AS 215L Midterm :(
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Chromatin
Threadlike granules dispersed throughout nucleus
Cytosol
Gelatinous fluid that contains organelles
Endoplasmic reticulum
Found in the cytoplasm and is a transport system within the cell - can be smooth or rough
Golgi apparatus
Processes and packages protein molecules for export
Haploid
one-half the chromosome number
Inclusions
Nonliving structures within cytoplasm
Integral proteins
Protein channels within the plasma membrane that allow certain substances to enter the cell
Lysosomes
Membranous structure in cell that contains potent digestive enzymes
Meiosis
Cellular reproductive processes that results in offspring with half as many chromosomes as the cell they originated from
Microfilaments
Contractile protein with ability to shorten; found within cytosol
Microvilli
Finger like folds in the plasma membrane that act to increase the surface area for absorption
Mitochondria
Manufactures energy for cellular use (powerhouse)
Mitosis
Cellular reproductive process that results in identical daughter cell
Nucleoli
Assembly sites for ribosomal particles - found within the nucleus
Nucleus
Control center for the cell, chromosomes are found within this structure
Organelles
Highly organized sub-cellular living system. Metabolically active structures that. have their own characteristic shape and function.
Persoxisomes
Membranous sacs found within the oxidase enzymes in cell
Phospholipids
Arranged in two layers in the plasma membrane called the fluid mosaic
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
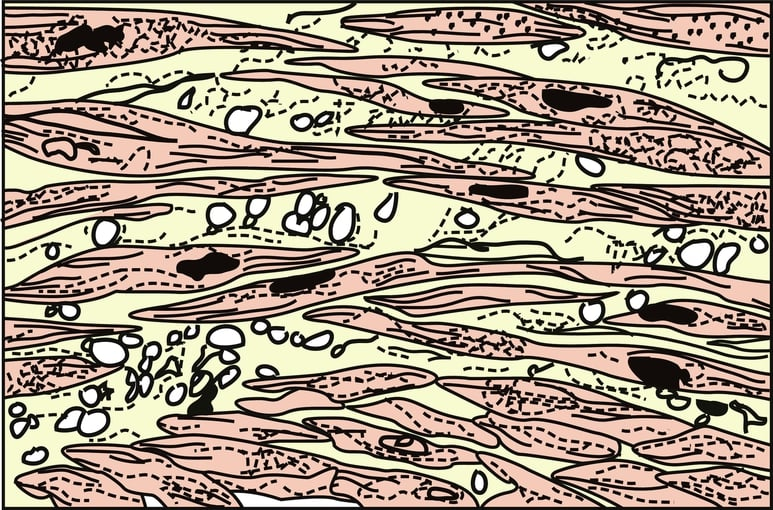
Cardiac muscle
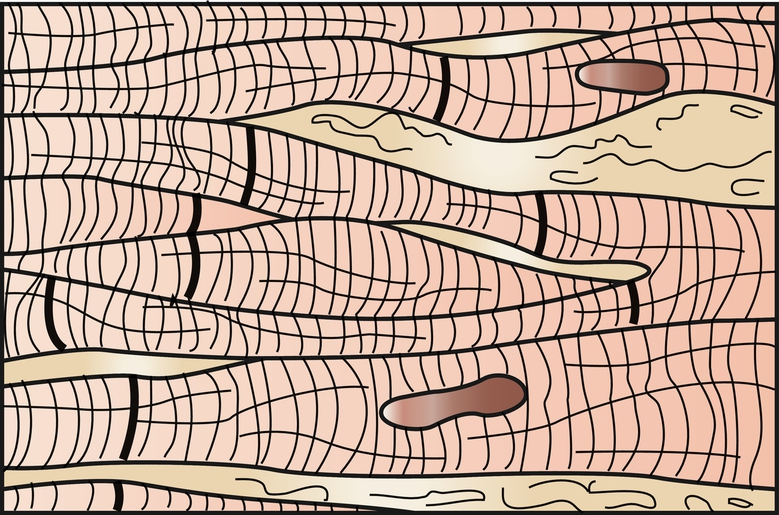
Skeletal muscle
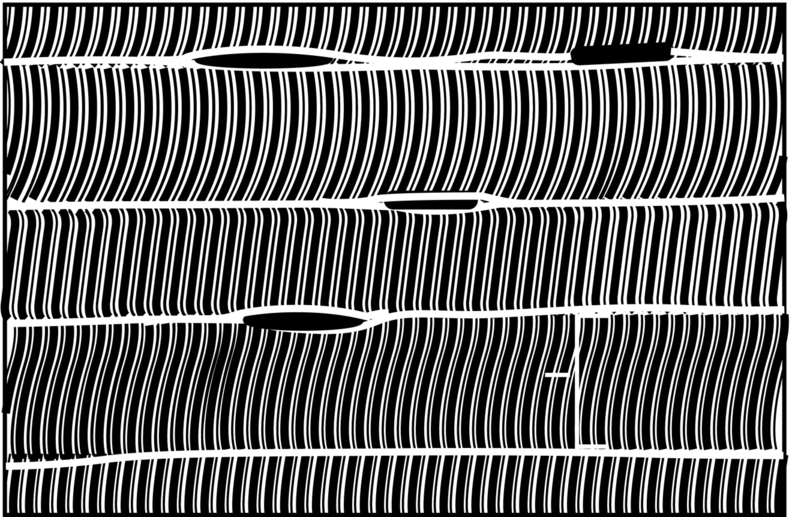
Smooth muscle
Cell body/soma
Controls metabolism of neuron
Axon
Conducts impulses away from the neuron
Dendrite
Receives impulses from other neurons
White matter
#1
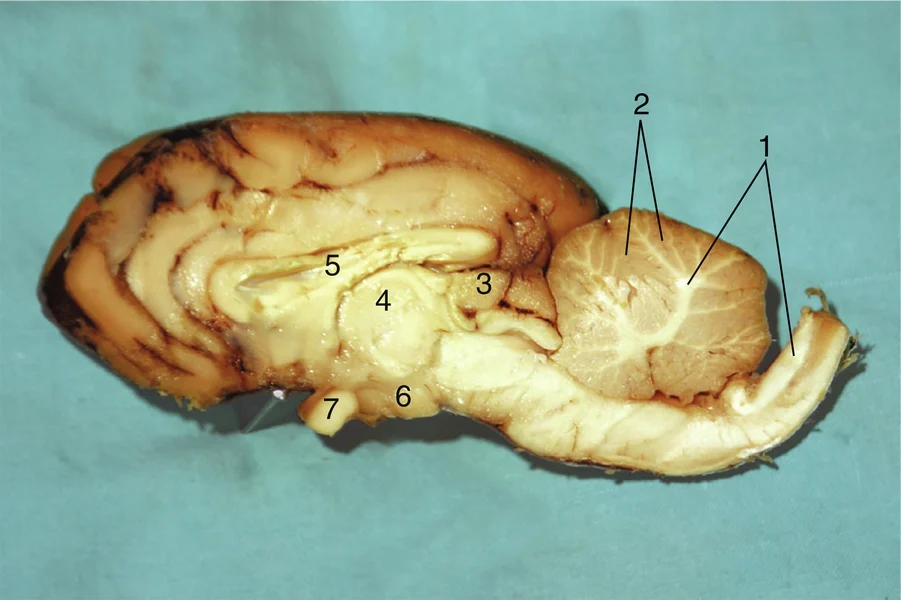
Gray matter
#2
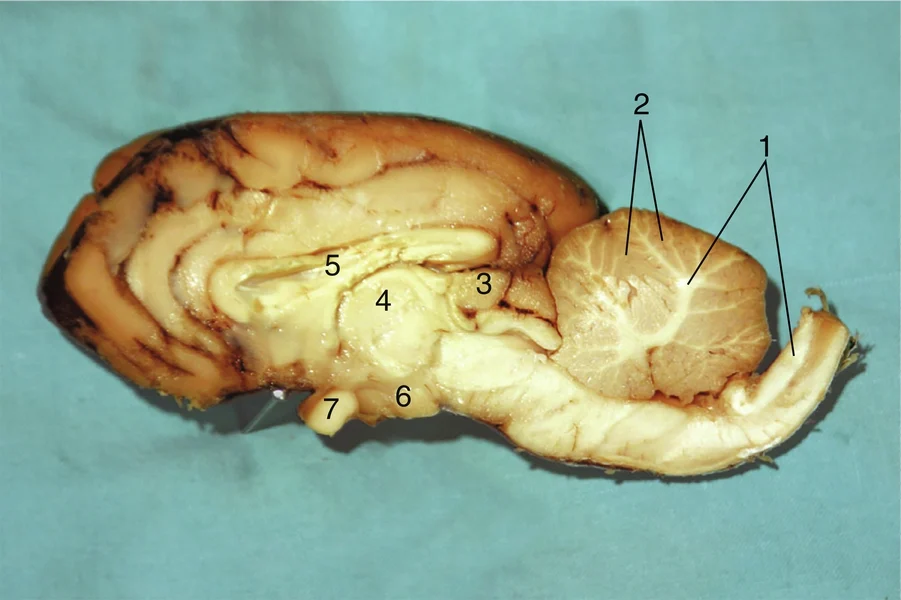
Pineal body
#3
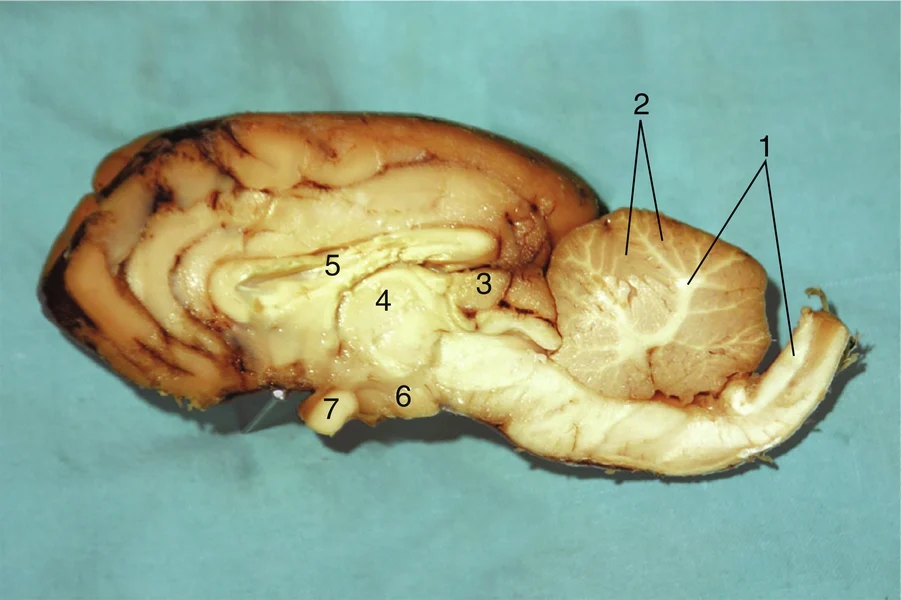
Thalamus
#4
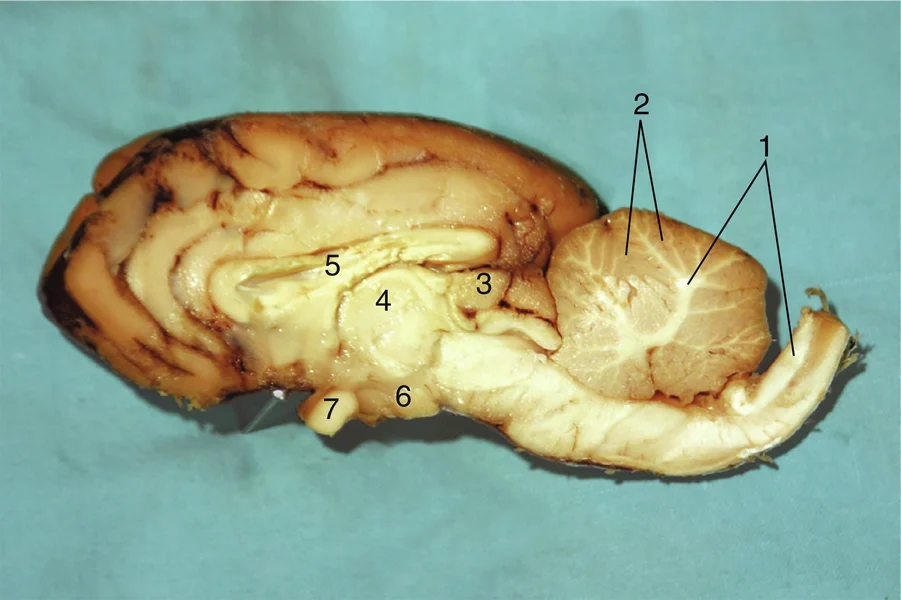
Corpus callosum
#5
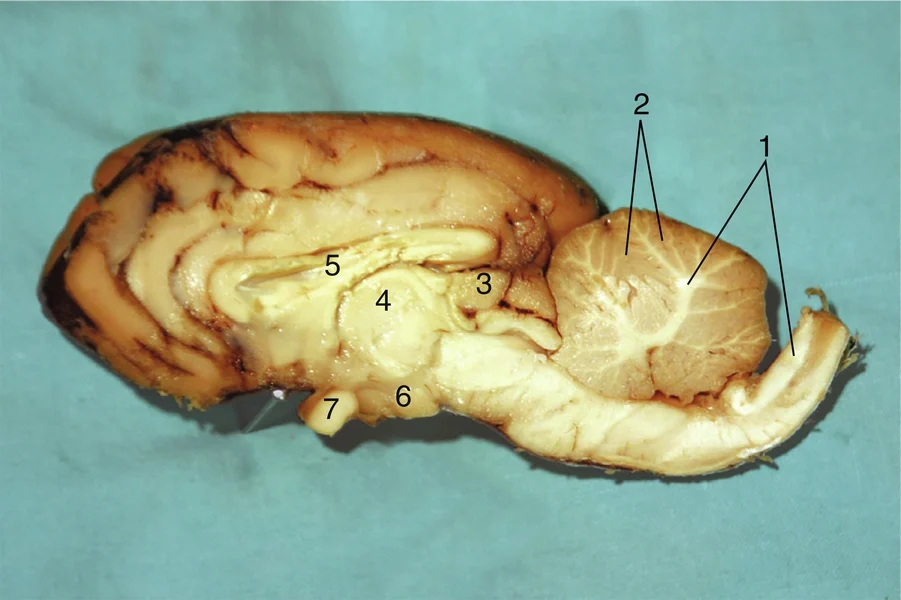
Hypothalamus
#6
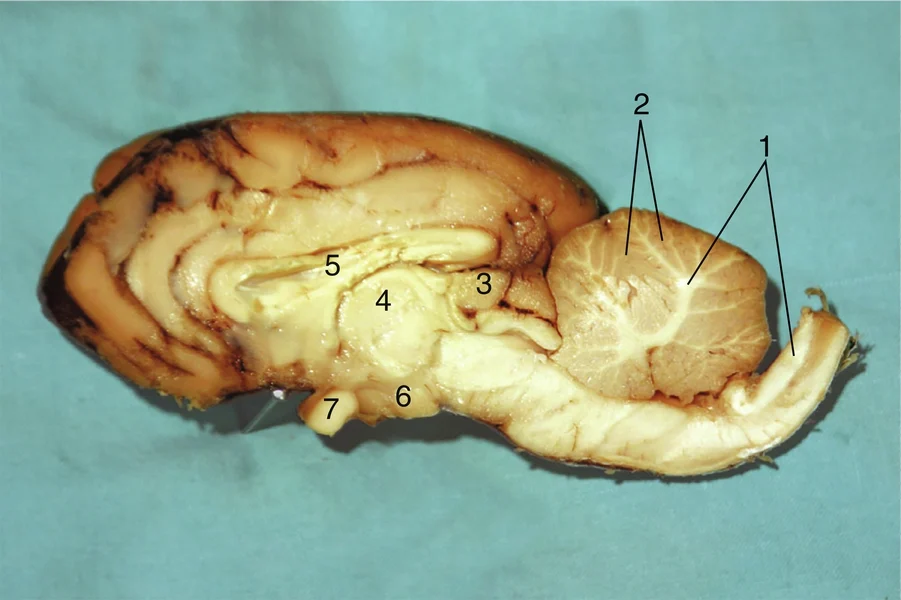
Sensory nerve fibers
Carry impulses toward the brain
Sulci
The little grooves/valleys on surface of cerebrum
Gyri
The little folds/hills on the surface of the cerebrum
