CH.11: Cell-to-Cell Interactions
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Cell-Cell Interactions
Communication and cooperation among multicellular organisms.
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
Integral Proteins
Proteins that span the membrane's bilayer.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins attached to membrane surface.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins forming tight junctions between cells; Regulates transport and cell environment
Cytoskeletal Elements
Structures that support cell shape and organization.
Extracellular Structures
Components outside the cell membrane.
Signal Transduction
Process of converting a signal into a cellular response.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate chains for cell recognition.
Intercellular Joining
Connections between adjacent cell membranes.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Network providing structural support to cells.
Cell Wall
Protective layer surrounding plant and prokaryotic cells.
Peptidoglycan
Polysaccharide forming bacterial cell walls.
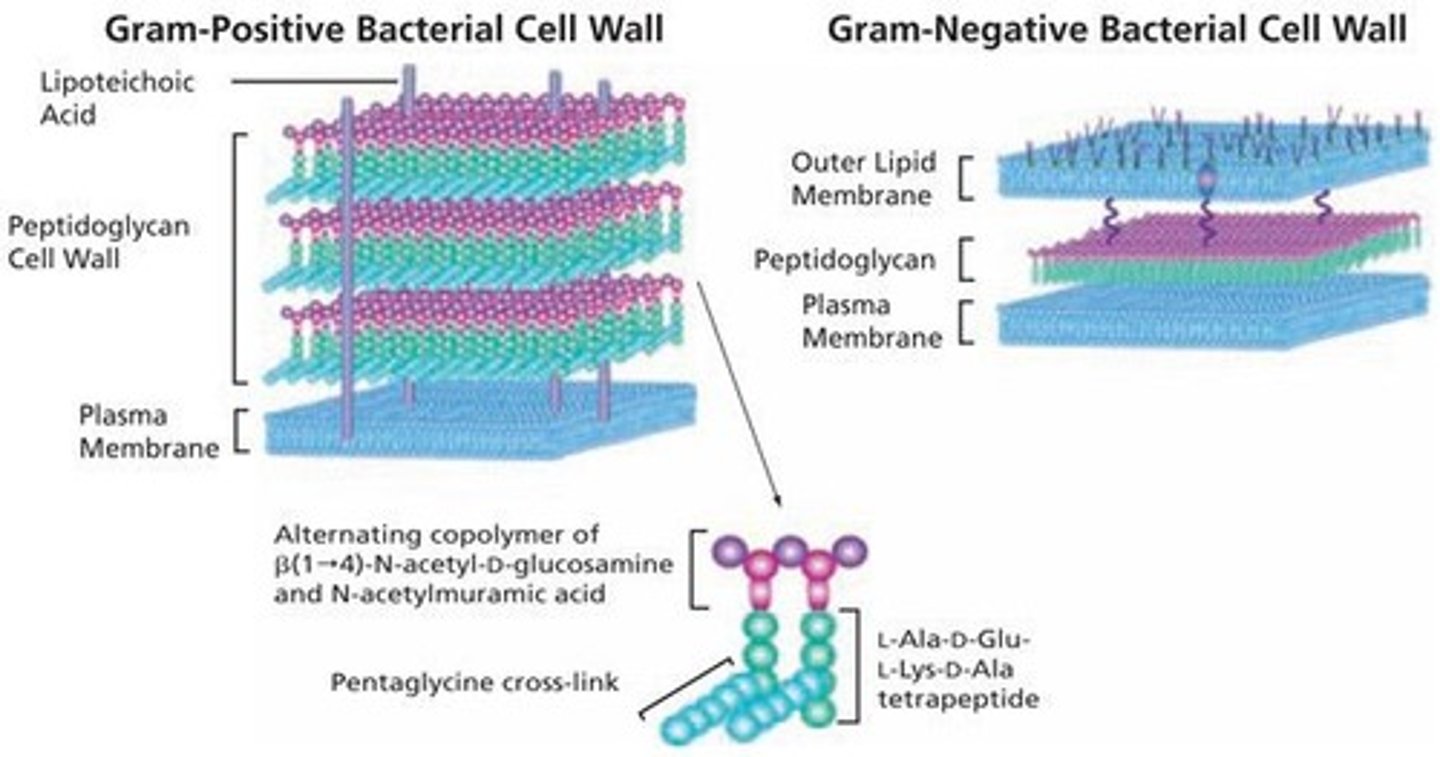
S-layer
Protein coat forming archaea cell walls.
Fiber Composite
Material providing strength and structure in ECM.
Microfibrils
Cable-like structures in plant cell walls.
Pectin
Gelatinous polysaccharide keeping cell walls moist.
Turgor Pressure
Pressure from water inside plant cells.
Expansins
Proteins that facilitate plant cell growth.
Secondary Cell Wall
Additional layer providing strength to mature plant cells.
Lignin
Complex organic polymer in woody plant cells.
Middle Lamella
Pectin layer gluing adjacent plant cell walls.
Collagen
Fibrous protein providing structural support in ECM.
