Bio Exam 2 w/ diagrams
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
in order to complete its life history, the malaria protozoan must produce _________ in the salivary glands of the mosquito hostas that are then transferred from the mosquito to the human hose, where they enter the bloodstream
sporozoites
________ are kinetoplast blood parasites that are responsible for Chagas diesease
Trypanosomes
chlorarachnion is an amoeba with filose pseudopodia that also bears chloroplasts (with clorophylls a and b) of secondary endosymbiotic origin. the chloroplast DNA in the chloroplast of chlorarachnion is similar to ________?
green algal chloroplast DNA
Some members of the Amoebozoa are the agents of_____?____
amoebic dysentry
Of the following, the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll b is found in all EXCEPT ___?___.
Phaeophya (brown algae)
porphya is cultivated to produce the wrap used to make sushi; also known as nori, what is porphyra is a member of ___?___
rhodophyta (red algae)
the ___?___ all have air spaces that lie near the cell boundary
Alveolata
eukaryotic microbes that live in freshwater generally have ___?___. whereas, most marine microbes lack this structure
contractile vacuoles
Laminaria differs from Chamydomonas in that __?__
Chamydomonas is UNIcelluar and laminaria is MULTIcell
Organisms like the one at the one at the right have an outstanding fossil record largely because ____?____
they have silica cell walls
some dinoflagellastes ____?____
are responsible for red tides
the n+n stage in fungi comes about due to ____?____
a delay of karyogamy that normally follows immediately after plasmogamy
the "fruiting body" in basidiomycota possesses or is characterized by all of the following EXCEPT ____?____
pollen
the gills of basidiomycota are ___?____
the site of basidiospore production
the cell walls of true fungi are comprised principally of ___?____
Chitin
the __?__ is an extension of a hypal cell that penetrates into living host cells
haustorium
the chlorophyta (green algae) lack all of the following EXCEPT ___?___
Mitochondria
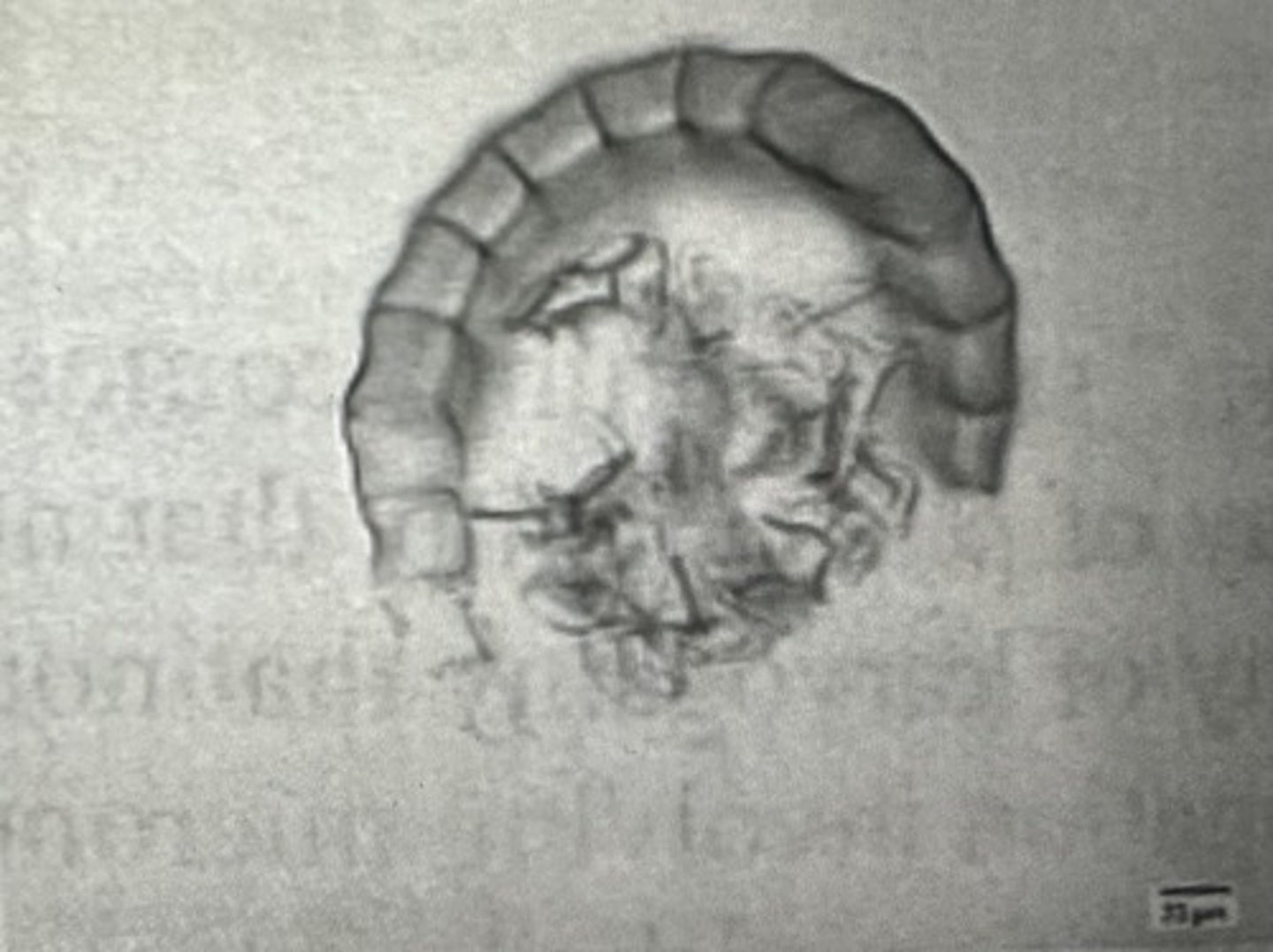
___?___ are produced in this structure (see at right)
spores
heterosporic meiosis directly results in the production of ___?___
megaspores and microspores
the cells that undergo meisosis in kingdom plantae are termed ___?___
spore mother cells (sporocytes)
microspores of angiosperms develop directly into ___?___
microgametophytes in pollen
the ovule of seed plants has the potential to develop directly into ___?___
a seed
external (free) water is not required for fertilization in ___?___
flowering plants (angiosperms)
double fertilization results in the formation of zygote and ___?___
endosperms
the role of triploid tissue produced during seed development in flowering plants is ___?___
to provide nutritional resources for the embryo
the meristem is primarily a region of ___?___
cell division
members of the kingdom plantae possess or produce all of the following EXCEPT ___?___
lobose pseudopodia
the monocots are generally characterized by all of the following EXCEPT ___?___
netted (reticulate) venation
a plant whose reproductive structure has 3 sepals, 3 petals, 6 stamens and a carpael with 3 segments is most likely a ___?___
monocot
the vascular cambium produces ___?___
Secondary xylem and phloem
the vascular cambium create mechanical stresses in plants because ___?___
it is an intercalary meristem
a flower is regarded as a forth plant organ, but rather appears to be comprised of ___?___
