SA#3 Bio Reviewer Cycle 6-7
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1
New cards
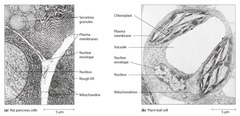
Prominence of Membranes
An essential feature of every cell is the presence of membranes that defines the boundary of the cells and any internal compartments
2
New cards
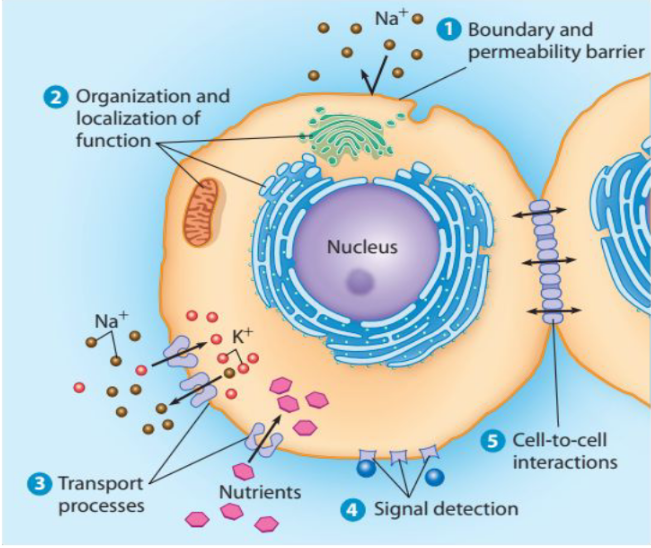
Functions of Membranes
Membranes not only define the cell and its organelles but important functions, including transports, signaling, and adhesion.
3
New cards
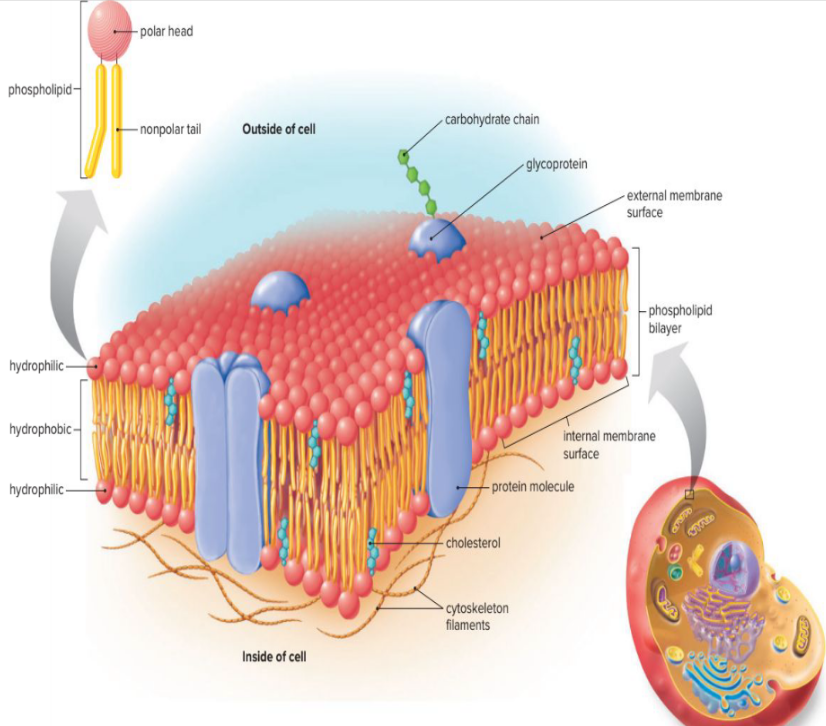
The Plasma Membrane
- In all cells, the plasma membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer with numerous proteins embedded in it.
- Cholesterol provides support
- Cholesterol provides support
4
New cards
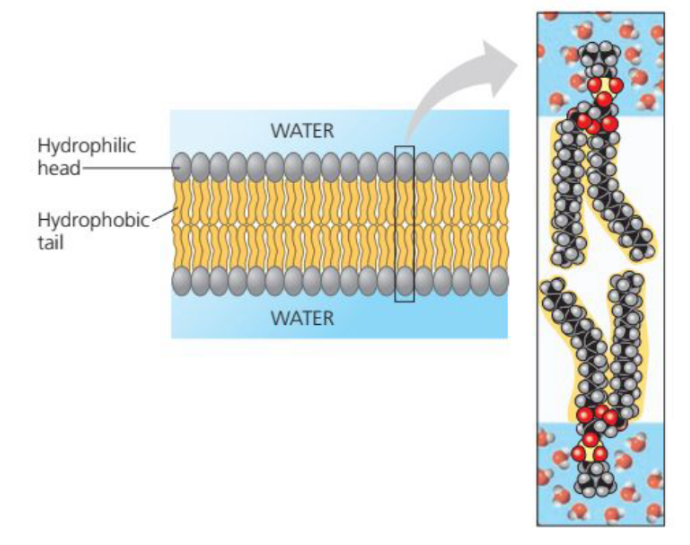
Phospholipids
- Amphipathic because it is composed of
- Hydrophilic regions - polar
- Hydrophobic regions - non-polar
- Lipids are small nonpolar molecules (e.g O2 and CO2) pass freely across
- Hydrophilic regions - polar
- Hydrophobic regions - non-polar
- Lipids are small nonpolar molecules (e.g O2 and CO2) pass freely across
5
New cards
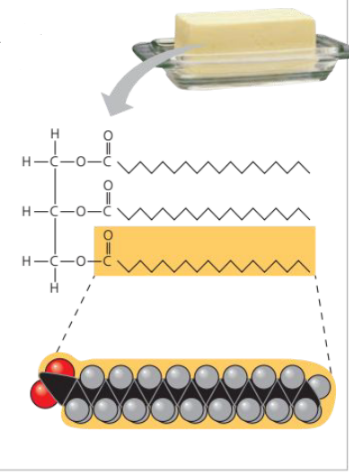
Saturated Fat
At room temperature, the molecules of a saturated fat, such as the fat in butter, are packed closely together, forming a solid.
Structural formula of a saturated fat molecule (Each hydrocarbon chain is represented as a zigzag line, where each bend represents a carbon atom; are not hydrogens shown.)
Space-filling model of stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid (red oxygen, = black carbon, gray = hydrogen)
Structural formula of a saturated fat molecule (Each hydrocarbon chain is represented as a zigzag line, where each bend represents a carbon atom; are not hydrogens shown.)
Space-filling model of stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid (red oxygen, = black carbon, gray = hydrogen)
6
New cards
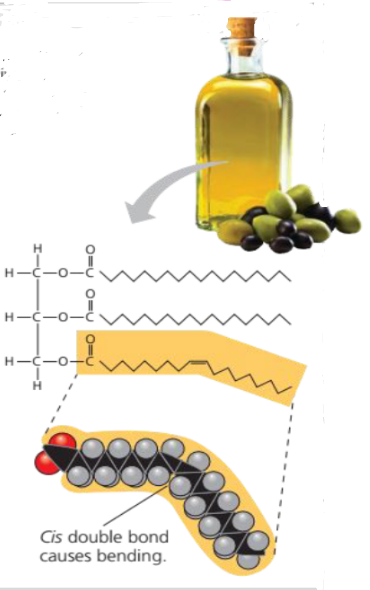
Unsaturated Fat
At room temperature, the molecules of an unsaturated fat such as olive oil cannot pack together closely enough to solidify because of the kinks in some of their fatty acid hydrocarbon chains.
Structural formula of an unsaturated fat molecule
Space-filling model of oleic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid
Due to the presence of double bonds in the hydrophobic tail of phospholipids, a kink (bend) is formed. This causes the membrane to be “fluid”
Structural formula of an unsaturated fat molecule
Space-filling model of oleic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid
Due to the presence of double bonds in the hydrophobic tail of phospholipids, a kink (bend) is formed. This causes the membrane to be “fluid”
7
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
The membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
Proteins bob around it which is the reason why it is called the Fluid Mosaic Model
Proteins bob around it which is the reason why it is called the Fluid Mosaic Model
