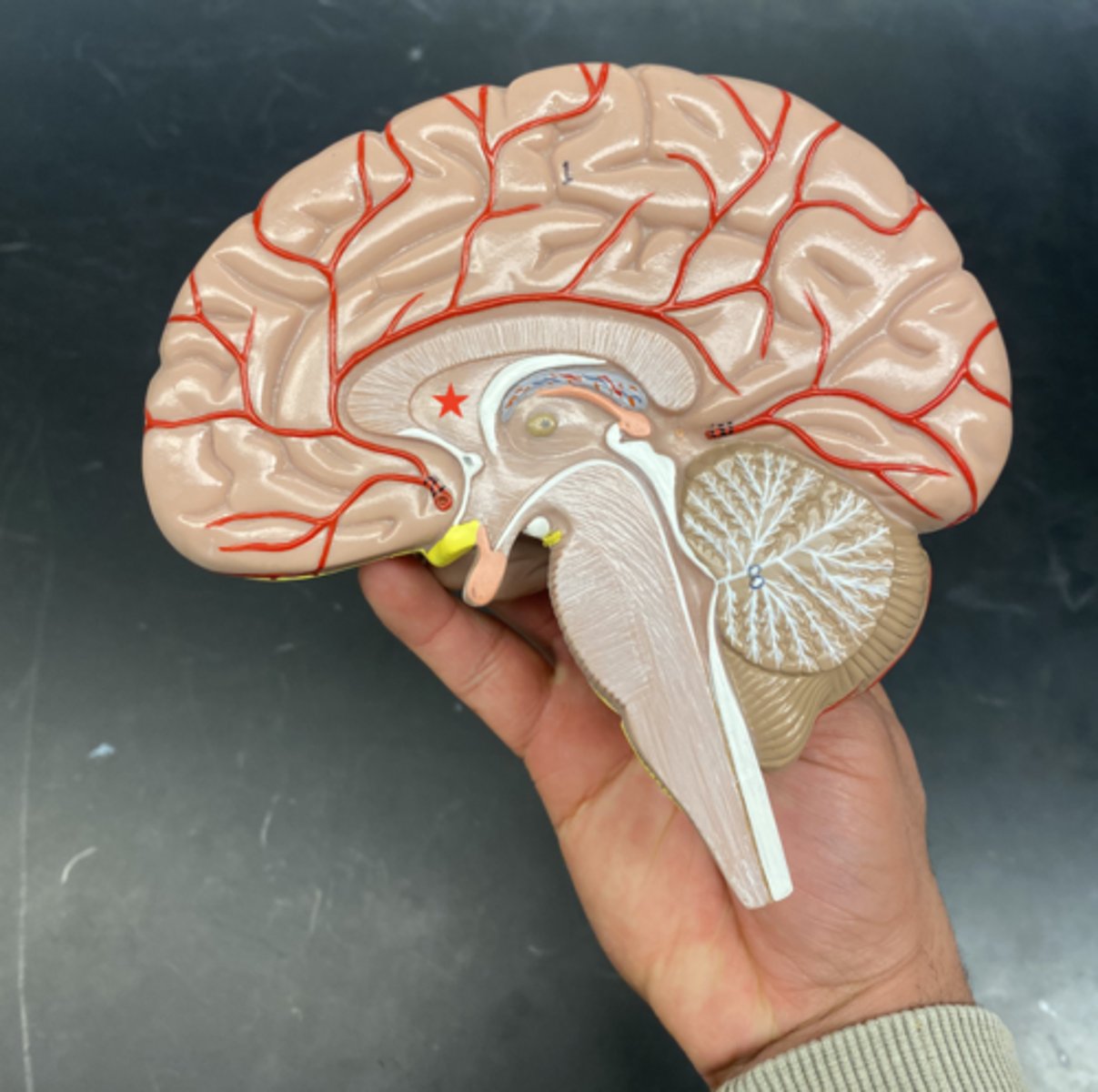
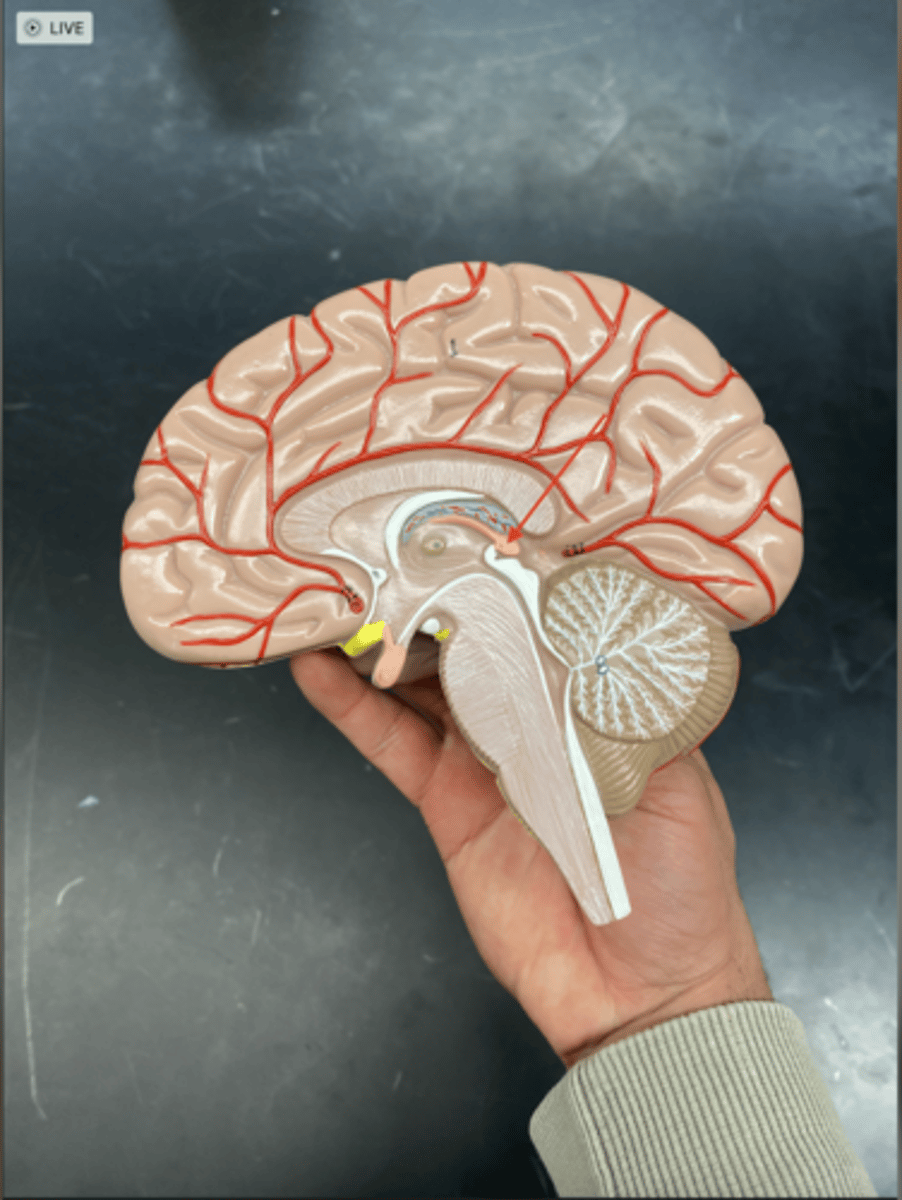
Brain Structures from a midsagittal view
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
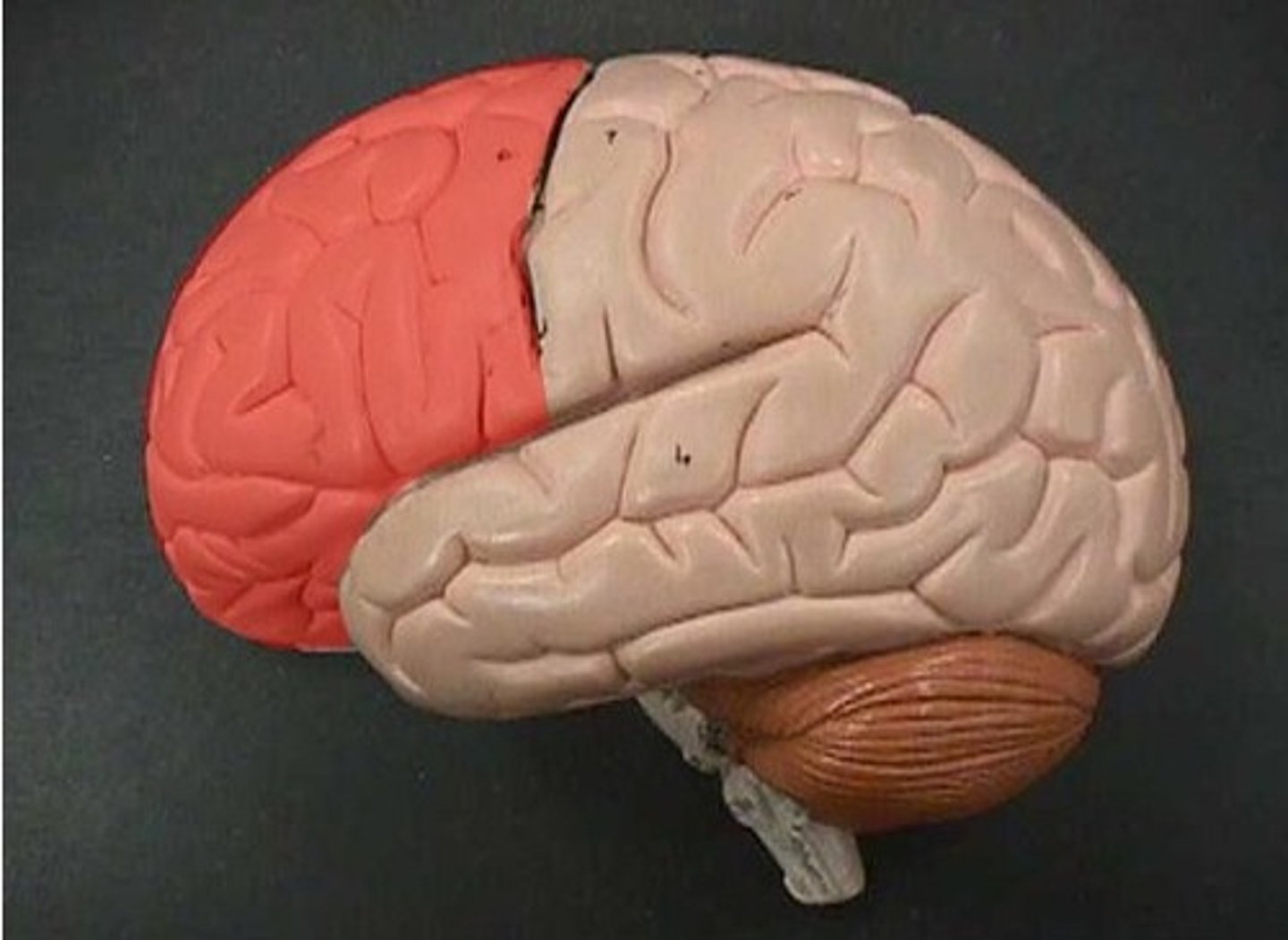
Frontal Lobe
is the part of the brain responsible for reasoning, decision-making, voluntary movement, and aspects of personality and behavior.
