Basic Learning Processes Final Exam
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
negative reinforcement
response leads to the absence of aversive stimulation
avoidance learning
another word for negative reinforcement
negative reinforcement
results in an increase in responding
negative reinforcement
negative contingency
positive punishment
response leads to aversive stimulation
positive punishment
positive contingency
positive punishment
results in a decrease in responding
similarity between NR and PP
subjects are changing how they respond to minimize exposure to the aversive stimulus
Hull, Thorndike, Skinner
behaviorists
two-factor theory
theory stating there are two processes that underlie avoidance learning
classical and operant conditioning
the two processes underlying avoidance learning according to the two factor theory
two-factor theory
theory states subjects don’t make the response to avoid shock, they do it to escape the stimulus that has become associated with the shock
miller and kamin
two people who tested two-factor theory (came up with evidence for and evidence against)
group 1 and 2
Which group groups should have learned to press the lever according to the two-factor theory?
group 1 consistently, groups 2 and 3 sometimes
Which groups actually learned to press the lever?
Kamin
Who’s experiment?
Miller
whose experiment tested if there are two factors, then we should be able to manipulate them independently (two-factor theory)
Miller’s experiment
training: Grp 1: White box = shock; Grp 2: no training
testing: Place each subject in white box (they can turn wheel to escape)
Results: Only Grp 1 learns to turn wheel to escape (only group motivated to escape)
learned helplessness
deleterious consequences of long-term, uncontrollable, aversive events
prior exposure to inescapable aversive events prevents learning about escape when escape is now possible
avoidance
problem with two-factor theory- predicts that fear to the signal would eventually extinguish, but ___ response never extinguishes
conditioned inhibition
new theory to replace two-factor theory
avoidance learning
learned helplessness is a form of what kind of learning
Seligman, Maier, Overmeyer
their experiments tested learned helplessness with a Yoked-Control Paradigm
learned helplessness experiment
Training: escapable shock vs. inescapable shock
Testing: subjects placed in shuttle-box and given access to escape
results: only the escape shock group could escape in the test
inescapable shock
in a yoked-control paradigm for learned helplessness, which group was the yoked group
how to escape
LH subjects can eventually learn to escape shock if they are shown…
associative and motivational
LH results in these deficits
associate deficit
subjects learn behavior and reinforcement are unrelated in one context so they have trouble learning they are related in another context
motivational deficit
subjects have no control over events, so they have little motivation to respond to stimuli
depression, anxiety, illness
LH subjects have higher levels of…
species specific defensive response
SSDR
species-specific defensive reaction theory
Premise x: Aversive stimuli elicit innate, species-specific defensive responses (SSDRs)
Premise y: Which SSDR is elicited depends on the situation and configuration of the environment.
Predatory Imminence Continuum Theory
Premise x: Which SSDR is elicited depends on the level of danger faced by the animal.
Premise y: A signal (CS) associated with an aversive event (US) will elicit an SSDR
closer
according to predatory imminence continuum theory, when the CS and US are presented ___ during training, the SSDR will be more like if there is imminent danger
amygdala
more danger perceived = more activation of this area of the brain
PTSD
parts of the brain that are activated during perceived danger moments are activated when there is no imminent threat in people with this disorder
likelihood of initial behavior, initial severity of punishment, contingency, time between R and P, schedule, reinforcement
factors that affect effectiveness of punishment
likely
punishment works if the behavior is initially ___ to occur
strong
punishment works if the initial punishment is ___
contingent
punishment works if the punishment is ___ on the target response
can only receive aversive stimulus when making the response
short
punishment works if the time between target response and punishment is ___
schedule
punishment works if the timing and frequency of the punishment, or the ___ is correct
reinforced
punishment works if the target behavior is not ___ in other situations
comparative cognition
the study of animal behavior that focuses on the mechanisms by which animals acquire, process, store, and act on information from the environment
general process approach
study learning in animals because of what it tells us about learning in general
comparative cognition
focus on the differences in cognitive mechanisms between humans and animals
differences vs. similarities
comp cognition vs. gen process approach
cognitive ethology
presumption that animals are capable of conscious thought and intentionality
argument from design and not all behavior is intentional
problems with cognitive ethology
anthropomorphism
problem with cognitive ethology which biases research, hampers knowledge, and overemphasizes the human experience
memory
the retention of information or experiences over time
acquisition, retention, retrieval
stages of memory
learning study
type of study that manipulates and then tests the same acquisition conditions
memory study
type of study that does not manipulate the acquisition condition, but manipulates the testing conditions
procedural memory
memory for how to do something
perceptual memory
memory for how things look
episodic memory
form of reference memory, recall episodes and experiences form the past
semantic memory
form of reference memory, recall facts and meanings of words
working memory
short-term memory
working memory
the retention of info just long enough to complete a task
reference memory
stored memory info that can be recalled to help use new info
type of stimulus, duration of exposure, and time between
factors that affect memory in delay-matching-to-sample
better
delayed-matching-to-sample: longer exposure = ___ recall
poorer
delayed-matching-to-sample: longer interval = ___ recall
delayed-matching-to-sample
a memory task in which the animal is first shown a sample stimulus and then, following some delay, is required to select that stimulus out of a group of alternative stimuli
choose same as sample
what is learned in DMTS if there is one rule
if x, choose x, etc.
