(BIO 386) Lec 18 (17) - Carbon cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The carbon cycle
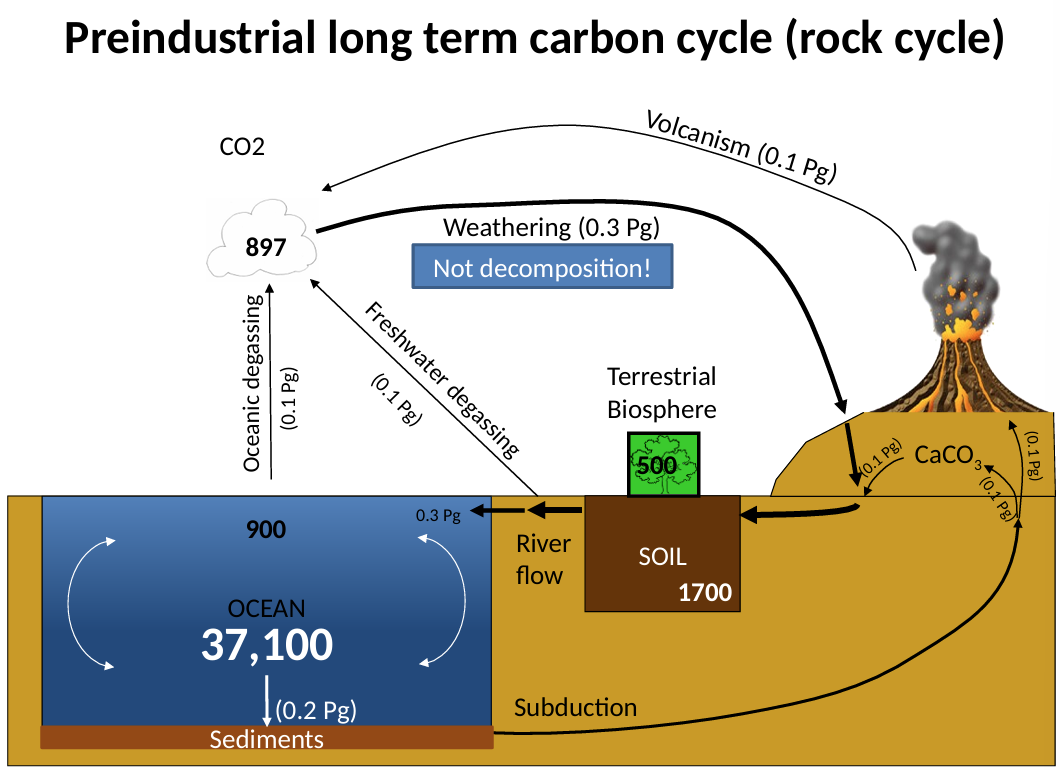
Changes in CO2 due to imbalances in these processes are slow
Inputs to atmosphere
Outputs from atmosphere
Upshot: Imbalance an take millions of year to affect atmospheric CO2
Slow changes in CO2: Time scale reflects differences in rate or periodicity of disturbances
1) Very long-term processes
Geological factors
Volcanism
Weathering
Evolution of plants
2) Medium-term processes
Changes in solar radiation
Ocean/atmosphere interactions
Weathering as a global thermostat
When Earth is warmer:
Weathering increases
CO2 declines
Earth cools
When Earth is cooler:
Weathering decreases
CO2 increases
Earth warms
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP: holds temp in a certain range
Change in solar luminosity _______ with temperature
increases
Counteracting solar intensity, CO2 concentrations have ______ over earth’s history
fallen
Living processes occur _______ than geologic processes
100x
Changes in CO2 could ________ response by increasing surface temperature
amplify
Changes would be global because CO2 stays in atmosphere for much longer
CO2 feedback
Possible oceanic mechanisms:
1) Temperature effect on bicarbonate system
2) Higher export of production to depth
Possible terrestrial mechanisms:
1) Temperature effects on plant biomass
2) Sequestration or release of soil C
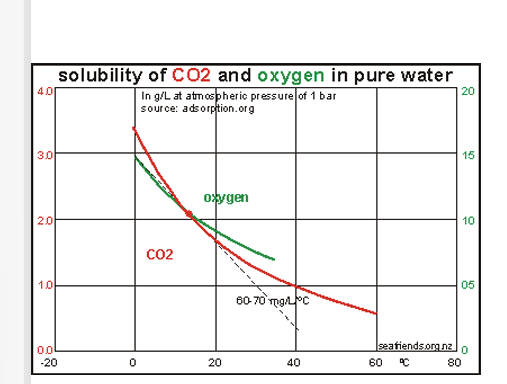
Solubility of CO2 (and other gasses) _________ with increasing temp
decreases
If phytoplankton do not use CO2, warming of water causes CO2 to leave water and enter atmosphere
This can enhance warming, result to more CO2 release from oceans
Cooling does the opposite
Occurs near ITCZ
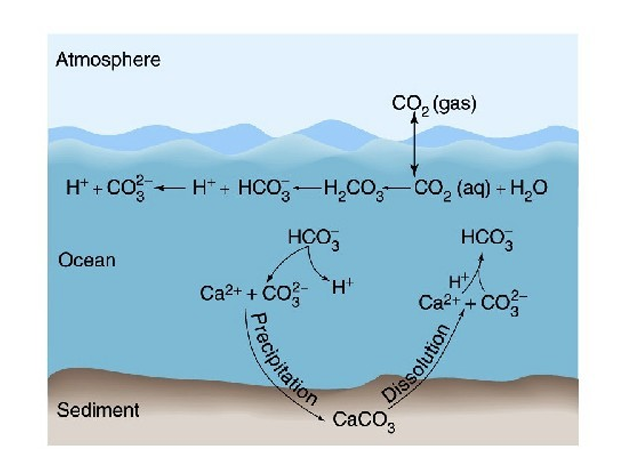
What happens to CO2 in ocean during warming?