Longitudinal fissure
Separates the cerebrum into right and left hemispheres
Corpus callosum
Structure made up of nerve fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres
Pia mater
The innermost layer of the meninges
Cerebrum
Part of brain associated with intelligence and learning ability
Medulla oblongata
The caudal part of the brainstem that becomes the spinal cord
Dura mater
The outermost layer of the meninges
Sciatic nerve
The nerve that lies just beneath the biceps femoris muscle
Cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, brain stem
4 divisions of brain
The brain and spinal cord
Structures make up the CNS
Thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal body
Structures of the diencephalon
Medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain
Structures of the brainstem
Cerebellum
Section of the brain that coordinates movements and helps an animal maintain balance and upright posture
The brainstem
section of the brain that controls primitive, autonomic functions
The dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
Three layers of meninges
Tapetum lucidum
Causes green reflection from the eyes of an animal in low light
Rods
Photoreceptors used for dim light vision and shapes
Iris
Part of the eye that controls how much light is let in
Limbus junction
Junction between the cornea and sclera
Optic disk
Blind spot of eye
Ciliary body
Muscular ring of tissue that surrounds lens and adjusts its shape
Lens
Helps focus clear image on retina
Cornea
Clear window that admits light into interior of eye
Retina
Inner nervous layer of the eye where photoreceptors are located
Vitreous humor
The soft, gelatinous substance that fills the vitreous compartment
Bulbar conjunctiva
The transparent membrane that lines the inner portion of the eyelid
Lateral canthus
Lateral corner of the eye where upper and lower eyelids connect
Cochlea
Cavity in the temporal bone that contains the hearing portion of the inner ear
Choroid
Portion of middle vascular layer in eye consisting of blood vessels
Cones
Photoreceptors that perceive color and detail
Tympanic membrane
What is the eardrum called
Sclera
White of the eye
Eustachian tube
Tube that connects the middle ear cavity to the throat for pressure relief
Malleus, incus, stapes
Ossicles
Compact bone
Solid bone found in shaft
Cancellous bone
Spongy bone found in ends
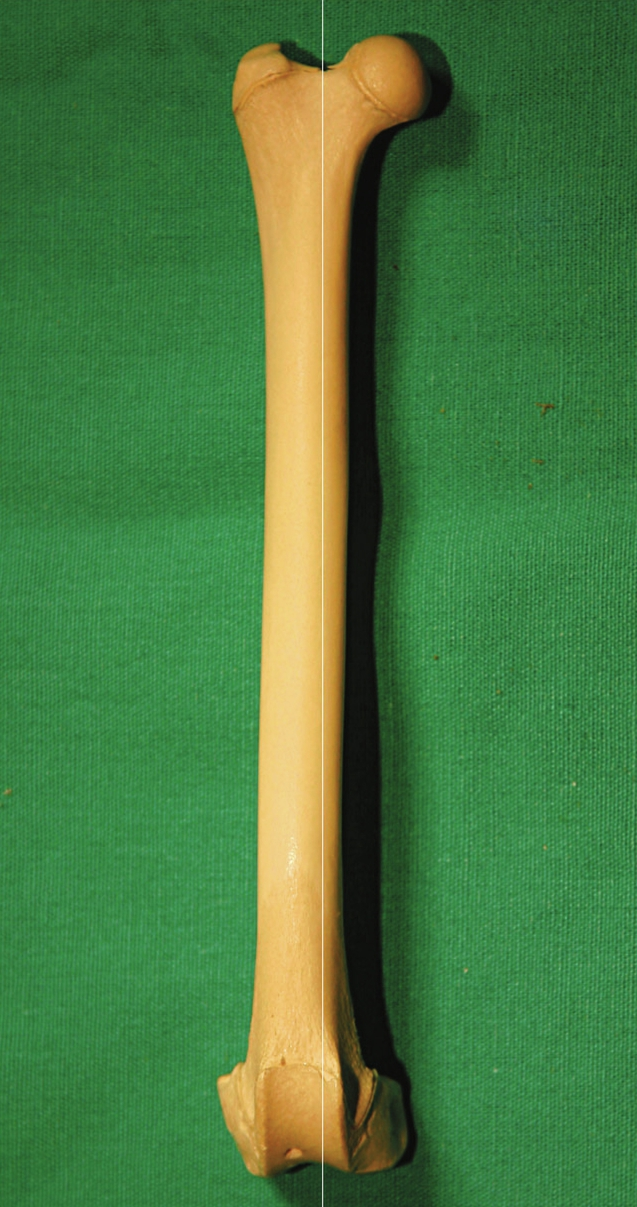
Long bone
Shape?

