Axial Skeleton Radiology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Spine Radiograph indications
Trauma/Fracture, degenerative disc disease (spinal instability), evaluation of primary and secondary malignancies, arthritis, suspected spinal instability, Shoulder or arm pain, Hip or leg pain, Occipital headache, Limitations in motion, Planned or prior surgery, Suspected congenital abnormalities, Syndromes associated with spinal abnormality, Evaluation of spinal abnormality seen on other imaging studies, Follow-up of known abnormality
Canadian C-Spine Rule
What is the following imagining referring to?
X-Ray Interpretations
alignment and Anatomy, disk height (as well as the facets)
Spine CT indications
Acute trauma, Degenerative conditions and osteoarthritis, Bone Density (Osteoporosis), Infectious processes of the spine, “With Contrast”- Intravenous injection to observe blood vessels and vascular tissues, Image guidance for spinal interventions, Neoplastic conditions, Inflammatory lesions, Congenital or developmental spinal abnormalities (ex. Scoliosis), Spinal cord syrinxes or intrathecal masses when MRI is contraindicated, Myelogram- water soluble contrast media into subarachnoid space to observe spinal cord, Post-op evaluation of bone graph or instrument fusion
CT Interpretations
Alignment and Anatomy, Bone Density Canal Space, Disk Integrity, Soft Tissues
What is the difference between a Spine MRI and spine CT
A spine MRI focuses more on soft tissue
Spine MRI indications
Suspected Disc Herniations or Degenerative Disc Disease (radicular symptoms), Extradural soft tissue, Intradural masses/tumors, Post-op soft tissue changes, Intrinsic spinal cord pathology, Bony neoplasm, Spinal vascular malformations, Spinal infections, MRI with contrast- outlines tissue with abnormal vasculature
MRI interpretations
Alignment, Bone Signal, Canal space and central nervous system, Disk integrity (Bulging, Herniation, Protrusion and Extrusion)
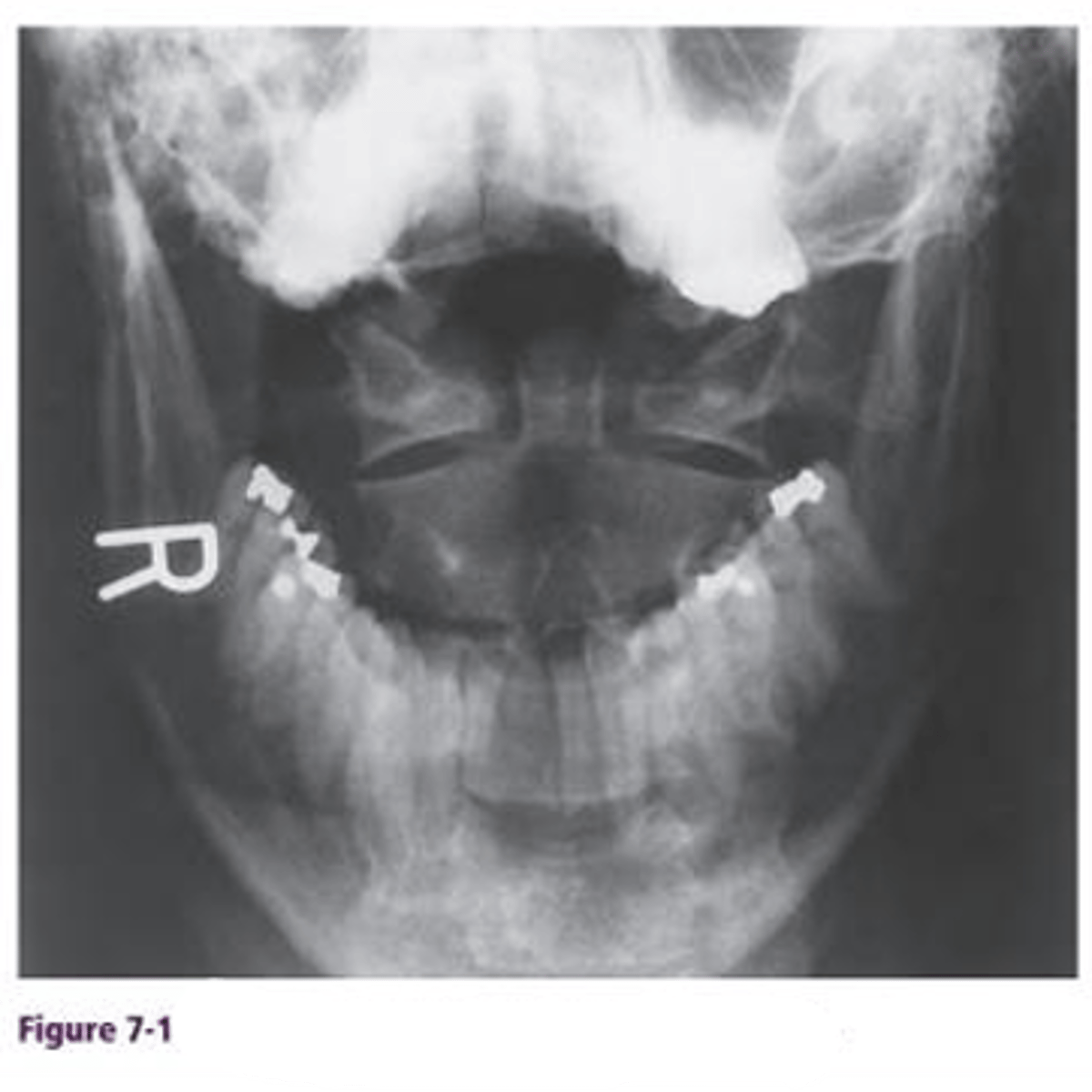
What's the view and what can you see in it?
AP open-mouth cervical spine, articulation of C1-C2 ( atlantoaxial joint). fracture of dens
When do you take an AP open-mouth cervical spine radiograph?
after head injuries
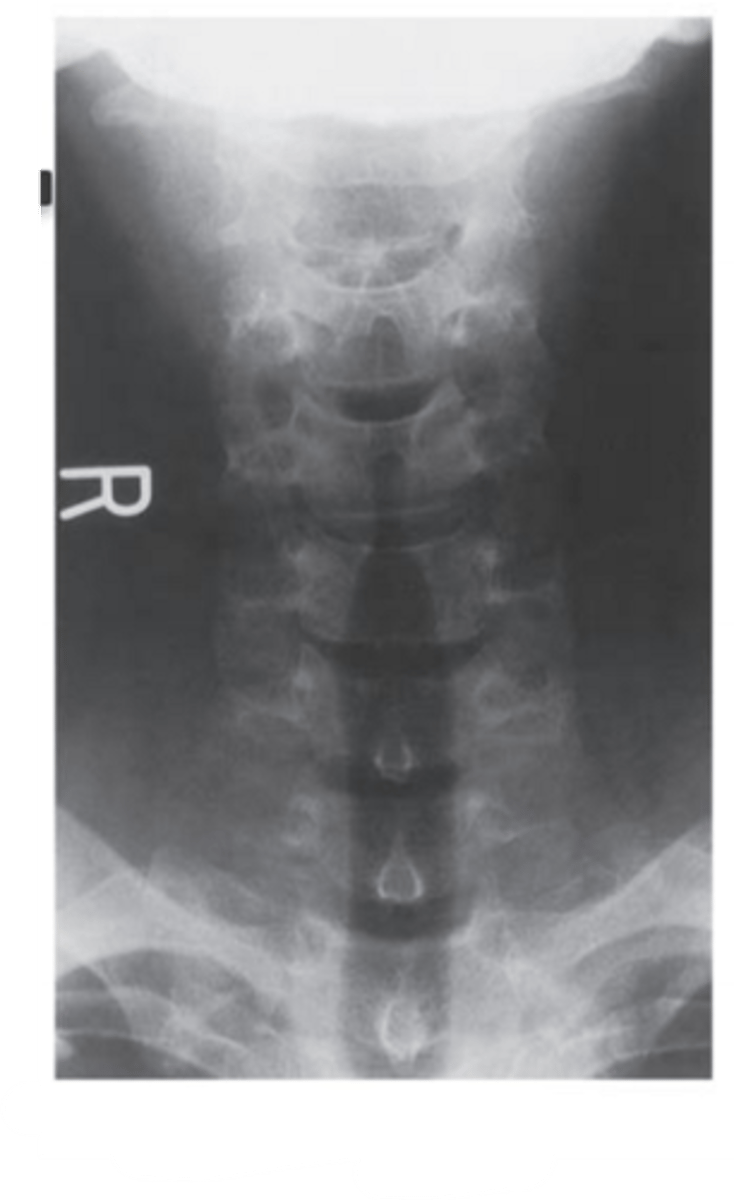
What view is this?
vertical column: A-P view. Spinous processes are midline. Lateral column: Lateral view
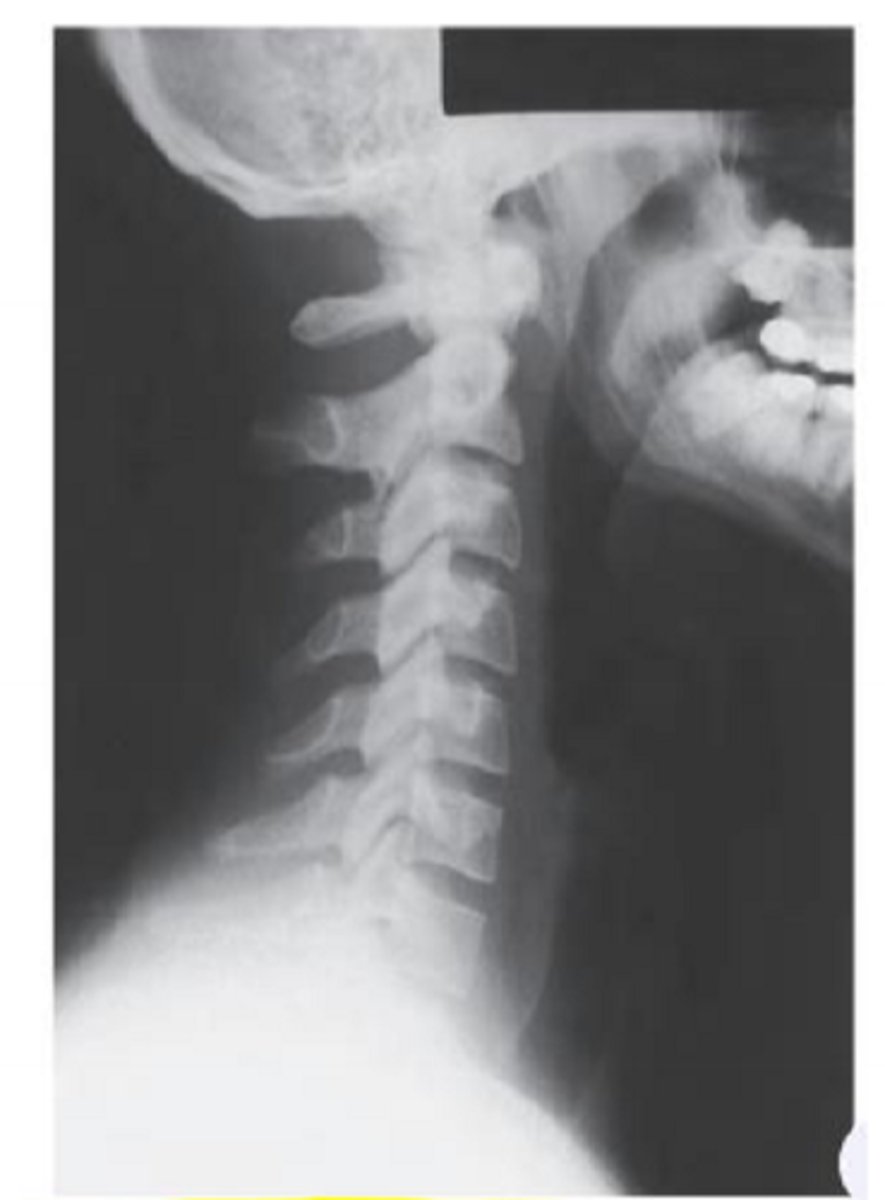
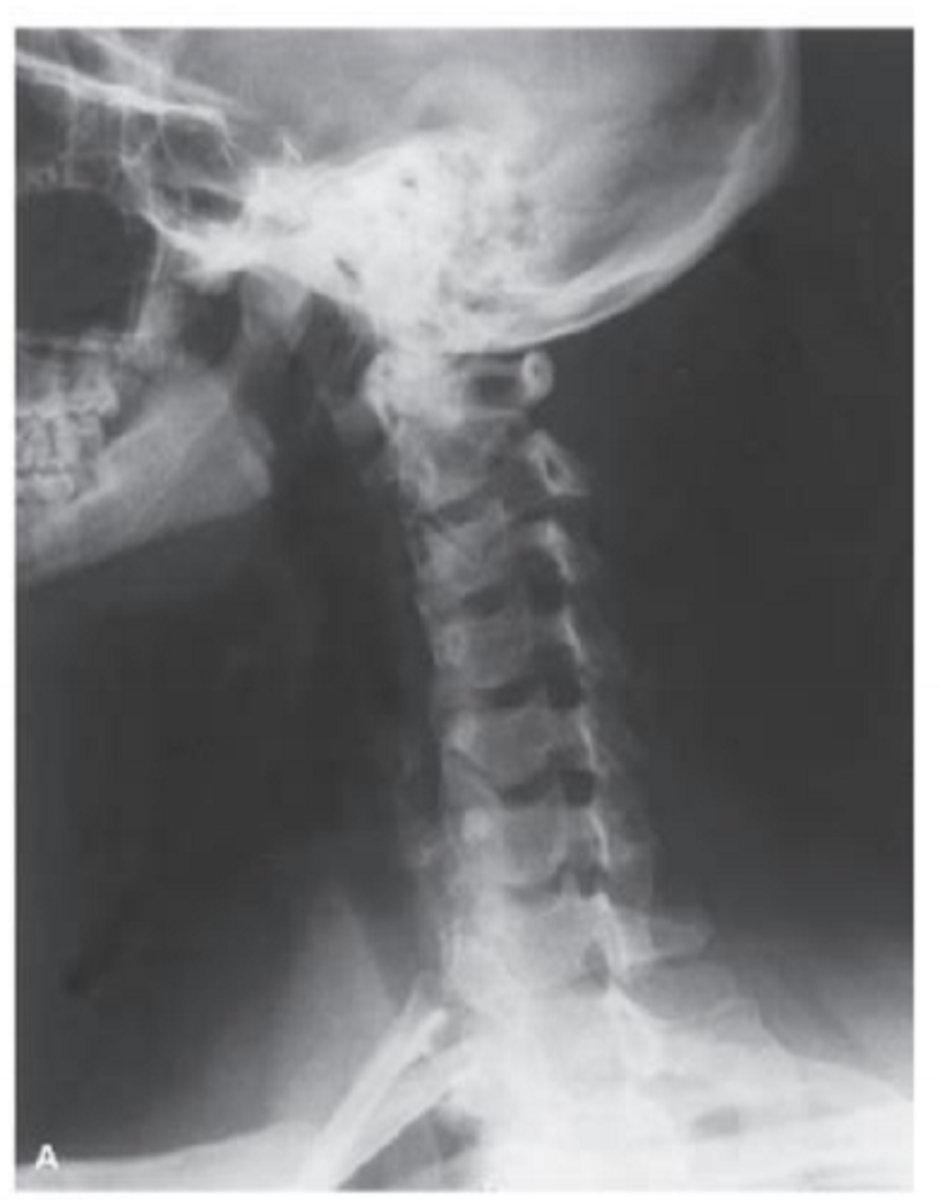
What view is this? What do you see in it?
lateral cervical spine radiograph.
