Social Psychology Study Guide
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is Social Psychology? What do they study
Scientific Study of how people think about/influence/relate with one another.
Focuses more on individuals.
What is correlational research? know correlation coefficient, what the number and sign indicate, positive and negative correlations
Correlational Research- Studies when ONE trait or behavior accompanies ANOTHER----> we can say the TWO correlate.
EX: Child and video games… aggression
Correlation Coefficient ‘r”- The statistical measure of the relationship between 2 variables.
Can be from 0-1
pos. Or neg.
On the graph: Closer to 1= more linear , and closer to 0= farther/scattered.
Closer to 1= strong relationship, closer to 0= Weak relationship
Understand how internal dispositions (characteristics) and external social forces (situations) influence our behavior (and be able to identify each if given a scenario)
How we behave in society is influenced by these influences when we are on the topic of how willing we are to help people, voting, and peer pressure.
Our attitudes also follow our behavior due to how we often believe strongly in what we commit within ourselves.
What is hindsight bias? Be able to choose an example if given one
Tendency to exaggerate one's ability to have foresaw how something turned out, only after learning the outcome.
“KNOW-IT-ALL”
EX: Friend breaks up with ex... “Knew it all along”----> (Had all the red flags and had hindsight bias due to overlooking and knew what “best”)
What is Objective reality?
We use our own perspectives and biases that influence our perception/reality.
… when something is actually what it is such as… the world and life is LITERALLY just that, it ISN'T what we perceive it as/ our own reality.
What is a hypothesis and what is its purpose?
Theories are formed from testable predictions to see if it is true.
how can survey results be influenced?
Through bias.
Bias limitations= desirability
---> Avoiding answers that might make them look bad and result in them lying---> not reliable results due to lying.
Know the following terms: demand characteristics, independent variable, dependent variable, random assignment
Demand Characteristics: The cues in an experiment that tell the participant what behavior is expected.
Ind. Variable: Factor that’s manipulated by the experimenter to see if it affects what's being studied.
Dep. Variable: A factor that might change due to the ind. Variable.
Random assignment:
Spotlight Effec
definition of spotlight effect and example of it
t
The belief that others are paying more attention to one’s appearance/behavior than they really are.
Ex: Seeing ourselves at centerstage…. Bad hair day---> Everyone is looking at it and making fun of it BUT in reality no one/barely anyone is actually paying attention to it.
Illusion of Transparency
The illusion that our concealed emotions leak out and can be easily read by others.
Self-Concept
what we know and believe about ourselves.
Most important aspect of ourselves!
Self-Schemas
Mental Templates by which we organize our worlds.
Ex: role as mother/student/friend/co-worker
Impact Bias
the tendency of people to overestimate the enduring impact of emotional-causing eventsTendency to neglect the speed/strength of their COPING MECHANISMS.
Ex: Getting over your ex after a breakup
Independent Self
Constructing identity as autosomes as a unique individual with particular attributes/ traits/values
Ex: separating from parents and being self-reliant, and defining one’s personal independent self
Interdependent Self
The extent where people describe the self as being fundamentally connected to other people
Interdep. Self vs Ind. Self
The Independent self is defined as thinking of yourself without concerning others VS. Interdependent self is when you define yourself by concerning others.
Individualistic Cultures
Associated with believing your power of personal control/ being your own person/ have own identity
Collectivistic Culture
Associated with identifying with a group vs as an individual.
Usually more self-critical and focuses less on positive self-views.
BUT… More cultures are leaning toward individualism!!!
Ex: Unique names
Self Esteem
A person’s evaluation of sense of self and self-worth
Can be measured through longitudinal studies over time.
Can be treated when comparing self to others.
Ex: Friend gets a promotion and is “doing better in life than you”
High Self-Esteem
Associated with feeling good about one's self.
When threatened: Tend to blame others vs. own self and help preserve positive feelings about self.
Extreme High Self-Esteem
Associated usually with narcissism.
low self esteem
Associated with when things are going bad.
More vulnerable to anxiety, depression, drug use, and eating disorders.
