Chem topic 3 PPQs got wrong
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms

The reactivity of the Group 2 elements Mg–Ba increases down the group. Explain why
increasing size
atomic radius increases OR more shells OR more (electron) shielding
Attraction
Nuclear attraction decreases OR (outer) electrons experience less attraction
Ionisation energy
ionisation energy decreases OR less energy needed to remove electrons
Write an equation with state symbols that accompanies the standard enthalpy change of atomisation of iodine
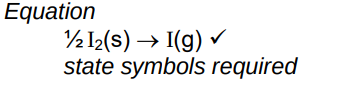



(6)
The reaction of barium with bromine is more vigorous than the reaction of calcium with bromine. Explain why. (3)
Atomic radius
Ba has a greater atomic radius than Ca OR Ba has more shells OR Ba has more shielding
Attraction
nuclear attraction is less in Ba OR outer electrons in Ba are less attracted to the nucleus OR increased distance/shielding in Ba outweighs increased nuclear charge
Ionisation energy
ionisation energy of Ba is less OR outer electrons in Ba are less attracted to nucleus OR easier to remove outer electrons in Ba
(5)
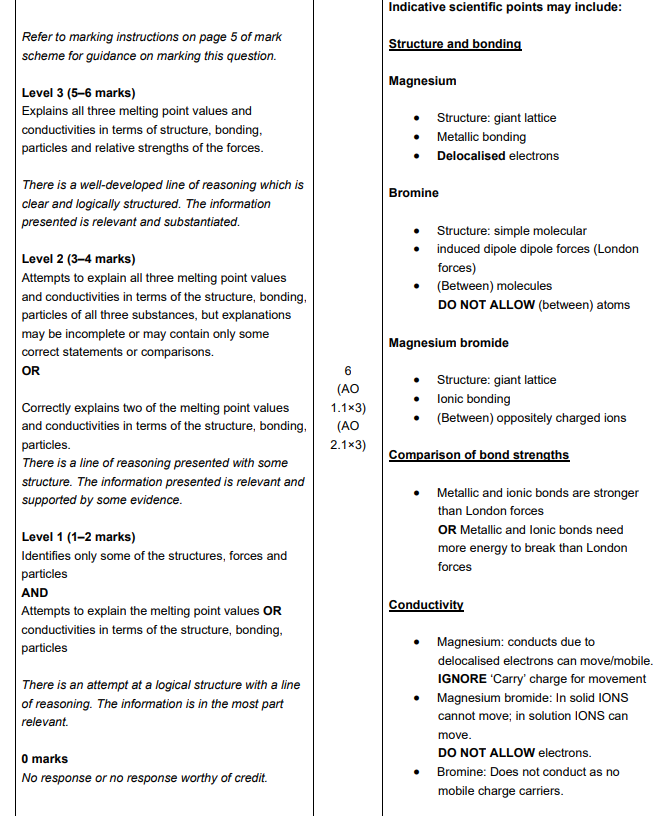
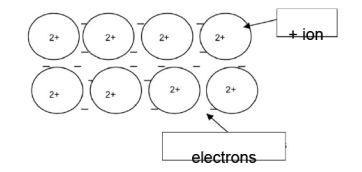
metallic bond or attraction between the electrons and positive ions/cations
bonds are strong/require a lot of energy to break AND high melting point
Delocalised electrons move AND good conductivity
Why are silicon, carbon, oxygen and chlorine all classified as p-block elements? (1)
Highest energy electrons in a p orbital/p sub shell

hydrogen
helium
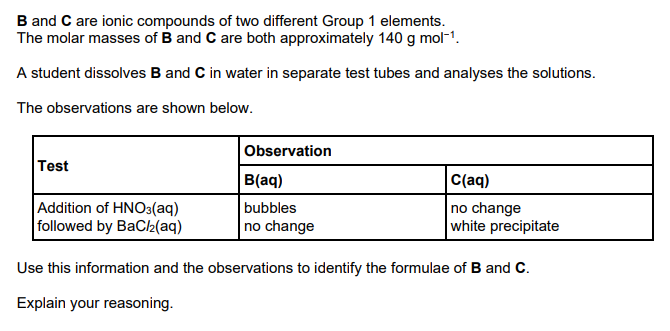
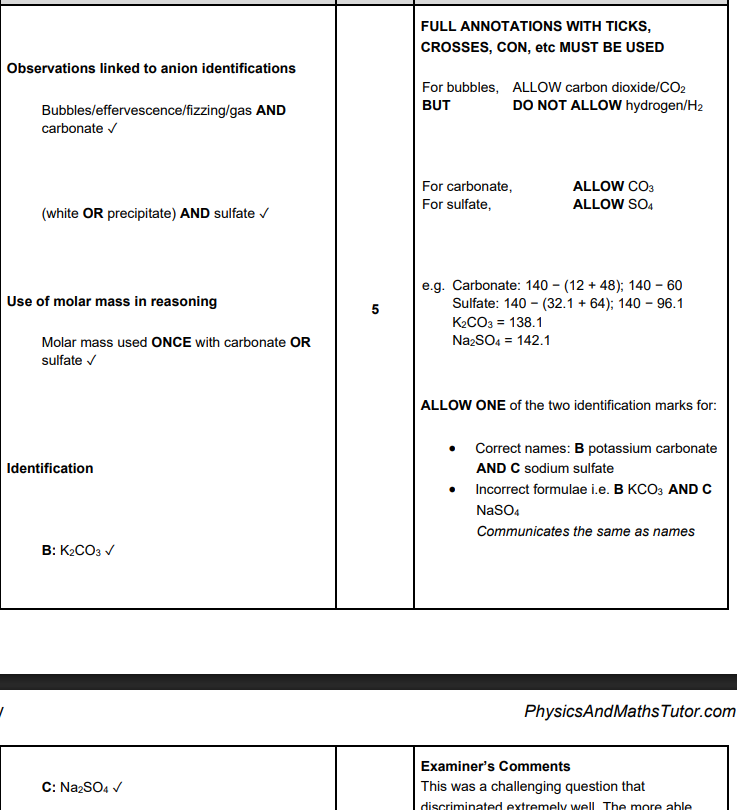
First ionisation energies decrease down groups in the Periodic Table. Explain this trend and the effect on the reactivity of groups containing metals. (3)
