Arousal, Stress, and Anxiety
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
arousal
generalized physiological and psychological activation of the person, with neural excitation varying on a continuum from deep sleep to extreme excitement
arousal has an ___ function, which reflects an intensity level of ___
energizing, motivation
arousal may start with a ___ or an ___ stimulus
thought, external
arousal results in autonomic nervous system responses such as …
increased heart and respiration rates
butterflies in stomach
muscle tension
sweating
activation
used synonymously with arousal, and refers to overall physical/mental state that’s required by an athlete to be ready to perform a task or activity
If increases in arousal/activation come from experiencing high stress when competing in sport or preparing to compete, what may result?
physical tension
competitive anxiety
situation-specific, negative emotional response to one’s view of competitive stressors and general involvement in competition (as threats)
competitive stressors
demands primarily/directly associated with competitive performance
competitive stressors examples
level of physical preparation
standard of the opponent
internal/external pressures/expectations to perform
organization stressors
demands primarily/directly associated with sport organization
organization stressors examples
performer’s role in the organization
sport relationships
interpersonal demands
personal stressors
demands associated primarily/directly with personal life of the individual
personal stressors examples
lifestyle issues
financial demands
relationships with family
state anxiety varies … and fluctuates proportionately to perceived …
from moment to moment; threat of situation
aspects of state anxiety
individuals assess how they feel “right now” - feeling that can change from moment to moment
[state anxiety] Competitive State Anxiety Inventory-2 (CSAI-2)
assesses intensity of state cognitive and somatic anxiety symptoms as well as self-confidence
trait anxiety
general predisposition to respond across many situations with high levels of anxiety because of typically appraising situations as threatening
aspects of trait anxiety
individuals rate how they feel generally
typical style of behavior
if you are predisposed to higher trait anxiety, you will be in a state of ___ more often than those not predisposed to trait anxiety
anxiety
Sport Anxiety Scale-2 (SAS-2)
measures trait anxiety and has a somatic scale and 2 cognitive scales
cognitive anxiety
concerned with internal, mental thoughts/worries that occupy the mind
somatic anxiety
concerned with external, physical symptoms
The Stress Process

[stress process stages] 1. environmental demand
physical and psychological
[SP stages] 2. individual’s perception of the environmental demand
amount of psychological or physical “threat” perceived
[SP stages] 3. stress response
physical and psychological
arousal
state anxiety (cognitive and somatic)
muscle tension
attention changes
[SP stages] 4. behavioral consequences
performance or outcome
How do the stages relate to each other?
once athlete hits stage 4, they cycle back to stage 1
complex tasks involve …
high in decisional demands and require fine motor skills
complex tasks benefit from ___ levels of arousal for optimal performance
low
complex task example
target rifle shooter
simple tasks involve …
gross motor skills, strength, speed
simple tasks benefit from ___ levels of arousal for optimal performance
high
simple task example
weightlifters
once athletes determine what range of arousal level is best for them on a given task, they should …
reproduce this arousal at next competition
inverted-U hypothesis describes the relationship between ___ and ___
arousal, performance
inverted-U chart & explanation
increases in arousal (low → high) result in progressive performance gains up to an optimal level of arousal (peak), but once this optimal level is hit, further increases in arousal result in performance decrements
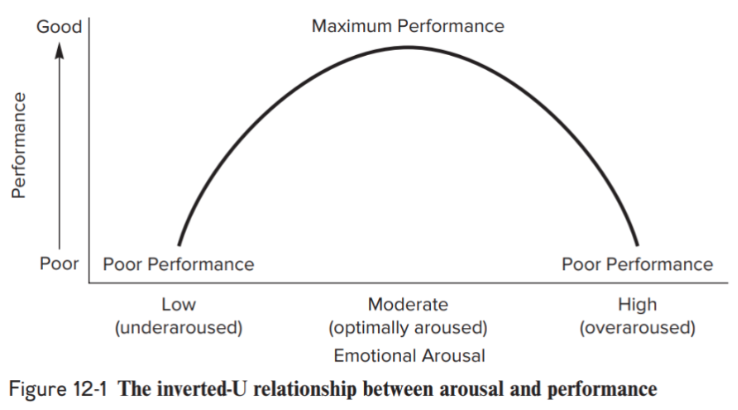
[inverted-U] What characteristics determine the optimal level of arousal?
