Sponges
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gross
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the four classes of sponges? And which one is the majority sp. in?
Demospongiae (majority)
Hexactinellida (glass sponges)
Homoscleromorpha
Calcarea (calcareous sponges)
Sponge Characteristics
-multicellular animals
-sessile metazoans w/ NO true tissues, organs, neurons, or symmetry
-have unique flagellated cells called choanocytes
-motile larva stage
What does “no true tissue” mean for sponges?
No true tissue, because tissue is defined as a layer of similar cells working together to preform a specific function
-Sponges have specific cells that preform a specific function based on type of cell (functional tissues)
choanocytes (collar cells) functions:
(sponges)
-generate water current by beating their flagellas (which line chambers connected by canals)
-feeding + digestion (capture food particles in current)
-reproduction (catch sperm)
How can sponges detect changes if they do not have neurons?
Their osculum (main opening) where cilia can detect water flow rate
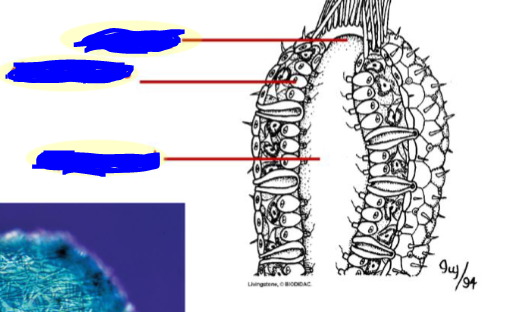
What are these?
-Osculum (main opening)
-choanocytes (lines the internal chamber—like—
-spongocoel
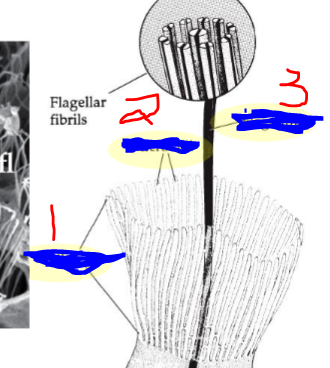
What are 1-3? + what kind of cell?
Collar
Microvilli
Flagellum
+ choanocyte
Two cell layers of sponges:
(1) pinacoderm and (2) choanoderm, with mesohyl (noncellular/nonliving gelatinous matrix with collagen fibers (in some) & spicules, providing shape & plasticity)
choanocytes remove nutrients carried in one-way water flow (what direction?
(sponges)
in through ostia (incurrent pores) through chambers/channels, then out through the osculm (excurrent pore)
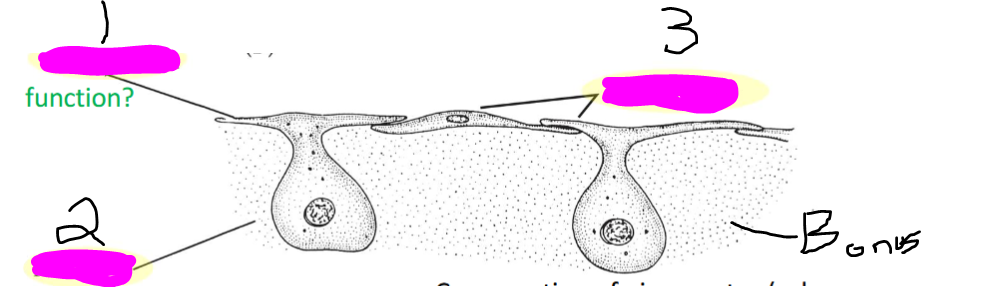
Name these
(sponges)
1) pinacoderm (provide external protective layer—like skin)
2) mesophyl
3) pinacocyte
Bonus: dermal pores
Pinacocyte (forms the?)
Choanocyte (forms the?)
(sponges)
Pinacoderm
choanoderm
Mesohyl holds:
(sponges)
digestion, gamete production, secretion of
skeleton (acts like an endoskeleton) transport of
nutrients and wastes by specialized ameboid cells
ameboid cells
(sponges)
stem cells in sponges (or called totipotent)
Others are irreversibly/specialized cells
(sponges)
-Sclerocytes (produce spicules)
-Proteins forming the fibrous skeleton:
Spongocytes (spongin, flexibility),
Collenocytes & lophocytes (collagen like)