Atomic radius
larger atomic radius OR more shells
Effect of nuclear charge/shielding
increased nuclear charge is outweighed by increased distance/shielding OR more/increased shielding
Reactivity AND nuclear attraction
reactivity increases AND less nuclear attraction OR less attraction on electrons
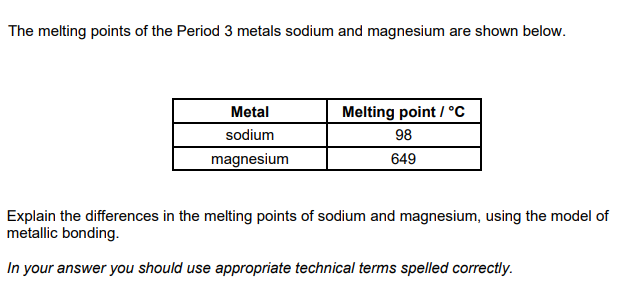
number of bonding electrons
magnesium has more outer OR bonding electrons
ionic charge mark
magnesium ions have a greater (positive) charge (density)
attraction
magnesium has a greater attraction between ions and delocalised electrons
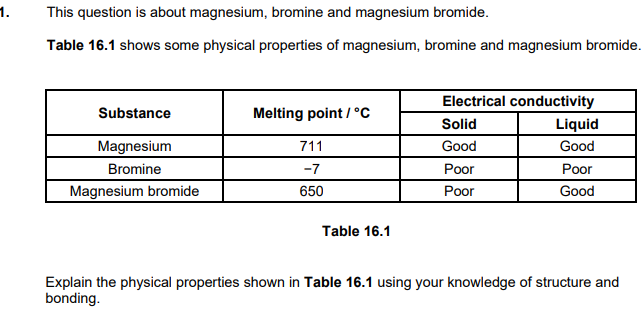
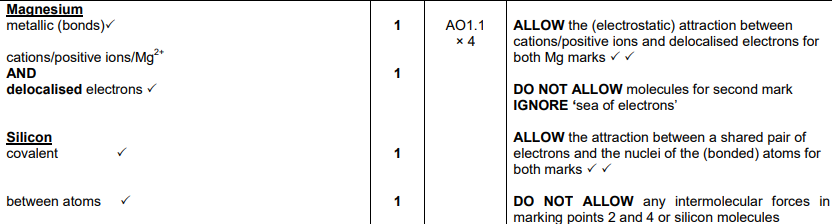
Magnesium and silicon have different types of giant structures. Describe the bonding in magnesium and in silicon. Include the names of the particles and describe the forces between the particles in the structures. (4)
Mg
metallic (bonds)
cations/positive ions/Mg2+ AND delocalised electrons
Silicon
covalent
between atoms
State how and explain why the attraction between nuclei and outermost electrons in gaseous atoms varies across Period 3. (2)
attraction (between nuclei and outermost electrons) increases (across the period) AND nuclear charge increases OR the number of protons increases
(outer) electrons are in the same shell OR (outer) electrons experience similar shielding OR same number of shells OR atomic radius decreases
. Describe and explain the electrical conductivity of sodium oxide, Na2O, and sodium in their solid and molten states. (5)
conductivity of Na
sodium conducts in the solid and molten states
reason for conductivity of Na
sodium has delocalised electrons (in both solid and liquid state)