those of both the task and performer
drive theory
increases in drive/arousal are associated with linear increases in performance, providing the task is well learned
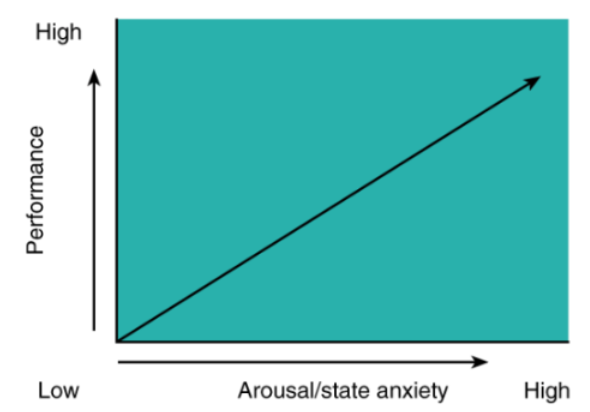
[drive] Is drive theory still used?
No, since there’s not enough evidence to support it
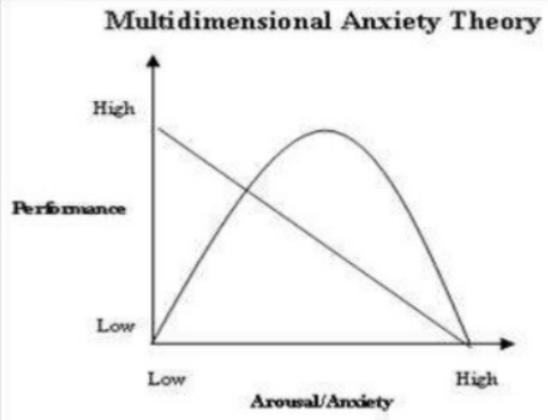
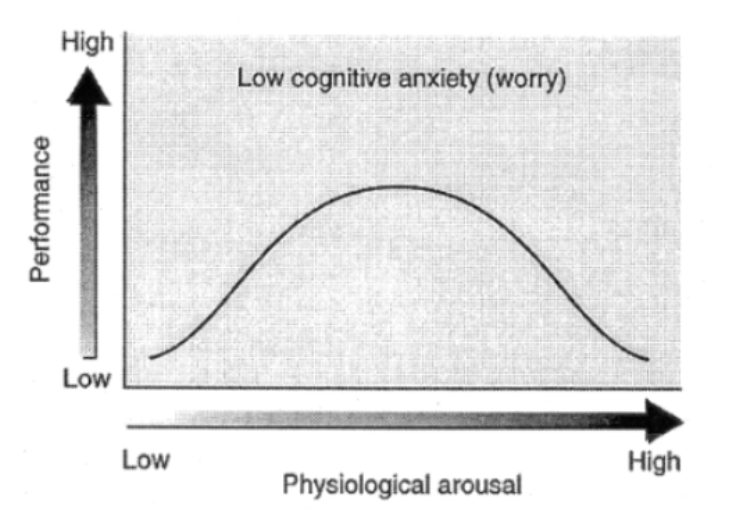
multidimensional anxiety theory - competitive state cognitive anxiety vs competitive state somatic anxiety
these types of anxieties have different antecedents and relationships to performance
[MAT] somatic anxiety is predicted to display an ___ relationship with performance
inverted-U
[MAT] What type of relationship do cognitive anxiety and performance display?
