MOLECULES to cells
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what is the central dogma
DNA→RNA→Protein
what are the three things DNA must do
replicated faithfully
have the coding capacity to generate proteins for cellular functions
transmit from parent cell to daughter cell
orchestrate any organismal functions
where are genes located
on chromosomes in the nucleas
what is DNA made of
nucleaotides, phosphate+sugar+base
what are the purine versus pyrimidine bases
A and G=purine
C and T=pyrimidine
how are phosphodiester bonds formed
5’ phosphate to 3’ hydroxyl
how was DNA structure determined
x-ray crystallography→DNA precipated from a solution by adding ethanol providing the fibres for crystallography
what is Chargaffs rule
A=T and C=G
how are bases paired in DNA replication
hydrogen bonding; C and G have 3 compared to and A and T with 2
job of helicase
to unwind and open up DNA
job of topoisomerase
deals with overwinding with nucleases to snip DNA while ligase reconnects
what is the main enzyme in DNA replication
DNA polymerase III
what is required for DNA polymerase initiation
RNA primers→created by primase
what can DNA pol I do
removes RNA primers
what directino does DNA synthesis occur
5’ to 3’ direction
how is the lagging strand created
Okazaki fragments→multple primers involved so DNA synthesis can still move from 5’ to 3’ direction
what are the enzymatic activities of DNAP I
5’ to 3’ dna polymerasation
3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity; backwards correcting base errors
5’ to 3’ exonucleasing removing RNA primers
whatis Rifamipicin
RNA polymerase inhibitor
what is the Nick translation
DNA polymerase I taking over from DNA polymerase III and removes the RNA primer replacing it with new DNA and then ligase seals the nicks between the DNA
what is the Haflick limit
telomere shortening→indicator of aging that cells can only divide a certain number of times
what is the role of transfer RNA