modified leaves
of the following, which tissue is comprised of cells that undergo apoptosis in order to attain their functional maturity
sclereids
the active site of RUBISCO permits fixation of both carbon and oxygen. fixation of the latter (oxygen) results in ___?___
photorespiration
of the following ONLY ___?___ is found in all organisms that bear plastids
C3 photosynthesis
C4 photosynthesis is characterized by ___?___
a spatial or physical seperation of carbon uptake and the calvin cycle
the bundle sheath (kranz anatomy) of C4 plants is the primary location for
the synthetic reactions that ultimately produce glucose
CAM (craassulacean acid metabolism) allow plants to
keep stomata closed during the day
water ALWAYS moves froms ___?___ potential
high and low
water that moves through vessels and/or tracheids would be utilizing a(n) __?___ route
apoplastic
the casparian strip (suberin) is largly responsible for forcing water to enter the symplast when crossing through the __?__
endodermis
transpiration has the capacity to pull water through the xylem tissue of a plant as a consequence of ___?___
cohesivness and adhesiveness of water
The loading of sucrose (ΔΨs) into a sieve tube member causes a _?_ which is followed by an influx of water that produces a spike in pressure (ΔΨp).
transient decrease in water potential
You determine that a root hair cl has a solute potential ("psi"s) = - 1.8 MPa and a pressure potential (Ψp)= 0.3 MPa. If the water in the soil adjaacnt to the root hair cell has a solute potential of -1.1 MPa and a pressure potential of 0.3 MPa, what is the net direction of water movmenet between root hair and the soil
from soil to root
true or false: the concept of a symplast (i.e a continuum of living plant cells) is based on the observation that all living plant cells are seperated by plasodesmata that permit the flow material from one cell to the next.
true
Engelmann's experiment demonstrating the action spectrum of photosynthesis in a green alga is based on the expectation that growth of aerobic bacteria will respond to the __?__
O2 produced by the alga during the light dependent reactions
engelmann experiment demonstarating the action spectrum of photosynthesis in a green alga is based on the expectation that growth of the aerobic bacteria will respond to the __?__
O2 produced by the alga during the light dependent reaction
phytochrome (photoreceptor proteins that respond to red and far-red light and play a vital role in plant growth, development, and stress resistance) can take two forms. one form is converted to the other form by __?__
exposure to specific wavelength of light (660nm or 730nm)
when considering the concept of control of development in plants by plant hormones (i e plant growth regulation), signal transduction generally requires ___?___
a second messenger like CA++
long day plants actually require a short night in order to __?__
induce flowering
__?__ is the plant growth regulator thought to exert control over plant growth phenomena generally reffered to as stress response
abscisic Acid (ABA)
Frits Went identified auxin as the diffusible sunstance that stimulate ____?____ in coleoptiles
phototropism
what is sporozoites
plasmodium cell type in salivary gland of mosquitos
what is merozoites
plasmodium cell types that infect Red Blood Cells
what is apicoplast
plastid-like organelles in plasmodium
what is phycobilins
photosynthetic pigment found in red algae and cyanobacterium
What is Foraminifera?
