Small Animal Reproduction
1/459
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
460 Terms
What are the top 2 reasons for failure to conceive?
poor semen quality
poor timing of insemination
What are weird differences of canine repro physiology?
'pre-lutenization' of granulosa cells by LH causes pre-ovulatory progesterone rise
prime sexual receptivity occurs during period of LOW estrogen and HIGH progesterone
ovulate primary and secondary oocytes that both require period of oviductal maturation
life span of CL is independent of pregnancy status
What are characteristics of the estrous cycle of the bitch?
non-seasonal, monoestrous
When does puberty occur in the bitch?
6 months (up to 24 months)
How long is the estrous cycle of the bitch?
81 days (60-115 days)
How long is proestrus of the bitch?
9 day (5-20 days)
How long is estrus of the bitch?
9 days (5-15 days)
How long is diestrus of the bitch?
60 days (57-63 days)
How long is anestrus in the bictch?
4-6 months
When does ovulation occur in the bitch?
begins 2 days after the onset of estrus
What is the interestrus of intrerestrus interval of the bitch?
diestrus and anestrus stages of estrous cycle
What do vaginal cytology changes occur in response to?
estrogen
What endocrine events occur during proestrus in the bitch?
FSH and LH pulses increase and peaks at estrus
estrogen rises early and peaks prior to estrus
progesterone rises late for pre-luteinization
What are clinical signs of proestrus in the bitch?
vulvar edema and reddening
serosanguineous vulvar discharge
vaginal epithelium begins cornifying
attractiveness (+/- receptivity) to males
**estrogen driven
What endocrine events occur during estrus in the bitch?
LH surge defines the beginning
progesterone continues to rise at predictable rate with serum levels correlating to timing of LH surge and ovulation
estrogen continues to decline to baseline
What are clinical signs of estrus in the bitch?
vulvar edema with decreasing discharge
vaginal cornification remains stable (greater than 90%)
attractive and receptive to males
What are characteristics of ovulation in the bitch?
asynchronous ovulation of primary oocytes over 1-2 days beginning 2 days post-LH surge
require additional 2 days of maturation to secondary oocytes in oviduct
secondary oocytes last 24-48 hours
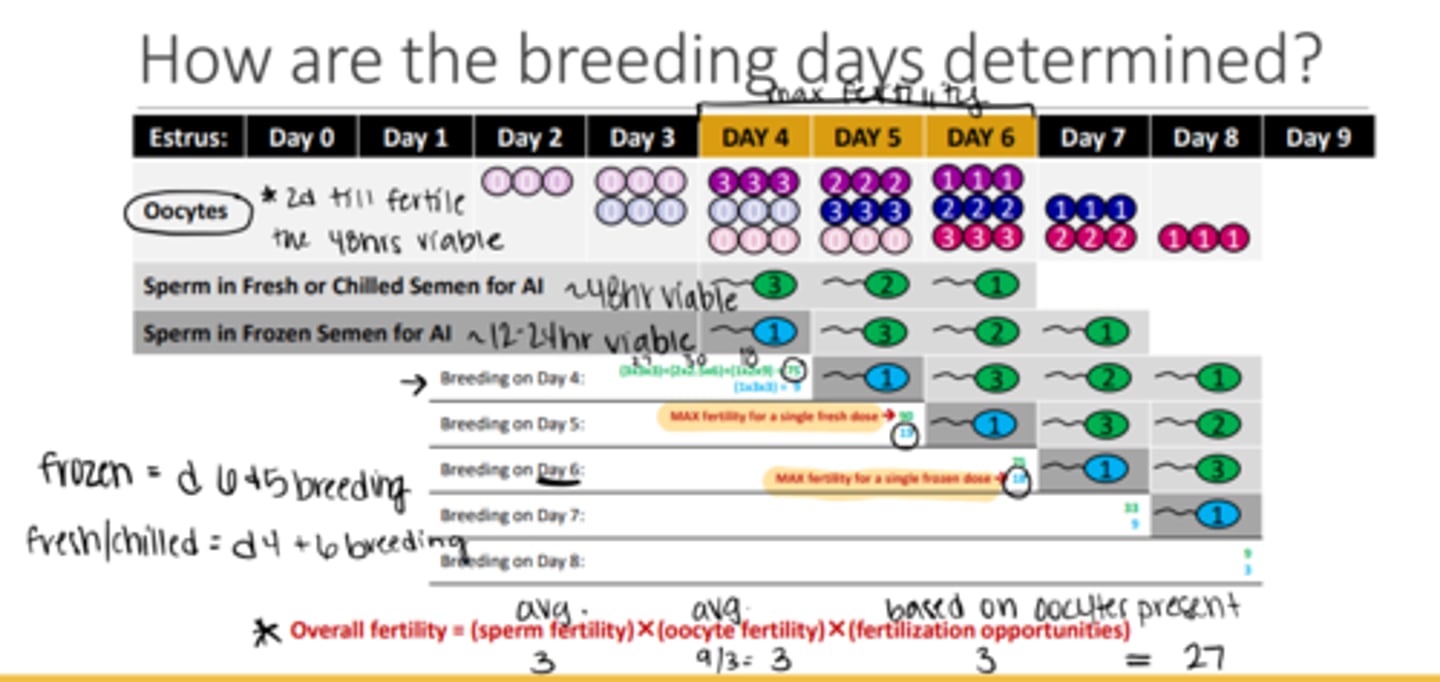
OVERALL = potentially fertile oocytes are present form Days 4-8 of estrus but fertility is HIGHEST of days 4-6
What are endocrine events during diestrus of the bitch?
progesterone plateaus 20-30 days post-LH surge then declines
prolactin rises 20-30 days post-LH surge, peaks day 40-50
estrogen remains low throughout
What are clinical signs of diestrus of the bitch?
diminished attractiveness to males
resistant to breeding/vaginal procedures
When does luteolysis occur in the bitch?
about 63 days post-ovulation REGARDLESS of pregnancy status
