(1st Edition) Top 104 Terms for the U.S. History Regents Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:55 PM on 5/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
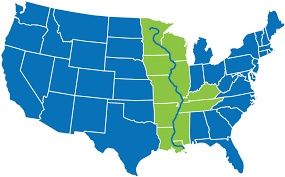
The geographic advantages to the United States of the _______________________ are the port of New Orleans at its mouth, and that it provided a convenient means of shipping western agricultural products to market.
Mississippi River
2
New cards
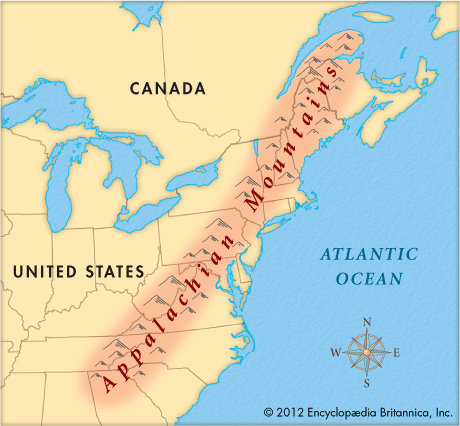
The __________________ formed the first barrier to westward expansion in the colonial era.
Appalachian Mountains
3
New cards
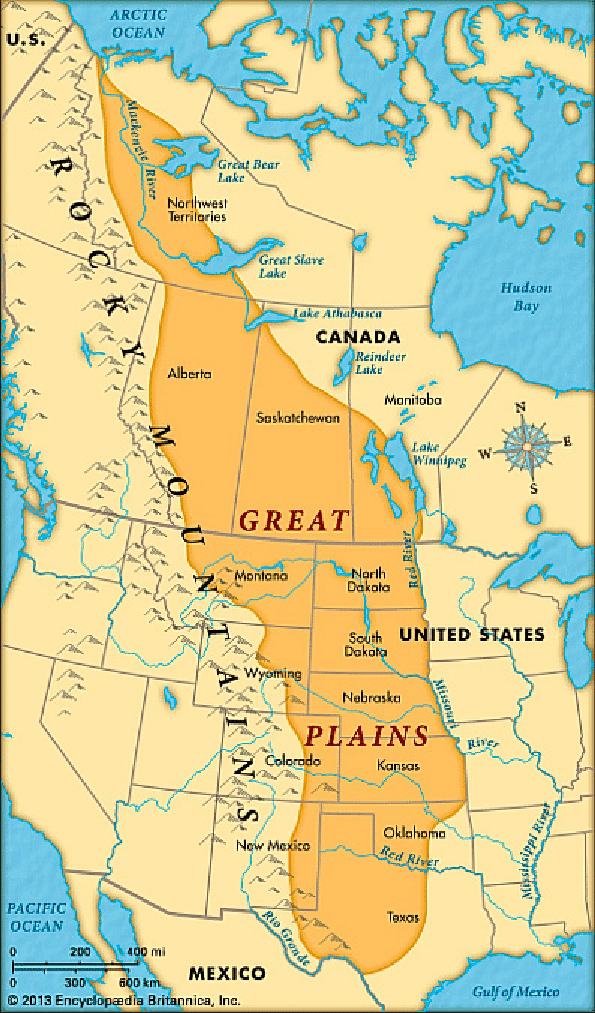
The very fertile land located between the Appalachian Mountains and the Rocky Mountains that produces huge annual corps of corn and wheat is the ____________________.
Great Plains
4
New cards
