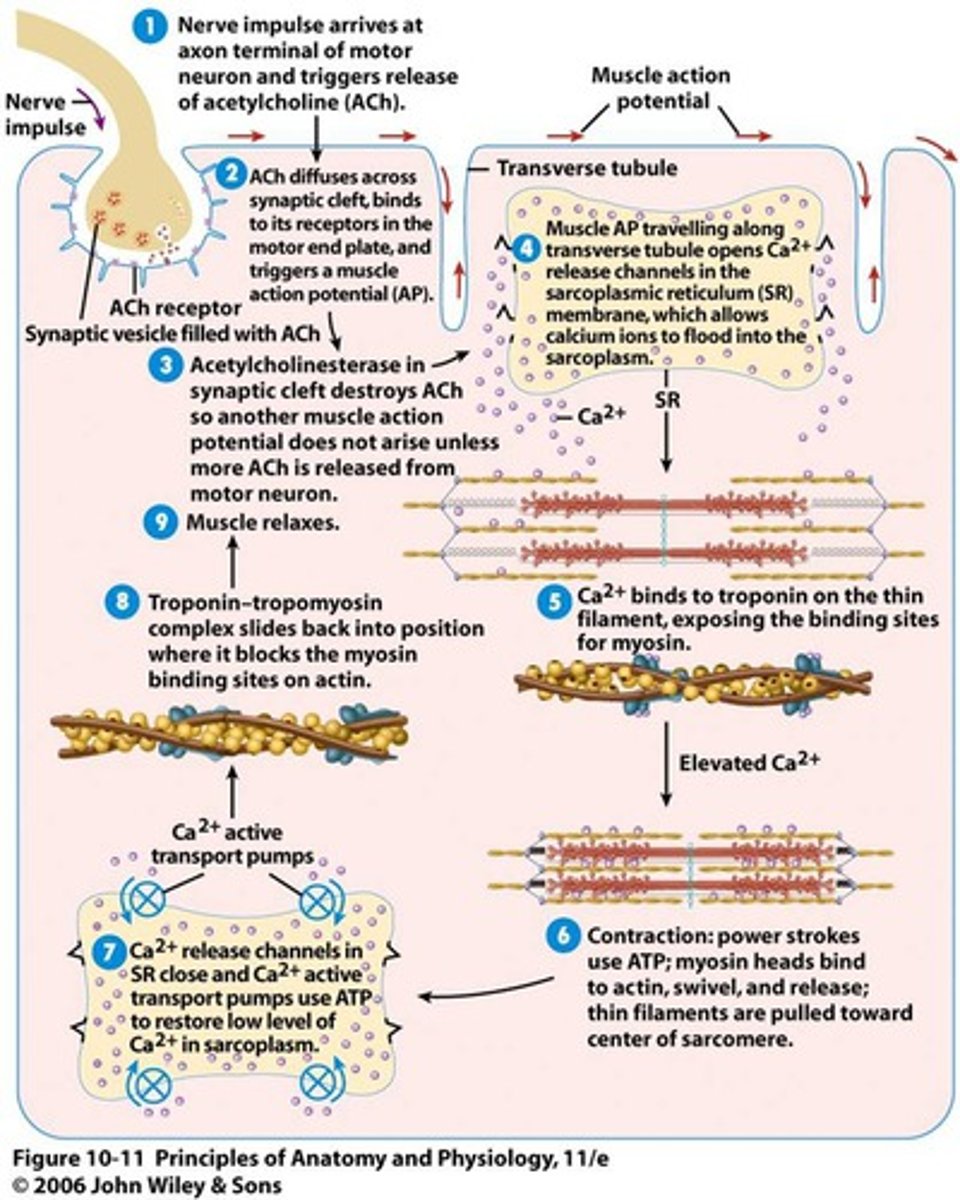
Contraction and relaxation in muscle