How does luteolysis occur in the bitch? (what's the mechanism?)
decreased prolactin and PGE2 and increased PGF2a
**PGF2a is produced by endometrium in non-pregnant dog
**fetoplacental unit produces PGF2a via uptake and conversion of PGE2 due to rising fetal cortisol at the end of gestation in the pregnant dog
What are characteristics of anestrus in the bitch?
at least 4 months of ovarian quiescence and endometrial repair that is REQUIRED for the HPG axis to reset and uterus to support a new pregnancy
What is the mechanism for ending anestrus?
unknown
What marks the termination of anestrus?
resumption of pulsatile FSH/LH release for folliculogenesis
When should canine breeding management start (when to start ovulation timing)?
5-7 days after onset of proestrus to be the most cost effective
What modalities are utilized to determine ovulation of the bitch?
serial progesterone assays
vaginal cytology
What is a 'split heat'?
proestrus and LH surge occurs but ovulation does not follow
progesterone level declines back below baseline
next proestrus occurs in 2-3 months with apparent normal fertility
What needs to be known to establish a breeding plan for a bitch?
Will any pregnancy do?
Is a large or small litter desired?
Is the sire deceased, foreign?
Interested in dual-sired litter?
Where is sire located? What is the quality of semen, if known?
What are recommendations on how and when to inseminate a bitch based upon?
owners goals and finances
type and quality of semen available from stud
What are different breeding methods?
natural cover
vaginal AI
transcervical insemination (TCI)
surgical AI
What are pros/cons of natural cover?
pro = least expensive (usually) and best semen longevity (usually)
con = no semen analysis available, stud must be local or travel to bitch
What are pros/cons of vaginal AI?
pros = reduces disease transmissions and injury, allows semen analysis
cons = more expensive and comparably successful vs. natural cover
What are pros/cons of transcervical insemination (TCI)?
pros = statistically highest conception rates and litter sizes
cons = more expensive vs vaginal AI, special training and equipment
What are pros/cons of surgical AI?
pros = technically east, can circumvent abnormal anatomy
cons = most expensive, risks of surgery and anesthesia, conception rates, litter size lower or same as TCI
What equipment is needed for vaginal AI?
mavic catheter
AI pipette
What equipment is needed for transcervical AI?
rigid vaginoscope
What is the 'breeding plan' for natural cover?
every other day from day 3-4 until female is unreceptive
What is the 'breeding plan' for fresh semen/cooled shipped semen?
any breeding method depending on quality of semen
breed ONCE on day 5 or TWICE on days 4 and 6
What is the 'breeding plan' for frozen semen?
transcervical or surgical insemination ONLY
Breed ONCE on day 6 or TWICE on days 5 and 6
What is the minimum recommended breeding dose for bitches?