translocation protein synthesis
what is meant by +1 in transcription
intiaition site
what is upstream versus downstream
upstream=-5
downstream=+5
what is the purpose of sigma subunits
in prokaryotes they are required for specific promoter recognition
does RNAP bind specifically or nonspecifcally
nonspecifcally→binds then scans looking for promoter sequence
simple versus complex termination of transcription
simple means without a protein factor and a hairpin structure forms near mRNA end causing RNAP dissociation
complex is rho depednent so a helicase protein called rho is required to terminate transcription
how is RNAP acitivate
through phosphorylation of C-terminal tail domain
how is mature mRNA produced
splicesomes remove introns
5’ cap and 3’polya tail are added
mature mRNA is transported from nucleas to cytoplasm via nuclear pores
what are the two components of a gene
1=coding sequence; what gets transcribed
2=DNA regulatory elements such as the promoter
are gene products always proteins
no they can function as RNA
what are the cell types that cannot still express all nessecary genes to build a new organims(Wilmut sheep)
cells that have lost there nucleai(erythrocytes)
senescent cells that lost telomeres such as skill cells and neurons
what are housekeeping genes
genes expressed in every cell type
job of small nuclear RNAS
splice mRNA to remove introns
what are mendelles principles
principle of dominance→allele can be cominant or recessive with dominant always being expressed when hetereozygous
principle of segregation→allelles of genes seperated during gametogensis
law of independant assortment→genes encoding different traits segregate indepednetly of one another
Huntingtons disease
autosomal dominant
what cells are assoicated with cancer and expressed in breast cells
BRCA
epidermolysis bullosa
mutation in keratin gene that is austosomal dominnant and causes blistering
describe DNA replication
always occurs 5’→3’
