BFCP1 S05 + S06
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
S05: Transcription; S06: Translation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
T/F: DNA → RNA is more common than DNA → RNA → protein
T
The most common type of RNA is _____, making up __% of total RNA
rRNA
80%
mRNA accounts for __% of all RNA
5%
What are discreet regions of DNA?
Specific, identifiable DNA sequences
Consensus sequences
Highly conserved sequences of DNA that are usually bound by regulatory proteins
Promoter sequences and splice sites (5’ and 3’ splice sites) are examples of ______.
consensus (conserved) sequences
T/F: the 3’ and 5’ noncoding regions (UTRs) are transcribed and translated
F: UTR (untranslated regions) are transcribed but not translated
Organize the following from 5’ → 3’ on a DNA strand: polyadenylation signal, promoter sequence, coding sequence, 5’ UTR’, 3’ UTR, transcription start site (+1)
5’ - promoter - transcription start site - 5’ UTR - coding sequence - 3’ UTR (including polyadenylation signal) - 3’
Are the following sequences found on DNA or mRNA strands?:
Promoter
3’ poly-A tail
5’ cap
Promoter: DNA only
3’ poly-A tail: mRNA only
5’ cap: mRNA only
TATA box
The site where the TATA binding protein (TBP) binds to ensure proper placement of RNA polymerase
What are common promoters and where are they found?
TATA box: proximal to coding region
CAAT box, GC box/GC-rich regions: distal to coding region
What is the main difference in function between the TATA box and the CAAT/GC boxes?
TATA box: ensures high fidelity
CAAT/GC box: determines frequency of transcription
Transcription factors
PROTEINS that control how much transcription occur, acting as on/off switches
Pre-initiation complex (PIC)
A group of transcription factor proteins (including that TATA binding protein (TBP)) that assembles at the promoter region to tell RNA polymerase where to bind
Explain the basal transcription complex formation
TBP (TATA binding protein) binds that TATA box, which recruits other transcription factors such as TFIID and RNA polymerase
T/F: the basal transcription complex travels with RNA polymerase throughout transcription
F: the complex stays behind as RNA polymerase transcribes
Where are enhancers/silencers found, and what do they do?
Found at any point in the DNA sequence
Influence levels of transcription
Function of activators/repressors
PROTEINS that bind to enhancers/silencers to influence frequency of transcription
Functions of RNA polymerase I, II, and III
I: creates rRNA
II: creates mRNA and miRNA
III: creates tRNA
Do DNA and RNA polymerase require a primer to start replication/transcription?
DNA polymerase: yes, needs the 3’ OH group present
RNA polymerase: no
4 steps of transcription
Pre-initiation: formation of basal transcription complex
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Purpose of the 5’ cap
Protects mRNA from degradation
T/F: all hnRNA get a 5’ cap
F: only those transcribed by RNA polymerase II get the cap
The poly (A) tail is added (upstream/downstream) of the polyadenylation signal on the ___ end of the mRNA sequence. This is done after the enzyme _____ cleaves nucleotides (upstream/downstream) of the signal.
The poly (A) tail is added downstream of the polyadenylation signal on the 3’ end of the mRNA sequence. This is done after the enzyme endonuclease cleaves nucleotides downstream of the signal.
AAUAA
Polyadenylation signal on the 3’ end of mRNA
Function of poly(A) tail
Protects the mRNA to help with nuclear transport
The 5’ end of an intron has the sequence ___ and the 3’ end has the sequence ___.
5’ end: GU
3’ end: AG
snRNPs = ______ + proteins
snRNAs (small nuclear RNAs)
Branch site
A specific adenine on an intron that attacks the 5’ splice site
During splicing, the _____ site will attack the __’ splice site with the help of snRNPs, creating a ___ that will then be liberated.
During splicing, the branch site will attack the 5’ splice site with the help of snRNPs, creating a lariat that will then be liberated.
What are 3 things that happen to go from hnRNA → mRNA?
Splicing
Addition of 5’ cap
Addition of 3’ poly(A) tail
Function of sigma factors
In prokaryotes, they bind with RNA polymerase to recognize the promoter sequence
Explain how the growing RNA strand and DNA strands stay together/separate in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes.