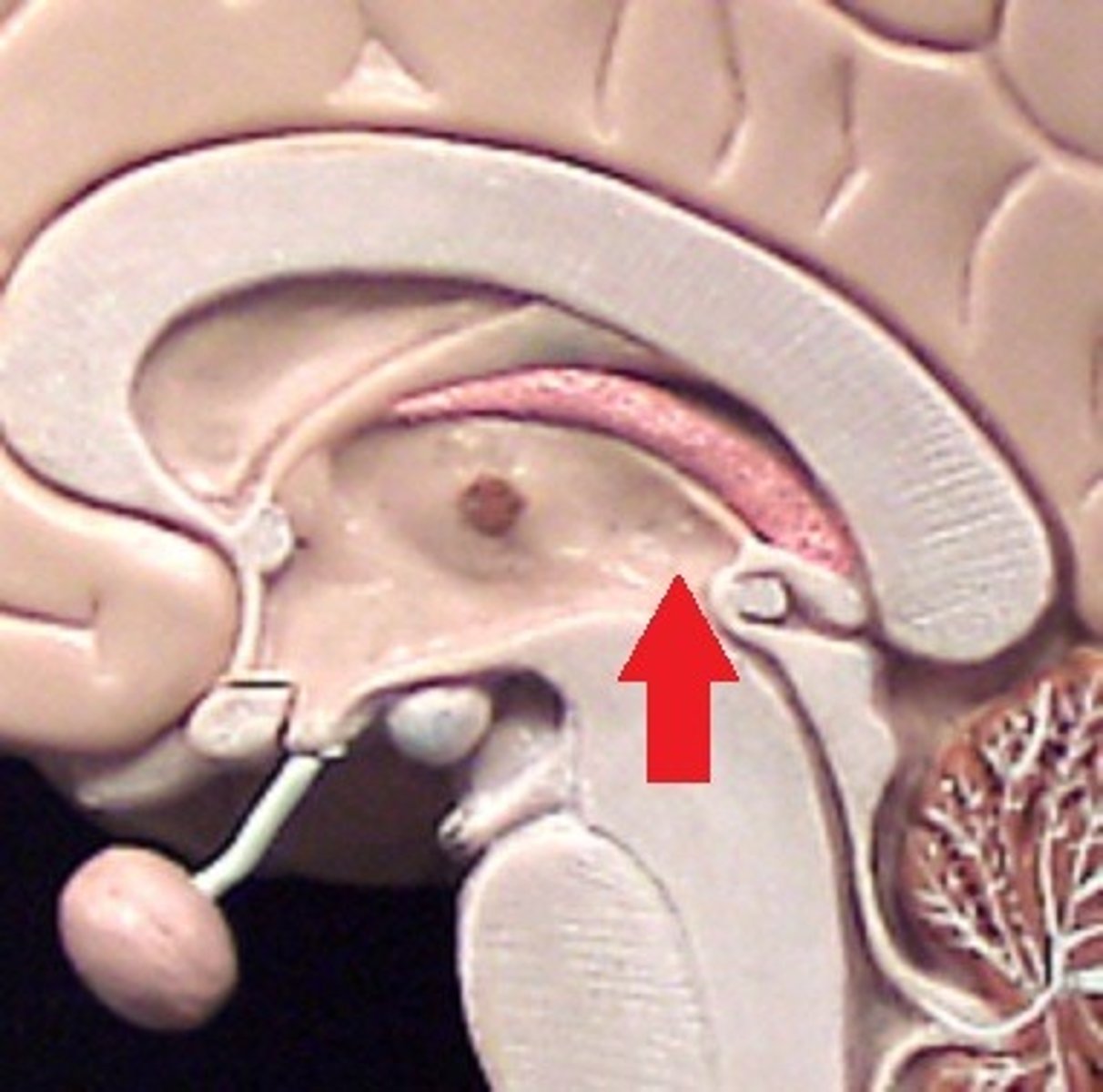
Septum pellucidum
is a thin, transparent membrane located in the midline of the brain, separating the two lateral ventricles.
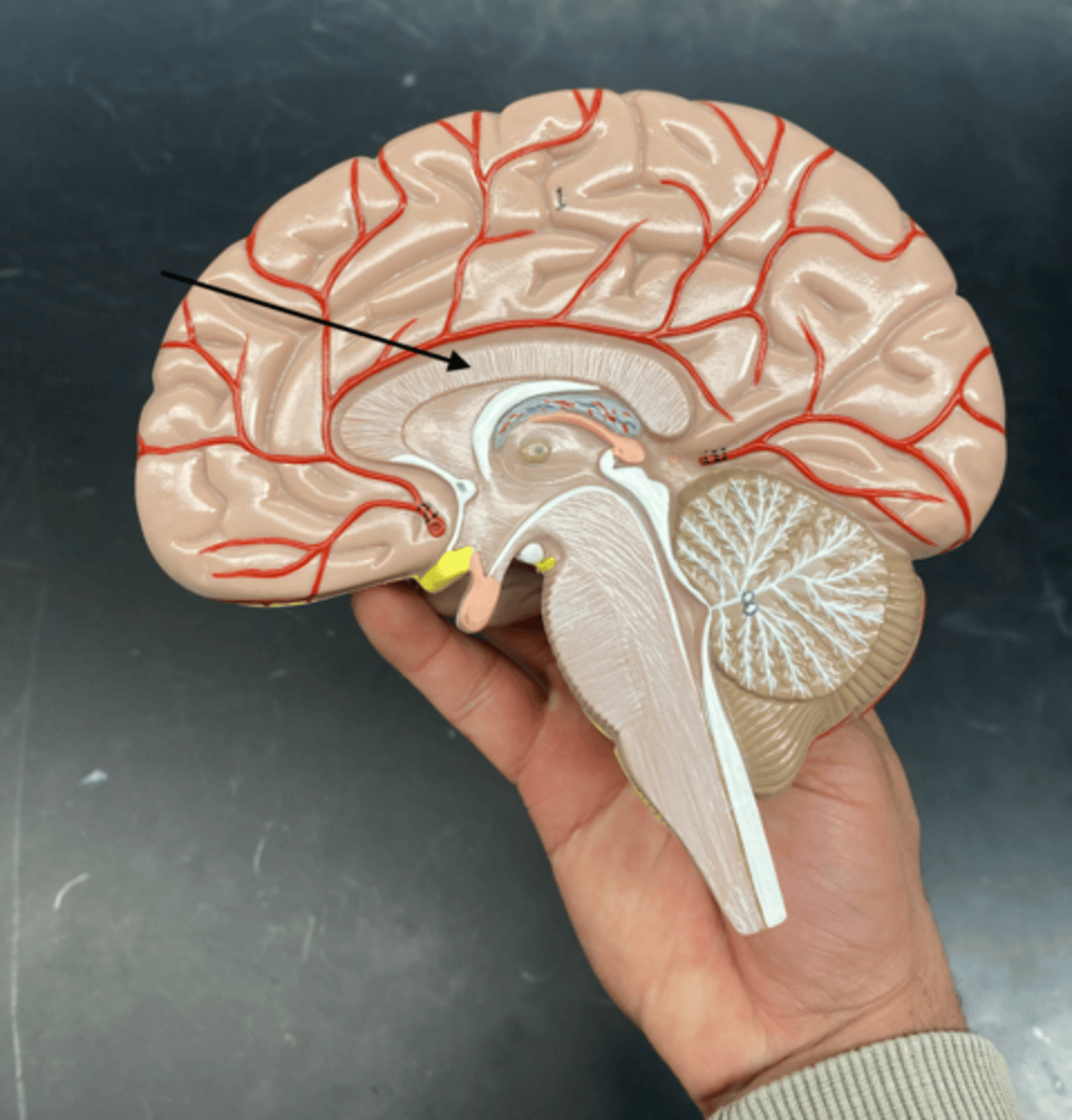
Corpus callosum
is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, allowing them to communicate and coordinate activities.
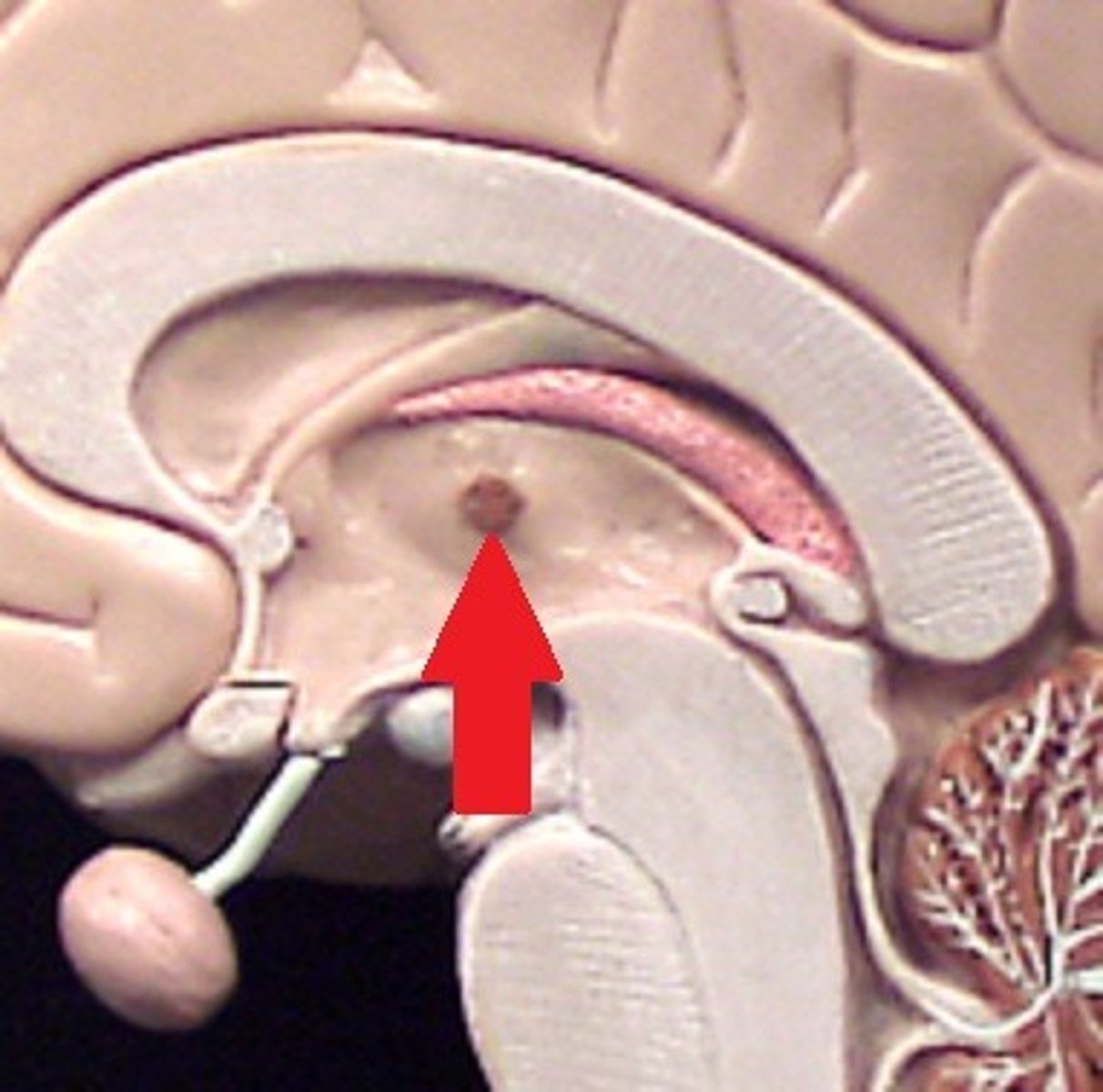
Epithalamus
is a part of the diencephalon that includes the pineal gland and habenula, playing key roles in regulating sleep-wake cycles and emotional responses.