the origin of replication is thymine and adenine rich since they only have two hydrogen bonds
pre initiation complex binds to DNA and opens up creating replication bubble
helicase unwinds DNA and SS binding proteins prevents reannealing and protects nucleotides from nucleases which want to break phosphodiester bonds
as it super coils topoisomerase uses nuclease to snap and then ligase to repair dna to un super coil
then the elongation stage involes primase which is an enzyme that attaches RNA primers allowing DNAP III to create DNA
the lagging strand gets multiple primers
DNAP I removes the RNA primers
polio
FLU
Polio=+ssRNA acts as mRNA so it immedicatly translated in cytoplasm using host ribosomes
FLU=-ssRNA so it gets transcribed in the nucleas by virion polymeriases and then translated
VSV chicken pox=dsDNA so it gets transcribed in the nuclease by host RNAP II
how do virusues move inside of cells
through microtubules and dyneines moving towards the nuclease
what info is versus is not contained in viral genomes
IS: virus genome replication, assembly and packing of genome, reuglating virus replication, modulation host defences, and spreading to other cells
NOT: genes for complete protein synthesis and those nessecary for energy production or membrane synthesis
inputs of photosynthesis
water, CO2, sunlight
relationship between stromata and thylakoids
stromata allow carbon dioxide in and out of cells and the thylakoids house chlorophyll which is a pigment in plants absorbing the suns photons
describe photosystem II→the first stage in light reactions
occurs in the thylakoid membrane that houses chloroplast
chlorophyll in PSII and electrons becomes excited
electrons flow into thylakoid membrane and it becomes negativly charged→beginning electron transport chain
as the electrons move thorugh thylakoid emebrane they operate on proton pumps which pulls hydrogen ions into the membrane