8
New cards
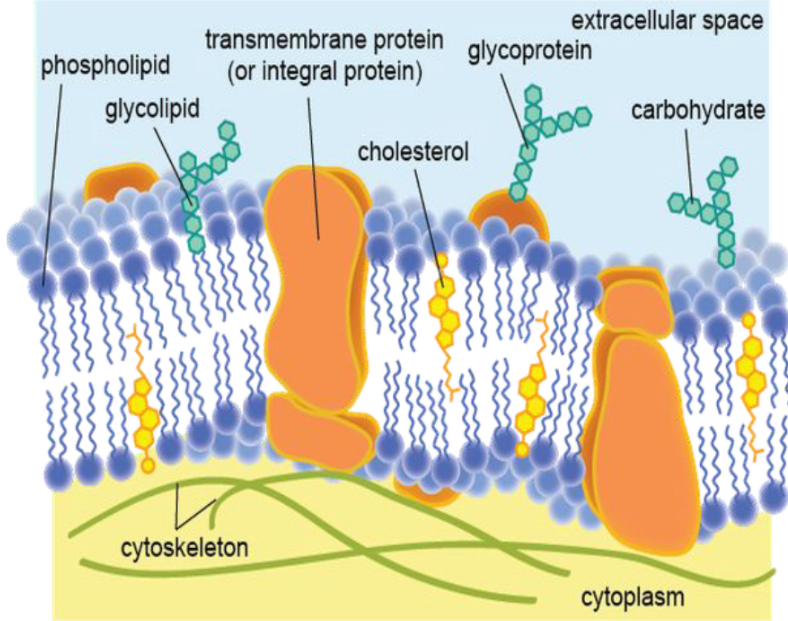
Membrane Lipids - Fluid Part: Phospholipid
Responsible for the selective permeability of cell
9
New cards
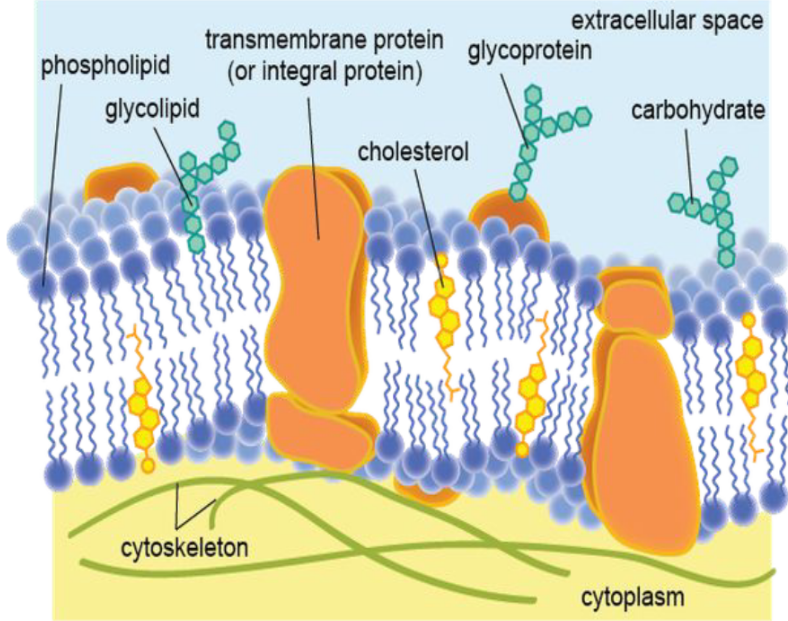
Membrane Lipids - Fluid Part: Sterols
Maintain the membranes fluidity as the temperature fluctuates (Cholesterol in animal membranes)
10
New cards
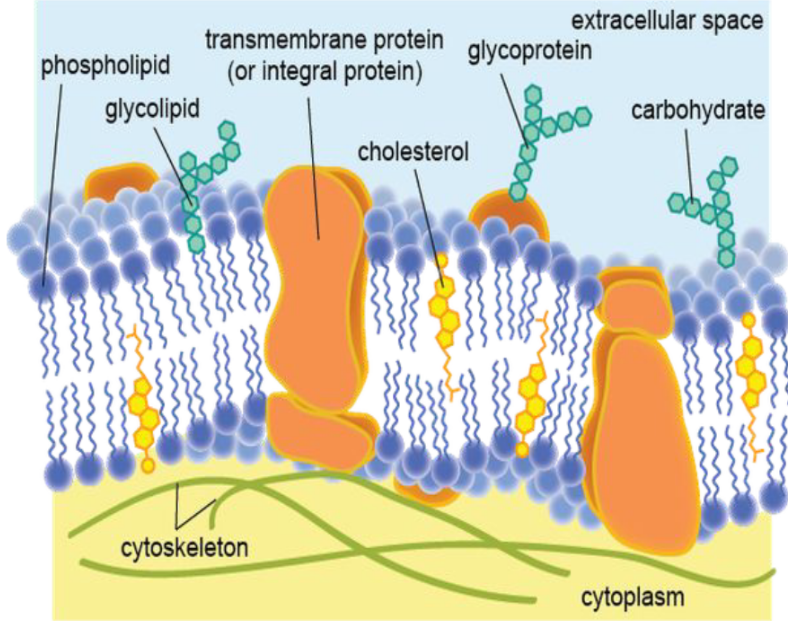
Membrane Proteins - Mosaic Part: Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded within the membrane
11
New cards
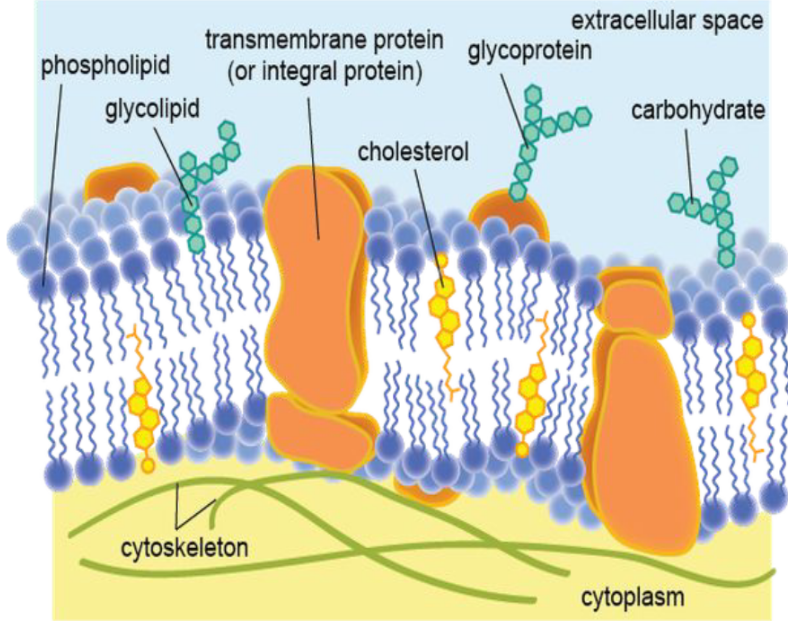
Membrane Proteins - Mosaic Part: Peripheral proteins
Proteins bound to the surface of the membrane
12
New cards
Membrane Proteins - Mosaic Part: Lipid-Anchored Proteins
Proteins located on the surface of the cell membrane that are attached to the lipids within the cell membrane
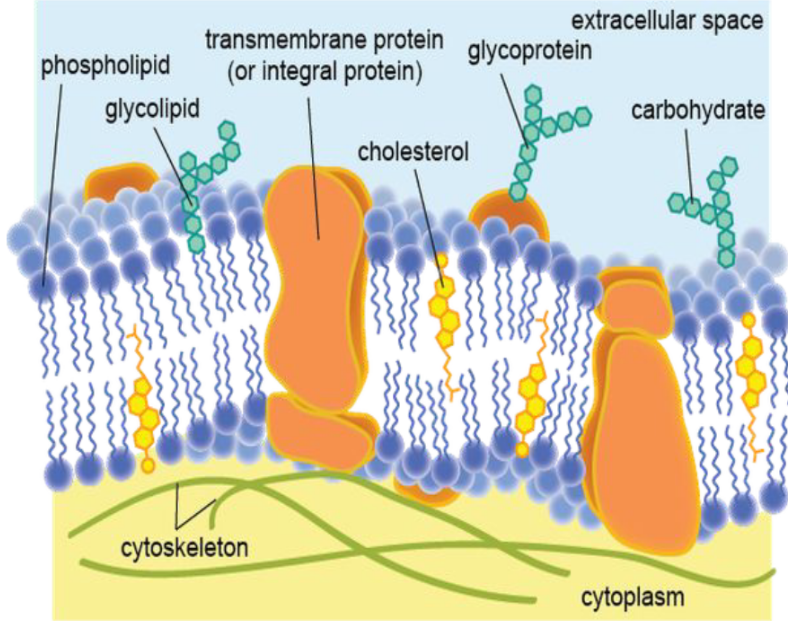
13
New cards
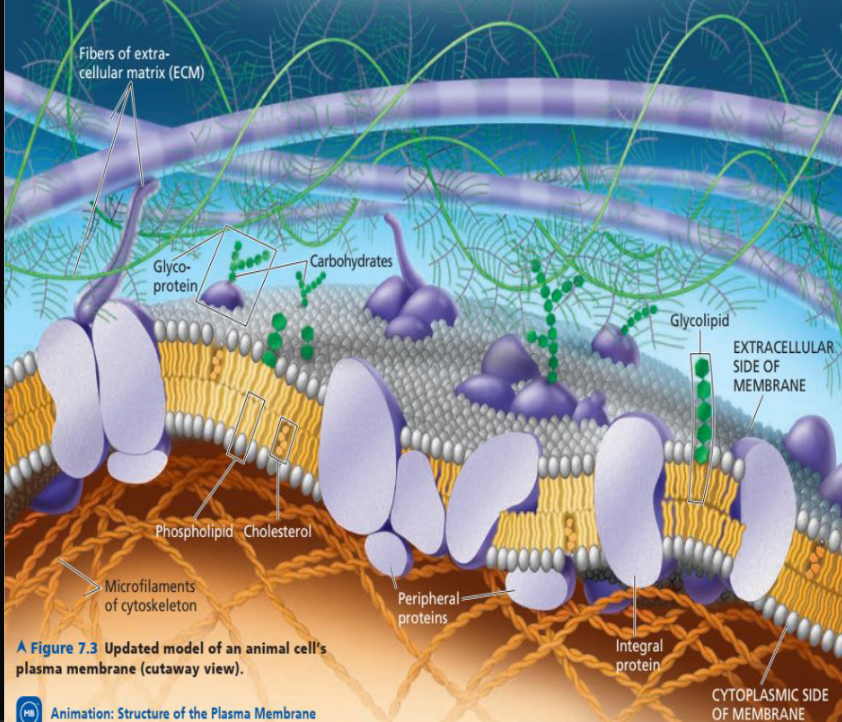
Cell to Cell Recognition: Glycolipids
Carbohydrate groups attached to lipids
14
New cards
Cell to Cell Recognition: Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate groups attached to proteins for cell recognition
15
New cards
Membrane Proteins
Are classified according to their mode of attachment to the membrane as integral membrane proteins (a-d), peripheral membrane proteins (e), or lipid-anchored membrane proteins (f-g).
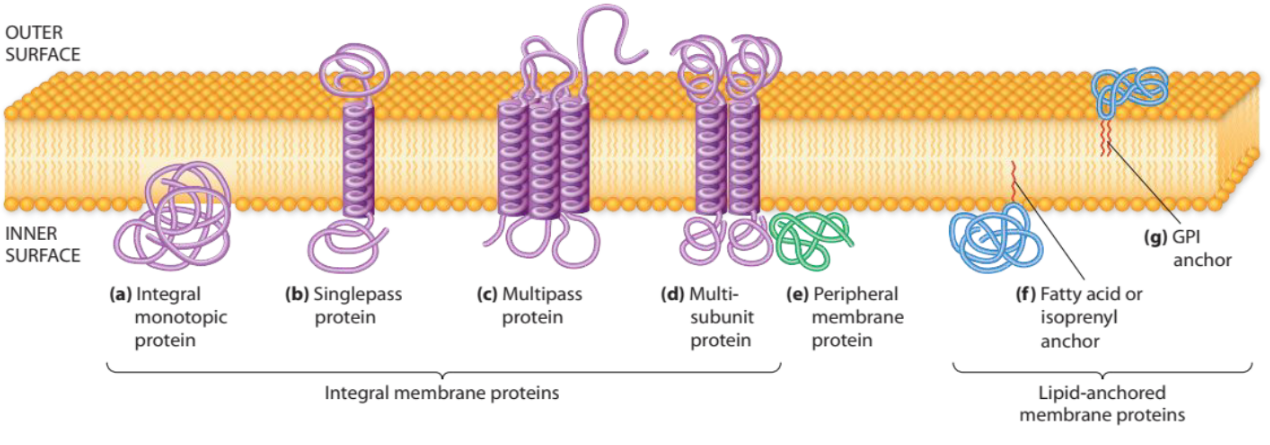
16
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Channel Proteins
Allows only one or a few types of specific molecules to move across
Ex: Aquaporins
Ex: Aquaporins
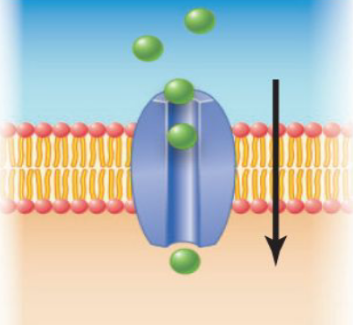
17
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Carrier proteins
Moves substances across the membrane
changes shape as solutes pass through.
changes shape as solutes pass through.
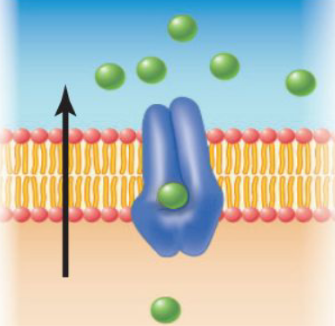
18
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Enzymatic Activity
Enzymatic proteins directly participate in metabolic reactions
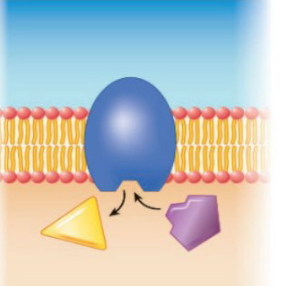
19
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Adhesion Proteins
The junctions assist cell to cell adhesion and communication
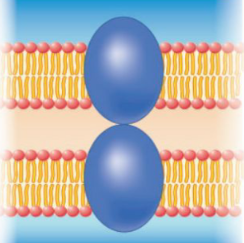
20
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Glycoproteins
Enable our bodies to distinguish between our own cells and others
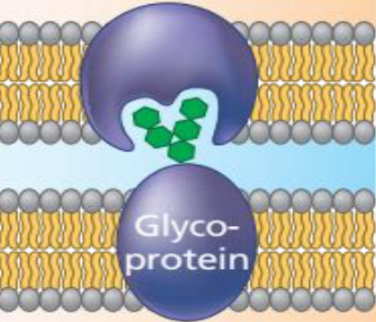
21
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Receptor Proteins
Has a shape that allows a specific molecule, called a signal molecule to bind to it.
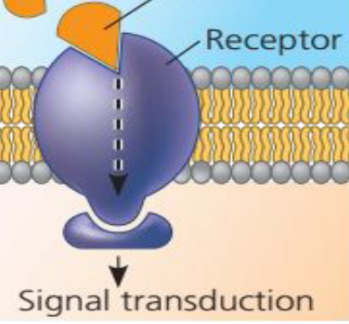
22
New cards
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)
Microfilaments of the cytoskeleton may be bound to membrane proteins to maintain cell shape and stabilize the location of certain membrane proteins.
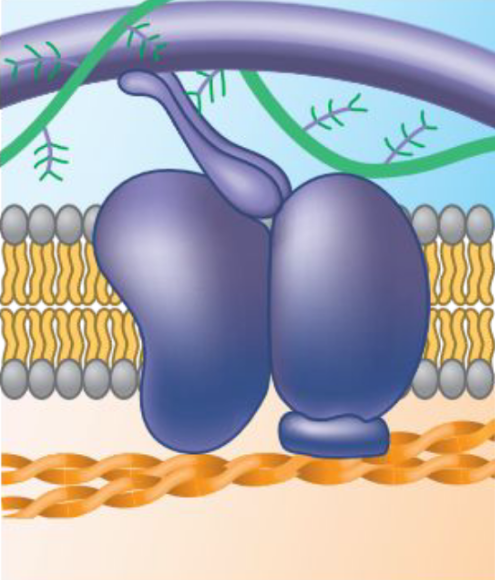
23
New cards
Fluidity of Membrane
Membranes are not static sheets of molecules locked rigidly in place.
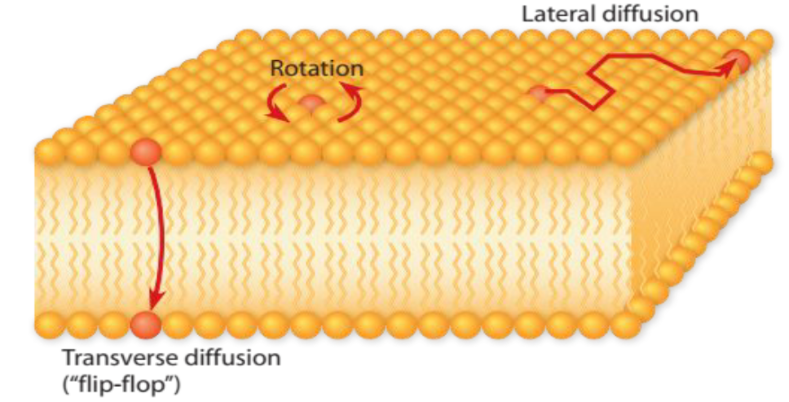
24
New cards
Do Membrane Proteins Move?