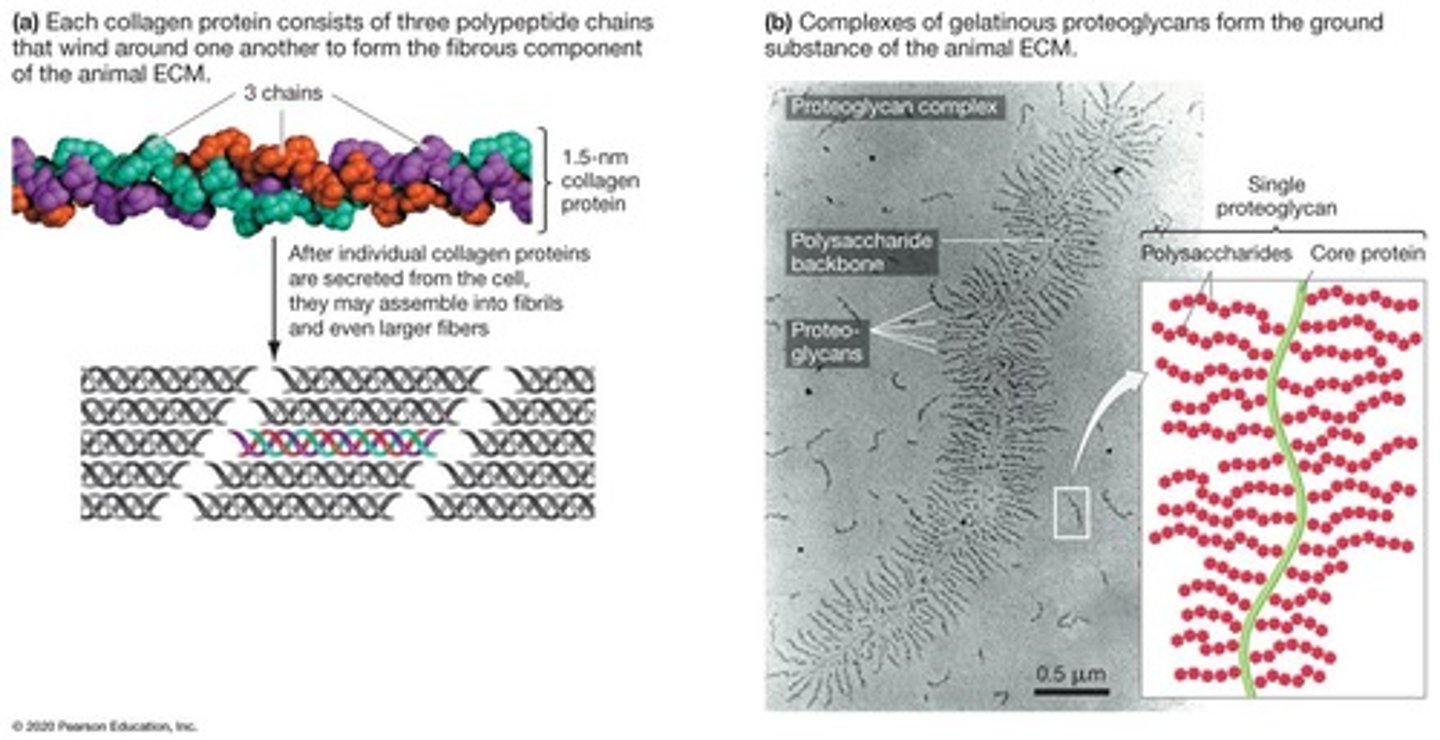
Proteoglycans
Proteins with polysaccharides, forming cartilage-like consistency.
Elastin
Protein allowing elasticity in lung tissue.
Integrins
Membrane proteins linking ECM to cytoskeleton.