in this process water molecules are broken down to supply the electrons from hydrogen and oxygen is realased
PSI chlorophyll gets excited and move through the thylakoid membrane to ATP synthase
in this process NADPH is created through electrons bonding H+ and NADP
large amount of hydrogens in the thylakoid want to diffuse through ATP synthase and bond ADP to another phosphate creating ATP
ATP and NADPH are important creations
what light stimulates most photosynthesis
red and blue
definition of photosynthesis
process that converts sunlight into glucose
calvin cycle light independent reactions of photosynthesis
RuBP bonds with CO2
ATP and NADH break down the six carbon molecule into phosphoglycerate→ 2 PGA
some of these will bond to create glucose and some will be broken down further to keep cycle going and create RuBP
formula of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
what inhibits beta oxidation (fatty acid breakdown)
malonyl CoA which is formed during synthesis of fatty acids
difference between CAT 1 and CAT 2
carnitine acyl transferase-1 functions in the mitochondrial membrane adding an acyl carntine and taking a CoA
carnitine acyl transferase-1 functions in the mitochondria in adding a carntine to leave with fatty acid CoA
catalyst
substance speeding up a chemical reaction but is not consumed in the reaction
what are required for enzyme activity
cofactors→vitamins and metals
process of converting pyruvate into acetyl CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase
B1= removes Co2
B3=NAD+
B5=CoA
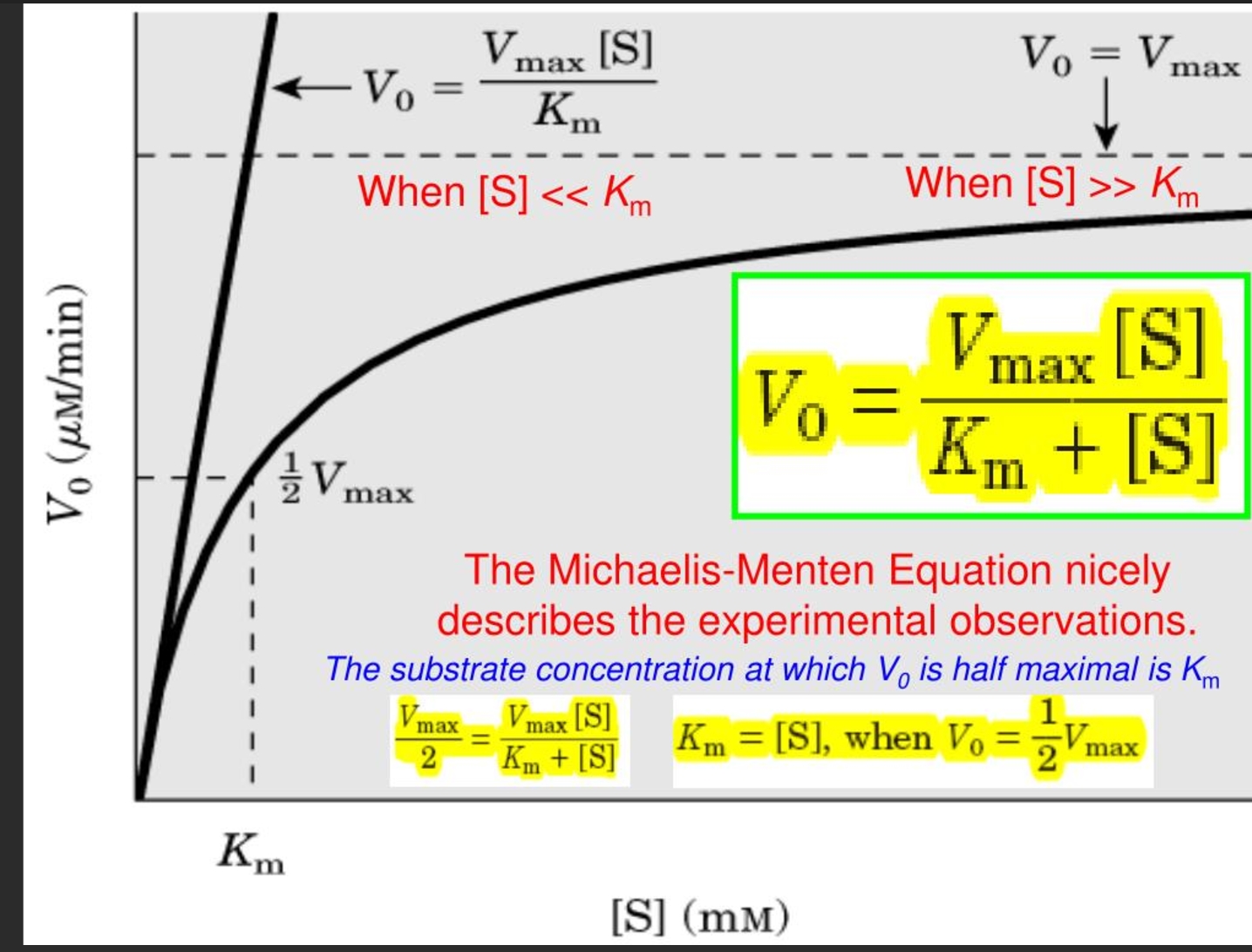
what is the michaelis menten equation
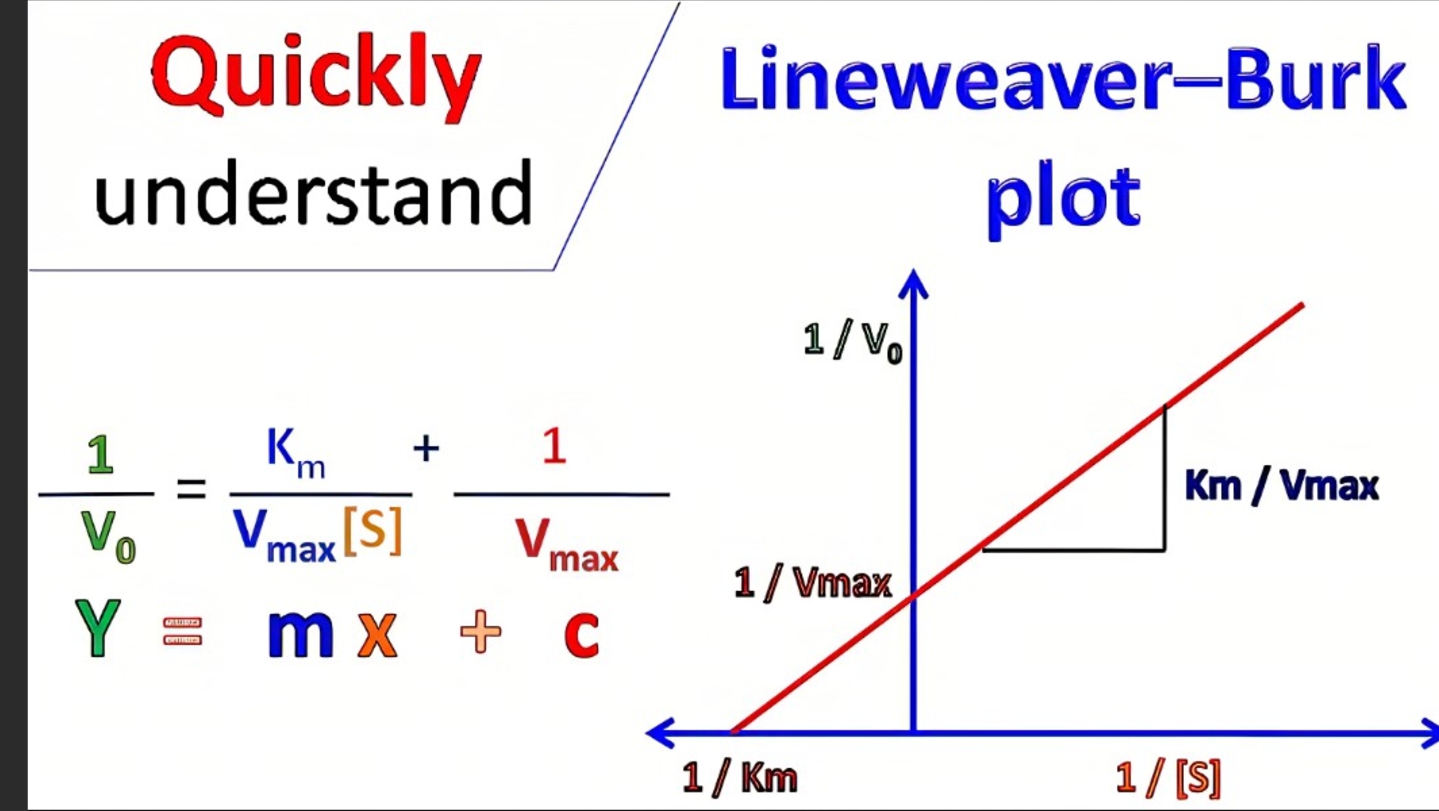
what is the line weaver burk plot equatin
differences in beta oxidation and fatty acid synthesis
fatty acid breakdown: two carbons sequentially removed, oxidizing agents are FAD+and NAD+,occurs in mitochondira
fatty acid synthesis: carbon units are added via molonyl-ACP, reducing agent is NADPH, and it occurs in the cytoplasm