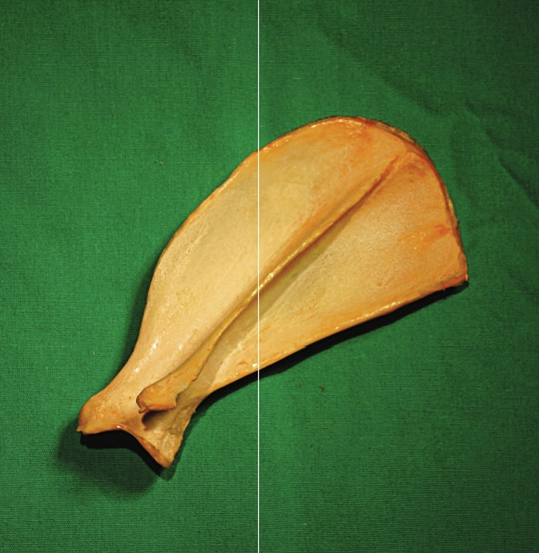
Short bone
Shape?
Flat
Shape?

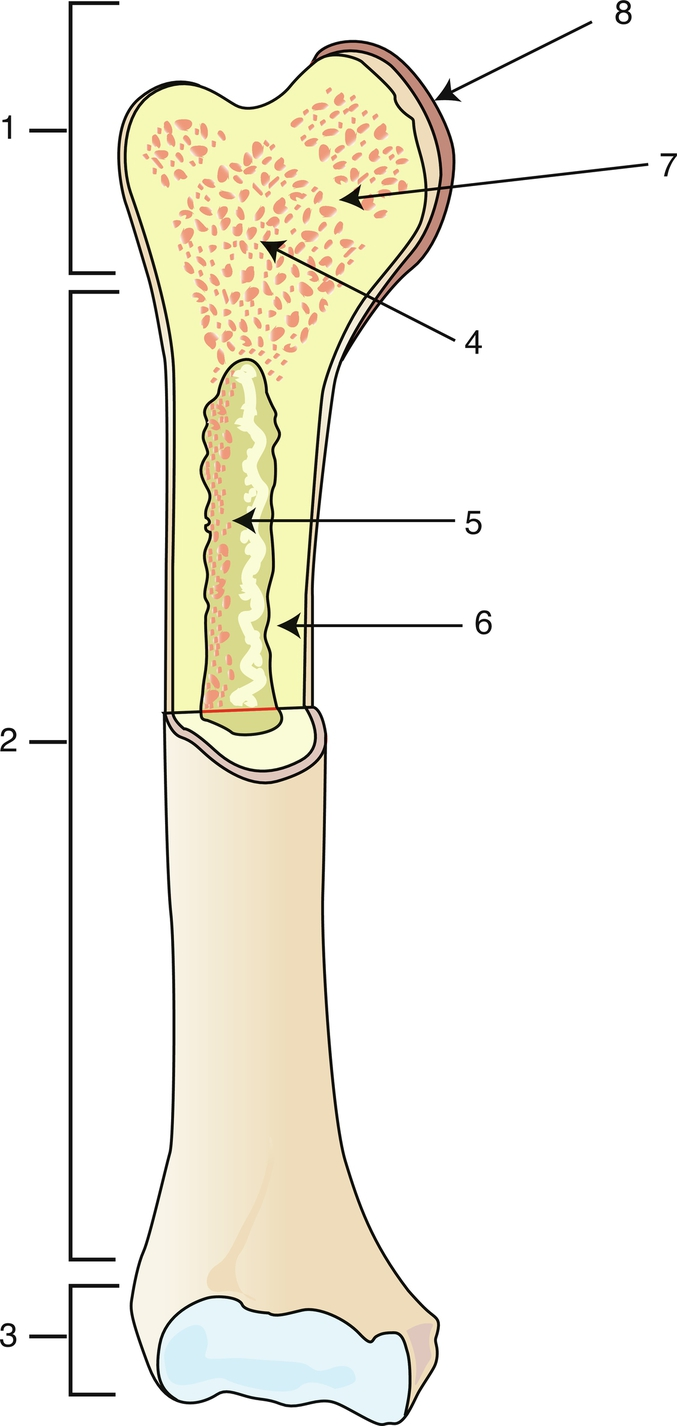
Proximal epiphysis
1
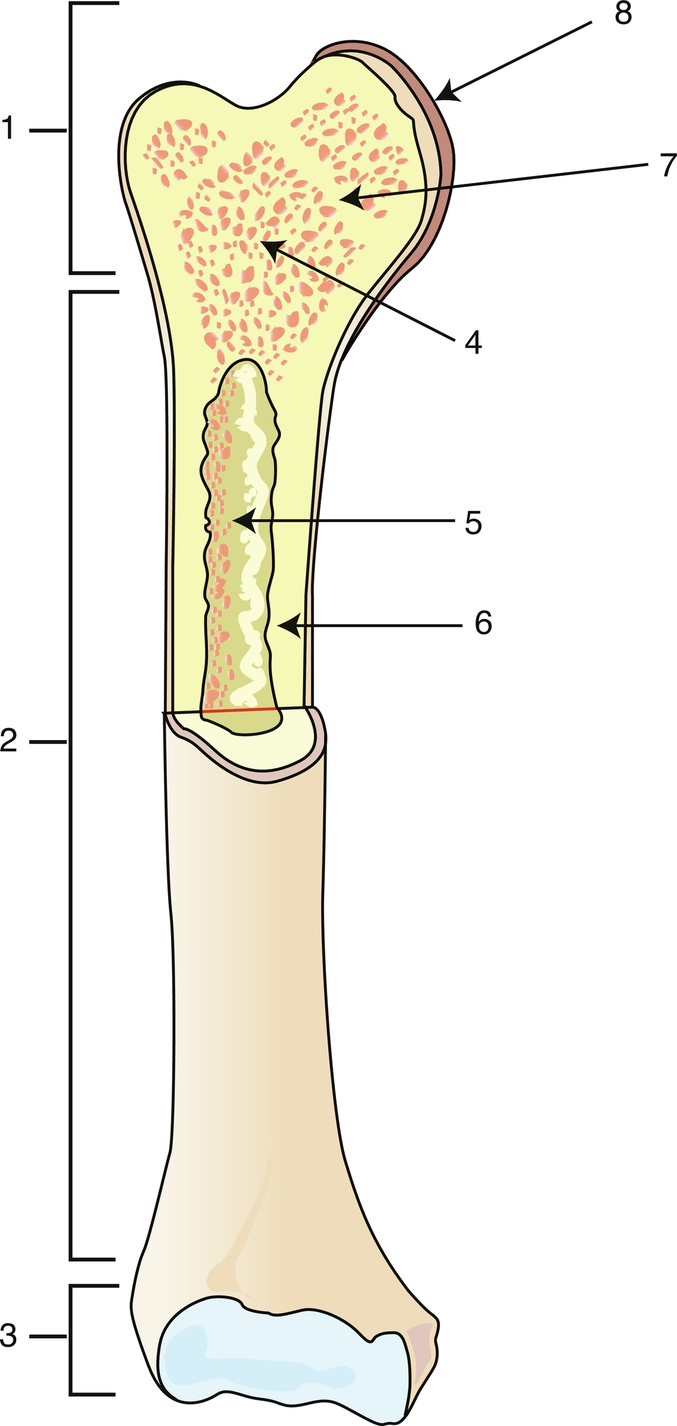
Diaphysis
2
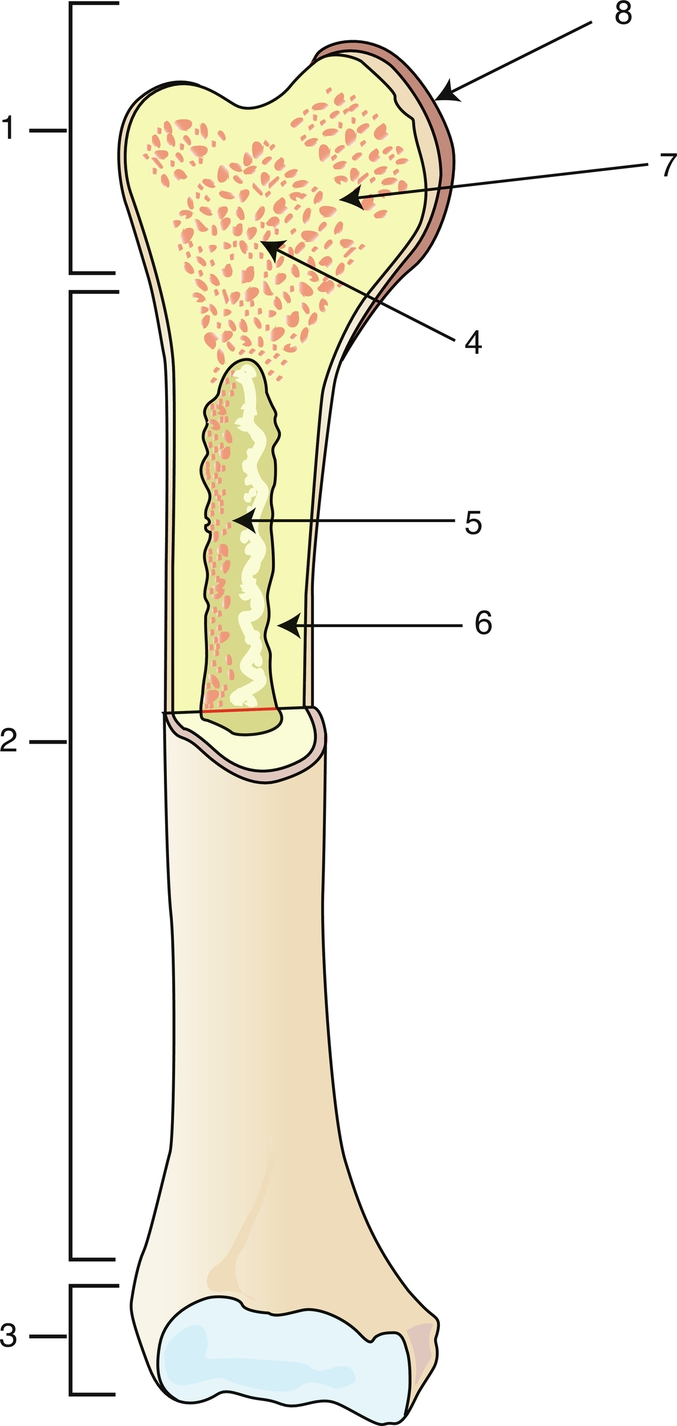
Distal epiphysis