Has more negative views in everything/ remembered negative and bad behaviors of others.
research shows that individuals with extremely high self-esteem and narcissism are more _____ than other people.
Answer= Problematic due to inflated sense of self.
How culture impacts self-esteem
debating on which culture you are in---> can influence one with a high/ low sense of self due to beliefs and values.
what is self-efficacy? what makes individuals with strong feelings of self-efficacy different than those with low?
Self-efficacy= How competent we feel on a task… “when you BELIEVE you can do something”
Grows when tasks are completed successfully/ lowers when unsuccessfully. Compare/contrast individuals with high/low self-efficacy
Strong feelings of self-efficacy: More persistent, less anxious, less depressed, healthier life, and more academically successful.
Low feelings of self-efficacy: Less persistent, afraid to try again due to failure.
Know the difference between system 1 and system 2 brain systems/thought processes
System 1 brain system/thought process: AUTOMATIC PROCESSING
Intuitive, unconscious thinking/intuition, quicker way of thinking.
System 2 brain system/thought process: CONTROLLED PROCESSING Deliberate, controlled, conscious, slower way of thinking.
Influences more of our actions than we realize!
Belief Perseverance
Persistence of one’s initial conceptions
Once accepted surprisingly difficult to demolish a falsehood!!!
Harder to challenge our belief when we start to examine if false.
Priming
Activating particular associations in memory
Can influence another thought/action, much of our social info processing is automatic due to not knowing how influences can subtly change our memory of events, and recall info.
Ex: Parent making sushi for daughter and boyfriend… daughter remembers boyfriend is allergic to sushi.
Overconfidence Phenomenon
Being too sure of ourselves, even when we shouldn’t be.
Ex. A student may believe they will ace an exam without studying, leading to poor performance due to overconfidence.
Representative Heuristic
Tendency to presume something despite contrary odds that someone/thing belongs to a particular group if representing a typical member.
Availability Heuristic
Cognitive rule that judges the likelihood of things of their availability in memory.
If instances of something come readily to mind… we presume it to be commonplace.
Attribution Theory
Attributing to the person's disposition and traits
Ex: Chiara dislikes playing with her classmates because she is an introvert.
Dispositional Attribution
When we explain someones’s behavior based on who they are on the inside.
Ex. Someone is always cheerful, you might say its because they have a naturally happy personality.
Situational Attributions
Attributing to the environment
Ex: Your boss is always cranky and assumes it's because he hasn't been given a raise for the last 10 years.
How do social psychologists measure people's attitudes?
A: mixture of both implicit and explicit (self-report) measures.
Self-report measures, (IAT)---> Implicit association test
Computer-driven assessment that uses reaction time to measure how quickly people associate concepts.
What are Attitudes?
Feelings are often influenced by the beliefs that predispose us to respond favorably or unfavorably to objects/people/events.
Main takeaways of Zimbardo’s Prison Experiment
Takeaway: This was used to see how when given a role (guard/prisoner) it can affect your attitude in ways that show people to be sadistic or not.
Stanford prison experiment.
Self-Presentation
Assumes that for strategic reasons we express attitudes that make us appear consistent
May not automatically pretend we hold attitudes consistent with our behaviors.
Cognitive Dissonance
Tension that arises when one is simultaneously aware of two inconsistent cognitions
Over-justification Effect
Result of bribing people to do what they already like doing
May see actions as externally controlled vs. intriguingly appealing.
Facial Feedback Effect
Tendency of facial expressions to trigger corresponding feelings such as fear/anger/happiness.
Potent Attitudes
can predict behavior if it is potent.
Becomes potent when we think about them.
Can predict behavior when attitude is stable… when forged with experience potent attitudes are more enduring and more likely to guide actions.
Norms
standards for accepted and expected behavior
Culture
enduring endeavors behaviors/ideas/attitudes/and traditions shared by a large group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next.
Personal Space
the buffer zone we like to maintain around our bodies.
personal space and boundaries
Evolutionary Psychologist
study of the evolution of cognition and behavior using principles of natural selection
know what natural selection says about survival and reproduction
The evolutionary process by which heritable traits that best enable organisms to survive and reproduce in particular environments are passed to ensuing generations.