Movement of membrane proteins are slower compared to lipids and are restricted to a limited area of the membrane.
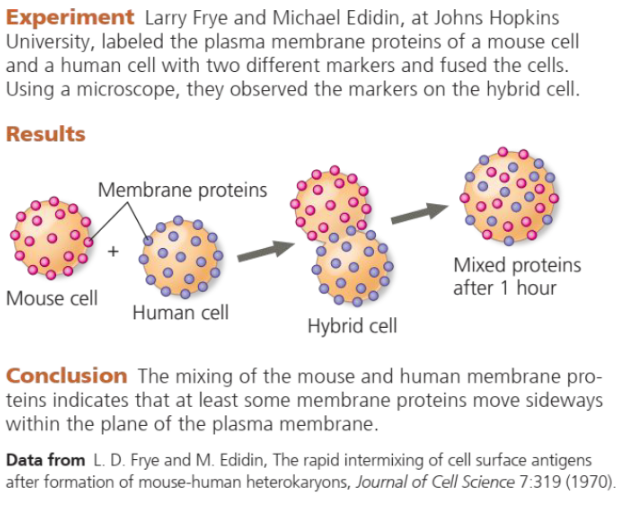
25
New cards
Factors Affecting Membrane Fluidity: Double Bonds
Because of the kinks in fatty acid chains where double bonds are located, unsaturated hydrocarbon tails cannot pack closely together, thus making the membrane more fluid
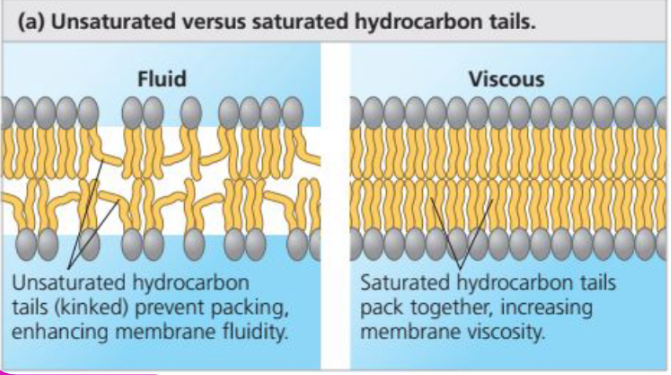
26
New cards
Factors Affecting Membrane Fluidity: Steroids
The steroid cholesterol, which is wedged between phospholipid molecules in the plasma membranes of animal cells, has different effects on membrane fluidity at different temperatures
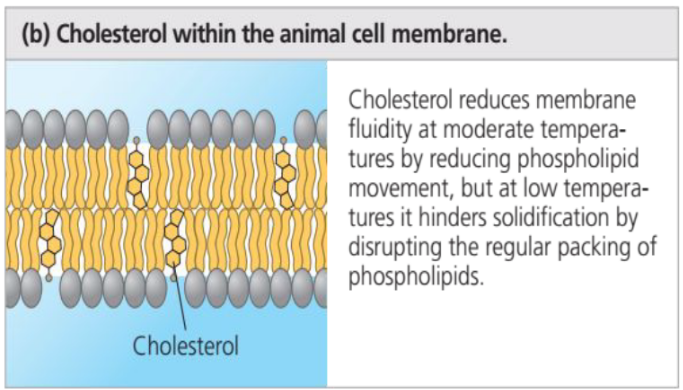
27
New cards
Evolution of Differences in Membrane Lipid Composition
Extreme environments pose a challenge for life, resulting in evolutionary adaptations that include differences in membrane lipid composition.

28
New cards
Most Organisms can Regulate Membrane Fluidity
• Most organisms can regulate membrane fluidity, primarily by changing the lipid composition of their membranes.
• An ability that is important for "cold-blooded" organisms
• An ability that is important for "cold-blooded" organisms

29
New cards
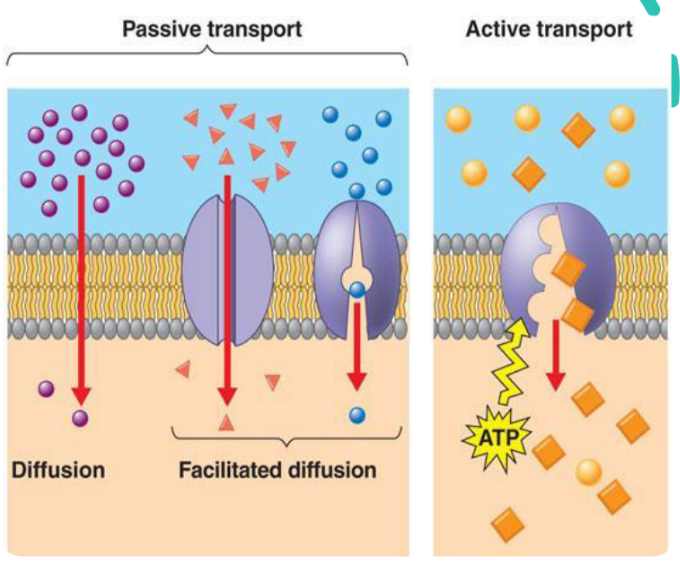
Passive Transport
A substance moves across a membrane without the direct expenditure of energy.
• Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, and Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion is considered a passive transport because the solute is moving down its concentration gradient, a process that requires no energy.
• Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, and Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion is considered a passive transport because the solute is moving down its concentration gradient, a process that requires no energy.
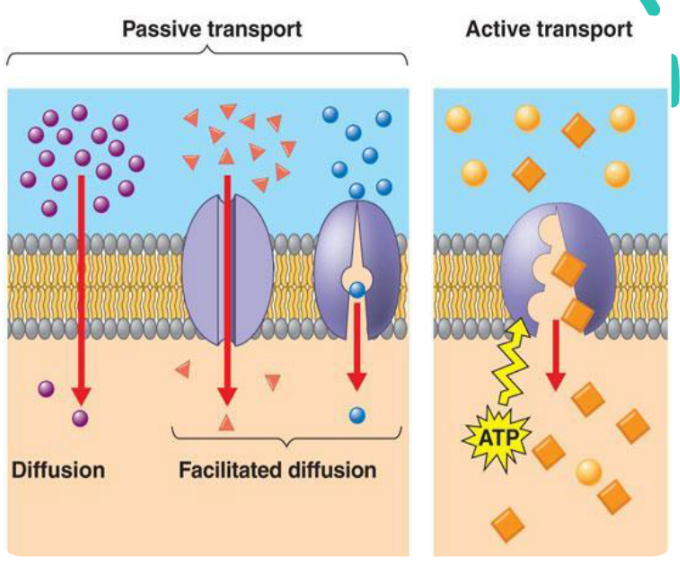
30
New cards
Active Transport
A cell uses a transport protein to move a concentration substance against its gradient from where it is less concentrated to where it is more concentrated
• Sodium-Potassium Pump
• Sodium-Potassium Pump
31
New cards
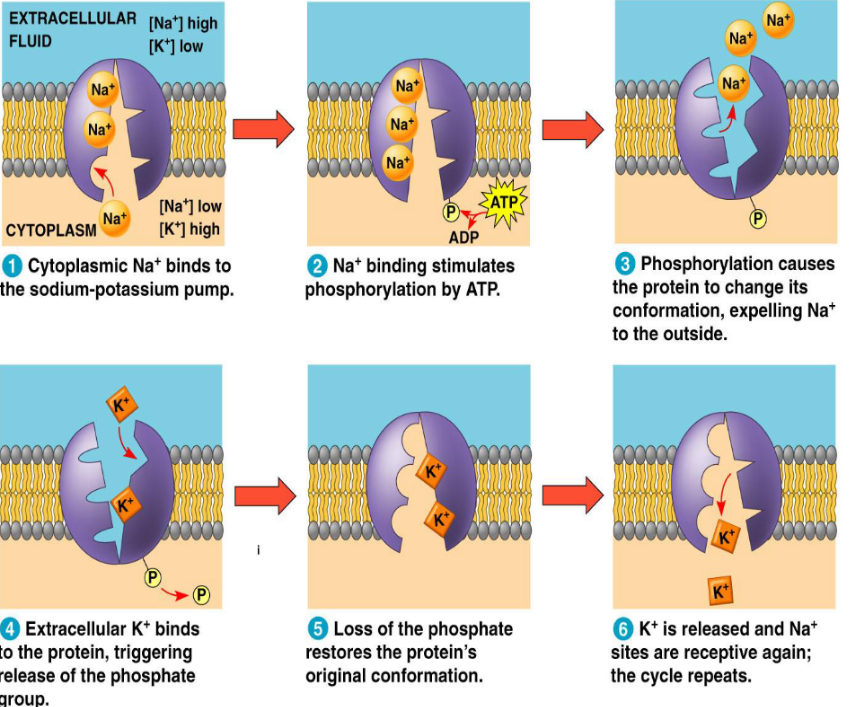
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Cells must contain high concentrations of potassium (K+) and low concentrations of sodium (Na+) to perform many functions.
32
New cards
Other examples of active transport
In Plants :
● lons moving from soil into plant roots
● Minerals traveling through a stem to various parts of the plant
● Sugars from photosynthesis moving from leaves to fruit
In Animals :
● Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract
● Glucose moving in or out of a cell
● Enzyme secretion
● Release of antibodies
● lons moving from soil into plant roots
● Minerals traveling through a stem to various parts of the plant
● Sugars from photosynthesis moving from leaves to fruit
In Animals :
● Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract
● Glucose moving in or out of a cell
● Enzyme secretion
● Release of antibodies

33
New cards
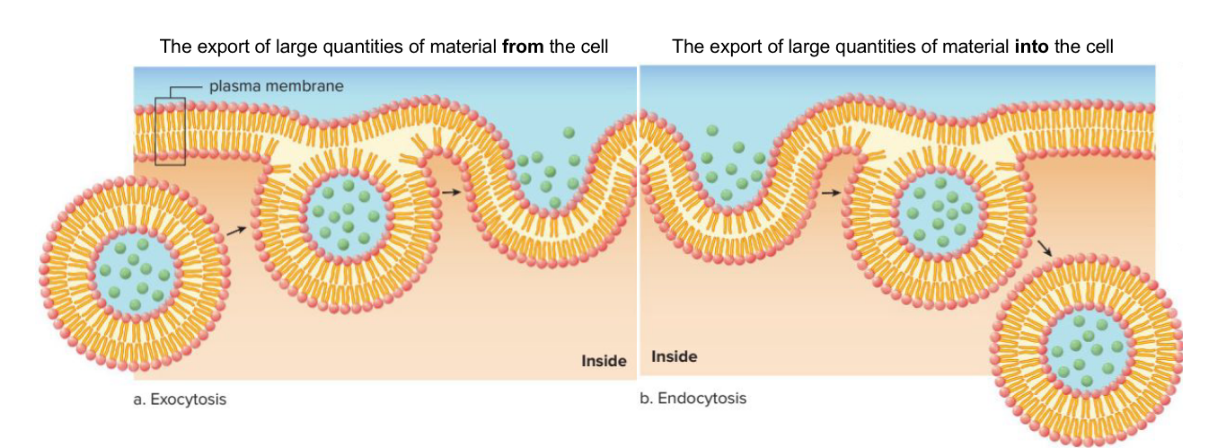
Bulk Transport
Macromolecules are often too large to be moved by transport proteins, so vesicles are formed
(Use vesicles to transport substances)
• Endocytosis and Exocytosis
(Use vesicles to transport substances)
• Endocytosis and Exocytosis
34
New cards
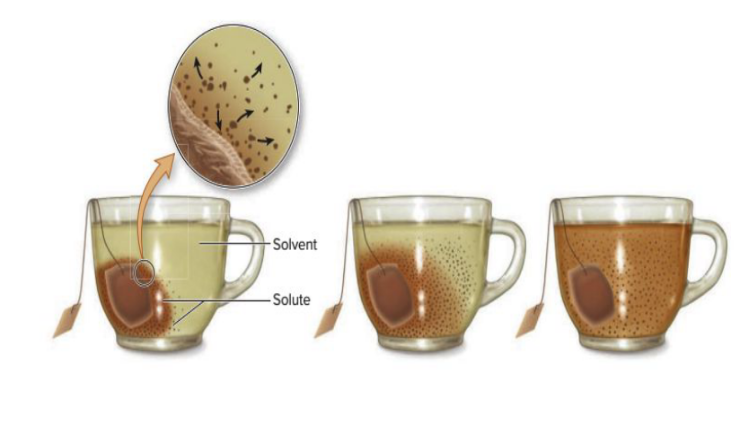
Simple Diffusion
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of a substance from a region where it is more concentrated to a region where it is less concentrated.