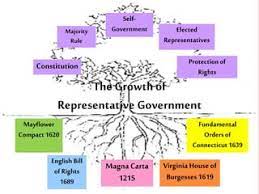
The colonial era featured examples of _____________________ like the Mayflower Compact, Virginia House of Burgesses, New England town meetings.
representative gov’t
5
New cards
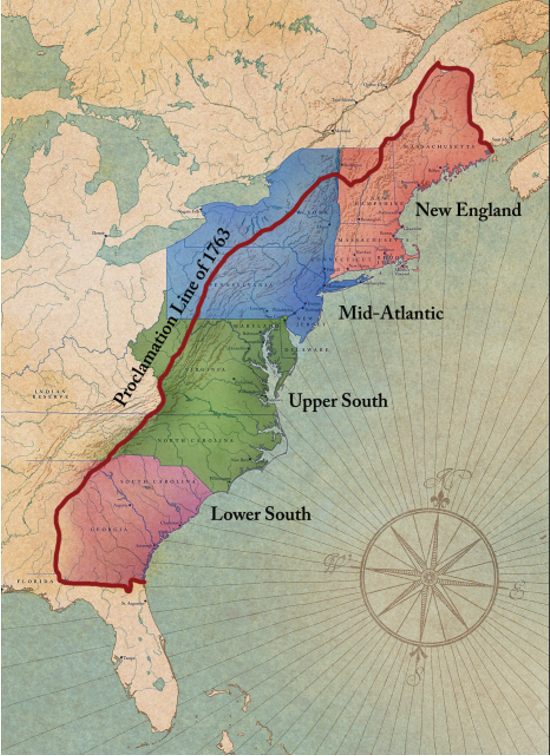
After the French and Indian War the British created the _____________________ to keep the colonists from expanding westward into Indian land.
Proclamation of 1763
6
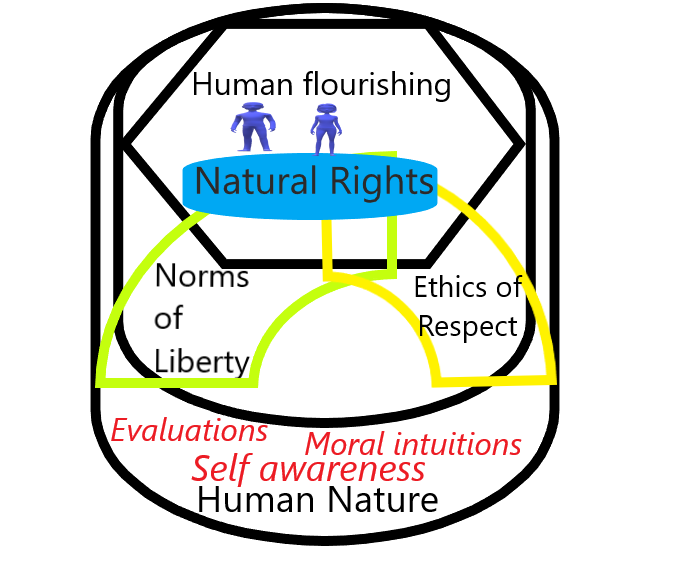
New cards
The Declaration Independence stated that all men have certain __________________ like life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness that government was obligated to protect.
natural rights
7
New cards
The influential pamphlet ___________________ was written in 1776 by Thomas Paine, explaining exactly why the colonists should declare their independence from Great Britain.
Common Sense

