ap psych 2.3-2.6 vocab
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information.
recall
retrieving info not currently in conscious mind - i.e. a fill in the blank question
recognition
identifying items prev. learned - i.e. multiple choice
relearning
learning smth more quickly the 2nd time around
overlearning
rehearsal of material already known; increases retention
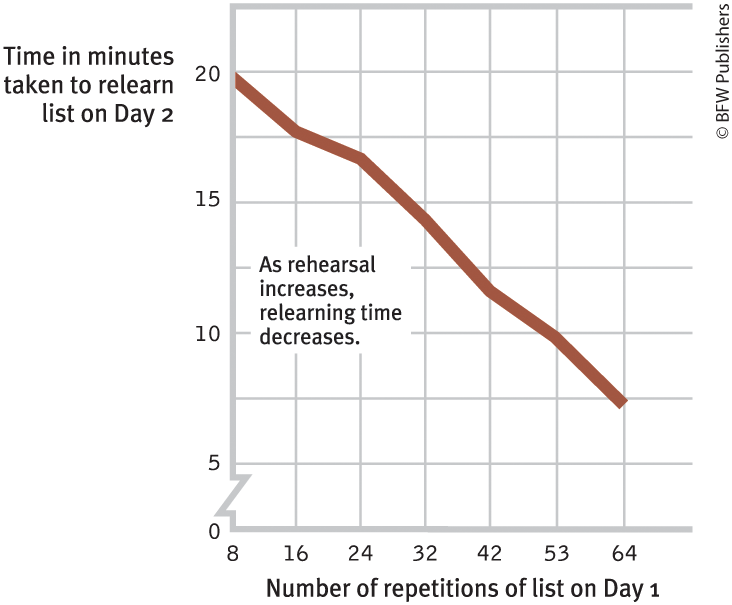
what’s this graph called
ebbinghaus’ retention curve
encoding
getting information into our brain
store
retaining the info
retrieve
later getting the info back out of our brain
parallel processing
procesing mutliple aspects of a stimulus simultaneously
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system.
short term memory
briefly activated memory of a few items (i.e. a friend’s phone number) before either being stored or forgotten
long term memory
relatively permanent and limitless archive of the memory system i.e. knowledge, skills, experiences
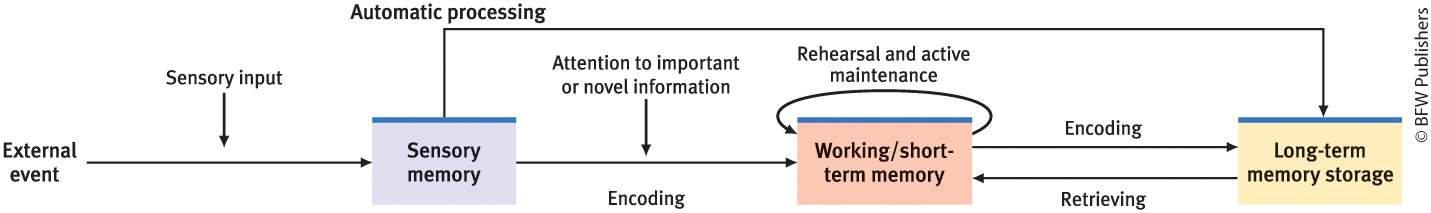
what model is this
modern version of the 3-stage memory model
working memory
new understanding of short-term memory: connecting new info to things from long-term mem. to help better comprehend the info being encoded
central executive
mem. component that coordinates the activities of the phonological loop & visuospatial sketchpad
phonological loop
holds auditory info in short-term memory
visuospatial sketchpad
holds info in short term memory about an object’s appearance & location in space
neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
long-term potentiation
an increase in a nerve cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; i.e. muscle memory or trauma
explicit memories
facts, events, experiences that we consciously know
implicit memories
learned skills/associations
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention + conscious effort; produces explicit memories
automatic processing
subconscious encoding that produces our implicit memories
ionic memory
fleeting sensory mem. of visual stimuli (few tenths of a sec)
echoic memory
fleeting sensory mem. of audio stimuli (3-4 sec)
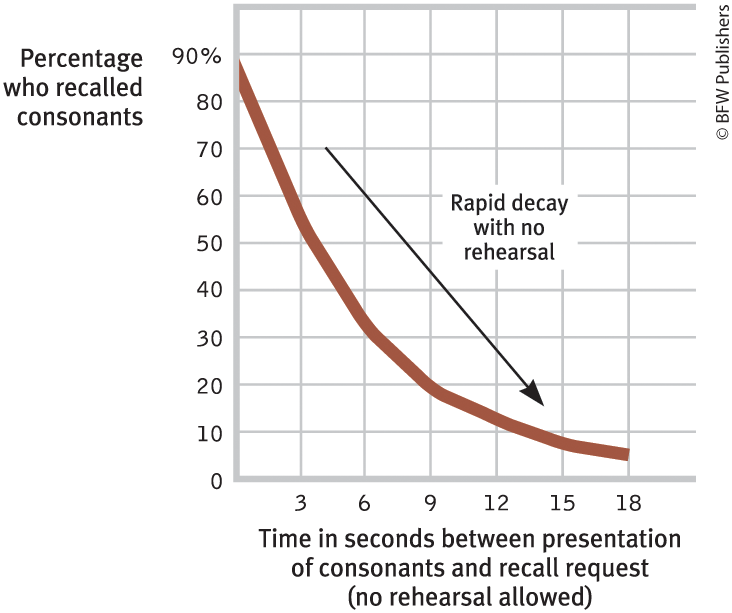
what does this represent
rapid decay of short term memory w/o rehearsal
chunking
organizing a bunch of info into familiar, more manageable chunks
mnemonics
memory aids that use vivid imagery/organizational devices (i.e. acronyms)
heirarchies
good memorization strat by organizing knowledge into broad terms and more specific ones under the broad categories (i.e. grouping random words into categories)
spacing effect
the effect that shows how distributed study yields better long-term retention vs cramming
testing effecvt
hand-in-hand w/ spacing effect; short quizzes after memorizing some stuff greatly improves retention
shallow processing
encoding on the basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words
deep processing
encodes semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tend to yield the best retention
self-reference effect
attributing information to personal details already stored in long-term memory
semantic explicit memory
memorizing facts & knowledge
episodic explicit memory
remembering experiences
prefrontal cortex
used to recall a past experience, also used for working mem. processing
hippocampus
likened to a “save” button for explicit memories (birds w/o one cached food in hundreds of places but couldn’t remember where they were after a bit)
memory consolidation
the transfer of memories from the hippocampus to the prefrontal cortex
cerebellum
key for storing implicit memoriews
basal ganglia
responsible for motor movement muscle memory
flashbulb memories
vivid ones b/c of the heightened emotional state
retrieval cues
associating encoded info w/ random stuff from your surroundings (i.e. when trying to remember the name of someone you also associate their face what they were wearing, etc.)
retrospective memory
past actions
prospective memory
remembering intended future actions
priming
subconscious association between smth learned and other stuff (even if you don’t remember seeing the rabbit, if you heard the word “hair” you’d spell it as “hare” if you saw it a few moments before)
encoding specificity principle
context helps us remember stuff; childhood home triggers memories
mood congruent memory
feeling good triggers good memories, feeling sad triggers sad memories, etc.
recency effect
ppl remember the last stuff on a list better than the middle
primacy effect
ppl remember the first stuff on a list better than the middle
interleaving
mixing study subjects to boost retention and also allowing for extra retrieval practice