Biopsychosocial Diseases and Conditions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
role of PT
- recognize complexity of condition/disorder
- provide support/patience to those afflicted
- identify when appropriate referral is needed
- submit thorough documentation of presentations
- know your boundaries!
IMPLICATIONS:
1. societal views
2. healthcare system views
3. your own views
biopsychosocial model of health
an approach to studying health and human function that focuses on importance of biological, psychological, and social (or environmental) processes
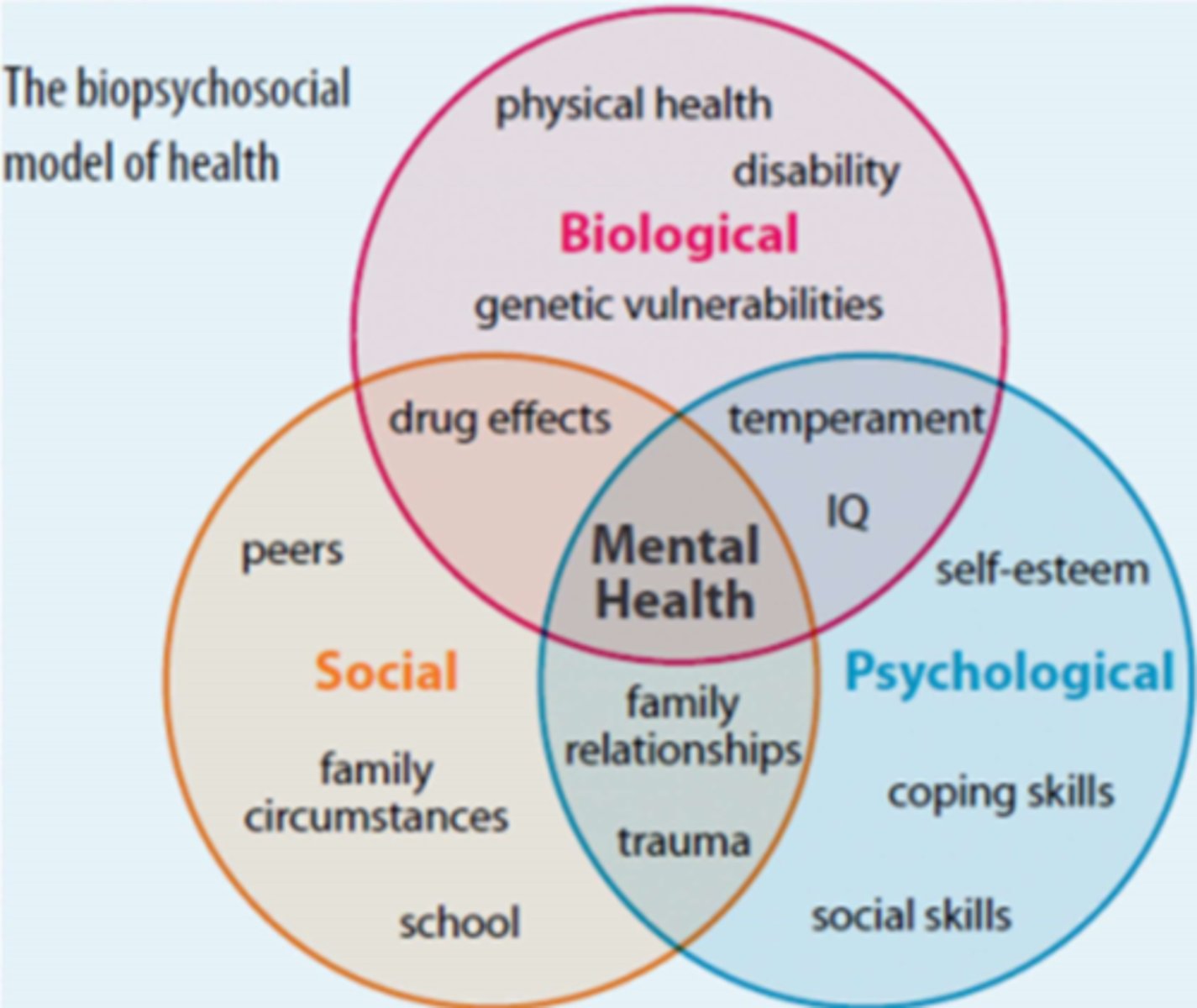
biopsychosocial (BPS) categories
1. depressive or bipolar depressive disorders
2. anxiety disorders
3. trauma-related disorders
4. personality disorders
5. psychotic disorders
6. eating disorders
7. substance abuse disorders
DSM-5
the most recent edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders

anxiety disorders
PANIC--> fight or flight is triggered
*short-lived episodes
1. panic attack
2. panic disorder