3
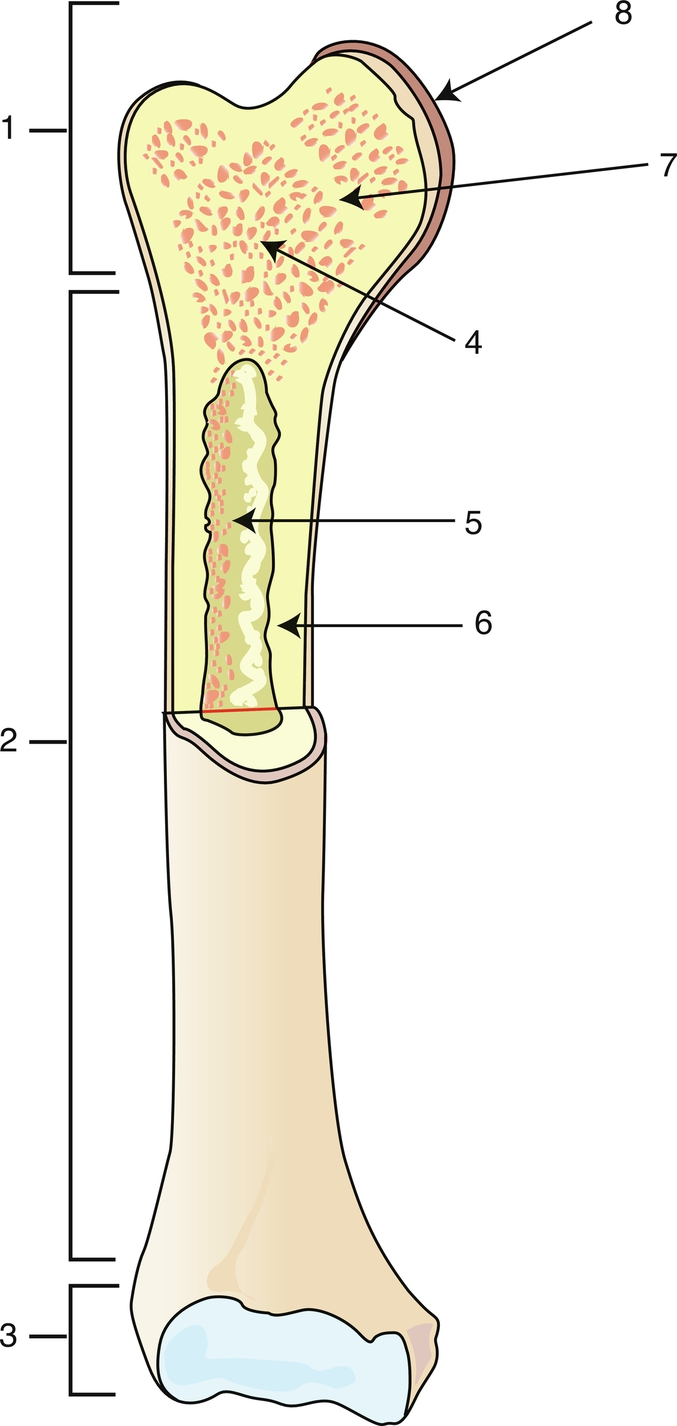
Spongy bone/red bone marrow
4
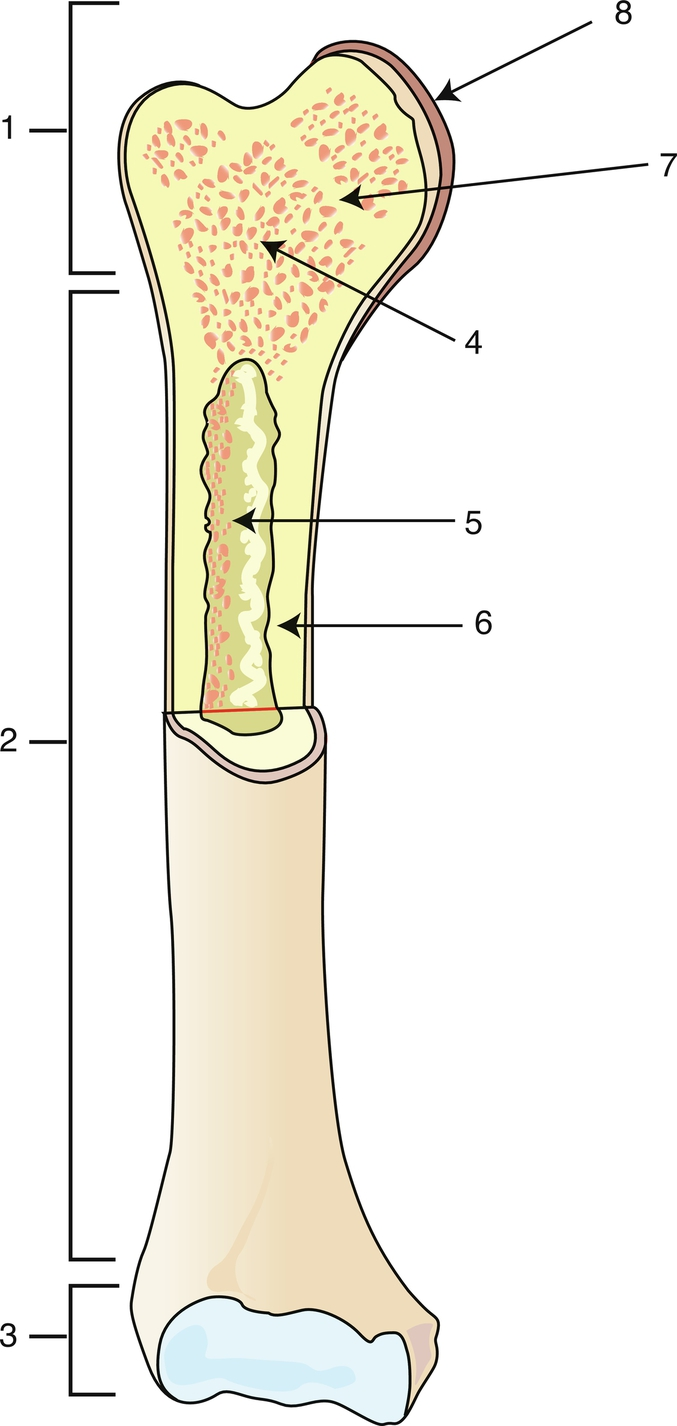
Medullary caity
5
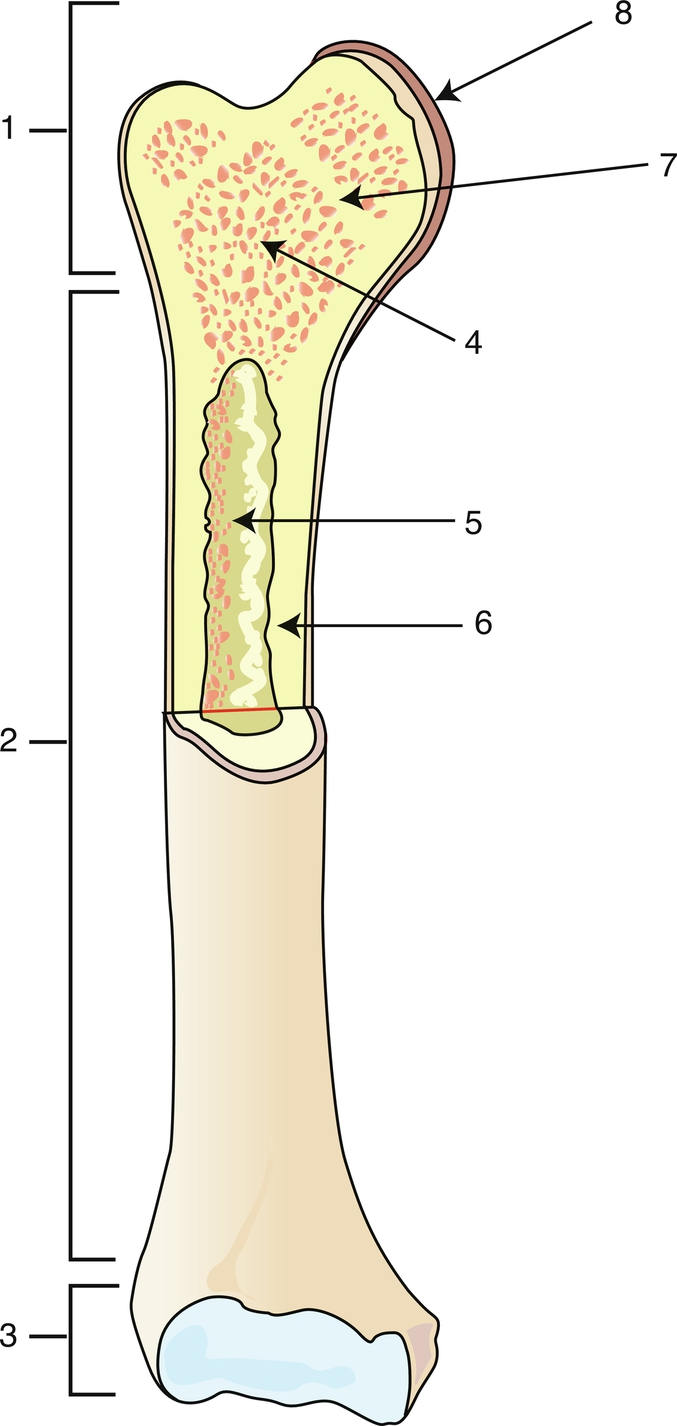
Endosteum
6
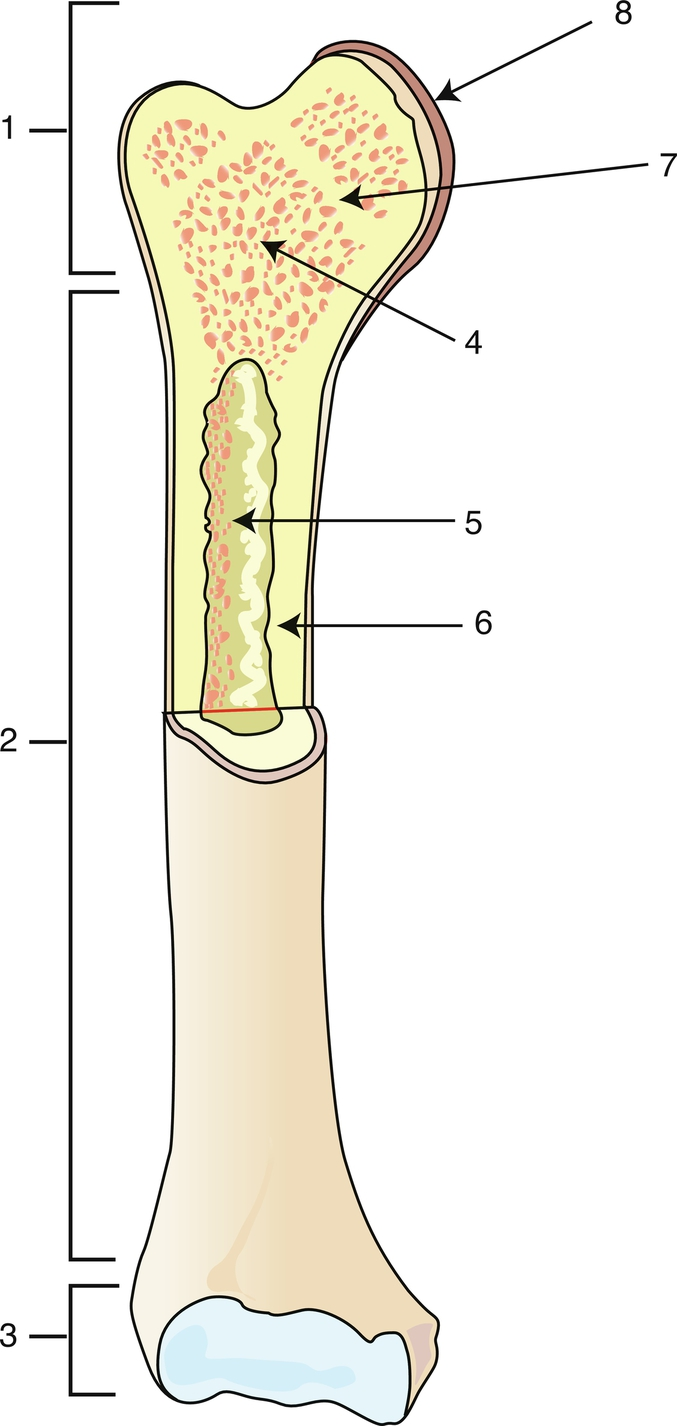
Epiphyseal line
