FM116 Fashion Business Practices Exam 2
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
small business
one that is independently owned and operated for profit and is not dominant in its field
span of control
the number of workers who report directly to one manager
organizational height
the number of layers, or levels, of management in a firm
wide span of management (flat organization)
exists when a manager directly supervises a very large number of employees
narrow span of management (tall organization)
exists when a manager directly supervises only a few subordinates
flat organization
high competence in managers and workers, standard operating procedures, and few new problems
tall organization
physical dispersion of subordinates, manager has additional tasks, high level of interaction required between manager and workers, high frequency of new problems
authority
the right to use power
responsibility
Being responsible for one's actions
Theory X
a concept of employee motivation generally consistent with Taylor's scientific management; assumes that employees dislike work and will function only in a highly controlled work environment
Theory Y
a concept of employee motivation generally consistent with the ideas of the human relations movement; assumes responsibility and work toward organizational goals, and by doing so they also achieve personal rewards
Performance Feedback Review
when a manager gives you a review and asks what do you think about that
franchise
a licence to operate an individually owned business as though it were part of a chain of outlets or stores
Why purchase a franchise?
It is a simpler way to get into business because you don't have to go through all of the things established
franchisee
A person who buys a franchise
Franchisor
an individual or organization granting a franchise
Advantages of a small business
personal relationships with customers and employees, ability to adapt to change, simplified record keeping, independence, profit retention, ease and low cost of going into or out of business, ability to keep business information secret
Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs)
university-based groups that provide individual counseling and practical training to owners of small businesses
franchise mediation program
program that settles things when theres conflict between franchiser or franchisee that avoids going to court and saves money
SWOT analysis
the identification and evaluation of a firm's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
internal
strengths and weaknesses
external
opportunities and threats
TQM (Total Quality Management)
the coordination of efforts directed at improving customer satisfaction, increasing employee participation, strengthening supplier partnerships, and facilitating an organizational atmosphere of continuous quality improvement
Steps in the decision making process
Problem recognition
Information search
Evaluation of alternatives
Product choice
top manager
an upper-level executive who guides and controls the overall fortunes of an organization
middle manager
a manager who implements the strategy and major policies developed by top management
first-line manager
a manager who coordinates and supervises the activities of operating employees
conceptual skills
the ability to think in abstract terms and to see how parts fit together to form the whole
analytic skills
the ability to identify problems correctly, generate reasonable alternatives, and select the "best" alternatives to solve problems
interpersonal skills
the ability to deal effectively with other people
technical skills
specific skills needed to accomplish a specialized activity
communication skills
the ability to speak, listen, and write effectively
leadership
the ability to influence others
Digital Communication
Data in a form that can be transmitted and received electronically
departmentalization
the process of grouping jobs into manageable units
departmentalization by function
grouping jobs that relate to the same organizational activity
(smaller and newer organizations do this, advantages include simplified supervision and easy coordination, disadvantages include slow decision making and it Tends to emphasize the department over the organization as a whole)
departmentalization by product
grouping activities related to a particular product or service
(used often by older and larger firms that produce and sell a variety of products.)
departmentalization by location
grouping activities according to the defined geographic area in which they are performed
departmentalization by customer
grouping activities according to the needs of various customer populations
best form of departmentalization is ______
a combination of bases
small business association
A federal agency that provides loans to small business investment companies (SBICs) that supply venture capital and financing to small businesses. Debentures sold by SBICs are fully guaranteed by the SBA.
forms of organizational structure
line structure
line-and-staff structure
the matrix structure
the network structure
delegation
assigning tasks to people
line structure
an organizational structure in which the chain of command goes directly from person to person throughout the organization
line-and-staff structure
an organizational structure that utilizes the chain of command from a line structure in combination with the assistance of staff managers
matrix structure
an organizational structure that combines vertical and horizontal lines of authority, usually by superimposing product departmentalization on a functionally departmentalized organization
network structure
an organizational structure in which administration is the primary function, and most other functions are contracted out to other firms
steps in the delegation process
1. assigning responsibility
2. granting authority
3. creating accountability
line managers
a position in which a person makes decisions and gives orders to subordinates to achieve the organization's goals, most effective in small-sized organizations
staff manager
a position created to provide support, advice, and expertise within an organization
matrix structure pros and cons
Advantages:
• Adds flexibility
• Increases productivity
• Raises morale
• Nurtures creativity and innovation
• Personal development experienced by employees
Disadvantages:
• Chain of command conflicts
• May take longer to resolve problems and issues
• Personality clashes
• Poor communication
• Undefined individual roles
• Unclear responsibilities
• Difficulties in finding ways to reward individual and team performance simultaneously
• Expensive to maintain
replacement chart
a list of key personnel and their possible replacements within a firm
skills inventory
a computerized data bank containing information on the skills and experience of all present employees
Human Resources
the people who work within an organization and are the most important and valuable resource for a business.