what is learned in DMTS if there are multiple rules
Premack
used baby chimps to test memory
Premack experiment
Training: delayed-matching-to-sample with set stimuli
Testing: Used new stimuli (chimp had not seen these presented before)
Results: Answered correctly to new stimuli
correctly, incorrectly
Premack’s experiment using baby chimps predicted if they were using “same as rule,” the chimps would answer ___ during testing, but if they were using a specific rule, they would answer ___ during testing
“same as”
Premack’s experiment using baby chimps found the chimps were using this rule
Morris water maze and Radial arm maze
procedures for testing spatial location memory
experiment testing memory for places
training: allow rats to only search 4 arms of 8-arm radial maze
testing: Four-hour delay (rotate maze 90 degrees) – changes spatial location of arms
- allow rat access to all arms
Results: Rats go to the spatial location that they had not yet visited
scent, spatial location cues
predictions for the radial arm maze test- if rat is using ___cues, it will visit arms it actually has not visited; if rat is using ___ cues, it will visit the arms it thinks it has not visited based on cues in the room
spatial location
results from the radial arm experiment show that rats use these kinds of cues to solve the maze
encoding information
the process of taking info in through your senses and translating it into a form that your brain can write down and store for later use
selective attention, levels of processing, elaboration, and mental imagery
factors that influence encoding
selective attention
focusing on a specific aspect of experience while ignoring others
cocktail party effect
phenomenon where items compete for our attention
levels of processing
a continuum of memory processing ranging from shallow to deep, with the deeper processing leading to better memory
shallow
level of processing- physical feature are analyzed
intermediate
level of processing- recognition and labeling
deep
level of processing- meaningful characteristics
elaboration
web of connections, associations, and relevant meanings given to a stimulus
mental imagery
creating a mental story or scene around stimuli that we would like to remember
dual-code hypothesis
theory that states memory is stored in either a verbal code or picture code, which means mental images are remembered better because they contain both picture and verbal codes
imagery in non-human animals
yuck face experiments tested this
Grill
person that tested conditioned taste aversion with rat yuck faces
P. Holland imagery experiment
training: Tone = Flavor 1
Noise = Flavor 2
Flavor 2 = illness
Test: Reaction to Tone? Reaction to Noise?
results: noise = yuck face
tone = no yuck face
P. Holland Mediated acquisition
training: Tone = Flavor 1
Noise = Flavor 2
Tone = “mental image of flavor 1” = Nothing
Noise = “mental image of flavor 2” = illness
Test: Reaction to F1? Reaction to F2?
Results: Avoid Flavor 2, even though it was never paired directly with illness.
mental time travel
ability to imagine past and future events
retrospective coding
memories for past events
prospective coding
remembering plans for future action
same brain areas
retrospective and prospective coding rely on…
retrospective, prospective
rats use ___coding, then switch to ___ coding while solving the radial arm maze
save room for dessert
what did chickadees learn to do in their mental time travel experiment?
directed forgetting
accuracy of recall can be modified by cues or instructions indicating that something should or should not be remembered
significance of directed forgetting experiment
memory is an active process that can be brought under stimulus contro
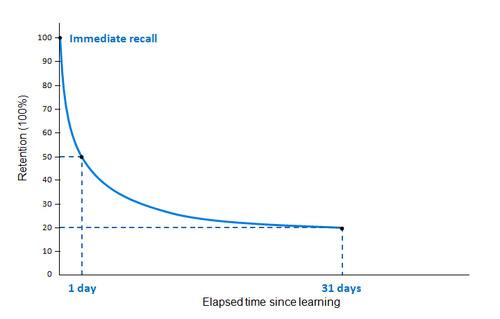
Ebbinghaus
who’s associated with the forgetting curve