Bio251a: Chapter 13 Microbe-Human Interactions Infection, Disease, and Epidemiology [part two]
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What are the 4 distinct stages of clinical infections?
Incubation period, Prodromal stage, Period of invasion, Convalescent period
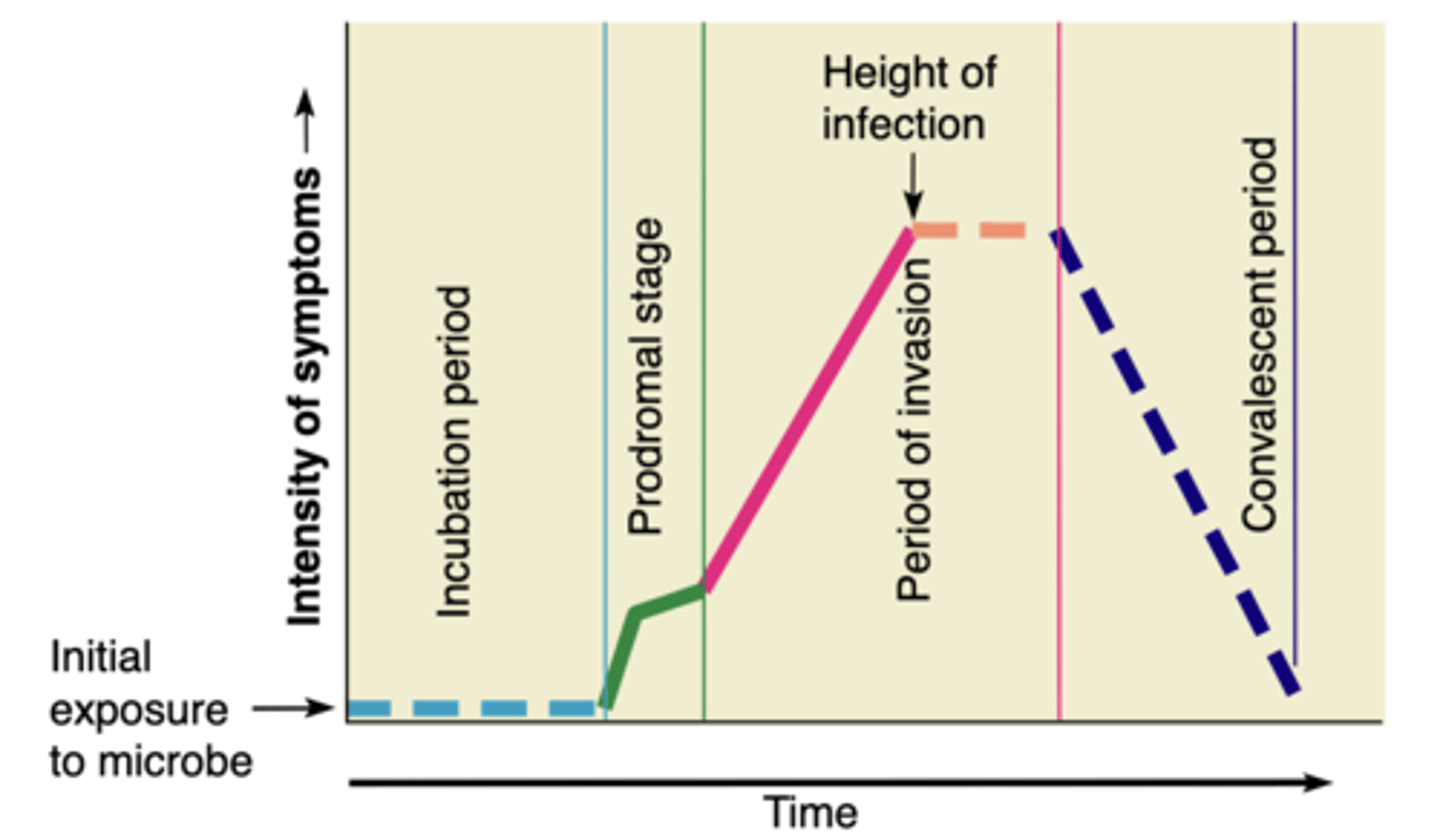
What occurs during Incubation period?
time from initial contact with the
infectious agent to the appearance of first symptoms; agent is multiplying but damage is insufficient to cause symptoms

How long does incubation period last?
several hours to several years
What occurs during Prodromal stage?
vague feelings of discomfort; nonspecific complaints

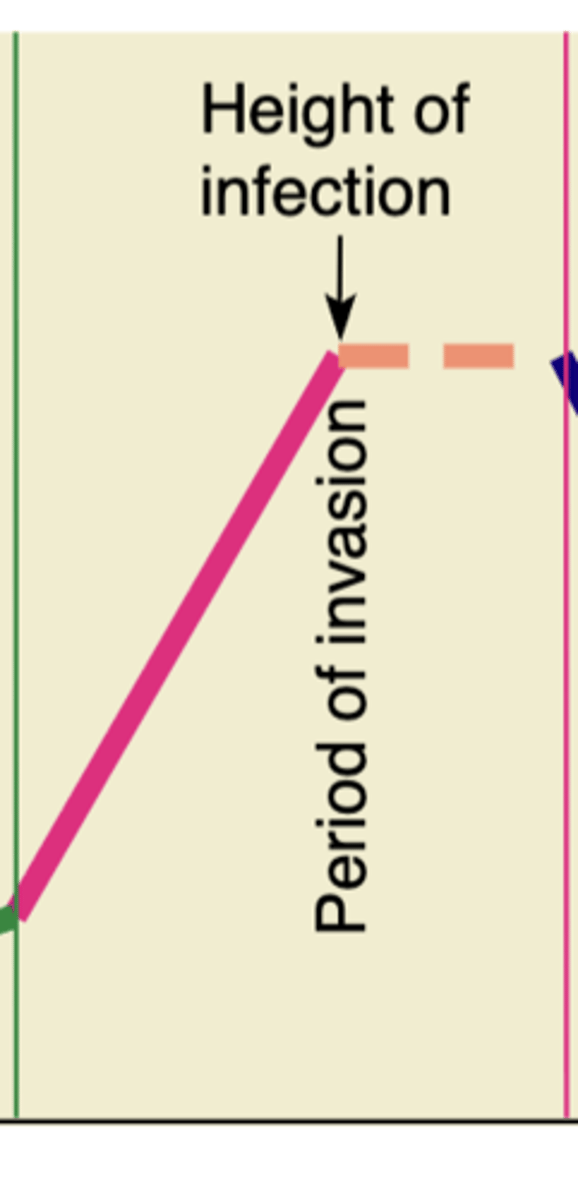
What occurs during period of invasion?
multiplies at high levels, becomes well-established; more specific signs and symptoms
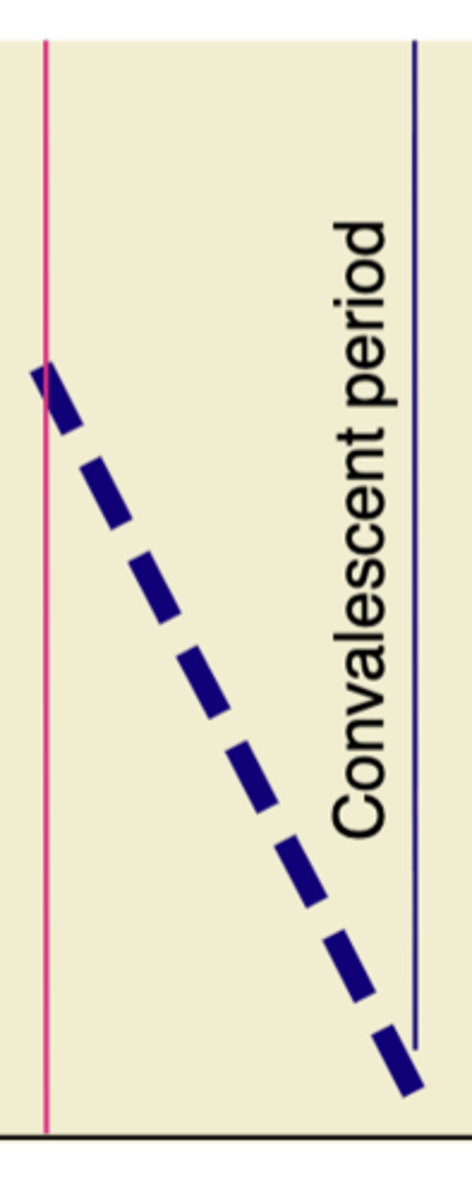
What occurs during Convalescent period?