calcium corbonate shells and filose pseudopodia
what is primary endosymbiosis
prokaryote engulfs eukaryote
what is secondary endosymbiosis
eukaryote engulfs eukaryote
what is trypanosoma
kineoplast organism and agent of sleeping sickness
what is euglena
bears chloroplasts derived from secondary endosymbiosis
what is chlorophyll C
photosynthetic pigment found in alveolata and stramenopila
what is chlorophyll B
photosynthetic pigment found in viridiplantae
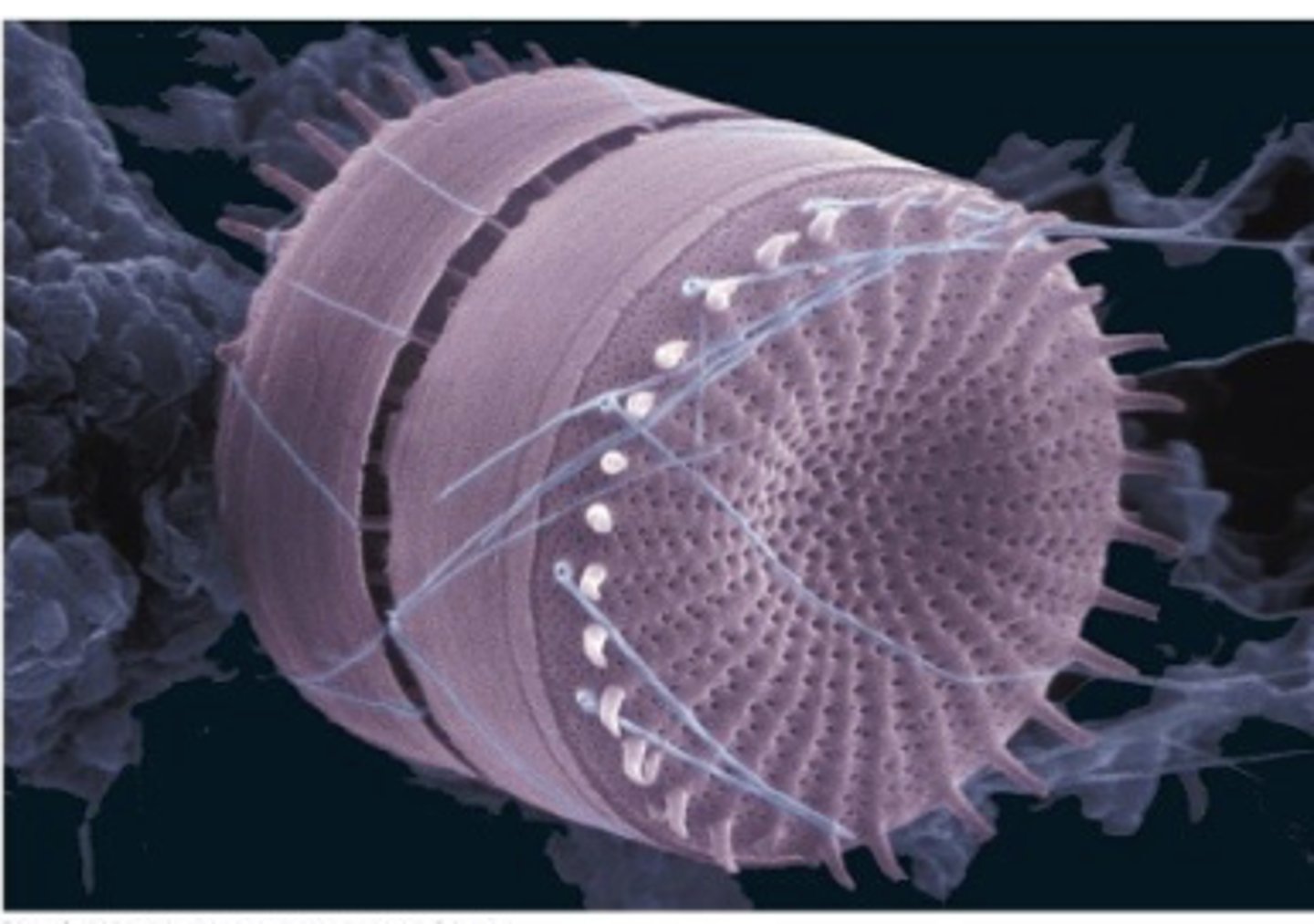
orgamisms like the one on the right have a cell wall comprise off ?
silica
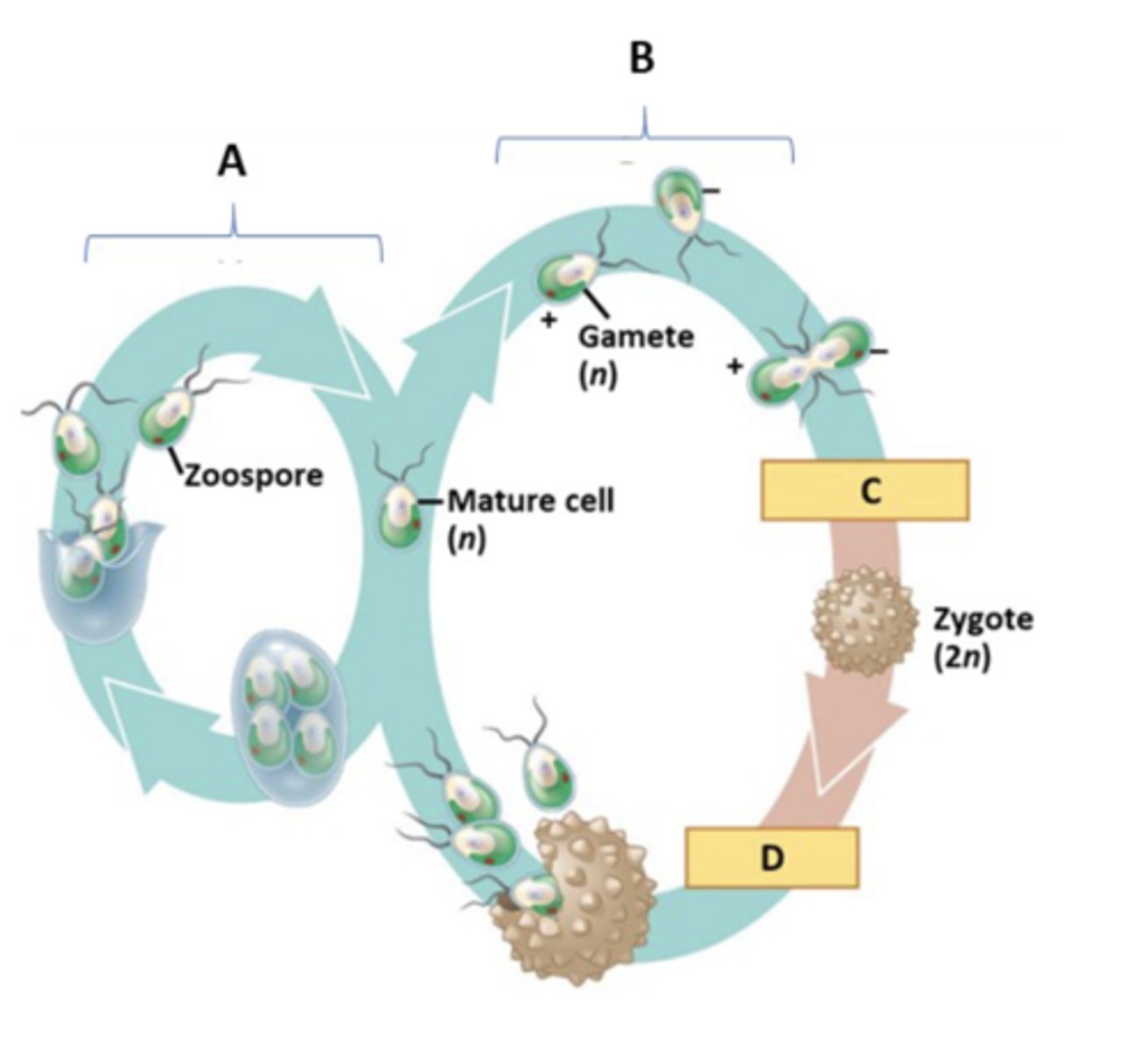