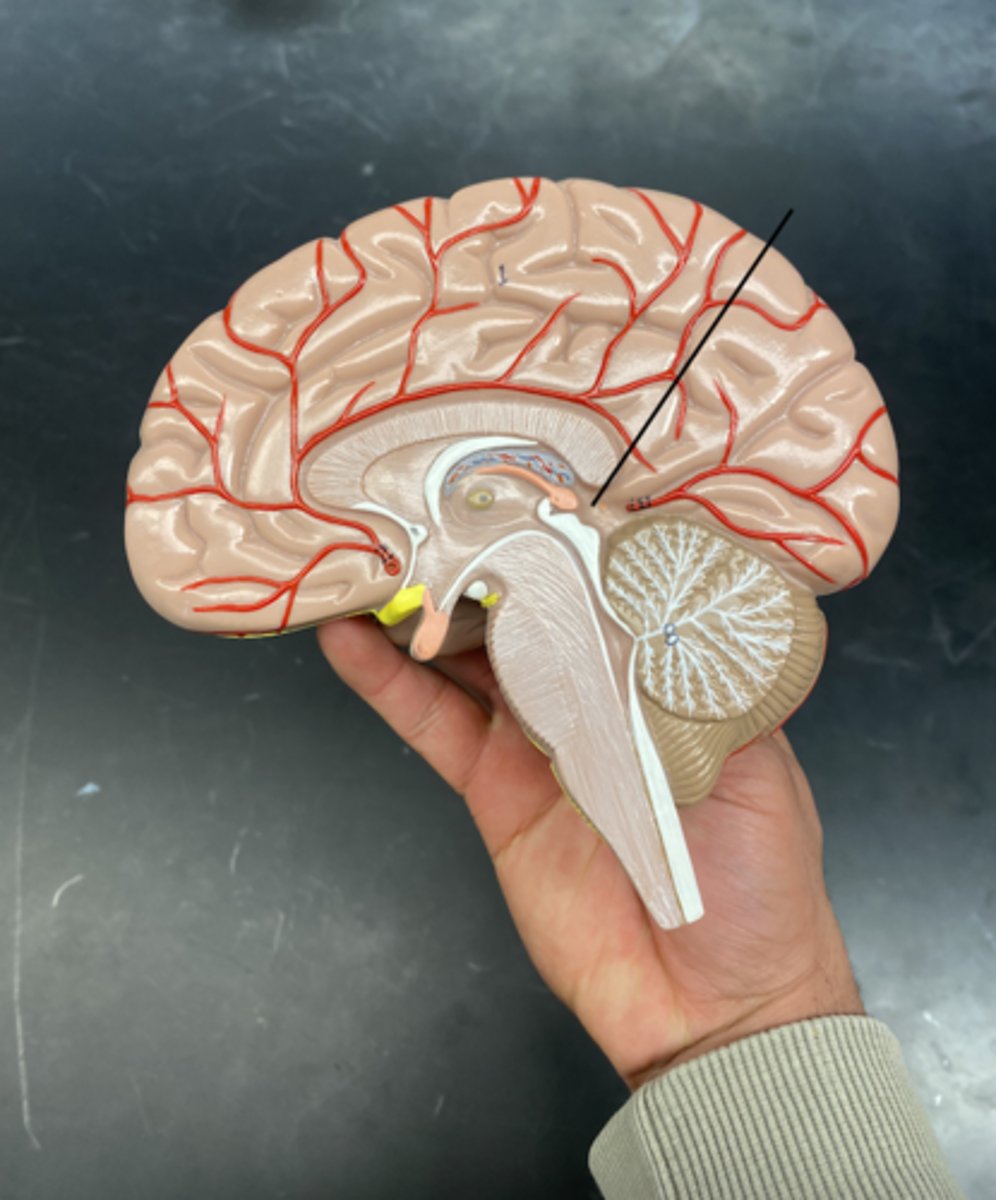
Pineal gland
.produces melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate the body's sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm), especially in response to light and darkness.
Thalamus
is a brain relay center that directs sensory signals (except smell) to the cerebral cortex and helps regulate alertness and motor function.
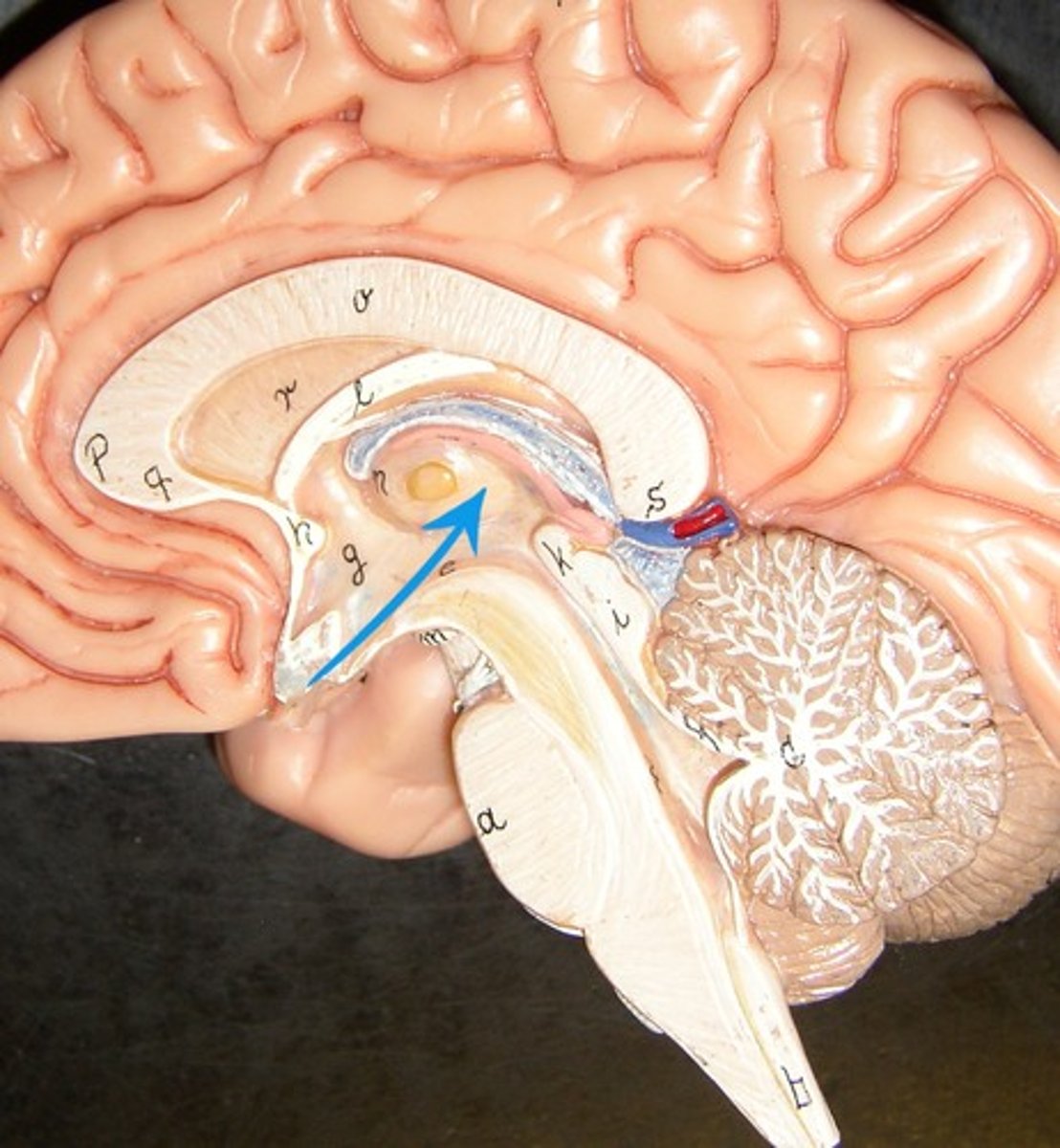
Interthalamic adhesion
is a small mass of gray matter that connects the left and right halves of the thalamus across the third ventricle.
Hypothalamus
controls vital body functions like temperature, hunger, thirst, hormone release, and the sleep-wake cycle.
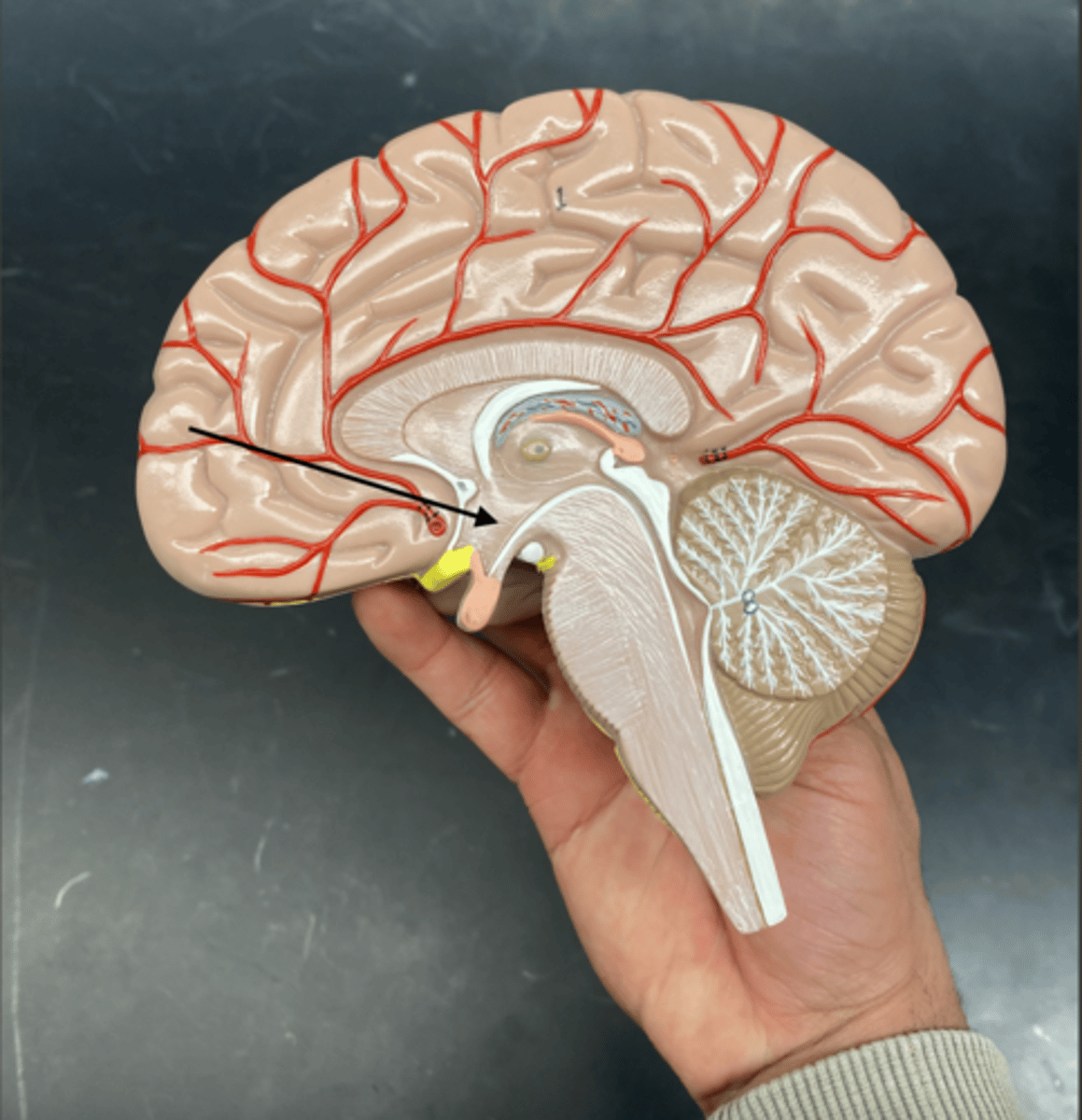
mammillary body
small, rounded structures located on the underside of the brain, part of the hypothalamus. They are involved in memory processing and are part of the limbic system.