8
New cards
As the first government of the United States, the __________________- was successful in winning the Revolutionary War, but would be replaced because it created a very weak national gov’t.
Articles of Confederation

9
New cards
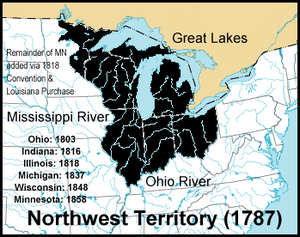
9\. Often cited as a great success of the Articles of Confederation, the ___________________ set the requirements for new states to enter the country, and banned slavery in the territory north of the Ohio River.
Northwest Ordinance
10
New cards
Several ________________ were reached at the Constitutional Convention, resolving complicated issues like representation in Congress and how to count the slave population.
compromises

11
New cards
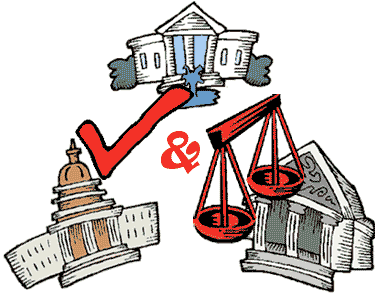
One of the core principles of the Constitution is the ability of one branch to limit each other branch of government. This is known as _______________________.
Checks and balances
12
New cards
The debate over whether or not to pass the Constitution is known as the ___________________ debate.
ratification
13
New cards
The __________ favored accepting the Constitution because they believed it was necessary to form a more powerful national government, while the ==______________________== were concerned that the Constitution created a national government that was too powerful.
\
\
Federalists and Anti-Federalists
14
New cards
The first ten amendments to the Constitution ratified in 1791, are known as the __________________, and are a listing of the civil liberties guaranteed to be protected by the government.
Bill of Rights
15
New cards
Interests groups use ________________ to pressure lawmakers into taking action on issues that concern them.
lobbyists
16
New cards
Because the Founding Fathers didn’t trust average Americans to make wise decisions, they created the controversial _____________________ as a means of selecting the President.
Electoral college
17
New cards
One of the Constitutional roles that the President plays is that of ____________________, and includes actions like planning military strategy.
Commander-in Chief

18
New cards
The Constitutional principle that divides government powers between the national government and the state governments is known as _____________________.
Federalism
19
New cards
The Constitution has proven to be a document that can change over time. This principle, best described as ____________________, occurs through the amendment process, interpretation of the elastic clause, and judicial review.
Flexibility
20
New cards
The influential first Secretary of the Treasury was _____________________, who established a financial plan that stabilized the economy of the United States, and included federal assumption of state debts, an excise tax on whiskey, creation of a national bank, and a protective tariff.
Hamilton
21
New cards
Many features of our government have evolved over time and tradition, and have remained part of our system of government, despite not specifically being listed in the Constitution. Some examples of this _________________ include judicial review, the presidential cabinet, and the formation of political parties.
unwritten constitution

22
New cards
The Constitution’s flexibility is partially based on this section of the Constitution, which states that Congress may pass all laws that are “necessary and proper.” This section is known as the _______________________.
Elastic clause

23
New cards
The Marshall Court established the principle of judicial review in the 1803 case ______________________.
Marbury v. Madison
24
New cards
Examples of the foreign policy of __________________ include Washington’s Farewell Address and the Monroe Doctrine, both of which stated that the United States sought to stay out of European conflicts.
neutrality

25
New cards
In 1823, the United States issued the ____________________, which stated that the Western Hemisphere was off limits to further European colonization.
Monroe Doctrine

26
New cards
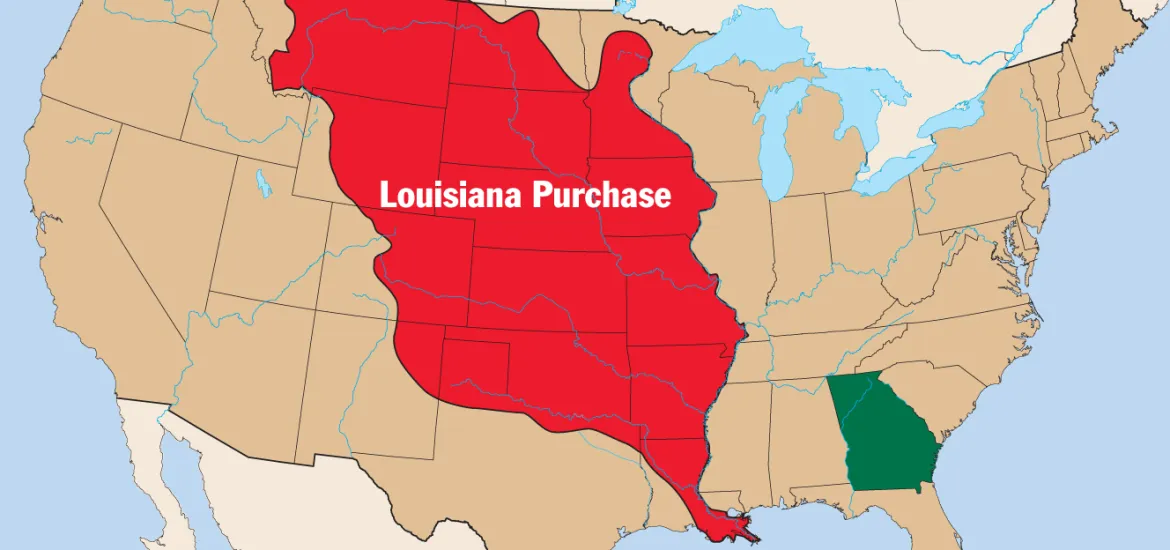
The United States added significantly to the size of the country when, in 1803, Jefferson negotiated the ______________________, despite his concerns about whether he had the constitutional authority to add land to the country.
Louisiana Purchase
27
New cards
The first organized meeting for women’s suffrage, led by Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Lucretia Mott, was the ___________________________ in 1848, which produced the Declaration of Sentiments.
Seneca Falls Convention
28
New cards
The mid-19th century reformers like William Lloyd Garrison and Frederick Douglass who called for an end to slavery in the United States are known as ____________________________.
Abolitionists