as person begins to respond tothe infection, symptoms decline
What are the different Patterns of Infection? (6)
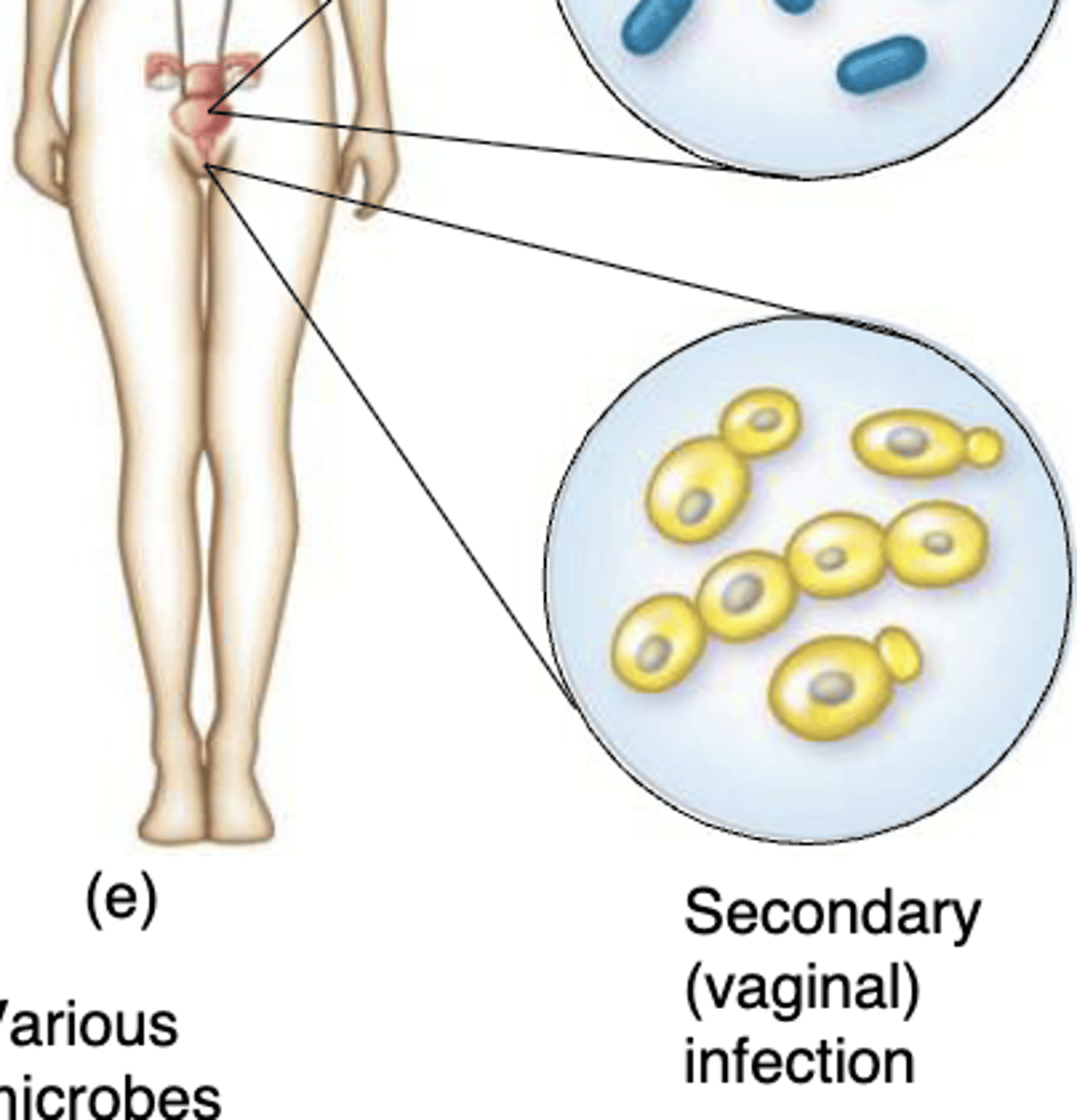
Localized infection, Systemic infection, Focal infection, Mixed infection, Primary infection, Secondary infection, Acute infection, Chronic infections
What occurs during Localized infection?
microbes enter the body and remains confined to a specific tissue
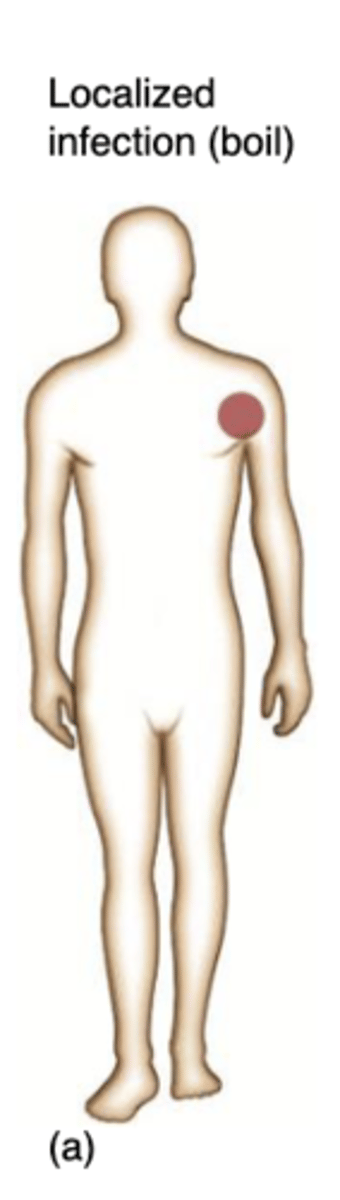
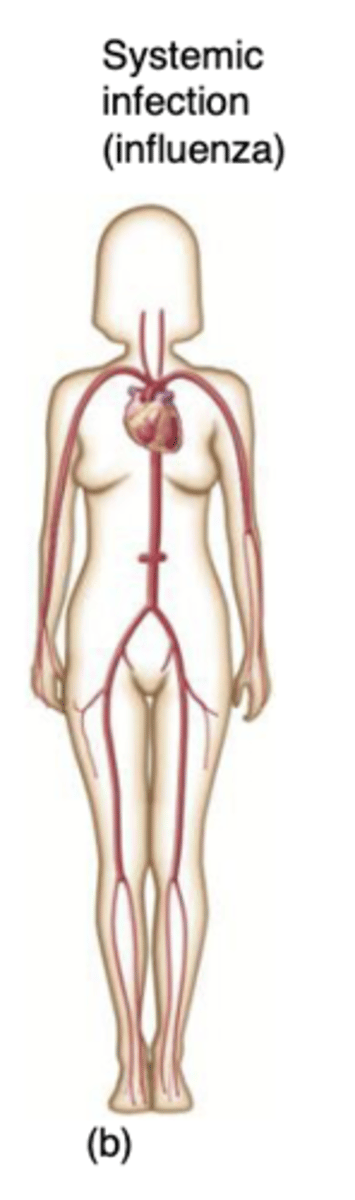
What occurs during systemic infection?
infection spreads to several sites and tissue fluids usually in the bloodstream
What occurs during Focal infection?
when infectious agent breaks loose
from a local infection and is carried to other tissues

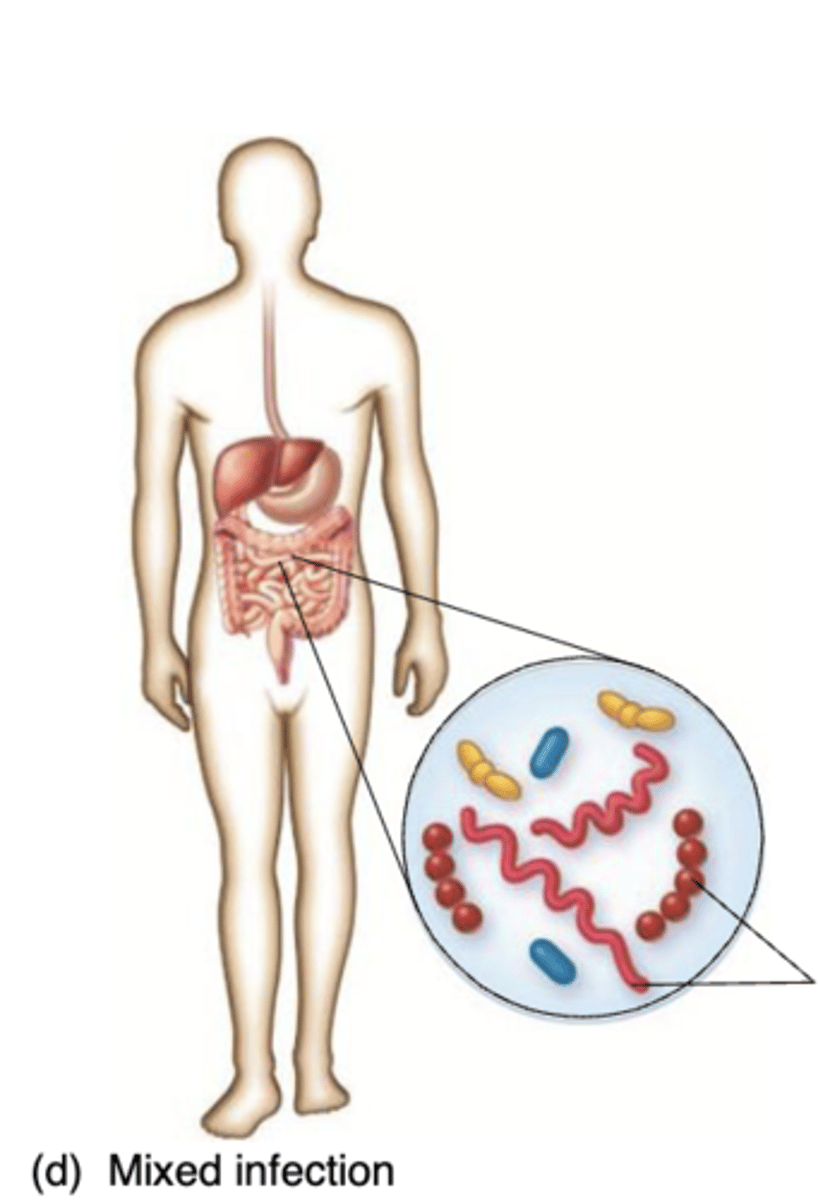
What occurs during Mixed infection?