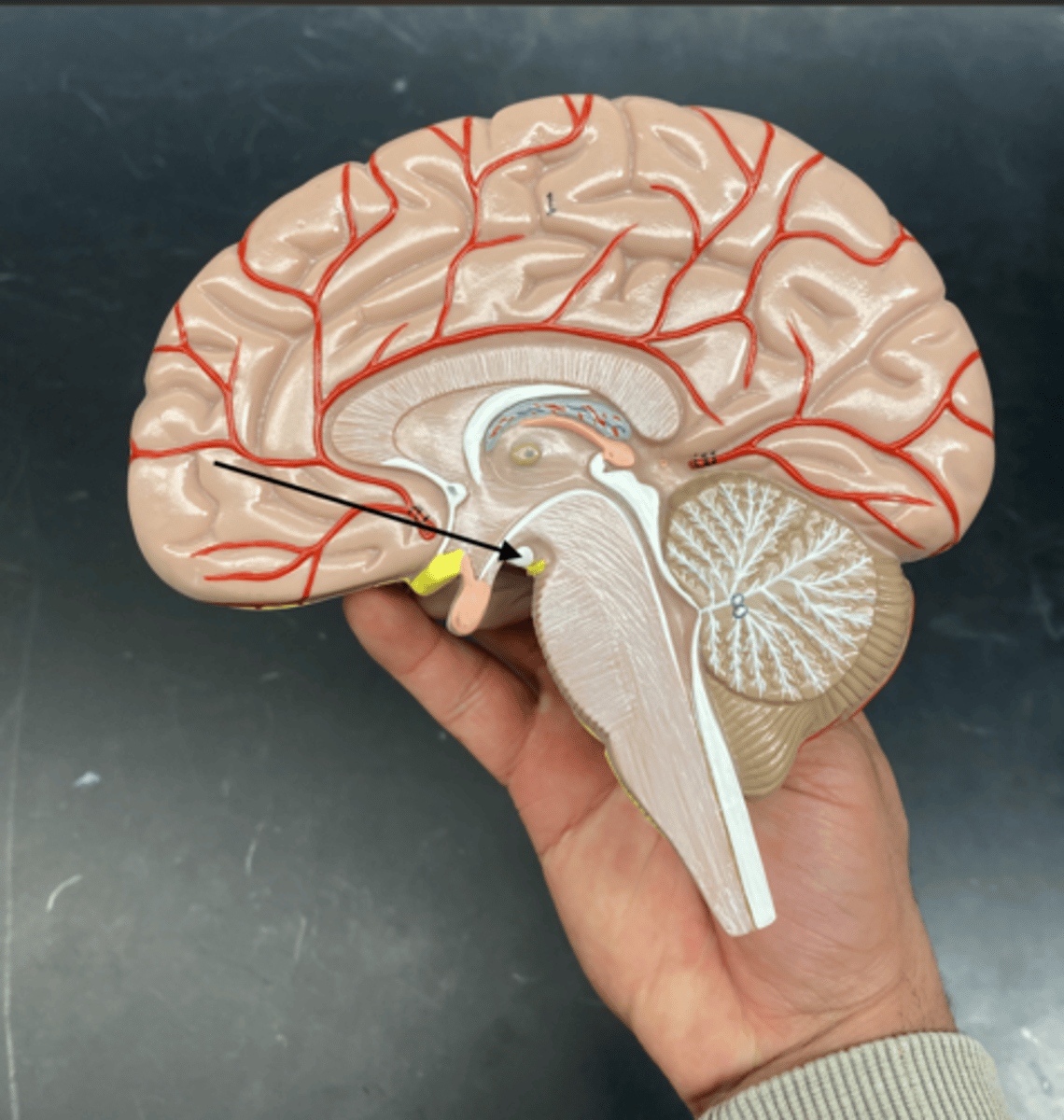
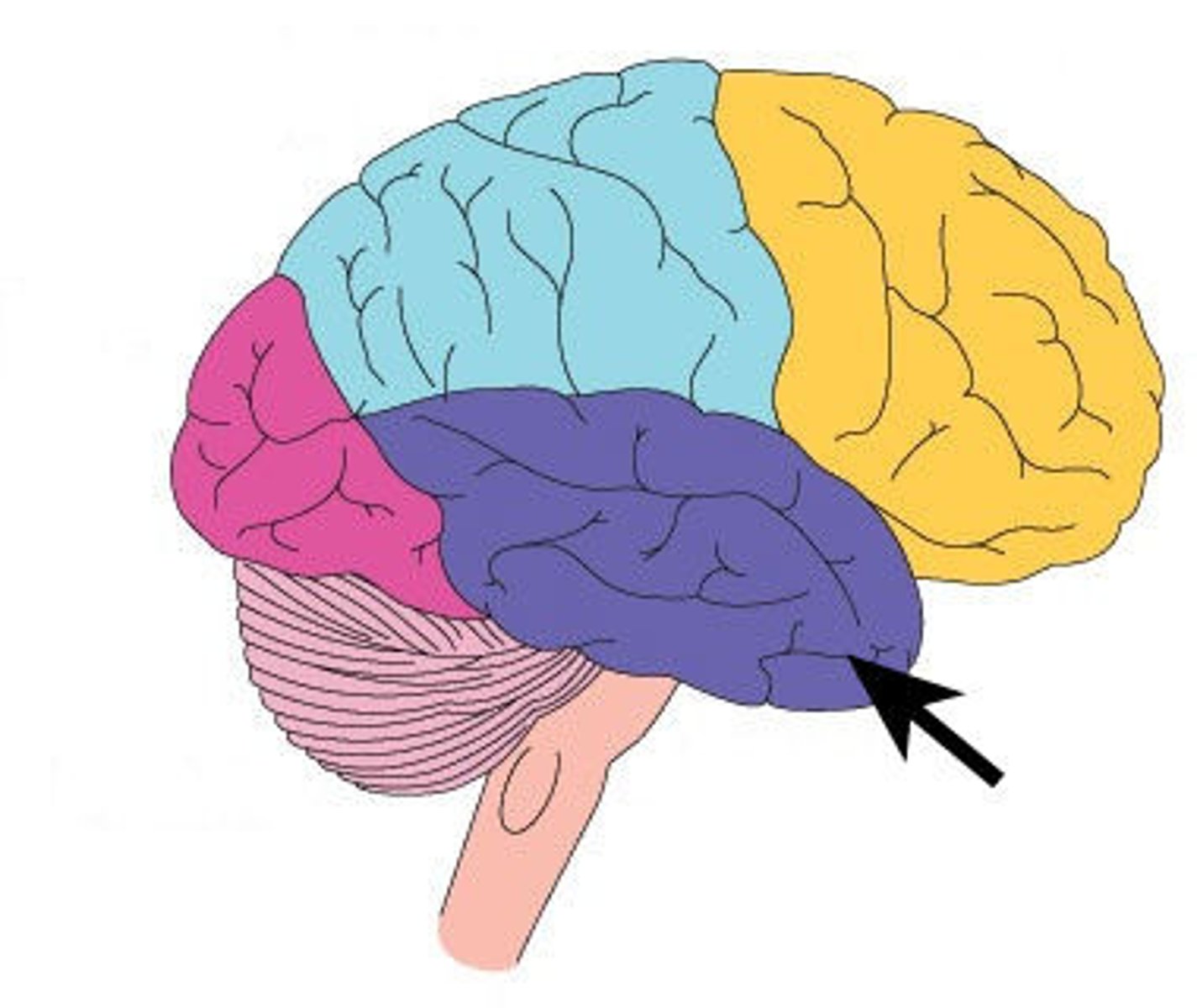
Temporal Lobe
It is involved in processing auditory information, memory, language, and emotions. It contains the hippocampus (important for memory) and Wernicke's area (involved in language comprehension).
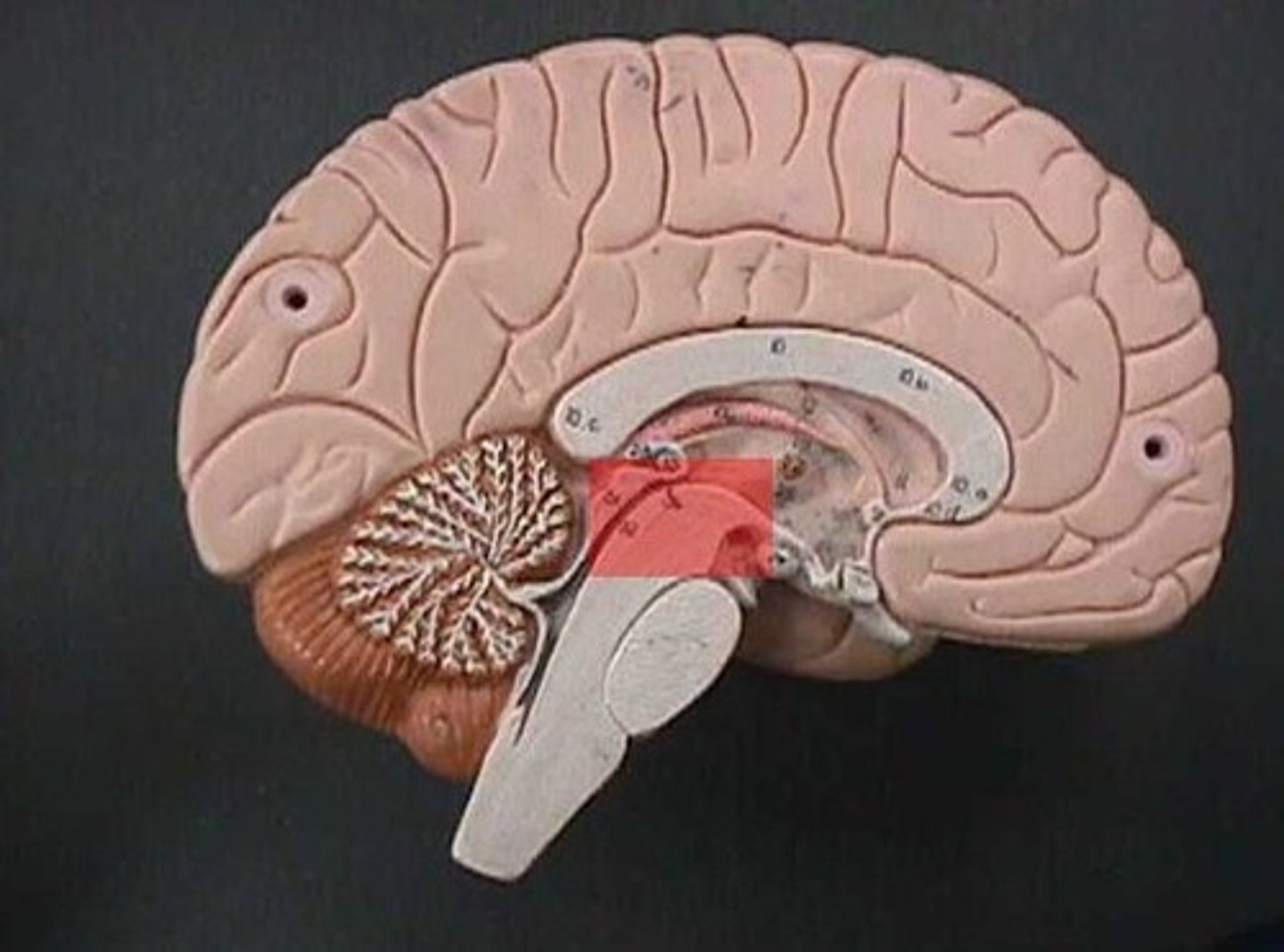
midbrain
vision, hearing, motor control, and regulating sleep and alertness. It also contains pathways for sensory and motor information.
Pons
It helps relay signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum and plays a role in breathing, sleep, and facial sensations and movements.