29
New cards
One of the more controversial government actions in American history was the passage in 1830 of the _______________________, which led to the forced march of the Cherokee Indians from Georgia to Oklahoma, known as the Trail of Tears.
Indian Removal Act
30
New cards
The _______________________ became a feature of our government during the Jackson presidency, and features rewarding political supporters with government jobs, regardless of their qualifications for employment.
spoils system
31
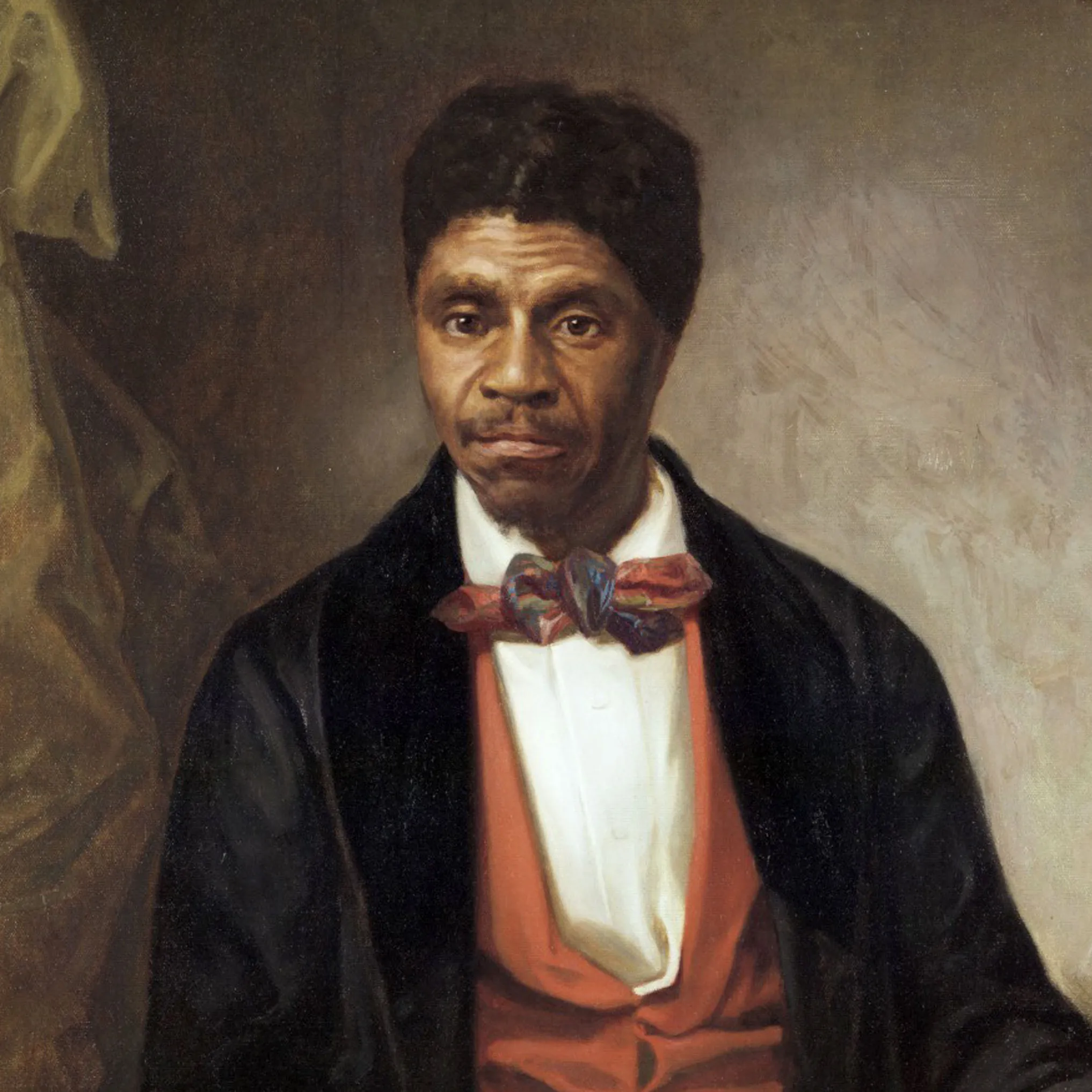
New cards
The 1857 __________________ ruling declared that the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional and that slaves were considered the property of their masters. It enflamed passions in the North and helped lead to the Civil War.
Dred Scott