WORRY--> anticipation of misfortune/doom
*cannot shut off perceived fears & worries
3. generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
anxiety
characteristics:
1. fear and apprehension
2. heightened physiological response
3. occurs suddenly and without warning
conditions:
- panic disorders
- panic attacks
- generalized anxiety disorder
- social and specific phobias
panic attack
short-lived, last 5-20 mins av. (<1 hr max)
- intense fear w/o trigger (no real danger)
- severe physical fight or flight response
- can occur waking up from sleep
panic disorder
reoccurring panic attacks in frequency
- usually begins in adulthood (after age 20)
- 2x as common in women
generalized anxiety disorder
severe/crippling, ongoing anxiety/worry that interferes with daily activities
*worry over countless "what if" events that they can't stop
common themes:
- health/safety of self or loved ones
- future
- $
trauma related disorders
CHARACTERISTICS:
- exposure to a traumatic or stressful event
- set-off by related-triggers (sounds, images)
1. posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
2. adjustment disorders
posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
recurring, intrusive recollections of an overwhelming traumatic event
*experience change in mood & cognition
**lasts for >1 month, begins 6 months after trauma
***unwanted thoughts (flashbacks) & nightmares
adjustment disorders
"overreact w/ reckless behavior"
abnormal and excessive emotional and/or behavioral reaction caused by an identifiable stressor
*symptoms show w/in 3 months after trigger and stop 6 months after trigger ends
ex. flood/fire, break-up/divorce, new job, parents fighting
normal response to stress
stress--> release of adrenaline & cortisol --> triggers endorphins
amygdala & adrenal gland --> adrenalin and norepinephrine

amygdala
What is the key to normal expression of emotions, especially fear?
endorphins
Alcohol increase ______________________ activity which therefore decreases stress and pain awareness.
amygdala
stores memory of situations to prep for similar events in future