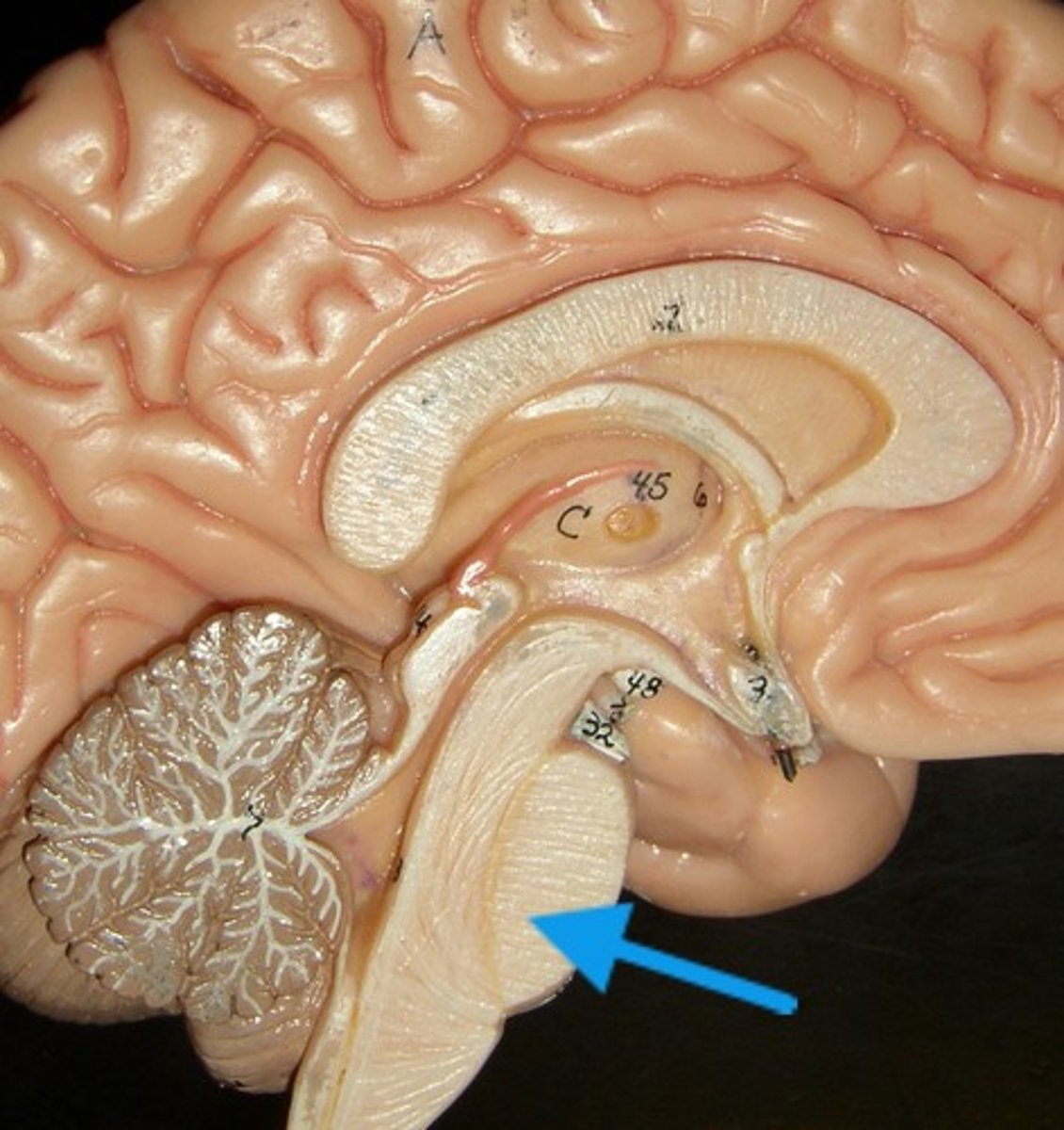
Medulla Oblongata
is the lowest part of the brainstem that controls vital involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
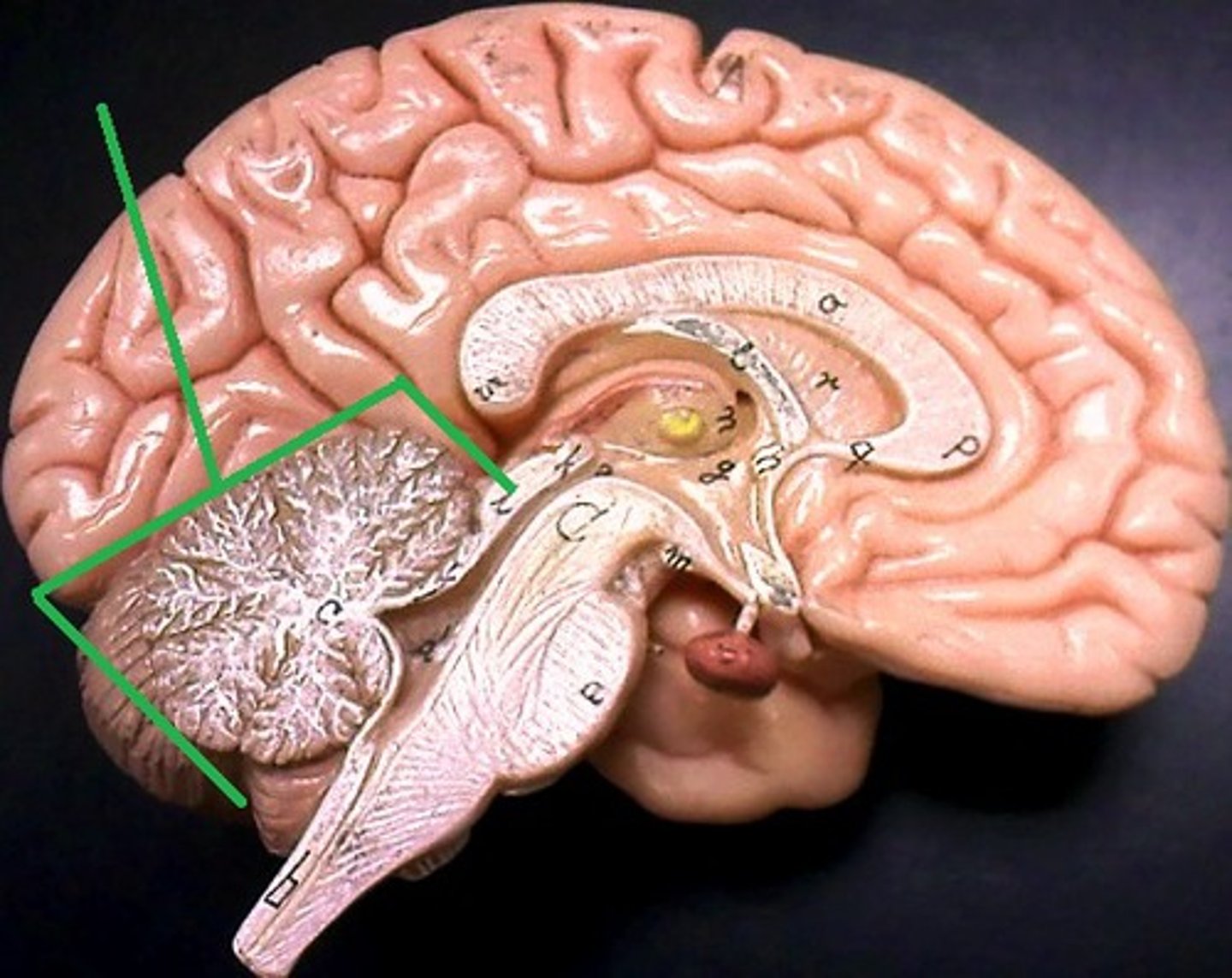
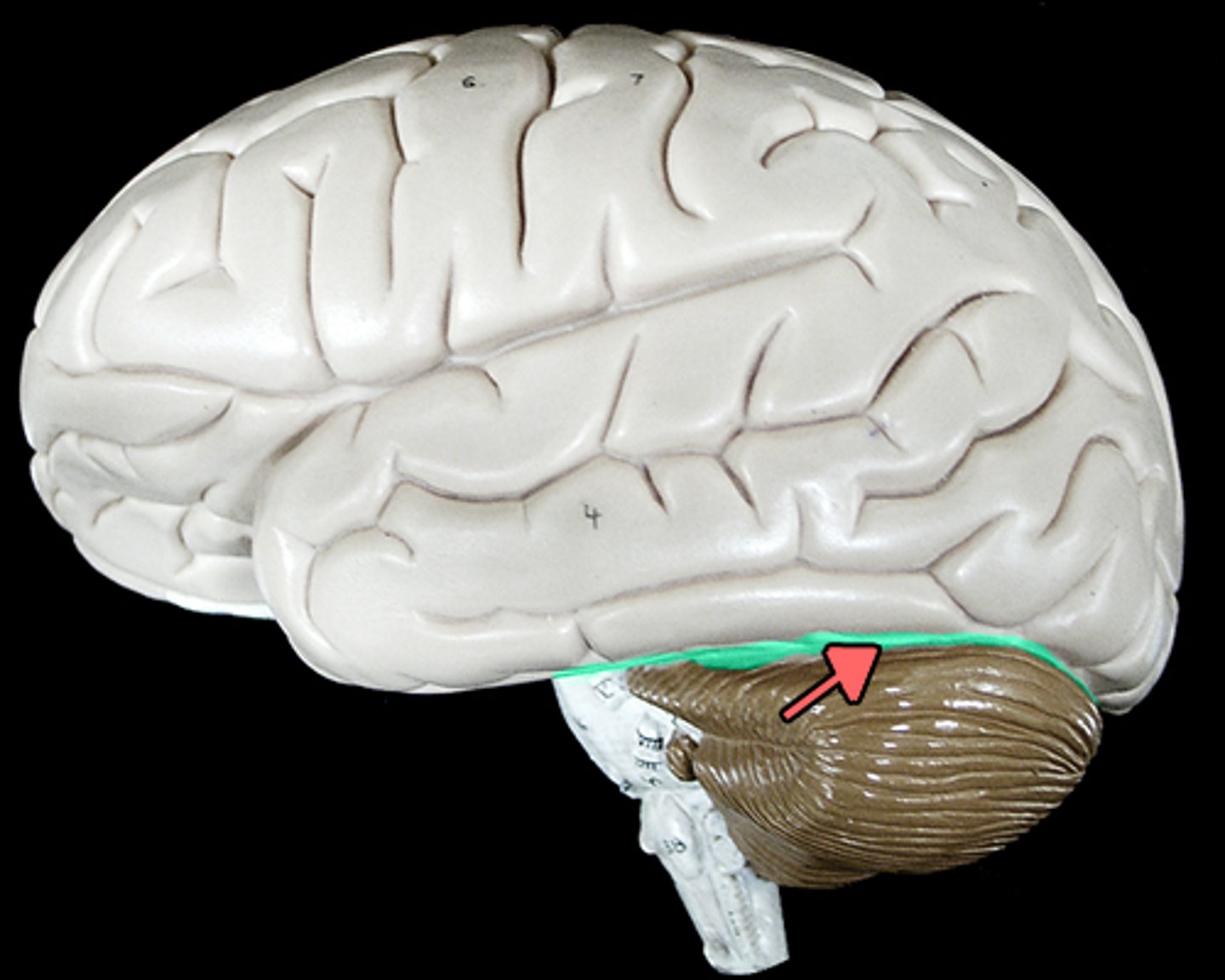
Cerebellum
is the part of the brain located at the back of the skull that coordinates voluntary movements, balance, posture, and motor learning.
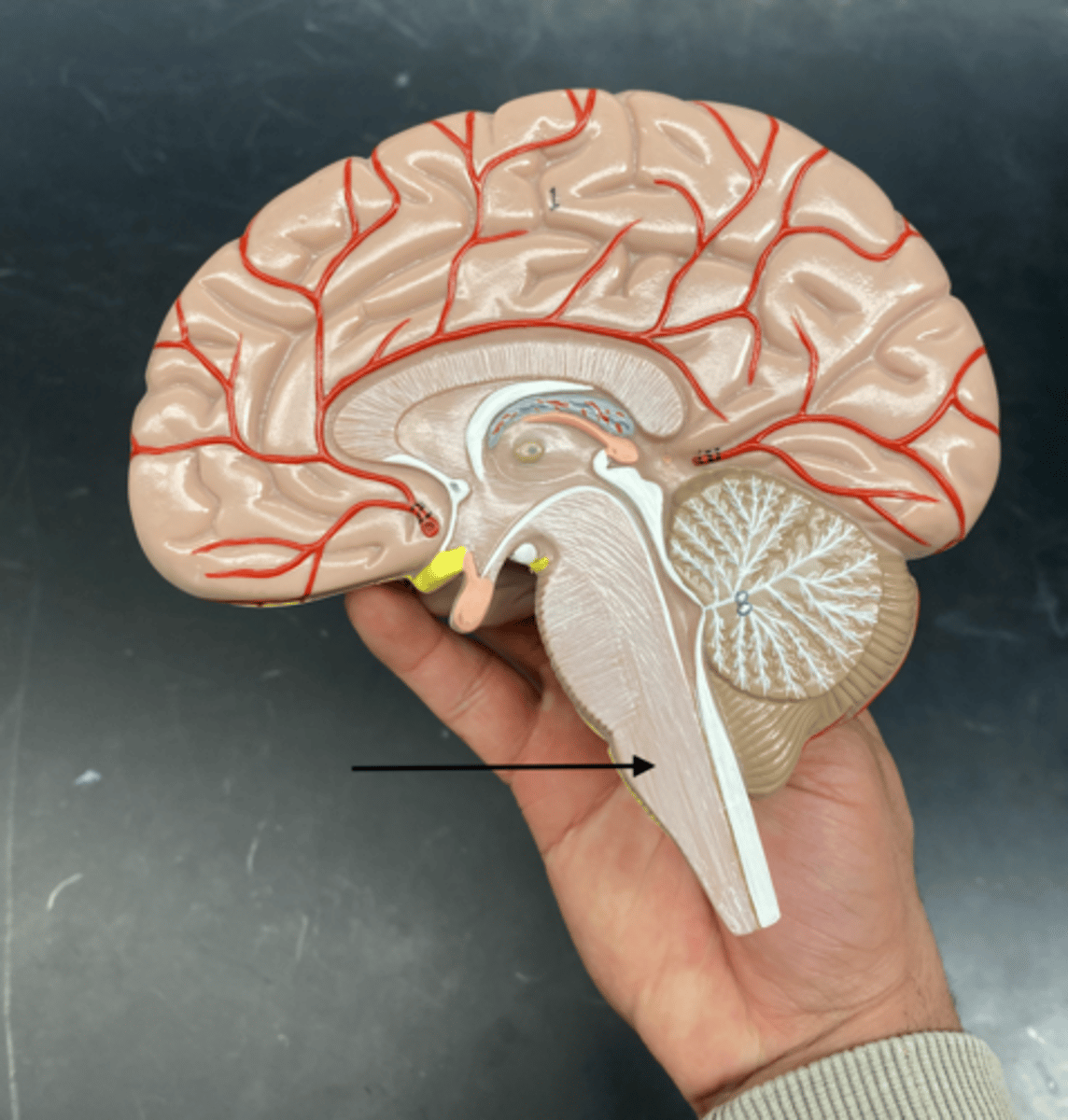
Four ventricle
is a fluid-filled cavity located between the brainstem and the cerebellum that helps circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) throughout the brain and spinal cord.