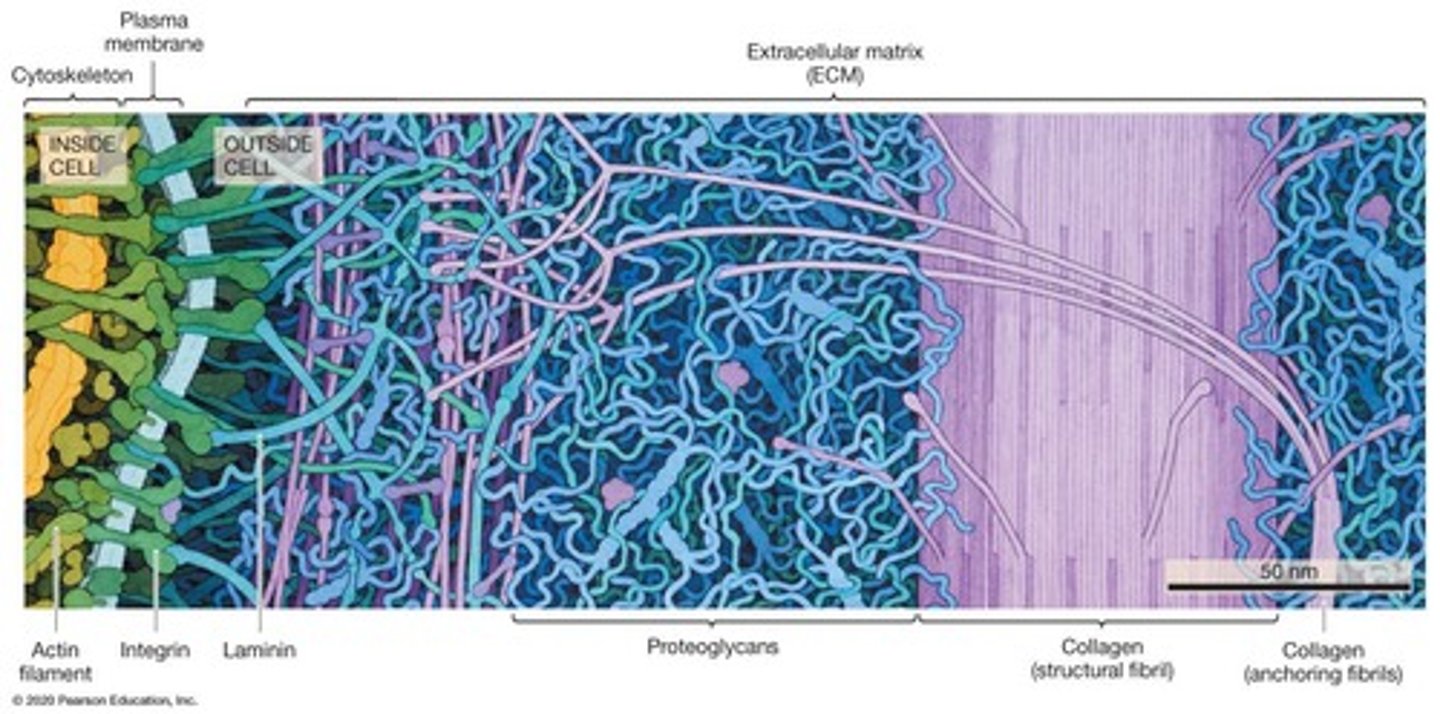
Laminins
Cross-linking proteins in the ECM.
Cell Communication
Mechanisms allowing cells to exchange information.
Multicellularity
Organisms composed of multiple interconnected cells.
Cell-Cell Attachments
Structures binding cells together in tissues.
Epithelia
Tissues lining surfaces of organs and cavities.
Pectins
Gelatinous substances in middle lamella of plants.
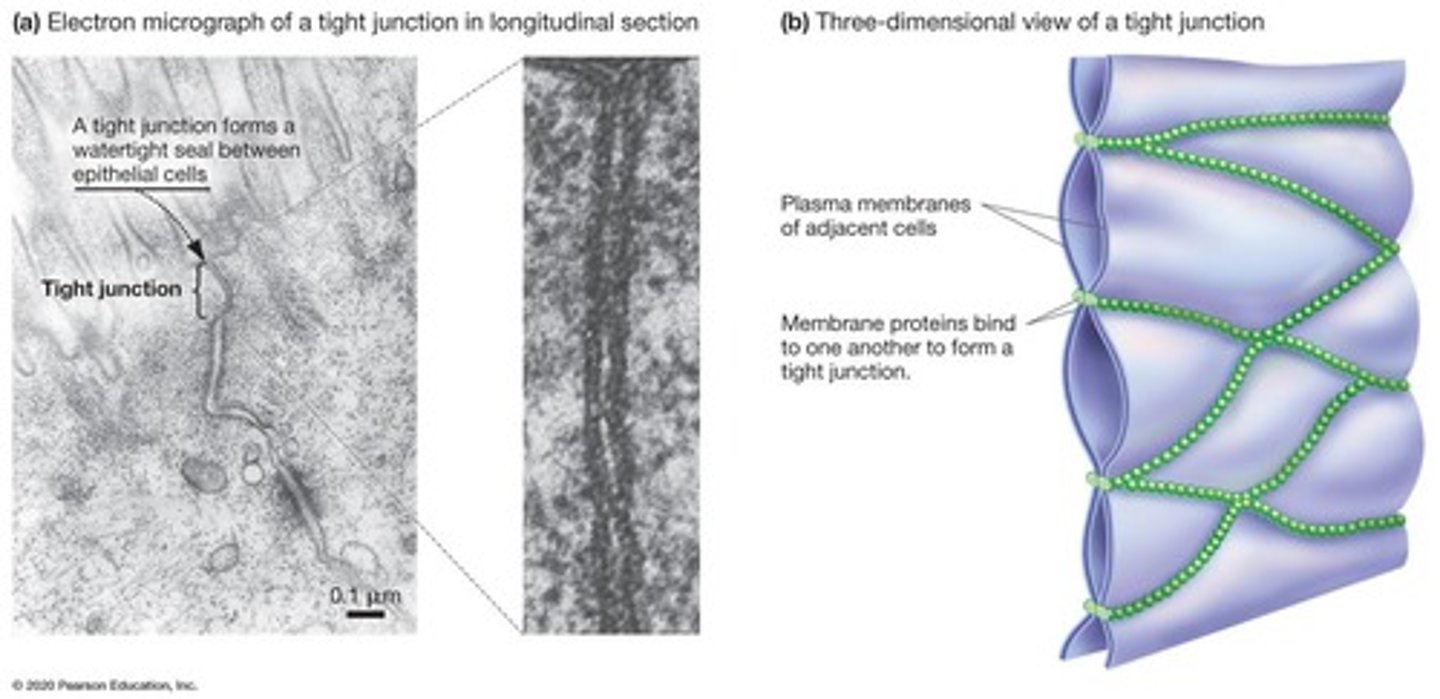
Tight Junctions
Waterproof seals between adjacent animal cells.