Substances may enter or leave cells by simple diffusion only if they can pass freely through the membrane
Substances may enter or leave cells by simple diffusion only if they can pass freely through the membrane

35
New cards
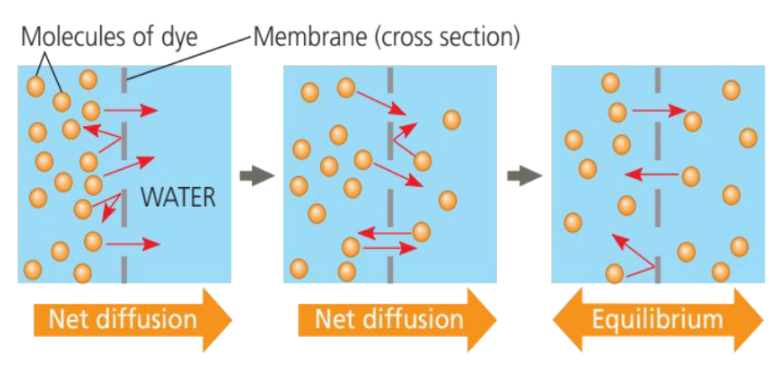
Diffusion of one Solute
Diffusion also occurs across membranes.
Random movement of dye molecules will cause some to pass through the pores; this will happen more often on the side with more dye molecules.
Random movement of dye molecules will cause some to pass through the pores; this will happen more often on the side with more dye molecules.
36
New cards
Diffusion of two solutes
Note that each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, unaffected by the concentration gradients of other substances
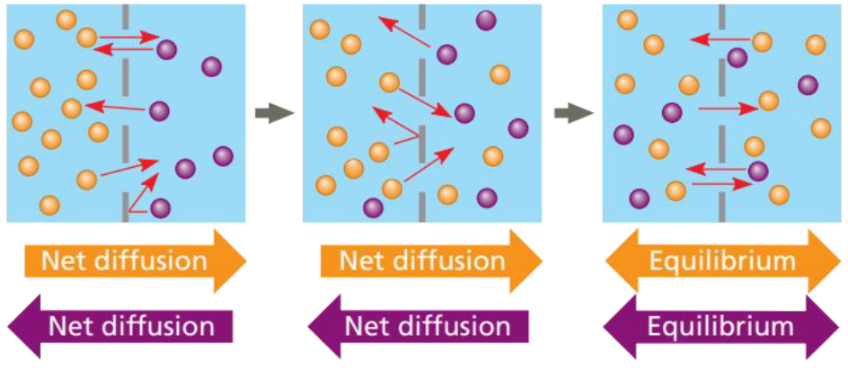
37
New cards
Osmosis
Solvent molecules move from low to high solute concentration
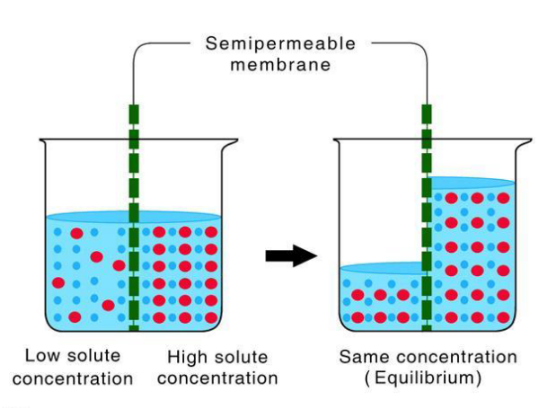
38
New cards
Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
Water diffuses across the membrane from the region of higher free water concentration (lower solute concentration) to that of lower free water concentration (higher solute concentration) until the solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane are more nearly equal.
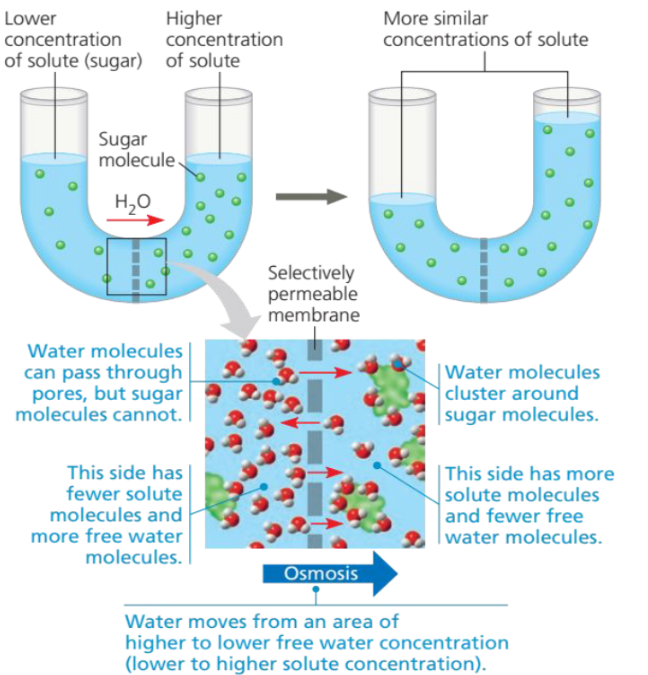
39
New cards
Effects of Osmosis on Cells
Tonicity is the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.
● Hypo (less than)
● Iso (same as)
●Hyper (more than)
● Hypo (less than)
● Iso (same as)
●Hyper (more than)
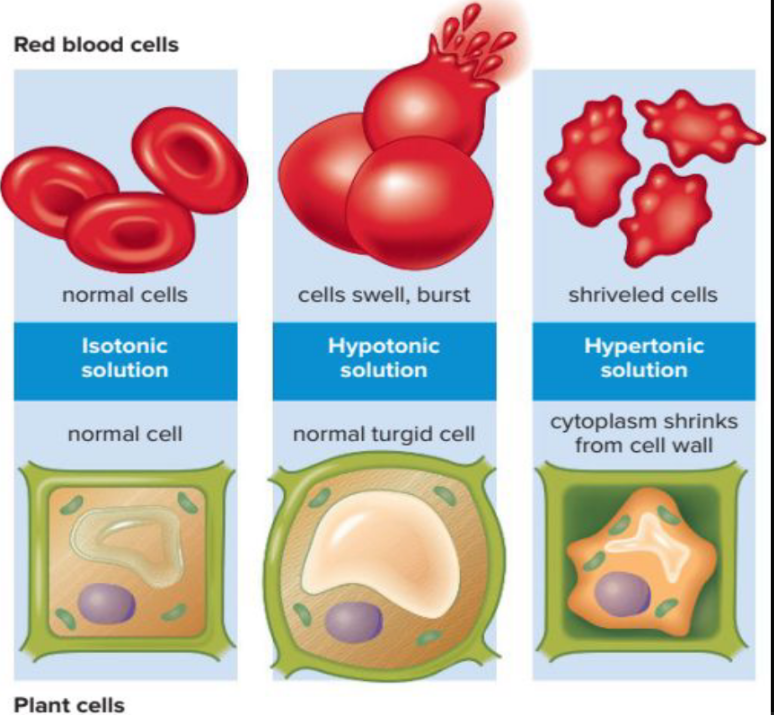
40
New cards
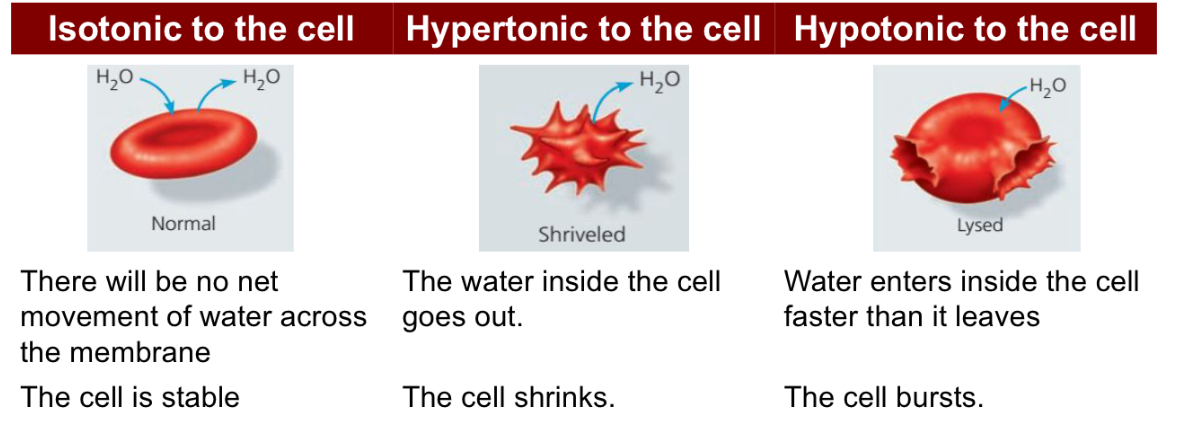
Effect of Osmosis on Animal Cells
There will be no net movement of water across the membrane
The cell is stable
The water inside the cell goes out.
The cell shrinks.
Water enters inside the cell faster than it leaves
The cell bursts.
The cell is stable
The water inside the cell goes out.
The cell shrinks.
Water enters inside the cell faster than it leaves
The cell bursts.
41
New cards
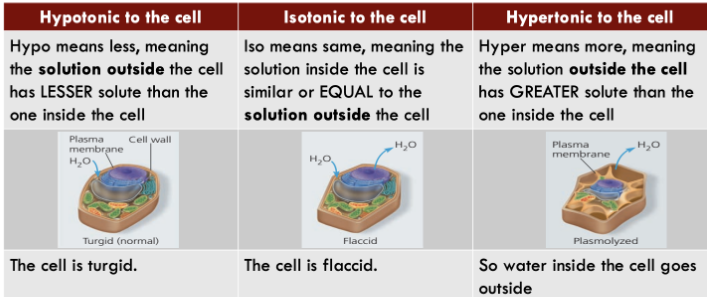
Osmosis in Plant Cells
Hypo means less, meaning the solution outside the cell has LESSER solute than the one inside the cell
Iso means same, meaning the Hyper means more, meaning solution inside the cell is the solution outside the cell
similar or EQUAL to the has GREATER solute than the solution outside the cell one inside the cell
Iso means same, meaning the Hyper means more, meaning solution inside the cell is the solution outside the cell
similar or EQUAL to the has GREATER solute than the solution outside the cell one inside the cell
42
New cards
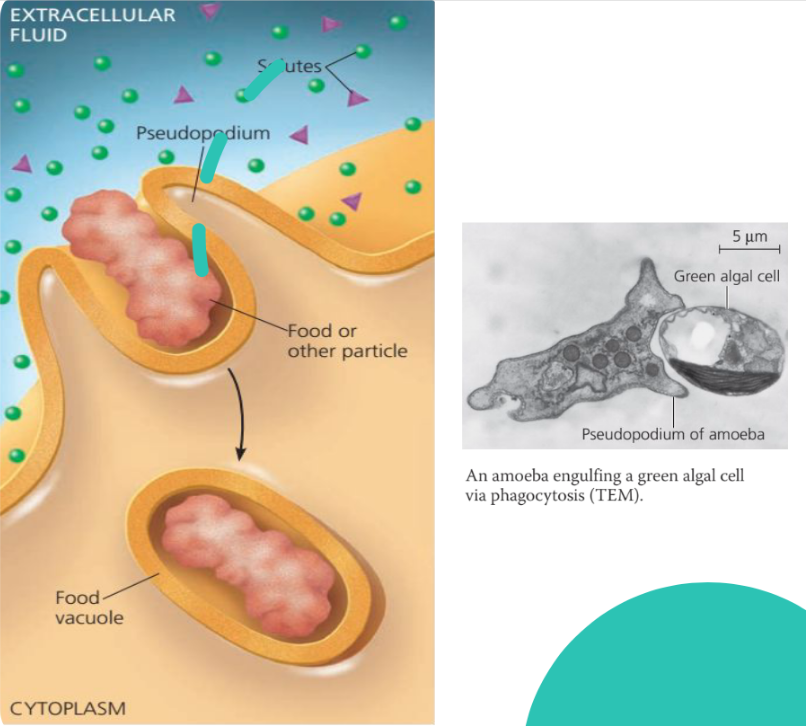
Phagocytosis
● Also known as cellular-eating
● Cell engulfs a particle by extending pseudopodia around it and packaging it within a membranous sac called a food vacuole.
● Cell engulfs a particle by extending pseudopodia around it and packaging it within a membranous sac called a food vacuole.