Anterior borders create lordotic curve. box like vertebral bodes. disk spaces. articular pillars and facet joints
What view is this? What is it useful for?
right posterior oblique cervical spine radiograph.
useful for observing the intervertebral foramen
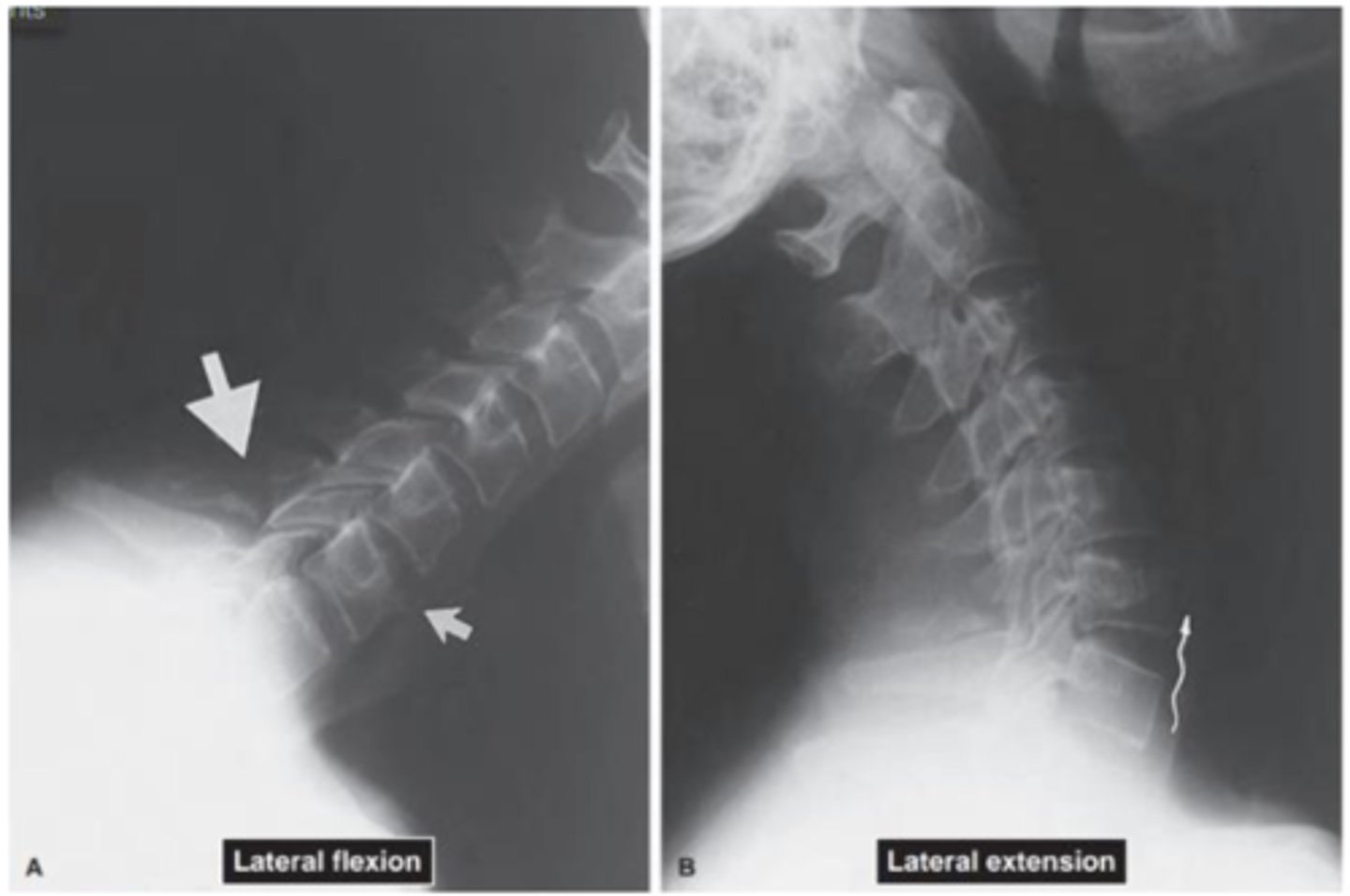
What is the picture showing? How do you know?
avulsion fracture and ligament rupture. disc height increased in the picture on the right in the lower vertebrae
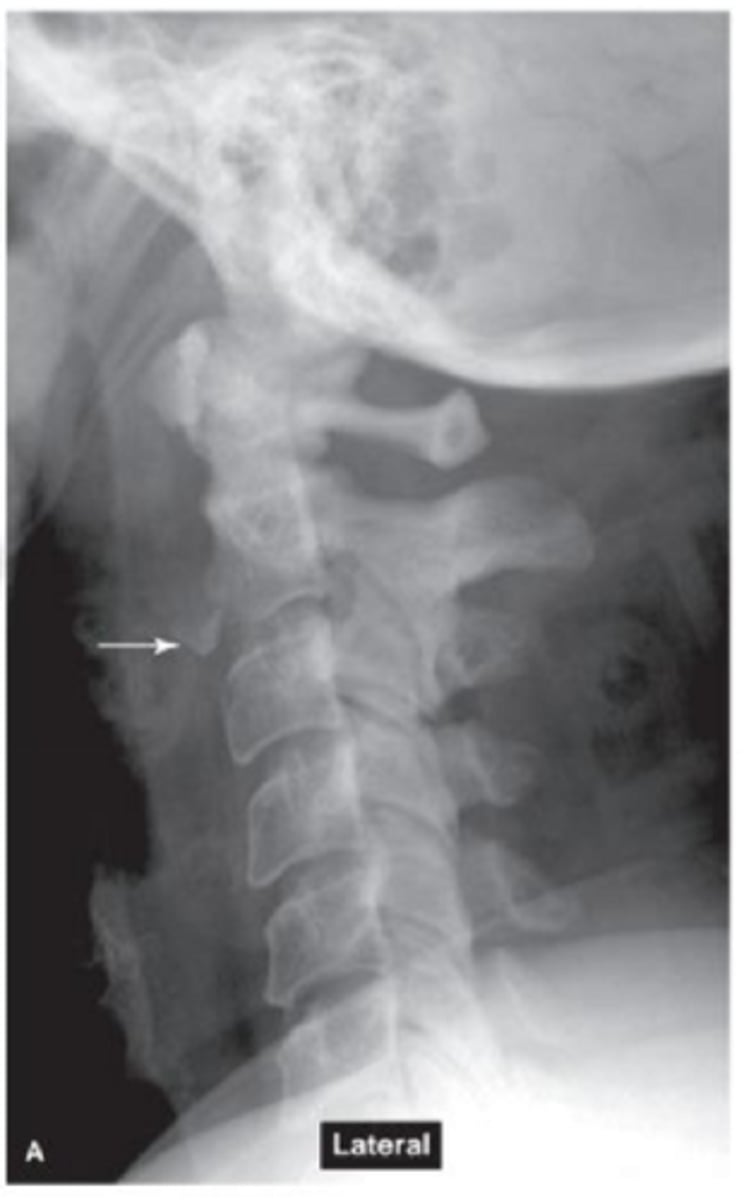
What is this picture showing? What is the MOI?
Tear Drop fracture. flexion or extension injury
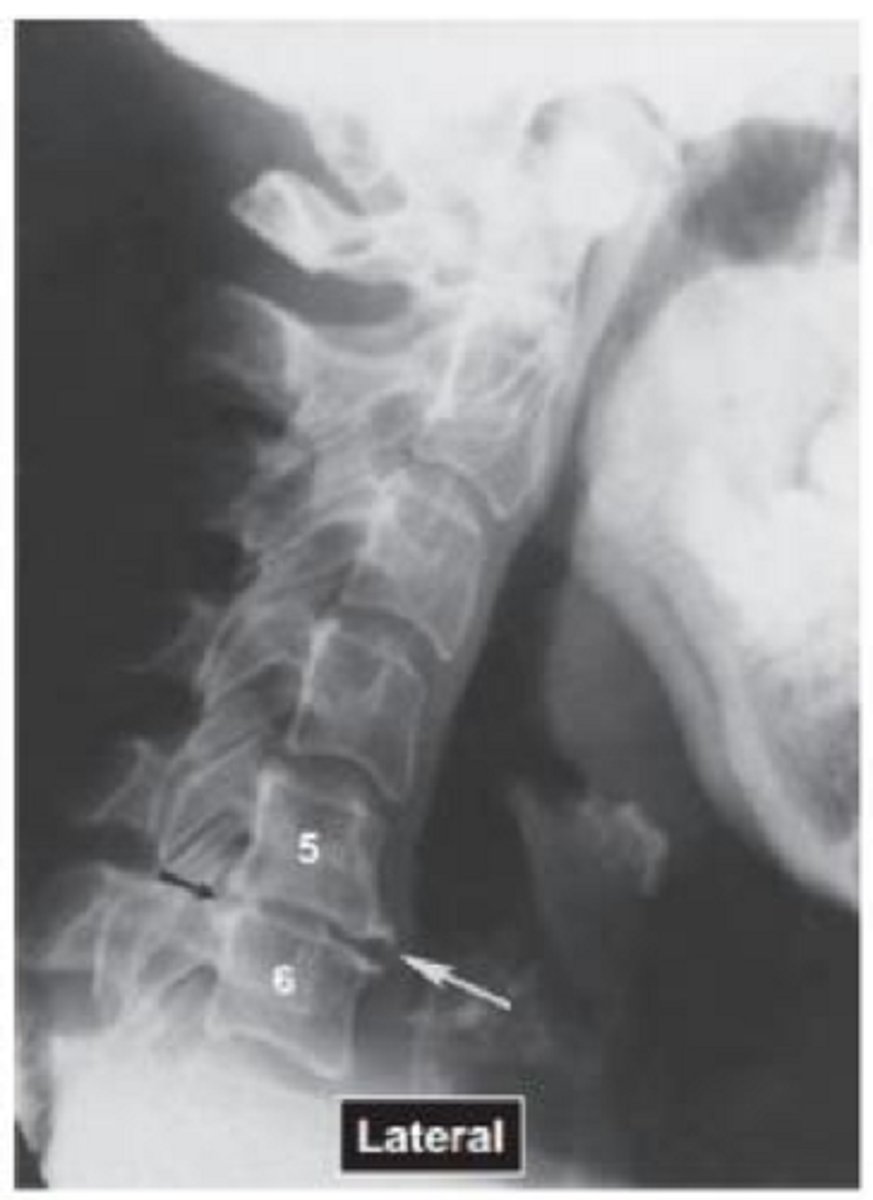
Name the pathology
Degenerative disk disease
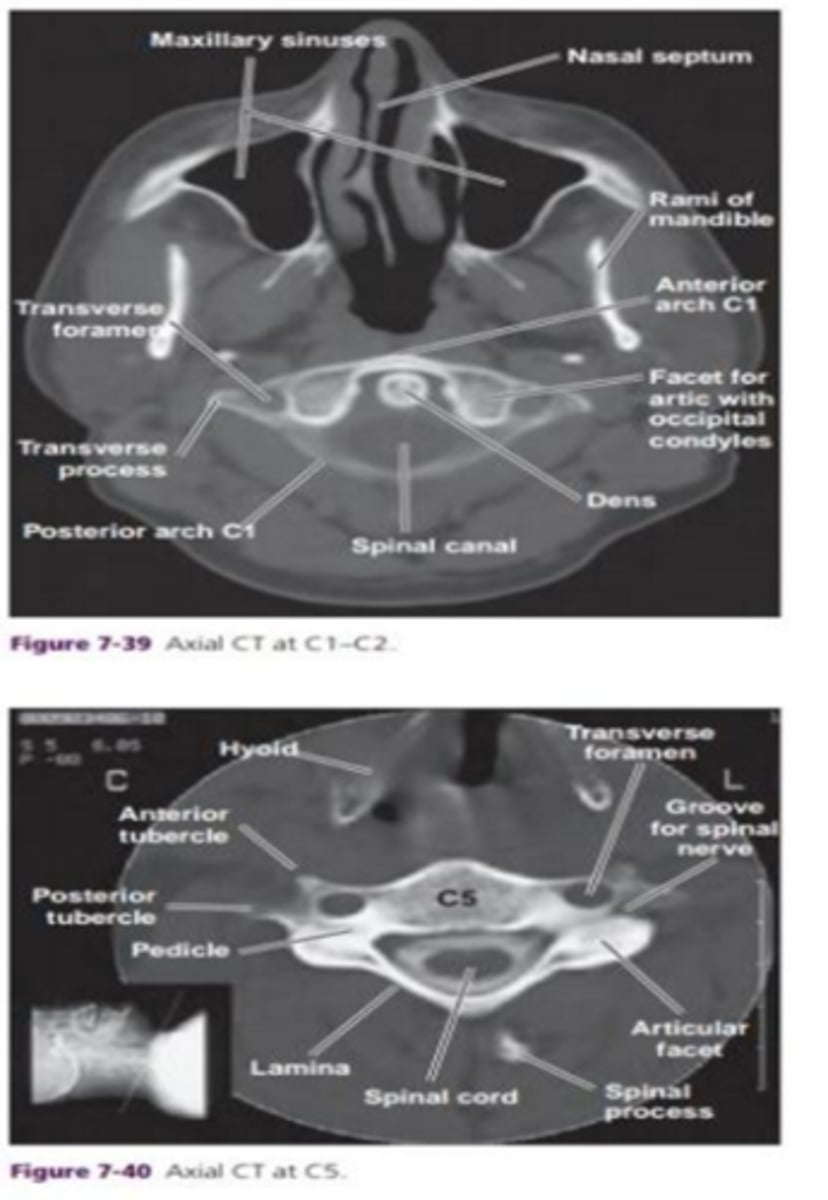
What should you note about the dens? and the spinal canal?