what connects carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and how
mitochondrial citrate carrier→citrate carried out of TCA if ATP is high for fatty acid synthesis which breaks down to acetyl CoA
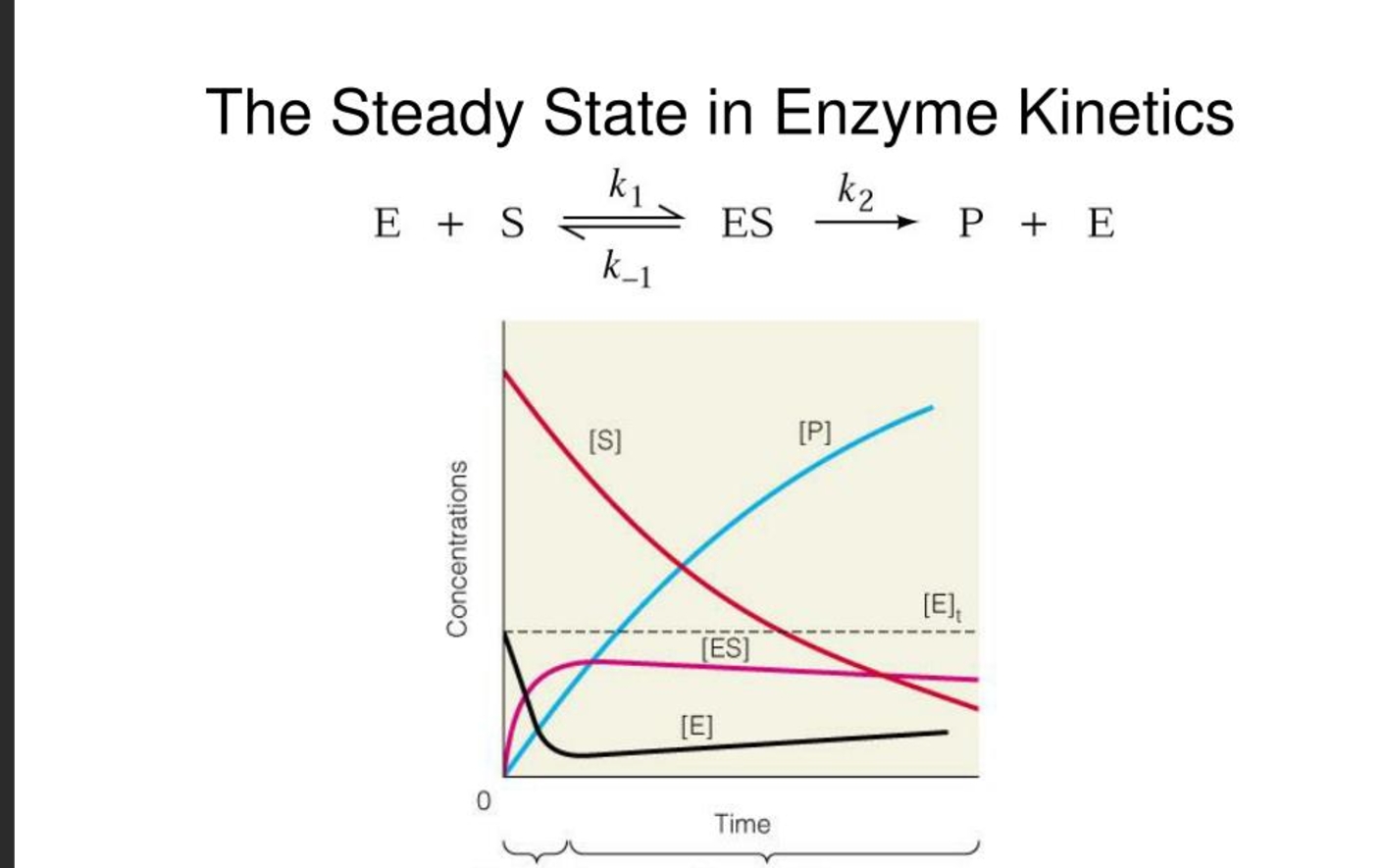
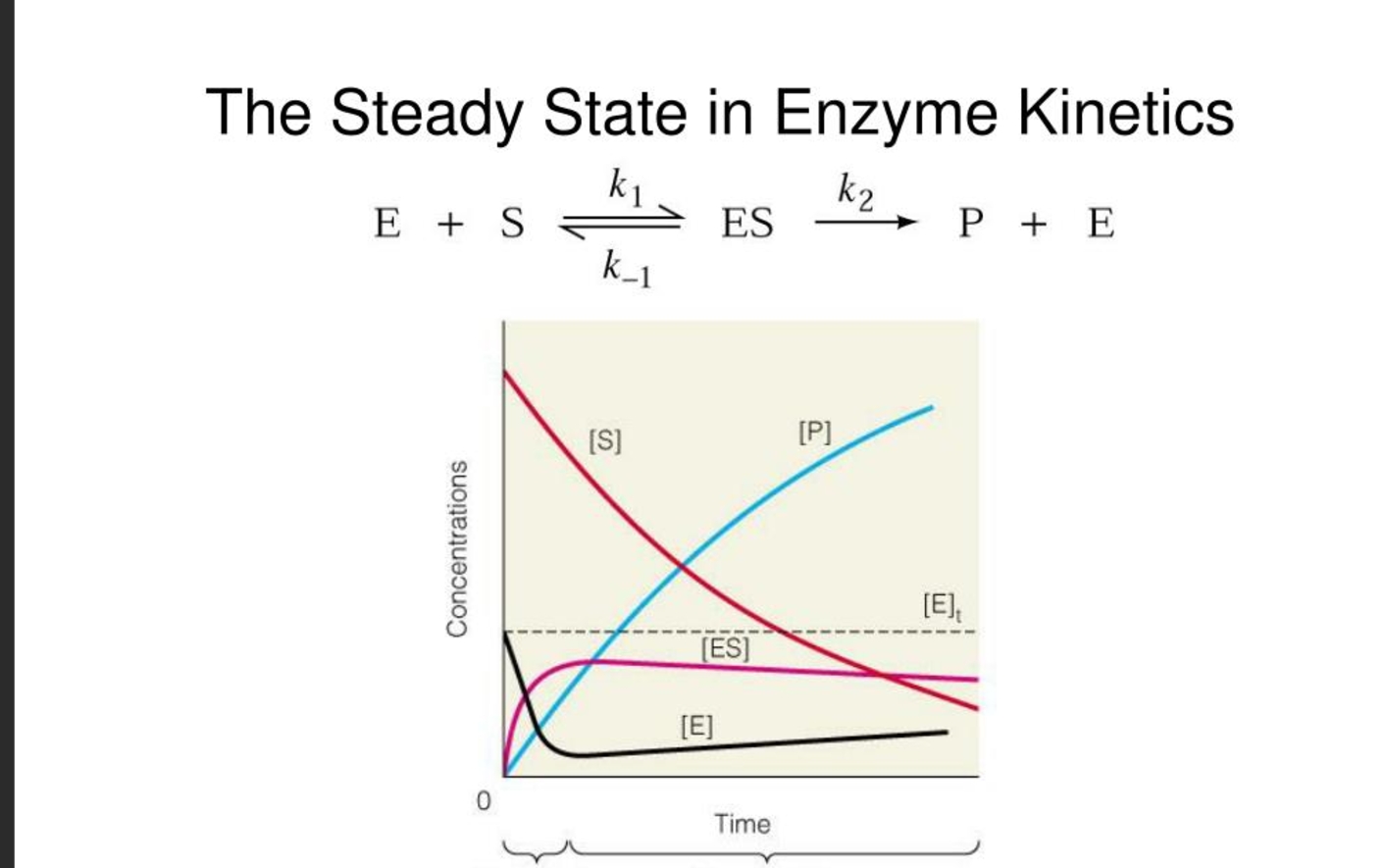
what is the steady state assumption in enzyme kinteics
what happens in competitive inhibition versus uncompetitive inhibiton
competitive→increase in kM because more substrate is needed byt Vmax unaffacted
uncompetitive→decrease in KM and decrease in Vmax
what is the purpose of signal sequences on proteins
used to sort where protein goes
three types of transport
via nuclear pores→requires a nuclear locator sequences
transport across membranes→proteins get folded and unfolded and transported via portein translocaters
transport through vesicles where the membrane fusion allows entry
what binds to protein when entering nucleas
nuclear transport receptor(NTR) which directs the protein to the nucleus and through RAN GTP is causes release itno the nucleus where ran GTP is hydrolyzed into RAN GDP
describe transport across membranes
transporter outer membrane complex(TOM) recoginzes protein destination and mitochondira via signal sequence→bound receptor complex then diffuses along the membrane to a contact site on the inner membrane(TIM) This then translocates across the outer and inner membranes throough chaperone proteins assisiting in translocation and refolding of proteins inside the organlle
purpose of the rough ER
it is the entry point for proteins destine for golgi, endosomes, lysosome, cell surface, ER itself;
once inside ER proteins will not re enter the cytosol and are transported by vesicle to other organelles
signal receptor particle and its receptor bind to the ER signal sequence in new protein as it emerges from the cytolsic ribsome and connect the ribsome to the ER for translational translocation
describe vesicle transport