32
New cards
The belief in the mid-1800s that the United States had a sacred obligation to fill up the North American continent from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean is known as ________________________.
Manifest Destiny
33
New cards
_______________________ is a government principle meaning that people get a chance to choose for themselves how they will be governed, and the best historical example is allowing residents of the Kansas Territory to vote on whether or not to become a free or slave state in the 1850s.
popular sovereignty

34
New cards
Lincoln expanded Presidential power during the Civil War by suspending _____________________, the legal protection that guarantees that someone arrested is accused of a crime and tried in a speedy manner.
habeas corpus
35
New cards
The federal government supported construction of the _______________________ by giving away land grants and loans to railroad companies through the Pacific Railway Act.
transcontinental RR
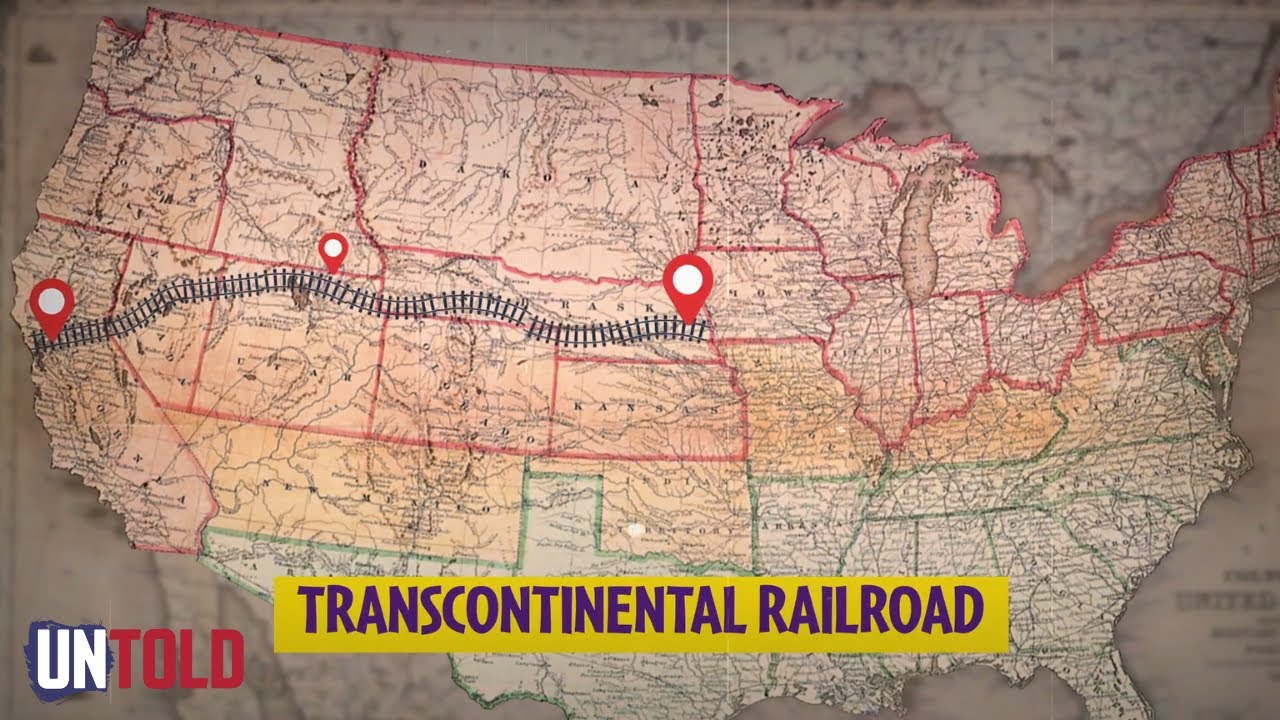
36
New cards
Westward expansion was accelerated by the __________________, through which Americans were allowed to claim 160 acres of land for free, provided that they farmed it for 5 years.
Homestead Act