Match the correct description of a phase or process to the appropriate position (A, B, C or D) on the diagram at the right:
D:Meiosis
C: Fertilization
B:Sexual Phase
A: Asexual Phase
Meiosis in the Plasmodium life history occurs __?__
in the mosquito
Dinoflagellates are members of the __?__ alliance due to the fact that small air sacs areobserved near the cell boundary of dinoflagellate cells
Alveolate
The theory of eukaryotic origins proposed by Lynn Margulis correctly predicted that the __?__of Chlorarachniophytes would be derived from __?__
chloroplast DNA; a green algal chloroplast
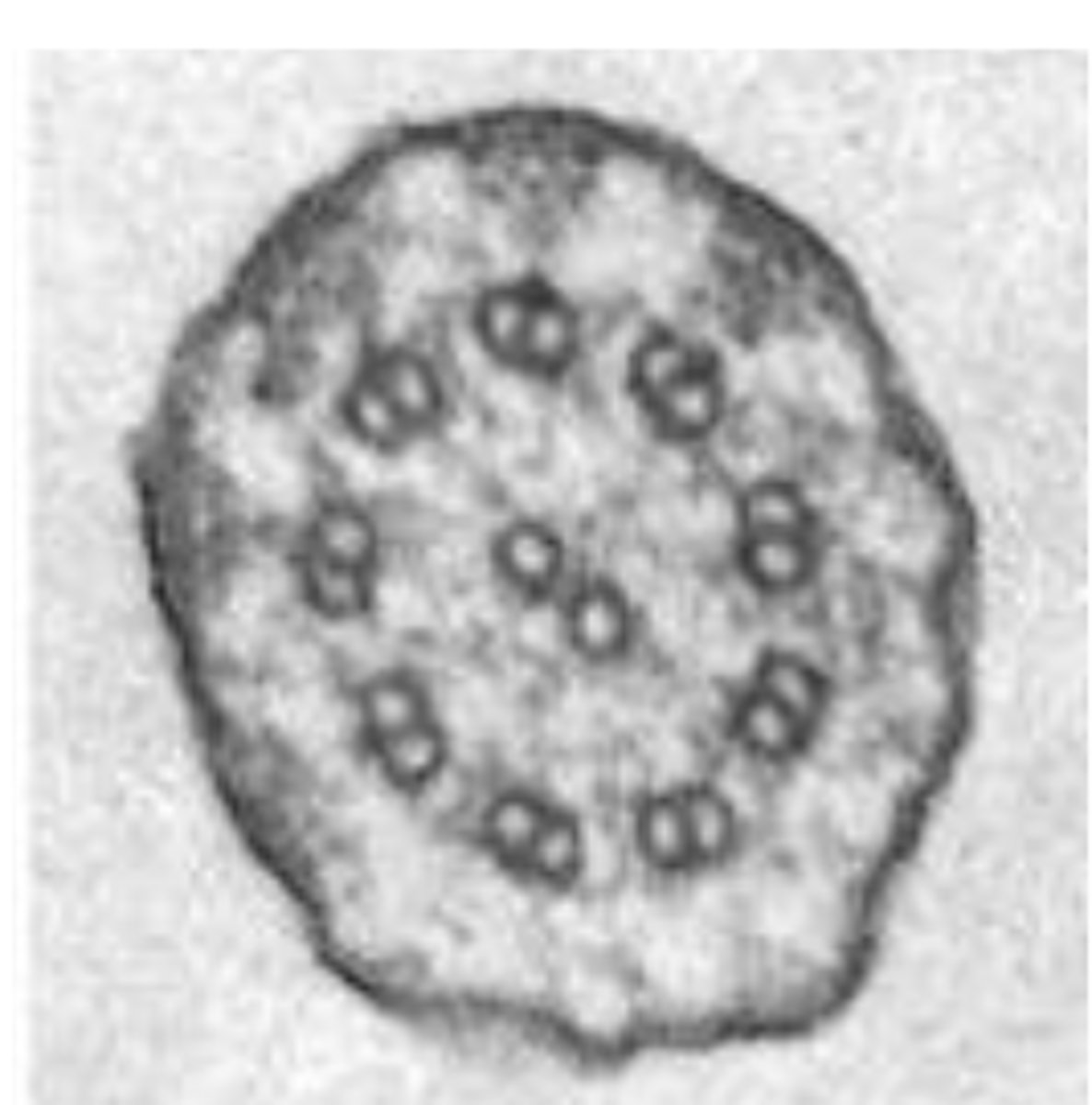