vesicles bud from one membrane and fuse to another transporting protein and membrane compenents to various cell compartments and extracellulary
protein coat shapes the membrane into a bud and captures molecules for transport
composed of Clathrins or coat protein complex proteins
Clathrins
protein coat shapes the membrane into a bud and captures molecules for transport
describe microfilaments(actin)
smallest and most flexible and are 7 nm helical
g-actin is the monomer and F-actin is the polymer with two polymers forming double helix
whats actin purpose
involved in cell migration and the cytokinesis portion in seperating 2 cells during divison
types of actin
alpha is in muslce cells and beta and gamma or in non-muscle
structure of actin
barbed end is positive and pointed end has polarity
they assemble to the plus end more readily than the - end
thymyosin
actin monomer binding protein→about fifty percent is in filament form and the rest is bound to allow for rapid actin polymerization
what does actin polymerisation do and give an example
pushes out sudopods false feet for movement for example with human fibroblasts moving forward through malipodia and lamilpoding which attach to cell surface and the rest move backawards causing ruffling
stages of actin polyemerization
there is nucleation, alongation, and steady with nucealtion being the rate limiting phase requiring the binding of three actin monomers for intniation
what is critical concentration
number of free actin monomers to polymerize and is influences through actin binding proteins such as thyomyosin
describe treadmilling with acitin
with monomer concetration beyween the 2 critical concentrations of the barbed and pointed end
monomers added to the plus end at the same rate they are lost from the minus end
ATP actin added and ADP actin lost is equal
regulated by prolifin andcollifin
nucealting proteins in actin
ARP nucleaor complex is attached to the sides of preexisiting actin filaments