IN PTSD--> becomes "hijacked" by stress/anxiety and reduces activity of PFC
*hippocampus and anterior cingulated cortex are smaller in those w/ PTSD
(YELLOW IN IMAGE)

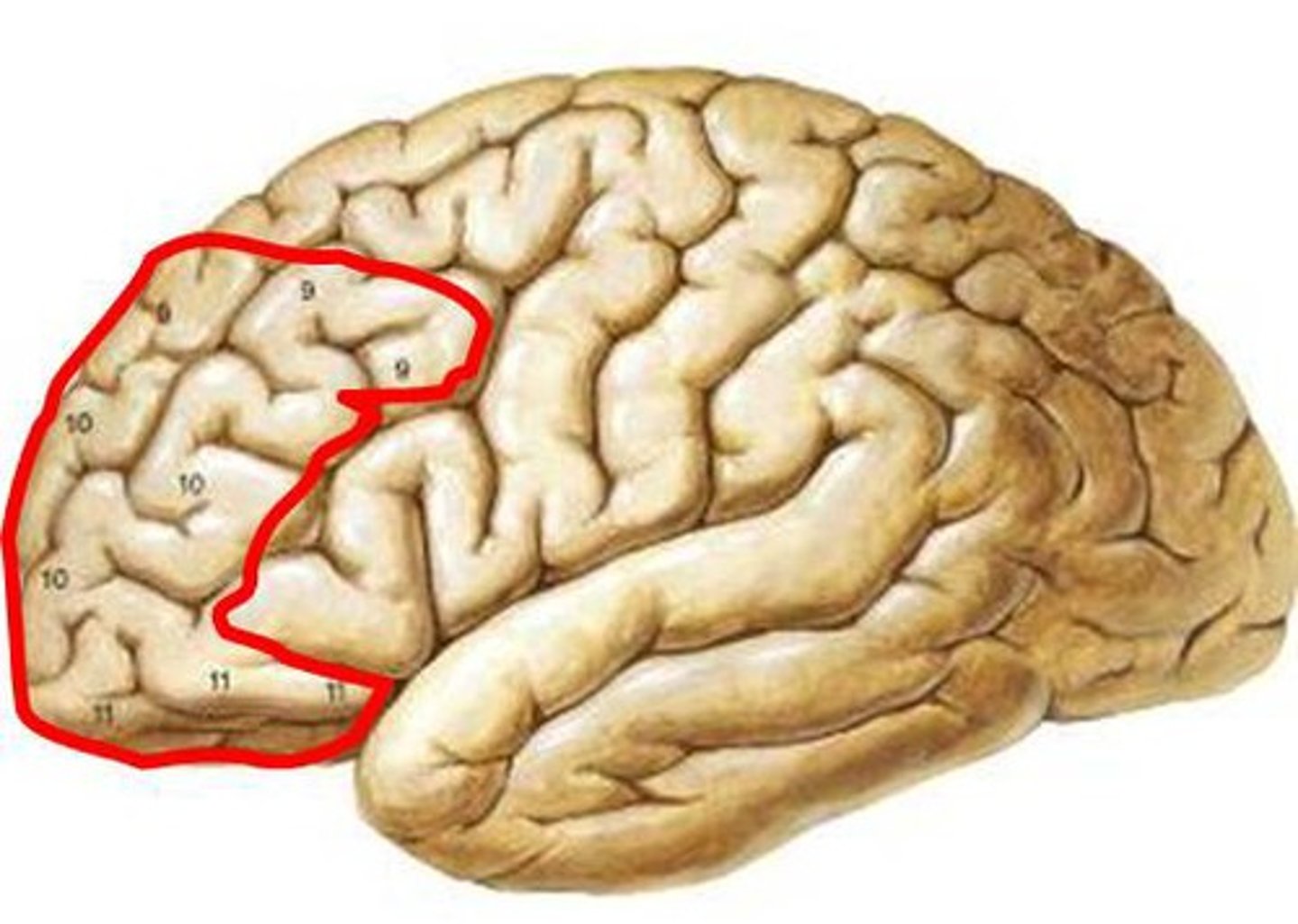
prefrontal cortex (PFC)
higher reasoning, so we don't runaway with our emotions
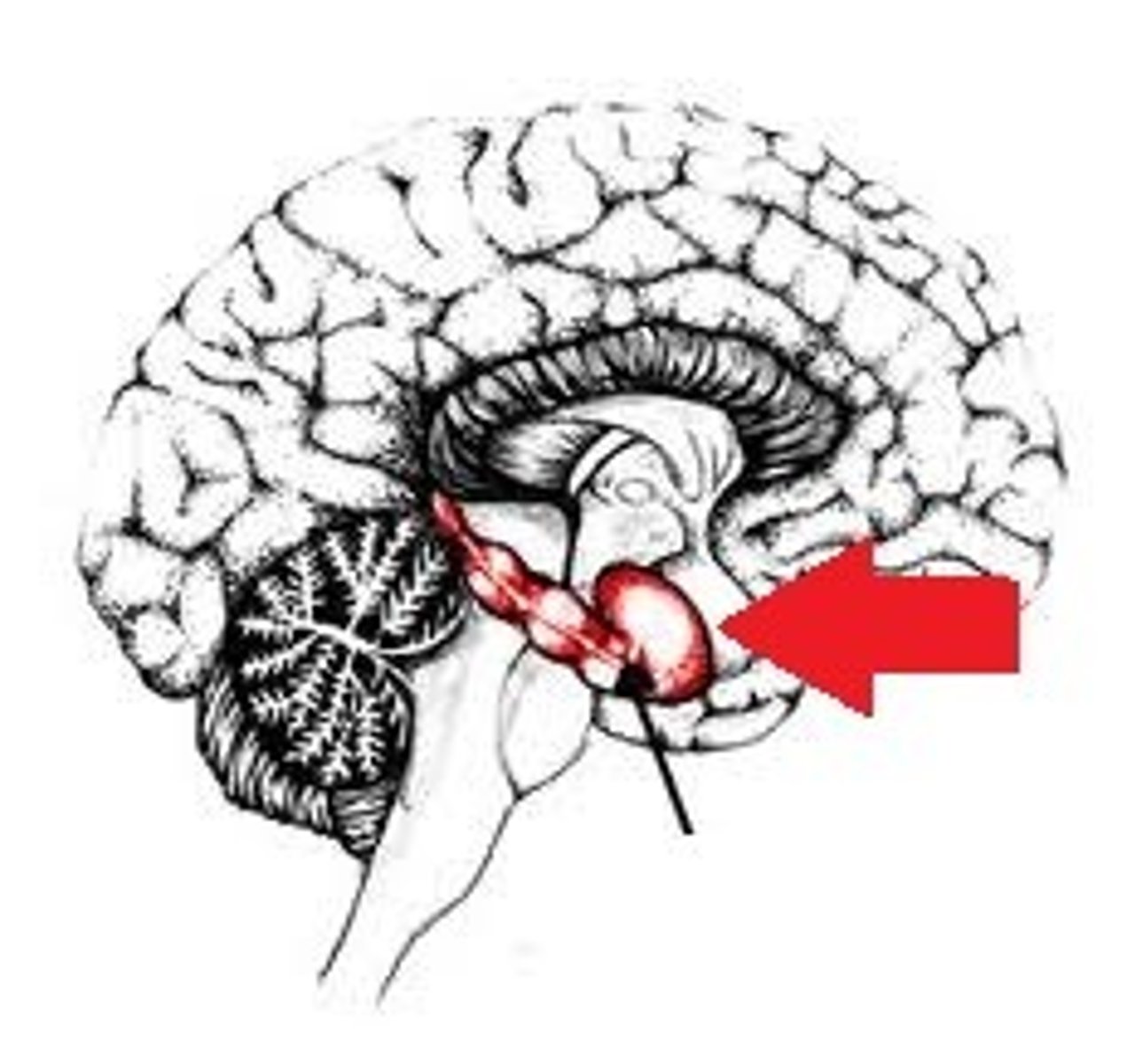
hippocampus
stores memories
*keep fear and anxiety in check
depressive and bipolar depressive disorders
CHARACTERISTICS:
- symptoms tend to occur in cycles with normal states in between
- multiple genetic and non-genetic factors
- link btwn neural activity, endocrine system, and immune system
1. major depression (unipolar)
2. bipolar (manic-depressive)
3. seasonal affective disorder
major (unipolar) depression
MOST COMMON MENTAL HEALTH DISORDER
period of 2 weeks or longer during which there is either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure and at least four other symptoms with change
- wide range of behavioral and physical symptoms (can alter sleep, appetite, energy, concentration, etc.)