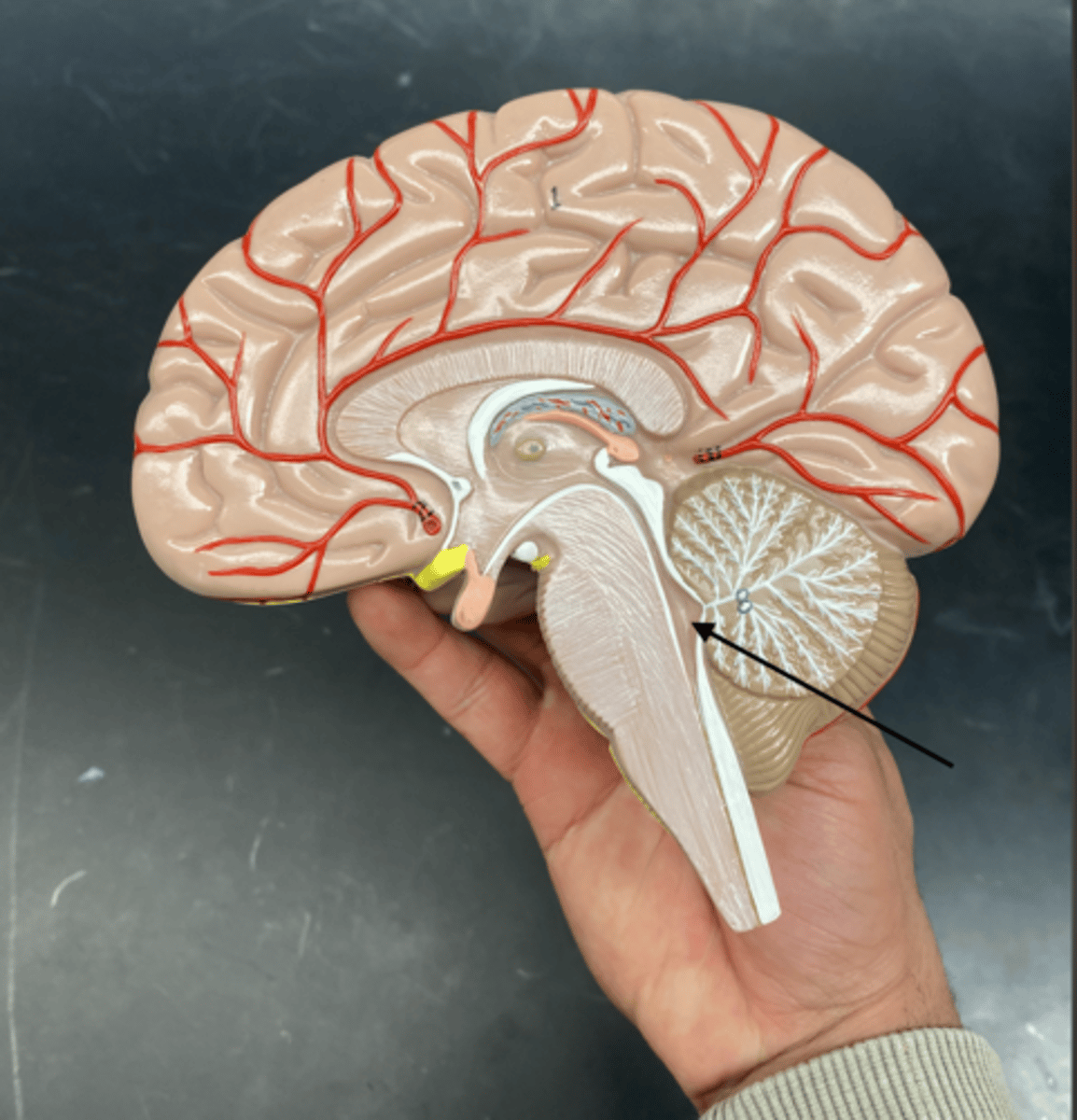
cerebral aqueduct
is a narrow channel in the midbrain that connects the third and fourth ventricles, allowing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flow between them.
4o
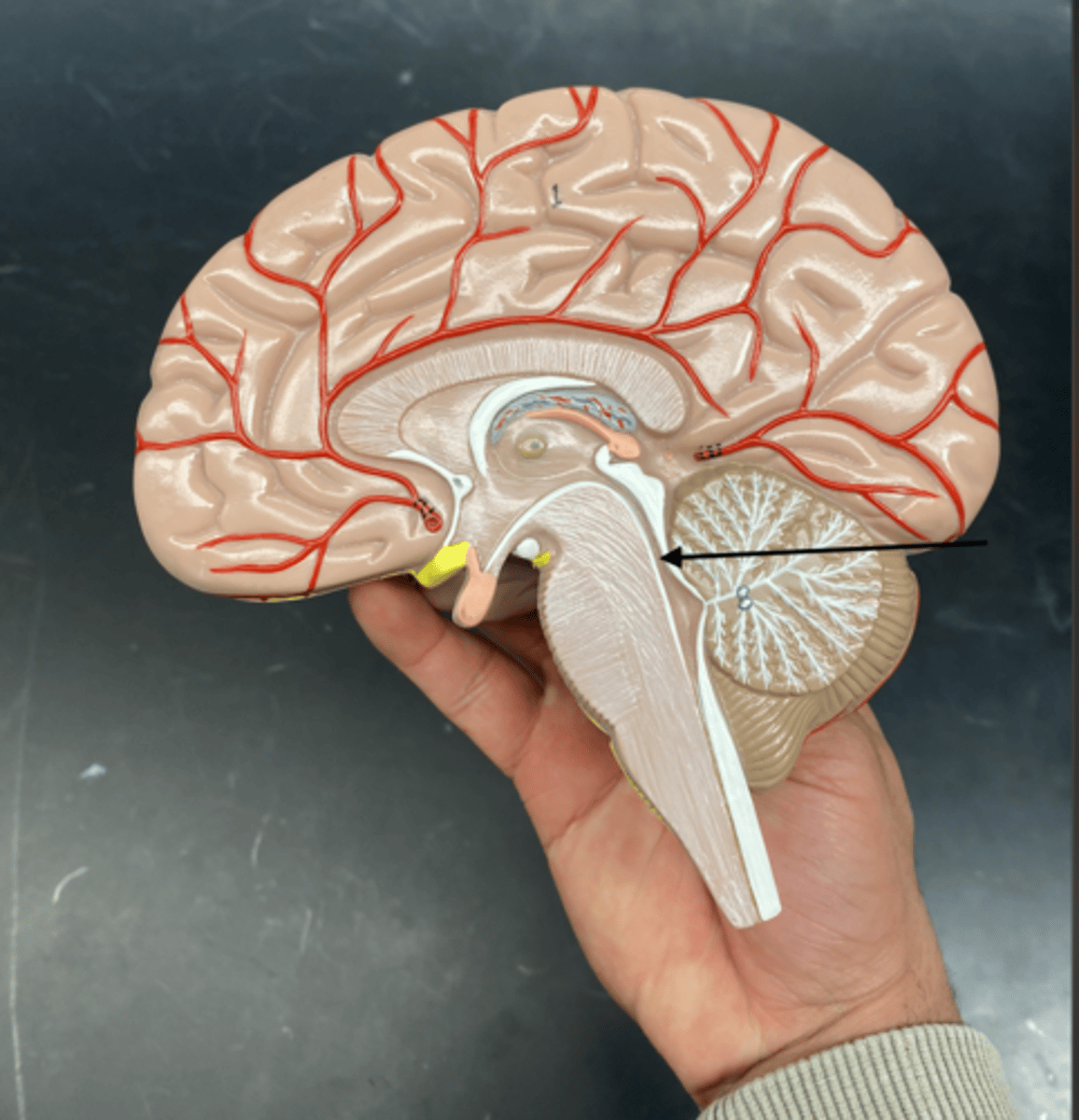
Tectal plate
is the dorsal part of the midbrain that contains the superior and inferior colliculi, which are involved in visual and auditory reflexes, respectively.
4o
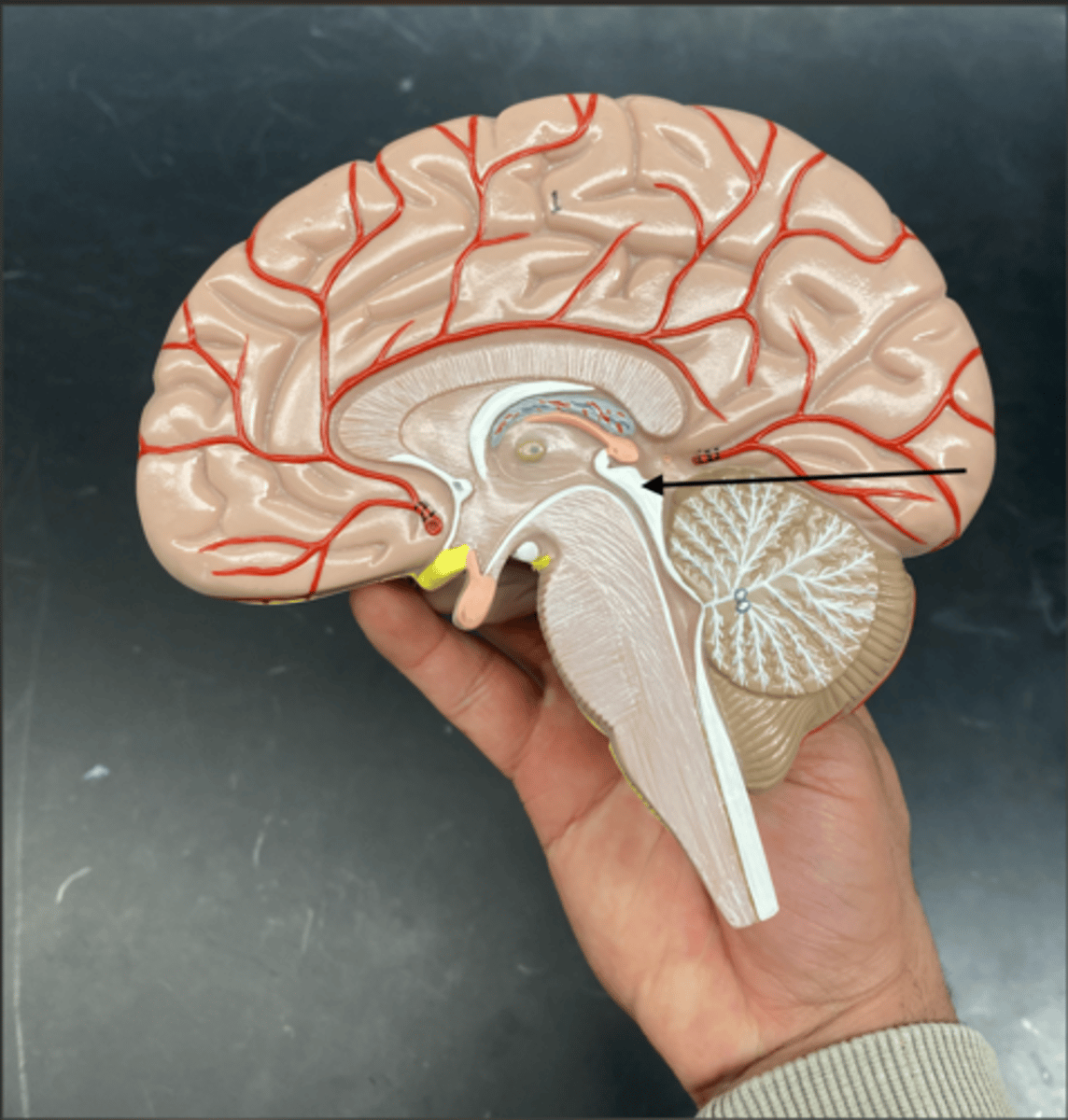
Occipital Lobe
is the region at the back of the brain responsible for processing visual information.