conductivity of Na2O
Na2O conducts when molten and not when solid
reason for conductibity of Na2O
molton Na2O has ions which are mobile
Solid Na2O has ions which are fixed (in postion) OR ions are held (in position) Or ions are not mobile
AND in an (ionic) lattice OR structure
Give chemical explanations for the following statements. Potassium is placed immediately after argon in the periodic table. (1)
Potassium atoms have one more proton (than argon)
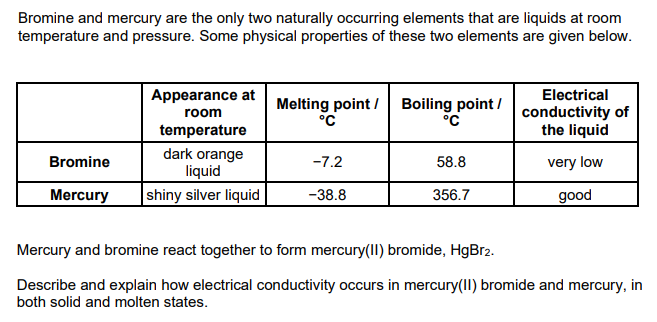
HgBr2 conducts when molten but not when solid
because ions are mobile in molten HgBr2
mercury conducts in both the solid and molten states
because delocalised electrons move (in both solid and liquid state)
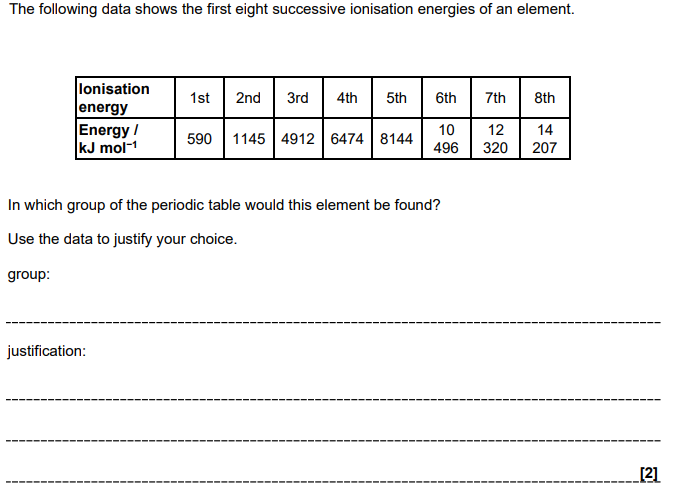
Group 2
large increase between 2nd and 3rd ionisation energy values
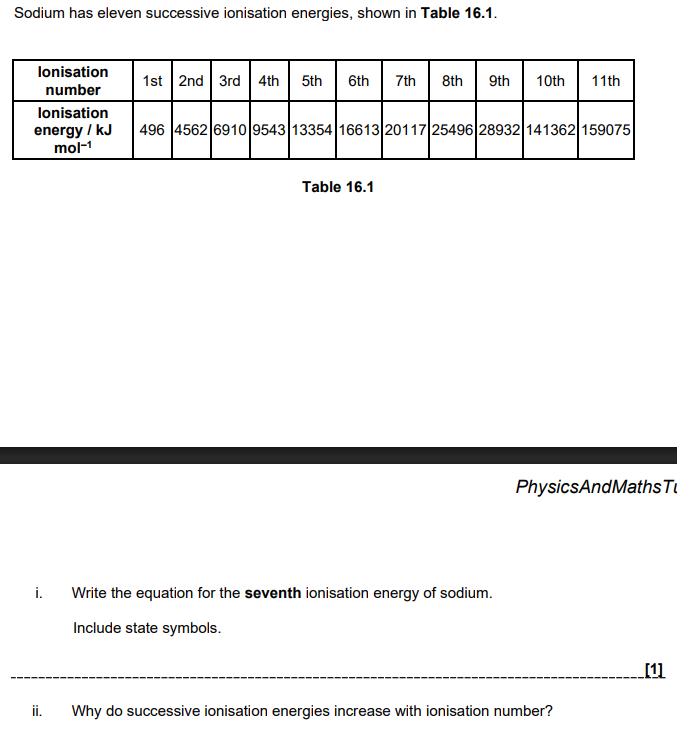
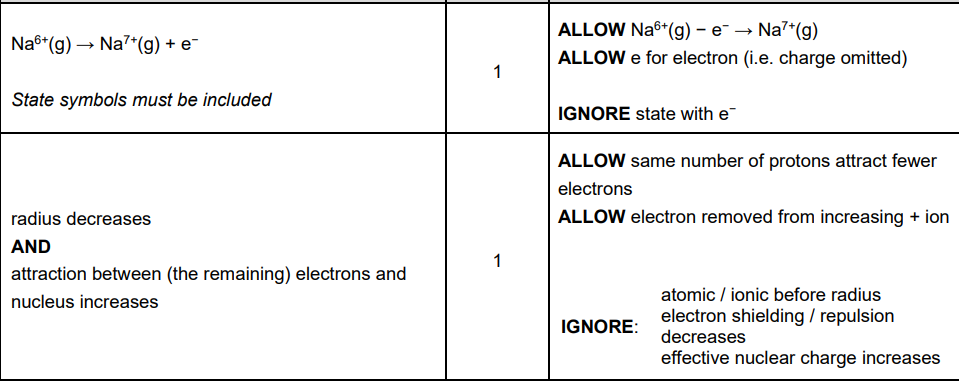
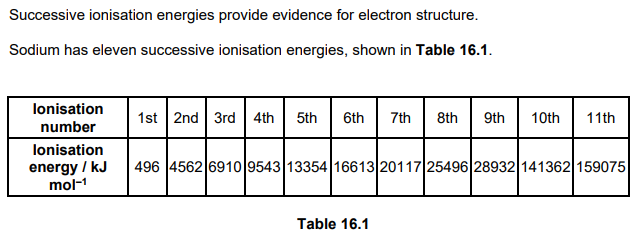
iii. Explain how the successive ionisation energies in Table 16.1 provide evidence for the electron shells in sodium atoms. (2)
large difference/increase/ride shows a different/ new shell
large difference/increase/rise between 1st and 2nd IEs AND 9th and 10th IEs
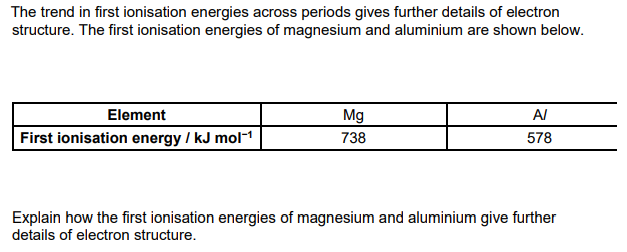
Mg has outer electrons in 3s sub shell AND Al has outer electron in 3p sub shell 3p sub-shell has higher energy than 3s sub shell
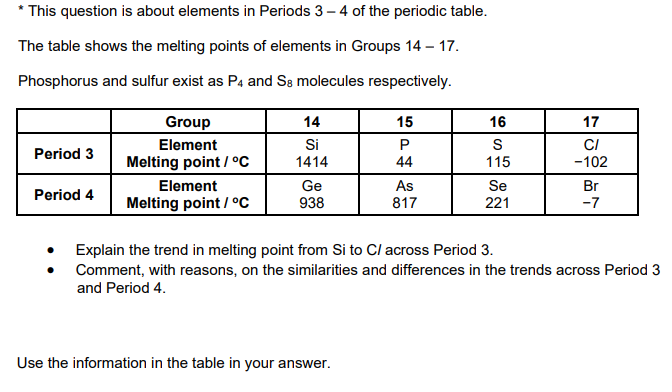
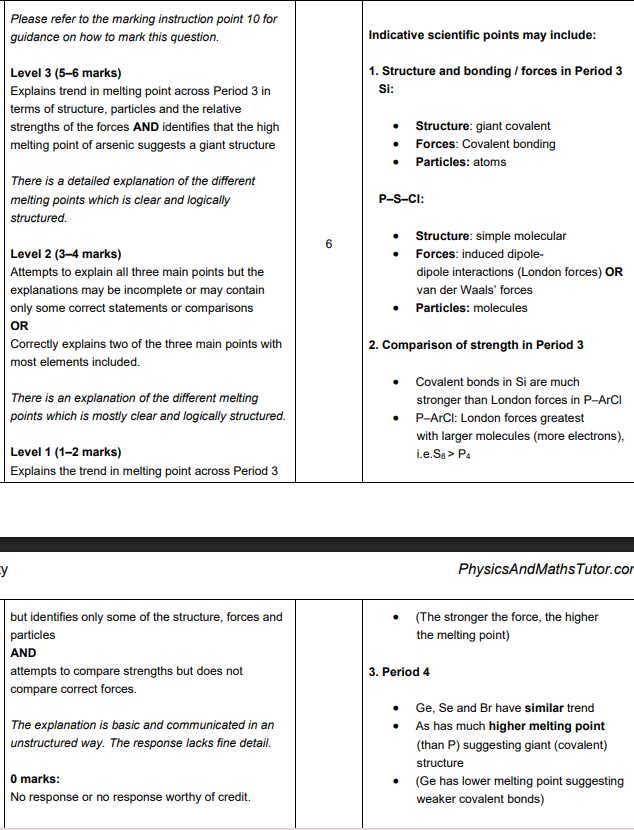
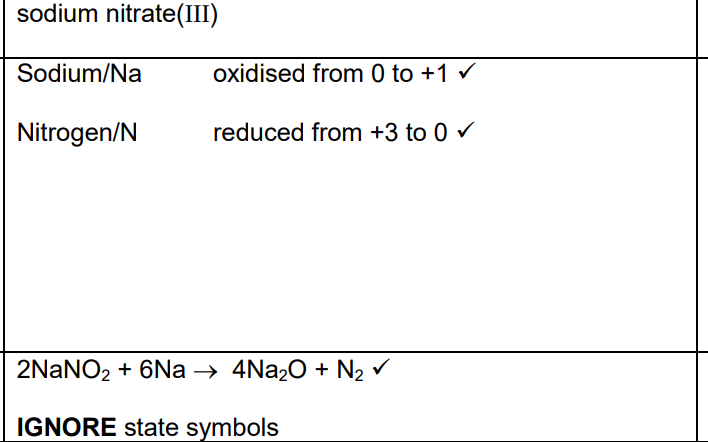
This question is about reactions and uses of the weak acids methanoic acid, HCOOH, and ethanoic acid, CH3COOH. A student adds magnesium metal to an aqueous solution of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH. A redox reaction takes place. Write the overall equation for this reaction and explain, in terms of oxidation numbers, which element has been oxidised and which element has been reduced. (3)