200 million progressively motile semen with ideally 60+% progressively motile and normal morphology
This chart for determine breeding days I starred multiple times. IDK how to create questions from it
What tools can we use to determine the reproductive status (stage and day of estrous cycle) of a bitch?
vaginal cytology
vaginoscopy
luteinizing hormone testing
progesterone (P4) testing
What does vaginal cytology tell us about the reproductive status of a bitch?
stage of cycle
What does progesterone tell us about the reproductive status of a bitch?
day of cycle
What must be understood to interpret vaginal cytology?
understanding of estrogenic effects on reproductive tract
** increased epithelial cell cornification causes exfoliation
** increased vascular permeability causes mucosal edema and diapedesis of RBCs
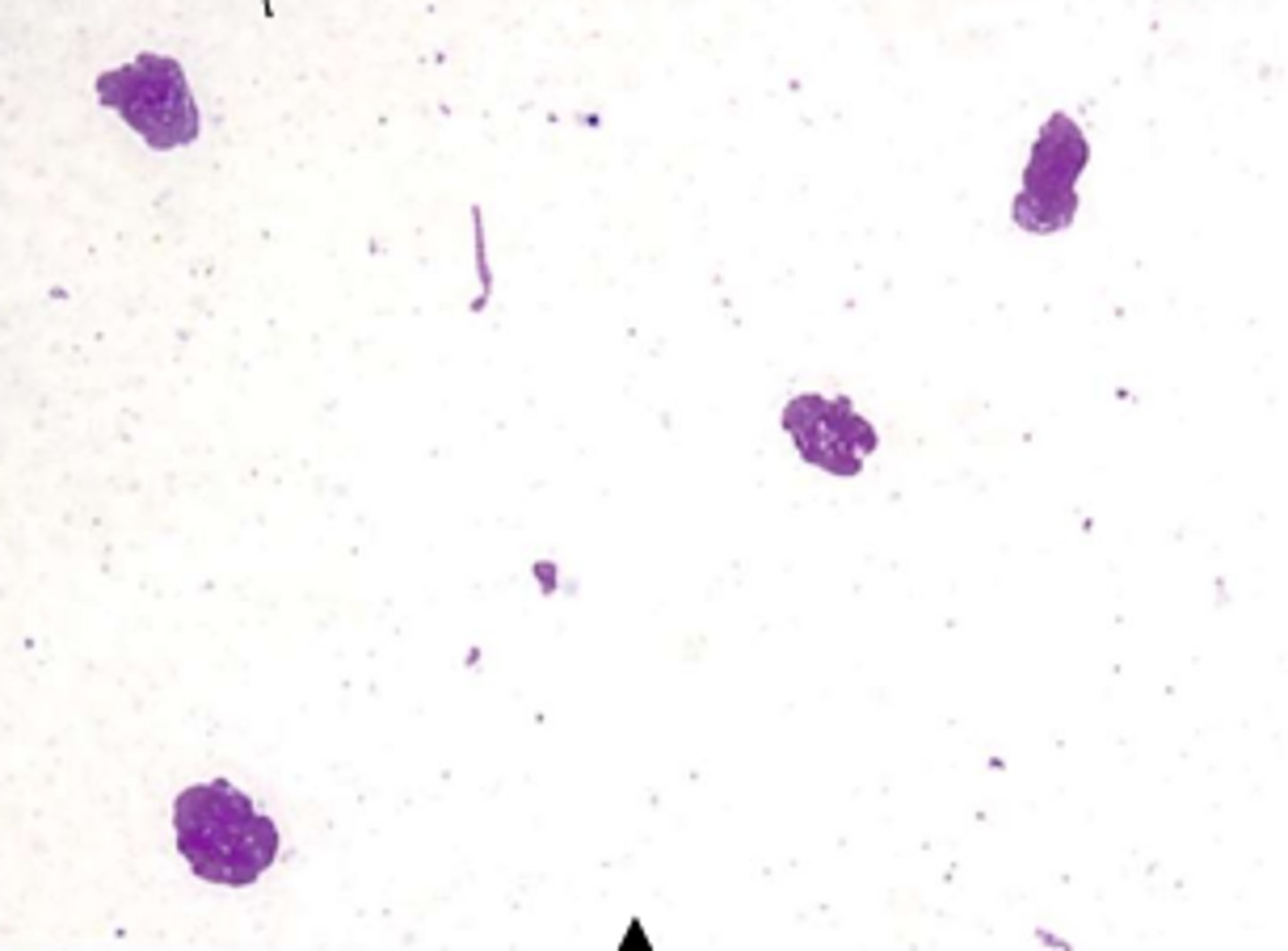
What are characteristics of vaginal cytology during anestrus?