Prokaryotes: growing RNA liberates from DNA as its being built
Eukaryotes: RNA is tightly bound to DNA throughout
Polycistronic vs monocistronic
Polycistronic: one mRNA strand codes for multiple proteins, in prokaryotes
Monocistronic: one mRNA strand codes for one protein, in eukaryotes
What is the significance of mRNA’s ½ life?
-Shorter ½ life for transiently needed protein
-Longer ½ life for proteins that are needed all the time
T/F: prokaryotic mRNA undergo splicing
F
The start codon is _ _ _ and encodes _____.
AUG
Met
The stop codons are _ _ _, _ _ _, and _ _ _ and they encode ______.
UAA, UAG, UGA
they don’t encode anything
What does it mean for genetic code to be degenerate?
Redundant - most AAs have multiple codons
Silent mutation
Codon is changed but codes for the same AA
Missense mutation
Codon change leads to AA change
Nonsense mutation
Codon change leads to a stop codon instead
Trinucleotide repeat expansion mutation
Excessive repetition of a trinucleotide
Splice site mutation
Mutation affecting the consensus sites in introns (GU and AG), causing improper splicing
Frameshift mutation
Adding or removing 1-2 bases to affect the reading frame of mRNA
T/F: there is exactly 1 tRNA for every AA
F - 50 tRNAs, but only 20 AAs. More than 1 tRNA for each AA.
Specify what the terms “charged” and “activated” mean in translation.
Charged: the name for tRNA when the appropriate AA is added to it
Activated: the name for the AA once its bound
EVERY tRNA has a conserved sequence 5’ _ _ _ 3’ on its 3’ end that is bound to its appropriate _____.
EVERY tRNA has a conserved sequence 5’ CCA 3’ on its 3’ end that is bound to its appropriate AA.
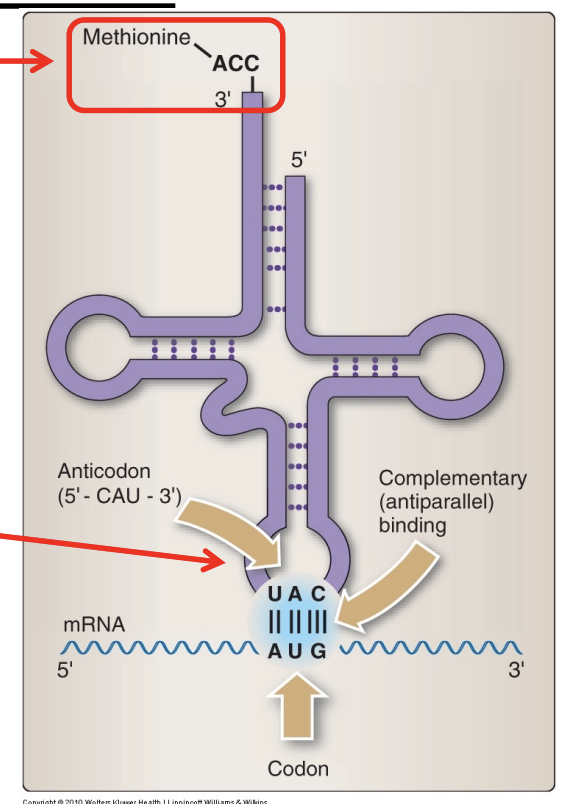
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Enzyme responsible for binding AAs to their appropriate tRNA, thereby “charging” it
T/F: aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases have the ability to remove mischarged AAs from the tRNA
T
What is the function of the large and small subunit of the ribosome in translation?
Large unit: catalyzes peptide bonds between AAs in the growing polypeptide
Small unit: ensures fidelity
Aminoacyl-tRNA vs peptidyl-tRNA and which ribosomal site they are found in
Aminoacyl-tRNA: an incoming tRNA carrying a single AA, found in A site
Peptidyl-tRNA: the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain, found in P site
3 ribosomal sites of translation
A: holds the incoming aminoacyl-tRNA
P: holds the peptidyl-tRNA with the bound polypeptide chain
E: holds the empty tRNA after the polypeptide chain is transferred
Where does translation take place?
On ribosomes that are free in the cytoplasm or in the rough ER
What is the role of ATP and GTP in translation?
ATP: required for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (to attach AA to tRNA)
GTP: required for binding aminoacyl tRNA to the A site and for translocation
What direction is DNA read in transcription?
What direction is mRNA read in translation?