43
New cards
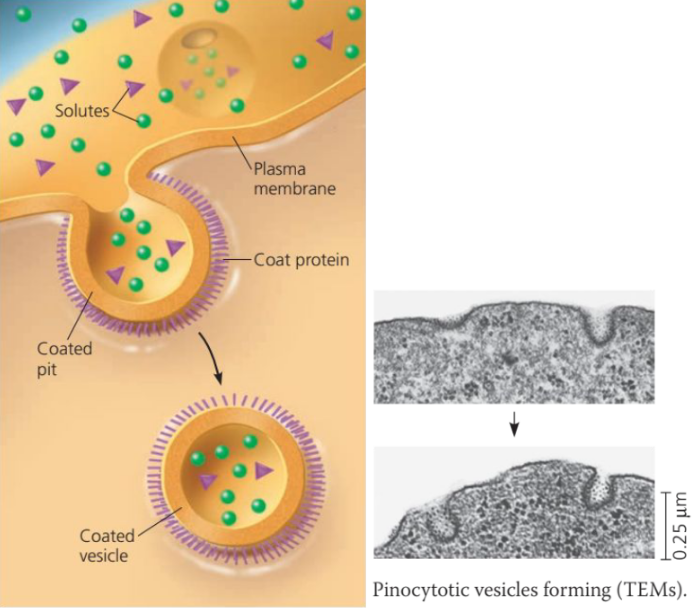
Pinocytosis
• Also known as cell drinking
• This occurs when vesicles form around a liquid or around very small particles.
• This occurs when vesicles form around a liquid or around very small particles.
44
New cards
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
A form of endocytosis in which receptor proteins on the cell surface are used to capture a specific target molecule.
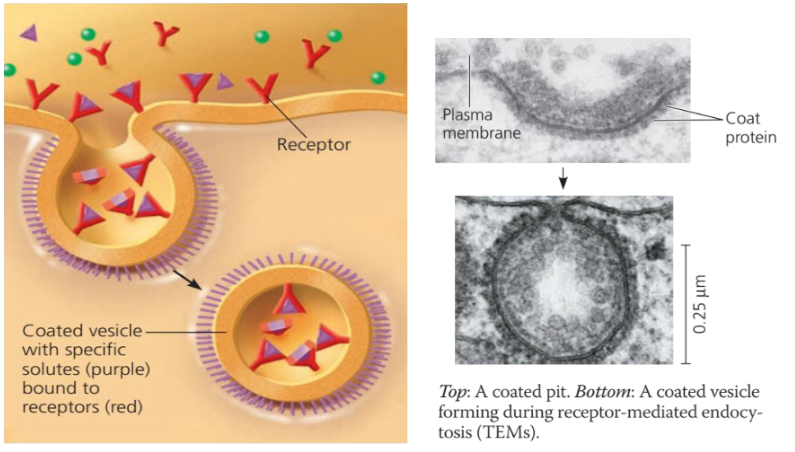
45
New cards
Biomolecules
Compounds can be classified into two types:
- Organic (living, proteins carbs, lipids, nucleic acid)
- Inorganic (non living, water, acid, bases, salts, co2)
- Organic (living, proteins carbs, lipids, nucleic acid)
- Inorganic (non living, water, acid, bases, salts, co2)
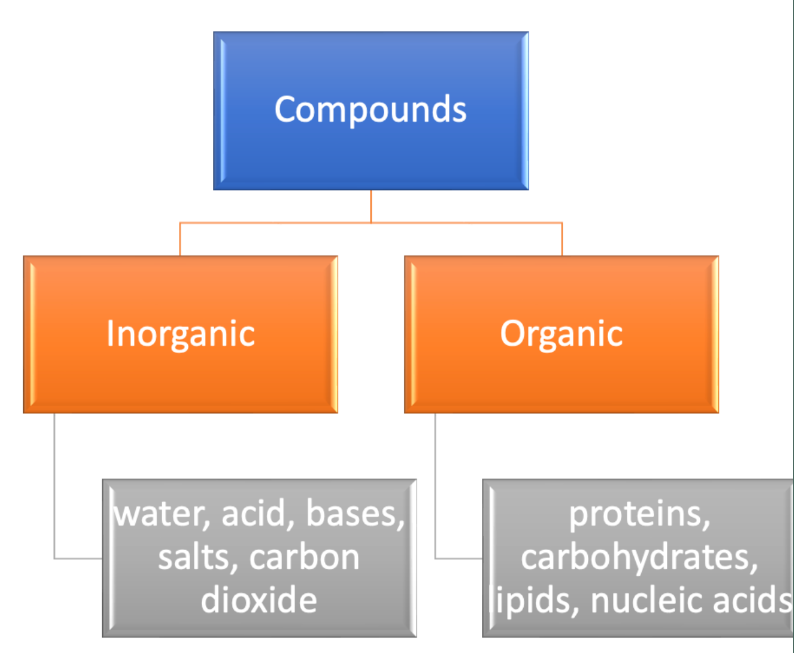
46
New cards
Element
- the simplest form of substance that cannot be simplified into another form.
- Major elements that makeup living systems: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Calcium
- Major elements that makeup living systems: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Calcium

47
New cards
Compounds
a substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined together
Compounds in Living Systems: Inorganic & Organic
Compounds in Living Systems: Inorganic & Organic

48
New cards
Inorganic Compounds
• any substance in which two or more chemical elements (usually other than carbon) are combined, nearly always in definite proportions
• water, acids, bases, electrolytes, carbon dioxide
• water, acids, bases, electrolytes, carbon dioxide
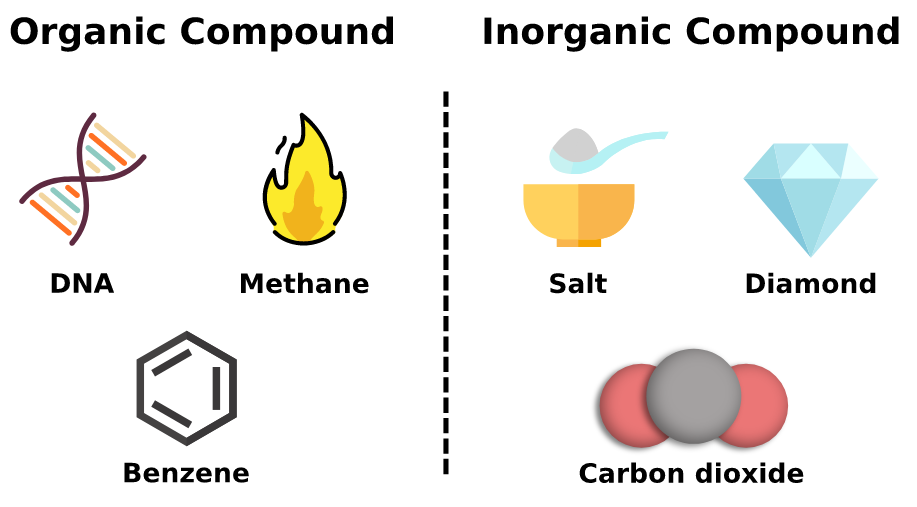
49
New cards
Water
The Universal and Versatile Solvent
- Most common biological solvent, (dissolves an enormous variety of solutes necessary for living)
- Can exist in nature as solid, liquid, gaseous states
- Most common biological solvent, (dissolves an enormous variety of solutes necessary for living)
- Can exist in nature as solid, liquid, gaseous states

50
New cards
Characteristics of Water: Biological solvent
ability to dissolve many substances including essential molecules in the body
51
New cards
Characteristics of Water: High heat capacity
A large amount of heat is needed to increase the temperature. It helps in maintaining a constant body.
52
New cards
Characteristics of Water: High heat of vaporization
Helps in preventing dehydration in an organism
53
New cards
Characteristics of Water: High heat of fusion
helps organism from freezing at a low temperature
54
New cards
Characteristics of Water: Medium for chemical and physical processes
can serve as a place for exchanging gases and nutrients, and elimination of waste
55
New cards
Characteristics of Water: Means of transport
Can serve as a transporter/vehicle in the distribution of nutrients gases and collection of waste product all throughout the body
56
New cards
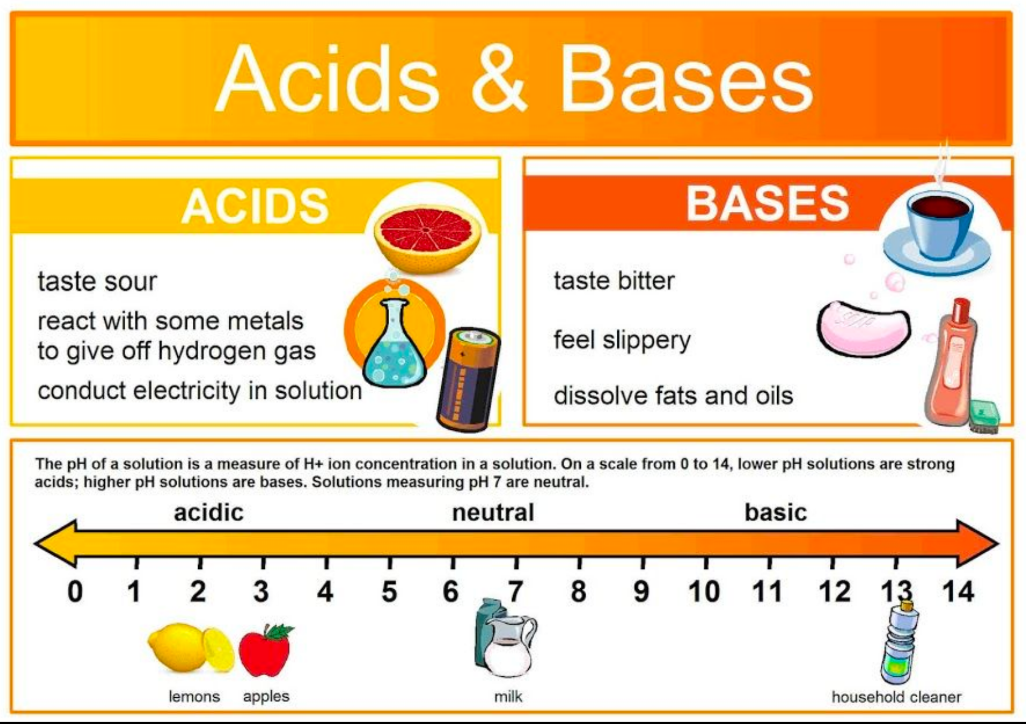
Acids
Taste sour, change the color of certain indicators
• react with some metals and bases
• promote chemical reactions (acid catalysis) in a water solution
• Ex: acetic acid, ascorbic acid, citric acid, carbonic acid, hydrochloric acid
• ptt: 2-4
• react with some metals and bases
• promote chemical reactions (acid catalysis) in a water solution
• Ex: acetic acid, ascorbic acid, citric acid, carbonic acid, hydrochloric acid
• ptt: 2-4
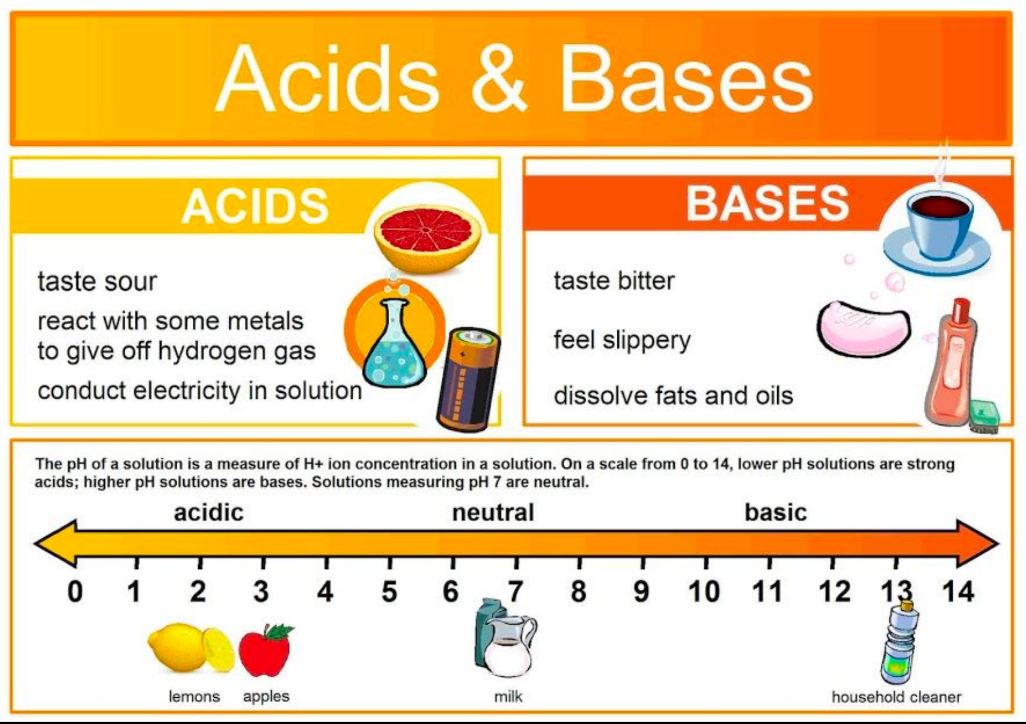
57
New cards
Bases
• bitter, slippery in consistency
• turns litmus paper to blue
• i.e. sodium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide, some antacids
• turns litmus paper to blue