negative linear - as cog anxiety increases, performance deteriorates
[MAT] IZOF and MAT suggest that an appropriate level of ___ anxiety can have ___ performance effects, but not so much for ___ anxiety
somatic, positive, cognitive
[MAT] MAT only has partial support, as it fails to consider …
beneficial effects of cog anxiety on performance
interactive effects of competitive anxiety subcomponents upon performance
[MAT] MAT in sum + chart
cognitive anxiety is negatively related to performance
somatic anxiety is related to performance in an inverted-U pattern
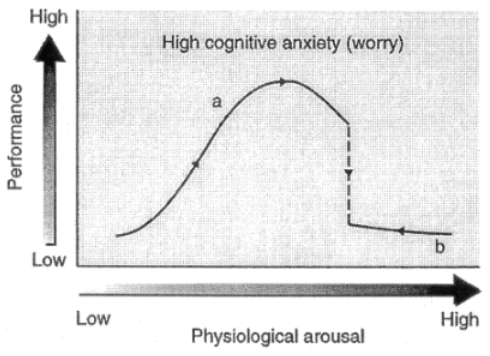
cusp catastrophe model
cusp model describes interactive effects of cognitive anxiety (not somatic) and physiological arousal on performance
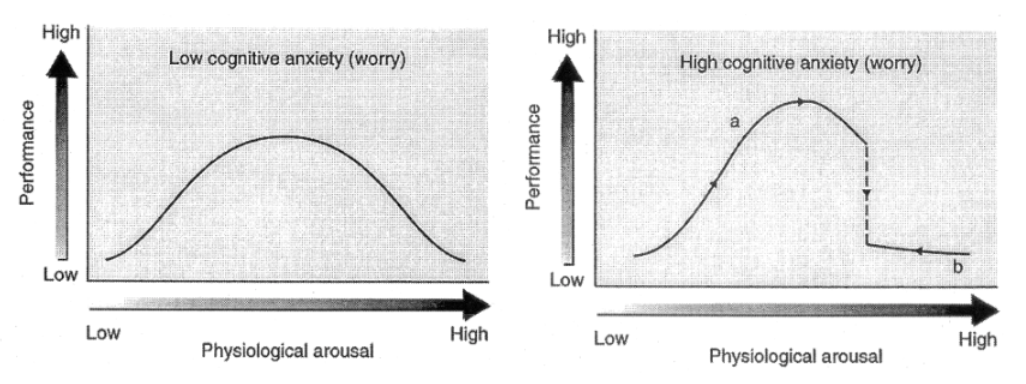
[CC] cog anxiety determines whether the effect of arousal on performance will be … (3)
smooth and small
large and catastrophic
somewhere in between
[CC] How is cusp different from MAT in terms of cog anxiety?
cusp catastrophe model says increase in cog anxiety can have positive performance consequences dependent upon levels of physiological arousal
[CC] When cog anxiety level is low, what will variations in arousal lead to?
small performance effects characterized by inverted-U
[CC] When cog anxiety is high, what happens when arousal increases?
positive effects on performance
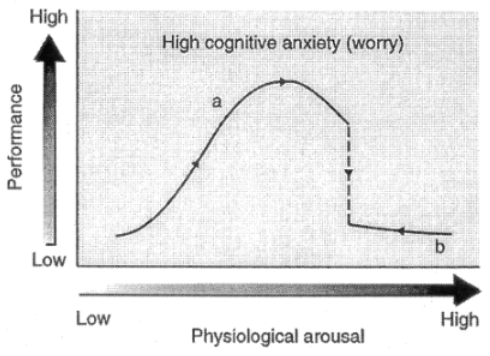
[CC] However, when cog anxiety is high and arousal increases beyond threshold, what happens?
