GENSCI FINAL 2ND QUARTER
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Chemistry
study of matter, its properties, composition, and the change it undergoes
Biochemistry
biological processes
Physical Chemistry
principles and measurements
Inorganic Chemistry
minerals, metals, non-living matter
Organic Chemistry
carbon compounds
Analytical Chemistry
composition and structure of substances
Microbiology
study of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa
Aerobic
requires oxygen
Anaerobic
does not require oxygen
Catabolic Metabolism
breakdown of complex substances into simpler ones
Anabolic Metabolism
building up of complex substances from simpler ones
Louis Pasteur
Father of Microbiology
1822-1895
“Benefactor of Humanity”
his discoveries form the foundation of microbiology and modern medicine
Professor Balard in 1846
Louis Pasteur became his laboratory assistant
Crystallography 1847
study of molecular structure of crystals
Molecular Asymmetry
discovered some compounds (like tartrate) exist in mirror-image crystal forms
recognize chirality and 3d molecular structure
Monsieur Bigo
was an industrialist who owned a distillery in 1856, producing alcohol from sugar beet, which became famous because he hired Louis Pasteur to solve fermentation issues when his sugar beet vats acidified instead of producing alcohol.
Fermentation
results from microorganisms metabolism
alcohol is the waste product of this
Rebuttal of Spontaneous Generation 1859
swan neck flask by Antoine Ballard
Louis Pasteur called this “chimera” or illusion
Germ Theory 1861
microorganisms are everywhere
Robert Koch
discovered what causes anthrax
Louis Pasteur
discovered the vaccine for anthrax
Bacillus anthracis
bacteria that causes anthrax
Pasteurization
heating of food for several minutes between 55-60C to kill harmful microorganisms
Jean-Baptiste Dumian
he called Louis Pasteur because the silk industry in deteriorating
Silk nosema disease and flacherie
illness that Louis Pasteur discovered from the silkworms
Hygiene and aseptic techniques
vital for preventing infections
Vaccine
help the body develop immunity to a specific disease
Fowl cholera
first experimental vaccine
small exposure had worked as a vaccine against the actual sickness
Anthrax
Louis Pasteur use a weakened virus and vaccinated 25 sheeps
vaccinated = alive
not vaccinated = dead
Rabies
disease following a bite by a rabid animal
uses rabbits spinal cord
Joseph Meister
first vaccinated for rabies on March 1, 1886
Joseph Lister
study of antisepsis
Antisepsis
method of using chemical to destroy germs that cause infections
Alexander Fleming
discovered Penicillin
mould juice = penicillin
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain
they won the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine with Alexander Fleming
physical change
change in shape, size, or physical state of matter but not its composition
chemical change
change in the composition of matter as a result due to chemical reaction
physical change
change of phases or states
dissolution process
change in physical properties
chemical change
formation of new substances
evolution of gas (formation of bubbles)
change in temperature
evolution of energy
chemical reaction
a process where reactants are transformed into other substances called products
indication of chemical reaction
change in color
change in temperature
formation of an odor
formation of a gas
formation of a solid/precipitate
chemical equation
is a written representation of a chemical reaction
chemical reactions are represented by this
left = reactants
right = products
separates reactants or products

separates reactants from products; produces, forms, yields

reversible reactions

substance is in solid state

substance is in liquid state
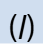
substance is in gaseous state
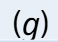
substance is in aqueous state
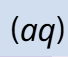
evolution of gas instead of (g)

formation of precipitate instead of (s)

application of heat

catalyst used in the reaction

combination reaction
synthesis reaction
involves 2 or more reactants forming a single product
A + B > AB
A + B > AB
combination reaction
decomposition reaction
reverse of combination reaction
compound is broken down into two smaller substances
may be initiated by heat, light, electricity of catalysts
AB > A + B
AB > A + B
decomposition reaction
monoatomi
carbonates
are decomposed to carbon dioxide (CO2) and metal oxide
chlorates
are decomposed to oxygen gas (O2) and metal chloride
single replacement reaction
an element replaces another element in a compound
the reaction yields a compound and a replaced element
A + BC > AC + B
single replacement reaction
double replacement reaction
occurs when two compounds react to from two new compounds
the reactants are ionic compounds that simply exchange ion partners
AB + CD > AD + CB
AB + CD > AD + CB
double replacement reaction
AC are positive ions, BD are negative ions
combustion reaction
when fuels (hydrocarbon) reacts in the presence of oxygen gas (O2) producing an immense amount of energy causing its products, carbon dioxide and water, coexist in steam from creating smoke
CH + O2 > CO2 + H2O
combustion reaction
solution
homogenous mixture of two or more substances
composed of solute and solvent
solute
minor component
solvent
major component
solid solutions
solvent is in solid state
mostly found in alloys
liquid solutions
solvent is in liquid state
gaseous solutions
solvent is in gas state
globally harmonized system of classification and labelling of chemicals ghs
classifies chemicals based on the type of hazard they pose with the use of universally recognized symbols
oxidizers

flammable

explosives

acutely toxic (severe)

burns skin

gases under pressure

carcinogen

toxic to aquatic environment

acutely toxic (harmful)

Sodium hypochlorite
NaClO
acts as a disinfectant, bleaching agent, and oxidizer
kills bacteria, viruses, and fungi
releases toxic chlorine gas when mixed with acids or ammonia
Sodium hydroxide
NaOH
stabilizer that maintains high pH to keep sodium hypochlorite stable and effective
corrosive
harmful if inhaled or ingested
Water
H2O
solvent
dilutes the bleach to a safe and usable concentration
generally safe
no harmful effects unless contaminated
Sodium bicarbonate
NaHCO₃
baking soda
acts as a leavening agent that releases carbon dioxide when heated or mixed with acid
Sodium hydroxide
NaOH
reacts with fats or oils during saponification to produce soap and glycerol
Fatty acids or oils
react with sodium hydroxide to form soap molecules (cleansing agents)
natural and biodegradeable
moisturize the skin
Glycerol
By-product of saponification
Acts as a humectant that retains skin moisture
Sodium chloride
NaCl
Fragrance compounds
Water
H2O
Acts as a solvent in soap-making
Preservatives
Prevent microbial growth and extend shelf life
Surfactants
Enhance foaming and cleaning power by reducing surface tension
Sulfate
Create lather
Reduce surface tension of water
Lift away dirt, oil, and product buildup from the hair and scalp
Cocamidopropyl betaine
Milder cleansing
Stabilizes foam
Reduces irritation from stronger surfactants
used to make products “tear free” and gentler on the scalp
Department of Trade and Industry
through Consumer Protection and Advocacy Bureau (CPAB)
Promotes fair trade practices
Ensures product safety
Empowers Filipino consumers to make informed choices
Republic act no. 7394
Consumer Act of the Philippines
Protect consumers from health and safety hazards
Protect consumers from deceptive and unfair business practices
Provide information and education
Provide adequate rights and means of redress
Include consumer representatives in policy-making
Food and drug administration
To ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of health products
Republic act no. 9711
Food and Drug Administration Act of 2009
Renamed the Bureau of Food and Drugs (BFAD)
Strengthened and enhanced the regulatory capacity of FDA