Desmosomes
Strong attachments in epithelial and muscle cells.
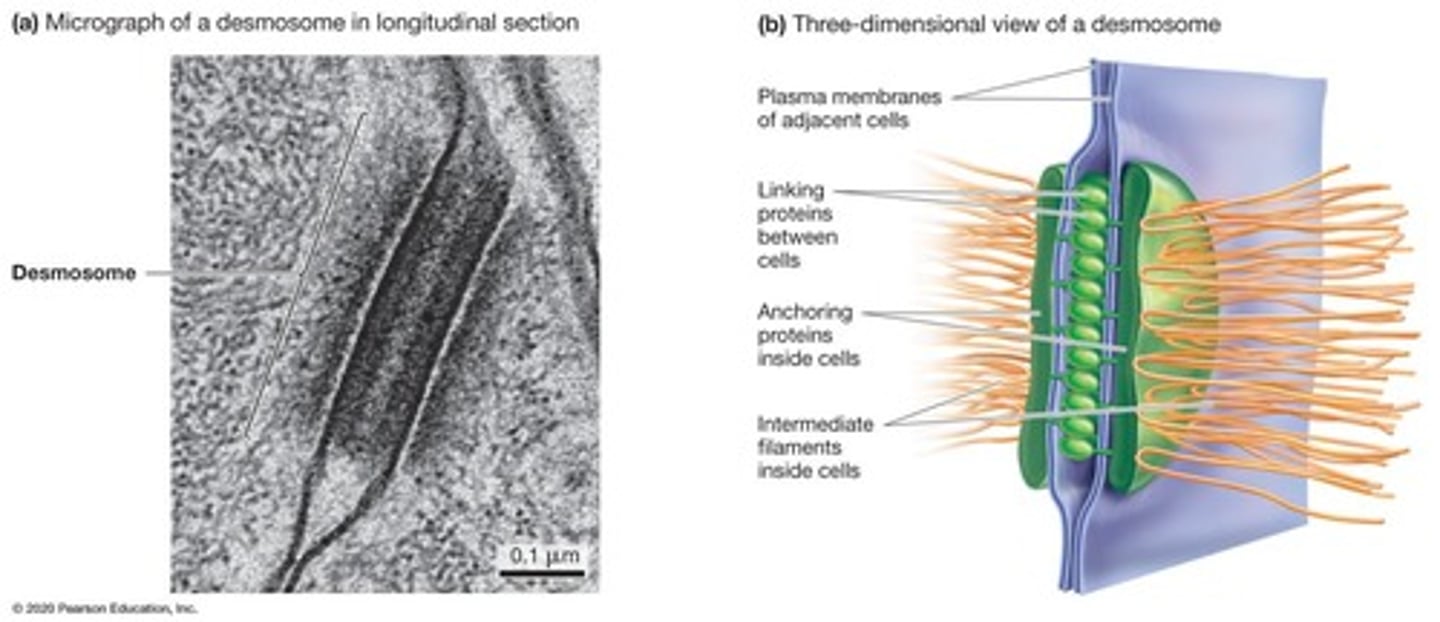
Cytoskeletal Intermediate Filaments
Reinforce desmosomes within cells.
Selective Adhesion
Cells bind only to similar tissue type cells.
Cadherins
Linking proteins in desmosomes for cell adhesion.
Antibodies
Proteins binding specifically to other proteins.