7
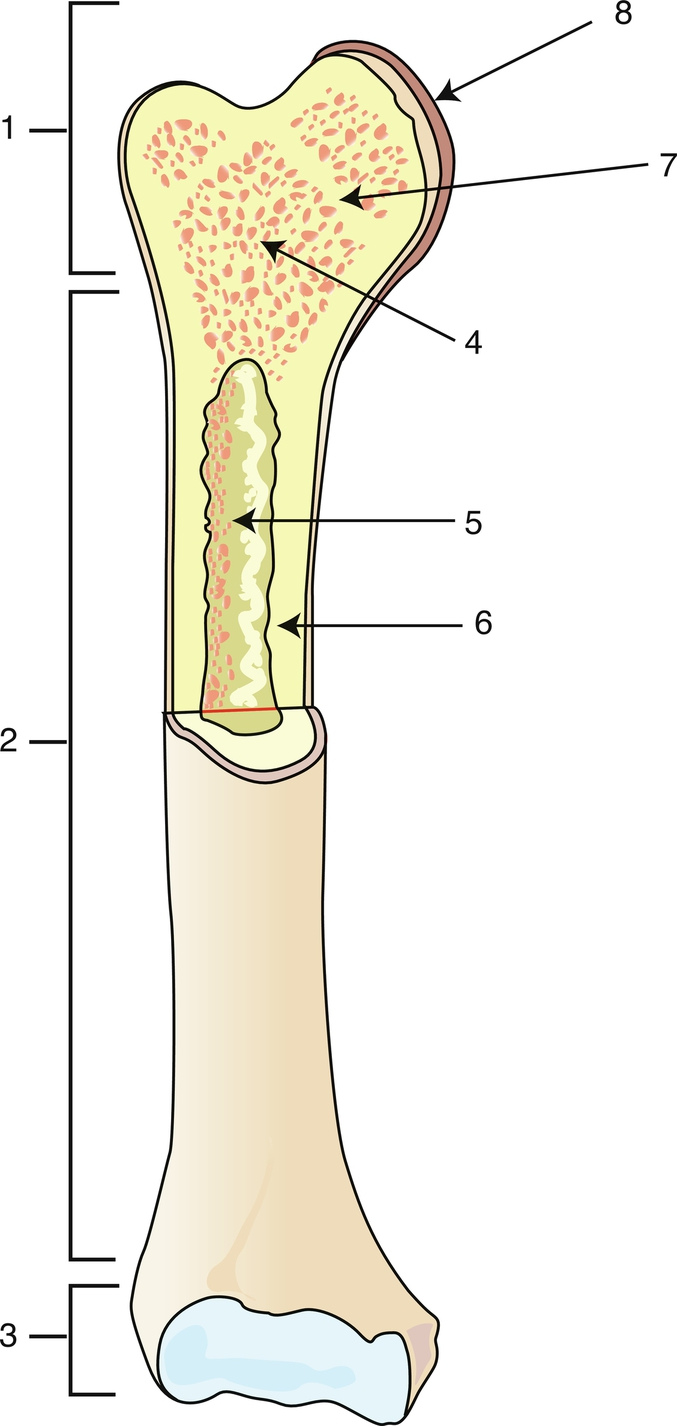
Articular cartilage
8
Masseter
Brachiocephalicus
in neck
Sternocephalicus
on neck
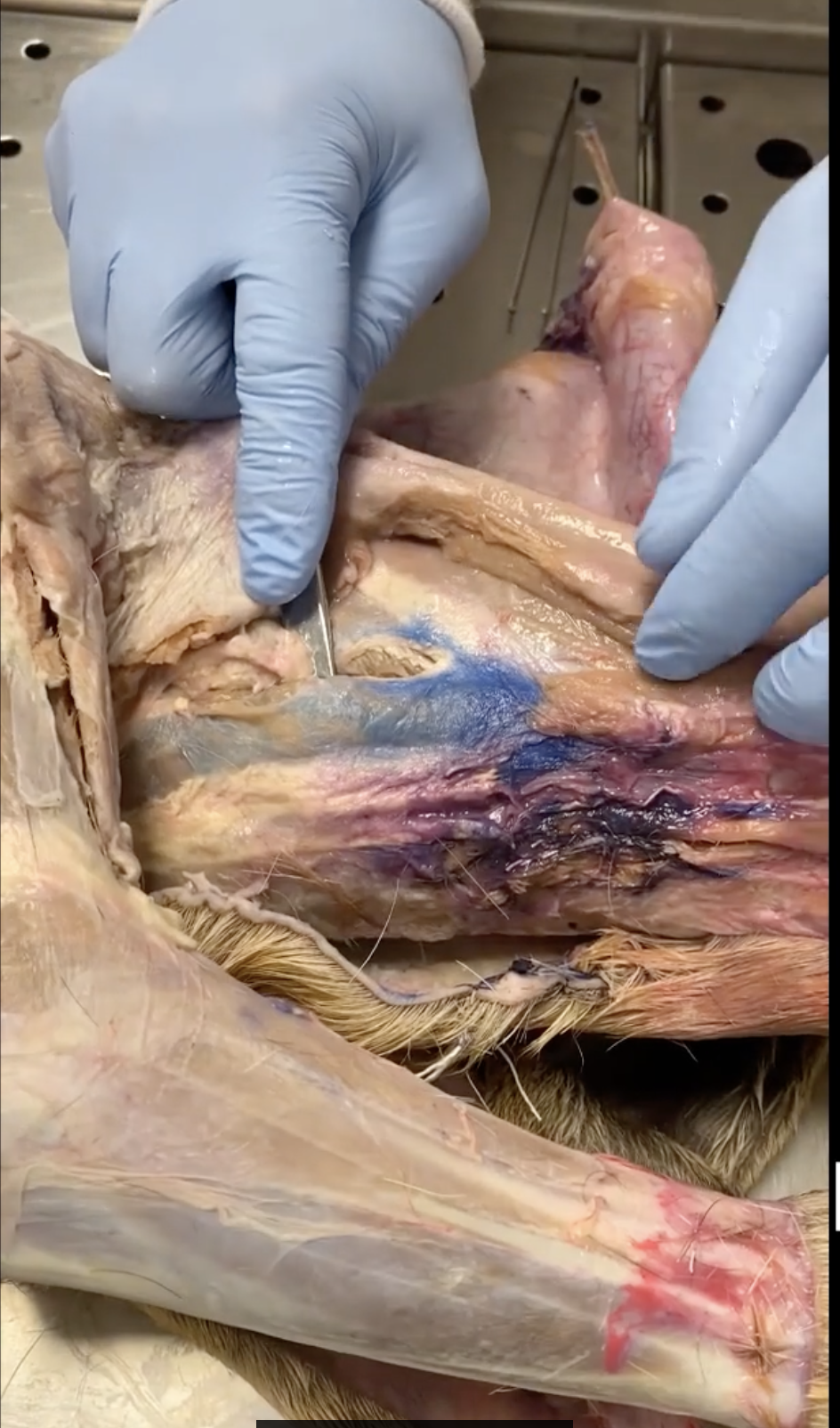
Trapezius
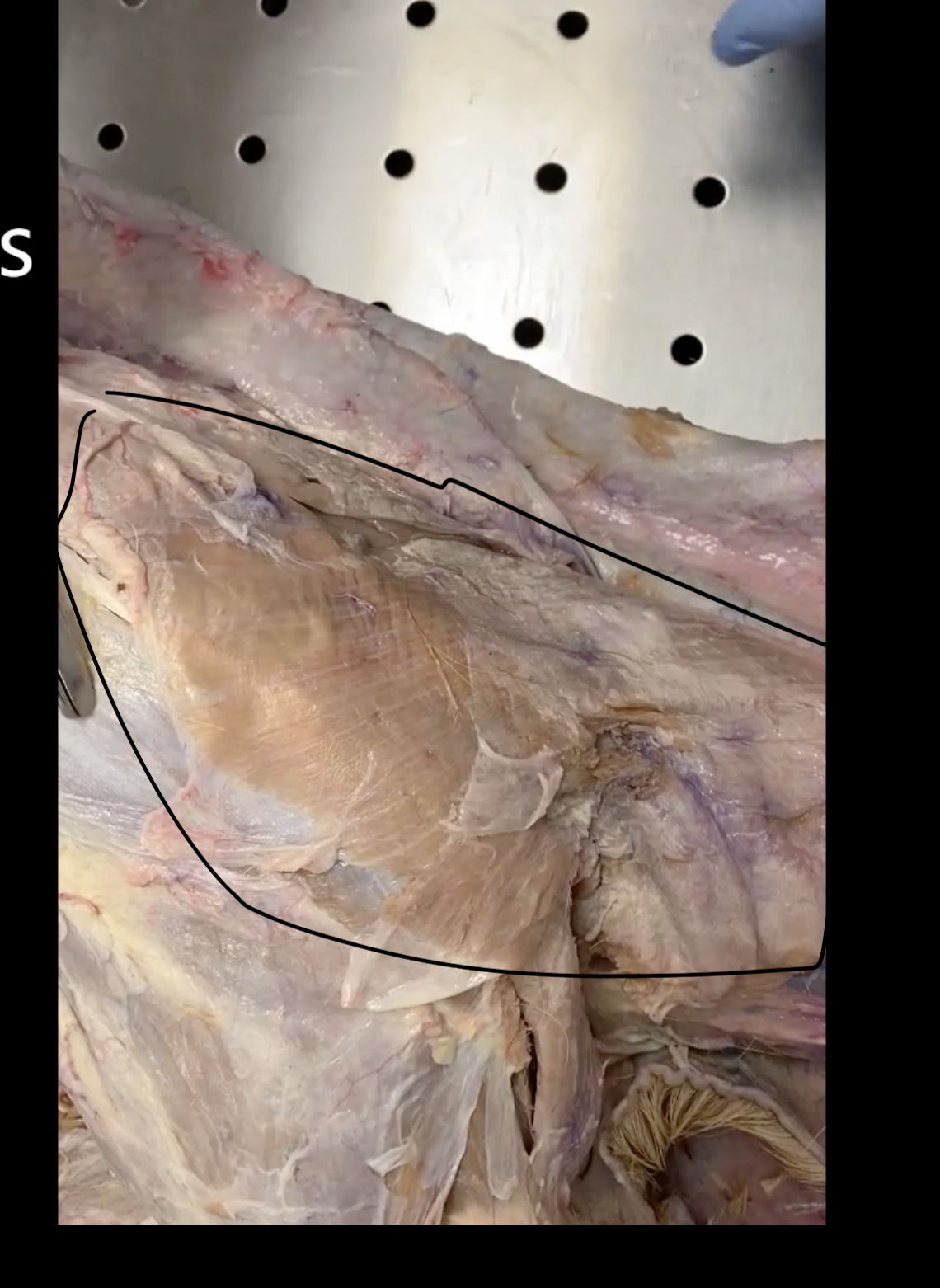
Serratus ventralis
