GEOL 102 Exam 1 GMU
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Physical geology vs. Historical geology
Physical geology deals with materials and processes that make up the Earth, Historical geology is applying chronology to events in Earth's past
Relative age
Determination that something is younger or older than something else
Absolute Age
Precise measurement of how much time has passed since something was created or modified
Fossils
Remains, traces, or other indications of life
Principal of Original Horizontality
Sediment is deposited in layers that are originally horizontal
Principle of Original Lateral Continuity
Rock layers extend in all directions until they thin out, encounter a barrier, or grade laterally into another rock type
Concept of Uniformitarianism
The present is the key to understanding the past. Past history of Earth must be explained by what is happening now
Principle of Actualism
Natural laws do not change with time
Concept of Catastrophism
History of life on Earth is marked by catastrophes. Each calamity extinguishes all life on earth and new animals and plants appear after
Principal of Natural Selection
Species evolve over time and the most favorable traits pass on to the next generation and the rest die off.
What are the Eon divisions in the Geologic TimeScale
Phanerzoic (541 Ma), Proterozoic (0.541 - 2.5 Ga) , Archean (2.5 Ga - 4.0 Ga) , Hadean(4.0 Ga - 4.6 Ga): Youngest to Oldest
Principle of Superposition
in undisturbed layers of rock, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rocks become progressively younger toward the top
Principle of Cross-Cutting
younger features cut across older features in rock strata
How can radioactive materials be used to determine the ages of geologic samples?
Radiometric dating uses the decay of specific element isotopes to determine the absolute age of a rock
What is half-life?
The time required for half of a given amount of an unstable parent to decay to a daughter isotope/element. It is nonlinear.
What are the requirements for a material to be a mineral?
Occurs naturally as an inorganic solid/Has specific internal structure/Has specific chemical composition
How are minerals defined?
Based on their properties and chemical composition.
What are some tests you can do to identify a mineral?
Microscopic analysis or a field test kit(Physical properties) that check color, streak, luster, cleavage, fracture, hardness, crystal shape.
Silicate minerals
Silicate minerals contain silicon(Si) and Oxygen(O) and bind together in the shape of a tetrahedron
Non-silicate minerals
Carbonates, sulfates, sulfides, chlorides, oxides
What are the requirements for a material to be a rock?
Rock is a solid material that occurs naturally and is composed of one or more minerals/organic material
How are igneous rocks formed?
Form from solidification of molten rock(magma or lava)/ melting of a rock
Do all minerals in igneous rocks crystalize at the same time?
No minerals crystallize from cooling magma in a systematic sequence
Intrusive vs. Extrusive Igneous Rocks
Intrusive solidifies underground and Extrusive solidify on the surface where they cool much faster and become fine-grained
What are the differences between felsic and magic magmas?
Felsic has more silica and less magnesium and iron and more viscous magma(Does not flow to the surface easily)
Viscosity
The state of being thick, sticky, and semifluid in consistency, due to internal friction
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
Formed from sediments that have been consolidated from compaction, cementation, or crystallization.
Formation process of sedimentary rocks involves
Weathering, Erosion/Transportation , Deposition, Lithification
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
Rocks that have been altered by heat or pressure, but not melted
Geologic Time Scale divisions
Eon → Era→Period→Epoch→Age
Metamorphic grade
the degree to which the parent rock changes during metamorphism
Folatiated vs Non-Foliated metamorphic rocks
Foliated rocks have parallel alignment of crystals or grains(planar orientation) and non-foliated are created when the stress on the rock is uniform or the crystals do not deform
What does well sorted mean in the context of sediments?
The grains are all the same size and it was most likely transported by wind or water
What does the shape of sediment grains tell you?
The farther sediments are transported, the rounder they become. They are angular if they haven't been transported far.
Why are some ripples in sediments symmetrical and some asymmetrical?
Symmetrical ripples are created when currents come from both sides or there is erosion on both sides of each structure.
What does cross-bedding in sandstone tell you about the formation mechanism?
Sediments were deposited as ripples or dunes
What is limestone made of?
Carbonates
What is the difference between bio-clastic and non-clastic limestone?
Most limestones are bio-clastic because they contain fossils but some are formed without biologic activity
Where are most limestones formed?
Marine environments
Stratigraphy
study of stratified rocks, especially their geometric relations, compositions, origins, and age relations
What environmental conditions are most favorable for fossil preservation?