37
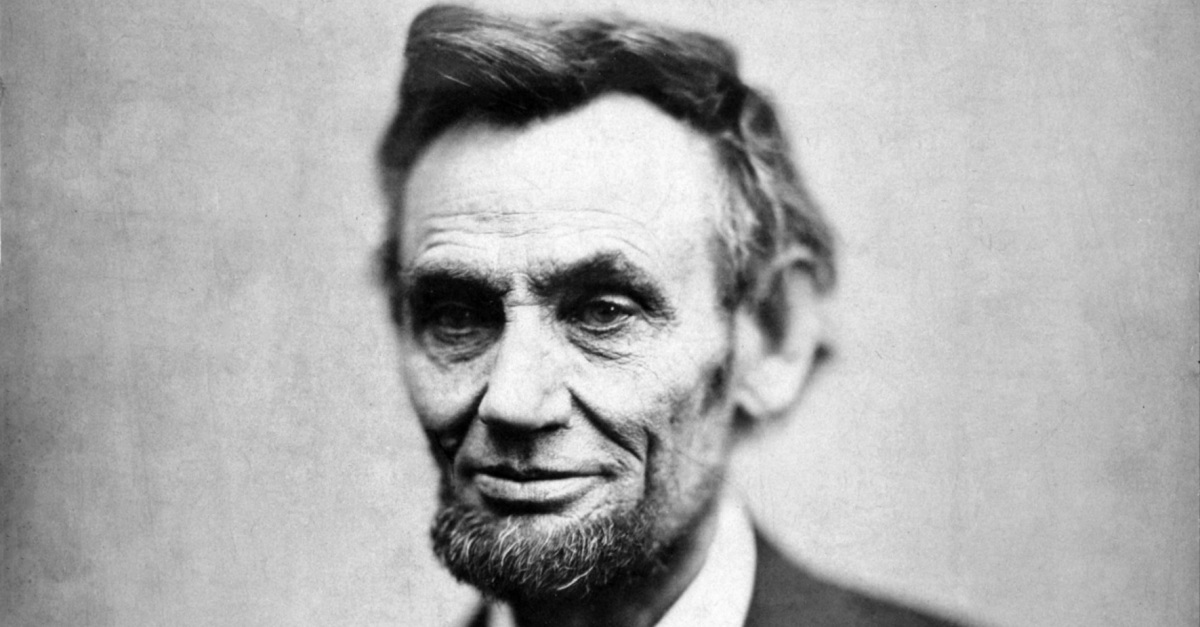
New cards
The most immediate cause of the secession of southern states was the election of _________________ in 1860.
Lincoln

38
New cards
The plight of the slaves was directly addressed following the Civil War by the ________________________, which abolished slavery, and granted the freedmen equal citizenship and voting rights.
13,14,15th amendments
39
New cards
The era immediately following the Civil War, in which the South was militarily occupied and dominated by the North, is known as ______________________.
Reconstruction
40
New cards
Following Reconstruction, Southern states passed ____________________, which created segregated facilities.
Jim Crow laws