position of the dens. diameter of spinal canal. width of spinal canal should equal width of vertebral body
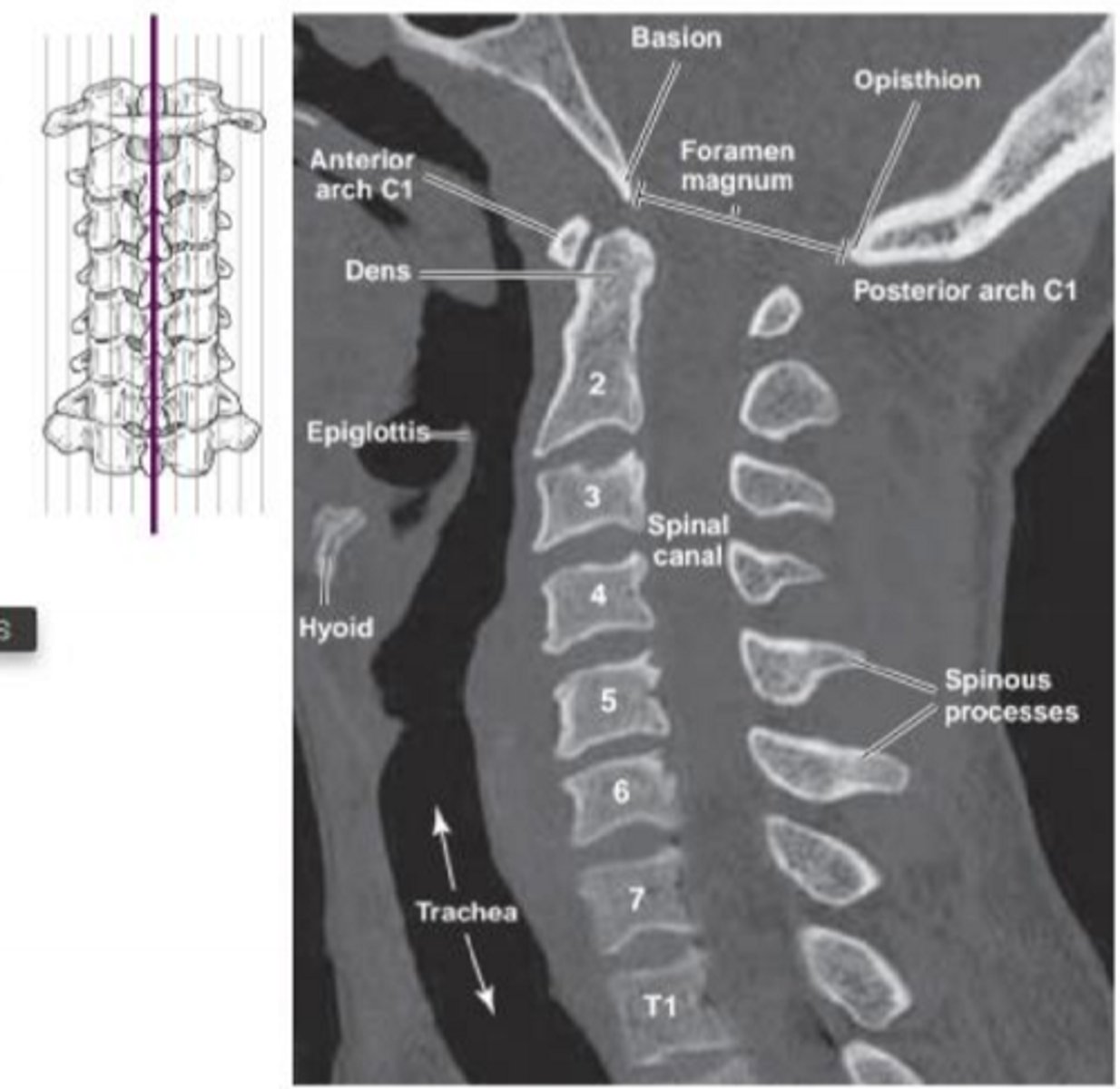
What is the picture showing?
vertebral alignment
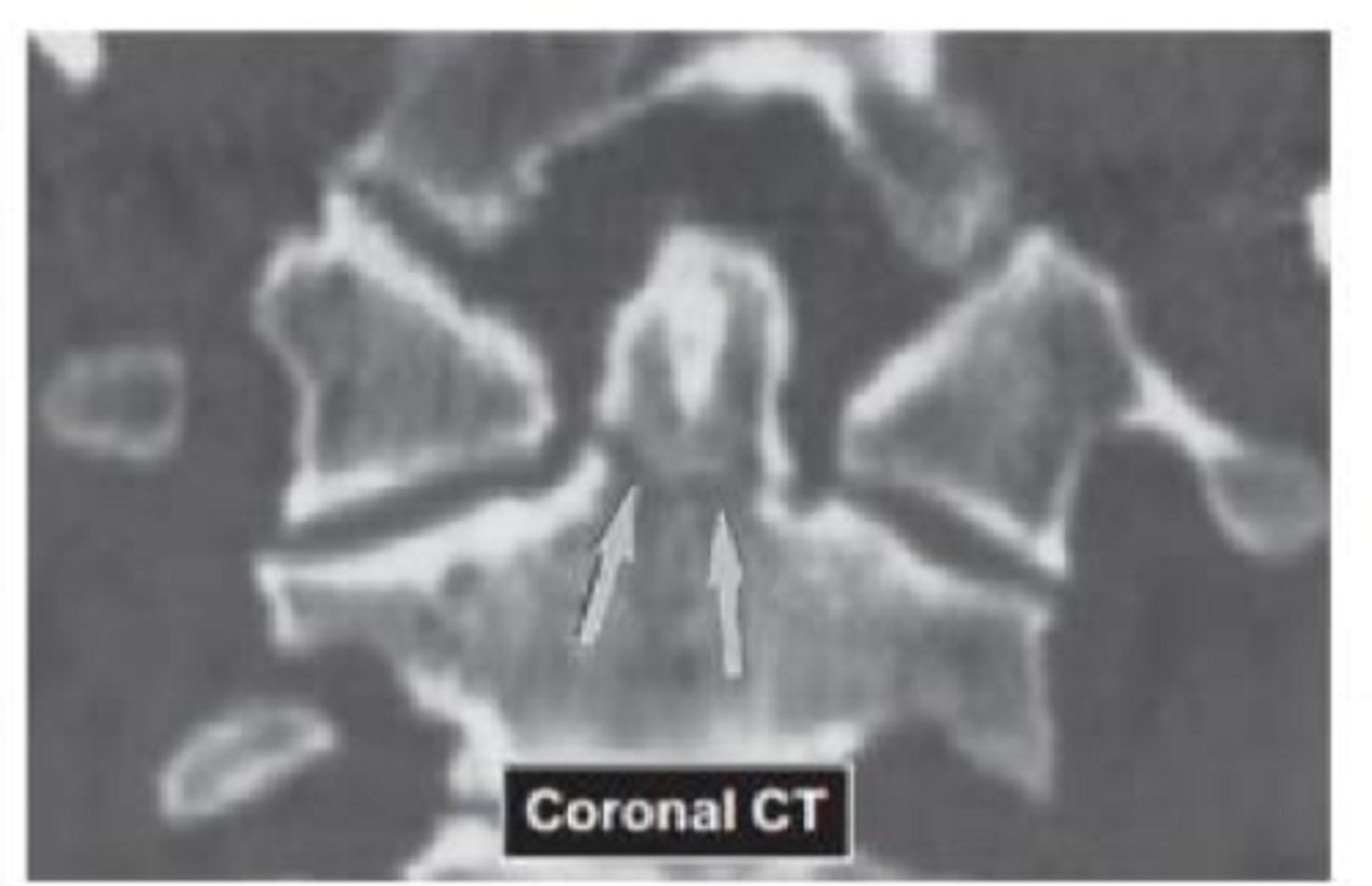
What is this picture showing?
dens fracture
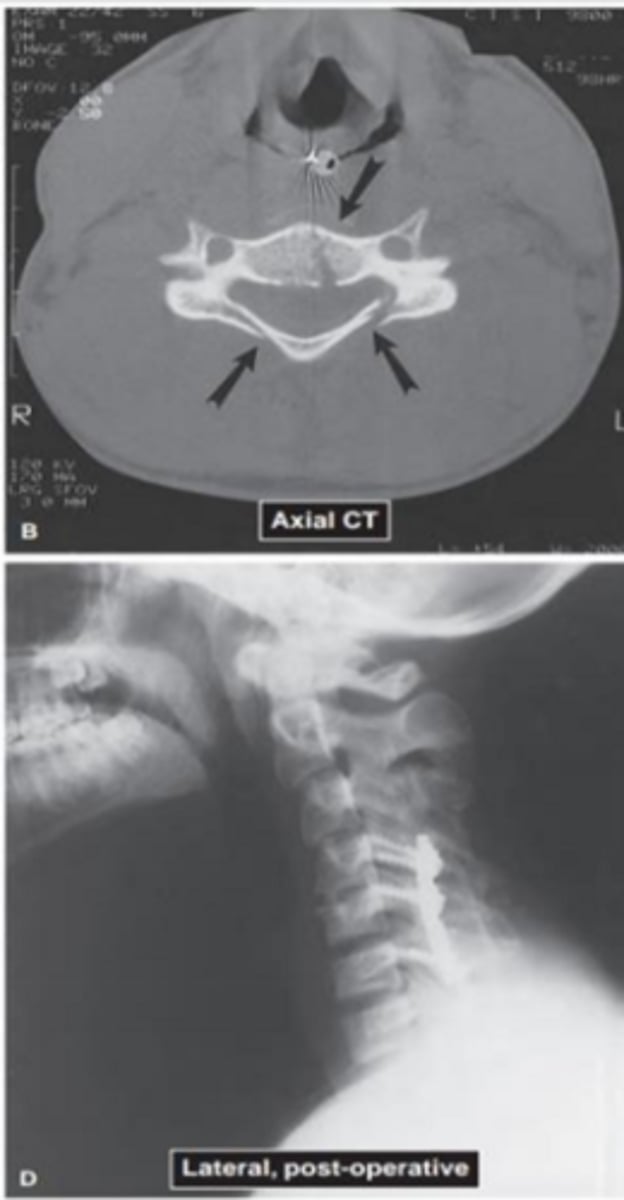
What is this picture showing?
Fracture through vertebral body
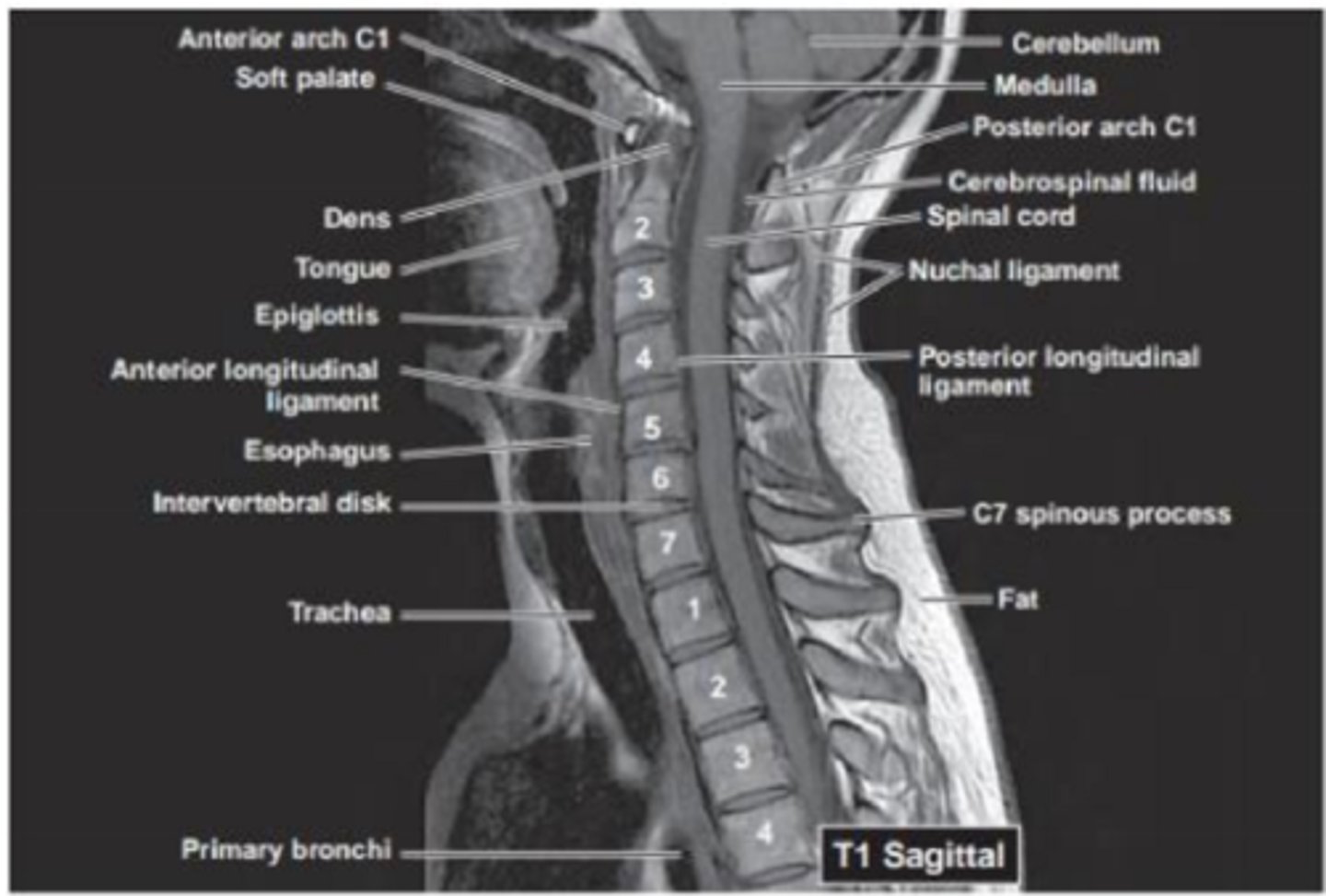
What view is this?