True or False: The high magnification image on the right could be across section through a cilium of Paramecium
true
the antheridia of ferns produce ___?___ through mitotic divisions
sperms
the plant cuticle is adaptive for embryophytes (i. e, land plants) because ___?___
it serves as vascular tissue
xylem
conducts water and dissolves ions
phloem
conducts sugars (photosynthesis)
embryo
immature sporophyte (diploid) stage
phragmoplast
system of microtublues that form perpendicular to plane of cell division in charophytes and higher plants
heterospory
megaspores and microspores
sporangium
Site of meiosis in higher plants
spore mother cell
cell that is destined to undergo meiosis
stomata
microscopic opening in plants that is bounded by gaurd cell
antheridium
male gametangium
archegonium
female gametangium
ovule
develops into seed
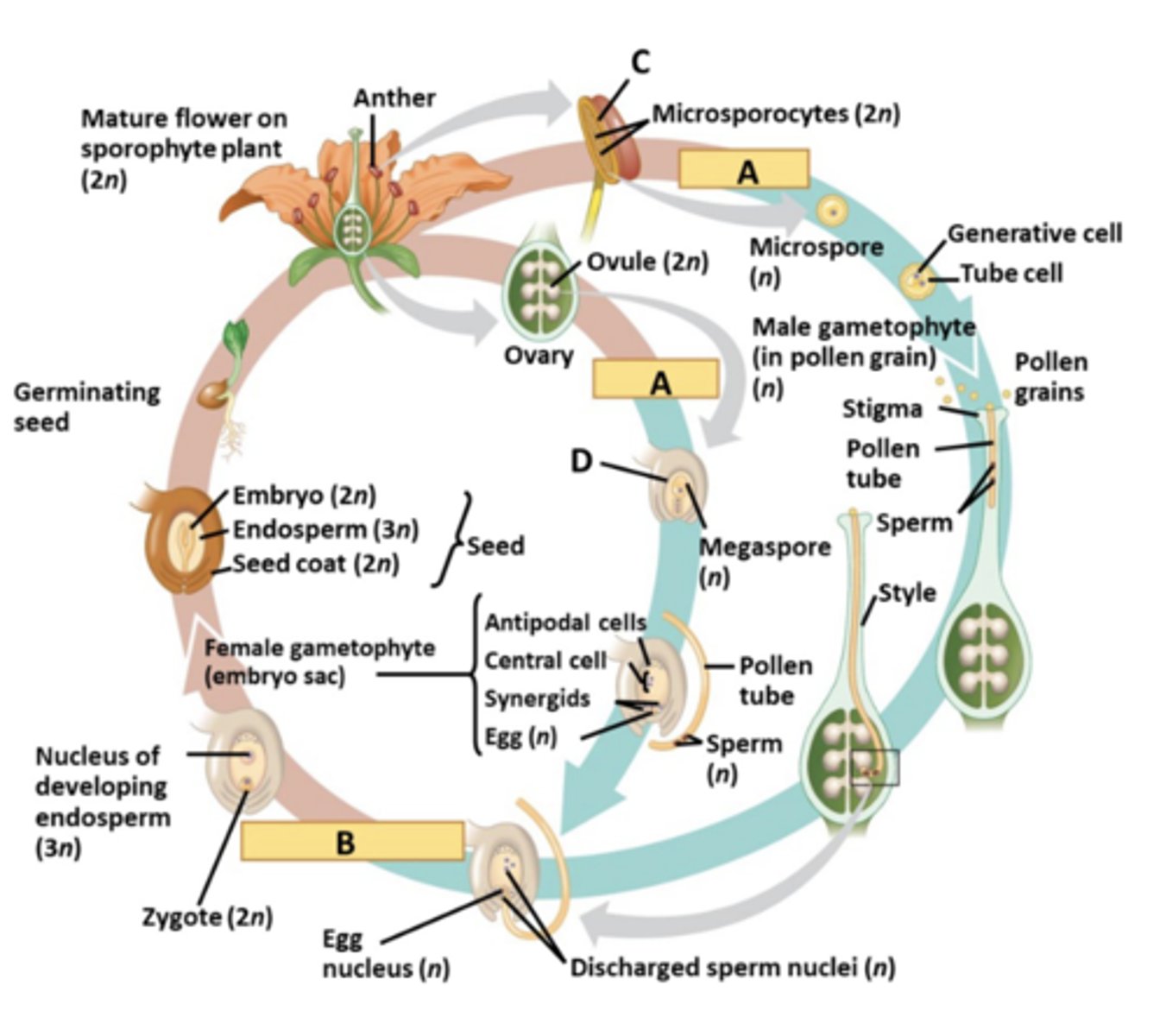
Match the correct description of a structure or process to the appropriate label (A, B, C or D) on the diagram at the right. NOTE: One answer (A) appears in two different spots in the life history
A. Meiosis
B: Fertilization
C: Microsporangium
D: Megasporangium
all of the following EXCEPT ___?___ are typical features of monocot plants
a eustele (ring of bundles) in the stem