overall low cellularity with many broken cells
predominant cell type = parabasal cells
mucus strands often present
NO red blood cells or neutrophils (unless vaginitis)
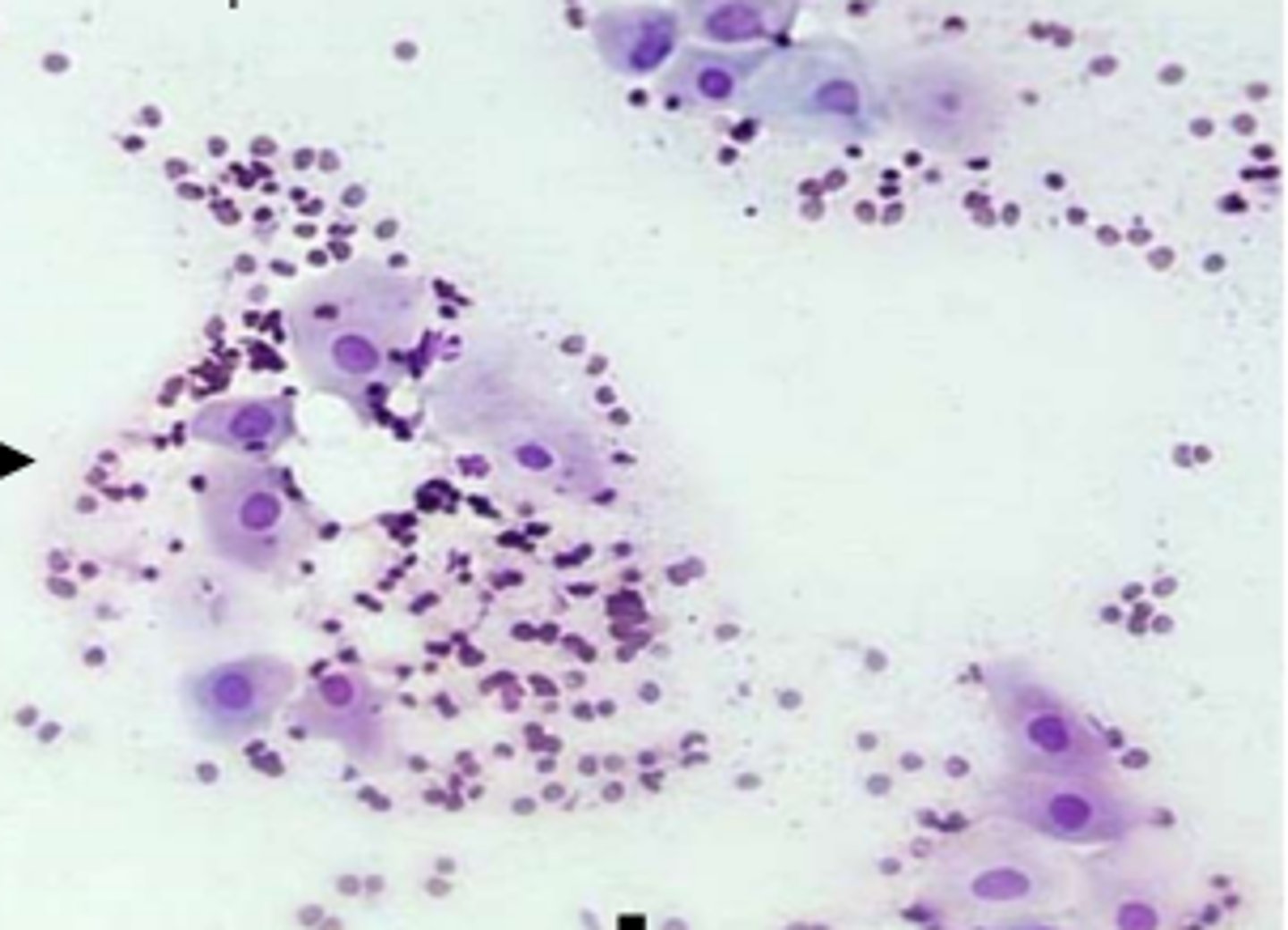
What are characteristics of vaginal cytology during proestrus?