• i.e. sodium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide, some antacids
58
New cards
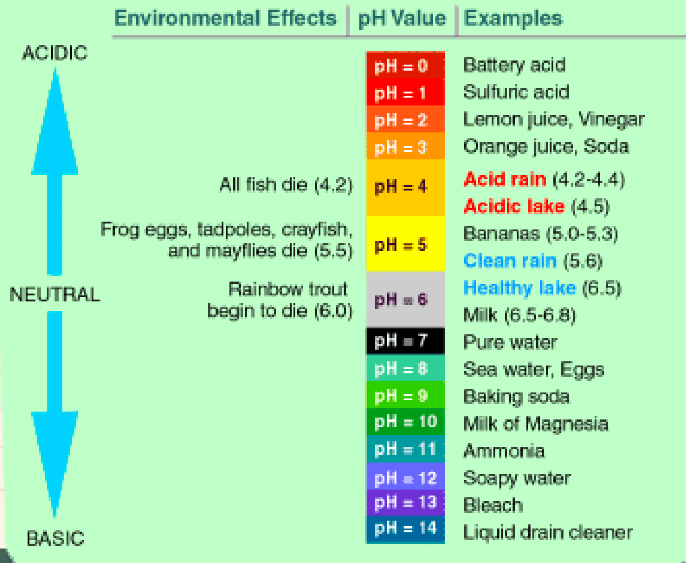
pH Scale
used to describe the acidity and basicity of a solution. (6 and lower = more acidic, 7 - pure water, 8 and higher = more basic)
59
New cards
Electrolytes
● can conduct electricity within the body
● cations - positively charged
● anions – negatively charged
● important in maintaining voltages in cell membrane
• sends electrical impulses in nerve cells and muscle cells
● cations - positively charged
● anions – negatively charged
● important in maintaining voltages in cell membrane
• sends electrical impulses in nerve cells and muscle cells
60
New cards
Carbon Dioxide
● plants : important for photosynthesis
● animals : waste product from the breakdown of glucose
● a by-product in ethanol production (fermentation)
● animals : waste product from the breakdown of glucose
● a by-product in ethanol production (fermentation)
61
New cards
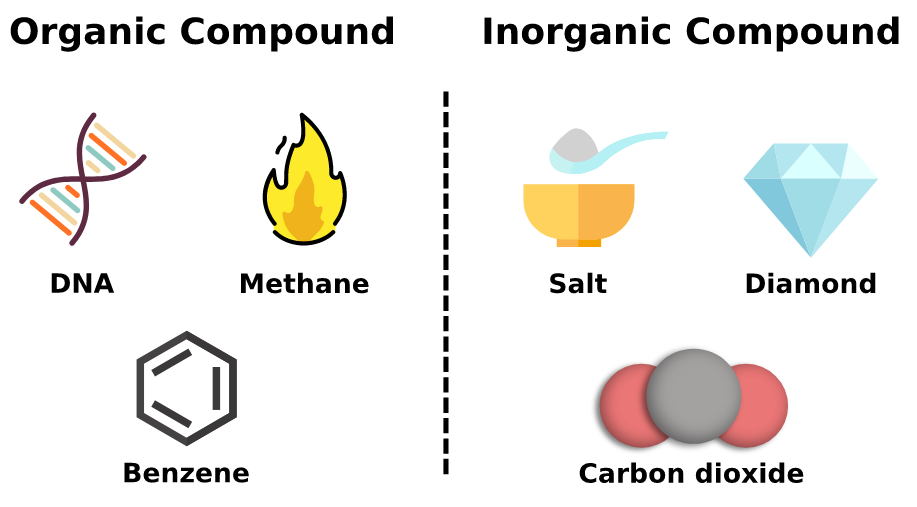
Organic Compounds
● contain carbon (except for carbon dioxide)
•● aka macromolecules - made up of hundreds or thousands of atoms
o individual units: monomers
● Types: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid
•● aka macromolecules - made up of hundreds or thousands of atoms
o individual units: monomers
● Types: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid
62
New cards
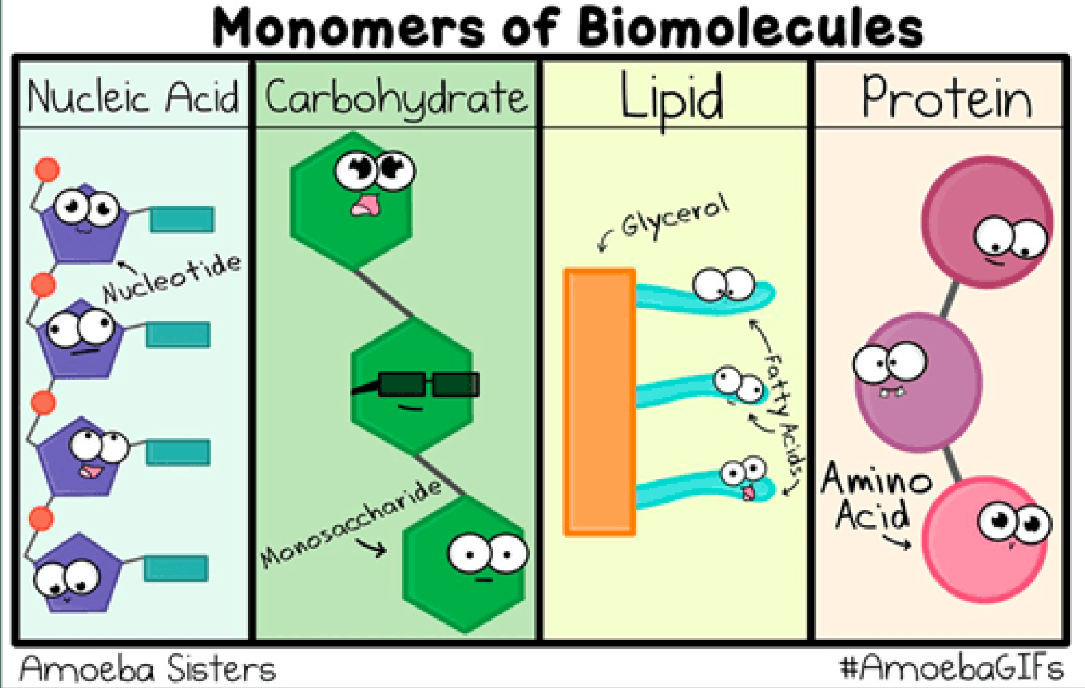
Monomers of Biomolecules
Nucleic Acid, Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein
63
New cards
Proteins
• most abundant
• proteios (greek) - first place
• monomer: amino acids
• serve as gene activators, membrane receptors, transporter, clotting factors, etc.
• proteios (greek) - first place
• monomer: amino acids
• serve as gene activators, membrane receptors, transporter, clotting factors, etc.
64
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Structural proteins
- found in the hair of mammals
- makes up tendons and ligaments
- makes up tendons and ligaments
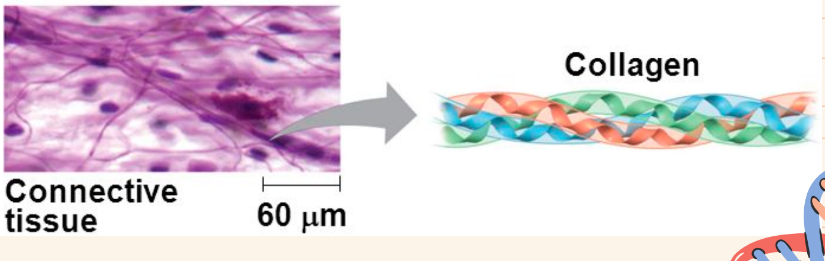
65
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Contractile proteins
- provides muscular movement
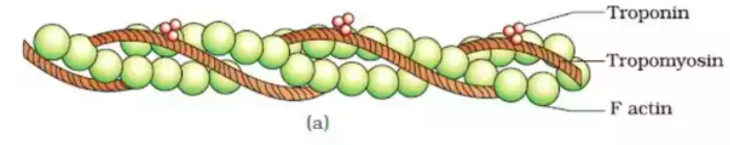
66
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Storage proteins
- serve as biological reserves of metal ions & amino acids used by organisms
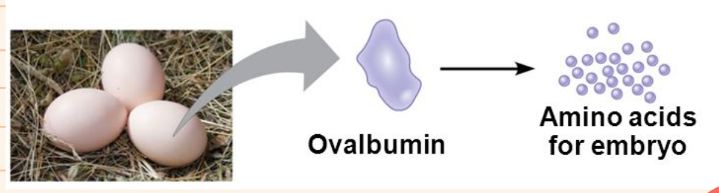
67
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Defensive proteins
- promote protection against foreign bodies
- antibodies
- antibodies
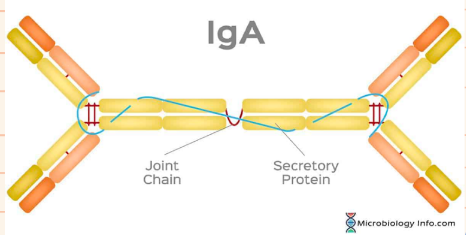
68
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Transport proteins
- serves the function of moving other materials within an organism
enzyme
enzyme
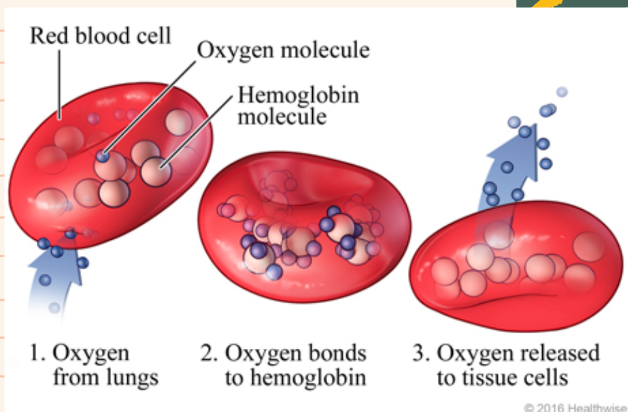
69
New cards
Classes of Proteins: Signal proteins
- hormones, insulin, enkephalins
- communicates with the rest of the body w/o blood vessels
Enkephalins
- found in the thalamus; help moderate pain by suppressing pain signals in the brain.
Insulin
- produced by the pancreas; allows your body to use glucose for energy and store it for later use.
Thyroid hormones
- important for the proper development of brain, skeleton, and organs.
- communicates with the rest of the body w/o blood vessels
Enkephalins
- found in the thalamus; help moderate pain by suppressing pain signals in the brain.
Insulin
- produced by the pancreas; allows your body to use glucose for energy and store it for later use.
Thyroid hormones
- important for the proper development of brain, skeleton, and organs.