"polymicrobial"; several microbes grow simultaneously
at the infection site
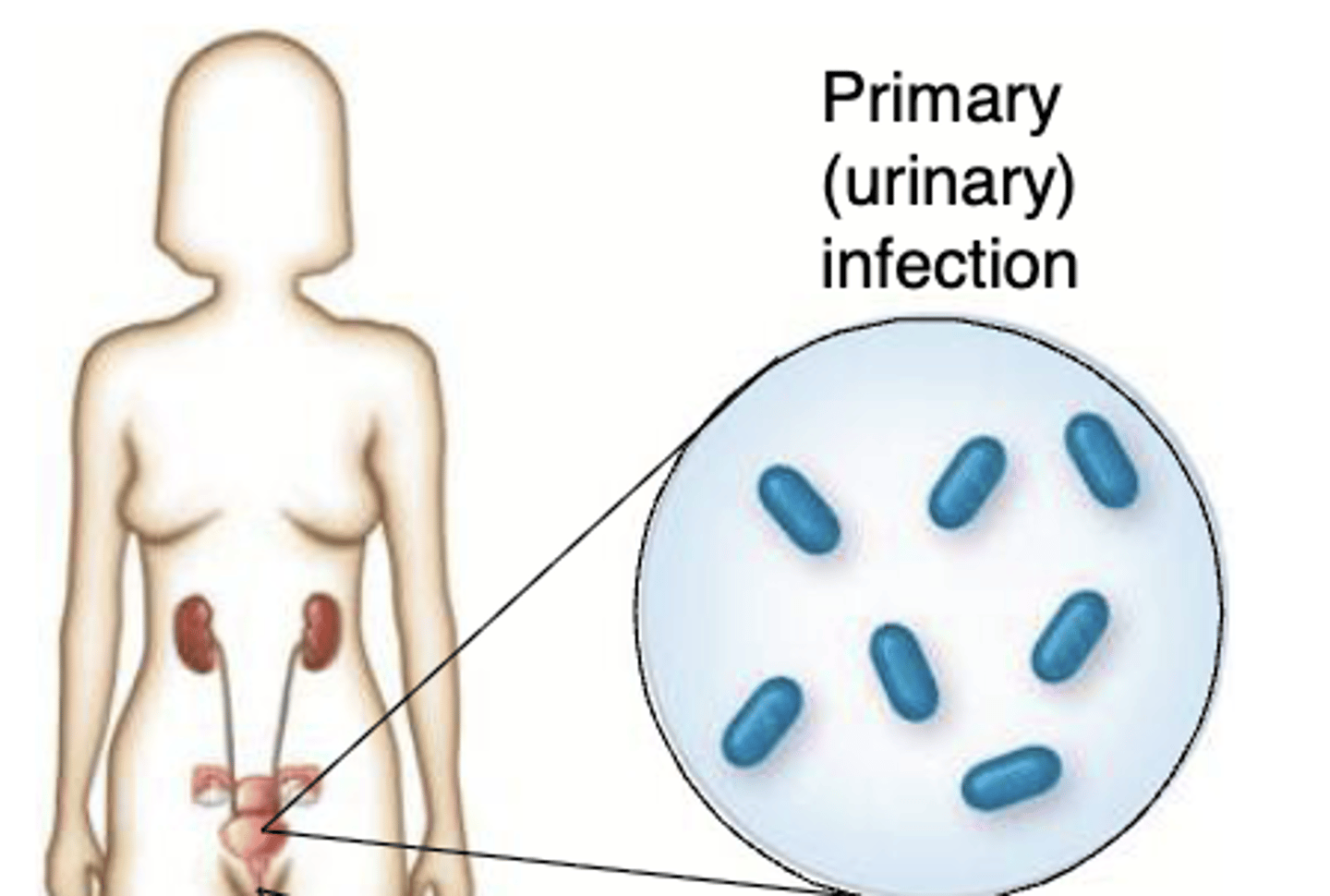
What is Primary infection?
initial infection
What is Secondary infection?
another infection by a different microbe
What is Acute infection?
comes on rapidly, with severe but short-lived effects
What is an example of acute infection? Explain
Common cold
• Symptoms begin 2-3 days after contact
• Resolve by ~ 10 days without therapy
What is common cold most commonly caused by?
rhinovirus
What are Chronic infections?
progress and persist over a long period of time
What is an example of Chronic infections? Explain
Cold sores- Herpes simplex virus- type 2
• Periods of infection and latency
Which is the state of infection when a person is most symptomatic?
Period of invasion
What are the earliest symptoms of disease? Why do they occur?
Fever, pain, soreness, swelling; SIGN OF INFLAMMATION result of the activation of the body defenses
What are signs of inflammation?
Edema, Granulomas and abscesses, Lymphadenitis
What is edema?
accumulation of fluid
What are Granulomas and abscesses?
walled-off collections of inflammatory cells and microbes
What is Lymphadenitis?
swollen lymph nodes
What are Signs of Infection in the Blood?
Changes in the number of circulating white blood cells
What are types of changes in the number of circulating white blood cells?
Leukocytosis, Leukopenia, Septicemia, Bacteremia, Viremia
What is Leukocytosis?
increase in white blood cells
What is Leukopenia?
decrease in white blood cells
What is Septicemia?
microorganisms are multiplying in the blood and present in large numbers
What is Bacteremia?
small numbers of bacteria present in blood not necessarily multiplying
What is Viremia?
small number of viruses present not necessarily multiplying
What are Asymptomatic/subclinical infections?
although infected, the host doesn't show any signs of disease
What occurs in result of Inapparent infection?
no signs or symptoms so person doesn't seek medical attention
What are Portals of Exit?
Pathogens depart by a specific avenue; greatly influences the dissemination of infection
What are the Portals of Exit?
Respiratory, Skin scales, Fecal exit, Urogenital tract, Removal of blood
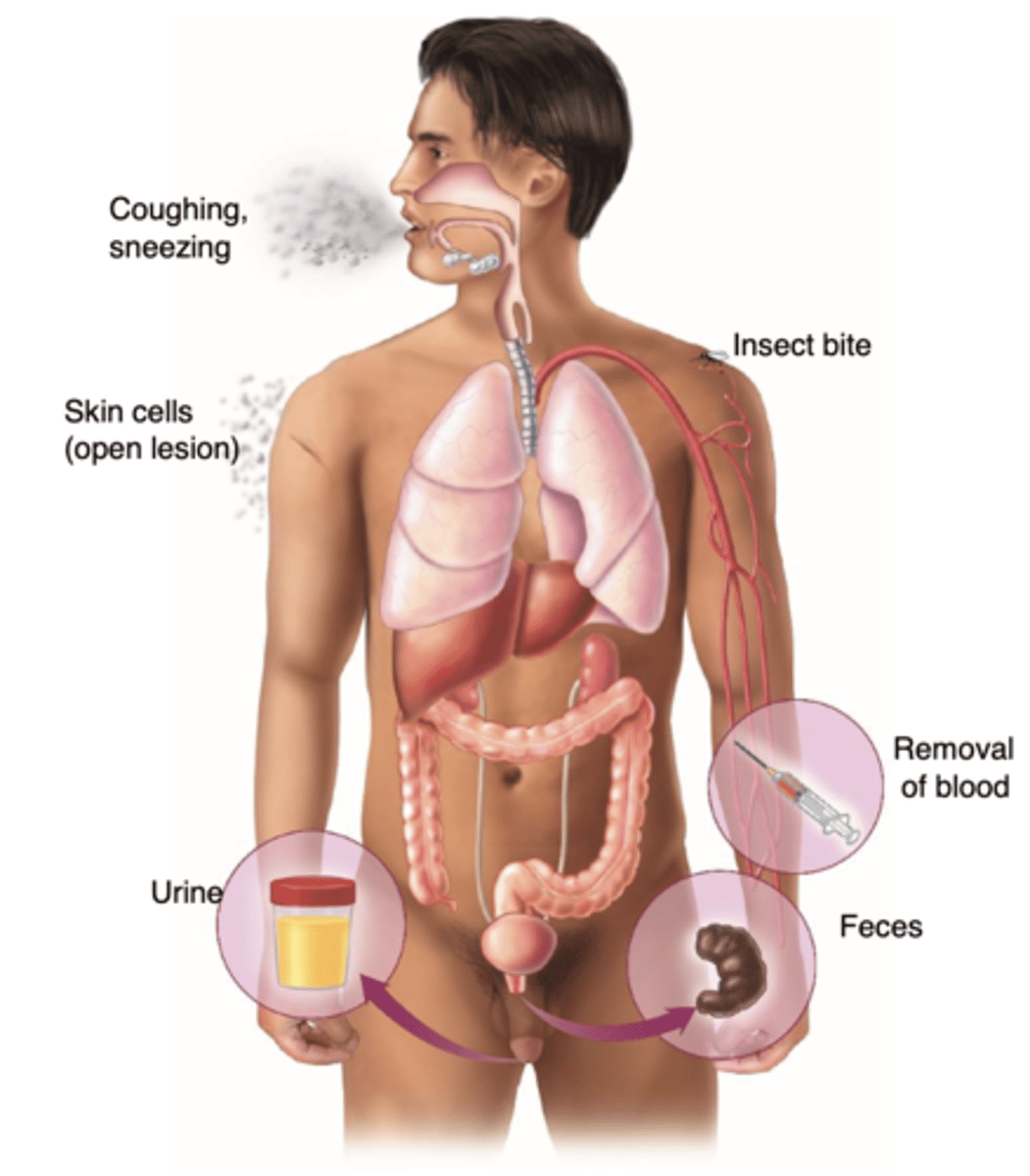
What components are included in the respiratory portal exit?