High deposition zones, Shallow sea, Low oxygen environments for organic material
Fossils are usually found
In sedimentary rocks
What physical traits or properties of organisms are most favorable for fossil preservation?
Hard body parts(Shells, bones)
How do fossils help with dating sedimentary rocks?
Some fossils were only around for a short period of time in the geologic time scale and if found inside a rock, it can be dated to that fossils short time period
Index fossil
a fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found
Principle of Fossil Succession
Fossil organisms succeed one another in a definite and determinable order, and any time period can be recognized by its fossil content.
How do fossils provide a record of the past environments?
Certain fossils can only be found in certain environments, so it shows how the environment has changed
What is meant by the Taxonomy of Life
The systematic naming and growing of organisms on Earth that is not absolute and can change
What level of Taxonomy marks the level of breeding between members
Species
How is Taxonomy classified
By observable traits
How do variations occur within a population?
Variations occur naturally through reproduction and mutations in genes
How do the traits of the population as a whole evolve?
The population as a whole evolves when the population without the favorable trait dies off
What is the evidence of evolution from paleontology?
Horse teeth have evolved be specialized from eating leaves to eating grass horse fossils have teeth that are more flat
What is the evidence of evolution from biology?
Similar structure of body parts in different modern day organisms/Useless organic structures/Humans having similar genome to chimpanzees
What are the major divisions of the Earth's interior?
Crust → Mantle → Core
2 Divisions of Earth based off of properties
Lithosphere(Hard outer shell of earth) → Asthenosphere(Soft, weak steel of upper mantle)
Seismic wave