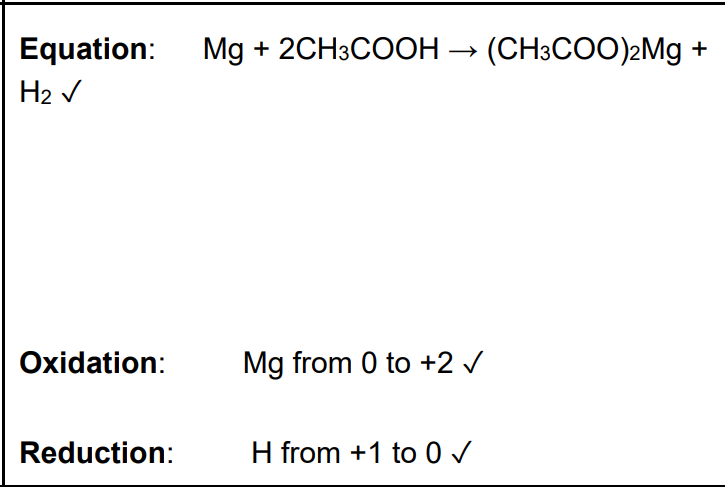
This question is about barium hydroxide. A student plans to prepare a solution of Ba(OH)2 from barium by two different reaction routes. Outline 2 reaction routes for preparing a solution of Ba(OH)2 from barium in the laboratory. Include relevant equations (4)
Describe two observations which would be different if the student had used calcium in place of strontium. (2)
less vigorous fizzing/bubbling/effervescense
dissolves more slowly/slower reaction
solution has a lower pH/less alkaline
precipitate forms/less soluble
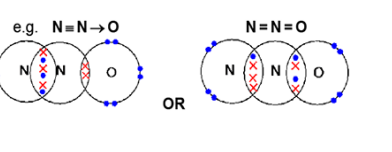
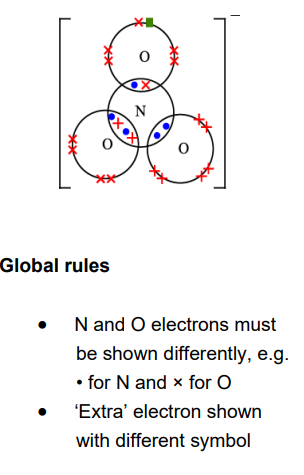
Nitrogen forms an oxide with the formula N2O. A molecule of N2O is linear and has a nitrogen atom in the centre. Draw a ‘dot-and-cross’ diagram for an N2O molecule. Show outer electrons only. (2)
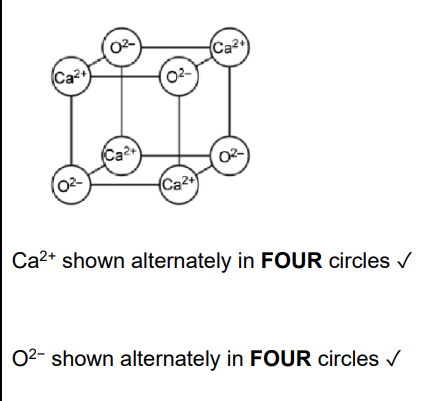
Identify a compound of calcium that could be used to convert a soil pH from 5.8 to 7.5
Ca(OH)2 / calcium hydroide
CaO / calcium oxide
allow calcium carbonate
A student prepared some calcium hydroxide by adding a small piece of calcium to a large excess of water. Describe what the student would observe and write the equation for the reaction. (2)


just (iii)
(3)
Greater volume with Ca
AND larger amount/more moles of Ca OR Ar of Ca is smaller
n(Ca) = 0.200/40.1 = 0.005(0) (mol) (1)
volume H2 with Sr = 55 cm3 AND volume with Ca = 120 cm3 OR 65 cm3 more H2 with Ca (1)
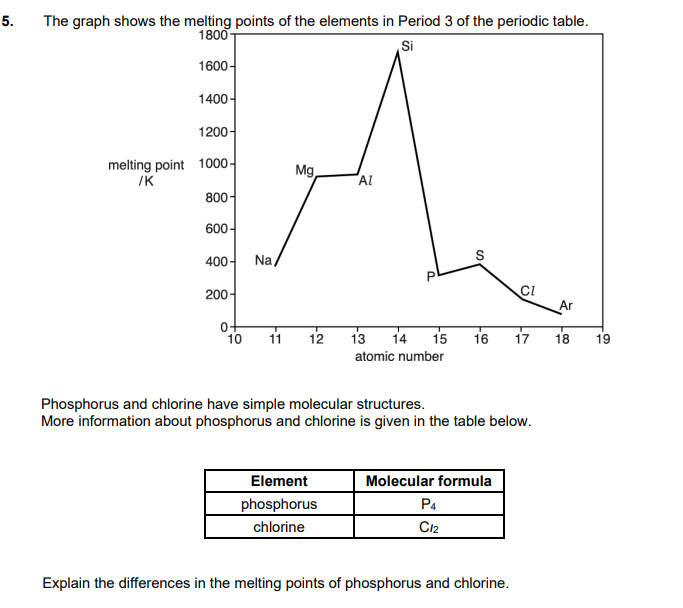
Explain why the boiling point of the halogens increases going down the group (3)