What are the gender differences when choosing leaders - which gender do we prefer in different situations?
We prefer men when looking at being socially dominant and holding the leadership position
Studies show that we perceive leaders as more of a cultural masc. Trait.
Associated with manhood
men are dominant vs women are nuturing
Know how men and women differ with respect to aggressiveness
Men exhibit more physical aggression vs. women being overall more verbally aggressive in less assaultive forms.
Know what women and men prefer in mating - how they differ and how they are similar
Differences: Men are more likely to initiate sexual activity, sexual fantasies differ from both sexes typically understood had something females have that men want
Similarities: They both desire kindness, love, and mutual attraction (love and kindness)
Know and understand Leung and Bond's five universal dimensions on social beliefs
1. Cynicism: “Powerful people tend to exploit others.”
2. Social Complexity: “One has to deal with matters according to the specific circumstances.”
3. Reward for application: “One will succeed if he/she really tries.”
4. Spirituality: “Religious faith contributes to good mental health.”
5. Fate control: “Fate determines one’s success and failures.”
Know how biology and culture both influence gender roles
Culture influence: helps us construct our gender roles, usually reinforces gender roles that may have originated with biological demands: hunter/gatherer mentality---> men have more strength which led to patriarchy= most common system and associated with social power, Women gathered because they needed to be close to home/men hunting
Conformity
A change in behavior/belief as the result of real or imagined group pressure.
Compliance
Involving publicly acting in accord with an implied or explicit request while privately disagreeing
Obedience
Involves acting in accord with a direct order or command.
Acceptance
Involving both acting and believing in accordance with social pressure.
Mass Hysteria
Suggestibility to problems that spread throughout a large group of people.
Mass hysteria:
Suggestibility to problems that spread throughout a large group of people.
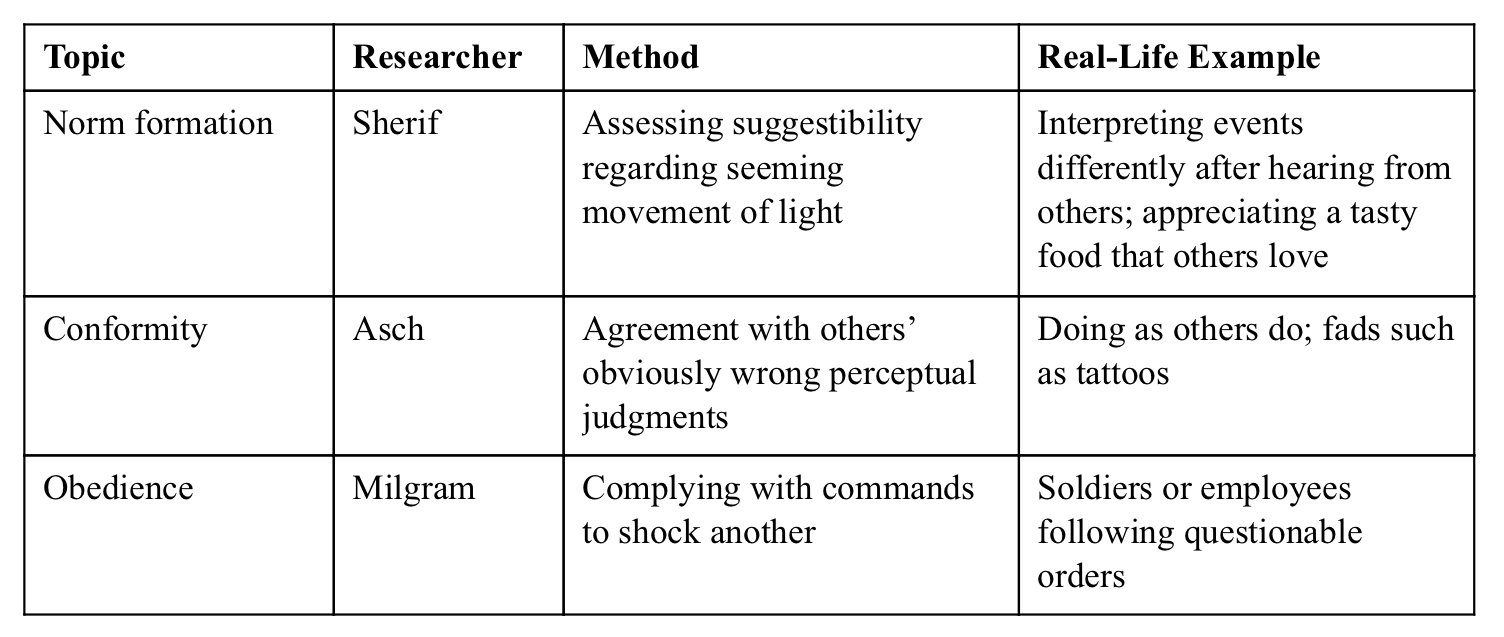
Norm Formation
How to figure out how people come to agree on something
The Chameleon Effect
unconscious tendency to mimic behaviors
Solomon Asch (line comparison)
A study that was ran to see how participants would react and conform to the answer that was said even if it was incorrect.