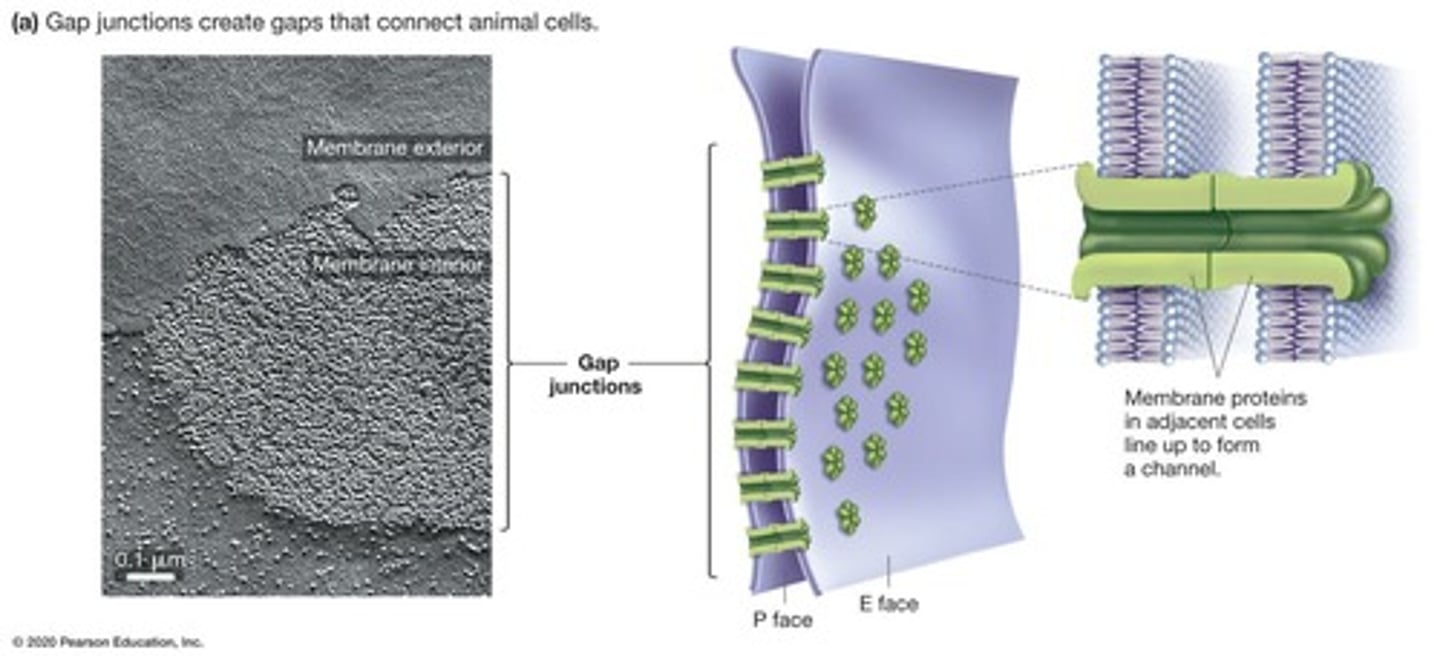
Gap Junctions
Channels connecting adjacent animal cells for communication.
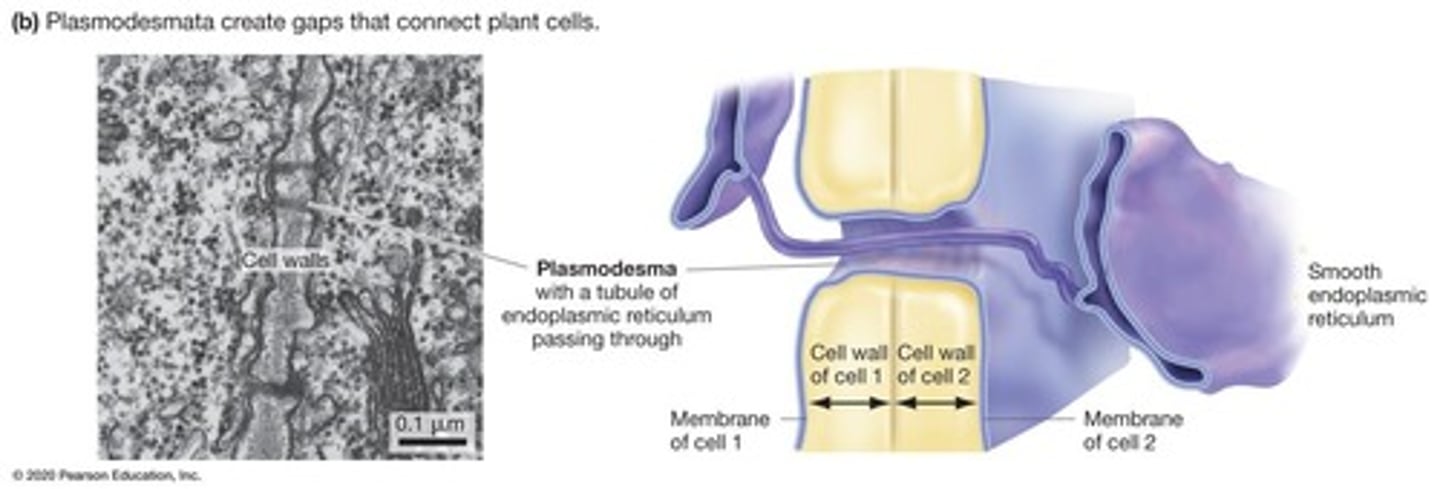
Plasmodesmata
Membrane-lined channels connecting plant cells.
Symplast
Shared cytoplasm within plant tissues.