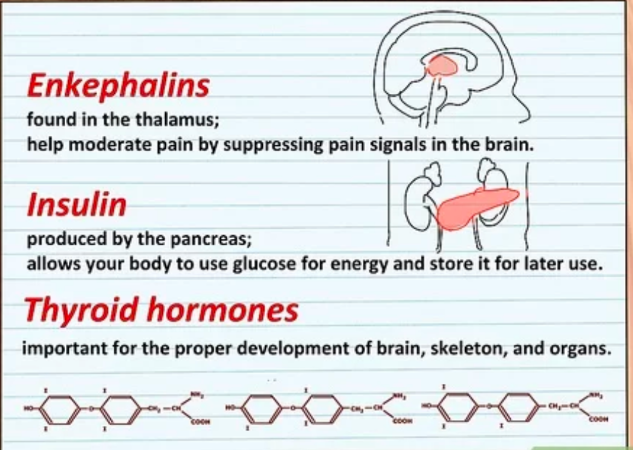
70
New cards
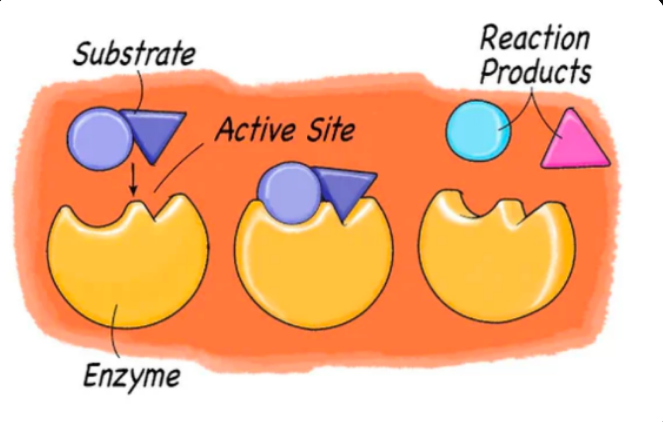
Enzyme
- serves as chemical catalyst, changes rate of reaction
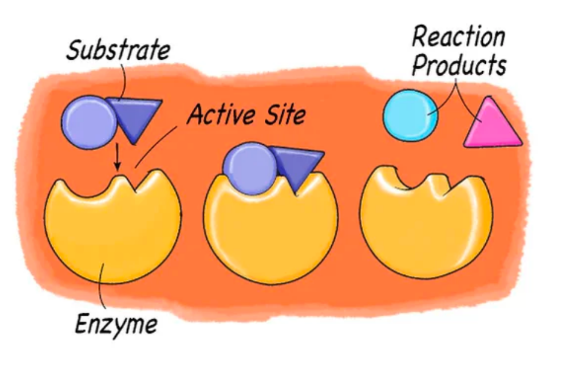
71
New cards
Substrate
the substance on which an enzyme operates
72
New cards
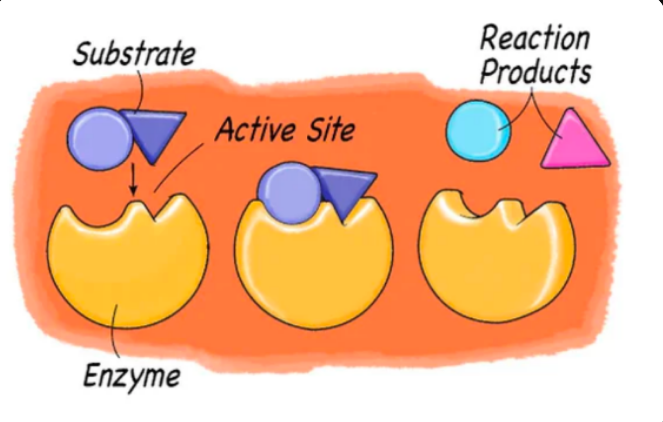
Active site
proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies
73
New cards
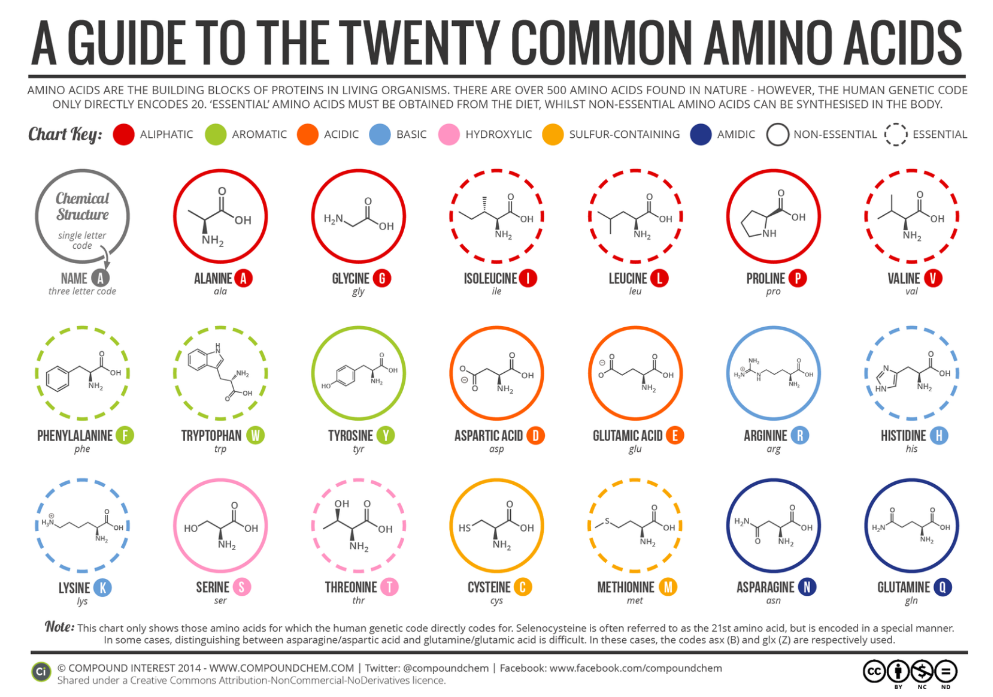
A GUIDE TO THE TWENTY COMMON AMINO ACIDS
74
New cards
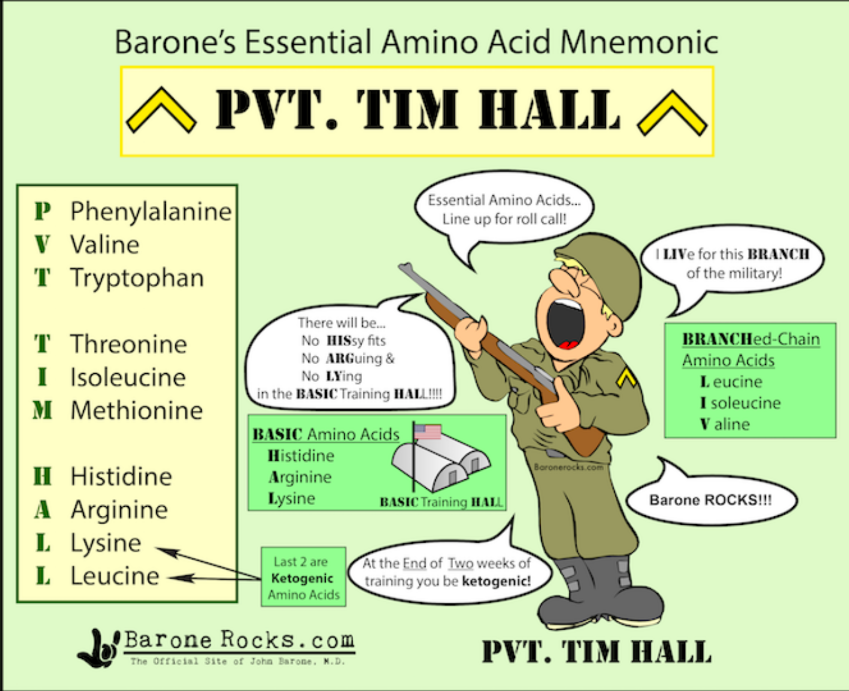
Barone's Essential Amino Acid Mnemonic ^ PVT. TIM HALL ^
75
New cards
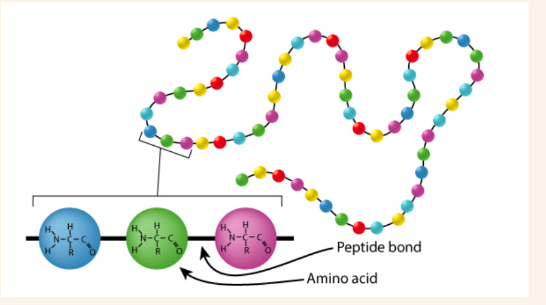
Primary structure
• shows the sequence of amino acids forming polypeptide chains
• attached together by covalent or peptide bonds done during translation
• one line of amino acids
• done via translation in protein synthesis
• attached together by covalent or peptide bonds done during translation
• one line of amino acids
• done via translation in protein synthesis
76
New cards
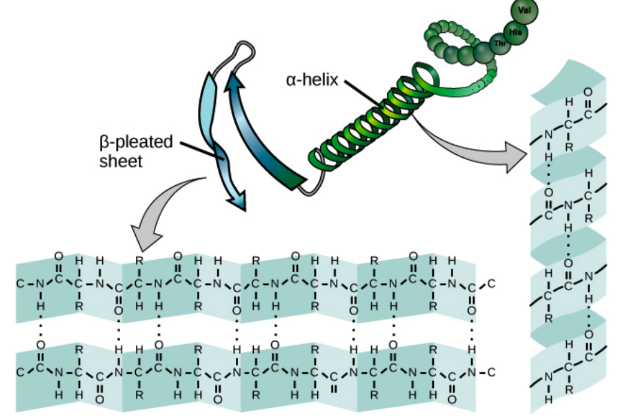
Secondary structure
• highly regular substructure
• can be alpha helix or beta strand
• defined by #/H bonds between the main chain peptide groups
• in a form of a helix
• can be alpha helix or beta strand
• defined by #/H bonds between the main chain peptide groups
• in a form of a helix
77
New cards
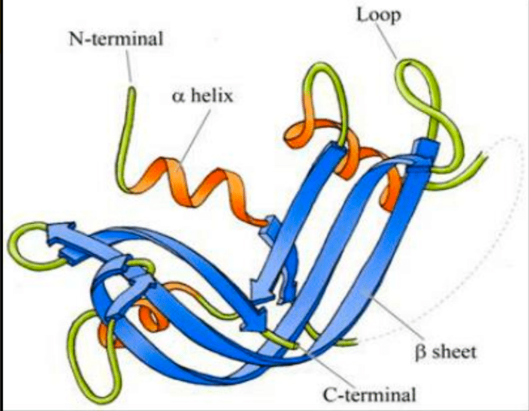
Tertiary structure
• overall 3D shape of polypeptide by a pattern of folding driven by hydrophobic interactions
• alpha helices and beta sheets are folded into a compact globule
• complicated
• alpha helices and beta sheets are folded into a compact globule
• complicated
78
New cards
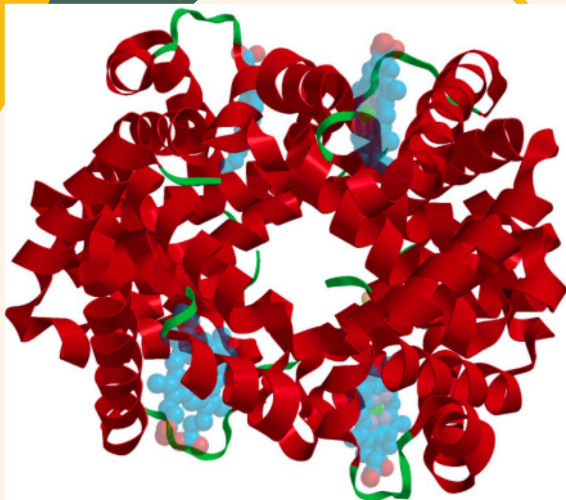
Quaternary structure
• arrangement of multiple folded protein or coiling protein molecules in a multi-subunit complex
79
New cards
Carbohydrates
• class molecules ranging from small sugar subunits to large polypeptides
• main source of energy for living organisms
• contains Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
• groups : monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide
• main source of energy for living organisms
• contains Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
• groups : monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide
80
New cards
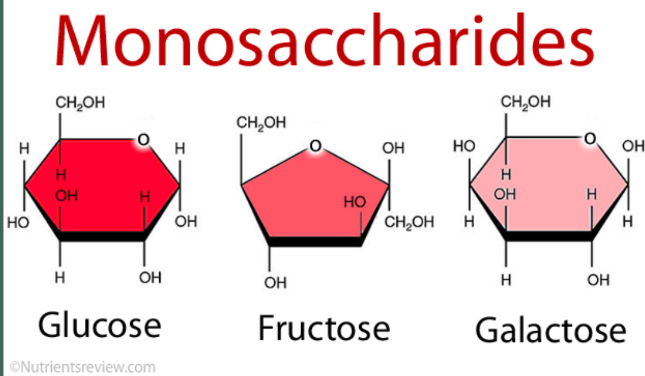
Monosaccharides
• Simple sugars
• 1 sugar unit
• glucose, fructose, galactose
• serve as starting material for some organic molecules such as fat
• 1 sugar unit
• glucose, fructose, galactose
• serve as starting material for some organic molecules such as fat
81
New cards
Disaccharide
• complex sugar
• made up of 2 molecules joined together
• sucrose (glucose fructose), maltose (glucose2), lactose (galactose glucose)
• made up of 2 molecules joined together
• sucrose (glucose fructose), maltose (glucose2), lactose (galactose glucose)
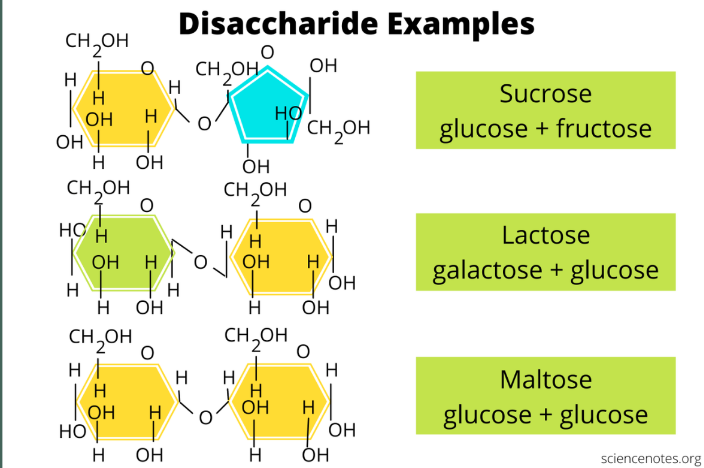
82
New cards
Polysaccharides
• complex sugar
• made up of chains/branches of monosaccharide
• storage and structure
• examples: starches
• made up of chains/branches of monosaccharide
• storage and structure
• examples: starches
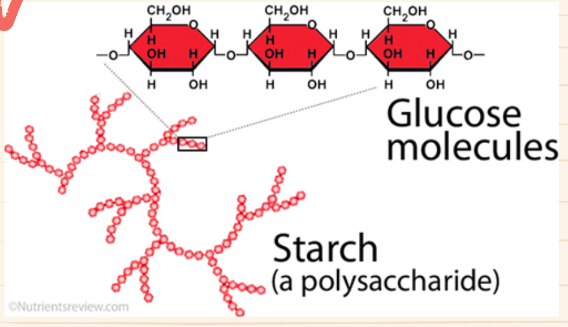
83
New cards
Lipids
• from lipos (greek) - fat
• includes fats and fat-like substances (phospholipid, wax, steroid, etc.)