Shown that 75%/majority would conform at least once, the total (37% conformed, 63% did not conform) and that through over the decades, other experiments prove that fewer students were willing to conform.
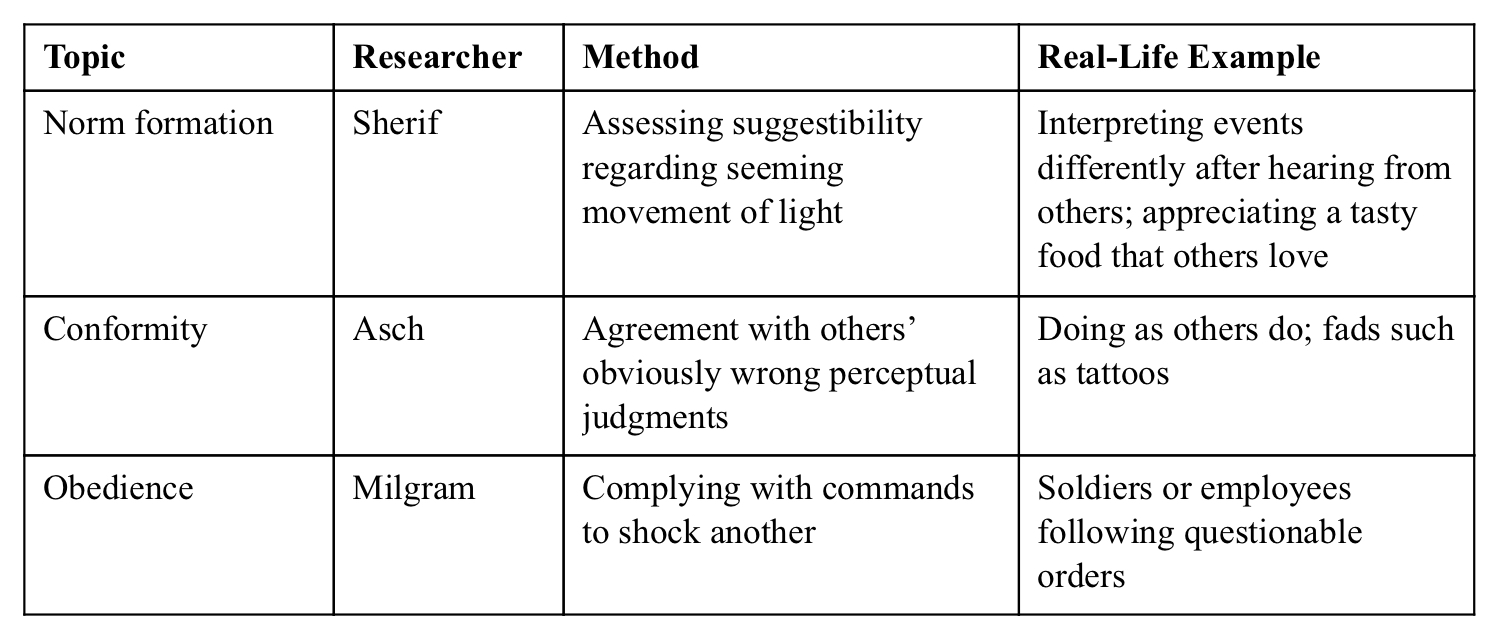
Stanley Milgram (shock)
ested to see what happens when demands of authority clash with the demands of conscience.
