containment - lecture 9 - Leishmania
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
facts leishmaniasis
neglected tropical disease
untensified disease management
difficult to diagnose treat and control
neglected means
neglected by local governments → very limited investments in control programmes
neglected by donors → no low hanging fruit for achieving disease control, hence little funcing
neglected by pharma → non profitable market so little investment in research
leishmanias
vector borned
protozoan parasite
different forms;
visceral leishmaniases (also called kala-azar)
cutaneuous leishmaniasis
mmucocutaneous leishmaniasis
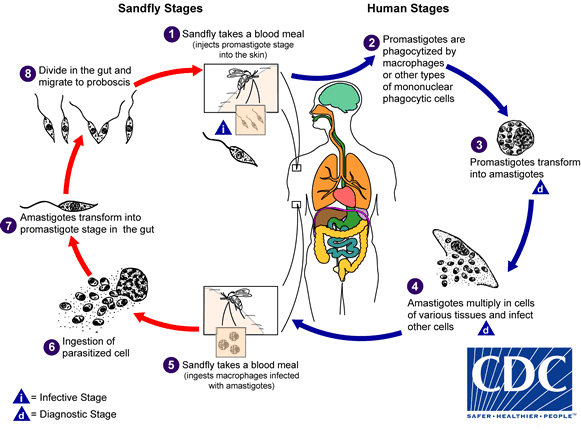
life cycle leishmaniasis
global burden and georaphical
south asia quite good at eliminating
east africa has no real decline
VL
parasite in both countries; leishmania donovani
vector; sandflies
transmission → antropnotic (human to human via bite sandfly).
systemic disease → of the visceral organs. the parasite multiplies in macrophages.
signs and symptoms → (not specific) fever, weight loss, cachexia, anorexia, spontaneous bleeding → difficult to diagnose
patients die of complications of disease→ immune suppression thus die from anaemia, malnutrition, opportunistic infections
VL IS FATAL IF NOT TREATED
in south asia and africa
succesfully treated in south asia
VL control strategies
early diagnosis and treatment
active case finding.
Access to free and effective diagnost
control of reservoir hosts
south Asia and East Africa: L. dononani -> anthroponotic transmission
Mediterranean and New World: L. infantum -> zoonotic transmission
vector control
Chemical control: spraying
Protection: bednets
Environmental control
epidemic response
vaccination
early diagnosis and treatment
active case detection
access to populations in endemic areas
simple, rapid and valid screening tools
easy acces to free
Health care infrastructure
Physical barriers/Transportation
Financial barriers
simple, rapid diagnostic test of high sensitivity and specificity
Treatment of high efficacy, safety and acceptability
VL in south sudan
very poor health infrastructure
sparsely populated → hard to do case finding
many floods
war/insecurity
population displacement
testing for leishmaniasis in east africa
same test as south sudan not working as well, because in asia the antibody levels are higher than in africa.
rK39 RDT
85-90% sensitivity → not enough because it is a fatal disease
PICTURE OF TESTS
they have other tests but can not be done in field need laboratory
direct agglutination test → very good test
if this test is not enough need to go to spleen, bone marrow or lymphnode aspirations
rapid diagnositc test
access in VL treatment in South Sudan went up when the rapid diagnostic test became available
did not need to go to the hospital to get tested.
mortality of patients went doen dramatically
treatment south asia
ambisome (liposomal amphotericin B)→ this is effective, safe, cheap and acceptible for patients
single intravenous dose
effective and safe
no or limited hospitalization
high cost of drug
cold chain requirement → not a problem in Soiuth Asia
treatment east africa
treatment with ambisome does nto work well → need multuiple doses
so they use SSG, + paramomycin
17 days intramuscular injections are needed from both drugs
effective but significant toxicity
high cost of long hospitilization
high dose L-Amb for vulnerable groups are needed
drugs not so expensive but long hospitalization is!
control of reservour hosts → meditteranean, middle east, central asia, latin america
L. infantum → zoonotic transmission, adress animal reservoirs
domestic animal reservoir hosts → dogs
tried to kill them but a lot of outrage stopped this.
wild reservoir hosts → canines, rodents
control of reservour hosts → east africa south asia
east african, south asia
l. donovani → anthroponotic transmission
VL patients
PKDL patient → lesions full of parasites
unknown zoonotic transmission cycle
only way to reduce human reservoir is early diagnosis and treatment
vector control
aim → reduced or interrupted transmisison
knowledge of local epidemiology is needed
vector habitats and behaviour
vector human interaction
vector control methods
insecticide spraying (IRS) → only works with endemic sandlflies
insecticide treated bednets
environmental management
domestic versus sylvatic sandflies in asia versus sudan
most commons is phlebotomus orientalis
habitat in south sudan
endemic
sylvatic
phlebotomus argentipes
habitat in south asia
not endemic
peri domestic
efectiveness bednets
94% distribution coverage
bednet utilisation during dry hot season (VL transmission season) was <10% this is bad because at the end of the dry season the sandflies are everywhere. but to hot and uncomfortable to sleep under bed nets.