• consists of Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen
• includes fats and fat-like substances (phospholipid, wax, steroid, etc.)
• consists of Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen
84
New cards
Functions of lipids
- store and produce energy
- serve as insulation to prevent heat loss
- protect against extreme cold
- serve as solvent for fat-soluble vitamins and hormones
- prevent water loss in skin
- serve as insulation to prevent heat loss
- protect against extreme cold
- serve as solvent for fat-soluble vitamins and hormones
- prevent water loss in skin
85
New cards
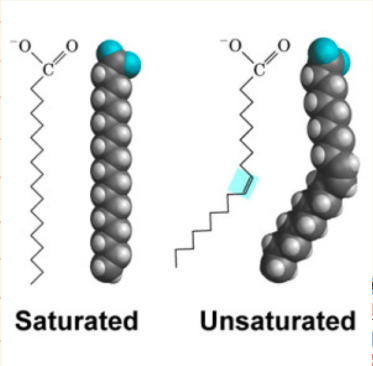
Types of fatty acid
• unsaturated
- liquid at room temperature
- found mostly in plants
- has a double bond
- healthier
•saturated
- solid at room temperature
- mostly found in animals
- no double bonds
- liquid at room temperature
- found mostly in plants
- has a double bond
- healthier
•saturated
- solid at room temperature
- mostly found in animals
- no double bonds
86
New cards
Other examples of lipids
• Wax
• Phospholipids
• steroids
• Phospholipids
• steroids
87
New cards
Wax
- solid of room temperature
- high melting point
- hydrophobic
• plants: protective structure
• animals: skin and fur maintenance
• humans: produced by glands in the outer ear canal
- high melting point
- hydrophobic
• plants: protective structure
• animals: skin and fur maintenance
• humans: produced by glands in the outer ear canal

88
New cards
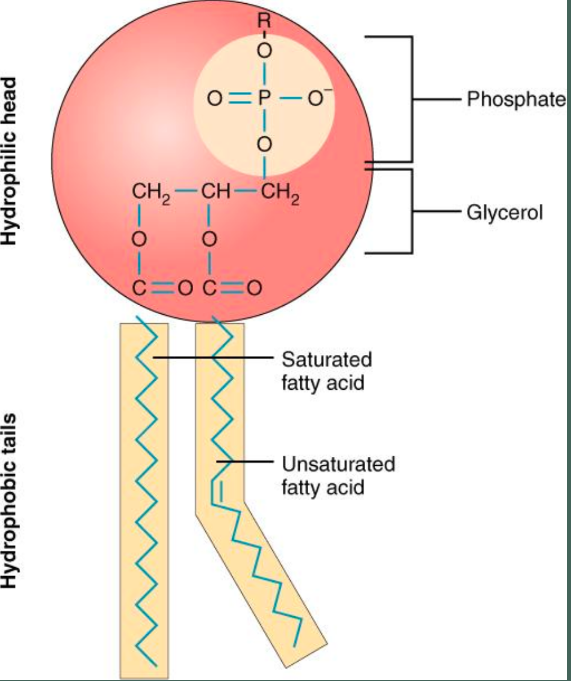
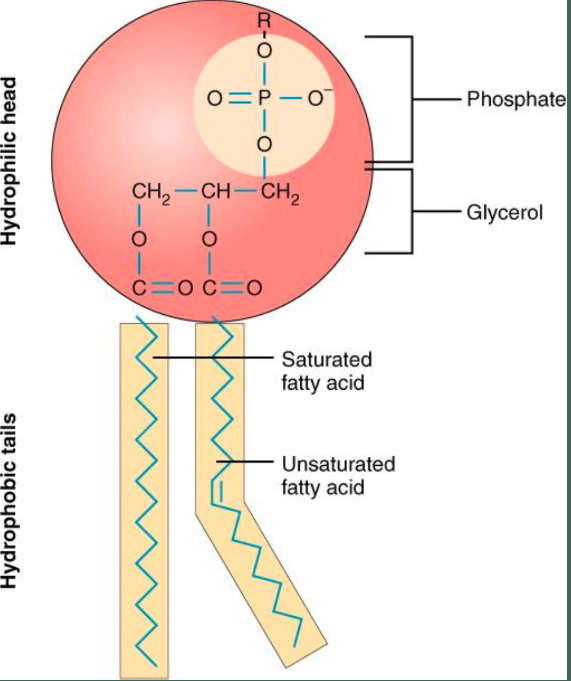
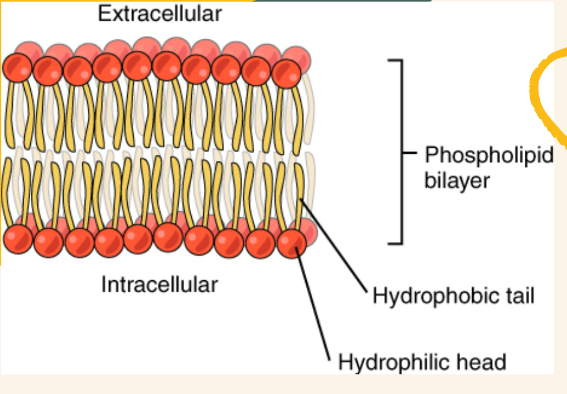
Phospholipids
- a major component of cell membrane
- 2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate group
- responsible for the polar and non-polar characteristics of cell membrane
- 2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate group
- responsible for the polar and non-polar characteristics of cell membrane
89
New cards
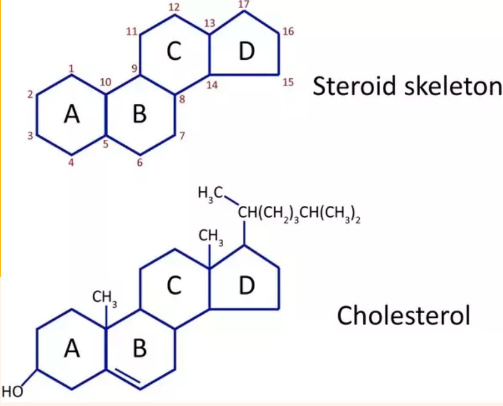
Steroids
- hydrophobic and insoluble in water, don't resemble lipids since they have -
- a structure composed of four fused rings
- cholesterol most common steroid
- a structure composed of four fused rings
- cholesterol most common steroid
90
New cards
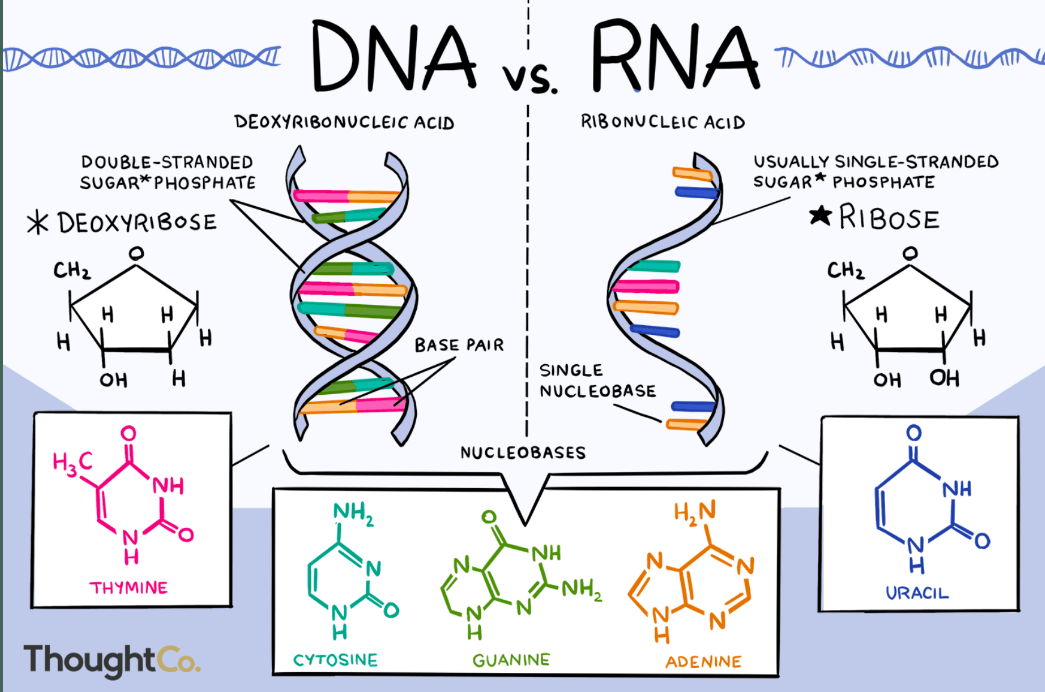
Nucleic acid
- serves as genetic information storage molecule
- provide info to make proteins
- monomer: nucleotide
- types: RNA, DNA
When a phosphate group is broken off the tail of an ATP molecule
(by hydrolysis) the molecule becomes ADP (adenosine
diphosphate). That hydrolysis is an exergonic reaction and it yields
energy. The bonds holding the phosphate onto ATP are weak.
- provide info to make proteins
- monomer: nucleotide
- types: RNA, DNA
When a phosphate group is broken off the tail of an ATP molecule
(by hydrolysis) the molecule becomes ADP (adenosine
diphosphate). That hydrolysis is an exergonic reaction and it yields
energy. The bonds holding the phosphate onto ATP are weak.
91
New cards
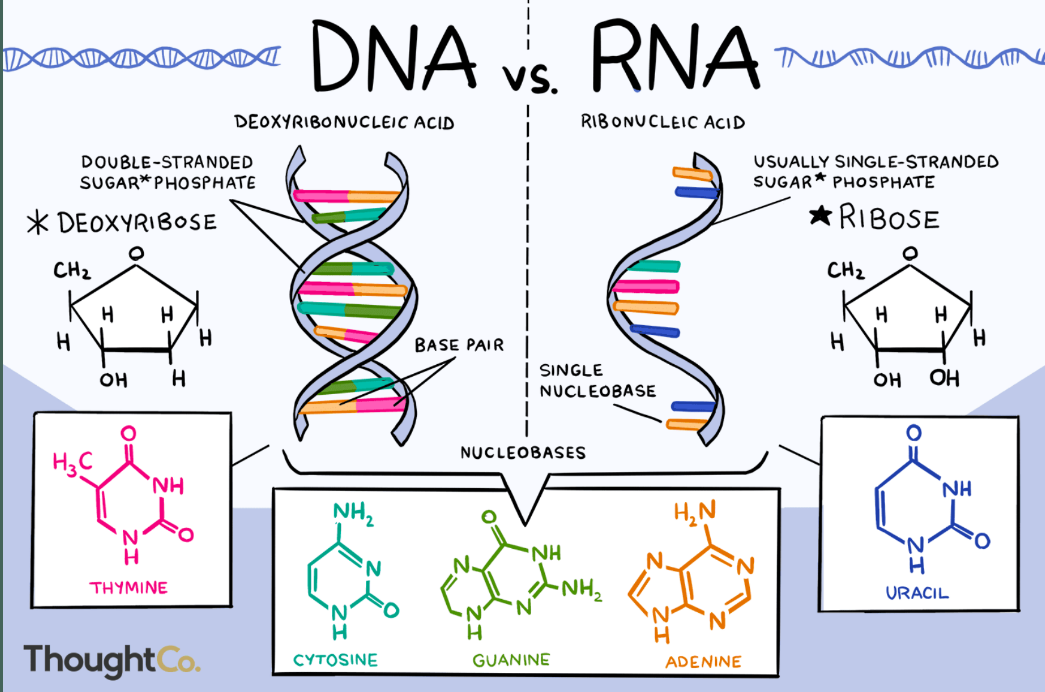
Difference of DNA & RNA
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain
of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which
has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its
own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its
own.
of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which
has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its
own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its
own.