Results showed that there are 4 factors that determine obedience:
1. Victims emotional distance or the level of depersonalization
2. Closeness and legitimacy of the authority
3. Institutional authority
4. Liberating effects of group influence
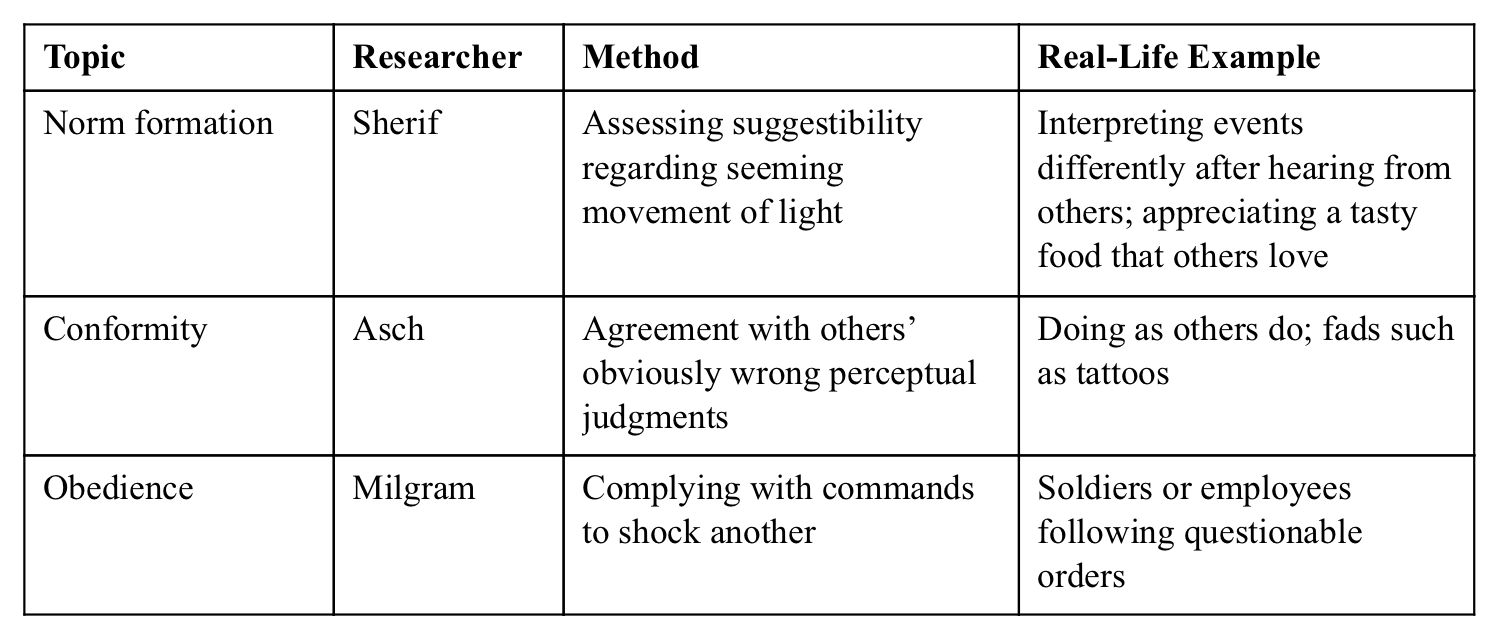
Muzafer Sherif (auto-kinetic) studies
a study that was ran to test norm formation to figure out how people come to agree to something
Had participants be exposed to light that did not change position but would ask participants to determine how much the light moved.
Results concluded that responses changed a lot
Autokinetic phenomenon: Self (AUTO) motion (KINETIC)
An apparent movement of a stationary point of light in the dark.