Tympanic Membrane
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Layers of the TM
Outer, Middle, Inner
Epidermal layer
Outer layer
Fibrous layer
Middle layer
Mucosal layer
Inner layer
Pars flaccida
Outer and inner layers
Ossicalr chain is attached here
pars tensa
Umbo
Where the malleus attaches to the TM
Pars tensa
Stiff and tense, contains all 3 layers. More commonly associated with TMs
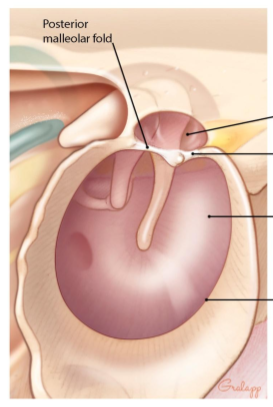
Pars flaccida, pars tensa, annular ring, posterior and anterior malleolar fold
TM quadrants
Anterior inferior, anterior superior, posterior inferior, posterior superior
T or F you should be able to see blood vessels in a healthy TM
F
Prevents foreign bodies from entering the middle ear
TM
Bulging TM
due to infection or pus in middle ear
Retraction
When the TM gets pulled into the space behind it
When does retraction happen
Middle ear pressure is too low
Chronic negative pressure in middle ear leads to what
erosion of the ossicles
Cholesteatoma
Cyst of sqamous eputhelium usually in the ME or mastoid
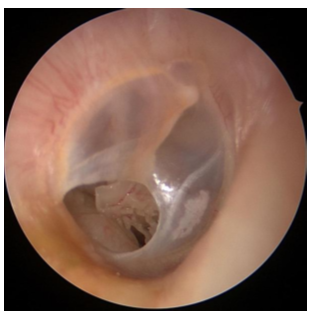
Perforation causes
middle ear dysfunction, infection, rapid pressure changes, trauma
small perforation tx
heal spontaneously
large perforation tx
tympanoplasty
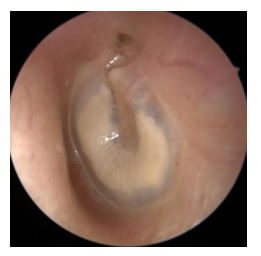
tympanosclerosis
white calcified plaques of connected tissue at TM or head of malleus
monolayer
Sometimes happens after the PE tube comes out
mimics perf
Prevent accumulation of fluid in the ME
PE tube
Tympanosclerosis
Perforation
Bubbles
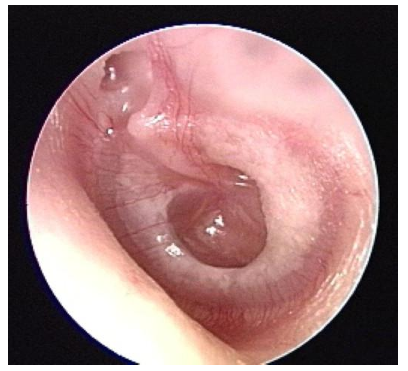
Retraction
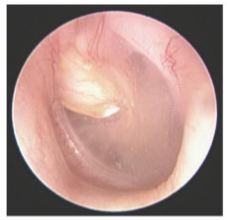
Cholesteatoma
Acquired cholesteatoma
Formed by retraction of TM and skin
congenital cholesteatoma
Caused by ETD and OM; causes CHL
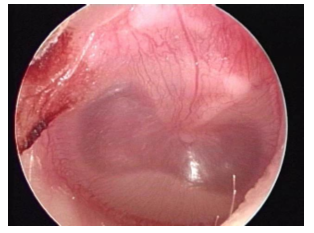
Yellow fluid in bubbly ear means what?
Could be infected
shape of ear canal
concave