social cognition part 2 - mirror neurones/ EMPATHY
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WATCH Last weeks video to unerstand empathy too
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
how od we test empathy and mirror neurons
mirror neuron
specialised neurones which activate both when a person is observing another’s actions nd they are performing the action themselves
who discovered mirror neurones
discussion of mirror neurones/ empathy
rizzolati et al,. discovered mirror neurones in the premotor cortex of macaques monkeys and coined the term - suggested basis for understanding others actions (1996)
later suggested could basis for empathy - humans emotional understanding (define term)
evidence for
lacoboni et al 1999
provided evidence that mirror neurones did exist in humans via fMRI
wicker et al 2003
singer et al,.2004 - empathy for pain
used fMRI to produce results which showed that the same brain regions such as the the anterior midcingulate cortex (aMCC) activated when participants experienced pain and watched a loved one experience pain overlap - supports simulation theory
study criticised lamm et al outline criticisms -
question specificity and sensitivity of shared activations
criticised for methodoligal limitation of neuroimaging lack of imperial evidence - detract from studies value (Lamm et al, 2016) - explain what they are
patients experience congenital insensitivity to pain activate the aMCC when observing someone in pain, but not when they are experiencing pain themselves (Danziger et al,. 2009)
evidence that mirror neurons enable understanding
numerous neuroimaging studies evidence activation during action observation and action execution in brain regions consistent with the proposal of a human mirror neuron network (Caspers et al., 2010)
these areas are also have anatmoical pathways which convey visual infrormation about others actions
criticised by - argued mirror neurons not primarily responsible for enabling understand of others actions/ intentions / emotions
neuroscience has identified two fundamental components : self other distinction and shared emotions representations between the self and other
empathy
our capacity to understand and respond to the unique affective experiences of another person (decety, Jackson, 2004)
function -
optimises our relation between self perception and the perception of others
understanding others perspectives
evidence that mirror neurones effect empathy
mirror neurons means by which wee recognise other people experience emotions (Bastiannsen et al,. 2009)
R - proposed that MNs enables a critical physiological mechanism called embodied stimulation to occur - that enables us to represent other internal state within our own bodies
R - evidence - its connected to structures linked to emotional processing : studies found that mirror neuron network and limbic system - (region responsible for generating and processing emotions) is anatomically connected by the insula (function - mainly governs perception, awareness and emotion)
furthermoer
L- Philleps et al, 1997 experiemnts found that:
the experience of disgust and perceptions of facial expressions of disgust activate similar areas in the (anterior - close to thew forehead) insula
evidence -
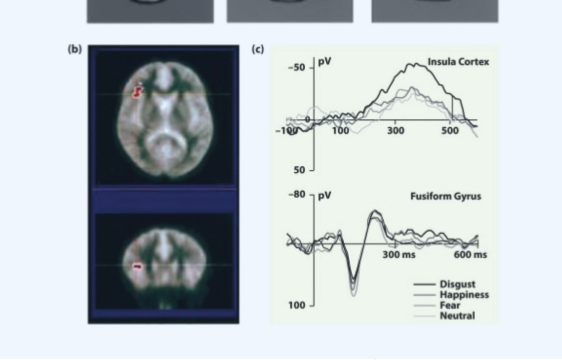
1 - Wicker et al 2003
fMRI study found that when participants inhale oders which induce feelings of disgust - the anterior insula become activated
the same areas become activated when observing expressions of perceived disgust -