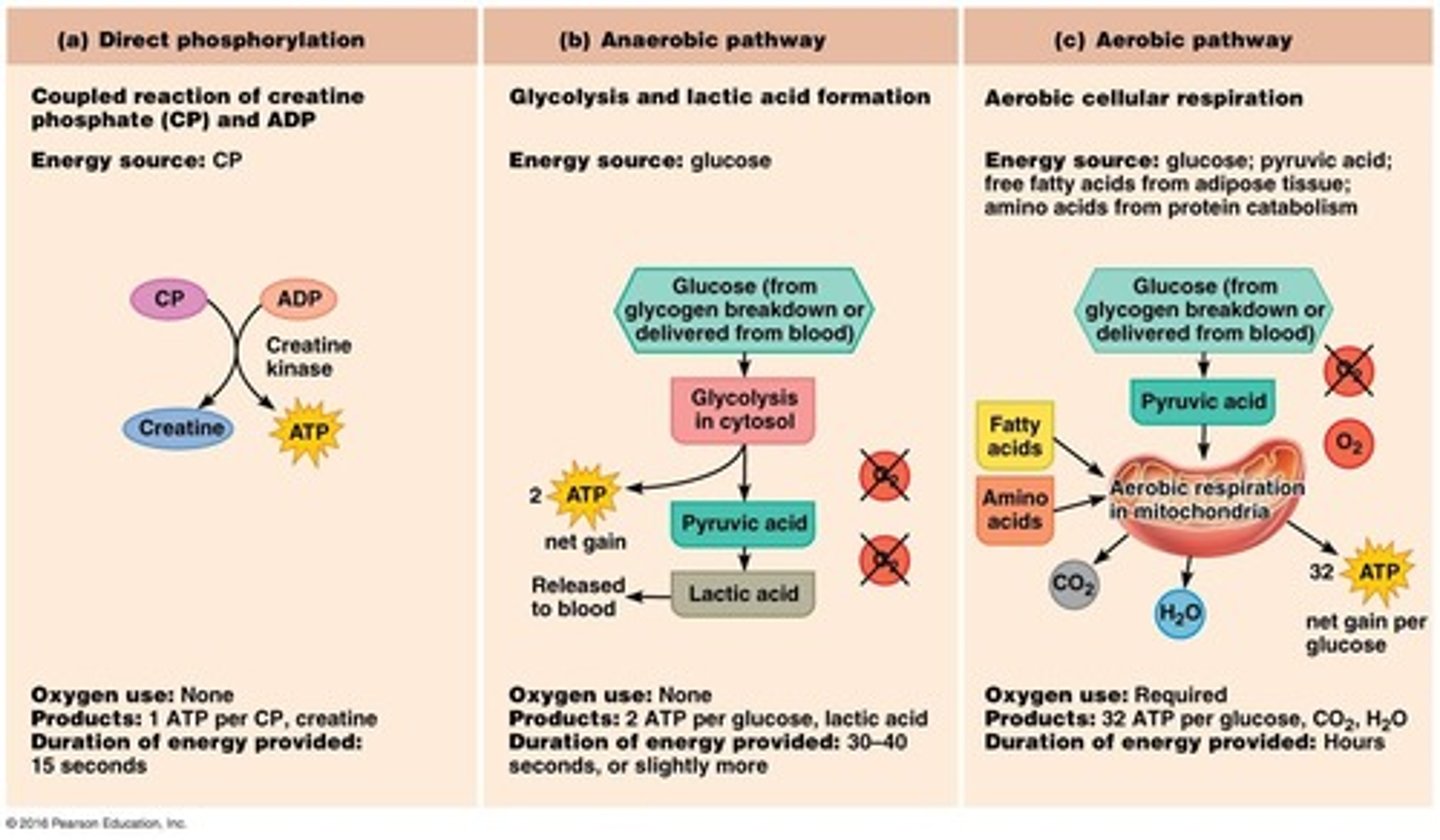
ATP for muscle contraction
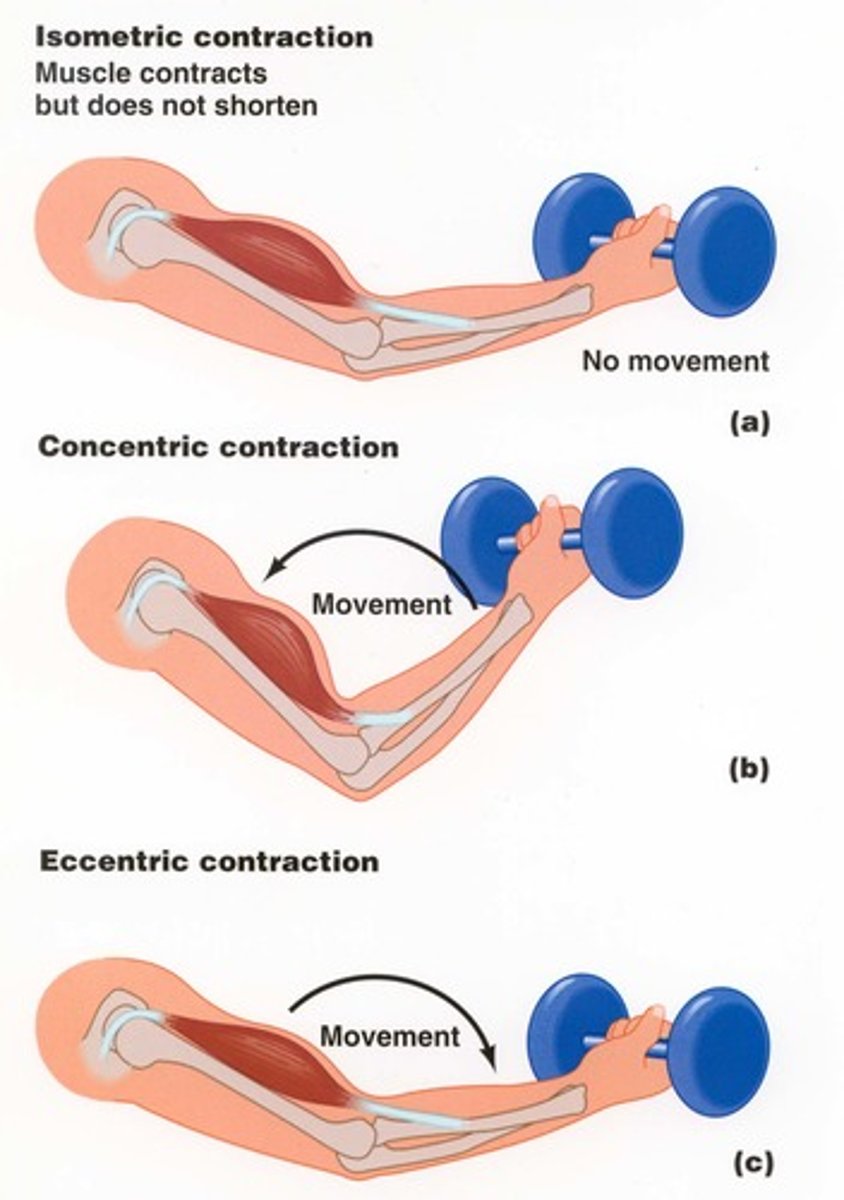