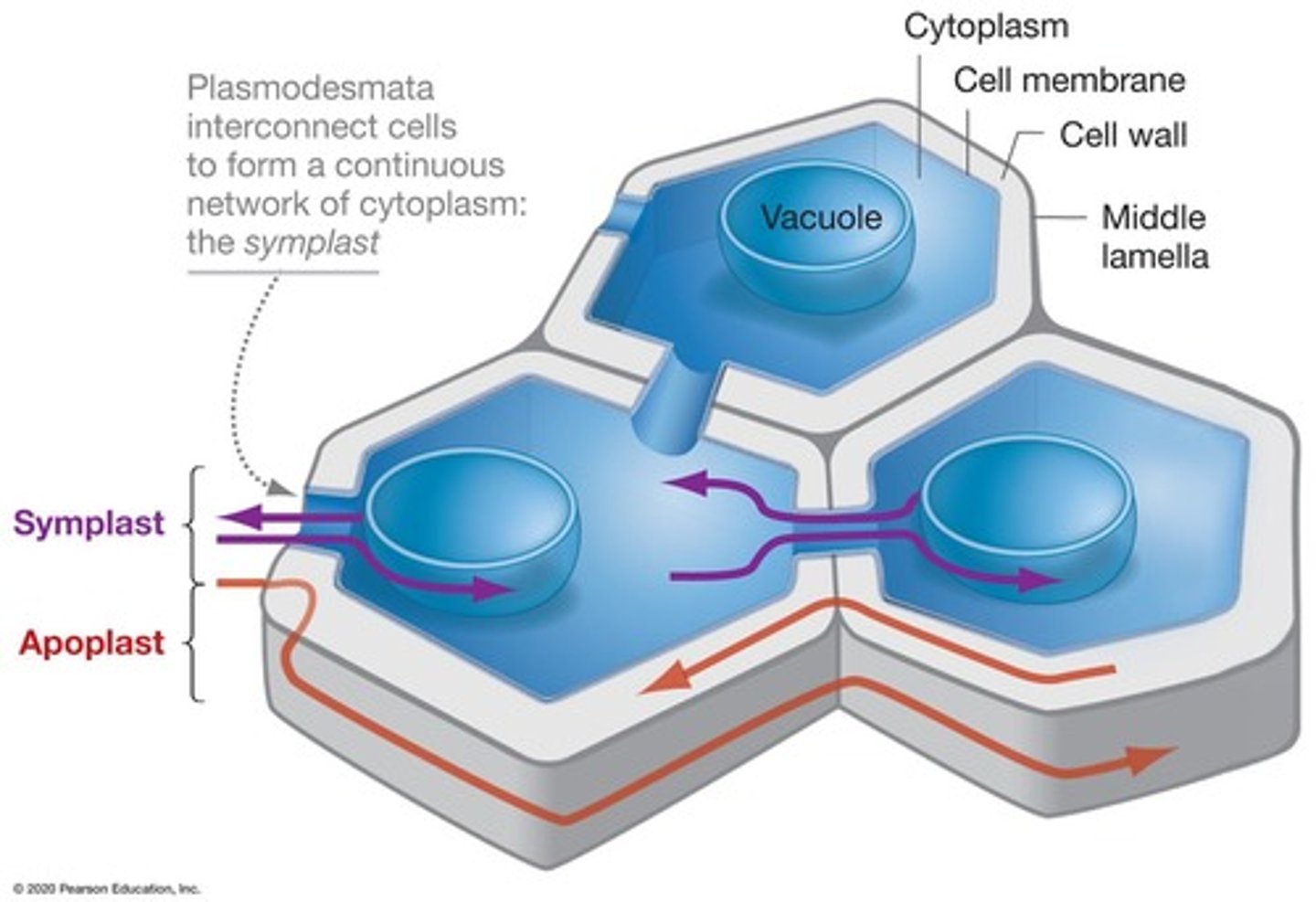
Apoplast
Extracellular space in plant tissues.
Waterproof Seals
Function of tight junctions in epithelial tissues.
Dynamic Tight Junctions
Tight junctions can change permeability based on conditions.
Cell Aggregation
Cells of the same type can reform tissues.
Adhesion Proteins
Different proteins enable selective cell attachments.
Cytoplasmic Connections
Ions and small molecules pass between adjacent cells.
Regulatory Ions
Small molecules facilitating cellular communication.
Cellular Coordination
Gap junctions help synchronize cell functions.
Intracellular Anchoring Proteins
Proteins anchoring cytoskeletal filaments to desmosomes.
Chemical Treatment Experiment
Wilson's experiment on sponge cell adhesion.
Functional Adult Sponges
Reformed from dissociated sponge cells.
Cellular Environment Response
Tight junctions can open/close based on stimuli.
Cellular Communication Portals
Gap junctions facilitate rapid intercellular signaling.
Cell communication
Interaction between cells without physical contact.
Signaling molecules
Molecules that transmit information between cells.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that influence distant cell activity.
