worksheet 2 + quiz nervous and sensory systems
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
affector cells
send signals to the CNS, sensory neurons
effector cells
effected by signals from CNS, motor neurons
interneurons
mediator between affector and effector
state one difference between the autonomic and somatic divisions of the PNS
autonomic is involuntary and splits further into empathetic and parasympathetic
somatic is voluntary actions, sensory and motor fibers
why are neurons found in white matter said to have fast rates of transmissions than those in grey matter?
white matter neurons have myelin sheaths, aka layers of Schwann (neuroglia) cells hat increase rates of transmission
what is the role of a neurotransmitter in the nervous system?
a signal to send information and transfer impulses
why is damage to the central nervous system a major concern and how does this differ from other tissues?
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, both of which tissues cannot regenerate as efficiently as other tissues. Damage to the CNS can result in irreversible damage
A sensation occurs via the following steps: transduction, conduction, translation and perception. What happens in each one of these steps?
transduction: sensory receptor converts stimulus into a nerve impulse
conduction: sensory receptor forwards impulse to CNS
translation: DNA translates impulse to sensation (Kind depends on ones genes)
perception: conscious awareness of stimulus
what is the difference between a general (somatic) and special sense?
special senses have associated special organs while general senses do not
general senses (5)
touch, pain, temperature, pressure, position
special senses (5)
smell, taste, hearing, vision, equilibrium
most sensory receptors are sensitive to a sudden change in a stimulus but soon adapt. Pain receptors are an exception they do not readily adapt. Why do you think this is?
Adapting to pain generally puts us in danger
based on what we know about super tasters, why might being one be harmful to your health?
super tasters are highly likely to become picky easters due to their heightened senses. This can lead to dietary changes such as adding extreme amounts of sugar to a coffee due to it being “too bitter”
describe the olfactory pathway once molecules enter the nasal cavity
chemoreceptors located inside the nasal cavity interact with the molecules and if a threshold is crossed the action potential is sent to the olfactory nerve
why do sensations like gustation (Taste) and olfaction (smell) change with age?
as we age, destruction of cells occur alongside decreased regeneration rates
list the pathway of the ear in which they are encountered by soundwaves (outer to inner most) start with the pinna (Earlobe)
pinna, auditory canal, tympanic membrane, auditory ossicles (Earbones), cochlea, auditory nerve
what type of receptor is found in the retina?
photoreceptors
what receptor is responsible for sense of head postion relative to gravity and hearing?
mechanoreceptors
what are the two types of photoreceptors?
rods: allow us to see in dim lighting, greyscale
cones: allow us to see in color
carnivores have front mounted eyes What is one advantage and one disadvantage
increased depth perception, decreased field of view
arrange the following parts of the eye (aqueous humor, cornea, lens, pupil, retina, vitreous humor) in which they are enchanted by photons of light traveling into the eye)
cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina
why do you think our night vision is mostly percieved in shades of grey rather than color
while our rods work in dim light, our cones depend on (Bright) lighting for color perception
What causes the blind spot in our eye?
a gap in the retina where the optic nerve enters through
what is the place where photoreceptors are most concentrated known as
fovea
In stimulus detection, sensory receptor cells convert a stimulus into a(n)
electric signal
You exercised to the point that you were breathing heavily. Your heavy breathing was the result of ________ relaying information about the amount of O2 in your blood to the medulla, which ultimately resulted in your increased rate of breathing.
chemoreceptors
Which option incorrectly pairs a class of sensory receptor with one of the stimuli it detects?
electromagnetic receptors light
chemoreceptors molecular structure
mechanoreceptors sounds
thermoreceptors touch
thermoreceptors, touch
explanation: thermoreceptors are paired with detecting temperature changes
Olfactory receptor cells are located in the
nasal cavity
One of the evolutionary advantages of having two eyes is that
overlapping fields of view provide uninterrupted images.
The functional unit of the nervous system is the
neuron
The two major anatomical divisions of the nervous system are the
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
You are sitting with a friend in the park next to some children who are playing Frisbee. You turn to talk to your friend and out of the corner of your eye you see a Frisbee quickly approaching your face. As an innate, protective behavior, you blink your eyes. The protective action of blinking is an example of a(n)
reflex
During transmission across a typical chemical synapse
a. the neurotransmitter molecules are stored in cleft
b. action potentials trigger chemical changes that make synaptic vesicles fuse
c. vesicles container neurotransmitters diffuse to the recieving cells plasma membrane
d. neurotransmitter molecules binds to the captors in the recieving cells plasma membrane
d. neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the receiving cell's plasma membrane.
The uniformity in the way nerve cells function within the animal kingdom is evidence that
the neuron was an early evolutionary adaptation.
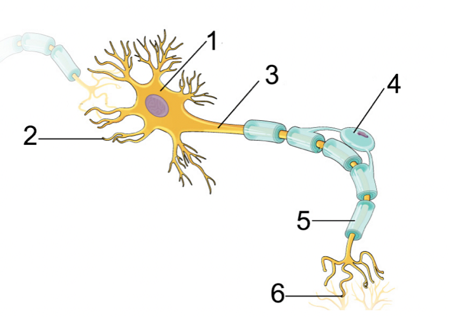
what structures do the numbered labels represent? IGNORE 4
cell body
dendrites
axon
myelin sheath
axon terminals/synpase
what would a schematic look like for a person going through alcohol withdrawal and why?
The schematic would be leaning more towards excitatory side because the body would be overcompensating for the (now missing) inhibitory neurotransmitters
what symptoms would a person going through alcohol withdrawal after long-term alcohol exposure experience based on the balance of neurotransmitters
anxiety, excitatory state