Human Resource Management
all the activities involved in acquiring, maintaining, and developing an organization's human resources
different forms of people leaving a company
layoffs
attrition
early retirement
buyouts
firing
Least offensive way to leave a company
Attrition
Worst way to leave a company
Firing
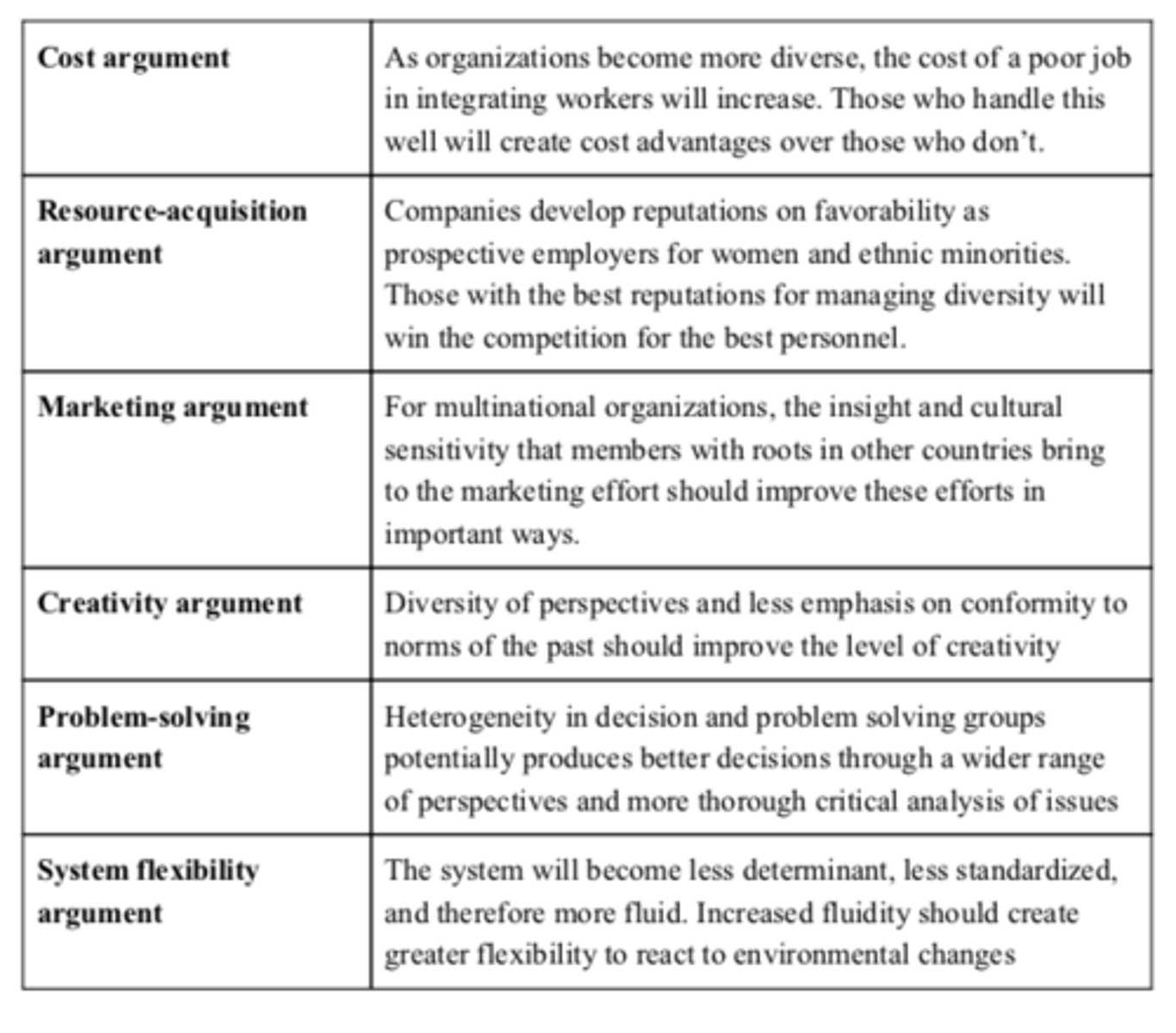
Advantages of a diverse workforce
cost friendly
resource acquisition, it affects the companies rep
marketing edge
flexibility
creativity
problem solving
bilingual skills
compensation
payment
hourly wage
a specific amount of money paid for each hour of work
salary
a specific amount of money paid for an employee's work during a set calendar period, regardless of the actual number of hours worked
commission
a payment that is a percentage of sales revenue
incentive payment
a payment in addition to wages, salary, or commissions
lump-sum salary increase
an entire pay raise taken in one lump sum
profit-sharing
the distribution of a percentage of a firm's profit among its employees
Job Analysis
a systematic procedure for studying jobs to determine their various elements and requirements
job description
a list of the elements that make up a particular job
job specification
a list of the qualifications required to perform a particular job
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
a sequence of human needs in the order of their importance; physiological, safety, social, esteem, self-actualization
Who created the theories?
Douglas McGregor
physiological needs
the things we require for survival
safety needs
the things we require for physical and emotional security
social needs
the human requirements for love and affection and a sense of belonging
esteem needs
our need for respect, recognition, and a sense of our own accomplishment and worth
self-actualization needs
the need to grow and develop and to become all that we are capable of being
extinction
not responding to undesirable behavior with the hope that the behavior will eventually go "extinct"
Forms of Reinforcement
positive reinforcement
negative reinforcement
punishment
extinction
goal
A result that a person aims for and works hard to reach, long term
objective
short term goal
Mission Statement
a statement of the organization's purpose - what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment
negative reinforcement
one that strengthens desired behavior by eliminating an undesirable task or situation
job sharing
an arrangement whereby two part-time employees share one full-time job
part-time job
permanent employment in which individuals work less than a standard work week
incentive pay
forms of pay linked to an employee's performance as an individual, group member, or organization member
benchmarking
a process by which a company compares its performance with that of high-performing organizations
#1 aspect of TQM
customer service or satisfying the customer