Computer morphing methods were used to generate a range of disgusted faces.- found that As the expressions of disgust became more intense, the BOLD response/ activation in the anterior insula increased. - evidencing insula activation increases when observing another persons expression of disgust increase
the same areas of the anterior insula were activated both when idnviidiuals experienced disgust and observed individuals express disgust - Wicker et al 2003
why disgust? - because it can be aroused experimentally
case study conducted on a patient with anterior insula damage who lost his ability to recognise disgust from facial expressions experienced. found that when presented with disgust inducing smell he felt less disgust than control participants (Calder et al,.2000)
^ evidence that regions in brain such as insula are integral in both individuals experiencing emotions but also enable yes to recognise emotional states epxeprieonced by others- micro neurone connects both regions together suggests it plays an integral role
the perception action model of empathy - assumes when perceiving another personal emotional state there same affective (mood) state is activated in the observe, trigger somatic and autonomic responses, enabling the observer to understand the other persons emotions by experiencing it
study on empathy pain
why? can be reliably activated
singer et al,.2004 (replicated and reviewed by others)
subjected participants to mild electric shocks via electrodes
there observed a loved one be subjected to the same chocks on their hand
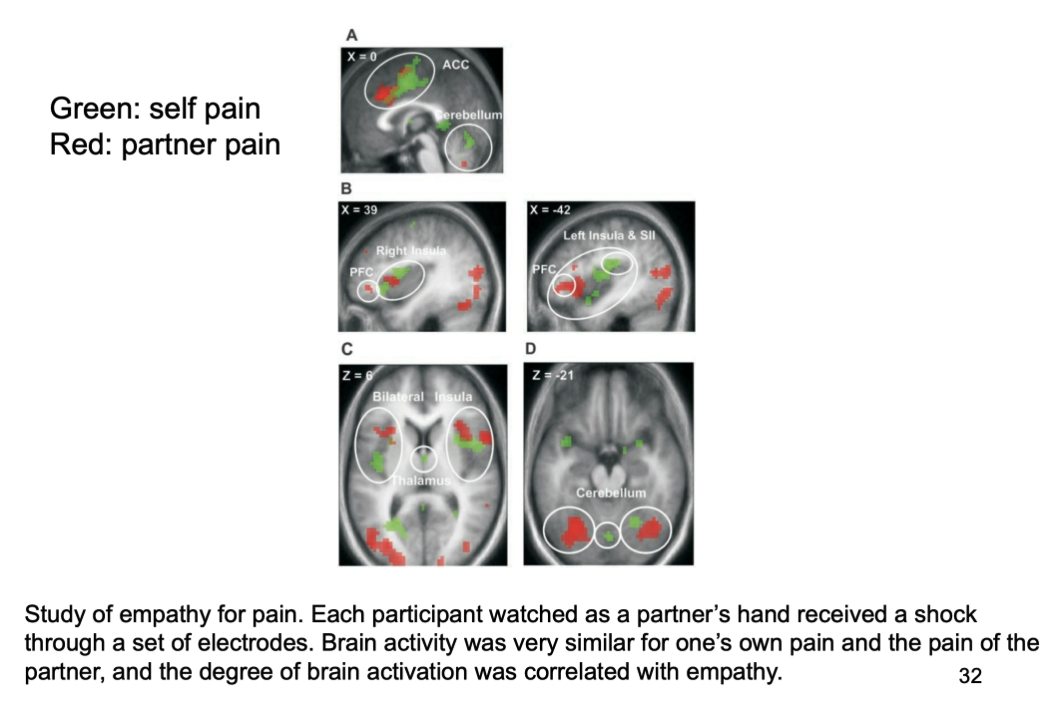
fMRI study found that insula and anterior cingulate where both activated when one is experience pain and when perceiving loved ones experience pain - brain activity similar
the degree of brain activation correlated with the participants empathy/ ability to empathise - as participants which had high empathy scores in queestionnaires showed greatest afctivation in these areas when perceiving others epxperience pain
how do they calculate empathy scores- via questtionaires such as
empathetic concern scale (EC . Davis)
balanced emotional empathy scale (BEES, mehrabian)
reading - explain the perception action model of empathy
where Is the insula located?
which areas f the brain were activated when experiencing pain and watching a loved one/ partner experience pain
Empathy MCQ
a) Relies on an abstract evaluation of events
happening to other creatures.
b) Is encoded in the orbitofrontal cortex
c) Is encoded by memory systems of the medial
temporal lobe.
d) Is aided by different types of mirror neurons that
help to emulate what others perceive.
e) Is restricted to psychopaths.
34
Answer - D
is empathy modulated by the perceived fairness of others?
singer / Raymond et al, 2006
subjects played a game with a “stranger”
exchange money with osmoen you either know or dont know
the game: variation of the Prisoner’s dilemma. First player can trust a second player by sending his/her 10 starting points (transferred to money at the end of the game) to the other player
knowing that each point sent will be tripled. The second player (confederate) then reciprocates
by sending an amount between 0 and 10 points back, which is also tripled.
Fair players reciprocate large amounts, unfair players reciprocate small amounts.
The first mover initially played with fair and unfair players outside the scanner and thus knew who was fair and who was unfair.