catastrophic drop in performance
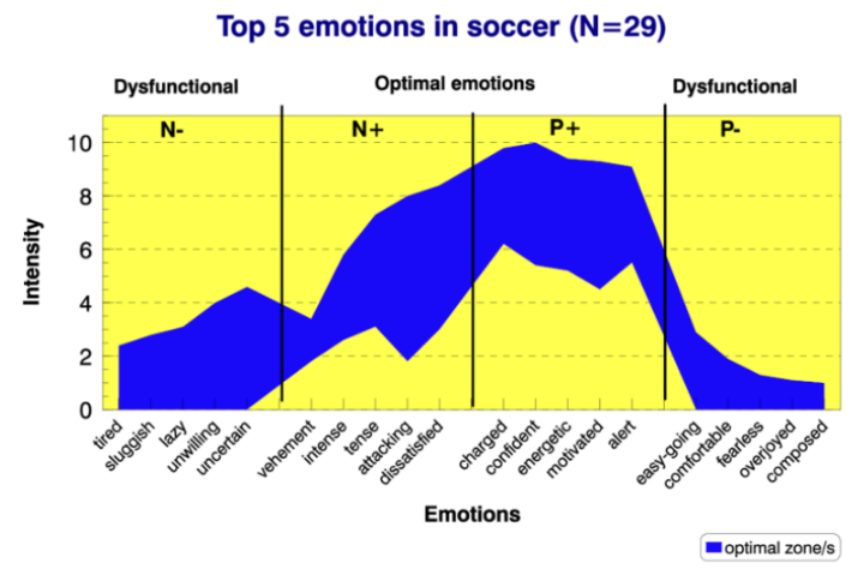
individual zones of optimal functioning
IZOF is a practical tool that helps athletes identify/establish a level of emotions experienced within which best performance occurs
[IZOF] if intensity of emotions is outside of the optimal zone …
performance will suffer
[IZOF] What does IZOF say about how athletes perceive their emotions in relation to their impact on performance (facilitative or debilitative)?
there is interindividual and intraindividual variability
[IZOF] Why has IZOF been criticized?
lack of explanation as to why different levels of emotions may be optimal or detrimental to performance
IZOF example #1
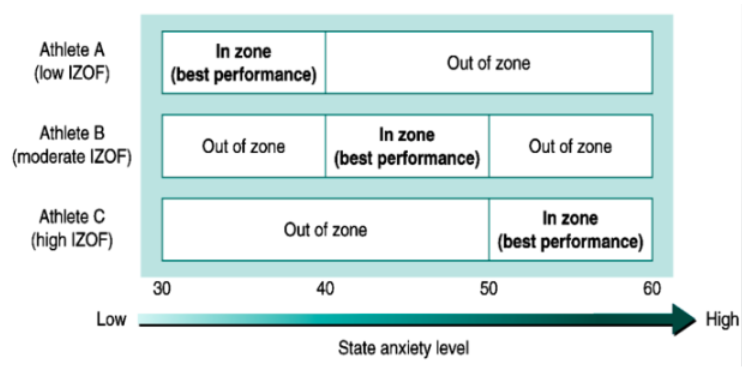
IZOF example #2
directional theory says that how arousal affects performance depends on an individual’s interpretation of
their arousal level
[directional] arousal can be interpreted as ___ or as ___
pleasant/excitement, unpleasant/anxiety
[directional] arousal can also be interpreted as ___ or as ___
facilitative, debilitative
[directional] when arousal is interpreted as pleasant and within personal control …
facilitative to performance
[directional] when arousal is interpreted as unpleasant and beyond one’s control …
debilitative to performance
muscle tension - bracing
when one muscle in a pair tightens, the other half of the pair sets up a counter tension to hold body in place → this double pull builds up tension in the body
[MT] What does muscular tension prevent?
movement coordination
[MT] If movement coordination is impaired, what does this interfere with?
skill execution
[MT] What does proper form require?
the right amount of tension
[attention - cue utilization theory] When attention and perception changes, what happens?
