Organic 7
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
What is a chemoselective reaction?
one in which 1 fg reacts in preference to another
2
New cards
What is the regioselective reaction?
one that leads to selective formation of one structural isomer (regioisomer)
3
New cards
what is a stereoselective reaction
one in which one enantiomer, one diastereomer, or one double bond isomer is formed selectively over others.
4
New cards
what is a protecting group
converts a reactive fg into an unreactive form such that after desired transformation(s) the original fg can be regenerated
5
New cards
what is a common protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones?
acetals
6
New cards
what are common protecting groups for alcohols
Silyl ethers
7
New cards
what are common protecting groups for amines
Carbamates
8
New cards
what are common protecting groups for carboxylic acids
esters
9
New cards
what is the target molecule
the molecule to be synthesised
10
New cards
what is a retro synthetic arrow
an open-ended arrow used to indicate reverse of a synthetic reaction
11
New cards
what is fg interconversion
converting one fg into another by substitution, addition, elimination, reduction or oxidation
12
New cards
What are synthons?
idealised fragments resulting from a disconnection
13
New cards
what do you draw if a double bond/2 single bonds are broken
precursors
14
New cards
key disconnections?
1) disconnect rings from chains
2) disconnect at a branch point
3) disconnect to form 2 equal sized pieces
2) disconnect at a branch point
3) disconnect to form 2 equal sized pieces
15
New cards
conditions for aromatic bromination
Br2/FeBr3
16
New cards
conditions for aromatic nitration
HNO3/H2SO4
17
New cards
conditions for adding SO3H to benzene
H2SO4/SO3
18
New cards
conditions for aromatic friedyl-crafts acylation
RCOCl/AlCl3
19
New cards
how do you form aryl grignargs (ArMgX)
react aryl halides (ArX, X=Cl,Br,I) w Mg in dry diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran
20
New cards
why are aryl grignards useful
strong nucleophiles (much stronger than benzene) and react w range of electrophiles to form C-C bonds
21
New cards
what are stabilised ylides
ones where the substituent stabilises the adjacent neg. charge
22
New cards
what are unstabilised ylides
ones where the substituent cannot stabilise the adjacent neg charge
23
New cards
how do you prepare stabilised ylides
deprotonation of a phosphonium salt, Ph3P+EWG (EWG= elec withdrawing group) using a relatively weak base
24
New cards
what do stabilised ylides react with
aldehydes but generally unreactive w ketones
25
New cards
what alkenes do stabilised ylides form
they react w aldehydes to give mainly E alkenes
26
New cards
how are non-stabilised ylides prepared
deprotonation of a phosphonium salt, Ph3P+CH2EDG (EDG=elec donating gr) using a strong base
27
New cards
what do non-stabilised ylides react w
both ketones and aldehydes
28
New cards
what alkenes do unstabilised ylides form
give mainly z alkenes
29
New cards
how do you form E alkenes from ketones
\-stabilised ylides unreactive w ketones
* Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction used
* uses deprotonated phosphonate ester (neg changed rather than neutral) so more reactivate to c=o
* MUST USE A STABILISED ONE
* Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction used
* uses deprotonated phosphonate ester (neg changed rather than neutral) so more reactivate to c=o
* MUST USE A STABILISED ONE
30
New cards
conditions to form E/Z alkenes from alkynes
E: Na/Nh3
Z: H2/Lindlars catalyst
Z: H2/Lindlars catalyst
31
New cards
what reaction type is the Heck reaction
a C-C bond forming reaction
32
New cards
what can the Heck reaction be used for
to form a disubstituted alkene from a terminal alkene and an aryl halide (ArX) or a vinyl halide (C=CX)
33
New cards
regioselectivity of the heck reaction
R group is introduced at the least hindered end of the C=C bond
34
New cards
stereoselectivity of heck reaction
the more stable E- alkene is formed
35
New cards
what attack are α,β-unsaturated carbonyls susceptible to
attack by nucleophiles at both the 2- and 4- positions
36
New cards
what is attack at the 2 position of a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl called
1,2-addition
37
New cards
what is attack at the 4 position of a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl called
1,4- addition or conjugate addition or Michael addition
38
New cards
examples of factors that affect whether the 2 or 4 position of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl is attacked
steric effects, type of organometallic
39
New cards
where do grignards usually attack a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl
the C=O bond
40
New cards
what is addition to a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl at the 2 position described as being and why
under kinetic control as stronger C=O bond is broken and weaker C=C bond is retained
41
New cards
what is an example of something that attacks at 4 position of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl
Organocopper reagents (RCu) and cuprates (R2CuLi)
42
New cards
what is addition to a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl at the4 position described as being and why
under thermodynamic control as the stronger C=O bond is retained and the weaker C=C bond is broken (i.e. more stable product is formed)
43
New cards
What is a hard nucleophile?
high δ- density - small nucleophile, charge on highly electroneg atom
44
New cards
What is a soft nucleophile?