cell numbers begin to increase due to estrogen-mediated proliferation of vaginal epithelium
predominant cell type = intermediate cells and red blood cells with fewer parabasal cells
increased ratio of large to small intermediates and superficial cells to large intermediates throughout stage
neutrophils may be present
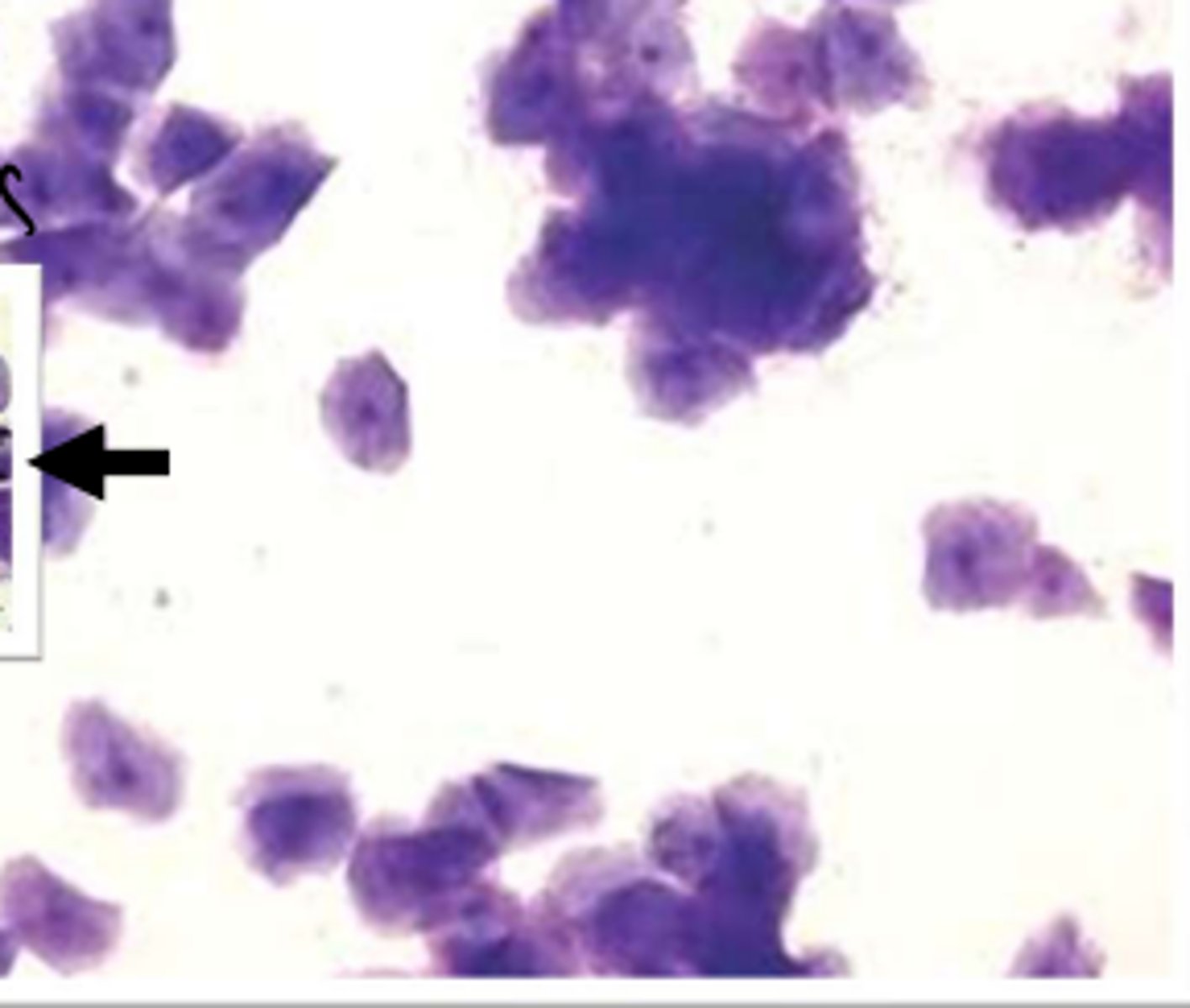
What are characteristics of vaginal cytology during estrus?