tracheid
narrow diameter water conducting cell
vessel element
large diameter water conducting cell
sieve tube element
phloem cell with perferated end walls; loses nucleus
companion cell
phloem cell that retains its nucleus; a specialized cell in a plants phloem that is closely associated with a sieve tube cell
vascular cambium
lateral meristem that produces wood and secondary phloem
sclerenchyma
exclusively structural tissue that is dead at maturity
collenchyma
structural tissue that remains alive
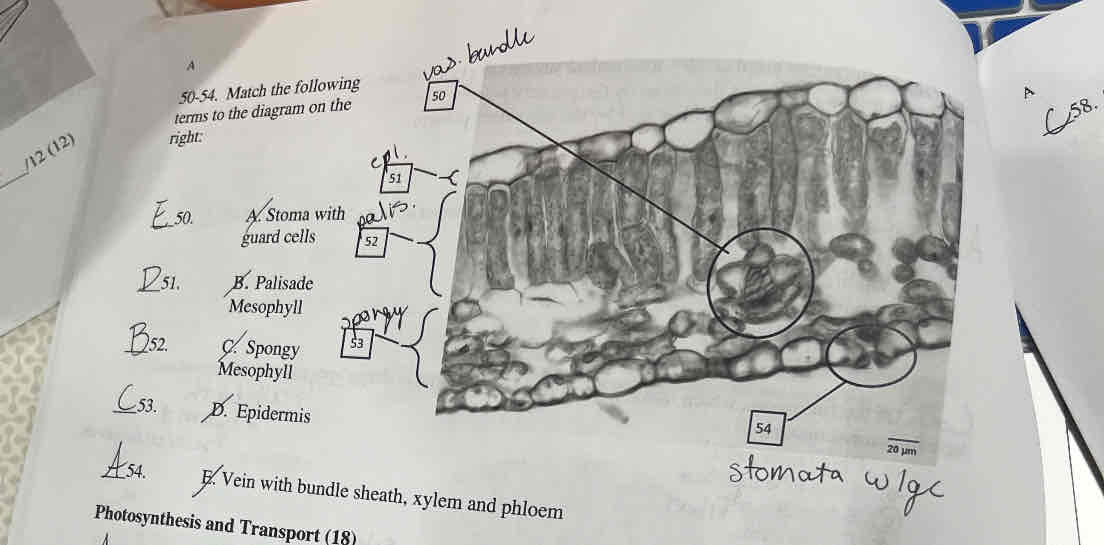
match the correct cell or tissue name to the appropriate label (A, B, C, D, or E)