Muscle contractions
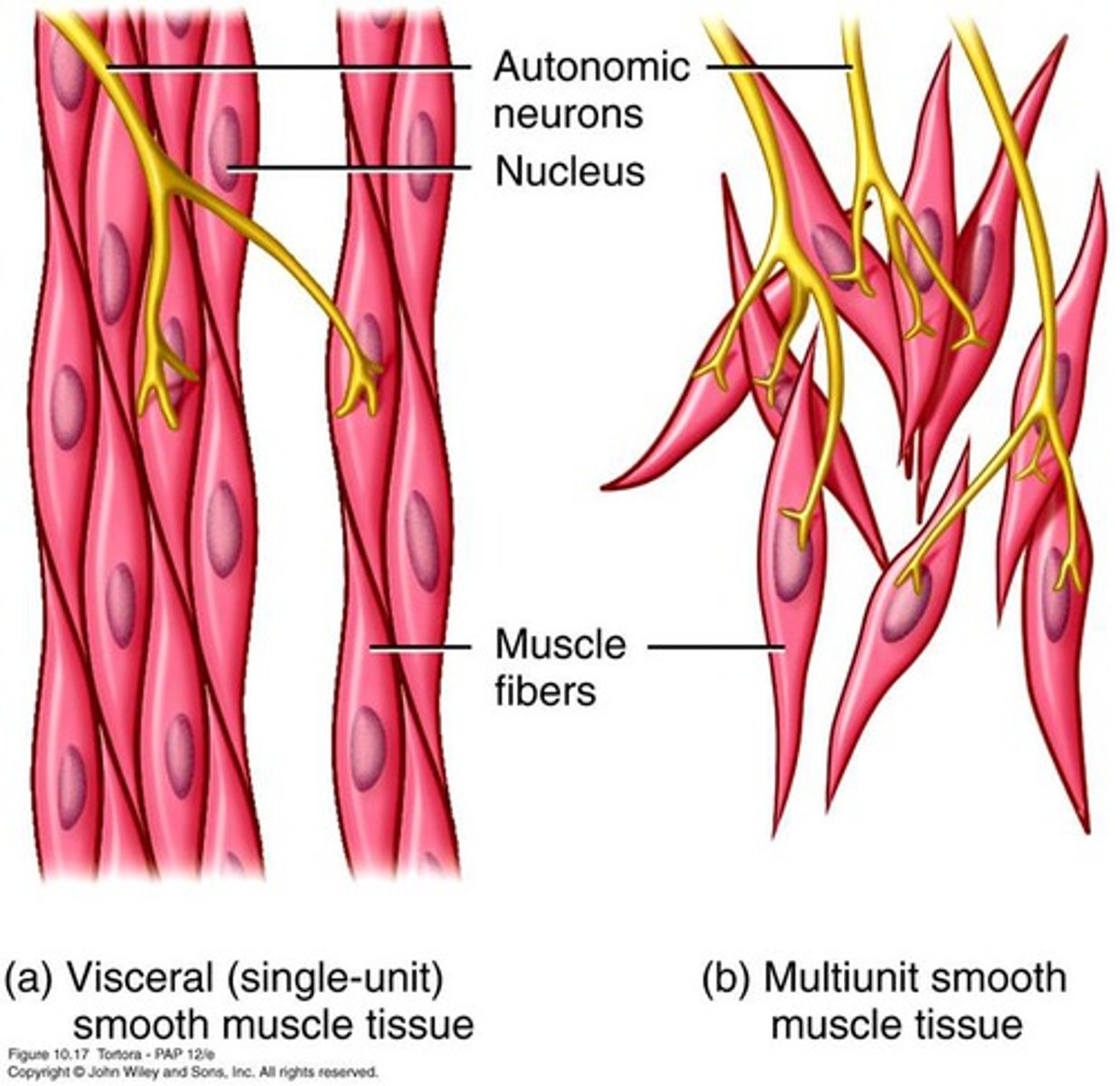
Visceral smooth muscle fibers
Cell cycle