predominant cell type = superficial cells and large intermediate cells over 80-90%
drop in estrogen reduces diapedesis of RBCs into vaginal lumen = no to minimal RBCs, cellular debris, and mucus
late in stage = large sheets/rafts of superficial cells
What are characteristics of vaginal cytology during diestrus?
predominant cell type = parabasal and small intermediate cells over 40-60%, neutrophils
RBCs, cellular debris, sperm cells vary
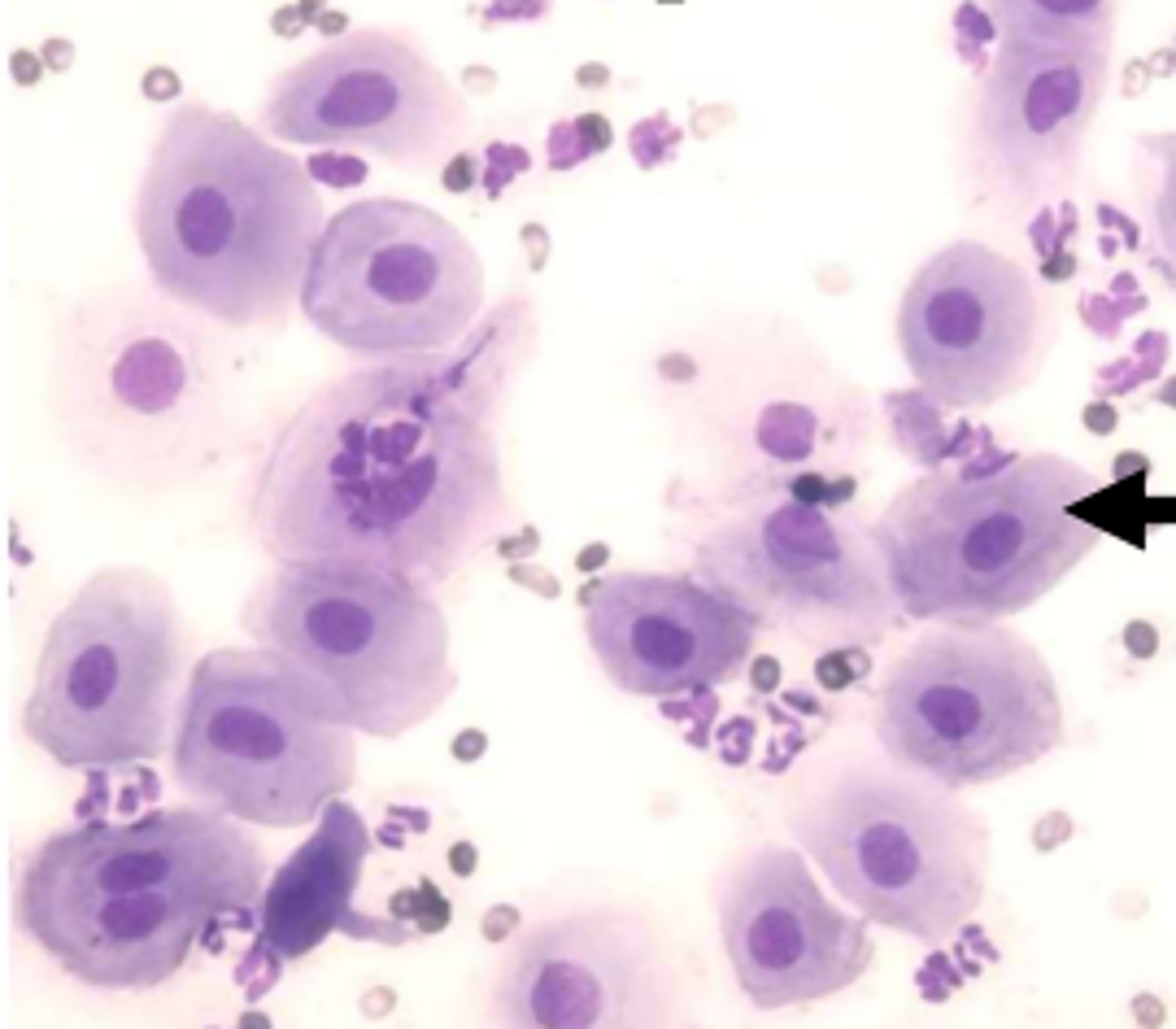
What test is utilized for LH testing in the bitch?