T1 sagittal MRI at midline
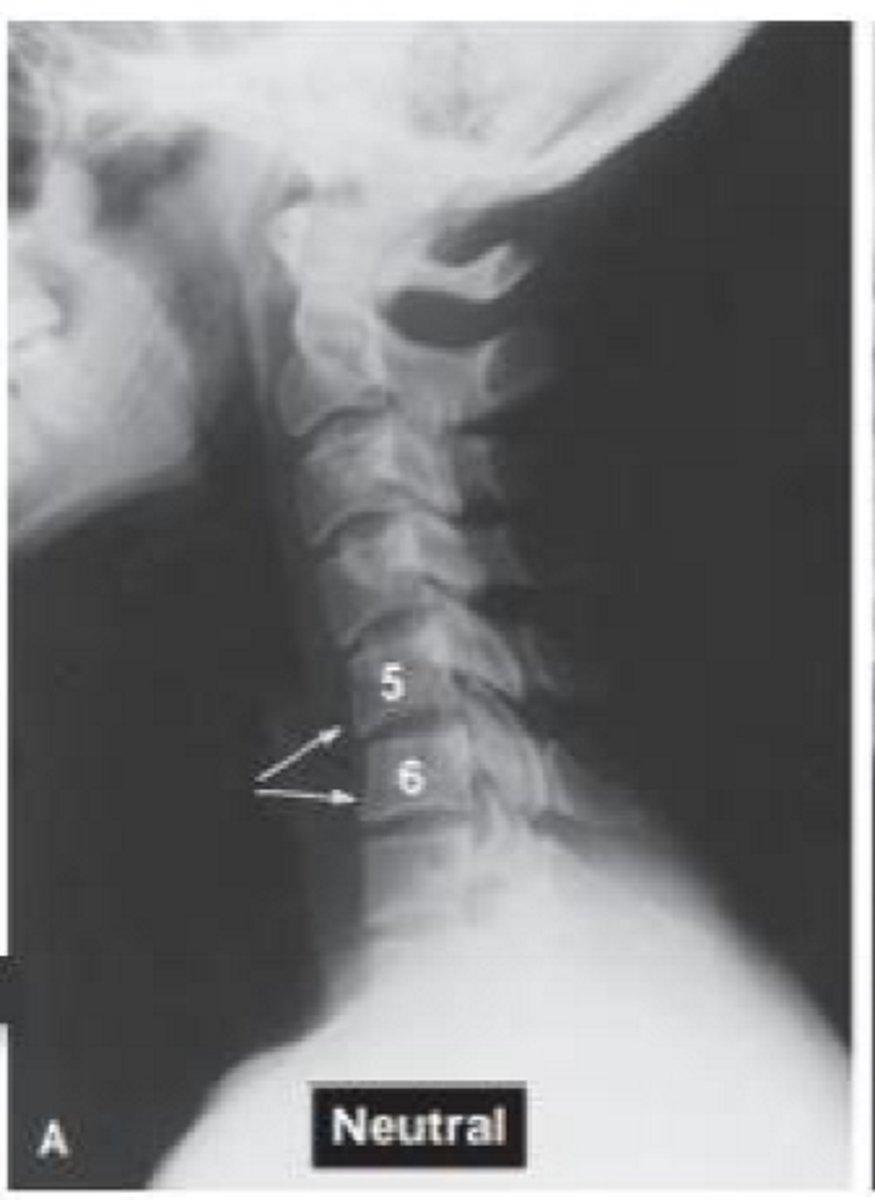
What pathology is this?
Whiplash
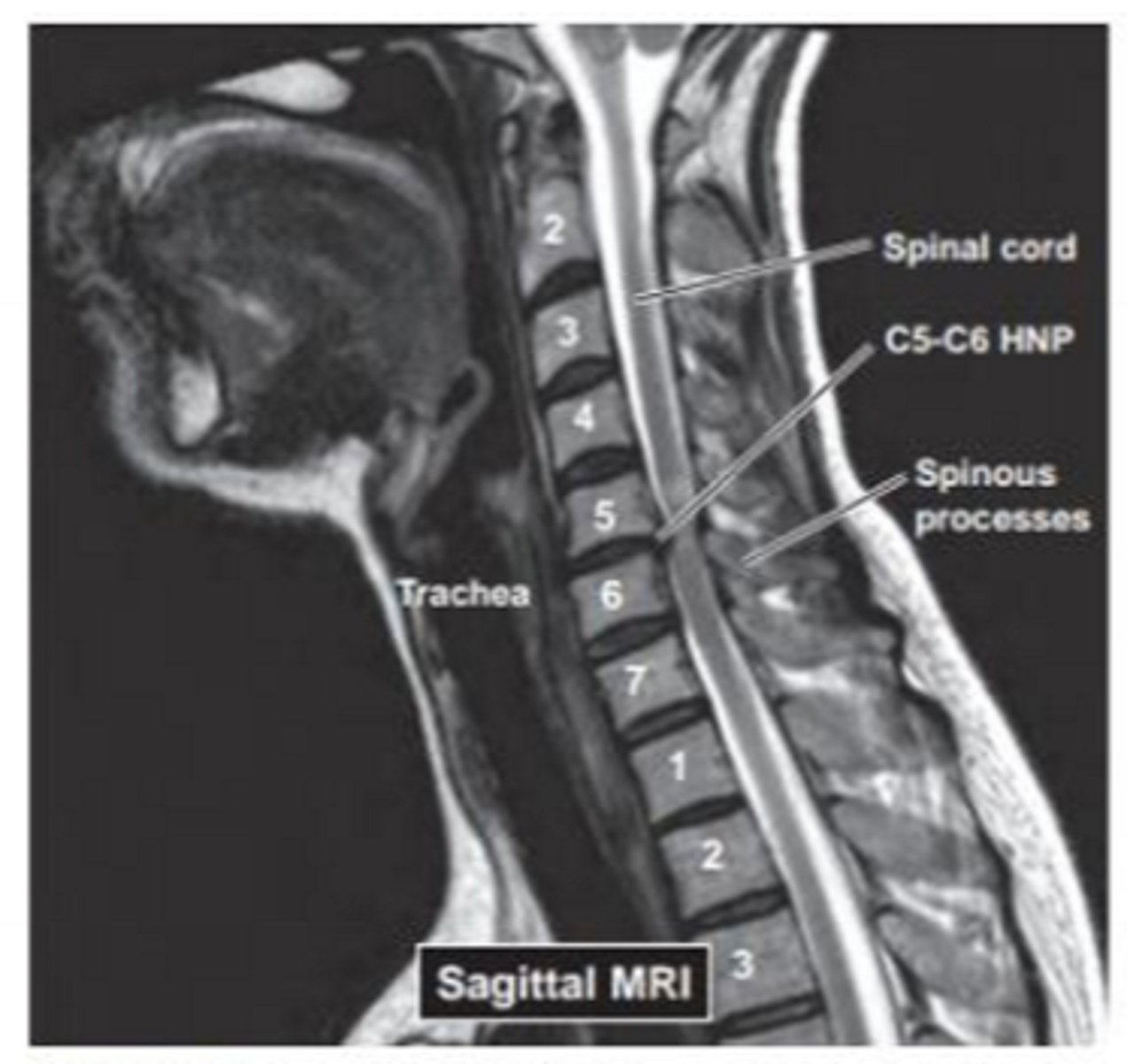
What pathology is this?
Disk prolapse with spinal cord compression
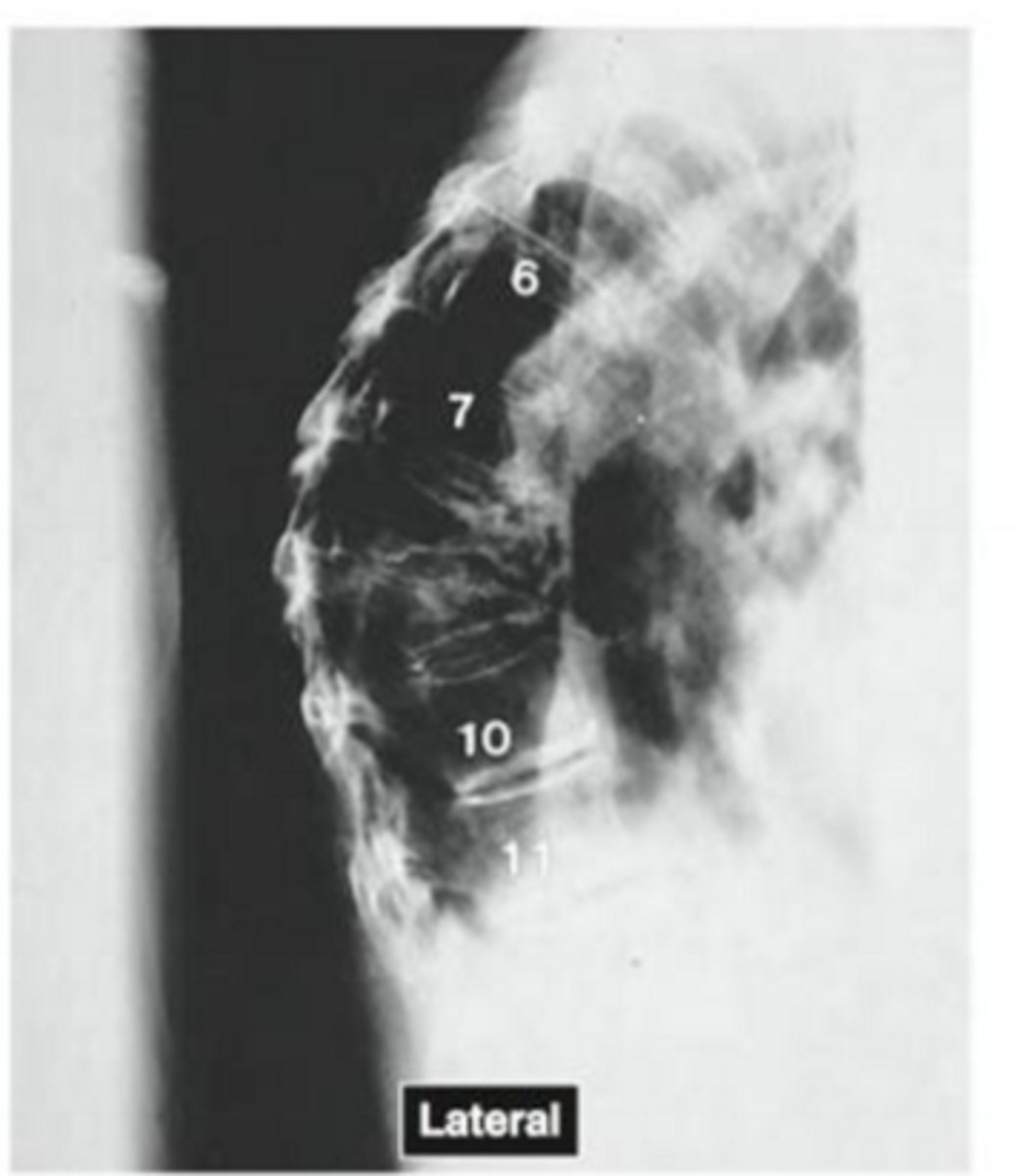
Name the pathology
kyphosis and compression fractures in osteoporotic female
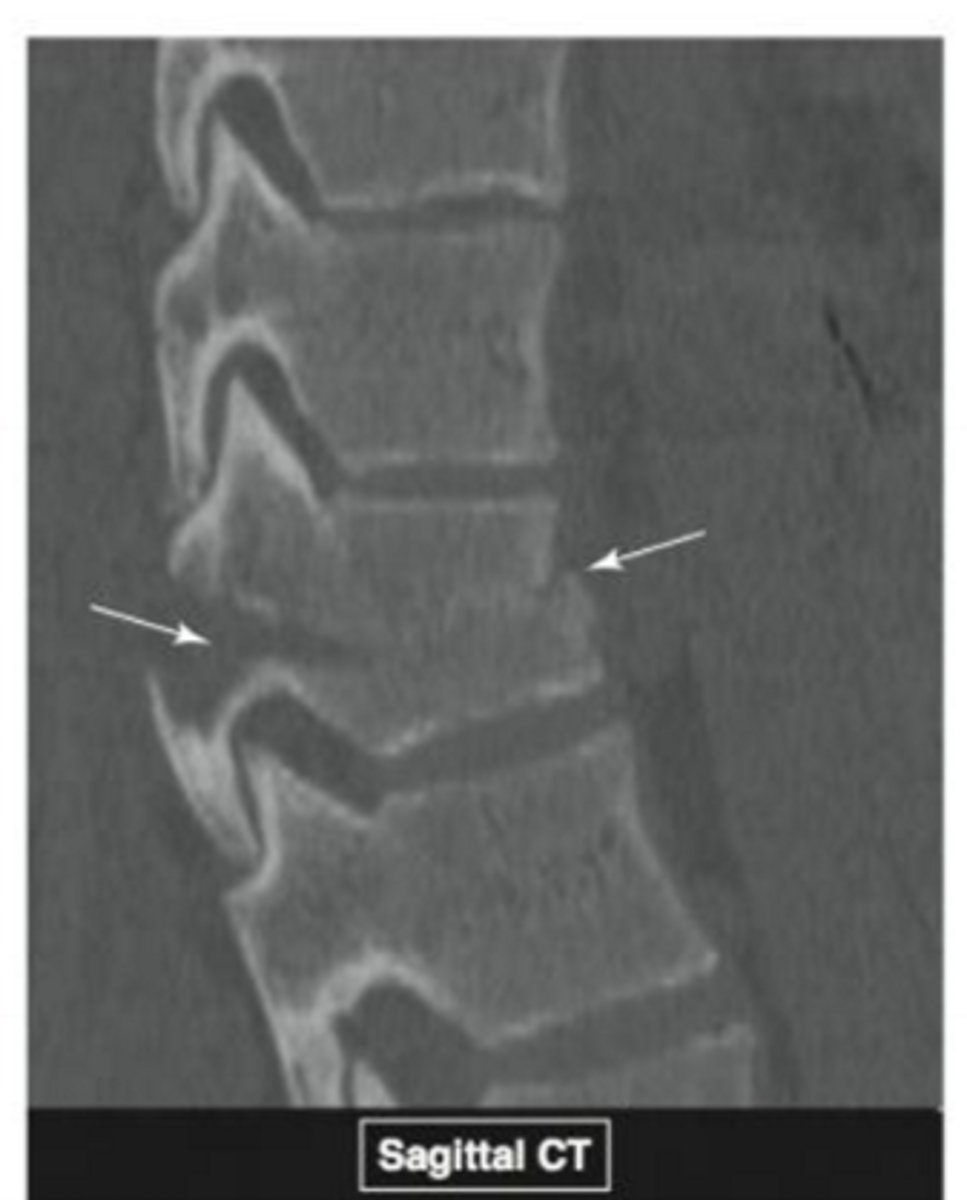
What type of fracture is this? When does it occur?