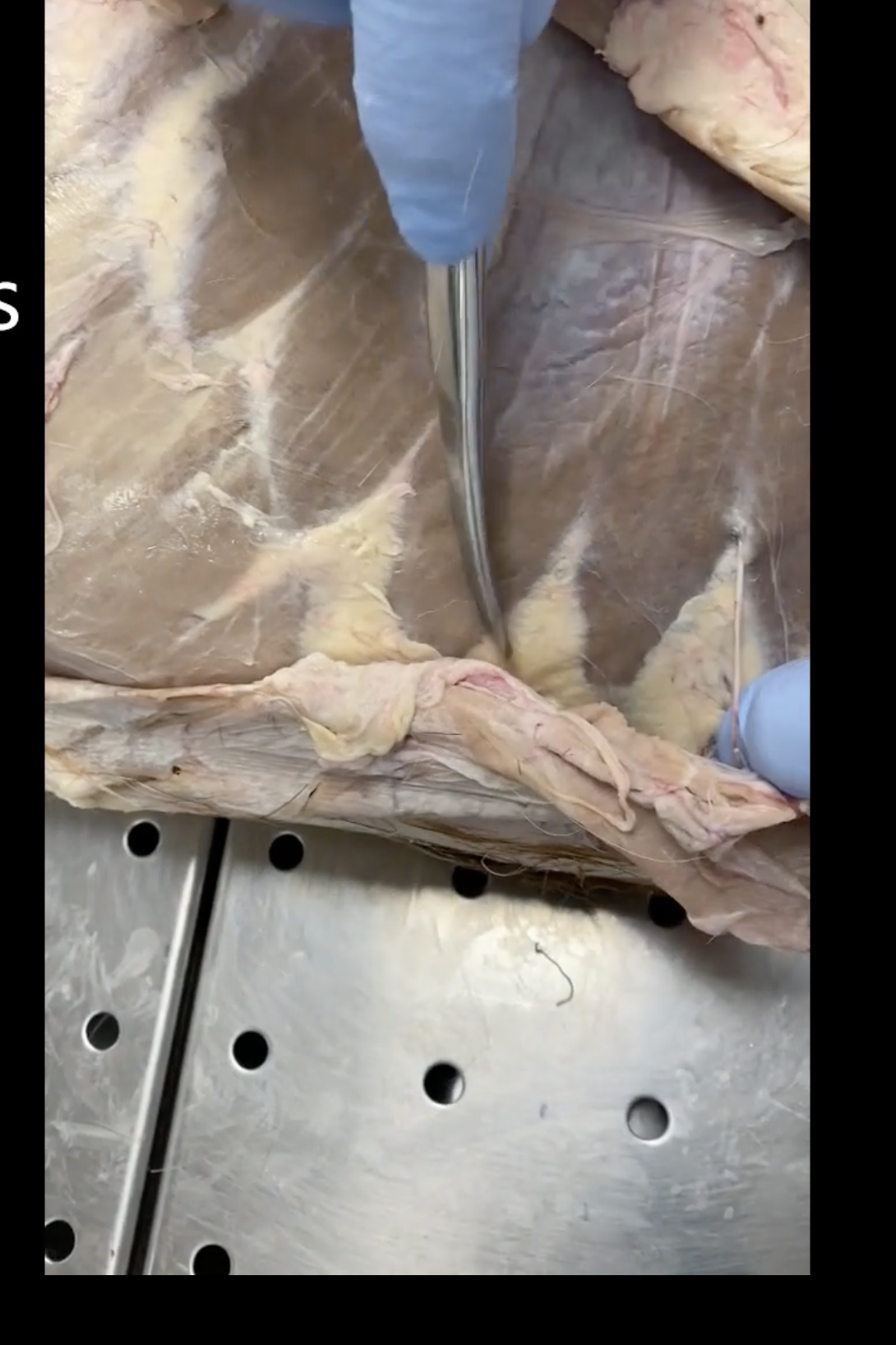
Latissimus dorsi
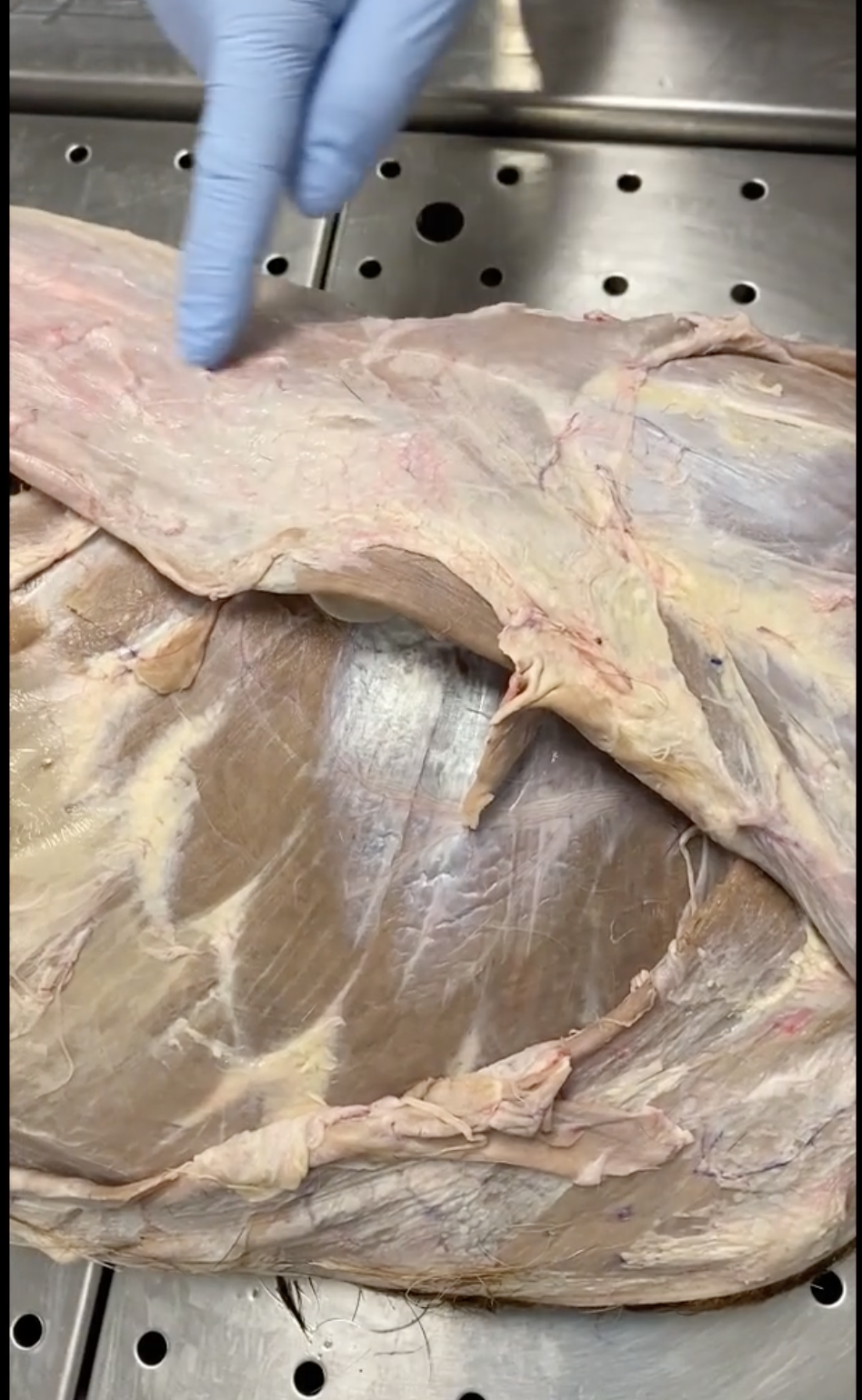
Deltoid
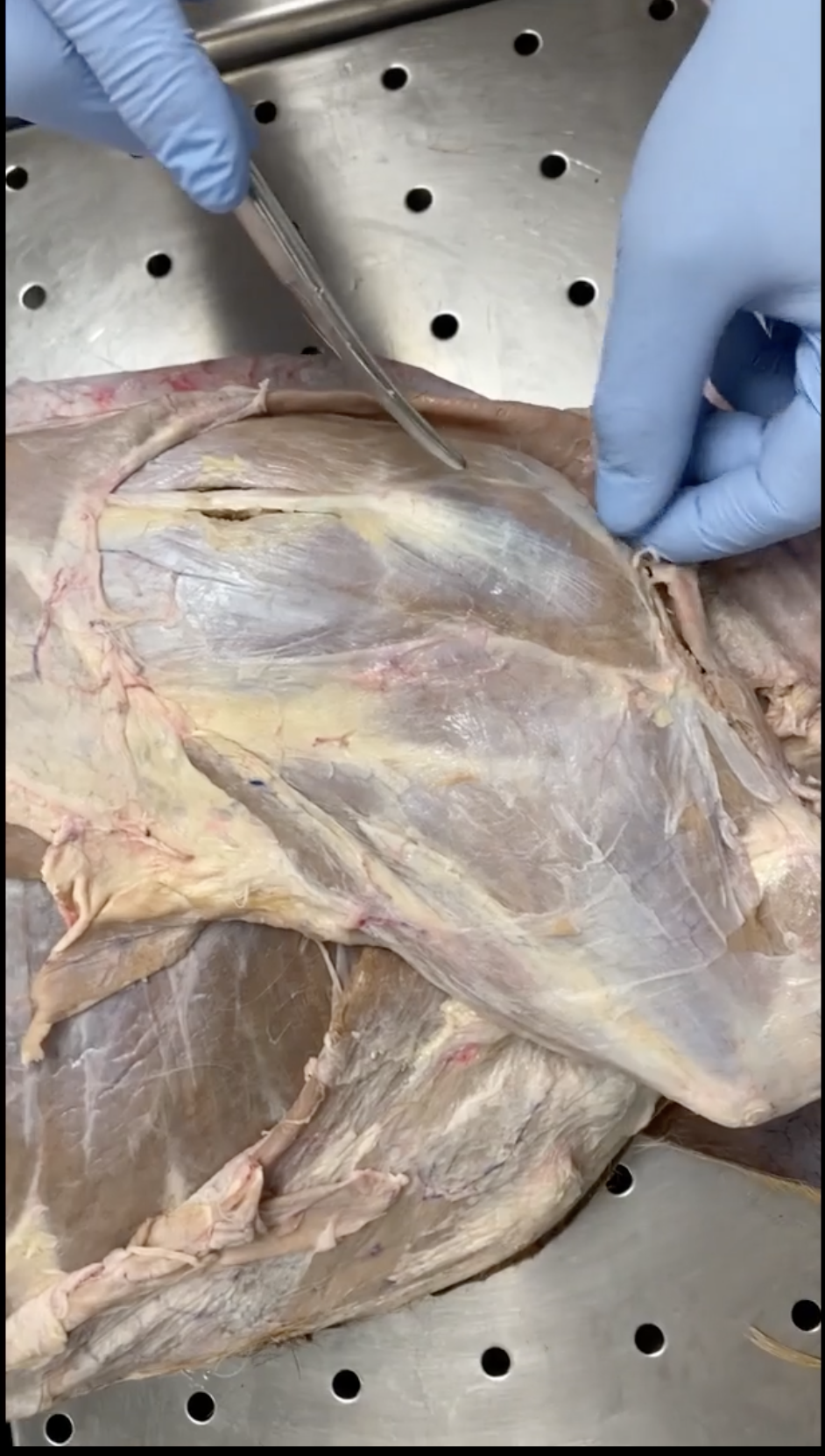
Supraspinatus
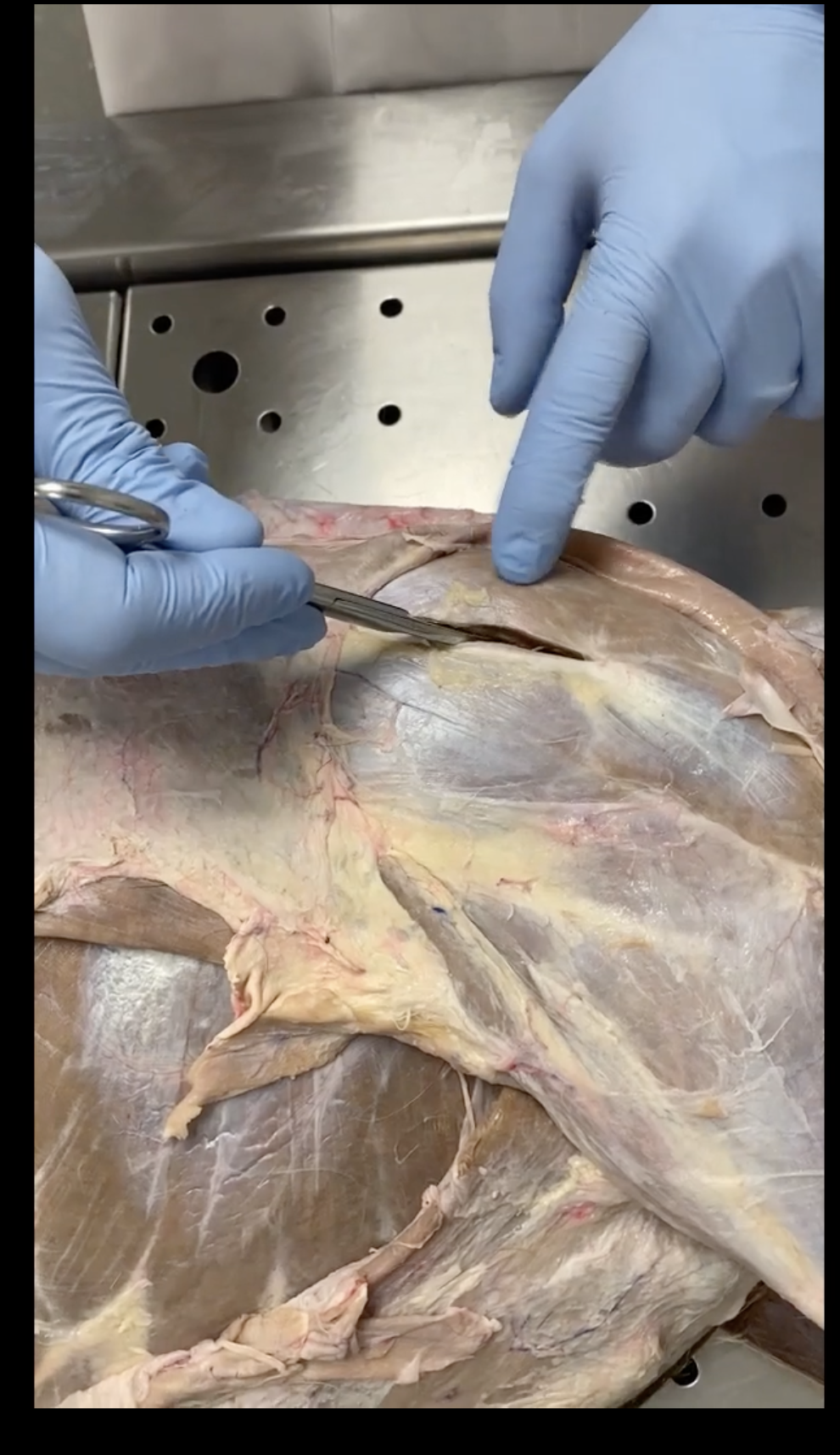
Infraspinatus
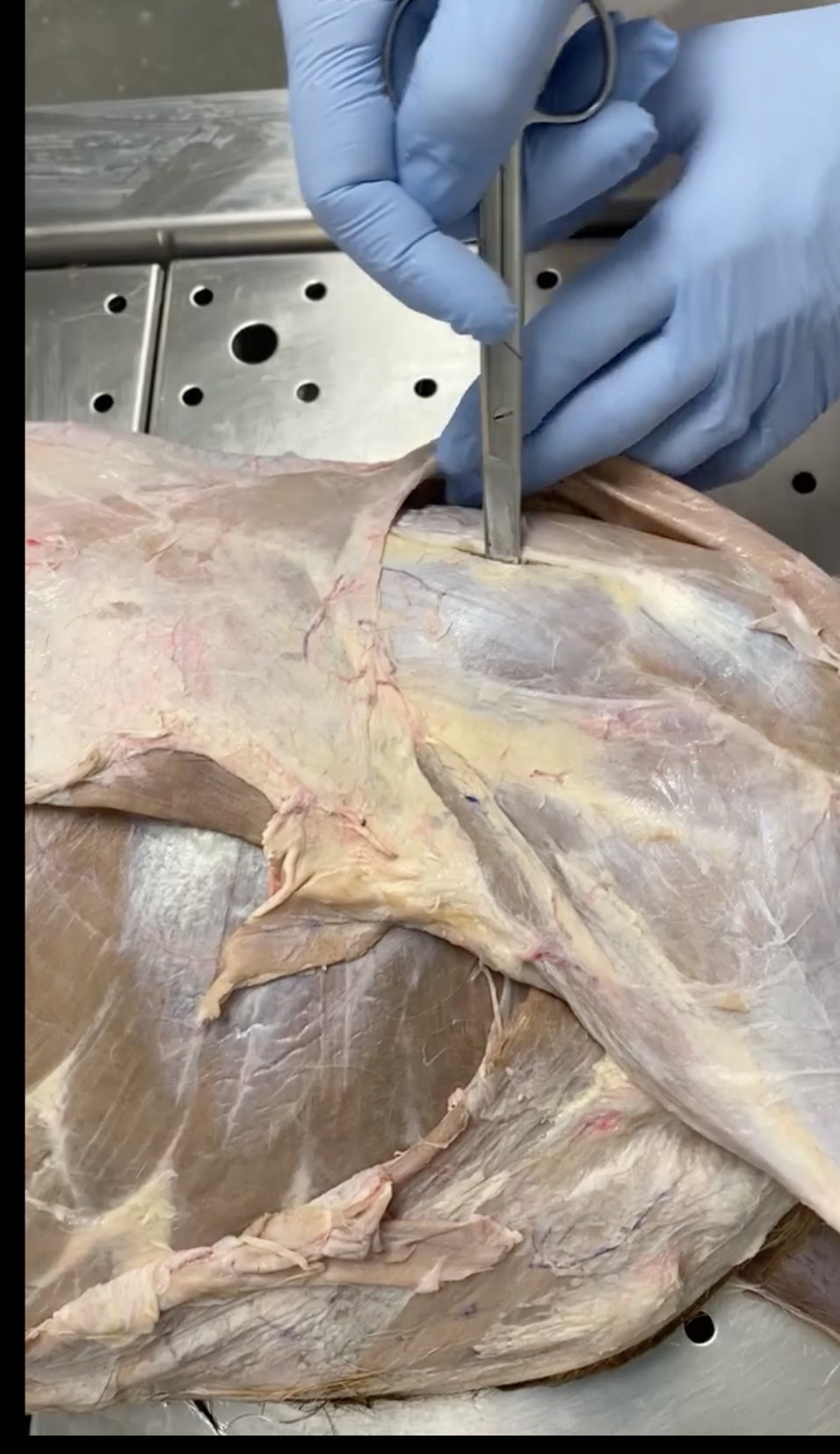