The first mover was then placed inside a scanner, and scanned when his own hands were painfully stimulated or when the hands of a fair player or of an unfair player were painfully stimulated.
findings
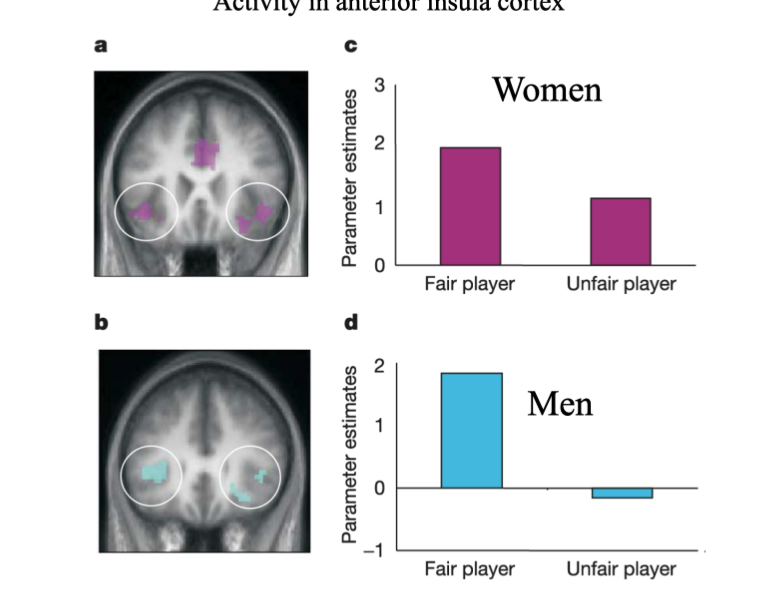
The activity in the anterior insula reflected the own person’s pain and differentially activated based on the ‘empathy’ they had with fair and unfair players.
men had more apathy for unfair player than women
lust for revenge was als measured
ask the person in scanner asked - would you like player (fair or unfair) to get punished? how much revenge do you want?
results - the nucleus accumbens increased in activation in men [who have more of a drive for revenge in the sample]) if player was punished
nucleus accumbens - a reward centre - (processes rewards and pleasurable stimuli and releases dopamine which makes us feel good - sent need to know bracket bit)
infer that we get pleasure/ joy from watching unfair player get punished - this effect and desire for revenge was stronger in men than in women
where is nucleus accumbens (n.acc) located in the brain?
(basal forebrain) - dont need to know
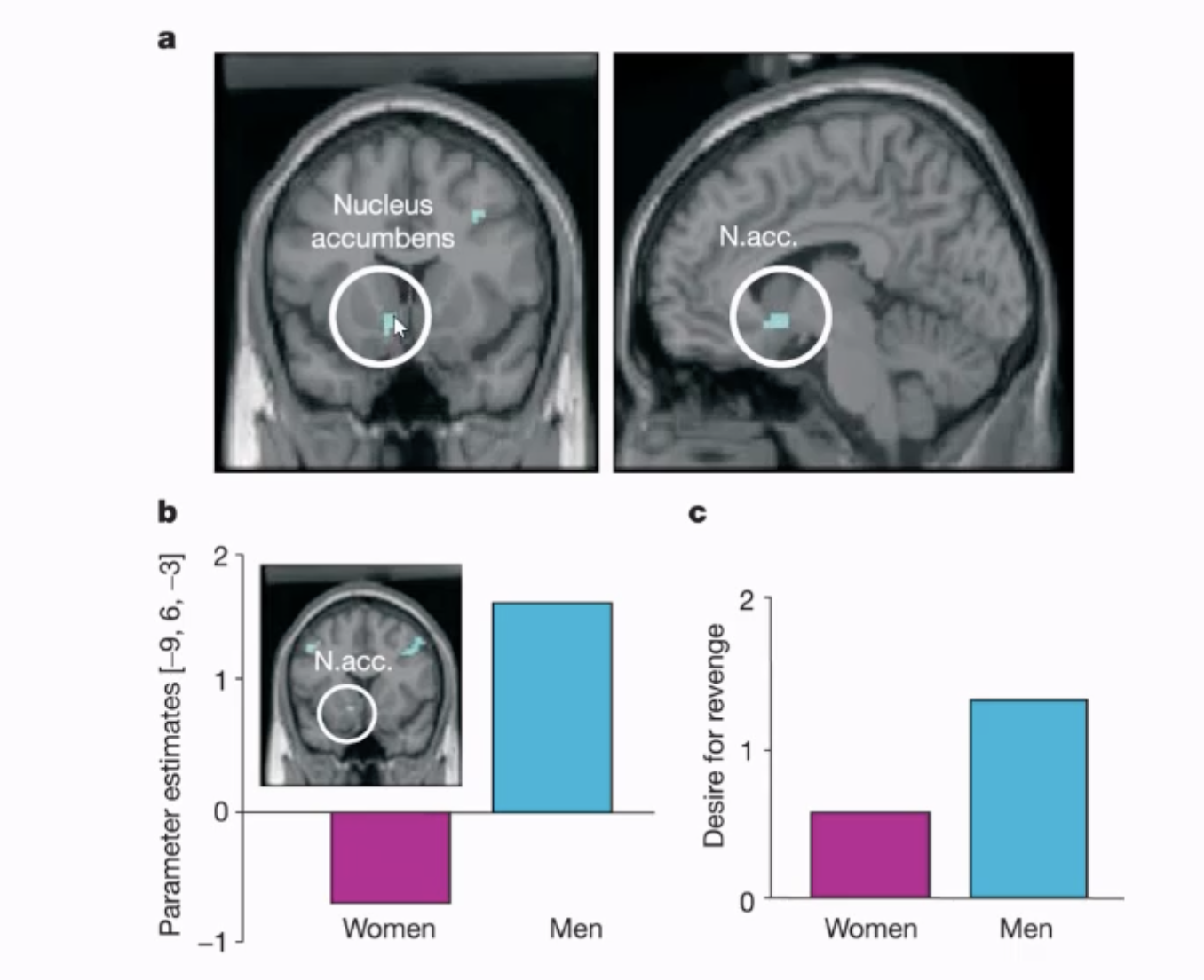
brain activation of n.acc correlates positivey with desire for revenge according to questionnaire
![<p>singer / Raymond et al, 2006 </p><p>subjects played a game with a “stranger”</p><p>exchange money with osmoen you either know or dont know </p><p></p><p><span>the game: variation of the Prisoner’s dilemma. First player can trust a second player by sending his/her 10 starting points (transferred to money at the end of the game) to the other player</span><br><span>knowing that each point sent will be tripled. The second player (confederate) then reciprocates</span><br><span>by sending an amount between 0 and 10 points back, which is also tripled. </span></p><p><span>Fair players reciprocate large amounts, unfair players reciprocate small amounts. </span></p><p><span>The first mover initially played with fair and unfair players outside the scanner and thus knew who was fair and who was unfair.