low δ- density - large delocalised nucleophile w charge spread out (eg. w resonance over to C=O groups) i
45
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for alkene to halogenoalkane
HX
46
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for terminal alkene to terminal alcohol
1) BH3
2) H2O2, HO-
2) H2O2, HO-
47
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for terminal alkyne to aldehyde
1) BH3
2) H2O2, HO-
2) H2O2, HO-
48
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for alkene to trans diol
1) RCO3H
2) H2O/H+ or H2O/HO-
2) H2O/H+ or H2O/HO-
49
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for alkene to cis-diol
KMnO4, HO-/H2O
low temp
low temp
50
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for ArNO2 to ArNH2
Sn, HCl
51
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for ArNH2 to ArNHCOR
RCOCL, base
52
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for ArSO3H to Ar
dilute H2SO4
53
New cards
hard nucleophile examples
OH-
Grignard
Grignard
54
New cards
reactants/ conditions needed for ketone to tertiary alcohol
1)RLi or RMgBr
2) H+
2) H+
55
New cards
reactants/ conditions needed for ketone to alkene
Ph3P=CHR
56
New cards
reactants/ conditions needed for ketone to diether
2 ROH
H+ (catalyst)
H+ (catalyst)
57
New cards
reactants/ conditions needed for aldehyde to enone (HCOCH=CHCH3)
2x aldehyde
OH- heat
OH- heat
58
New cards
precursors for witting
ketone and Ph3P=R
59
New cards
precursors for imine
ketone and primary amine
60
New cards
precursors for acetal
diol and ketone
61
New cards
precursors for epoxide
H2C=CHR (RCO3H used)
62
New cards
precursors for cis-diol
z alkene
63
New cards
common synthon for R+ (R=alkyl not aryl)
R-I, R-Br, R-OSO2Me (R-OMs) , R-OTs (add LH to C)
64
New cards
common synthon for RC+OH(R/H)
ketone or aldehyde
65
New cards
common synthon for RCHOHR+
epoxide
66
New cards
common synthon for RC+=O
carboxylic acid derivatives
67
New cards
common synthon for RC=OCH2CH2+
an alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl RCH=OCH=CH2
68
New cards
common synthon for R-
R-MgX, R-Li, R2CuLi
69
New cards
common synthon for Ar-
ArH, Ar-MgX, Ar-Li, Ar2CuLi
70
New cards
common synthon for RC=OCH2-
RCH=OCH3 + base
71
New cards
common synthon for ROC=OCH3-
ROC=OCH3 + base
72
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: secondary alcohol to ketone
CrO3, H+
73
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: primary alcohol to aldehyde
CrO3, H+, distillation
or milder oxidising agent e.g. PCC
or milder oxidising agent e.g. PCC
74
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
CrO3, H+
75
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: terminal alkene to epoxide
RCO3H (Peracid)
76
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: terminal alkene to cis diol
aq OsO4
77
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: ketone to secondary alcohol
NaBH4/LiAlH4 then H+
78
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: carboxylic acid to primary alcohol
LiAlH4 then H+
79
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: imine to secondary amine
NaBH4 then H+
80
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: ArNO2 to ArNH2
Sn, HCl
81
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: alkyne to z-alkene
H2, Lindlars catalyst
82
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: alkene to alkane
H2, Pd/C
83
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: secondary alcohol to secondary halogenoalkane
PX3
84
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: carboxylic acid to acyl chloride
SOCl2
85
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: acyl chloride to amide
RNH2, base
86
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: carboxylic acid to ester
ROH, H+
87
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: halogenoalkane to alkene
base e.g. tBuO-
88
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: alkene to halogenoalkane
HX
89
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for FGI: ArNH2 to ArOH
NaNO2, HCl then H2O heat
90
New cards
examples of small molecule RASM (that may not be listed in a q)
CO2, MeBr, MeCOCl, MeCO2H ...
91
New cards
what reagents are needed in the forward steps of a Heck reaction
Pd(0) catalyst, base
92
New cards
alkene + HBr, ROOR/heat =
anti-markovnikov addition- Br adds to least substituted end of C=C
93
New cards
what is a carbamate, how do you turn an amine into one and how do you deprotect at the end?
RNHCOOR
react amine w e.g. BOC (tertbutoxy carbonyl)
to deprotect react w TFA (acid)
react amine w e.g. BOC (tertbutoxy carbonyl)
to deprotect react w TFA (acid)
94
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for dialkyl ether to carboxylic acid
H2O
95
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for dialkyl ether to ester
react w ROH then remove RCO2H
96
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for R-C(tb)N to amide
H2O, H+
97
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for ester to amide
NH3
98
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for ester to tertiary alcohol
2 RMgX then H+
99
New cards
reactants/conditions needed for acyl chloride to amide
NH3
100
New cards
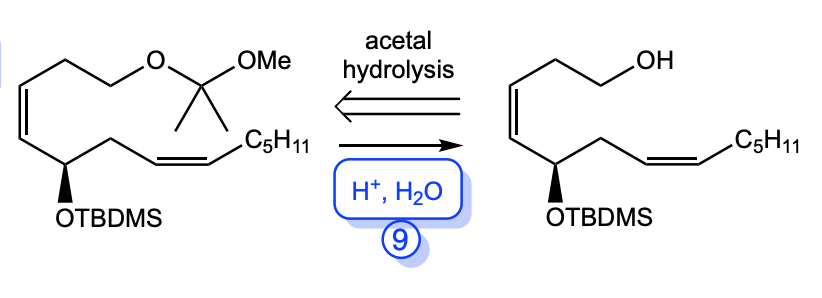
acetal to alcohol
H+, H2O