mucus, sputum, nasal drainage, saliva
Does recovering from illness mean that microbe is removed?
no
What are the components of Persistence of Microbes and
Pathologic Conditions?
Latency, Chronic carrier, Sequelae
What is latency?
infection in which the pathogen is not active or causes disease
What is Chronic carrier?
person with a latent infection who sheds the infectious agent
What is Sequelae?
long-term or permanent damage totissues or organs
What are two types of Sources and Transmission of Microbes?
Reservoir, Source
What is reservoir?
primary habitat of pathogen in the natural world; Human or animal carrier, soil, water, plants
What is an example of Reservoir? explain
Influenza virus, the reservoir is birds since they can harbor the virus without showing signs of infection
What is Source?
individual or object from which an infection is actually acquired
What is an example of source? explain
Door knob, roommate, two year old daughter
What is a Living Reservoir called?
carrier
What is a carrier?
an individual who inconspicuously shelters a pathogen and spreads it to others; may or may not have experienced disease due to the microbe
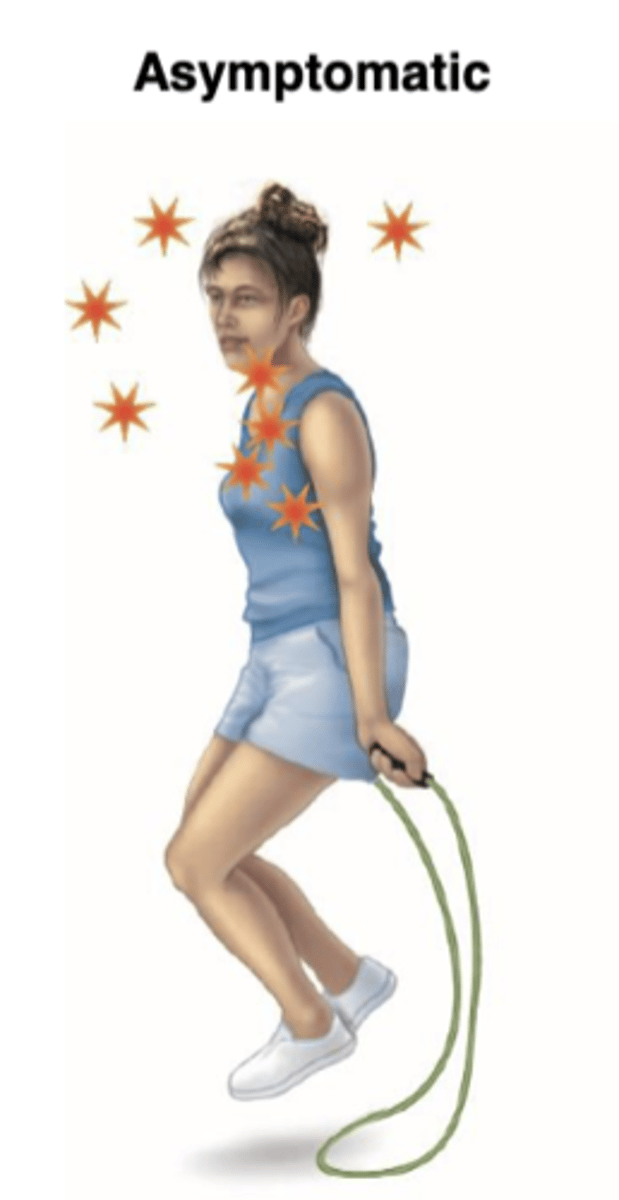
What is an Asymptomatic carrier?
shows no symptoms

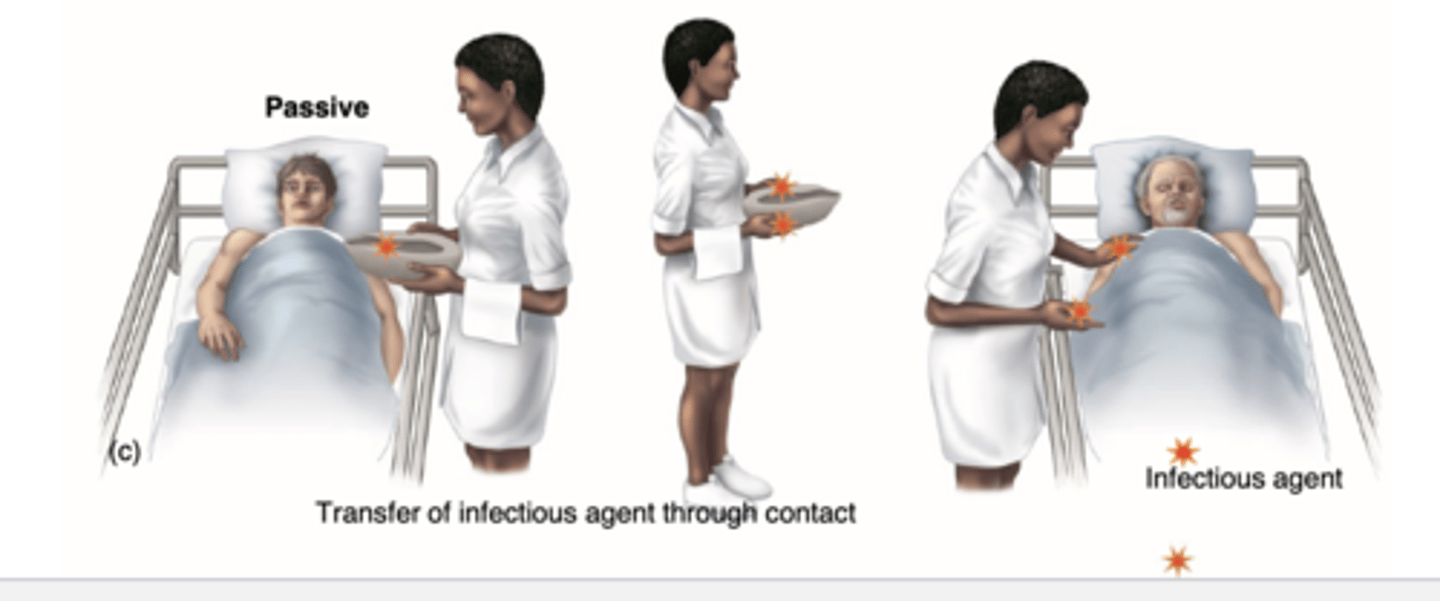
What is a passive carrier?
contaminated healthcare provider picks up pathogens and transfers them to other patients
How can health care workers be passive carriers?
Carries the pathogen on their skin or a fomite (an inanimate object) that can transport a pathogen.
- Ex: ties, mops, blankets,
clothing, stethoscope.