Vibrations that travel through Earth carrying the energy released during an earthquake or artificially
Types of body waves
P(Primary) waves and S(Secondary) waves
P-wave
Compressional(push-pull) wave that can travel through all materials
S-wave
Shear wave(Oscillation movement) that can only travel through solids
How can P and S waves be used to understand the Earth's interior
P waves can travel through the core and S waves can't therefore there exists liquid in Earths core
What is a lithospheric plate?
Different sections of the lithosphere that move around on the asthenosphere
What does the movement of lithospheric plates say about the continent locations in the past?
The continents were once connect
What are the ways the lithospheric plates can move in respect to each other?
Converge(Against Each other)/Diverge(Away from each other)/Transform(Slide past each other
What is a fault?
A fracture in a rock along which motion has occurred
Types of faults
Normal(Hanging wall falls), Reverse(Hanging wall rises), Strike-slip(Lateral walls slide past each other)
What is a fold?
A bend in layers of rock created by compression
Types of folds
Anticline, syncline, dome, basin, monocline
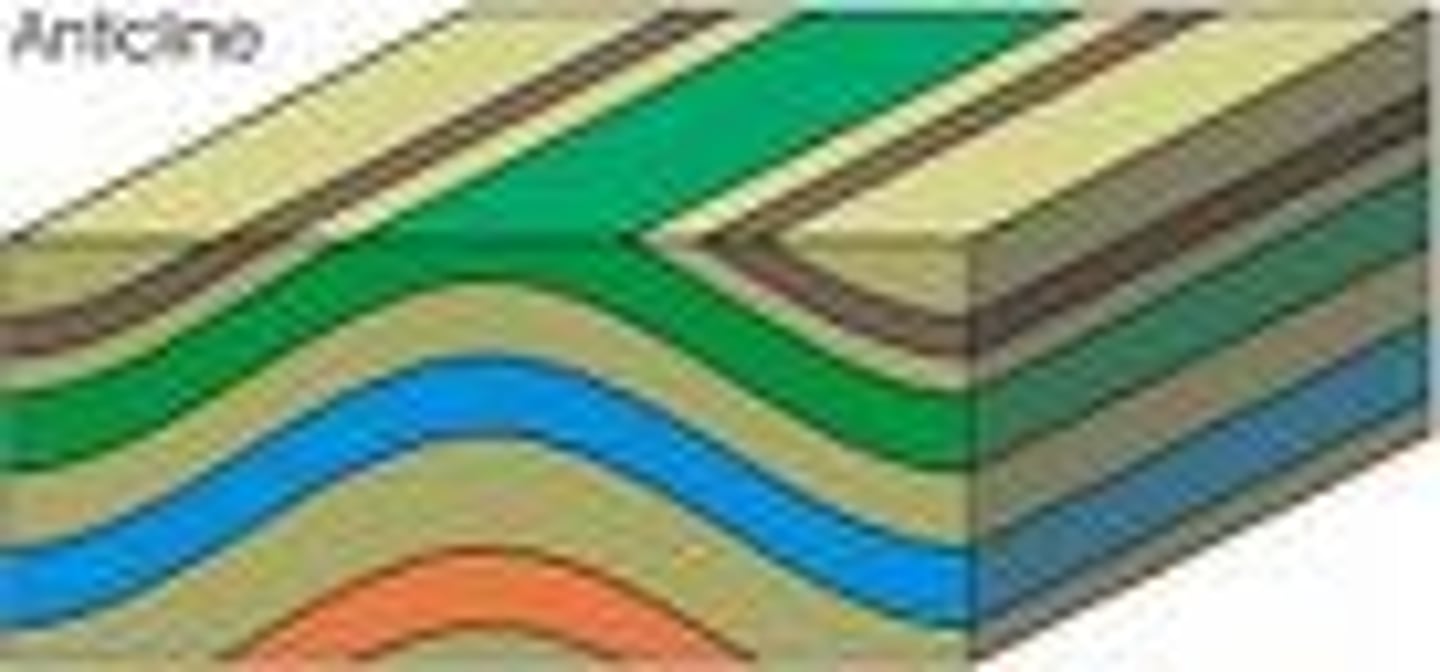
Anticline
Oldest rocks in center

Syncline
Youngest rocks in center
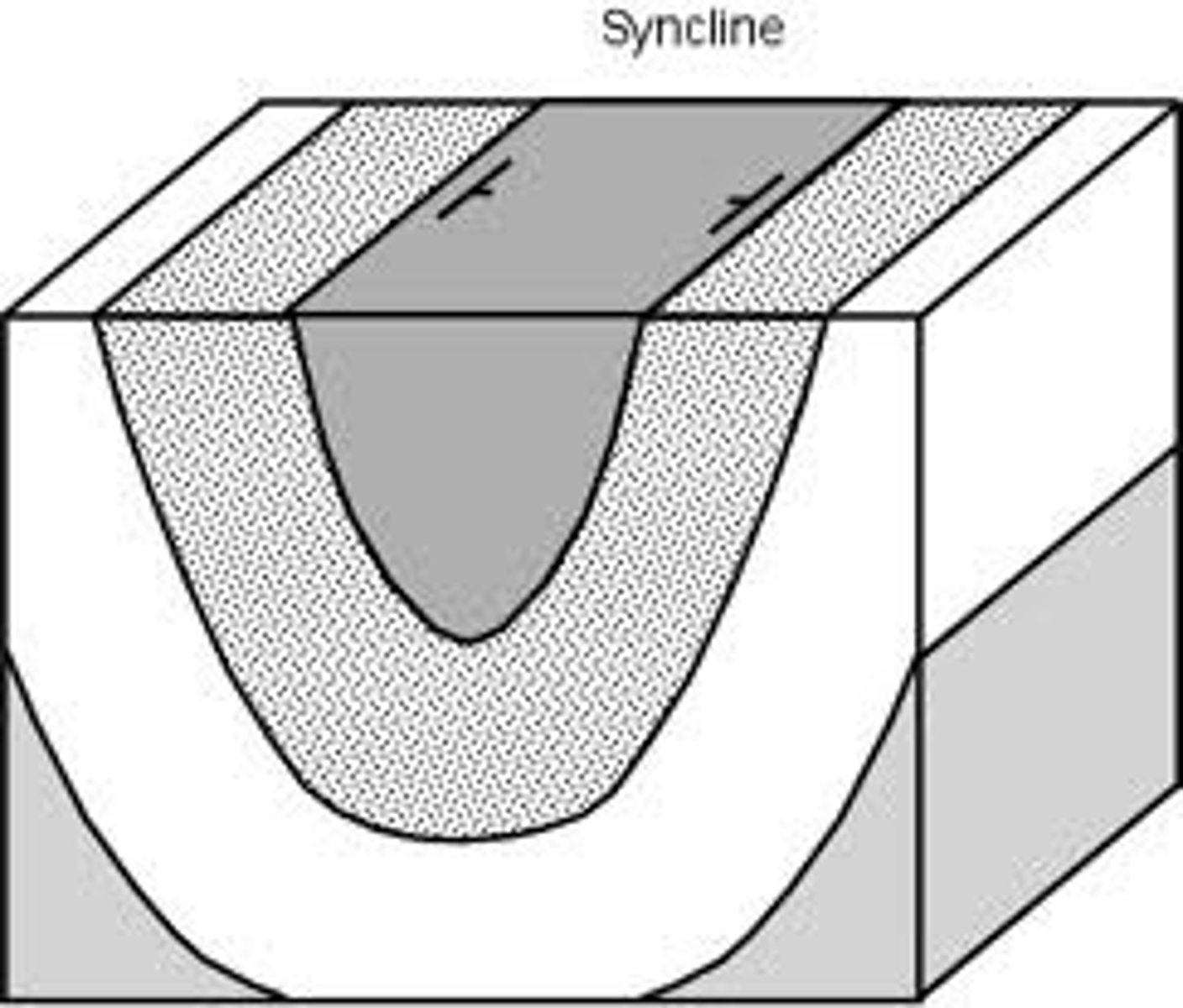
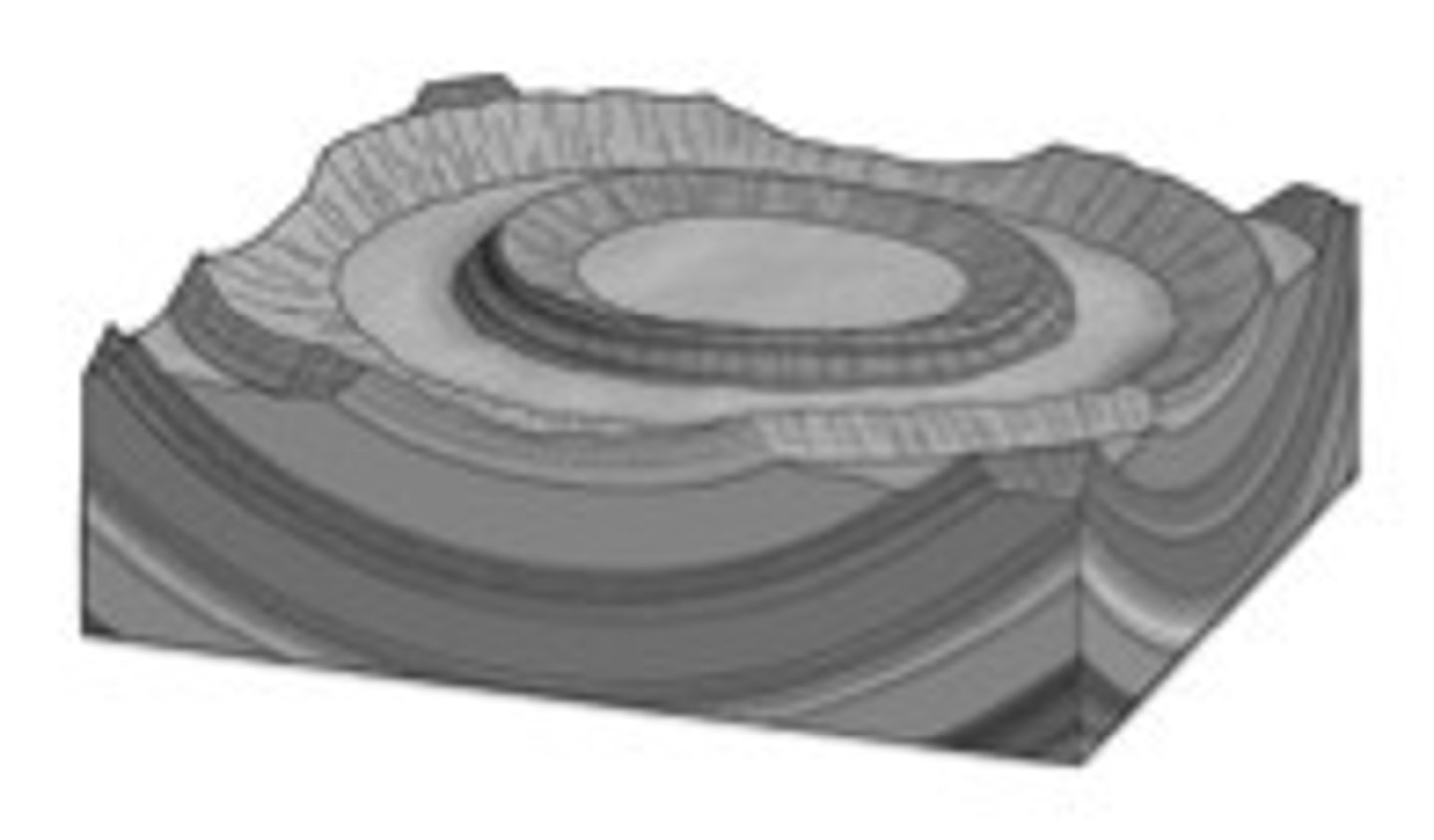
Basin
Downfolded circular features with youngest strata in center
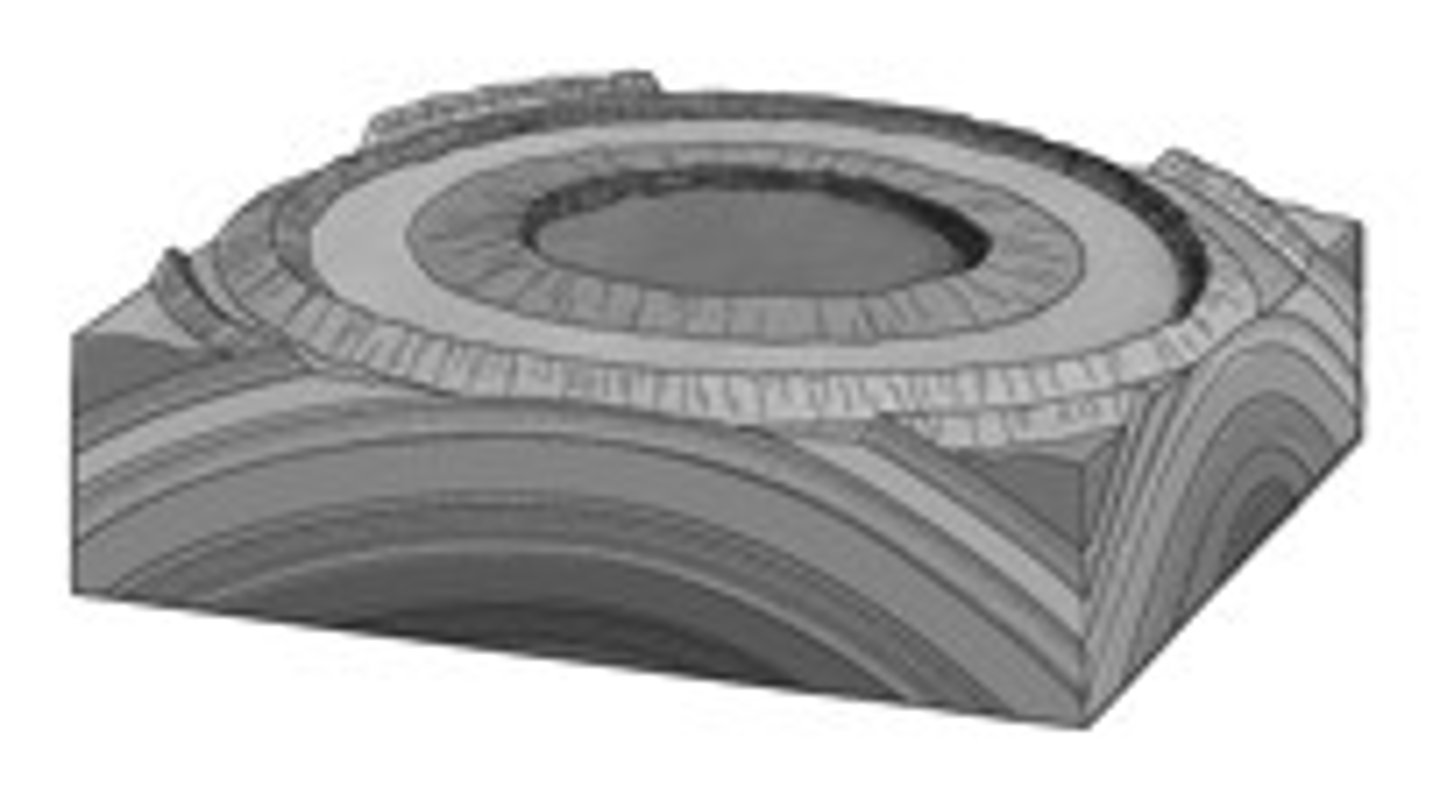
Dome
Upfolded or arched features with oldest strata in the center
What are some of the lines of evidence that support Plate Tectonics Theory?
Earthquakes occur along plate borders/Volcanoes located on pacific rim/Wandering of magnetic poles/Crust age correlate with distance from mid-ocean ridge
Types of Surface Waves
Rayleigh- up down
Love waves- side by side(cause earthquakes)
Surface waves vs Body waves
Surface waves can only move on the surface while body waves travel through the interior of Earth