Seatbelt fracture (horizontal split of the vertebrae). When the spine is forcefully flexed forward, often during a MVA
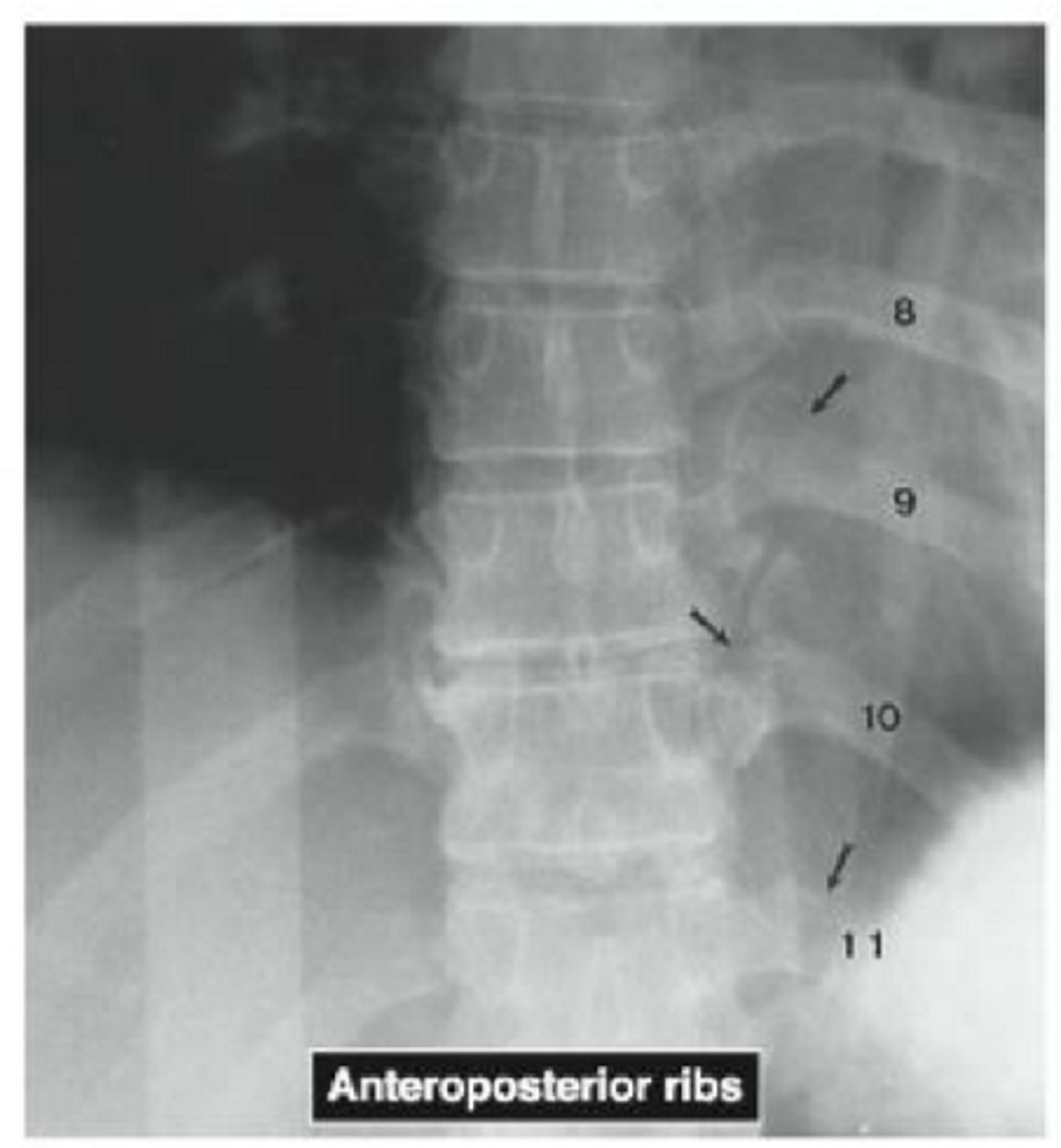
What is this radiograph showing?
multiple rib fractures
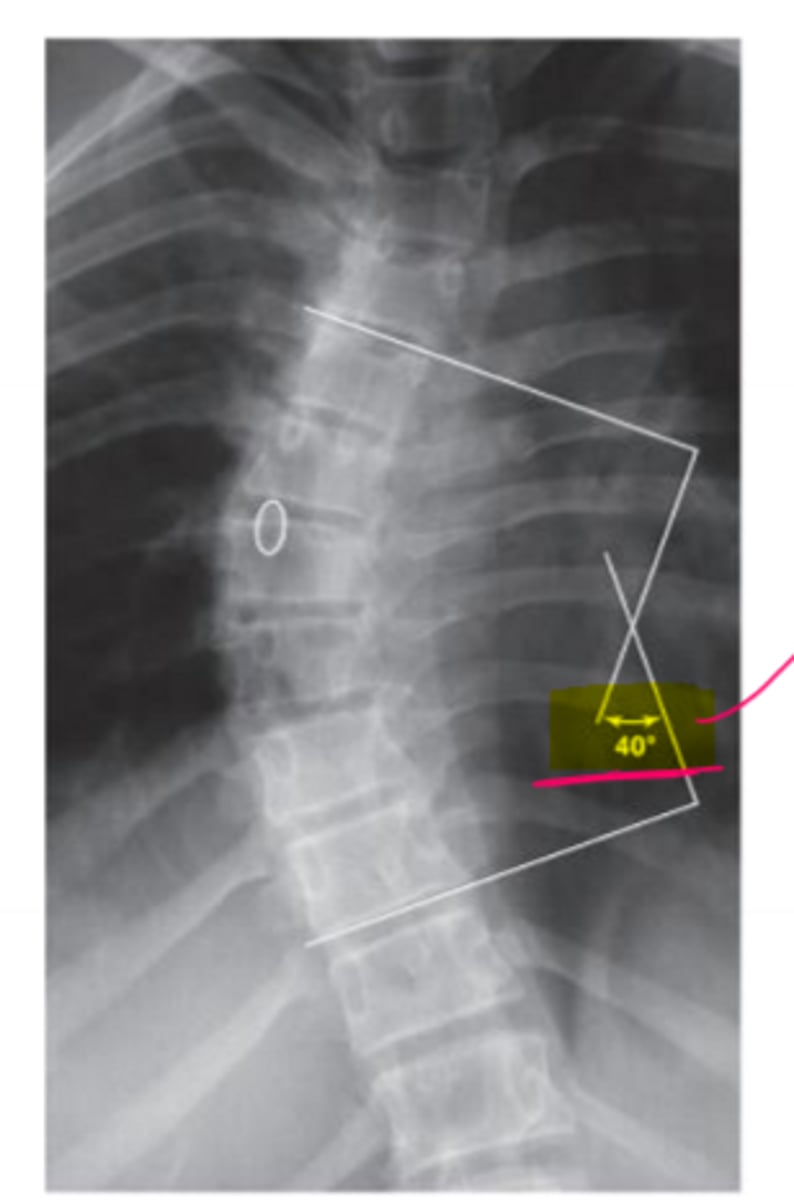
What is this radiograph showing?
the cobb angle
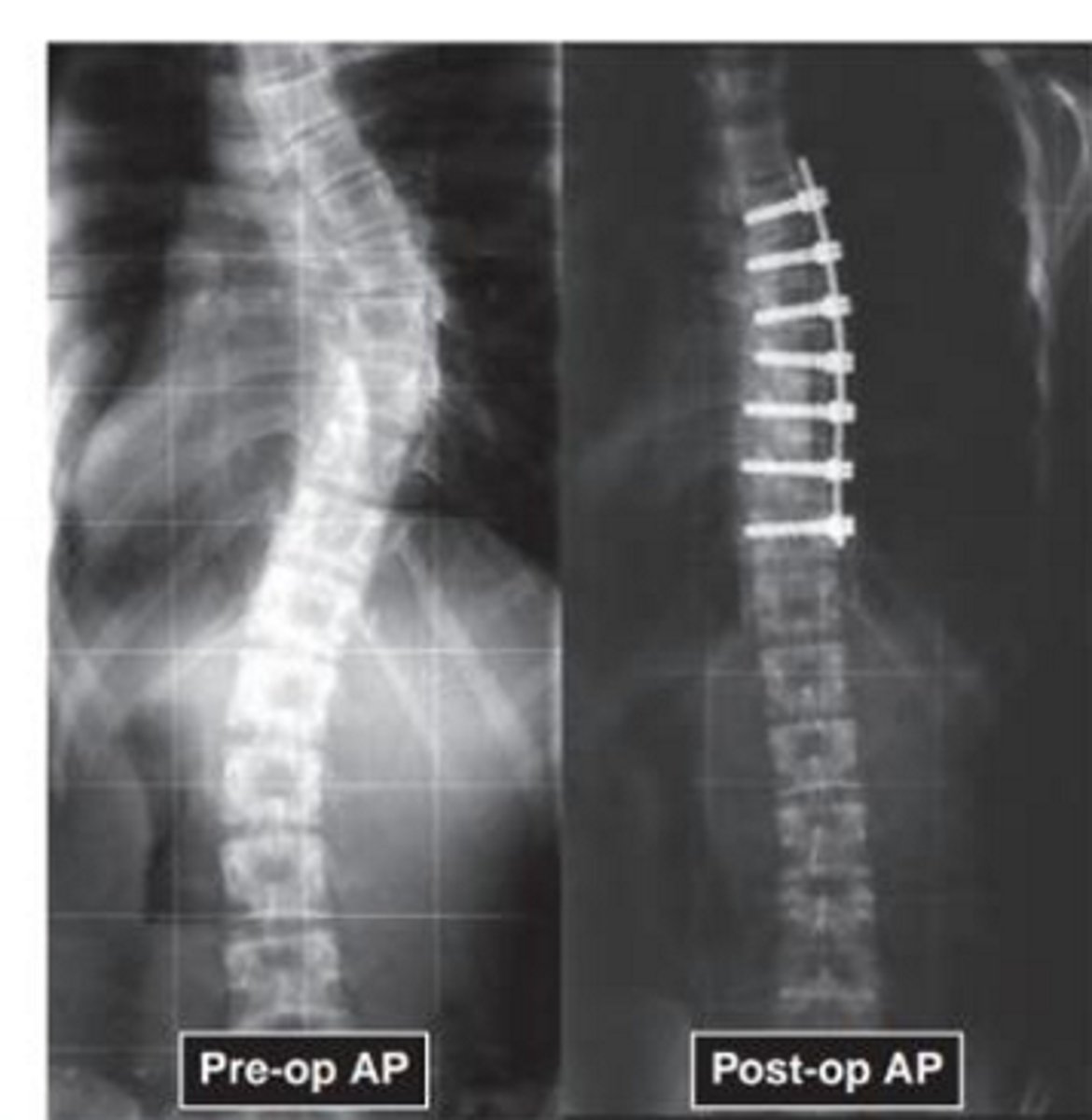
Name the pathology
scoliosis
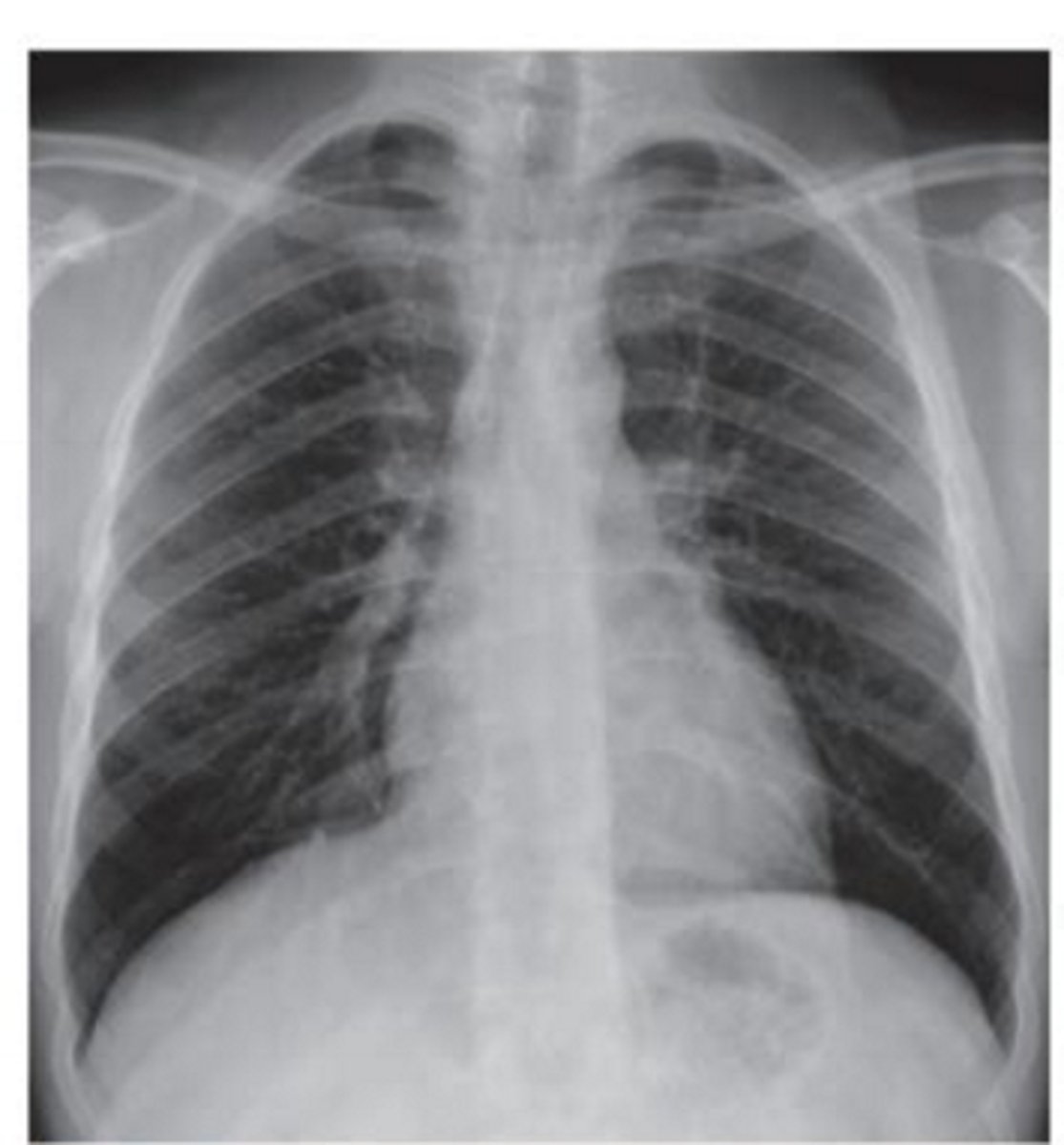
Name the view. What structures can you see in it?