Forces
London forces increase OR induced dipole(-diople) interactions increase
Reason
number of electrons increases
Link to energy and particles
more energy to break intermolecular forces OR to break London forces OR to break induced dipole dipole(-dipole) interactions
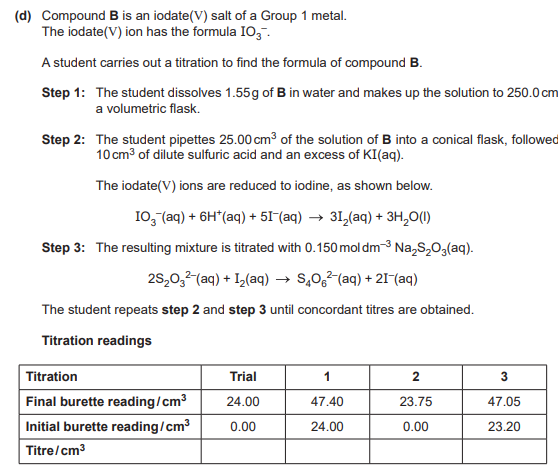
Describe and explain how the student should determine the end point of this titration accurately.(2)
Add starch near end point
blue to colourless
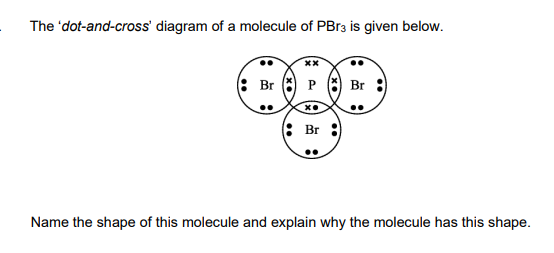
Pyramidal
because there are 3 bonded pairs and 1 lone pair around the central phosphorus atom
and electron pairs repel each other as far apart as possible so will take on a tetrahedral arrangement giving a pyramidal shape overall
State what is meant by the term ionic bond. (1)
Electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
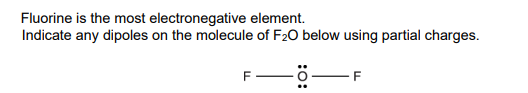
δ− on each F AND δ+ on O ✓
What is the oxidation number of oxygen in F2O? Include the sign in your answe
+2
Suggest the shape of the F2O molecule and the F−O−F bond angle.
non - linear
Bond angle: 104.5°
(3)
phosphorus has more electrons
stronger London forces OR stronger induced dipole(-dipole) interactions
more energy required to break the intermolecular forces/bonds OR London forces
Explain what is meant by electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
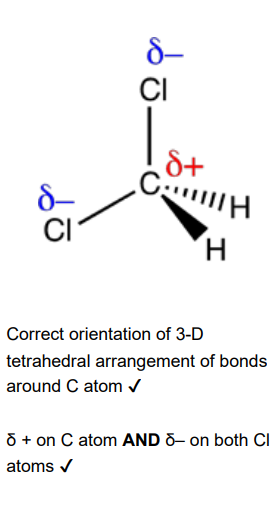
Draw a 3-D diagram of a molecule of CH2Cl2. Use partial charges to indicate polar bonds. (2)
Explain why a CH2Cl2 molecule is polar. (1)
The dipoles do not cancel out OR the molecule is not symmetrical
What is meant by the term ionic lattice? (2)
repeating pattern
of oppositely charged ions
What is meant by the term covalent bond?