- may be associated with thoughts of suicide
bipolar depression (manic-depressive illness)
4 basic types with 3 components (last several days)
1. manic episodes
2. depressive episodes
3. sudden mood swings
IMPACT--> varying shifts in mood, energy, activity level may effect ability to carry out day to day tasks; erratic thoughts, sleep cycles, & behavioral patterns
INFLUENCES--> genetics, environment, altered brain chemistry & structure
manic episode
bipolar swing
- feel elated
- lots of energy
- trouble sleeping (awake >24 hrs)
- talk fast about a lot of different things (not necessarily logical)
- grandiose thoughts
- think they can do a lot of things
- do risky things
depressive episode
bipolar swing
- very sad, down, empty
- little energy
- trouble sleeping (too little or too much)
- can't enjoy anything
- trouble concentrating
- forget things
- think about death/suicide
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
subcategory of personality disorders and a condition
*hoarding is included in the O-C disorder subgroup
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. obsessions
2. compulsions
ex. germaphobe continuously wash hands, constantly check locks, specifically arrange items
obsessions
intrusive thoughts or actions which are unwanted but repeated & cause significant anxiety but must by fulfilled
ex. fear of contamination, illness, harming, self-doubting
compulsions
repetitive behaviors designed to reduce anxiety or prevent bad things from occurring
ex. checking, washing, counting
compulsive hoarding
O-C subgroup
DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS:
1. excessive accumulation of items, regardless of actual value or financial situation
2. difficulty discarding or parting with possessions because of a perceived fear if lost them & need to save them
3. inability to use the living space/rooms as intended
- items can cause distress/problems w/ everyday activities
*highly associated w/anxiety, ADHD, bipolar, depression, OCD
- often triggered by life event
- respond well to CBT
somatic symptom disorders
bodily symptoms caused or exacerbated by psychological factors
*physical symptoms are inconsistent with or cannot be fully explained by any underlying general medial or neurologic condition
1. somatic
2. illness anxiety
3. factitious disorder
4. psychogenic
5. functional neurological symptom disorder
illness anxiety disorder
a somatic disorder where person is preoccupied w/ having or getting a serious illness despite having mild or no symptoms and despite absence of physical findings
*will subject themselves through a battery of tests AND still not believe negative test results
somatic symptom disorder (SSD)
a somatic disorder where person has extreme anxiety about physical symptoms such as pain or fatigue, to the point it can interfere with daily life
*cannot work and typically lose family & friends
**preoccupied with illness for at least 6 months
1st it is believed, then somatic symptoms actually manifested
functional neurological symptom disorder (FNSD)
somatic disorder where person presents with neurological symptoms without identifiable neurological cause
ex. motor/vision/speech dysfunction, paralysis ,seizures
*dramatic and inconsistent presentation
**Hoover sign is positive
***unconscious attempt to resolve an internal psychological conflict
factitious disorder (FD)
somatic disorder where person appears ill or injured w/o external reward, to point of exaggerating symptoms, hurting self, even altering medical records
*to draw attention, sympathy, reassurance
FD imposed on another (FDIA)
somatic disorder where a person projects medical problems on another for their own attention/sympathy
*childhood trauma, depression, personality disorders, and working in the healthcare field all can be causes
psychogenic movement disorder
somatic disorder where the subconscious responds to stress and creates unwanted muscle movement such as a spasm or tremor
*cause is NOT neurogenic
**CUREABLE
malingering
illness is pretended as a way to achieve a secondary goal such as the acquisition of drugs or disability benefits
NOT RECONGINZED BY THE APA
personality disorders
1. chronic pain
2. symptom magnification syndrome
chronic pain
episode of pain that persists beyond normal healing time (3-6 months)
*lingering acute pain is typically related to anxiety
**CP associated with mental health diagnosis (commonly depression)
TREATMENT FOCUS:
- treat underlying condition
- pharmacologic support --> weaning w/ close monitoring
- CBT effective
*focus on function and want the patient CAN do
chronic pain disorder
personality disorder when magnified emotional pain manifests as unrelenting physical pain
BEHAVIORAL SYMPTOMS:
1. fear
2. isolation
3. tension
4. fatigues
*association with depression
**refer out when coping mechanisms appear impaired
symptom magnification syndrome
self-destructive, attention seeking
*symptoms reported or demonstrated which function to control the person's life
**reinforced behavioral patterns
NOT RECOGNIZED BY APA
psychotic disorder
1. schizophrenia
schizophrenia
psychotic disorder where person may hear voices, see things that aren't there, believe that others are reading or controlling their mind
*hallucinations and delusions
**onset 20-30s (earlier in males), but not typically diagnosed until mid-40s
***GENETIC LINK
COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS:
- difficulty with learning comprehension
- difficulty focusing or paying attention
- 10% die of suicide
VIOLENCE = NOT COMMON
TREATMENT:
- anti-psychotic meds (Thorazine, Haldol, Risperdal - bad side effects)
- CBT
- self-help groups
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
low electric brain current under anesthesia which triggers seizure
*used in the past for treatment of schizophrenic patients
**negative stigma from ECT history
eating disorders
affects both men and women and typically occurs during teens and young adults years
*usually coexists with other illnesses (depression, substance abuse, anxiety)
RISK FACTORS:
- women
- personality traits
- yo yo dieting
- family history
- social pressure
- women with DM 1
1. anorexia nervosa
2. bulimia nervosa
3. binge-eating disorder
cardiac issues
What is the #1 chronic clinical impact associated with eating disorders?