normal PA chest radiograph. Diaphragm at T10 and ribs T1-T10
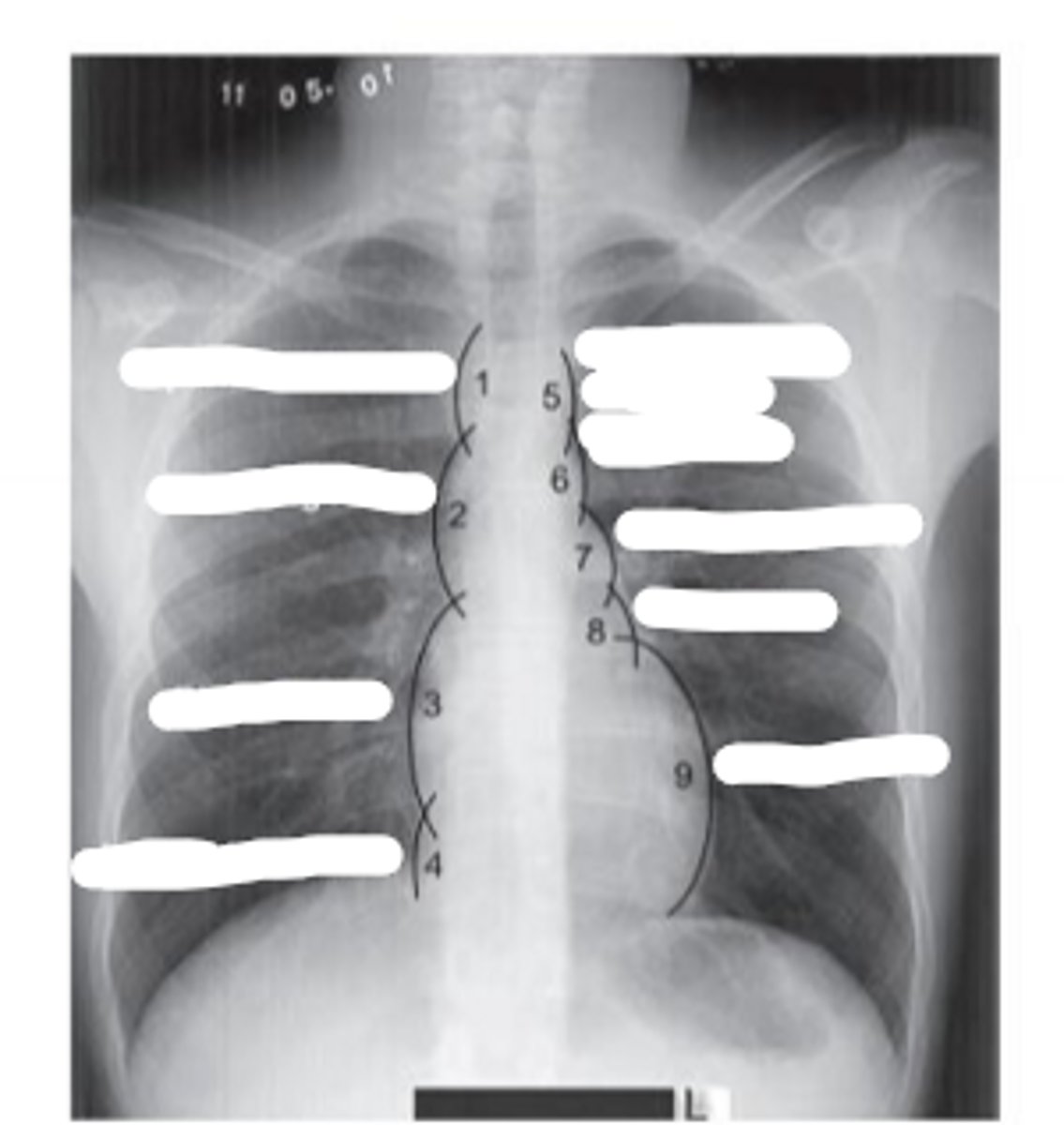
Number the picture
1. superior vena cava
2. ascending aorta
3. right atrium
4. inferior vena cava
5. left subclavian vein/artery
6. aortic arch
7. pulmonary artery
8. left atrium
9. left ventricle
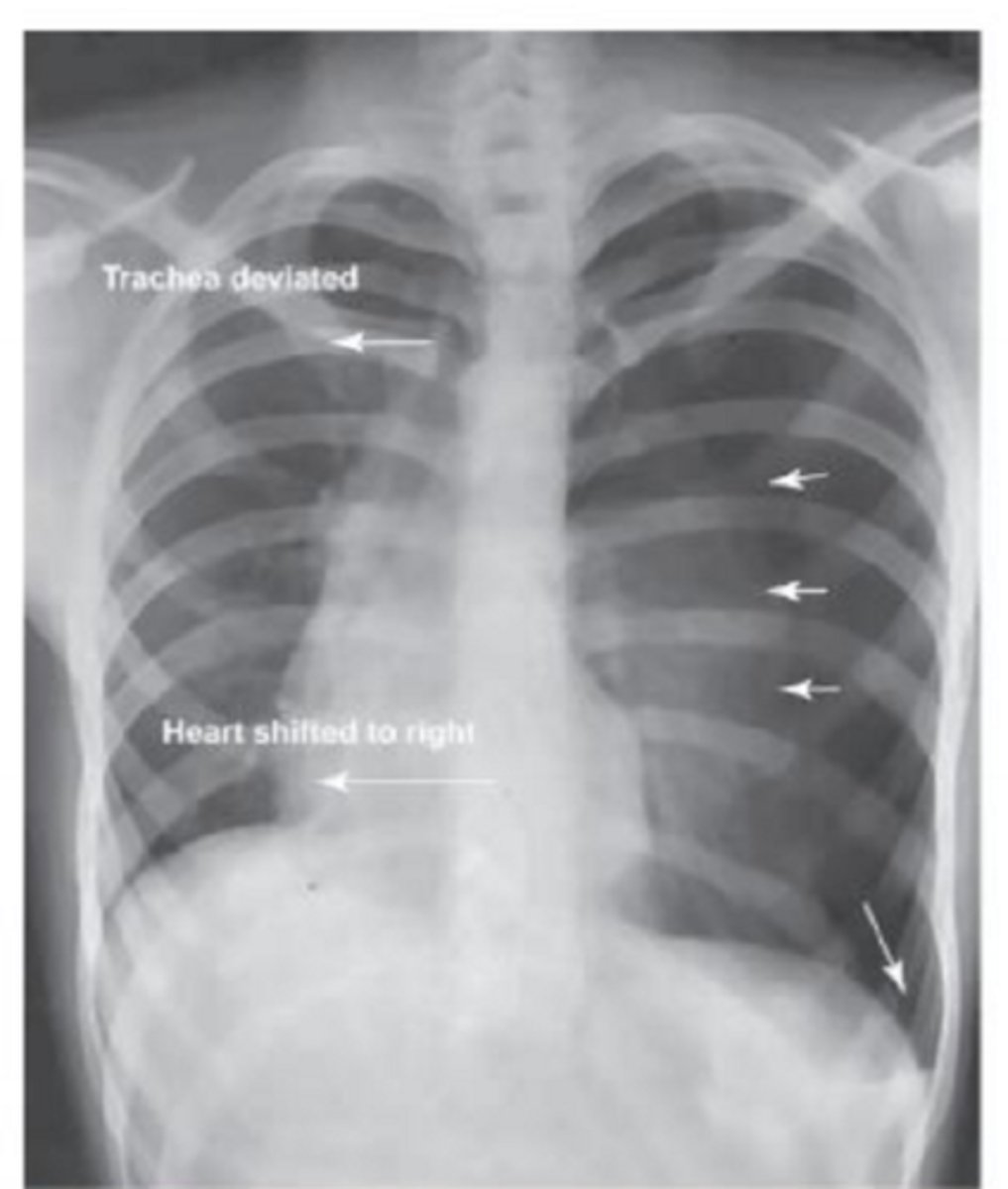
Name the pathology
pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
Which way does the trachea deviate in a pneumothorax?
the trachea deviates away from the side of the pneumothorax
What position is this?
AP projection
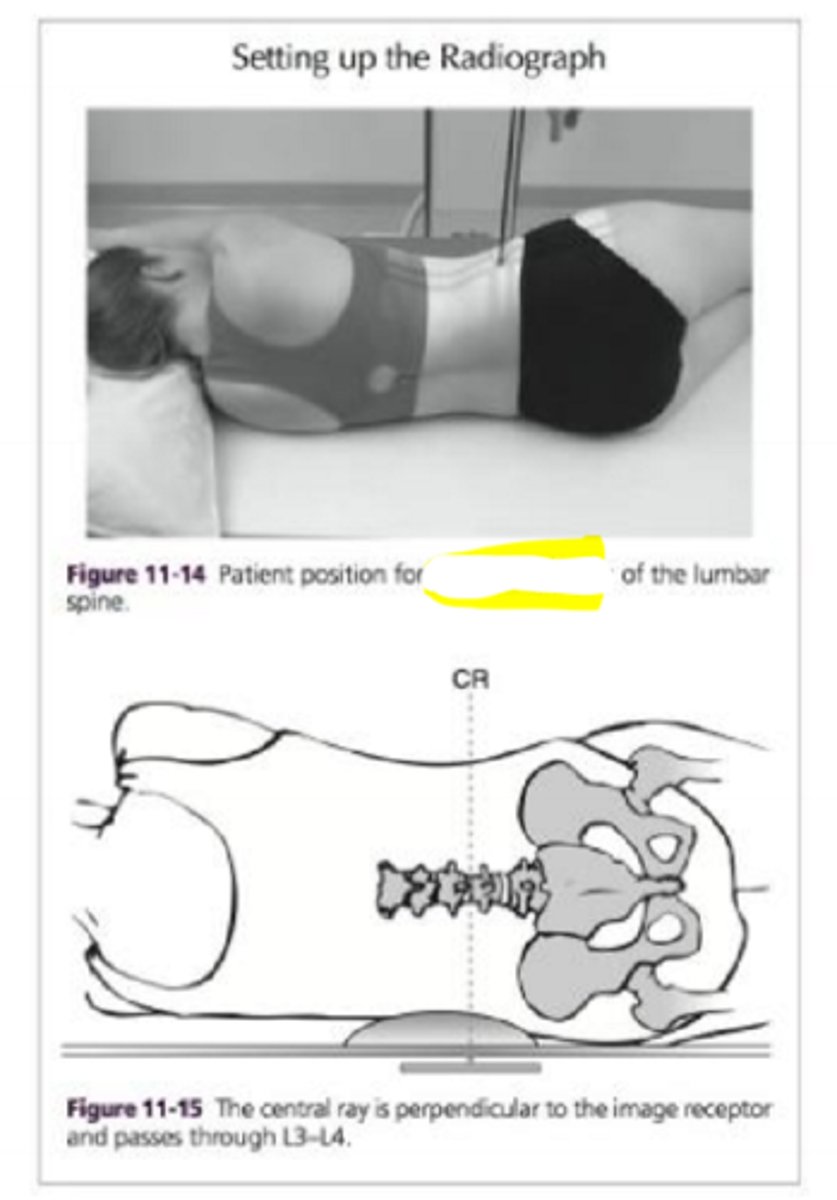
What position is this?