A shared pair of electrons
Draw dot and cross of boron tribromide
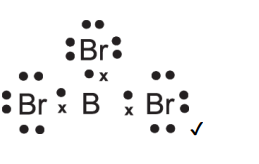
State an explain 2 anomoulous properties of ice cause by hydrogen bonding
Property 1
ice is less dense than water
Explanation 1
the molecules in ice are held apart by hydrogen bonds OR ice has an open lattice OR structure
Property 2
ice has a relatively high melting point
Explanation 2
hydrogen bonds are relatively strong OR hydrogen bonds are stronger (than other intermoelcular attractions or forces) OR more energy is needed to overcome hydrogen bonding
Draw a ‘dot-and-cross’ diagram to show the bonding in CO2
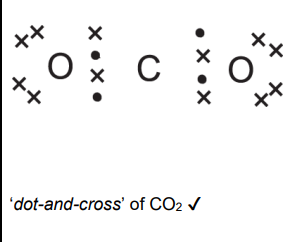
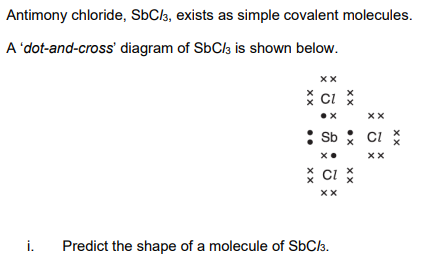
Trigonal pyrimidal
Sb has three bonding pairs AND one lone pair of electrons
pairs of electrons repel
SbCl3 molecules are polar
there is a difference in electronegativites (between Sb and Cl) OR (Sb-Cl) bonds are polar OR have a dipole OR dipoles seen on the diagram
The molecule is not symmetrical AND dipoles do not cancel out
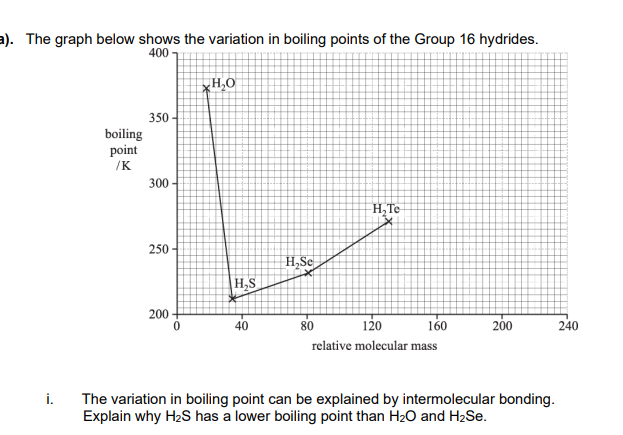
(4)
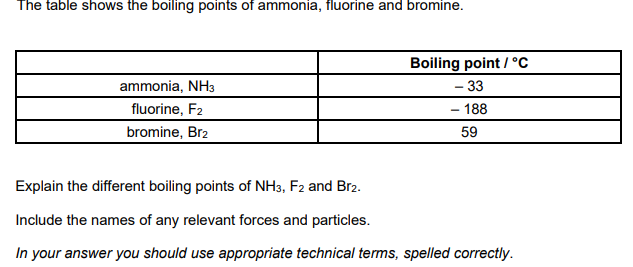
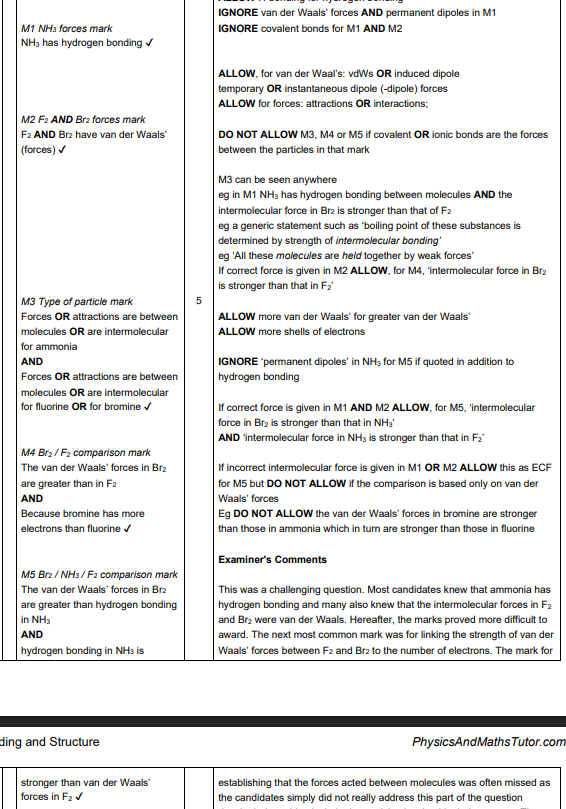
H2O has hydrogen bonding
hydrogen bonding is stronger OR more energy is required to overcome hydrogen bonding
Induced dipole-dipole interactions/London forces in H2S are weaker
H2S has fewer electrons OR less energy is required to overcome induced dipole-dipole interactions
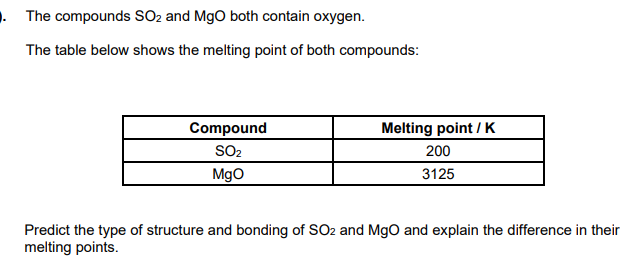
(4)
MgO - giant ionic
SO2 - simple molecular
ionic bonds in MgO are much stronger than intermolecular bonds in SO2
ionic bonds in MgO need more energy to overcome/break than intermolecular forces in SO2

Interpretation of results
orange contains bromine AND no reaction AND violet contains iodine
Ionic equation
Br2 + 2I– → 2Br– + I2
Reactivity (down the group)
Reactivity decreases AND oxidising power decreases OR gains electrons less easily OR forms negative ion/1- ion less easily OR less energy released when electron gained OR more negative electron affinity
Size/shells/shielding (down the group)
Greater atomic radius OR more shells OR more shielding
Attraction down the group
less nuclear attraction down the group
State one disadvantage of using chlorine for the purification of water
chlorine is toxic/poisonous
OR
forms halogenated hydrocarbons
OR
forms carcinogens/toxic compounds
Explain why iodine is less reactive than bromine
iodine has a larger atomic radius
iodine has greater shileding/more shells
iodine has weaker/less nuclear attraction (on electron gained than bromine)
Bromine disproportionates when it reacts with potassium hydroxide solution. Suggest an equation for the reaction
Br2 + 2KOH → KBr + KBrO + H2O
Write the electron configuration of a bromide ion, in terms of sub‐shells.
1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6
The Group 7 element chlorine reacts with sodium hydroxide, NaOH, under different conditions to give different products. i. Chlorine reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form bleach. Write the equation and state the conditions for this reaction.(2)
Equation 2NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO + H2O
Conditions cold AND dilute (sodium hydroxide)
Name the apparatus that could be used to separate the two liquid layers present at the end of the experiment. [1]
Separating funnel
A student bubbles chlorine gas through aqueous potassium iodide. A reaction takes place. i. State what the student would observe
solution turns yellow/ornage/brown
A student adds a small volume of aqueous silver nitrate to an aqueous solution of bromide ions in a test-tube. The student then adds a similar volume of dilute aqueous ammonia to the same test-tube. Describe what the student would see in the test-tube after the addition of aqueous ammonia.