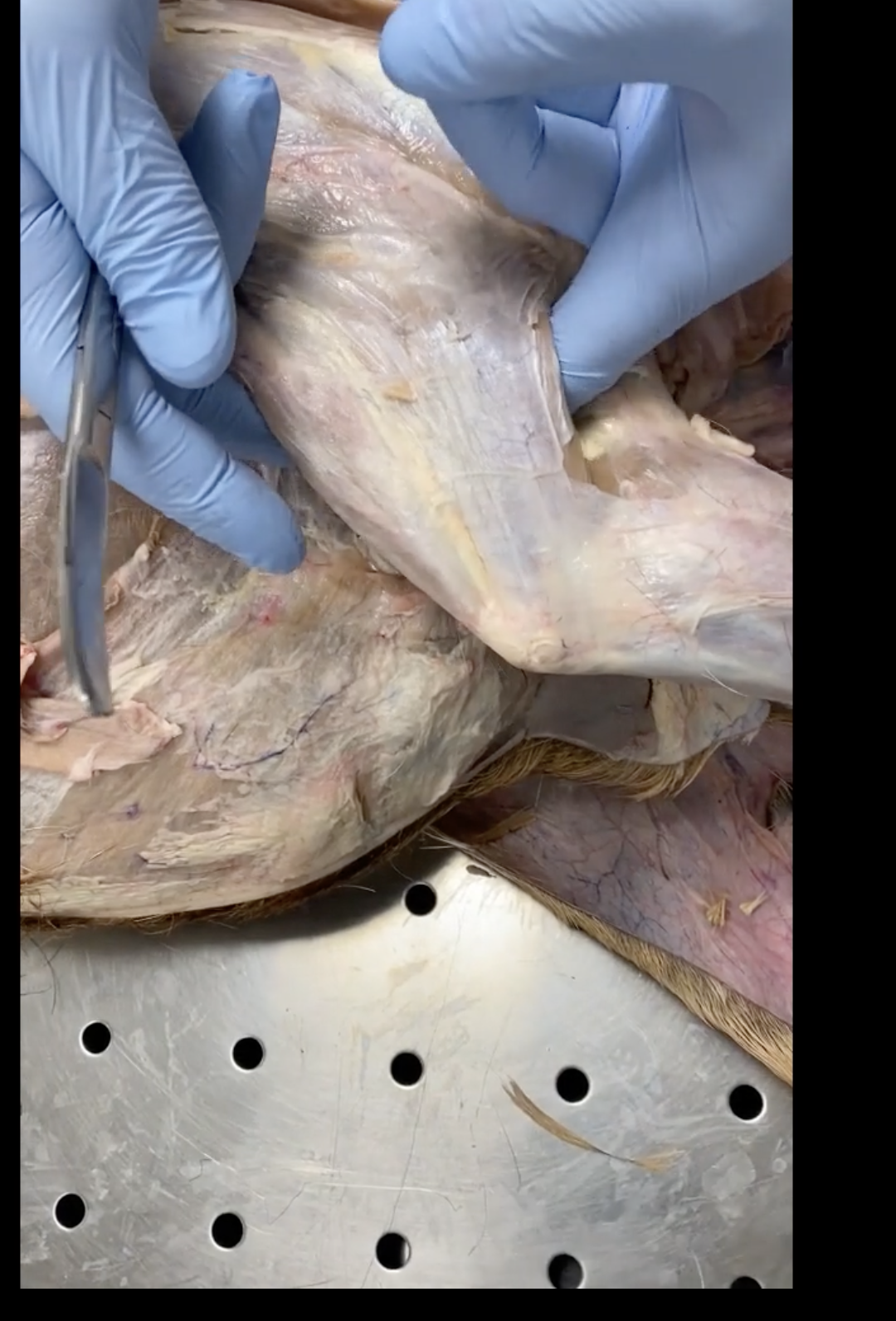
Pectoral
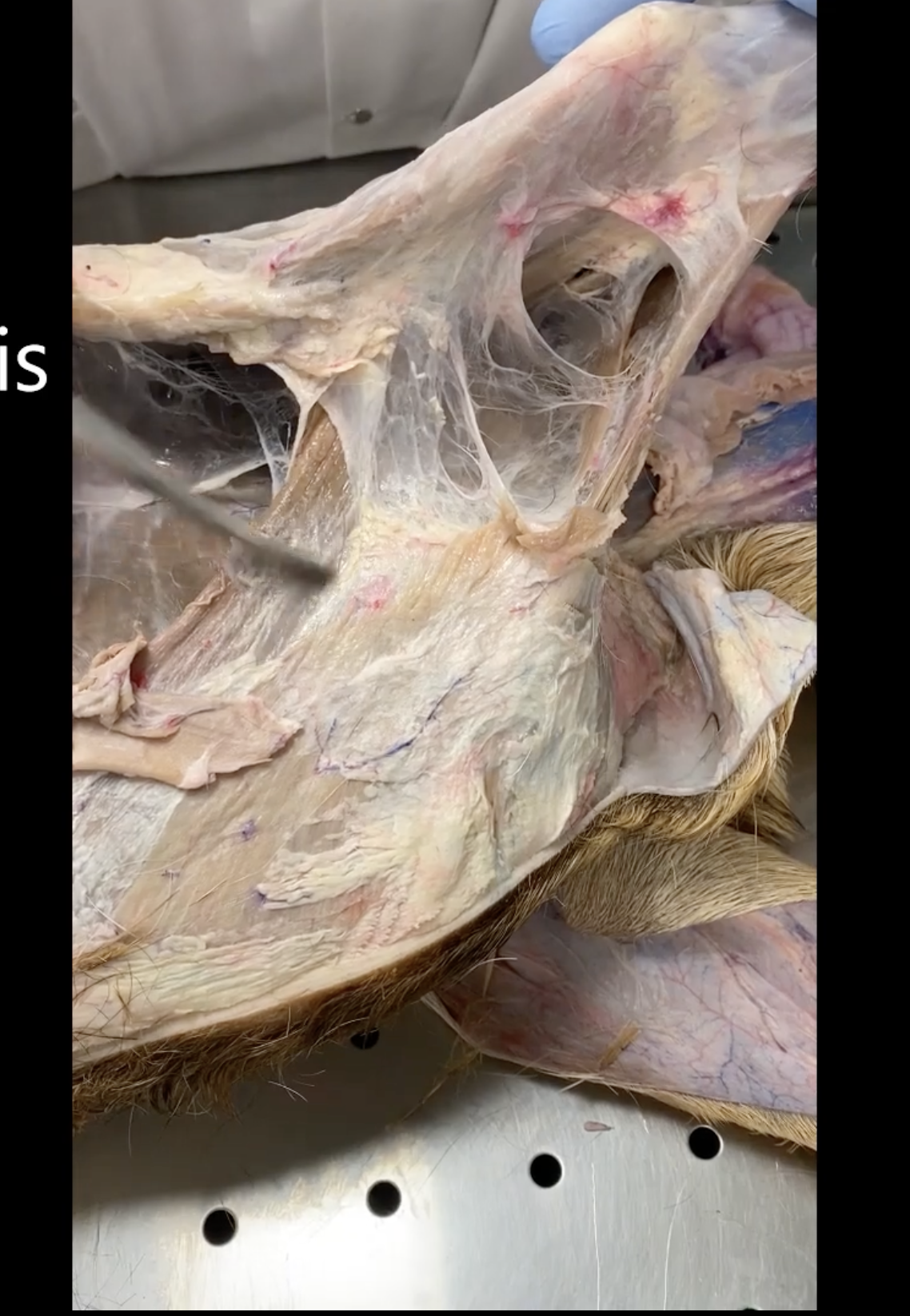

Triceps brachii
in thoracic limb
External intercostal
Caudal-ventral
External intercostal fiber orientation
Internal intercostal
Cranial-ventral
Internal intercostal fiber orientation
Diaphragm
External abdominal oblique
In abdomen
caudal-ventral
External abdominal oblique muscle fiber orientation
Internal abdominal oblique
cranial-ventral
Internal abdominal oblique muscle fiber orientation