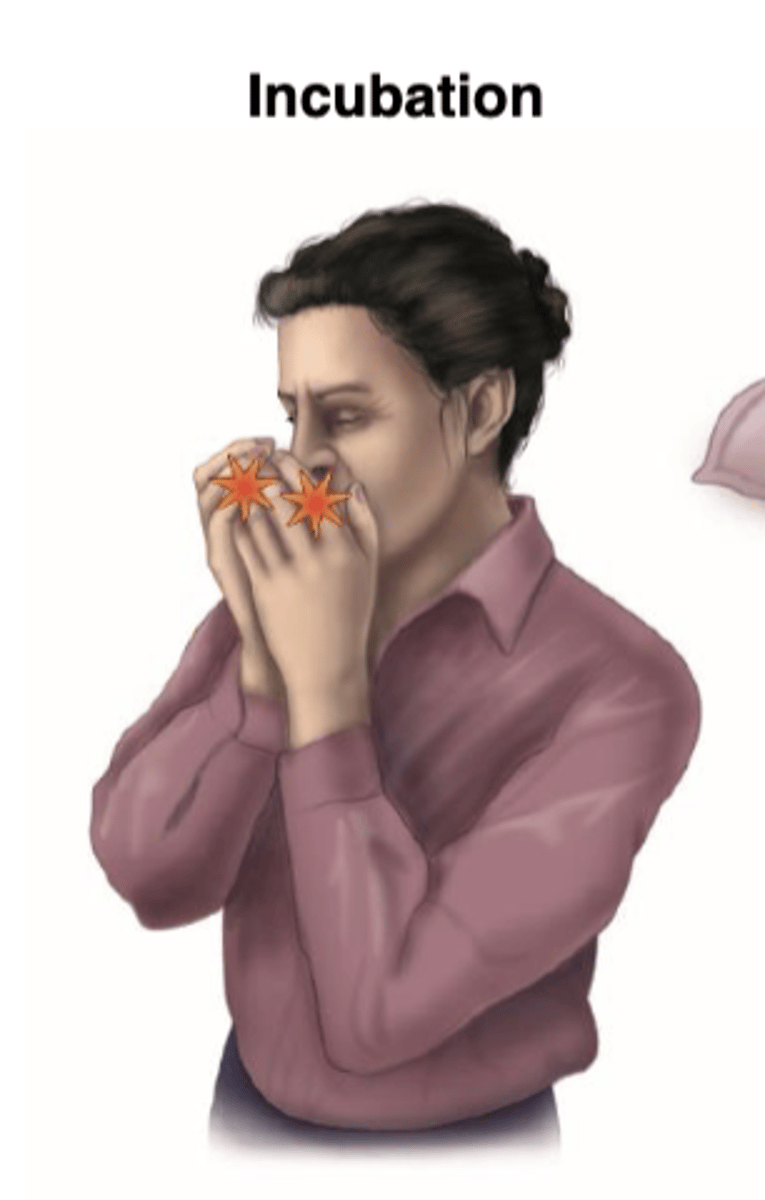
What are Incubation carriers?
spread the infectious agent during the incubation period

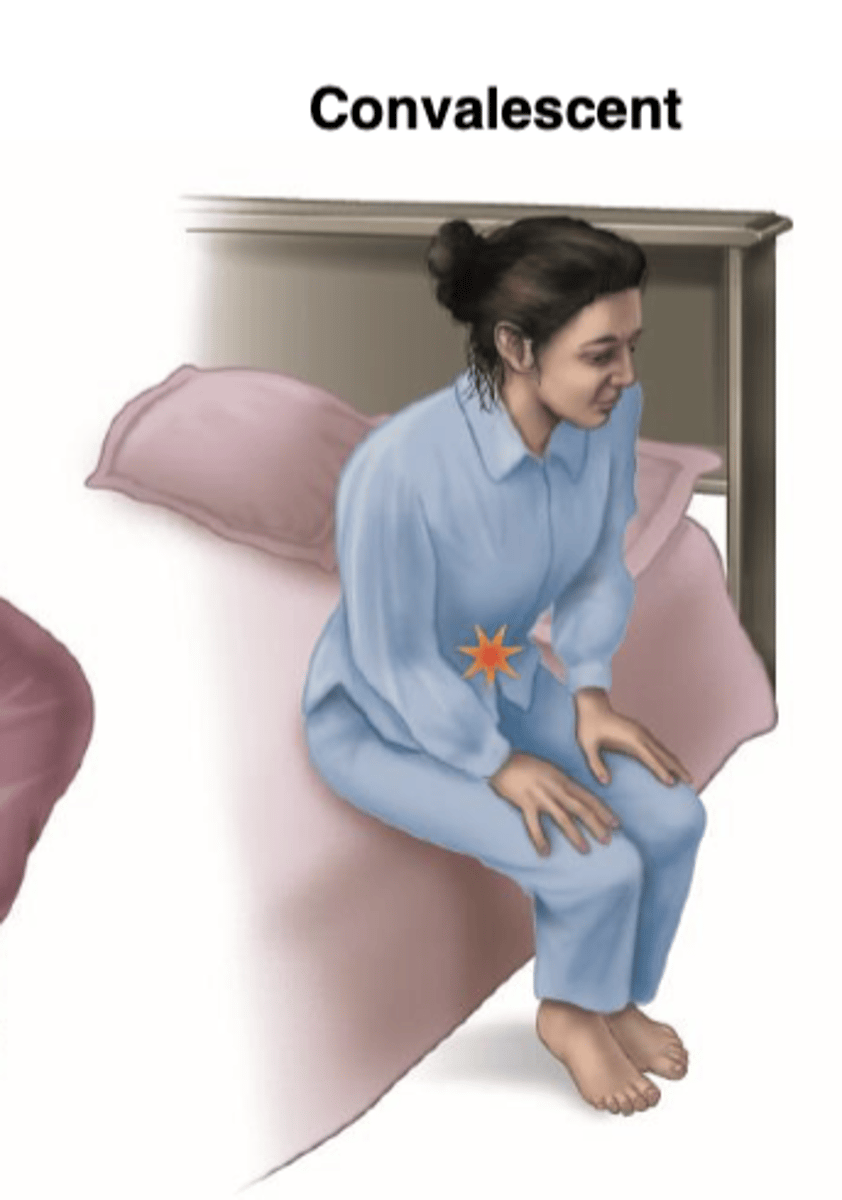
What are Convalescent carriers?
recuperating without symptoms
What are Chronic carriers?
individual who shelters the infectious
agent for a long period
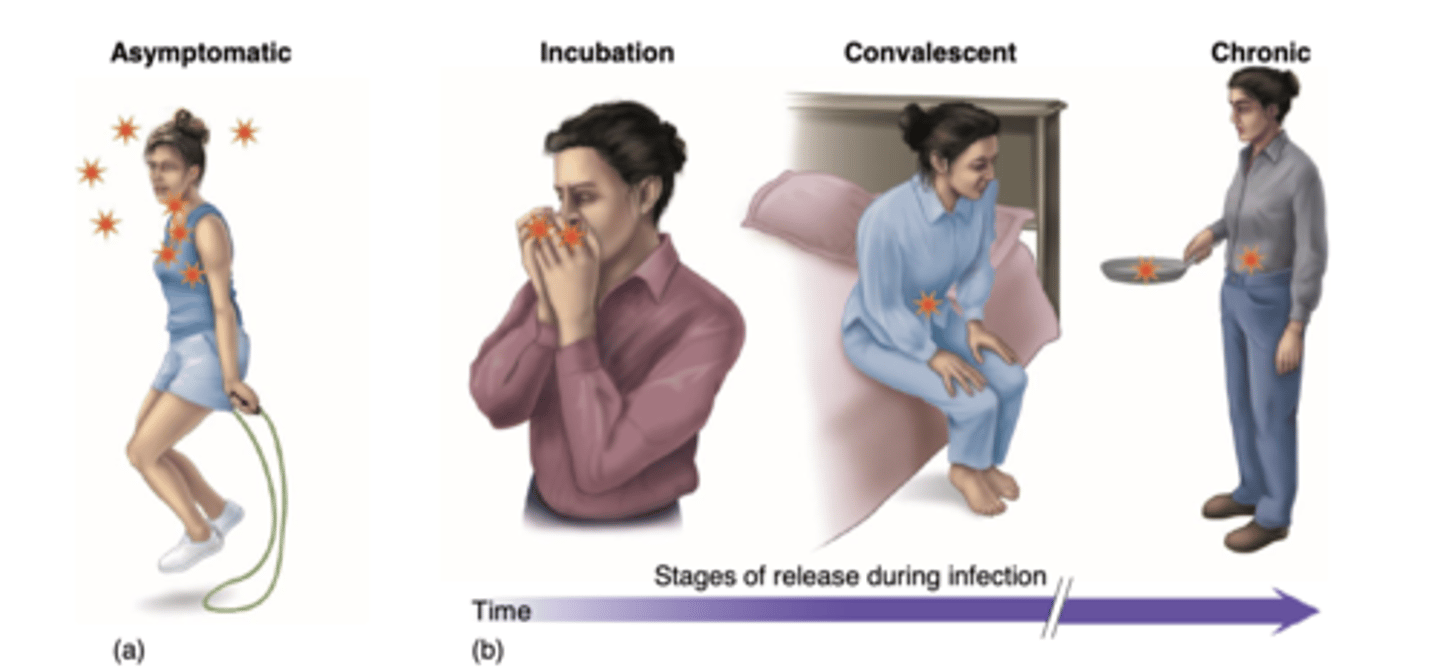
What is the progression for Living Reservoir carriers?
1.) Asymptomatic carrier
2.) Incubation carriers
3.) Convalescent carriers
4.) Chronic carrier
If a nurse transfers a pathogen between patients without becoming infected herself, the nurse as acted as the
Passive Carrier
What are the two Acquisition and Transmission of Infectious Agents?
Communicable disease and Non-communicable infectious disease
What is Communicable disease?
when an infected host
can transmit the infectious agent to another host
and establish infection in that host
What type of communicable disease is contagious?