spire=binds four actin monomoers to act as nucleating seed for new filaments
formins serve to help with progressive elongation assocated with the barbed end to generate longer filaments
myosin
actin filaments moto protein which hydrolizes ATP into ADP and pi
when stimulated and uses hdyrolysis to move along the filament
shorters in actin bringing them closer together during muscle contraction
describe muslce
huge multinucleated cellls with majoirty of cytoplasm consisting of myofibrils which are the contractile units of muscle fibres and are made up of sacromeres which are the contractile unit of muscle
how are actin and myosin arranged
geomtrically with the sliding theory of muscle
whats an actin mutation
actin myopahty→ACTA1 gene mutations→mild to sever generalized muscle weakness and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopahty is cardiac mysoin mutations
describe microtubules
the longest filaments and are 25 nm and rigid
made of tubulin and the alpha is the negative end and the beta is the + end
13 stack around each other to form long hollow cylinders
microtubules nucleation occurs via gamma tubulin rig complex at the end of the microtubules organizing center with the + end growing
MTOC is at the centrosome and microtubules extend out from here
dynamic instability with micro tubules
rapid growth with GTP capped end followed by catastrophe phase due to accidental loss of GTP cap end with rapid shrinkage
gtp hydrolysis controls growth of microtubules
kinesins and dyinen’s
kinesisn function towards the plus and aid in forming mitotic spindle during mitosis whereas dyneisns are associated with flagella and cilia
describe intermediate filaments
rope like structures made up of 70 different protein types about 10 nm in diameter→provide rope like structure to combat mechanical stress→nuclear lamens
monomer→dimer→tetramere→protofilament
describe desmosomes
connect two cells and are a king of intermediate filament