increasing bed net use during rainy season (mosquitos)
calculated average prtective effect is 27%
effectiveness of ITNs depend on behavioral factors, which differ between communities.
bed net efectiveness in north versus south sudan
north sudan
live in fenced compounds→ little nuiscance of insects during hot season
people don’t use bed nets because they live in privacy, can sleep outside
south sudan
population move with their vee (semi-nomadic)
open compounds
a lot of insects
privacy main reason for using nets in hot season → impact bed nets bigger
northern ethiopia
walk day and night other measures necessary
impregnated plastic sleeping mats
impregnated socks / wrist bands
not sure yet if it is effective and if the people will accept it
epidemic response in south sudan
in south sudan huge epidemic
people left their villages because of active conflict, famine happened → more likely to get diseased
no access to treatment
100 000 people died without access to treatment (1/3rd of population)
WHO + MSF provided drugs + diagnostic in another conflict → 40 000 VL cases treated, mortality < 3%
THUS first priority is early diagnosis and treatment . ONLY after this a vector control could be considered.
vaccination
no vaccine now
first generation vaccine candidates
whole hilled parasites or extracts
efficacy inconclusive or negative
second generation vaccines
recombinant protreins and genetic vaccines
unlikely that a prophylactic vaccine will be available within the next 5-10 years for any form of leishmaniasis.
conclusion
south east asia;
VL disease lemination is tool-ready and feasible
VL elimination target (<1/10000 / year at sub district level
elimination in south asia envisioned by 2025
east africa
poor health infrastructure
inadequeate diagnostic and treatment tools
limited vector control objectives
the tools they had improved access to diagnosis and treatment resulted in decreased mortality.
global burden cutaneous leishmaniasis
very underreported (only 20-35%)
different forms of CL
cutaneous (CL) → single lesions
mucocutaneous (MCL)→ on mucosa
disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis (whole body covered with lesions) (DCL)
leishmaniasis recidivans (LR) → complication, occurs 1 year after treatment around original lesion, hard to treat.
zooonotic transmission - leihmania major
often in rural and suburban environment.
gerbils
typically rural and suburban environment
phlebotomus papatasi
phlebotomus salehi
anthroponotic transmission l. tropica
typically urban environment
sandfly eats infect human, then bites another human
leishmaniasis, conflict and political terror
correlation between levels of conflict and incidence of leishmaniasis
CL incidence 2.5 times higher.
Historical analysis indicated association through a process of population displacement and health system deterioration
factors affecting transmission
population movements
Non-immune people moving to endemic areas
Infected people moving to non-endemic areas where vector is present
socio economic factors
poor housing and poor sanitation
crowding (refugee camps)
environmental factors
poor housing in suburbs
With high density of rodents
Climate (rainfall, temperature, humidity)
clinical presentation CL lesions
Starts as a raised papule at the site of inoculation.
Grows over several weeks to a plaque.
A crust develops centrally, covering an ulcer with a raised edge and variable surrounding induration
treatment of CL
No reference rapid diagnostic test for CL
gold standard remains direct identification of amastigotes.
majority will self heal (2-15 months)
decision to treat base done
speeding up recover
reducing possibility of progresison to MCL
prevent scarring
treatment options GRAFIEK
topical treatment → few small lesions
systemic → multiple large lesions
Intramuscular injections
oral treatment (fluconazole)
self treatment
nail polish, battery acid etc.
not effective
very harmfull!!!
very ugly scarring
control of reservoir hosts
l. major → gerbirls
destroy animal burrows
l. tropica → human reservoir
early diagnosis and treatment
active case finding and access to free and effective diagnositc and treatment services
vector control
reduced or interrupted transmission
local epidemiology (vector habitats and behaviour, vector-human interaction)
vector control methods
chemical control → insecticide spraying
protection → impregnated bednets
environmental control
environmental management
long lasting insecticide treated bednets → need to be stored inside during the day
reduce vector breeding places (remove waste etc.)
vaccines
nothing being researched on CL
conclusions CL
CL is an emerging, uncontrolled and neglected infection affecting millions yearly.
current CL management is for a large part non evidence based
therefore, intensified research to improve vector control, diagnosistcs and the therapeutic arsenal is needed