Cream precipitate
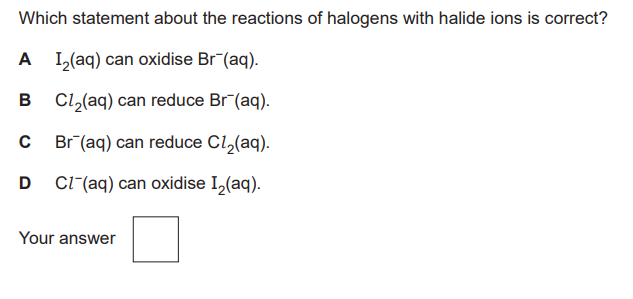
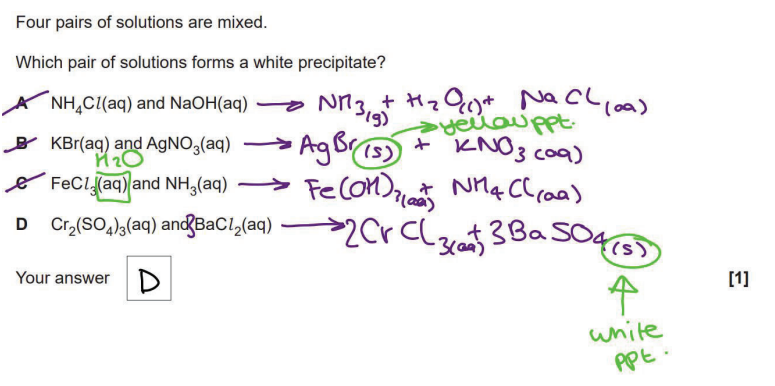
C
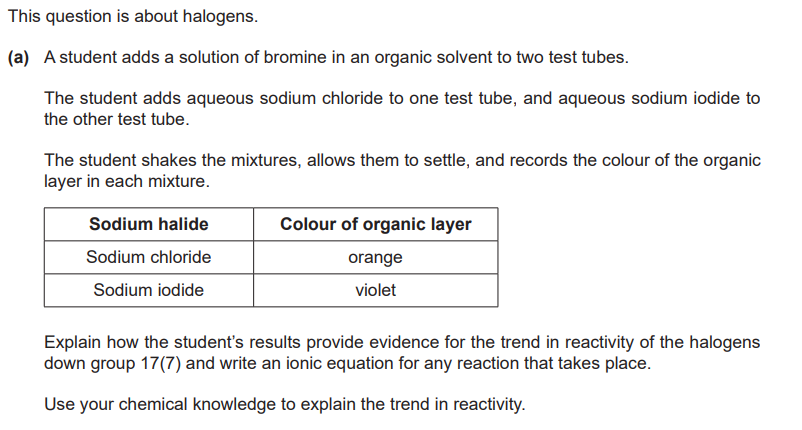
Interpretation of results
orange contains bromine AND no reaction AND violet contains iodine
Ionic equation
Br2 + 2I– → 2Br– + I2
Reactivity (down the group)
reactivity decreases AND oxidising power decreases
OR gaines leelctrons less eaily
OR forms negative ions/1- ions less easily
OR less energy released when electron gained
OR more negative electron affinity
Size/shells/shileding (down the group)
greater atomic radius
OR more shells
OR more shileding
Attraction (down the group)
less nuclear attraction down the group
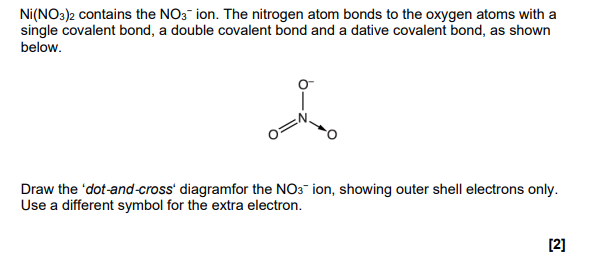
This question is about nickel and its compounds. A student is provided with samples of three nickel compounds. One sample is nickel(II) bromide, another is nickel(II) sulfate and the third is nickel(II) carbonate. The student doesn’t know which sample is which. Describe the tests that the student could carry out to identify the anion (negative ion) in each sample, and write equations for any reactions (6)
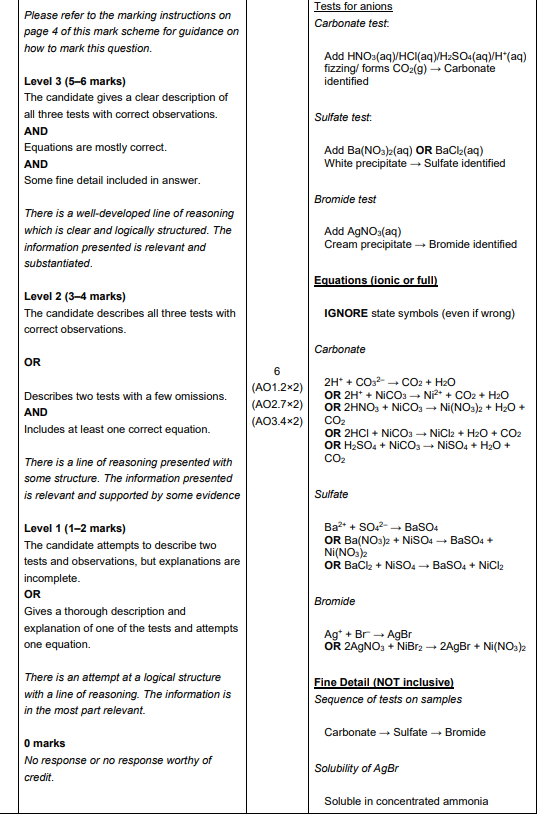
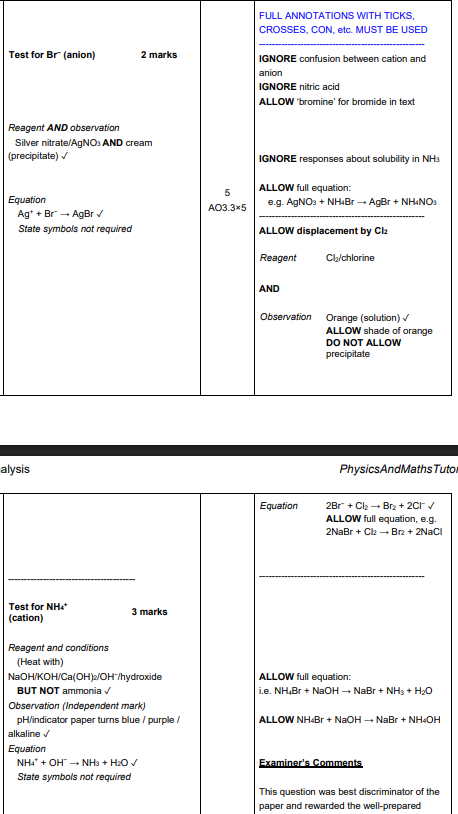