lateral projection
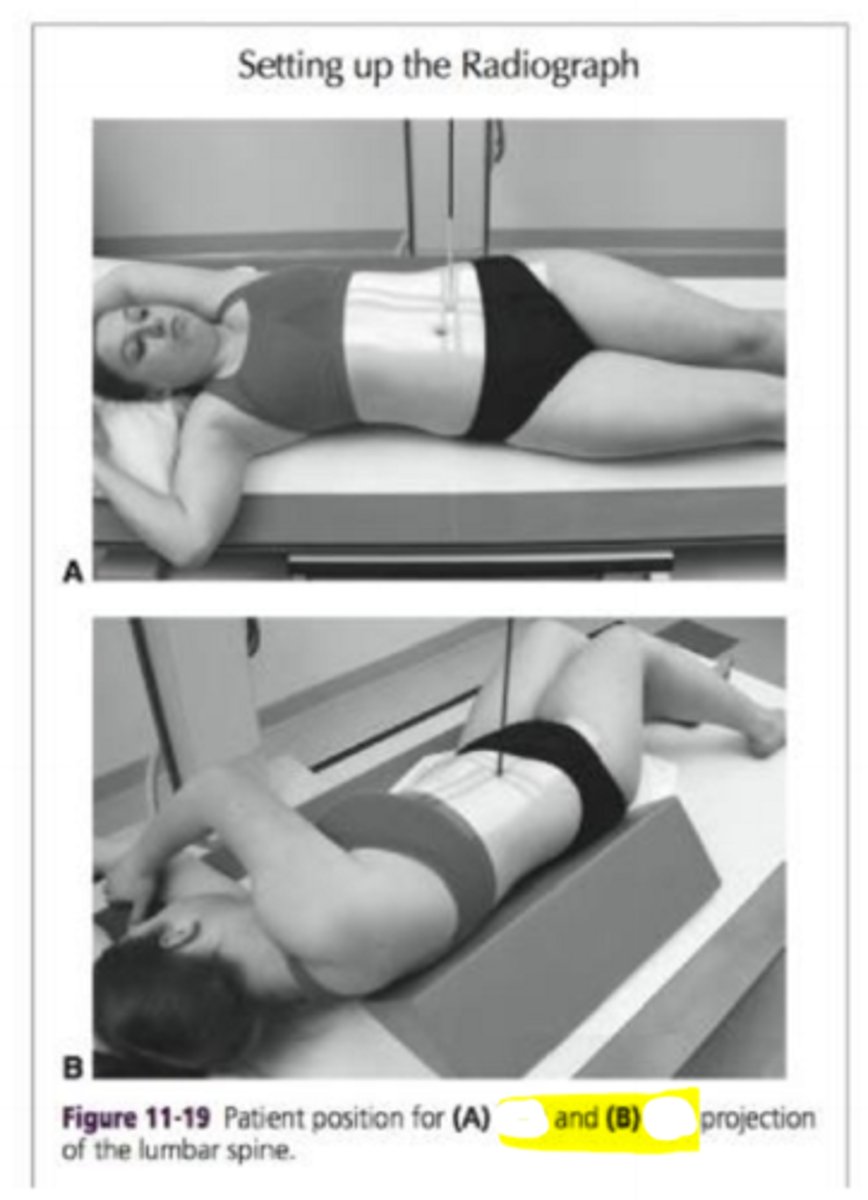
What positions are these? A and B
A. RPO (right posterior oblique)
B. LPO (left posterior oblique)
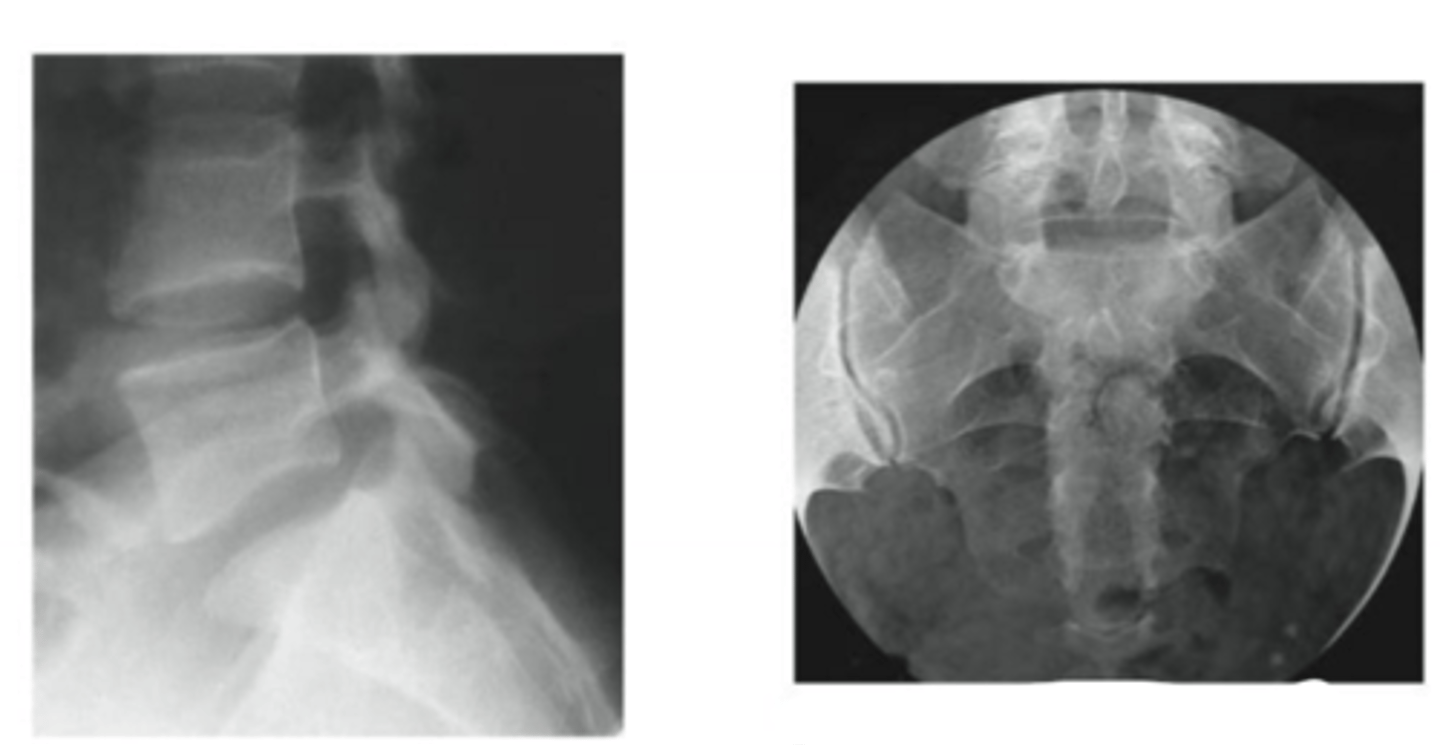
what joints can we see in these radiographs
L5-S1 and S1 joints
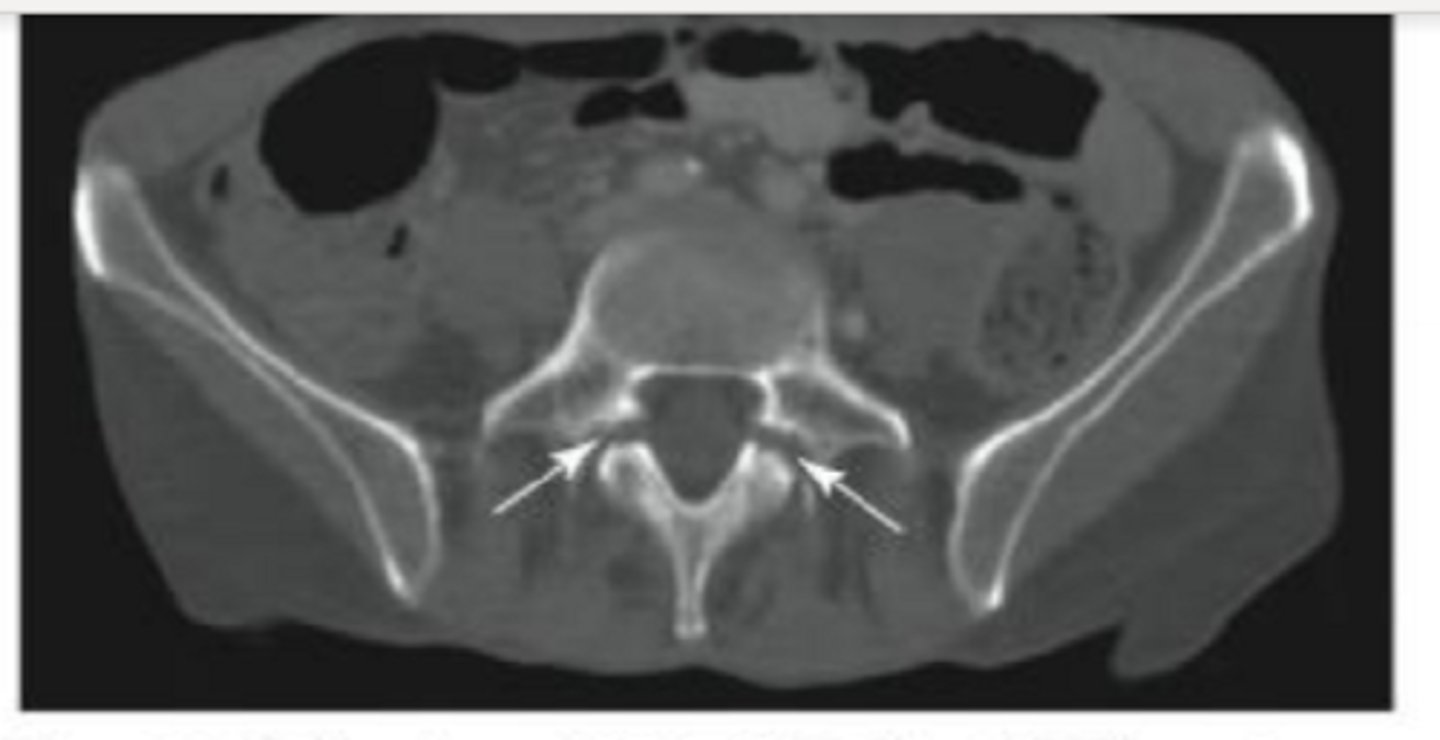
Name the pathology
spondylolysis
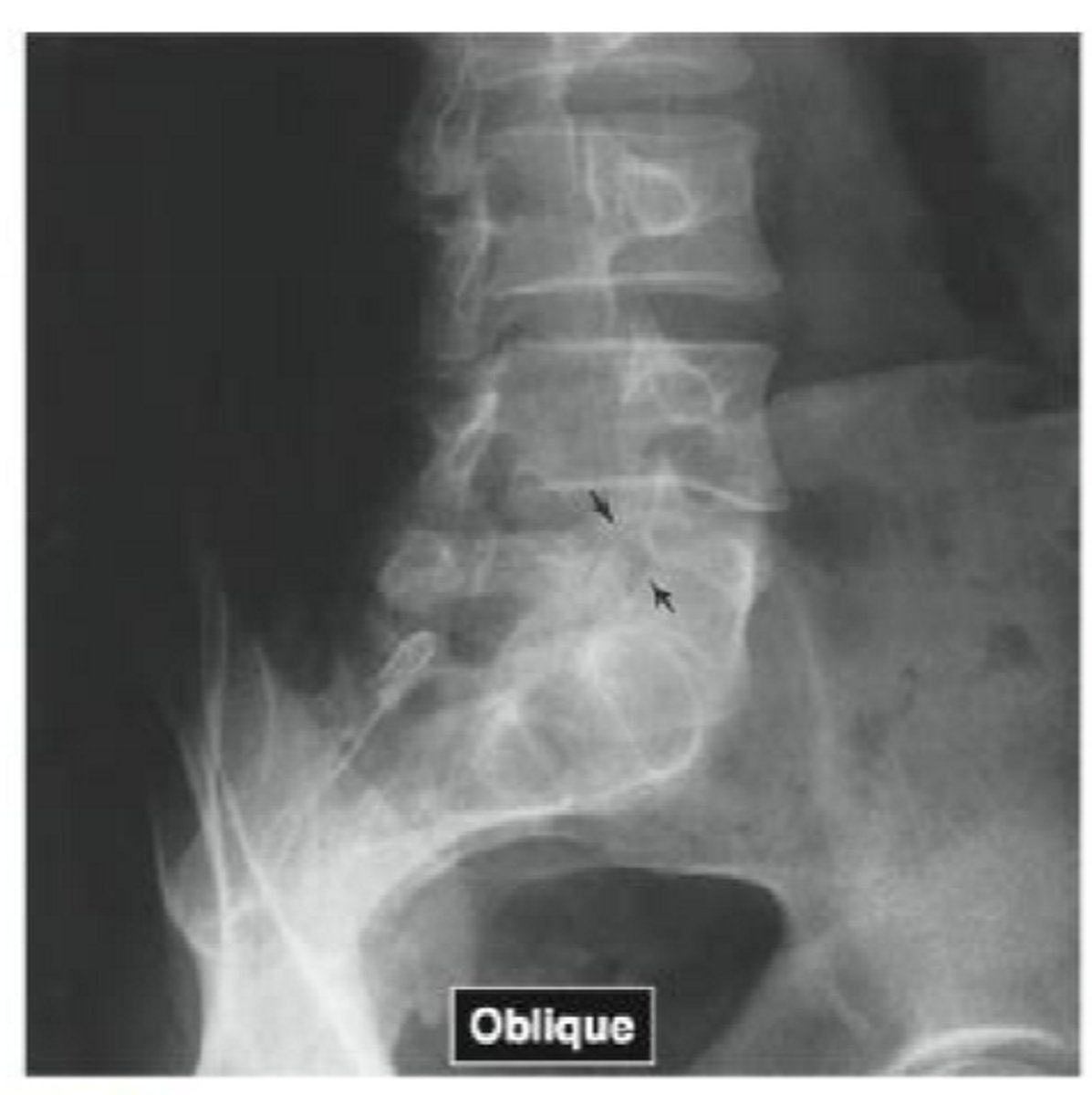
Name the pathology
spondylolysis
What is spondylolysis
disruption of pars interarticularis or a scotty dog fracture
what is spondylolisthesis
slippage of superior vertebrae on inferior vertebrae
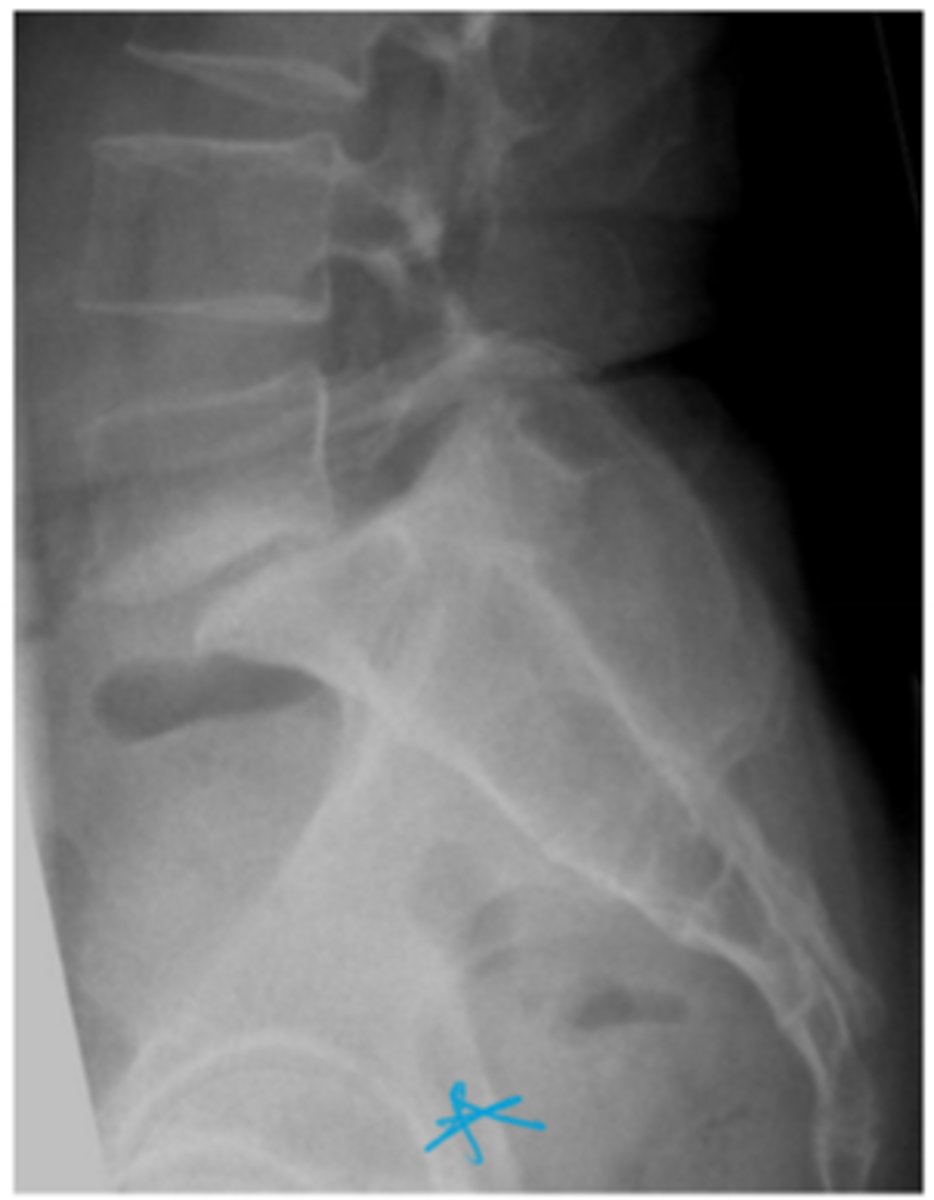
Name the pathology
spondylolisthesis
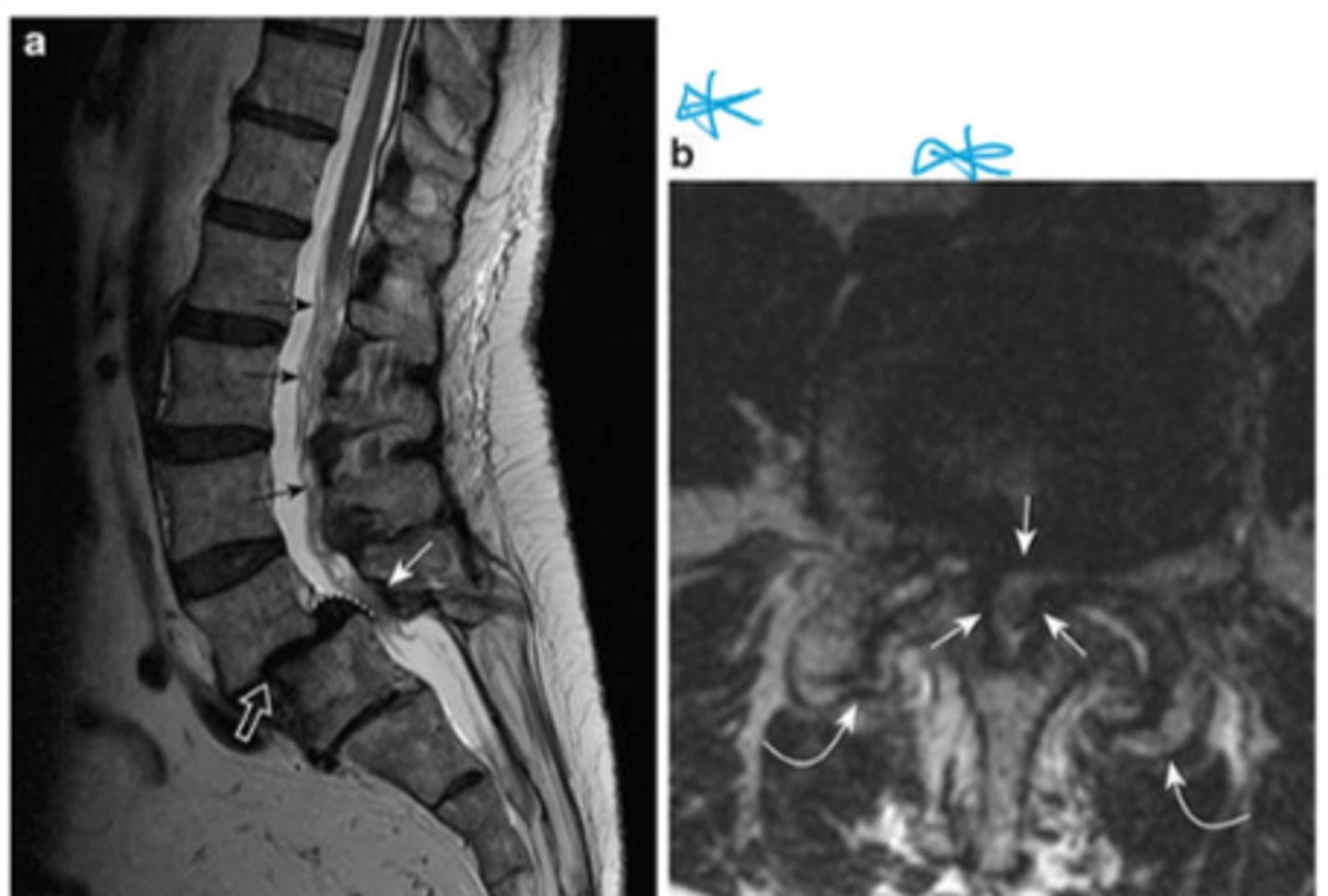
Name the pathology
spondylolisthesis
What is spinal stenosis?