binge eating disorder
MOST COMMON EATING DISORDER
engaging in short feasts wherein they consume a large amount of calories
*NO purging afterwards and thus struggle with weight
**usually occurs due to feelings of shame and depression, lack of self-esteem or self-worth
anorexia nervosa
restricts eating intentionally
- self-purge any intake
- starvation leads to reduced cardiac function and electrolyte imbalance
*CAN BE LIFE THREATENING W/ CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS*
CLINICAL PRESENTATION:
- lethargy
- brittle hair/nails
- mild anemia and muscle wasting
- brain damage
- organ failure
TREATMENT:
- restore weight
- attend psych issues
bulimia nervosa
binge eating and purging several times/week or day
CLINICAL PRESENTATION:
- usually eat/purge in private
- do NOT want others to know
*chronic inflamed sore throat
*worn tooth enamel
*intestinal distress
TREATMENT:
- nutritional counseling
- CBT
disordered eating
abnormal behavior/thoughts on food/diet
muscle dysmorphia
negative body image and an obsessive desire to have a muscular physique
sleep-related eating disorder
recurrent episodes of eating or drinking after arousal from nighttime sleep w/ amnesia of episodes
substance-related disorders
21 million Americans have an addictive disorder
1. tobacco
2. alcohol
3. illicit drugs
4. prescription drugs
suicide
4th leading cause of adult death
(2nd among college students)
500,000 people attempt, 30,000 are successful
RED FLAG SIGNS:
- saying goodbye
- giving away possessions
- making final arrangements
- purchasing a gun or collecting RX drugs
WARNING SIGNS:
- mood changes
- loss of interest socially
- changes in sleep patterns
- signs of depression
RISK FACTORS:
- impulsive
- alcohol and drug abuse
QPR--> question, persuade, refer
suicide PT role
- education
- know side effects of meds
take all threats seriously
serotonin
helps to balance impulsive and aggressive behaviors
*produced during exercise (PT intervention)
mental health treatments
1. cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT)
2. exposure-based therapy
3. medications
4. transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
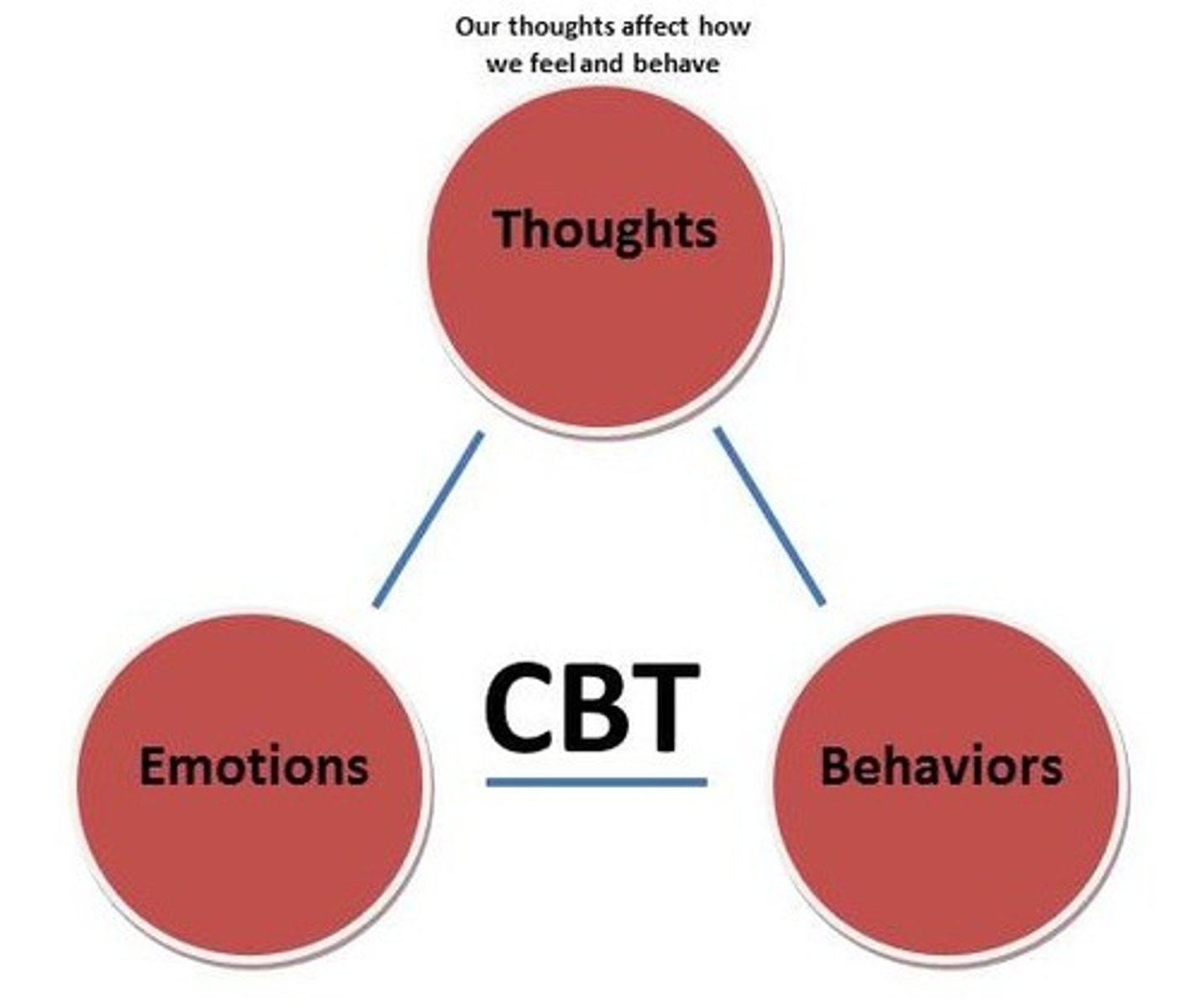
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT
