Earth Science
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
super skibidi simulator
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Geosphere
It is composed of naturally-occurring solid aggregate of minerals, organic material or natural glass called rocks, and loose particles of rocks called regolith.
Hydrosphere
All the water at and near the surface of the earth, 97% of which is in oceans
Atmosphere
A mixture of gases that envelops the earth.
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
Cryosphere
Permanently frozen part of the hydrosphere
Rock
naturally-occurring solid aggregate of minerals, organic material or natural glass called
Regolith
loose particles of rocks
Mineral
defined as a naturally-occurring, inorganic solid with a definite chemical composition and an ordered internal structure
naturally occurring
formed by natural processes
Inorganic
coal are not considered minerals due to them being formed from organic material
solid
naturally occurring substances like petroleum or natural gases aren't minerals because of this characteristic
definite chemical composition
The chemical composition of minerals should express the exact chemical formula with the elements and compounds in specific ratios
ordered internal structure
The atoms in minerals are organized in regular, repetitive geometric patterns or crystal structure.
Mineraloid
a substance that passes all but one characteristic of mineral. Examples are opal, pearl, obsidian & amber
Silicates
composed primarily of silicon-oxygen tetrahedrons (SiO42-). _____ are the major rock-forming minerals, including olivine and Quartz.
Oxides
consist of metal cations bonded to oxygen anions. Common minerals includes magnetite and hematite.
Sulfides
consist of metal cation bonded to ion S2-.Examples of this are galena and pyrite.
Sulfates
consist of a metal cation bonded to the SO2-4 anionic group. An example of this is gypsum
Halides
are composed of a halogen ion such as chlorine or fluorine, which forms halite or rock salt and fluorite
Carbonates
are characterized by the presence of carbonic ion(CO32-) which bonds elements such as calcium or magnesium to form calcite or dolomite.
Native Metals
consist of single metals like copper or gold
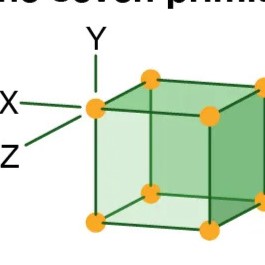
Isometric
Three axes, all of equal length
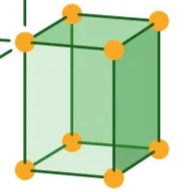
Tetragonal
Three axes, the height axis is unequal to the width and length axes
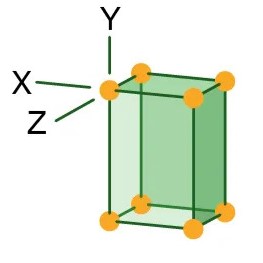
Orthorhombic
Three axes, but all are unequal to each other
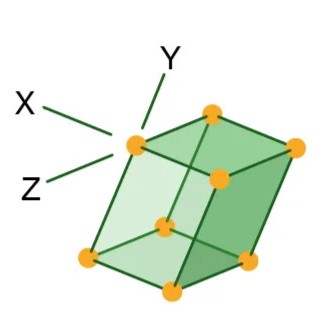
Monoclinic
Three axes, all are unequal in length, and two are perpendicular to each otherF
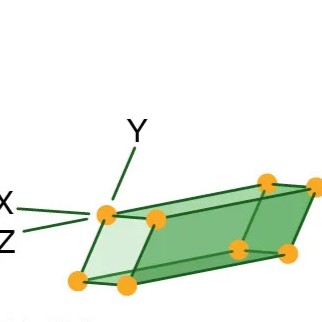
Triclinic
Three axes, all are unequal in length, but none are perpendicular to each other
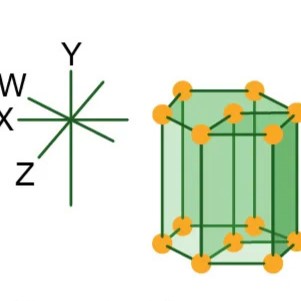
Hexagonal
Four axes, three are of equal length, the fourth axis is perpendicular to the plane of the other three axes.
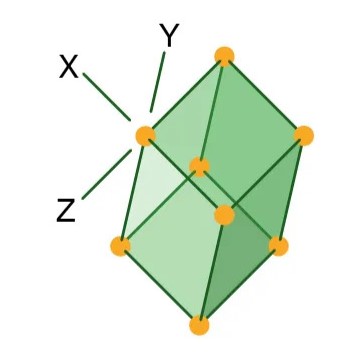
Rhombohedral or Trigonal
All three axes are of equal length, and none of the axes is perpendicular to another, but the crystal faces all have the same size and shape
crystal form
minerals form a definite structure which crystallizes into specific form.
habit
outward appearance of the mineral's crystal form
Cleavage
The tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weakness
Conchoidal Fracture
Curved, smooth fracture caused by a poor cleavage
Dana Classification
Systematic method of identifying minerals using their physical properties
Mohs Scale of Hardness
a scale to measure hardness of minerals (1-10). Softest is Talc, hardest is diamond.
Luster
appearance of light as reflected of a mineral's surface
Color
not a reliable feature for identifying minerals because it can be altered by chemical impurities within it's structure.
Streak
color of a mineral in it's powdered form
Quartz
colorless mineral but slight impurities within it's structure can produce a variety of colors.
Hardness
measurement of the strength of chemical bonds in it's structure.
Density
the degree of compactness of a substance.
Specific Gravity
the measure of the density of a mineral
Rock Cycle
Magma-->Igneous Rocks-->Sediments-->Sedimentary Rocks-->Metamorphic Rocks-->Repeat
Magma
molten rock that becomes lava when it goes to the overground
Igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface. The most common type of rock on earth.
Sediments
Loose materials formed from weathering & erosion of uplifted igneous rock
Sedimentary Rock
formed from sediment compaction
Metamorphic Rock
formed when rocks are subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral-rich fluids