Narrowing of the spinal canal
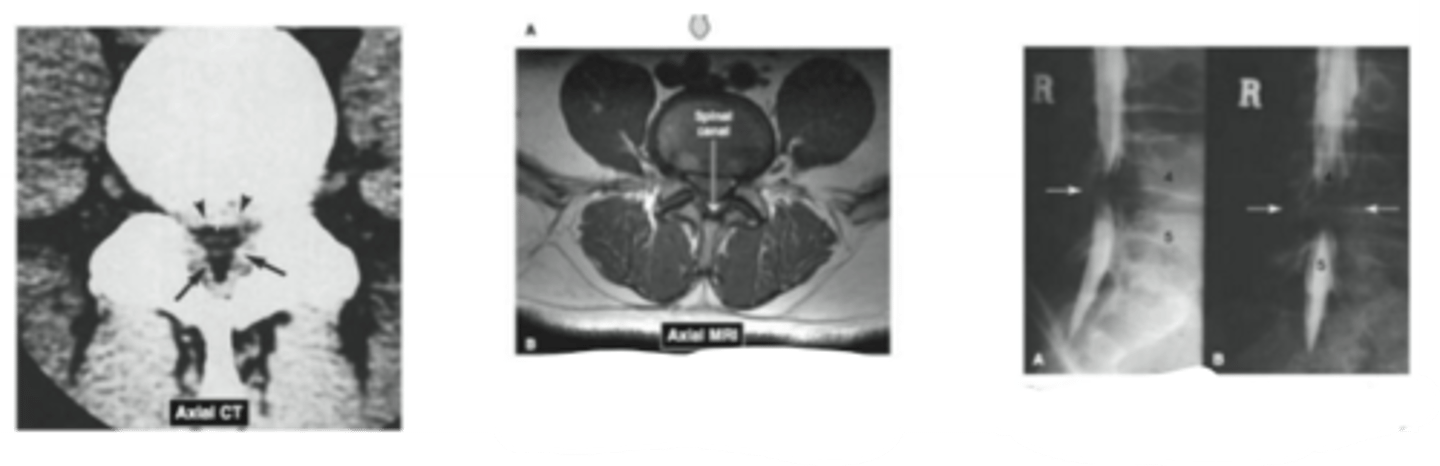
Name the common pathology
spinal stenosis
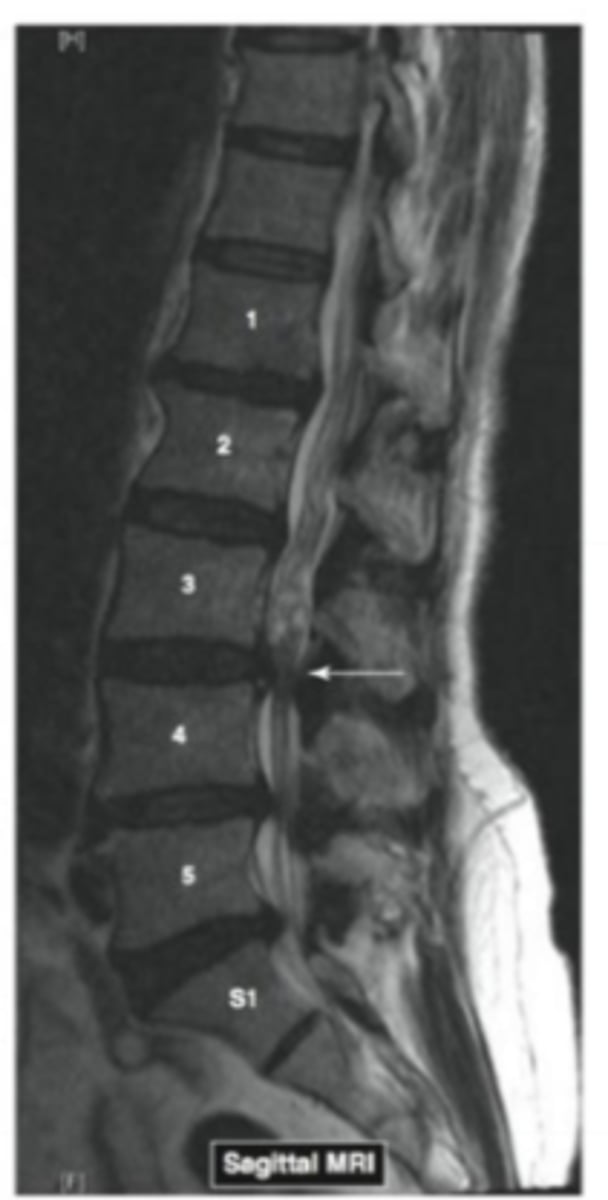
Name the pathology
disk herniation
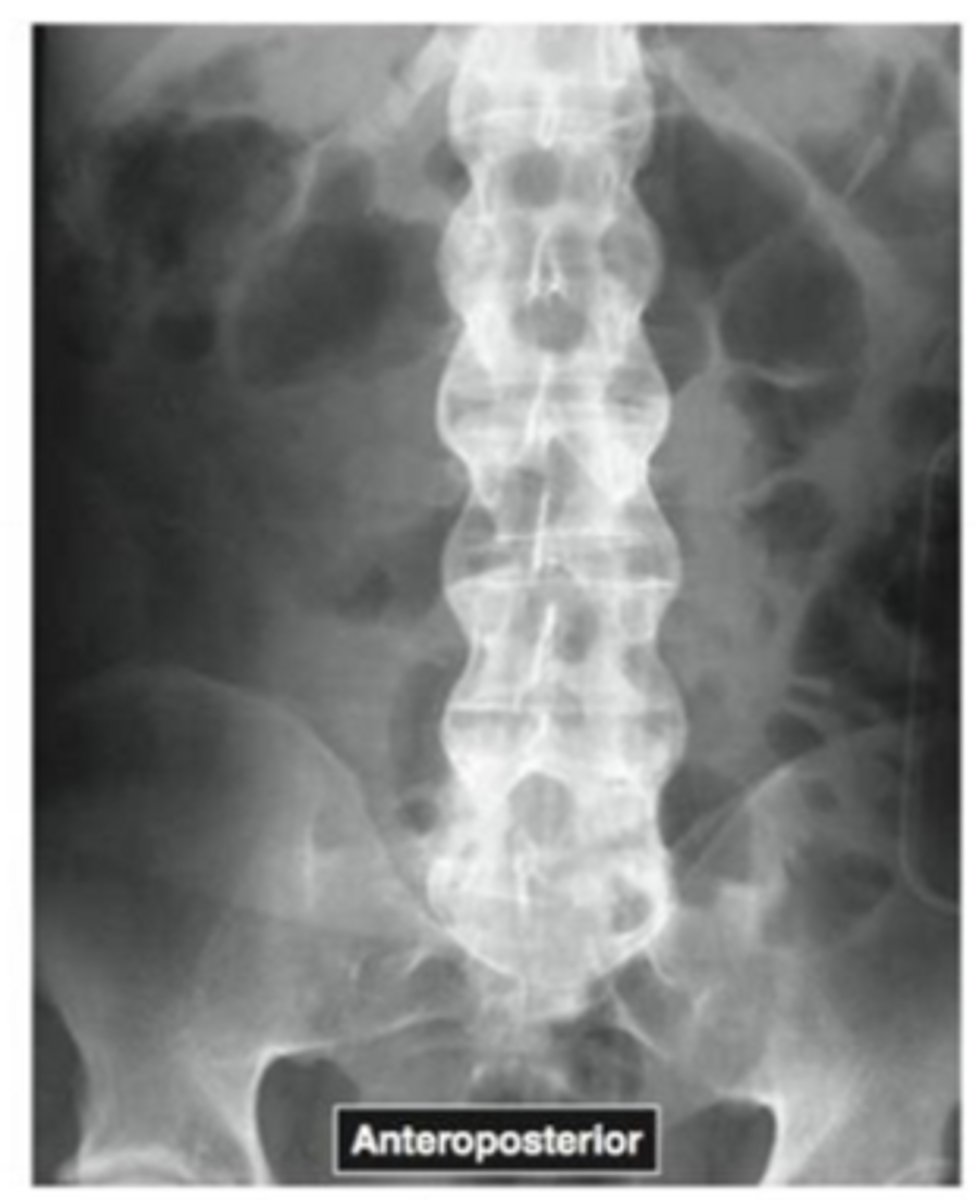
Name the pathology
ankylosing spondylitis
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
inflammatory disease of the spine
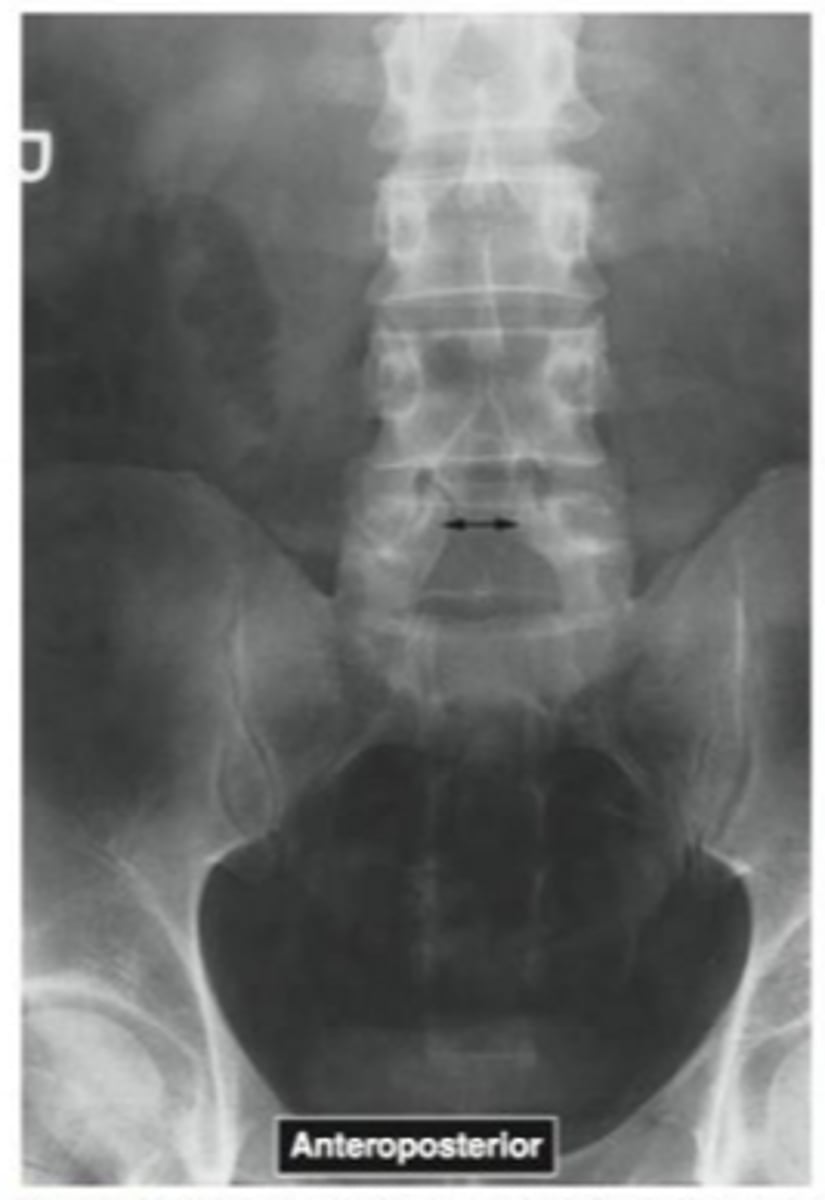
Name the pathology
Spina bifida occulta
what is spina bifida occulta?
vertebrae do not completely close during fetal development
The main indications for a spine radiograph are
Trauma/fracture, degenerative disc disease, evaluation of primary and secondary malignancies, arthritis
What is the Canadian C spine rule used to determine?
If a radiograph is indicated in a patient with neck pain
Main indications of a spine CT
Acute Trauma, Degenerative conditions and osteoarthritis, bone density (osteoporosis), infectious processes of the spine