individual and/or group therapy which includes:
- reframing negative trauma-related thoughts w/ positive ones
- behavior experiments
- relaxation techniques & stress management
- role play
exposure-based therapy
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT
exposing the phobia or trauma through discussion or imagery
medications
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT
takes time to build to therapeutic dose (2-6 weeks)
*often requires numerous trial and error prescriptions
**requires persistence
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT
stimulates brain nerve cells to reduce depressive symptoms
*also found helpful for patients with anxiety and OCD
CONS: expensive, temporary fix, questionable success
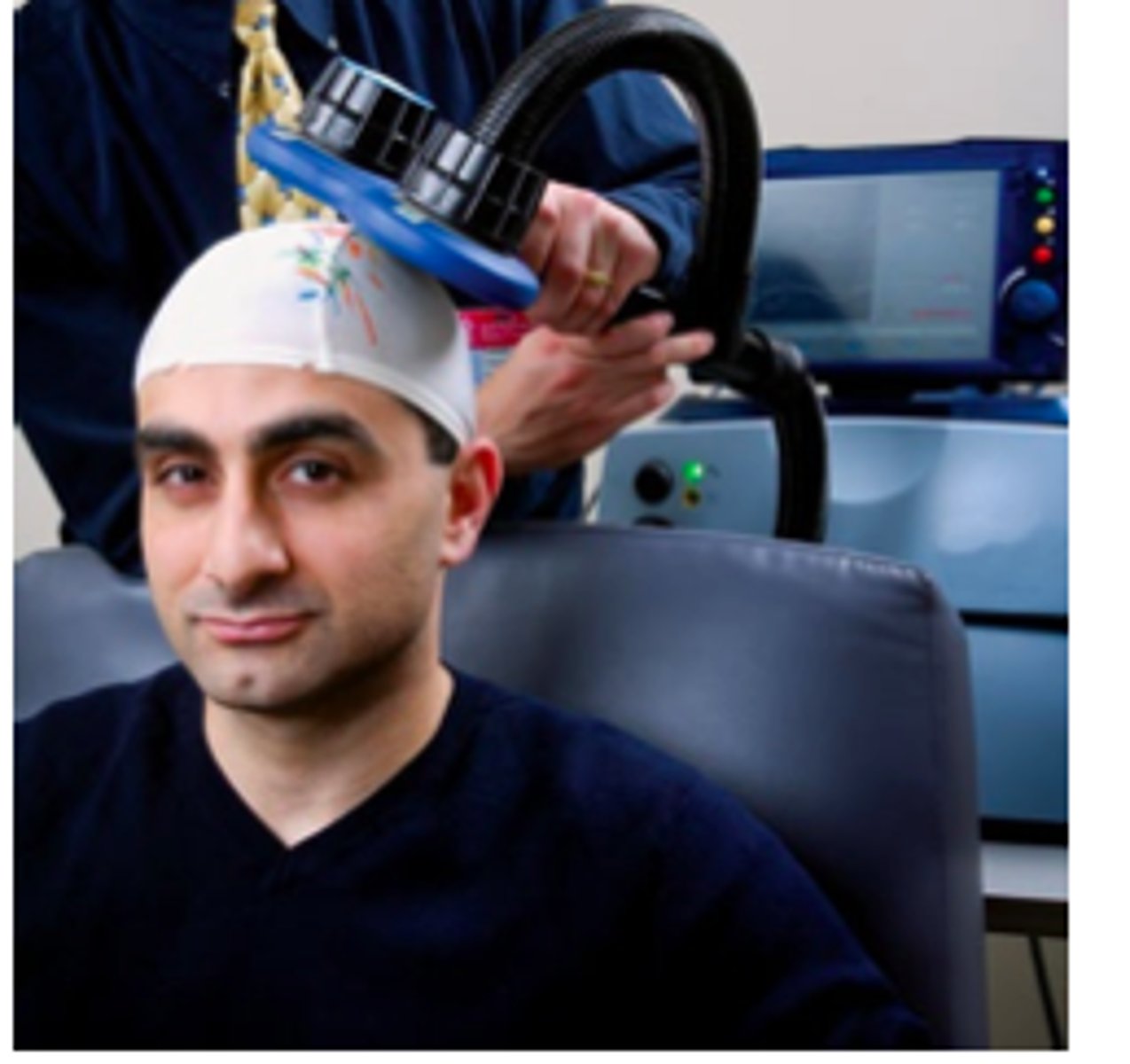
implication for PT
exercise and physical activity
*benefit those with mental health conditions
**aerobic exercise releases endorphins
1. neuropeptides--> improve mood and relieve pain
2. reduces cortisol--> linked to stress and depression
3. increases serotonin--> aids w/ relaxation and sleep
when to refer for other health services