E: Vein with bundle sheath, xylem, and phloem
D: Epidermis
B: Palisade Mesophyll
C: Spongey mesophyll
A: Stoma with guard cells
collenchyma
structural tissue that remains alive
vessel element
large diameter water conducting cell
sieve tube element
phloem cell with perferated end walls; loses nucleus
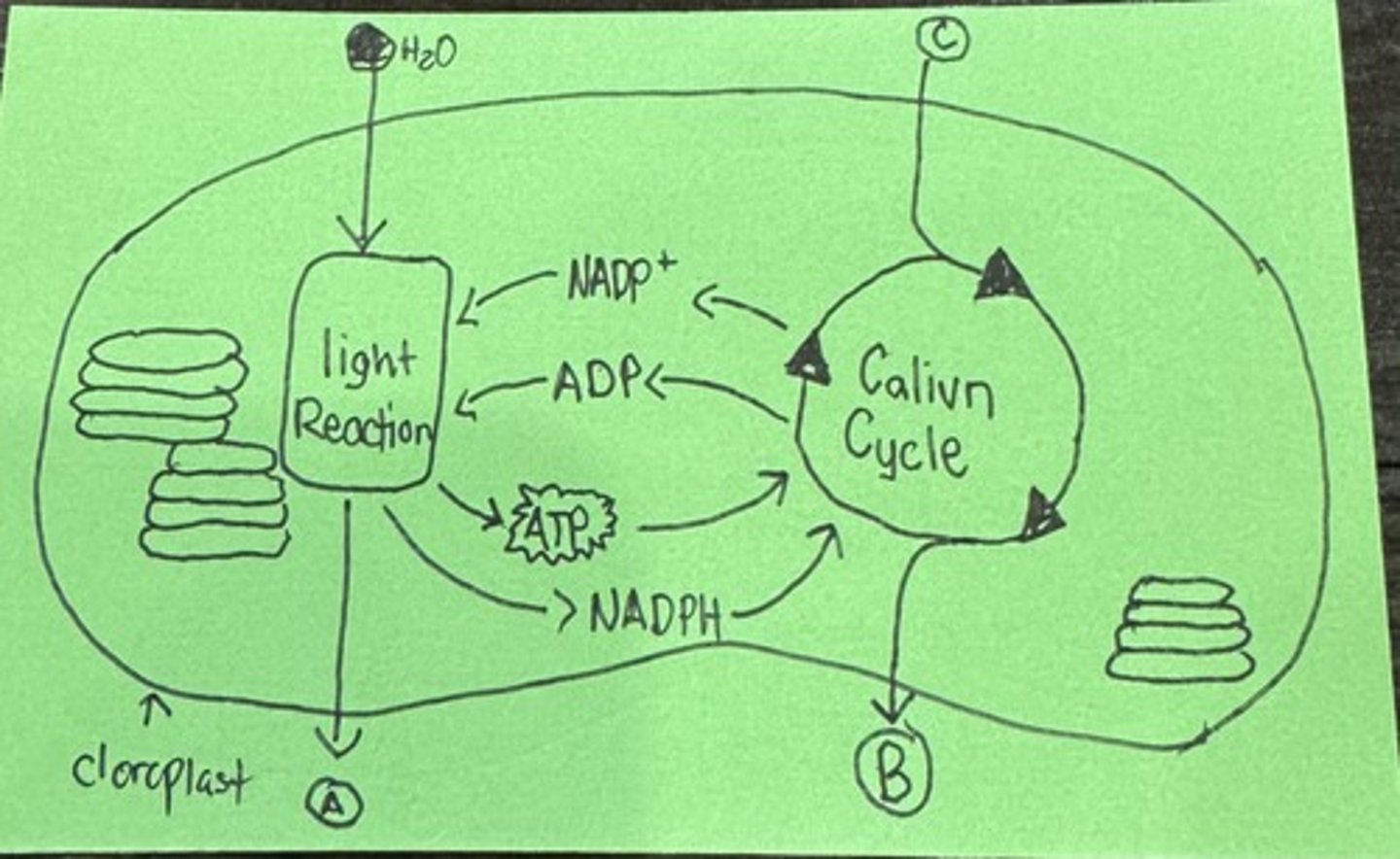
What is A
Oxygen
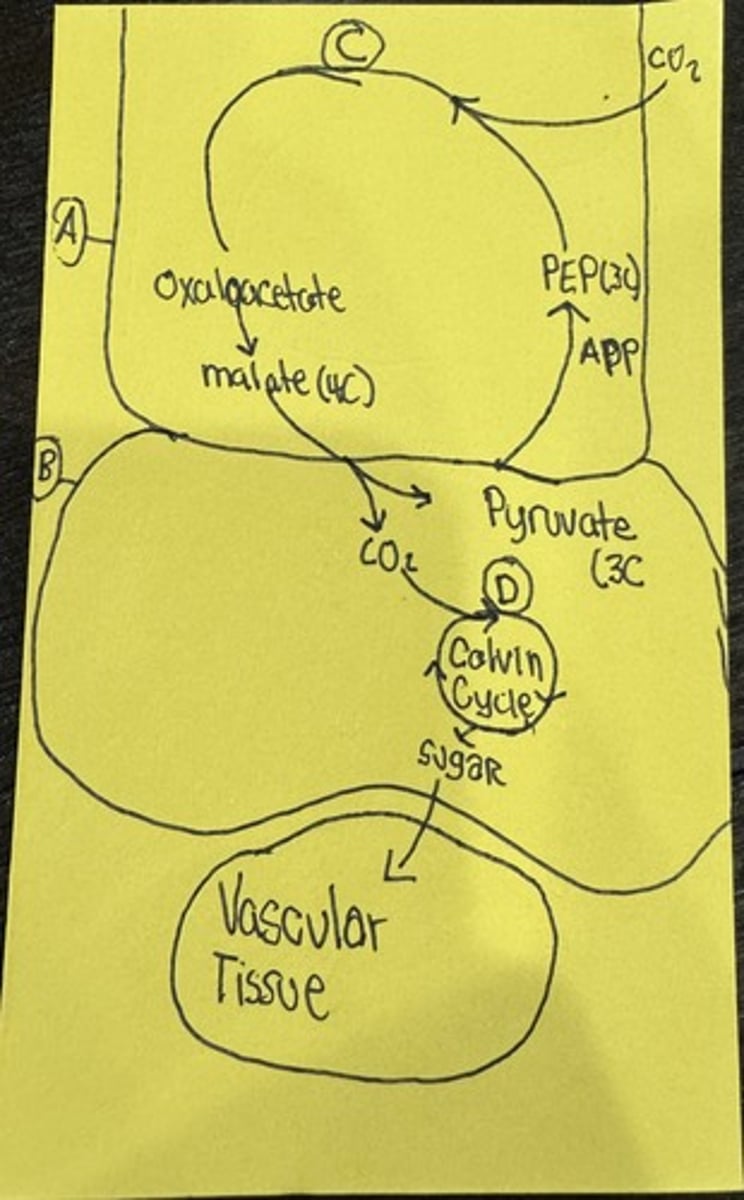
What is A
Mesophyll Cell
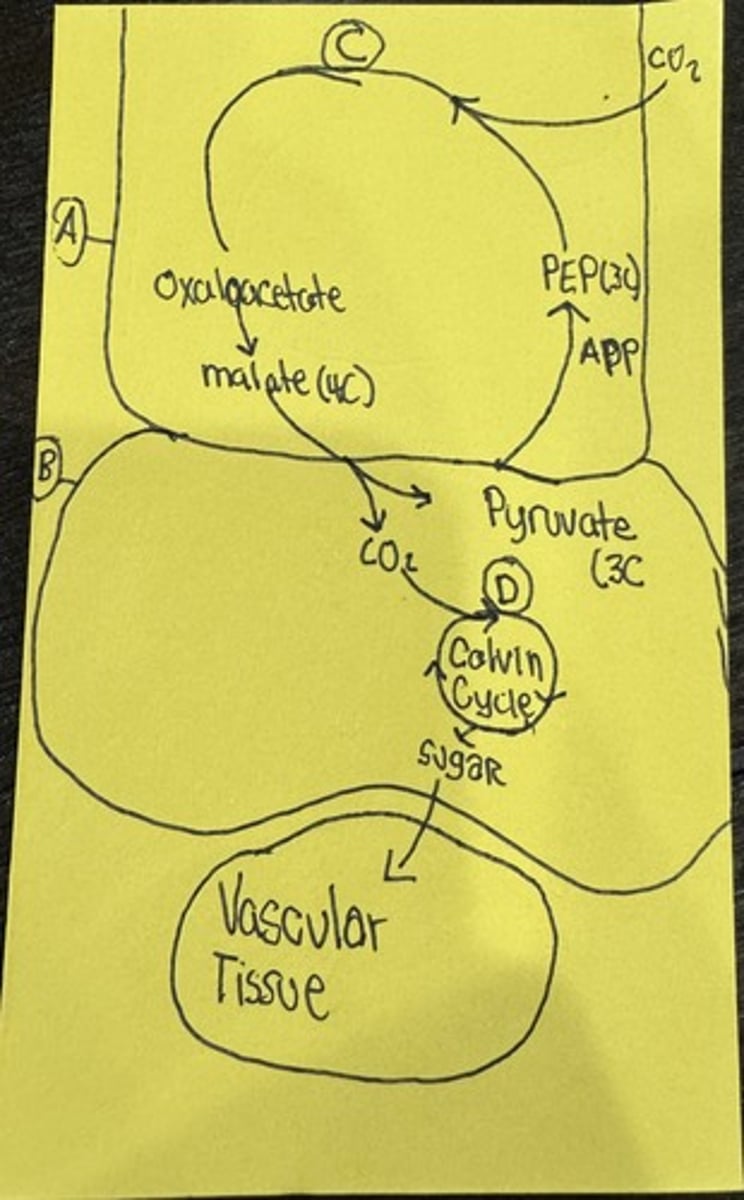
What is B
Bundle Sheath Cell
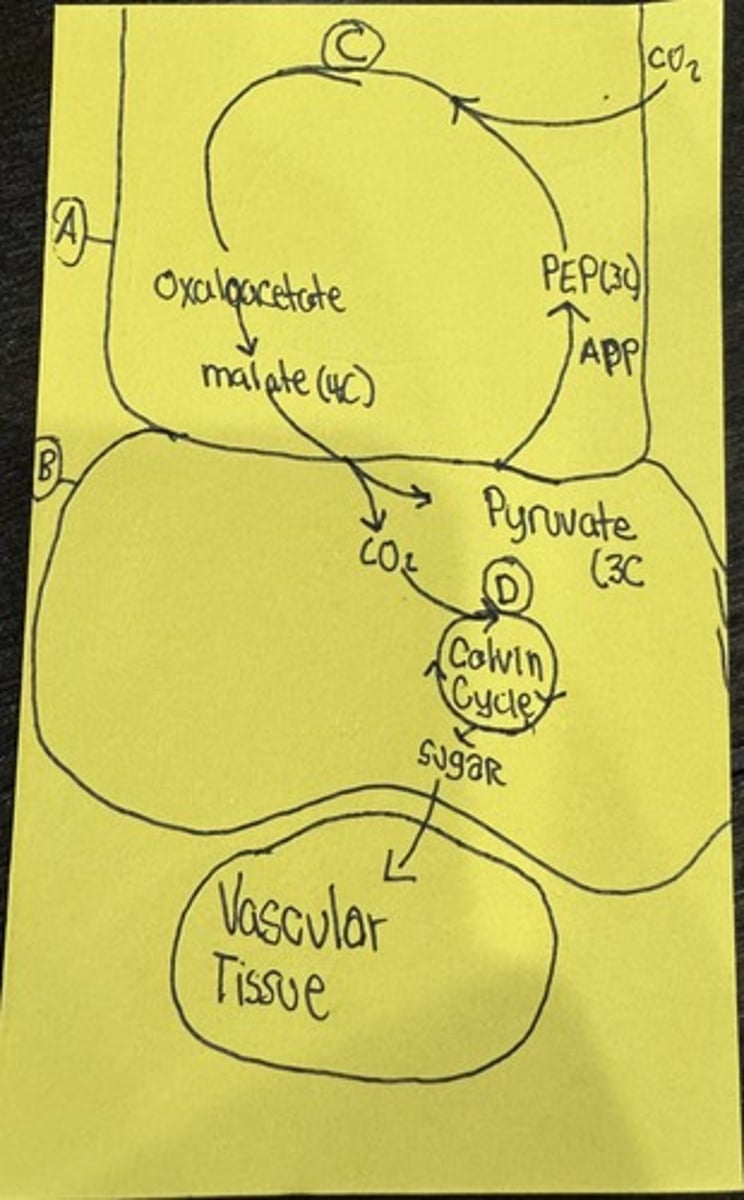
What is C
PEP Carboxylase
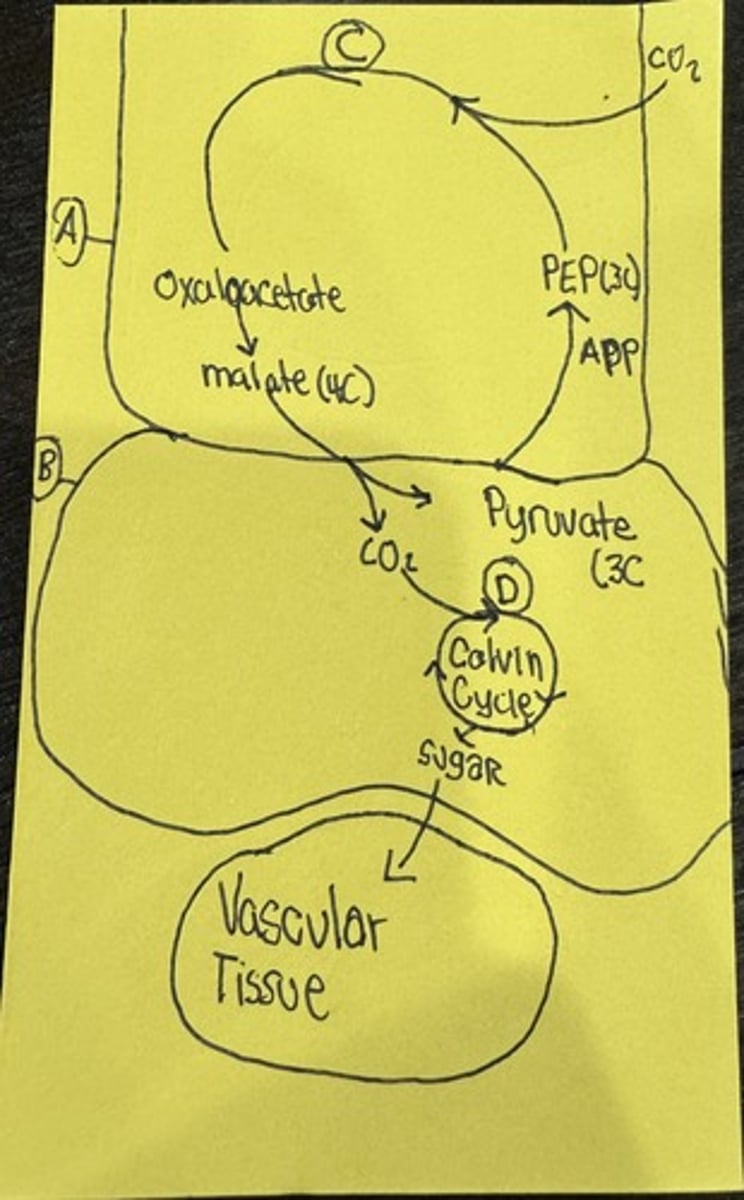
What is D
RUBISCO