Highly communicable diseases; direct contact
What is non-communicable disease?
does not arise through transmission from host to host; Contact with organism (facultative parasites,
fungal/bacterial spores) in natural, non-living reservoir
When does non-communicable disease usually occur?
when a compromised person is invaded by his or her own normal microflora
What are the two Patterns of Transmission?
direct contact and indirect contact
What is direct contact?
physical contact or fine aerosol droplets
What is indirect contact?
passes from infected host to intermediate conveyor and then to another host
What is vehicle?
inanimate material, food, water, biological products, fomites
What is airborne?
droplet nuclei, aerosols
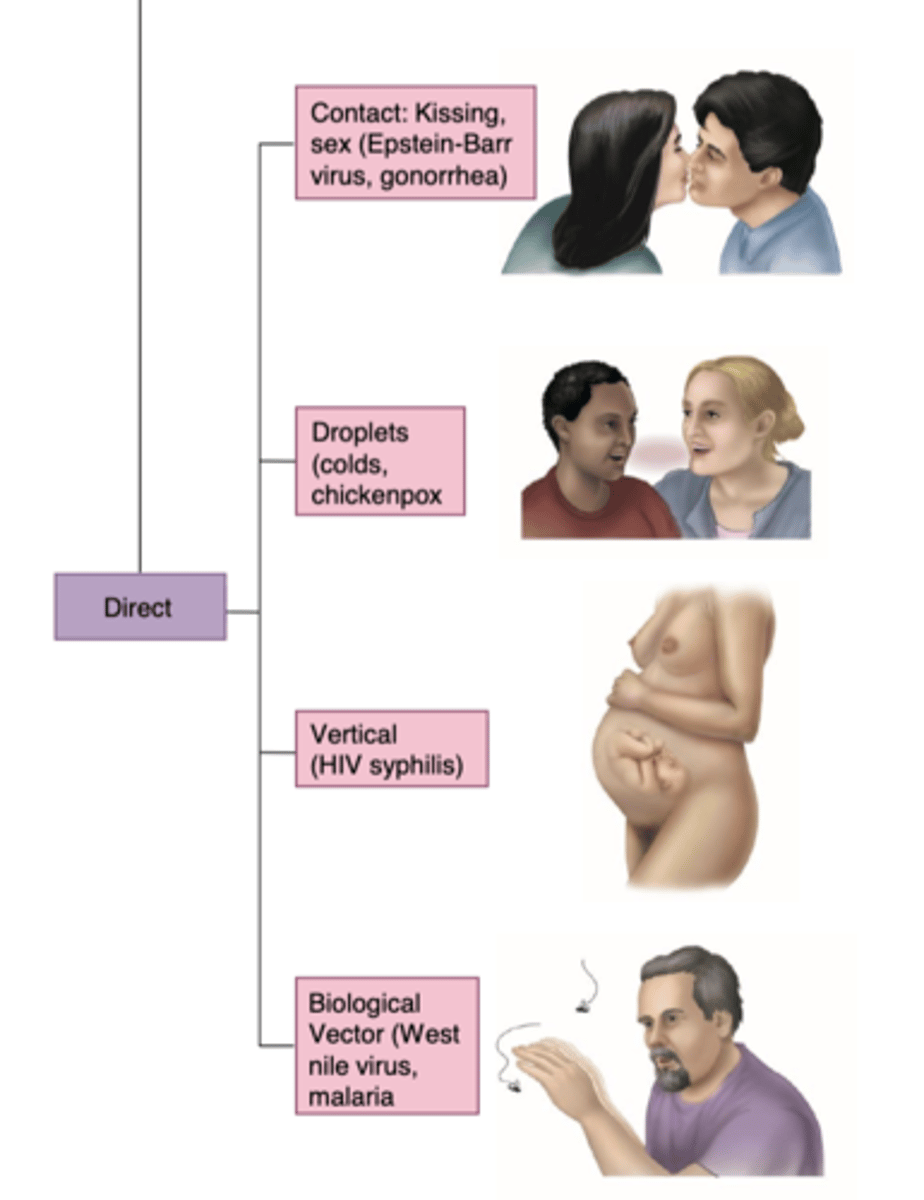
How is direct infectious disease acquired?
- contact; kissing. sex
- droplets; colds, chickenpox
- vertical; HIV, syphillis
- biological vector; west nile virus, malaria
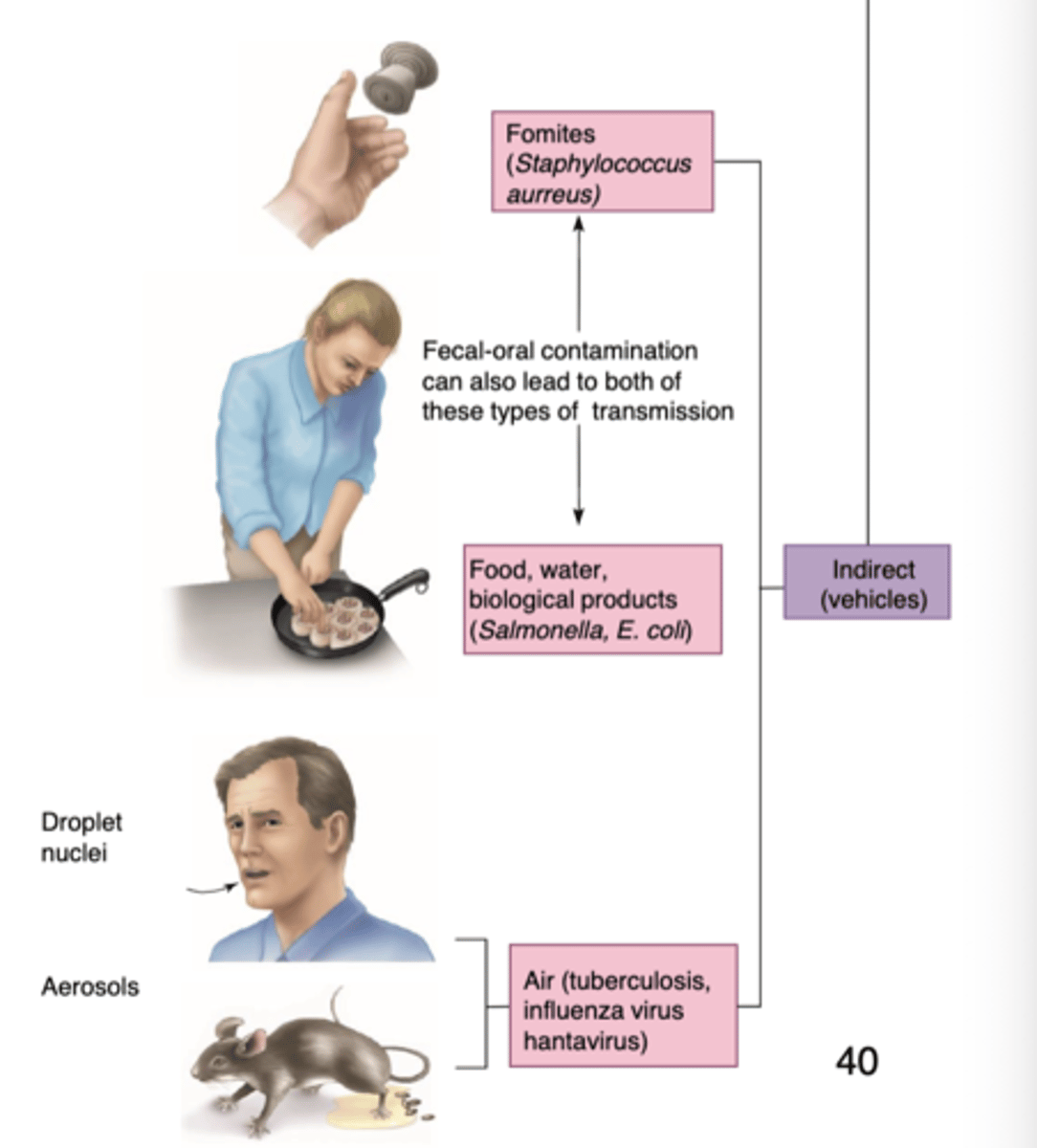
How is indirect infectious disease acquired?
- fomites; staphylococcus
- food/water/biological products; salmonella, e. coli
- air; tuberculosis, influenza virus, hantavirus
What are Nosocomial Infections?
Diseases that are
acquired or developed
during a hospital stay
How do Nosocomial Infections occur in the hospital?
From surgical procedures, equipment, personnel, and exposure to drug-resistant microorganisms
How many cases and deaths are there due to Nosocomial Infections in the US?