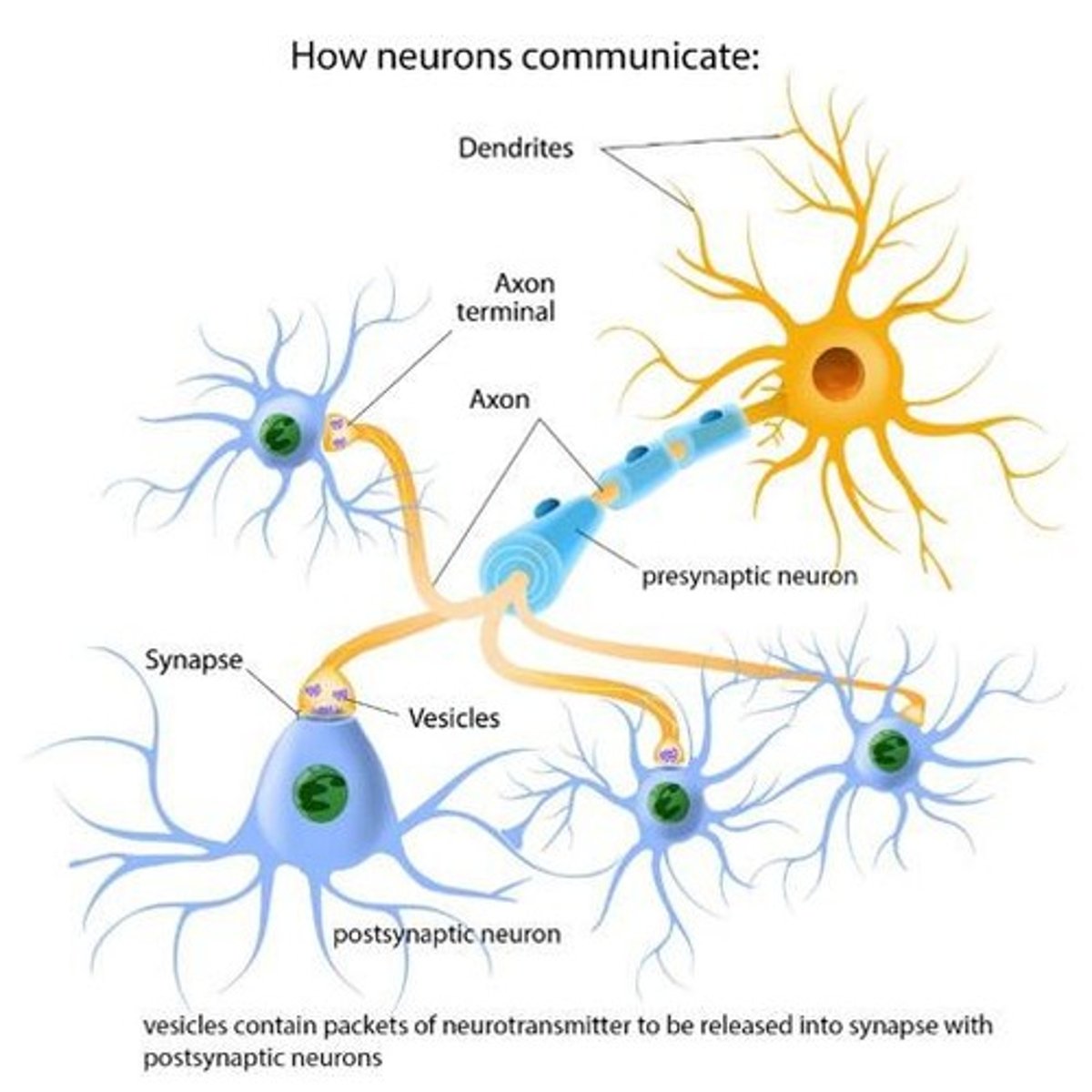
Hormones
Information-carrying molecules secreted into circulation.
Target cells
Cells that respond to specific signaling molecules.
Signal reception
Process of binding signaling molecules to receptors.
Receptor molecules
Proteins that change shape upon binding signals.
Lipid-soluble signals
Molecules that diffuse across plasma membranes.
Cytoplasm receptors
Receptors located within target cell's cytoplasm.
Lipid-insoluble signals
Molecules that cannot cross plasma membranes.
Cell surface receptors
Receptors located on the plasma membrane.
Dynamic receptors
Receptors whose number and sensitivity can change.
Beta-blockers
Drugs that block hormone-receptor interactions.