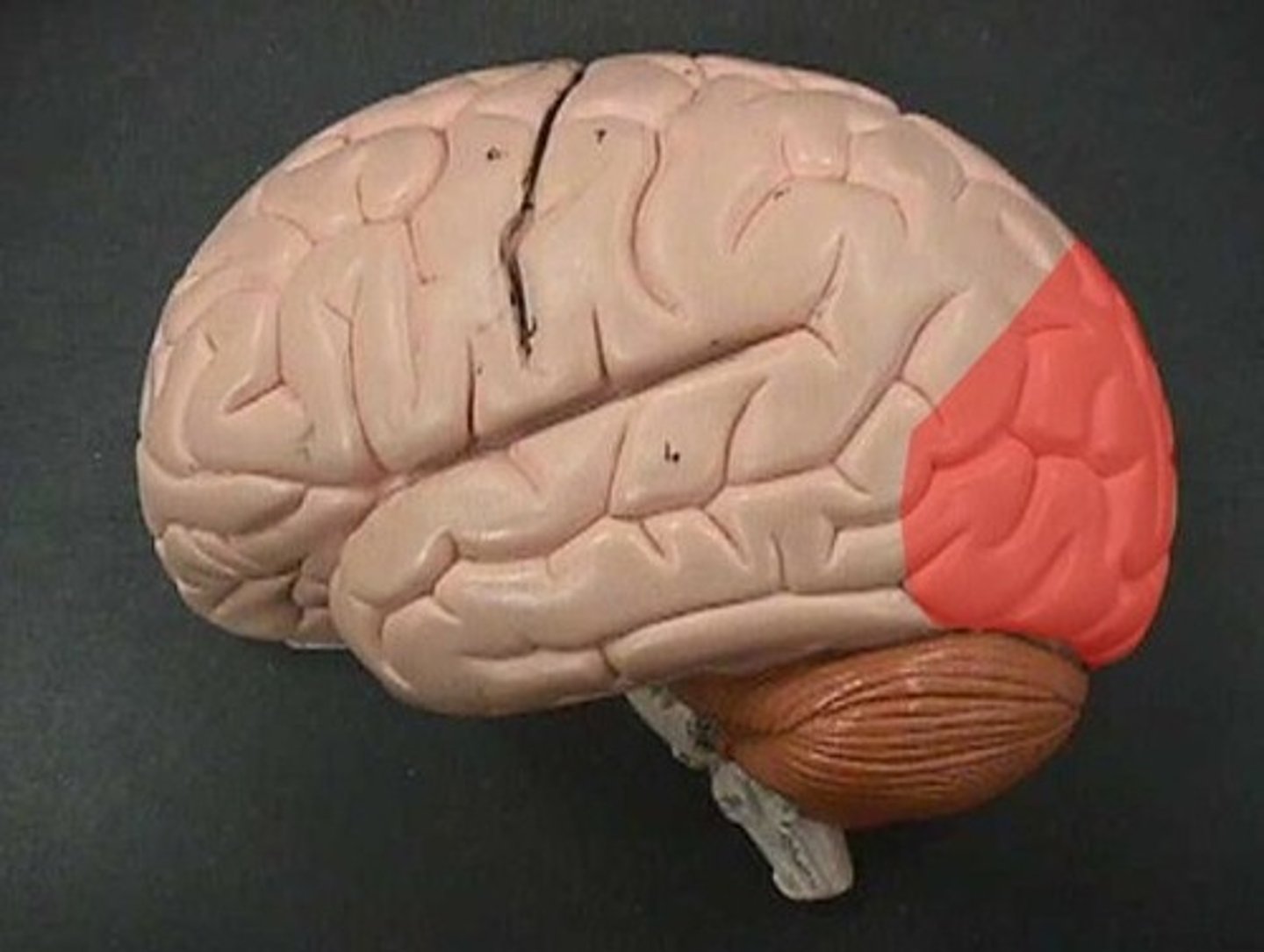
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Parietal Lobe
is a region of the brain located behind the frontal lobe that processes sensory information like touch, temperature, pain, and spatial awareness.
4o
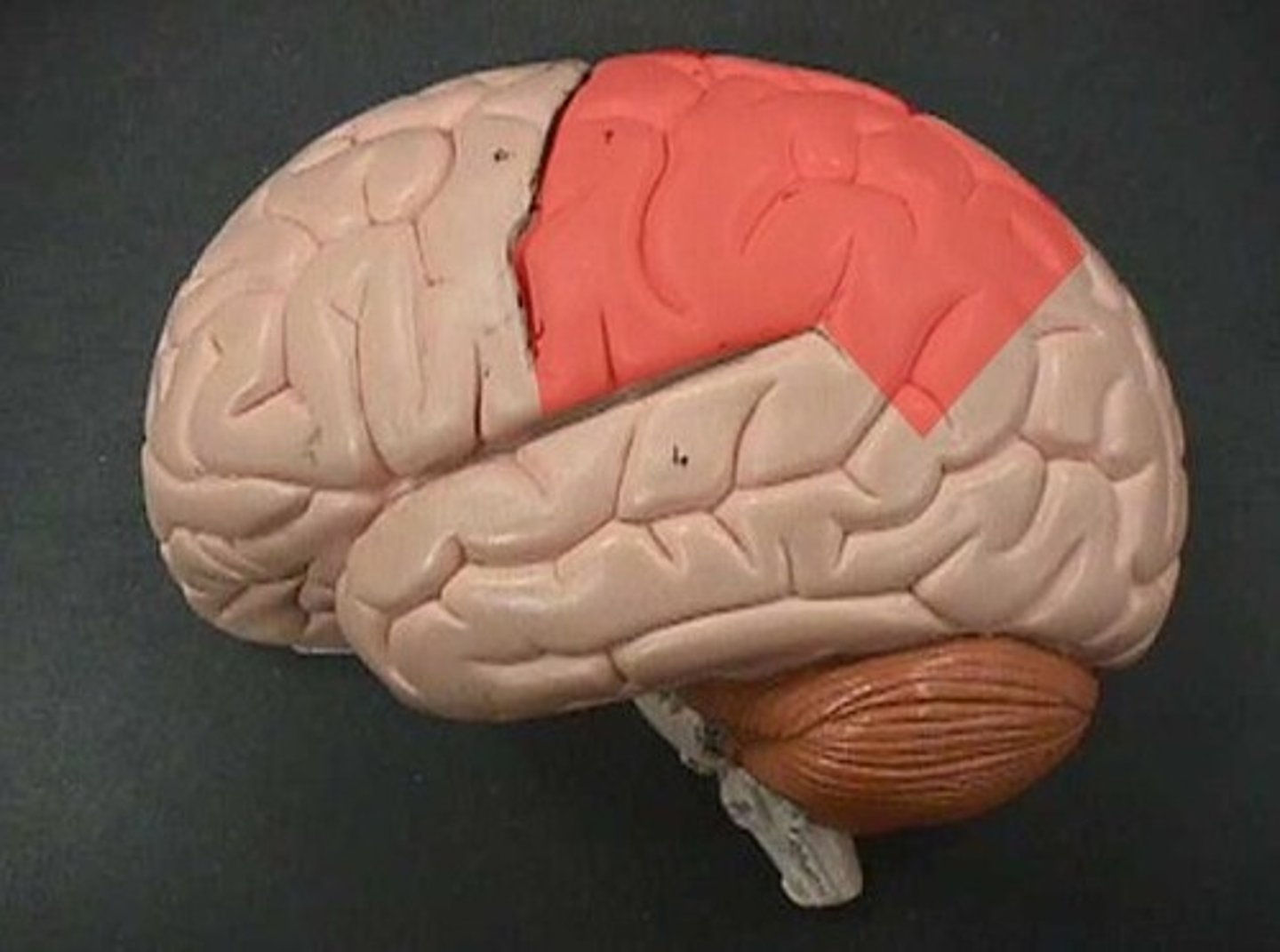
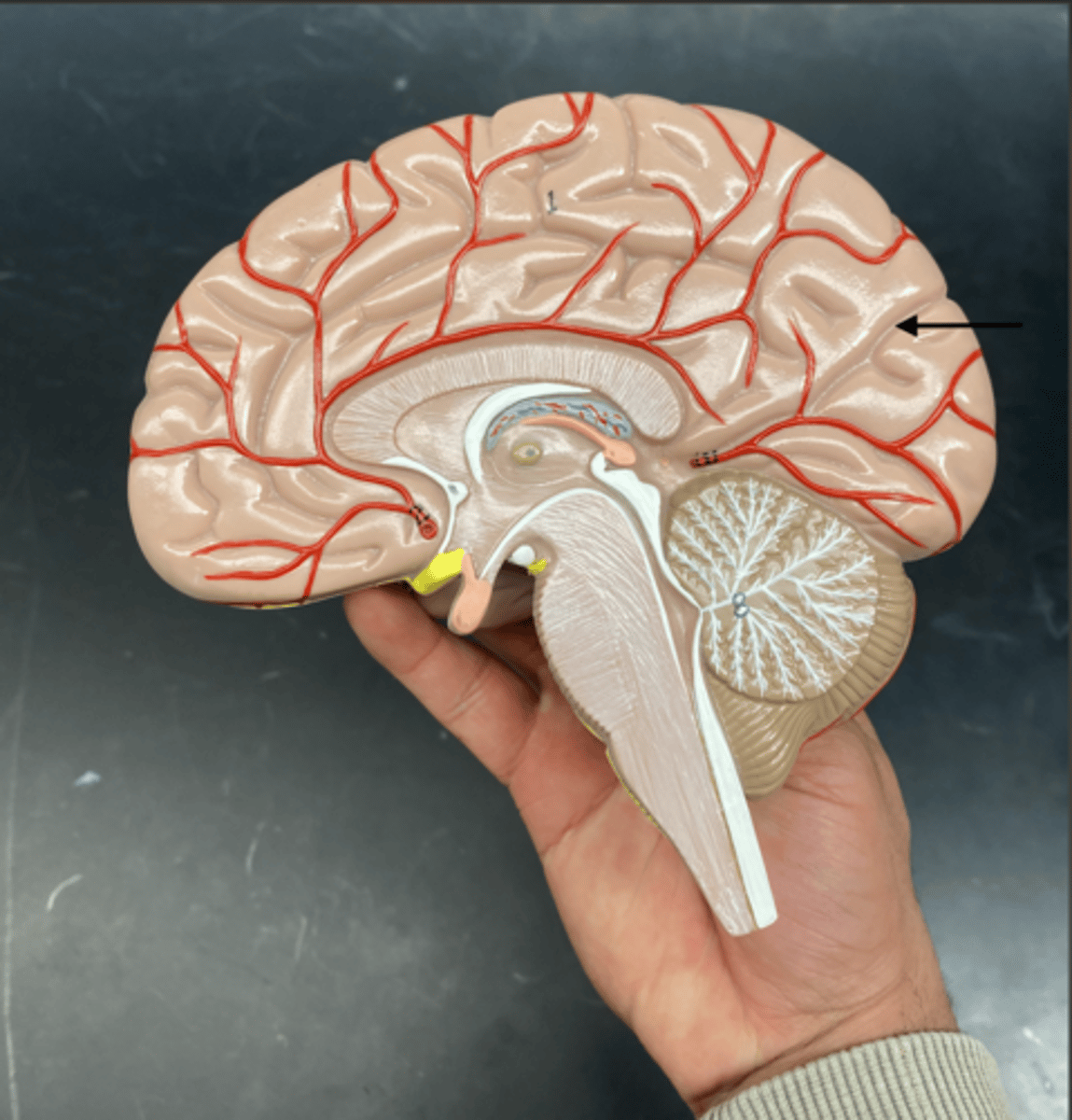
Central sulcus
is a prominent groove in the brain that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe and divides the primary motor cortex (in front) from the primary somatosensory cortex (behind).