2 to 4 million cases/year in U.S.with approximately 90,000 deaths
What is Epidemiology?
describe Frequency of Cases
What is Prevalence?
total number of existing cases with respect to the entire population usually represented by a percentage of the population
What is Incidence?
measures the number of new cases over a certain time period, as compared with the general healthy population
What is Mortality rate?
the total number of deaths in a population due to a certain disease
What is Morbidity rate?
number of people afflicted with a certain disease
What is Endemic?
disease that exhibits a relatively steady frequency over a long period of time in a particular geographic locale
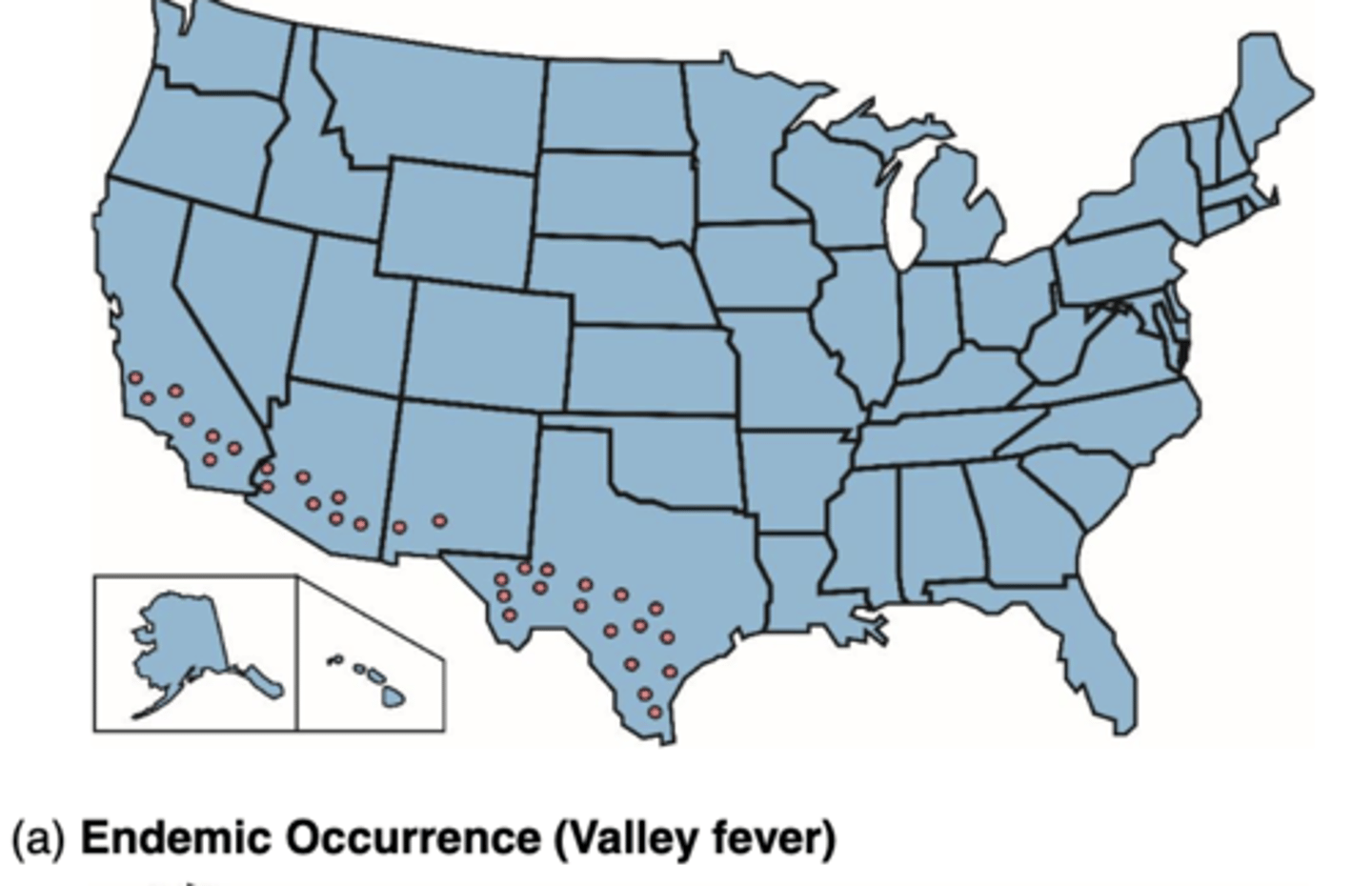
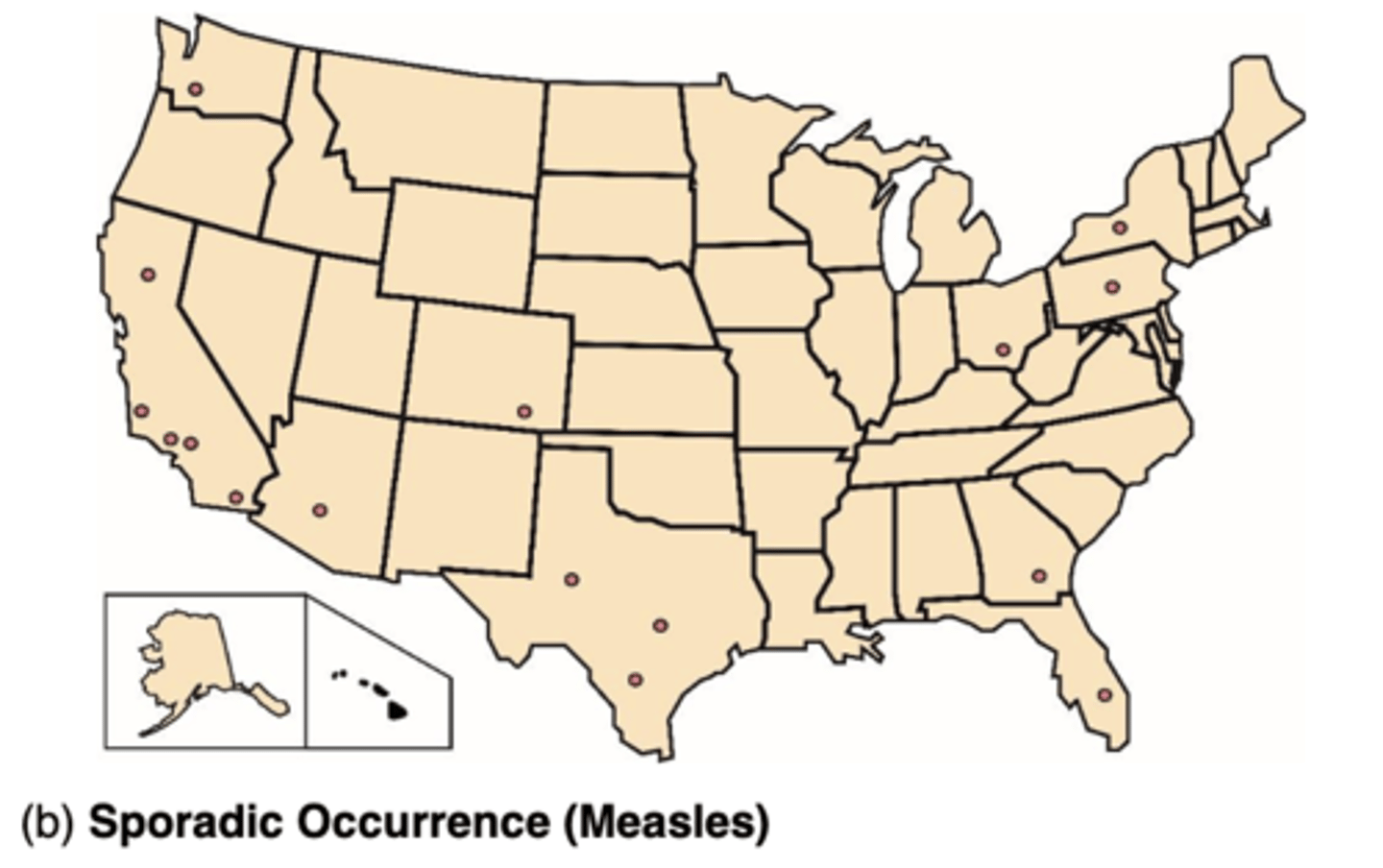
What is Sporadic?