WITNESS LH rapid test, a semi-quantitative test
**CANNOT confirm beginning or completion of ovulation
How many WITNESS LH rapid tests are needed to accurately determine the LH surge?
3 daily test as the surge lasts 12-24 hours with 'positive' levels for 36-72 hours and detectable levels for 60-120 hours
What are options for quantitative progesterone tests?
radioimmunoassay (RIA) - historic gold standard
chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) - current gold standard
How is a 2 ng/ml progesterone interpreted?
LH surge
How is a 5 ng/ml progesterone interpreted?
ovulation begins
How is a 10 ng/ml progesterone interpreted?
ovulation considered complete
What is the range of progesterone level for the fertile windo?
10-15 ng/ml = day 4ish
15-20 ng/ml = day 5ish
20-22 ng/ml = day 6ish
What may be occurring if a progesterone rises slowly?
split heat
stalled heat
physiologic stress
What may be occurring if a progesterone rises quickly?
erratic first or second heat
prolific ovulation
What is the 'rule of 2' for canine breeding management?
2 ng/ml progesterone is LH surge x 2is = 5 ng/ml (ovulation) x2 = 10 ng/ml (ovulation complete, start of fertile window) x2 = 20 ng/ml (end of fertile window)
2 days after LH surge = ovulation begins
2 days after ovulation = start of fertile window
2 days after = end of fertile window
What is the most accurate for estimation of canine due dates?
63 days from ovulation
What are other ways to estimate canine due dates?
65 days from LH surge
57 days from cytologic diestrus
57-72 days from single mating
if multiple mating = 57 days from first breeding and 72 days from last breeding
Why is the range so large for canine due date estimation based on only matings?
maximum sperm longevity is 11 days
maximum oocyte longevity is 2 days
female is potentially receptive before, during, or after ovulation
How does the steroid hormone profile differ post-ovulation between pregnancy and diestrus?
virtually identical besides relaxin (only pregnancy) and prolactin
How does maternal recognition of pregnancy occur in canines?
no evidence of any molecular mechanism and is not believed to be 'necessary'
What is the length of gestation in the canine?
61-65 days post-ovulation
varies with size of litter
What type of placentation occurs in the canine?
endotheliochorial, zonary with 3 defined segments
How is pregnancy maintained in the canine?
CL-dependent
What are the 3 zones of the placental sac of the canine placenta?
transfer zone
pigmented zone
avascular zone
What is the transfer zone of the canine placentation?
area with full contact of endometrium for the exchange of nutrients and waste
'true' region of endotheliochorial with 5 layers of tissue
What is the pigmented zone of the canine placentation?
partial erosion of layers especially the maternal endothelium allowing direct blood flow = 5-10% of total IgG transfer
What is the avascular zone of the canine placentation?
no true exchange with maternal side
How is canine pregnancy diagnosed?
ultrasound
hormone testing
radiography
What is the only single way to simultaneously diagnosed, stage, and assess viability of a canine pregnancy?
ultrasound
What do we want to know about a 'maybe' pregnant dog?
Is she pregnant? When is she due?
**from history determine = if intentionally bred or mismating, clarify dates and management, determine options and viability
Remember why due date calculation is such a wide range from a single mating.
maximum sperm longevity is 11 days
maximum oocyte longevity is 2 days
female is potentially receptive before, during, or after ovulation
When multiple matings occur what is the length of the possible window for due dates?