DNA: READ 3’ to 5’
mRNA: read 5’ to 3’
Wobble hypothesis
The base at the 3’ end of the anticodon can be non-traditional because it isn’t as important for fidelity
3 steps in protein translation
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation of translation:
Small subunit meets the _____ codon of mRNA
tRNA carrying ____ (___-tRNA) is bound to the small subunit
________ subunit joins
____ plays a role in combining the subunits
the tRNA goes to the ___ site
Small subunit meets the start codon of mRNA
tRNA carrying Met (Met-tRNA) is bound to the small subunit
Large ribosomal subunit joins
GTP plays a role in combining the subunits
the tRNA goes to the P site
Elongation of translation:
Peptide bonds between AAs are catalyzed by _______
Translocation is the process of _______ and requires ____ to power it.
_________ factors play a role in delivering the correct aminoacyl-tRNA to the ___ site and also require ___.
Peptide bonds between AAs are catalyzed by peptidyl transferases.
Translocation is the process of moving the ribosomal subunit to the next codon and requires GTP to power it.
Eukaryotic elongation factors play a role in delivering the correct aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site and also require GTP.
Peptidyl transferase is the _____ of the large ribosomal unit and functions to _______.
rRNA
catalyze peptide bond formation in the growing polypeptide chain
Termination of translation:
______ factors recognize the ___ codon and release the polypeptide
Eukaryotic release factors recognize the stop codon and release the polypeptide
Polysomes/polyribosomes
Multiple ribosomes reading different parts of the same mRNA to make copies of the protein quickly
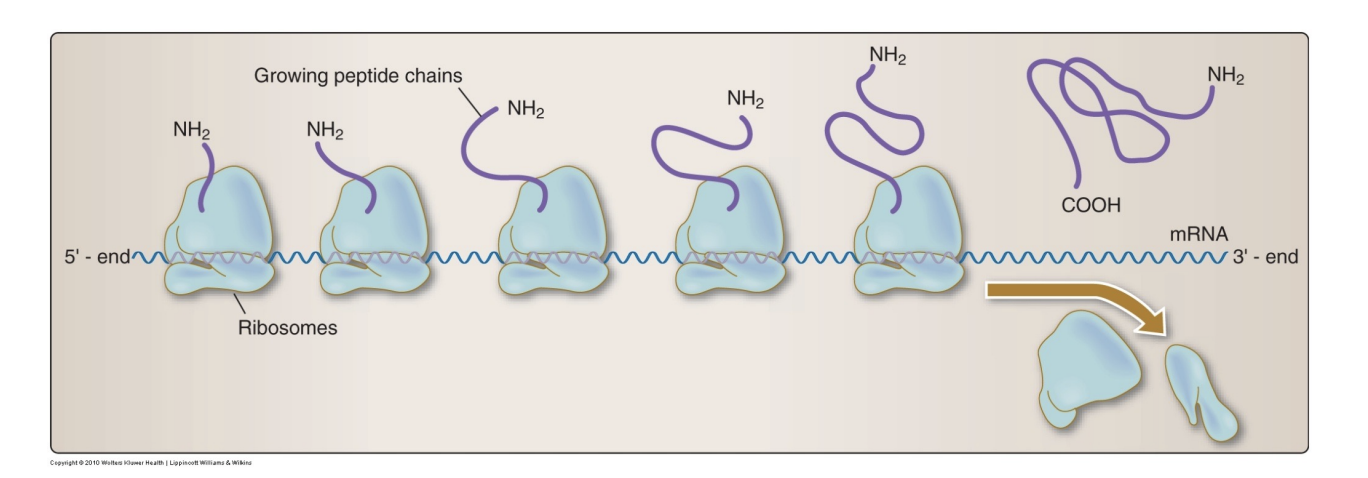
Identify the oldest and newest ribosome (aka the direction of translation)
The leftmost ribosome is the newest one and will continue to move right, in the 5’ to 3’ direction
Translational trimming
Post-translational modification where the protein is cleaved to make a functional protein
Zymogens
Pre-cursors to functional proteins that require trimming
What is the generic term for post-translational additions to proteins?
Covalent modifications (ex: phosphorylation, hydroxylation, etc)
Streptomycin, tetracyclien, erythromycin, cycloheximide, puromycin
Drugs that inhibit translation