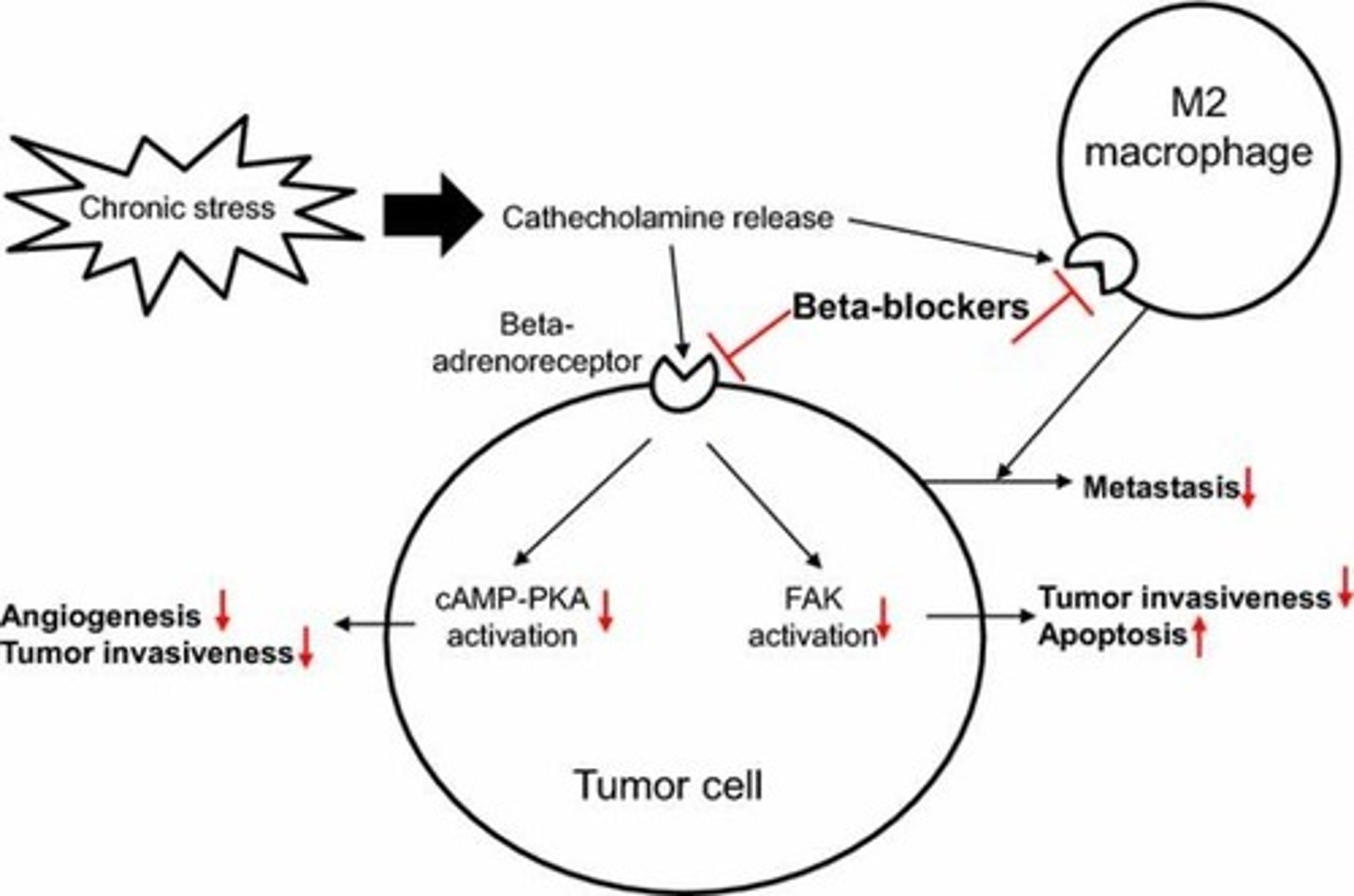
Steroid hormones
Lipid-soluble hormones like estrogen and cortisol.
Hormone-receptor complex
Complex that triggers gene expression changes.
Signal transduction
Conversion of extracellular signals to intracellular responses.
Second messengers
Small molecules that amplify intracellular signals.
G-protein-coupled receptors
Receptors that initiate second messenger production.
Enzyme-linked receptors
Transmembrane proteins catalyzing reactions and phosphorylate proteins inside cells.
G proteins
Peripheral proteins activated by signaling receptors.
GDP and GTP
Nucleotides exchanged during G protein activation.
Signal amplification
Process of increasing signal strength within cells.
Intracellular signals
Signals generated inside cells from external stimuli.
Gene expression changes
Alterations in protein production due to signals.
Signal diversity
Variety of responses generated from a single signal.
Plasma membrane
Barrier that separates cell interior from environment.
G protein subunit
Activates nearby enzyme for signaling.
Second messenger
Small molecules amplifying hormone signals.
Protein kinases
Enzymes adding phosphate groups to proteins.
Calcium ion (Ca2+)
Activates proteins via calmodulin complex.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Activates specific protein kinases.
Cyclic GMP (cGMP)
Opens ion channels and activates kinases.
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Activates certain protein kinases.
Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
Opens calcium channels for cytosol entry.
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
Best-known group of enzyme-linked receptors.
Phosphorylation cascade
Series of protein phosphorylations amplifying signals.
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)
Activate cell division via phosphorylation.
Signal response
Change in gene expression or protein activity.
Abscisic acid
Hormone regulating plant response to drought.
Signal deactivation
Mechanisms to turn off intracellular signals.
Phosphatases
Remove phosphate groups in signaling pathways.
Crosstalk
Integration of multiple signaling pathways.
Quorum sensing
Bacterial communication based on population density.
Biofilm
Community of microbes adhering together.
Threshold response
Signal response varies with population density.
Slime mold aggregation
Free-living cells aggregate via signaling.