Warmer conditions result in less absorption of CO2 by sinking water
The water that upwells to the surface also looses more CO2
What happens to CO2 in the ocean during cooling?
Cooler conditions result in more absorption of CO2 by sinking water at poles
The water that upwells to the surface in tropics looses less CO2 because it warms less
This results in a net movement of CO2 from the atmosphere to the ocean
Reestablishing equilibrium after warming/cooling slows down takes about…
200-1000 years
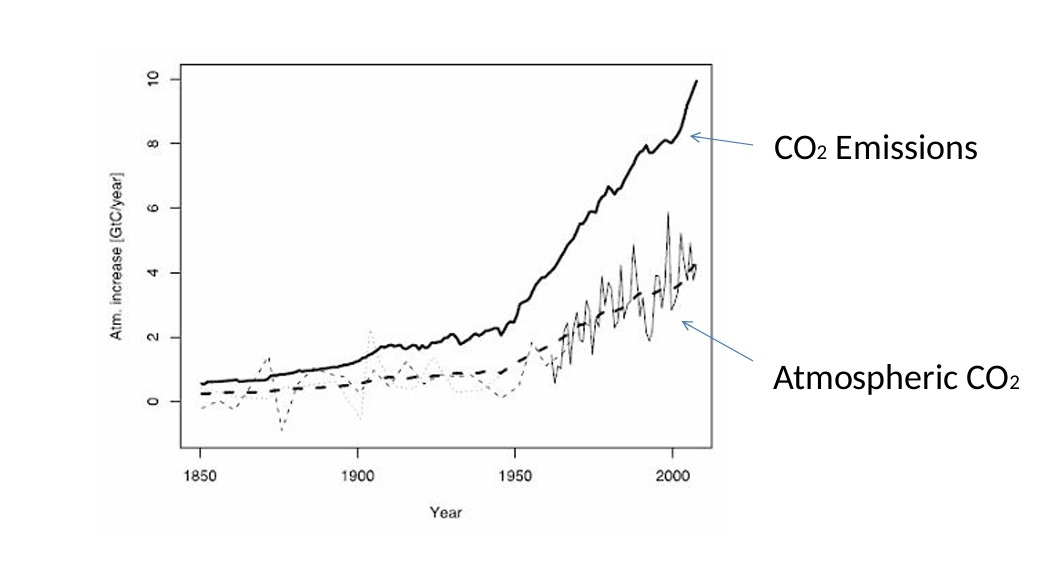
The effects on the carbon cycle in the future are complex and uncertain because
In the past, non-human processes initiated the change
Now humans are altering the carbon cycle directly in many ways
Not all of CO2 emitted stays in the
atmosphere
Burning of biomass causes a release of
CO2
Main causes of loss of vegetation and global C cycle
human-set fires
shifting fire regimes
Net effect of fire intensity can only be…
as large as the pool
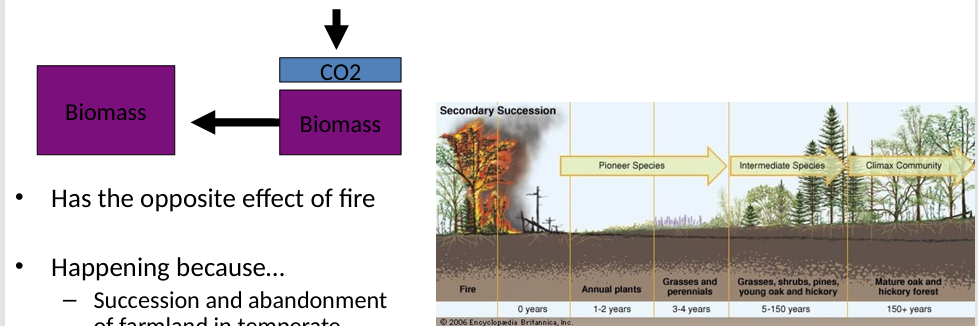
What is the expansion of woody vegetation through succession
Caused by:
Succession and abandonment of farmland in temperate zones
Northward expansion
Effect is limited by the amount of vegetation that can be supported in a particular environment
Has the opposite effect of fire
Net effects on vegetation
Traditional slash and burn
At low human population densities - forests have time to regrow
Eventually frequency of burning is too fast to allow any of forest to attain maximum biomass
Intensive farming and animal agriculture
Suppresses regrowth of forest in certain locations
Animal agriculture requires much more land in rangeland or grassland state
Spatial changes in vegetation carbon results from changing centers of agriculture
What will happen to soil C as temperature and CO2 increase
Could go up
Temperature allows range expansion
CO2 fertilizes plants
Precipitation allows for better growth
Could go down
Increase in temperature results in decomp of soil carbon
Likewise for increasing precipitation
Fires could burn the accumulated peat with loss of permafrost
The solubility pump8