narrowed attention
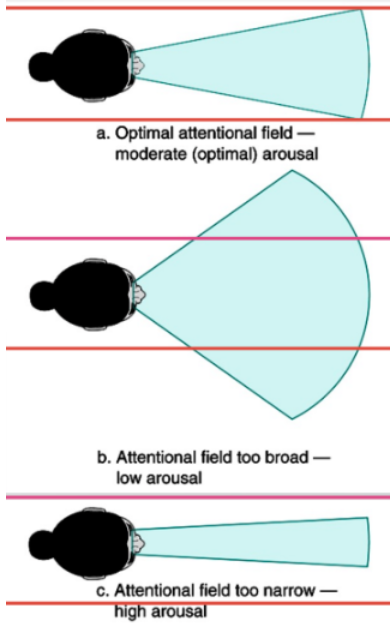
[CUT] things that happen when attention narrows
decrease in scanning
shift to one’s dominant style
attend to inappropriate cues
signal detection theory
[CUT] signal detection theory
sensitivity to stimuli
errors of omission vs commission
cue utilization theory in sum
As arousal increases, the athlete’s attentional field narrows.
processing efficiency theory
explains debilitating and facilitating effects of cognitive anxiety on performance described by catastrophe model
[PET] when one is anxious …
a proportion of their attentional capacity for the task is filled by task-irrelevant worry
[PET] when attentional capacity is filled by task-irrelevant worry …
working memory capacity is reduced
[PET] when working memory capacity is reduced …
cognitive processing efficiency is impaired as well as performance
[PET] cog anxiety may also signal ___ of the task to the individual, leading to ___ investment in task
importance, increased
processing efficiency theory in sum
Worry drains working memory → less efficient thinking.
attentional control theory
anxiety impairs efficiency of attention because it causes a shift in attention to threat-related stimuli rather than toward task and goal relevant info → performance negatively affected
[ACT] What may the inability to exercise attentional control be compensated for?
inhibition and shifting functions that stop the effect of threat-related stimuli and shift attentional resources to task demands
[ACT] effiency
relationship between effective task performance and use of attentional resources
[ACT] While anxiety influences efficiency, it does not influence ___
effectiveness
[ACT] Both PET and ACT assert there is fundamental distinction between ___ and ___
performance effectiveness, processing efficiency
[ACT] performance effectiveness
quality of performance
[ACT] processing efficiency
relationship between performance effectiveness and use of processing resouces
[ACT] high levels of cog anxiety are not inherently ___
negative
[ACT] benefit of high cog anxiety
it can motivate athletes to increase effort to prevent their anxiety from impairing performance, but at the expense of using greater amount of concentration
attentional control theory in sum
Anxiety hijacks attentional control → more distractible.
conscious processing hypothesis
CPH attempts to explain mechanisms underlying anxiety-induced performance decrements
[CPH] What do high anxious performers start to use?
excessive thinking
[CPH] What does excessive thinking lead to? What type of attention is involved?
execution of skills with inward attention
[CPH] What does inward attention lead to?
failure to execute skills - “paralysis by analysis”
[CPH] athlete adopts mode of control based on explicit ___ associated with early stages of ___
factual knowledge, learning a skill
[CPH] attempts to only focus on encouraging athletes to exert control over previously automated skills will cause …
performance impairments
[CPH] anxiety may induce regression from automatic control to …
explicit/verbal control
[CPH] Choking is a result of misguided ___ control combined with elevated ___
attentional, arousal
[CPH] Choking is caused by concern with excessive ___ and mechanics of skill ___
self-consciousness, execution
conscious processing hypothesis in sum
Anxiety makes athletes overthink movements → choking.
goal of muscle-to-mind and mind-to-muscle approaches
reduce physiological arousal and competition anxiety
muscle to mind is focused on the ___
body
[muscle-to-mind] Breathing exercises are aimed at what type of anxiety control?
somatic anxiety