</span><br><span>The first mover was then placed inside a scanner, and scanned when his own hands were painfully stimulated or when the hands of a fair player or of an unfair player were painfully stimulated. </span></p><p><span>findings</span></p><p><span>The activity in the anterior insula reflected the own person’s pain and differentially activated based on the ‘empathy’ they had with fair and unfair players. </span></p><p><span>men had more apathy for unfair player than women</span></p><p><br></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f170a5ba-a358-4629-98ea-342fe24ede01.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>lust for revenge was als measured</p><p>ask the person in scanner asked - would you like player (fair or unfair) to get punished? how much revenge do you want?</p><p></p><p>results - the <span>nucleus accumbens increased in activation in men [who have more of a drive for revenge in the sample]) </span>if player was punished</p><p></p><p><span>nucleus accumbens - a reward centre - (processes rewards and pleasurable stimuli and releases dopamine which makes us feel good - sent need to know bracket bit)</span></p><p></p><p><span>infer that we get pleasure/ joy from watching unfair player get punished - this effect and desire for revenge was stronger in men than in women </span></p><p></p><p><span>where is</span> nucleus accumbens (n.acc) located in the brain?</p><p>(basal forebrain) - dont need to know</p><p></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8afa80a0-0106-4aaf-b877-c2e785747810.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>brain activation of n.acc correlates positivey with desire for revenge according to questionnaire<br></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/28d7a4d3-73d8-4027-a199-896c0b17696b.png)
summary
1) Empathy activates brain networks that are
normally active when we (ourselves) perceive
pain, pleasure, fun, agony,.... .
2) The strength of empathy feelings is related to the
strength of ‘liking’ and that in turn differentially
activates empathy brain centers when feeling for
others.
3) Revenge (when obtained and desired) activates
centers in the brain that normally process
rewards.
key points - from both parts
1. The ‘self’ is likely processed by the ‘default mode
network’.
2. Orbitofrontal cortex is vital to monitor behaviour
according to social norms and to support decision
making.
3. Theory of mind tests activate the rTPJ, and other
structure involved in default mode processing.
4. Is empathy a reflection of mirror neuron activity?
41
incorporate these into final notes - also do extra reading