when occasional cases are reported at irregular intervals
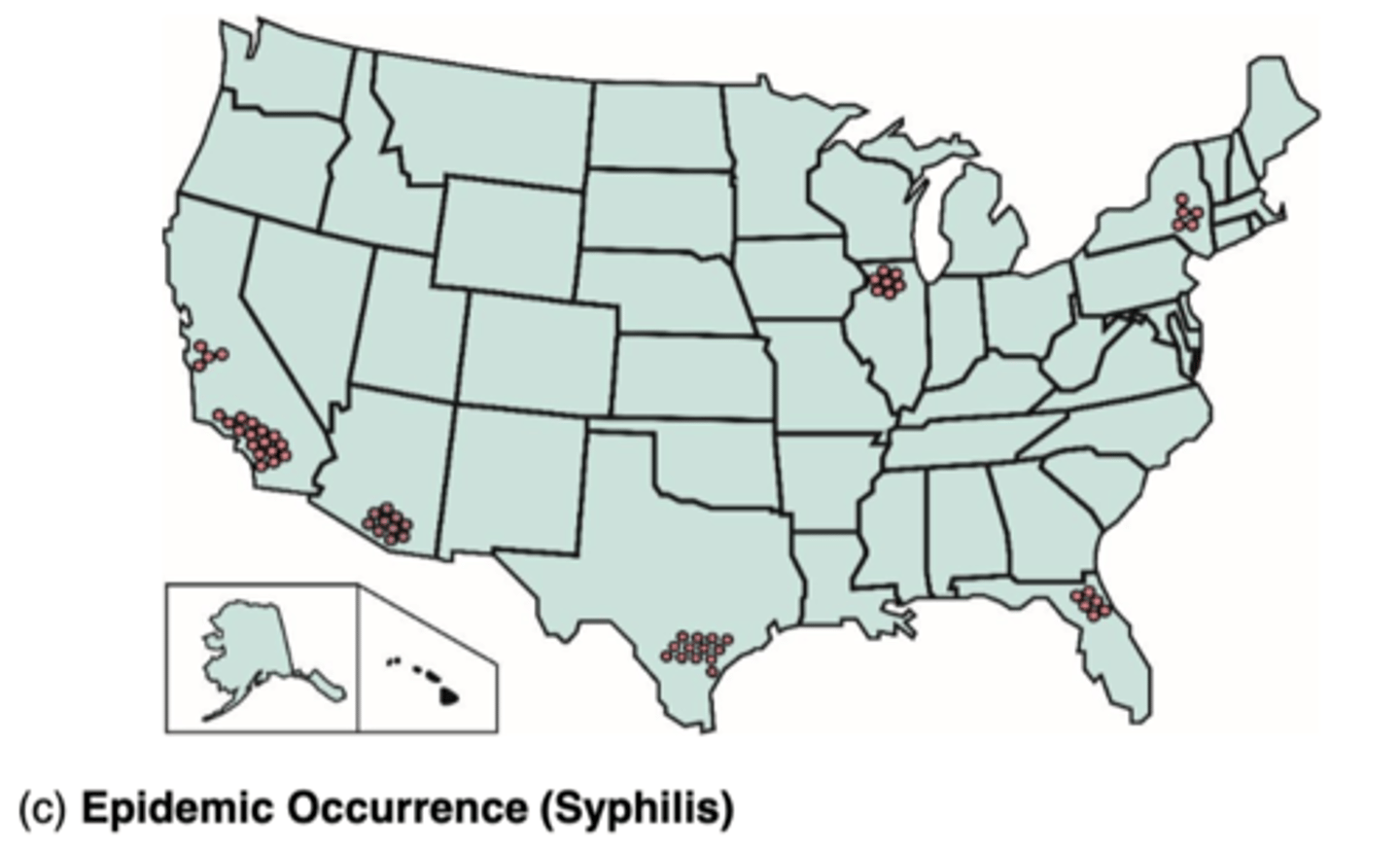
What is Epidemic?
when prevalence ofa disease is increasing beyond what is expected
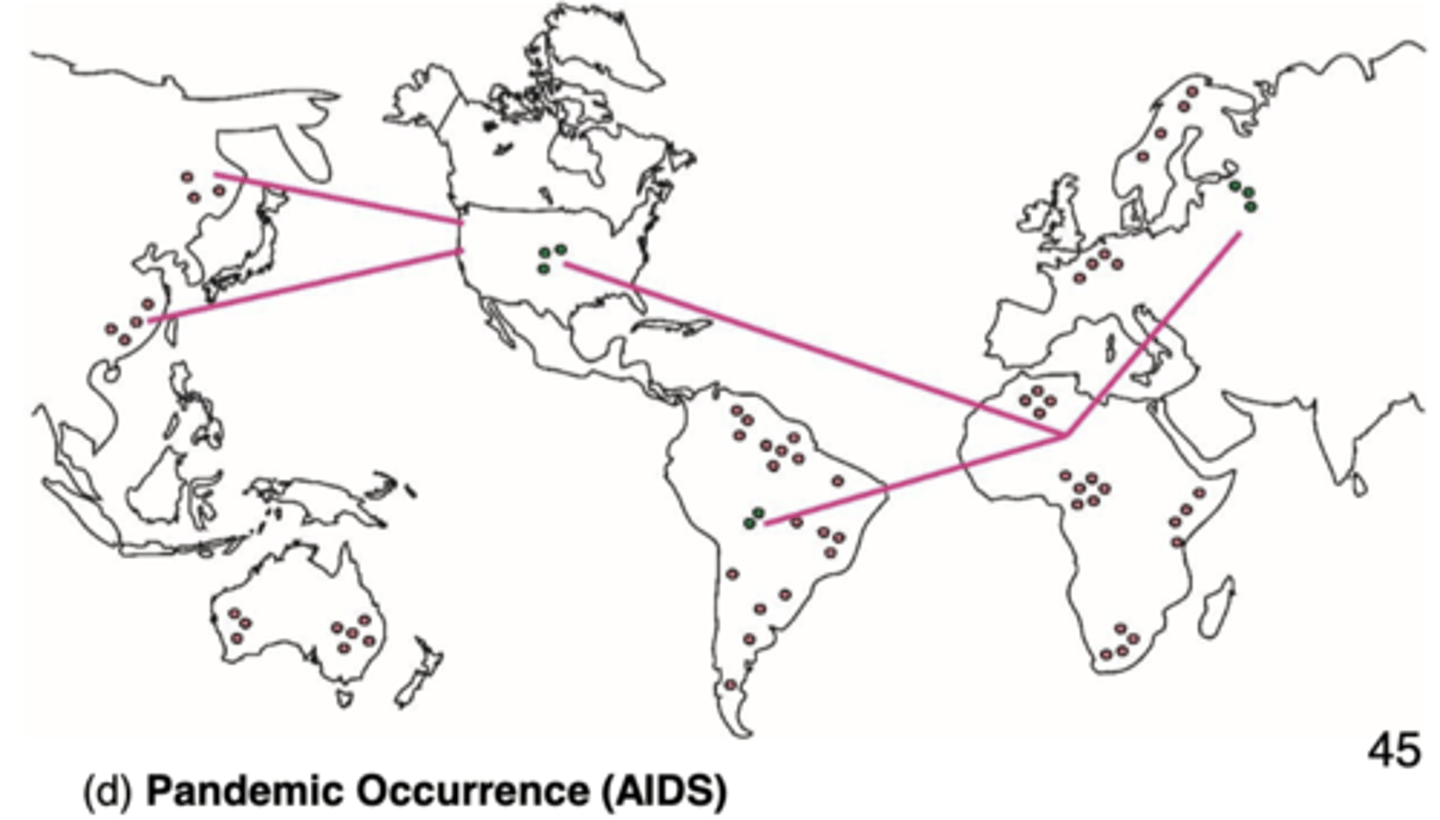
What is Pandemic?
epidemic across continents
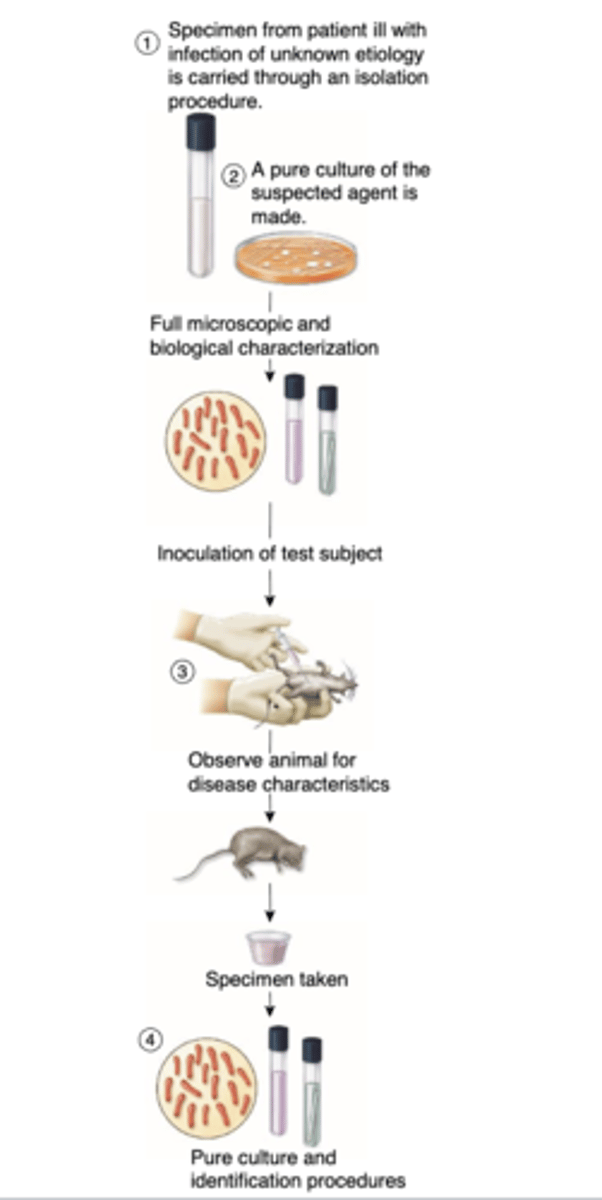
What is the function of Koch's Postulates?
Determining the causative agent of a disease
What are the steps of Koch's Postulates?
1. Find evidence of a particular
microbe in every case of a
disease
2. Isolate that microbe from an
infected subject and cultivate it
artificially in the laboratory
3. Inoculate a susceptible healthy
subject with the laboratory
isolate and observe the
resultant disease
4. Reisolate the agent from this
subject