3.5 weeks (over 1/3 the length of gestation)
What can provides the earliest and most specific diagnosis of canine pregnancy? What days can it be preformed?
ultrasonography
**day 17-19 = small uterine swelling/gestation sacs
**day 21-28 = embryo proper, fetal heartbeats, and resorption sites
**NOT sensitive method for litter size estimation
What is the recommended timing for ultrasonographic diagnosis of canine pregnancy?
4 weeks post-ovulation (30 days post-mating)
**allows diagnosis, reasonable fetal count, and viability assessment
What are the most commonly used methods for pregnancy staging via ultrasound?
First Ultrasonographic Detection (FUD)
Fetal Biometry
How is First Ultrasonographic Detection (FUD) utilized for pregnancy staging?
relies on appearance of developmental markers with usefulness for litters of any size
What is the relative 'order' of appearance of developmental markers for First Ultrasonographic Detection (FUD)?
gestational sac
embryo proper and heartbeat
zonary placenta and embryo polarity
anechoic head area
limb buds
skeletal structures and DPTV
urinary bladder
fetal movement
stomach and abdominal-thoracic distinction
kidneys
What is the minimum day of gestation that the gestational sac can be visualized ultrasonographically?
day 17
What is the minimum day of gestation that the embryo proper and heartbeat can be visualized ultrasonographically?
day 21
What is the minimum day of gestation that fetal movement can be visualized ultrasonographically?
day 32
What is used for fetal biometry for pregnancy staging?
measurement of fetal and extra-fetal structures with formulations that determine gestational age OR days to parturition
What types of pregnancy is fetal biometry the most accurate for?
medium-sized breeds
litters mid-gestations
What are different fetal biometry calculations?
crown-rump length (CRL)
biparietal diameter (BPD)
body diameter (transverse at liver and stomach) (BD)
deep portion of diencephalo-telencephalic vesicle (DPTV)
outer uterine diameter (OUD)
inner chorionic cavity (ICC)
What hormone is used for diagnosis of canine pregnancy?
relaxin
What is the ONLY source of detectable levels of relaxin in the dog?
fetoplacental unit (trophoblast cells)
What is used as a semi-quantitative relaxin assay?
WITNESS Relaxin Rapid Test
When is the WITNESS Relaxin Rapid Test the most sensitive and specific
after day 31 of gestation
What is the most sensitive method for estimating litter size?
orthogonal radiographs counting paired skulls and spines
What can radiographic diagnosis of pregnancy allow determination of?
100% specific for presence of fetuses if after day 42 (when skull faintly visible)
MAY provide information on viability
What is the recommended timing of radiographic evaluation of pregnancy?
7-10 days prior to due date
What diet is recommended for the pre-partum dog?
balanced COOKED diet and increase over 22% crude protein in final month
ad libitum water throughout with ad libitum food in final week
supplements and probiotics are unnecessary if otherwise healthy
supplemental CALCIUM should not be provided
What activity is recommended for the pre-partum dog?
no strenuous activity in first 2 weeks or final 2 weeks
light-moderate beneficial during gestation
NO SWIMMING
What health/welfare is recommended for the pre-partum dog?
limit grooming to non-stressful, non-submersive methods
vaccines 2 weeks prior to proestrus OR wait until postpartum
Fenbendazole = 14 day prior, 2 days into, and 14 days postpartum
if product is untested in pregnancy/lactation, assume its harmful - whole list of things that are safe
How should owner's prepare the hours/environement for whelping?
box in quiet, low traffic area with 85-90 degree ambient temp
isolate dam/litter from novel dogs 3 weeks pre and post-partum
What whelping/rearing equipment should owners have on hand?
clean towels, water, and lubricant
mucus traps or suction bulbs
umbilical tape or clamps
scale and weight charts
+/- puppy identification
+/- milk replacer, bottles, feeding tubes
+/- 25G needles, stethoscope, hemostats
What are reliable predictors of whelping?
drop in rectal temperature
drop in progesterone
(others = loss of cervical mucus plug, nesting behavior, anxiety, tachypnea, rise in cortisol)