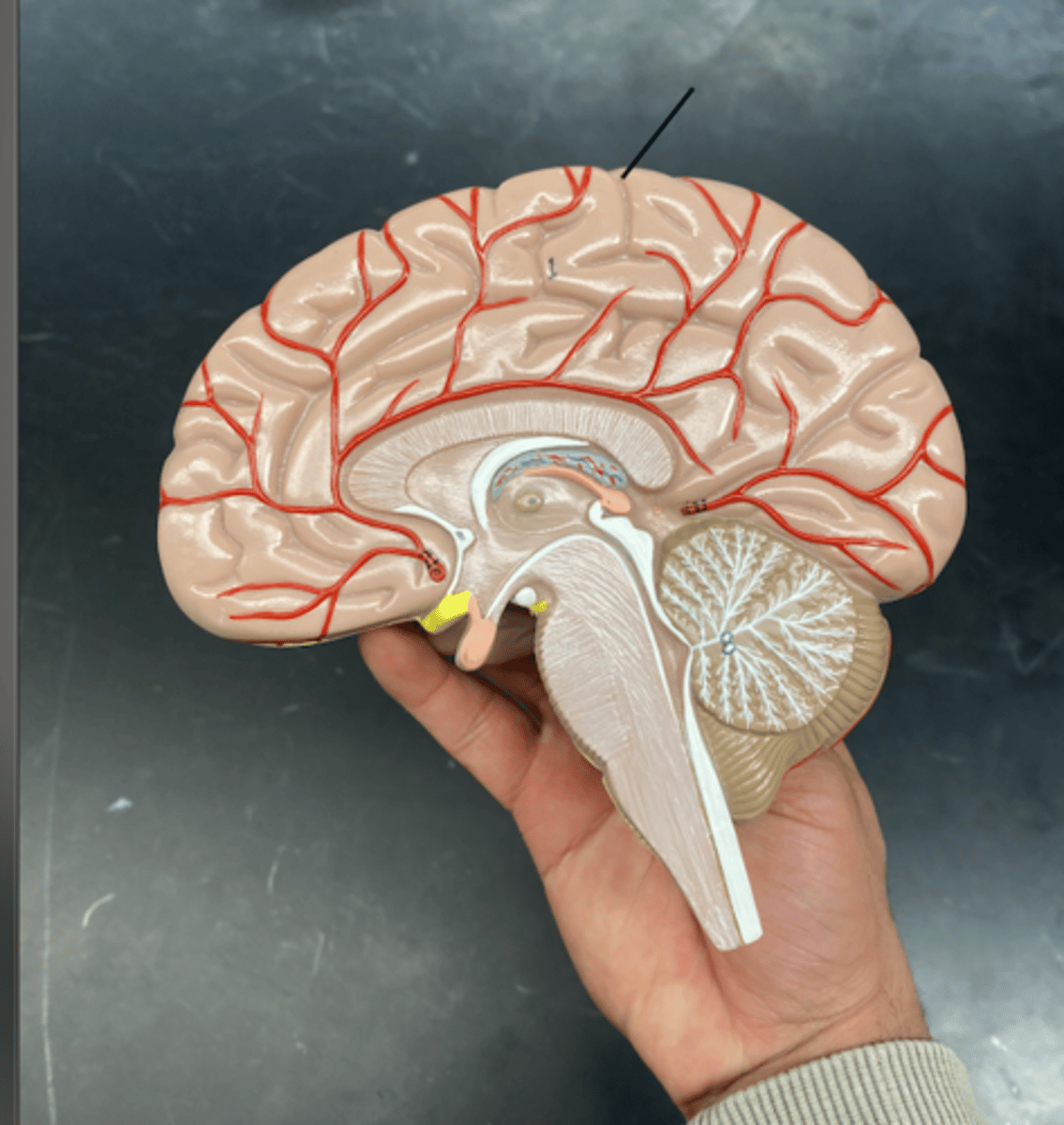
pituitary gland
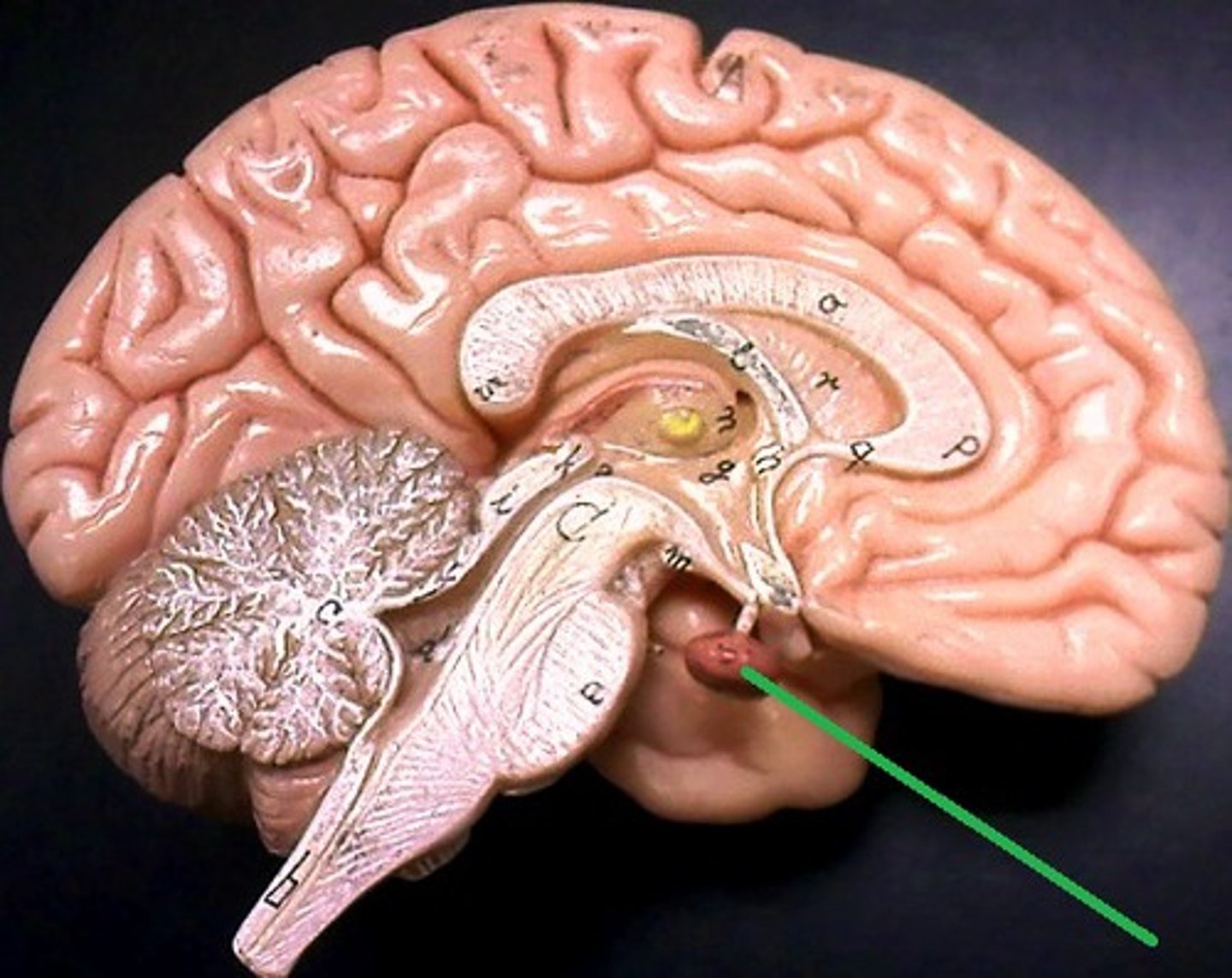
cingulate gyrus
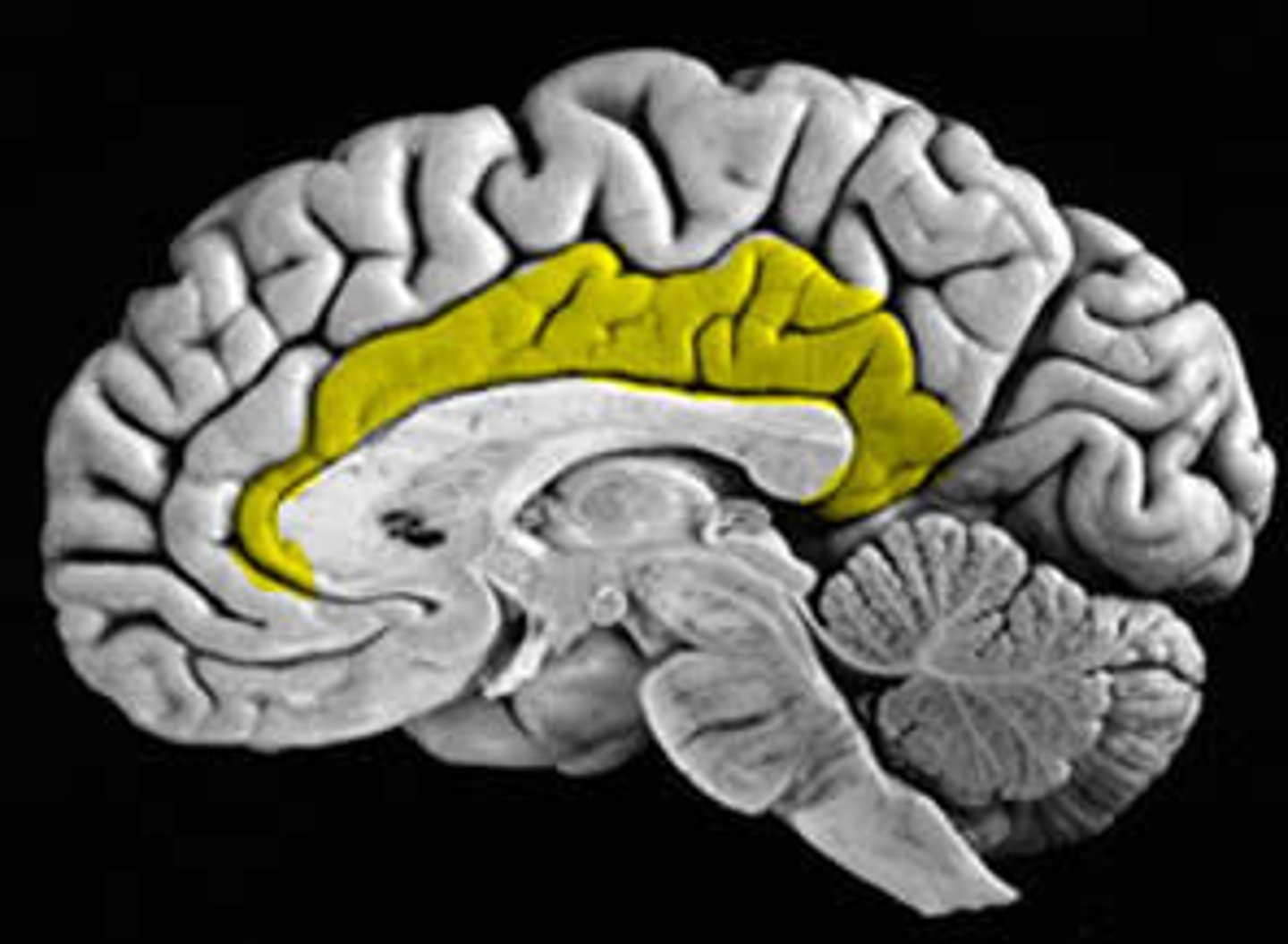
transverse fissure
third ventricle