You are supplied with a sample of ammonium bromide. Describe simple tests that would identify the cation and anion present in ammonium bromide. Include reagents, expected observations and relevant equations. (5)
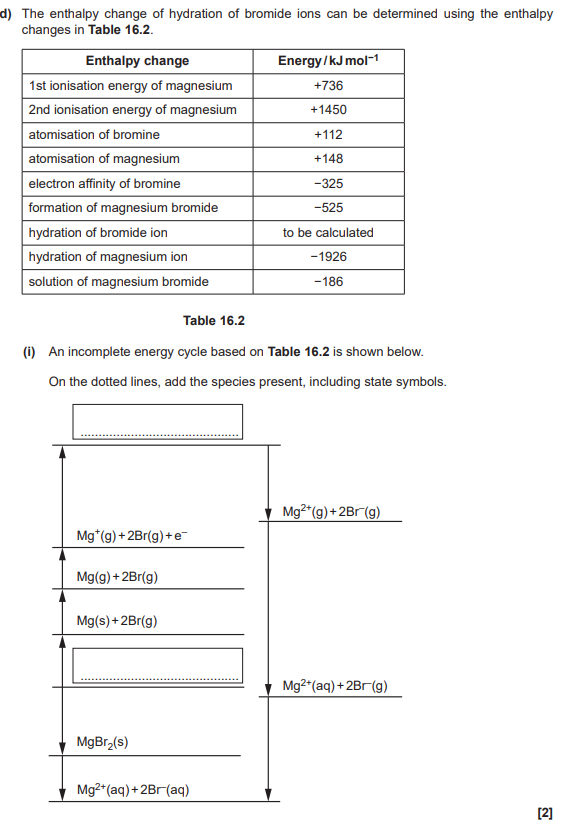
Barium chloride, BaCl2, is soluble in water. i. Compare the electrical conductivities of solid and aqueous barium chloride. Explain your answer in terms of the particles involved (2)
Barium Chloride does not conduct electricity when solid AND because it has ions which are fixed (in position/in lattice)
Barium chloride conducts when in aqueous solution AND because it has mobile ions
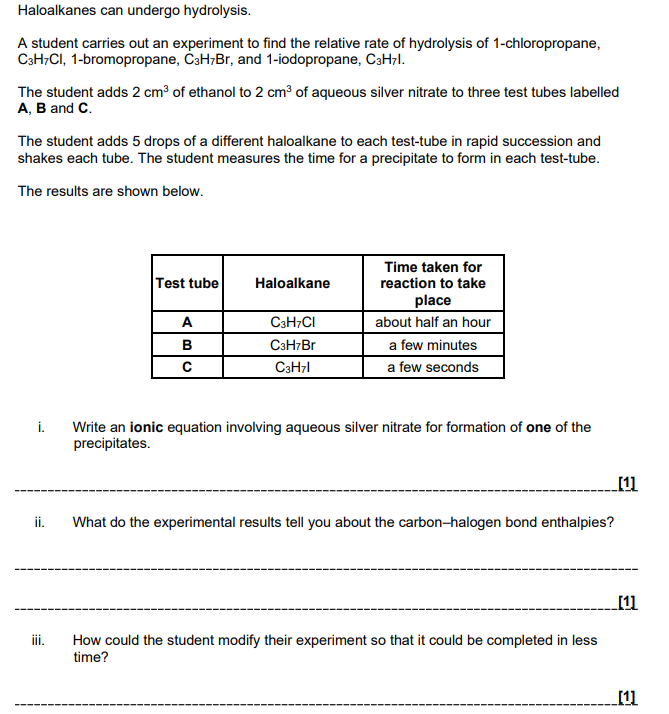
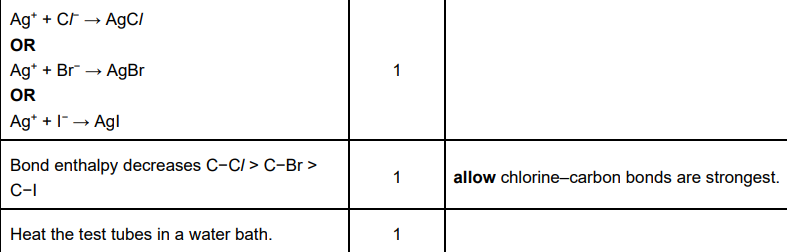


Explain what is meant by the term weighted mean mass (1)
The mean/average mass taking into account the relative abundancies of the isotopes
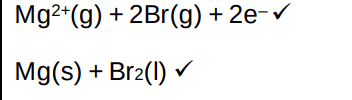
Magnesium and silicon have different types of giant structures
Describe the bonding in magnesium and in silicon
Include the names of the particles and describe the forces between the particles in the structures (4)
What is meant by the term average bond enthalpy (2)
The average enthalpy change when 1 mole of bonds of gaseous covalent bonds is broken