Tipping points - Lecture 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a tipping point?
Characterized by a relatively small input or change that results in a disproportionately large outcome.
When was the idea first populised
Malcolm Gladwell. Book talks about tipping points in social systems.
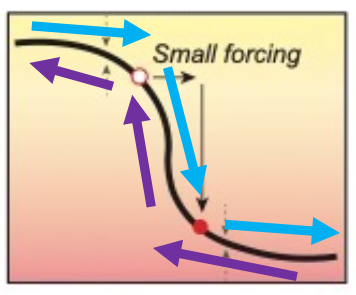
what is a no threshold change tipping point?
referes to where a system can swing back and forth
what is a step change tipping point?
a small force which causes a large change e.g. pushing a ball of a cliff - can be reversable.
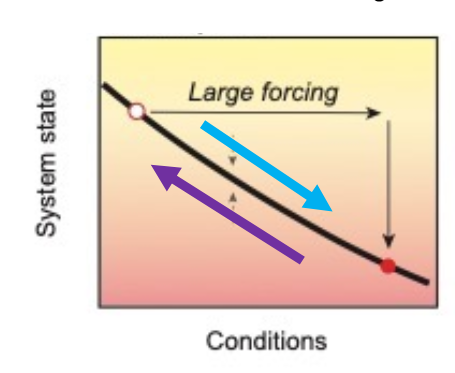
what is catastrophic bifurcation tipping point?
there is a threshold that is not reversible.
what is the theory of alternative stable states
you can have a system which has two different states. One extreme or the other. You dont get half and half. e.g. eutrophic lakes - you only get green or not, on or off.
what is hystresis
the dependence of the state of a system on its history. If you are in a state you cannot go back to the original state without going past the point that it originally was. e.g. ice sheets melt more quickly than they can build up.
what is the definition of a positive feedback mechanism
a process which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. The effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation.
what is a regime shift
a substantial reorganization of a complex system with prolonged consequences, as the system moves from one functioning state to another across poorly understood thresholds (high to low resilience)
what is critical transition
a catastrophic fold bifurcations
how are tipping points and resiliance intertwined
the resilience of a system refers to its tendency to avoid such tipping points and maintains stability. A tipping point is the minimum amount of change within a system that will destabilise it, causing it to reach a new equilibrium or stable state.
why is understanding system resilience
for predicting and potentially mitigating tipping points
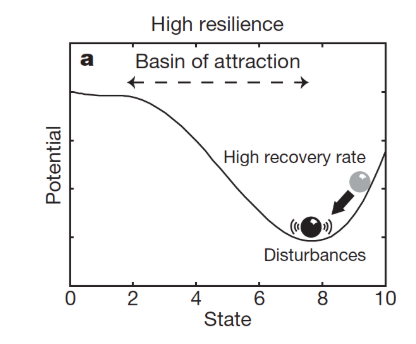
high resilient systems have:
high recovery rate, low autocorrelation, low variance, - slow
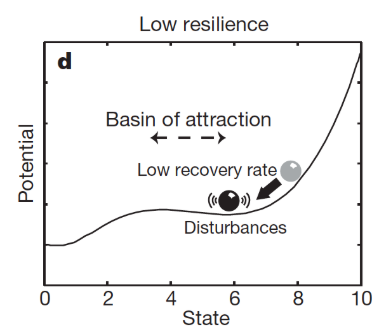
low resilient systems have:
low recovery rate, high autocorrolation, high variance - fast
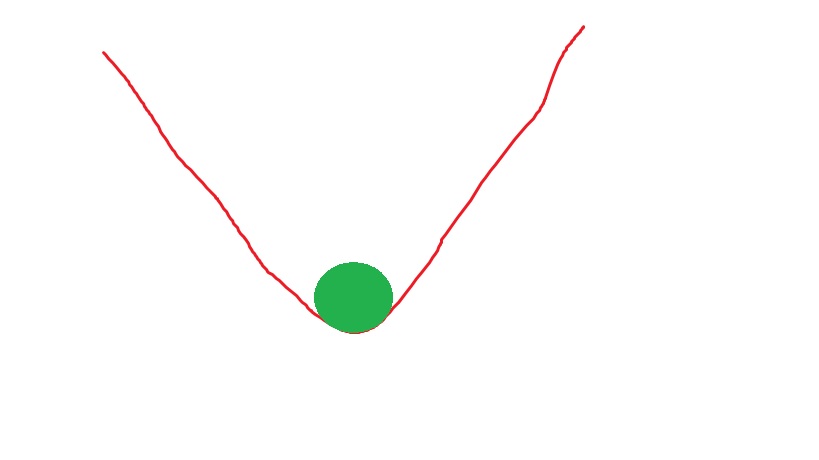
what does this image show?
high resilient - cant move!
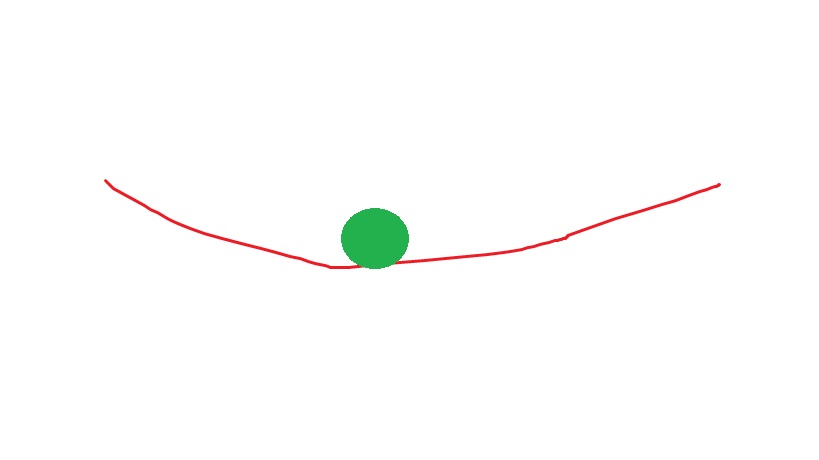
what does this image show?
low resilient - as can rock!
what is critical slowing down
slower recovery rate as tipping point approaches. The system takes longer to recover from small perturbations
what happens to resilience when critical slowing down decreases
it decreases.
what are early warning systems?
autocorrelation, variance, skewness
how can early warning systems be predicted
mathematically detected by looking at the patterns of fluxtuations in the short term trends of the data before the transition takes place
what is autocorrelation
the system becomes more and more like its past state
what is variance
the system becomes increasingly more variant, goes further and further from its point of equilibrium
what is skewness
the basin of attraction becomes deformed ad the system preferentially goes to one side of the basin rather than the other
what is flickering
referes to flickering to an alternative state as a warning signal in highly stochastic systems. In such situations, the frequency distribution of the states can be used to approx the shape of the basins of attraction of the alternative states
what level of variance does flickering have
high variance and aka less resiliance
what is an example for observing early warning signs
lake yukon. had a low eutrophic state, clear water however after 2002 hyperutrophic state - algal blooms and emergent macrophytes only. the time series show evidence of flickering prior to critical transition. rising variance was also observed. It was able to be predicted 20 years before regime shift
what are the problems with tipping point analysis
conjunction fallacy - alternate steady state shifts are assumed (it is not rigorously tested enough)
how can critical slowing down be used elsewhere
ecology
medical
engineering
geohazards
economic crashes