41
New cards
The 1896 _______________________ ruling declared that “separate but equal” segregated facilities were legal based on the equal protection clause of the 14th amendment.
Plessy v. Ferguson
42
New cards
The creation of _________________ as a form of business was an improvement over sole proprietorships, because they had greater access to capital.
*fill in an answer*
43
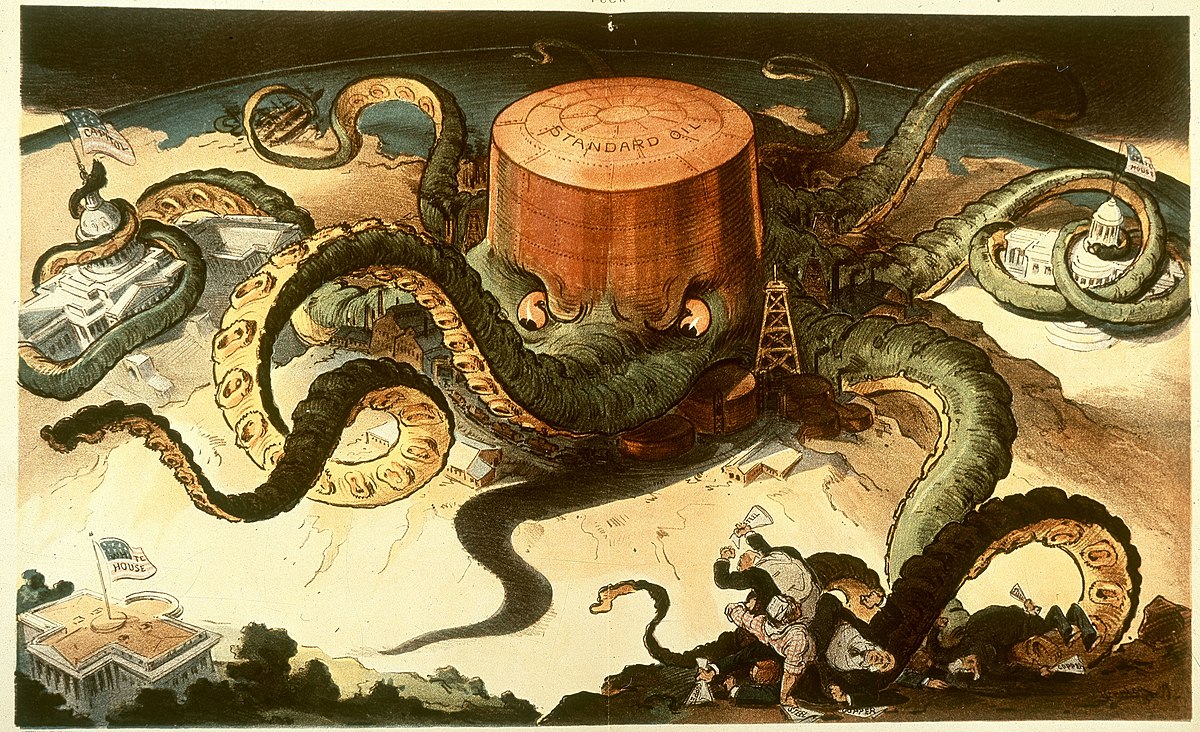
New cards
Negative portrayals of industrial leaders, like referring to them as ___________________, generally emphasize their ruthless business tactics, and how the dangerous working conditions they subjected workers to.
robber barons

44
New cards
Throughout the 19th century, the United States maintained high protective _______________ to protect business from foreign competition.
tariffs
45
New cards
Our government’s economic philosophy during the Industrial Revolution was _________________, which means interfering as little as possible in business activity.
laissez-faire
46
New cards
The political party that formed in the late 1800s to address concerns of the farmers was the ________________.
Populists
47
New cards
A belief in ____________________ was common in the late 1800s, and was used to explain why certain individuals like Carnegie succeeded in business, while others were less successful.
Social Darwinism
48
New cards
The Industrial Revolution led to __________________, and other problems like pollution and the spread of disease in major cities.
urbanization
49
New cards
Unlimited __________________ was sought by industrial leaders, and opposed by labor unions, to provide a consistent and cheap labor force during the Industrial Revolution
immigration
50
New cards
The 1887 law that attempted the assimilation of the Native American Indians by forcing them to speak English and become farmers on reservations was the ________________.
Dawes Act

51
New cards
The group of Americans who sought to use the political process in the early 1900s to correct the evils of the Industrial Revolution, and to expand democracy in the country were the ___________________.
Progressives
52
New cards
Jacob Riis, Upton Sinclair, and Ida Tarbell were ________________, investigative journalists who exposed problems that existed in Industrial America.
muckrakers
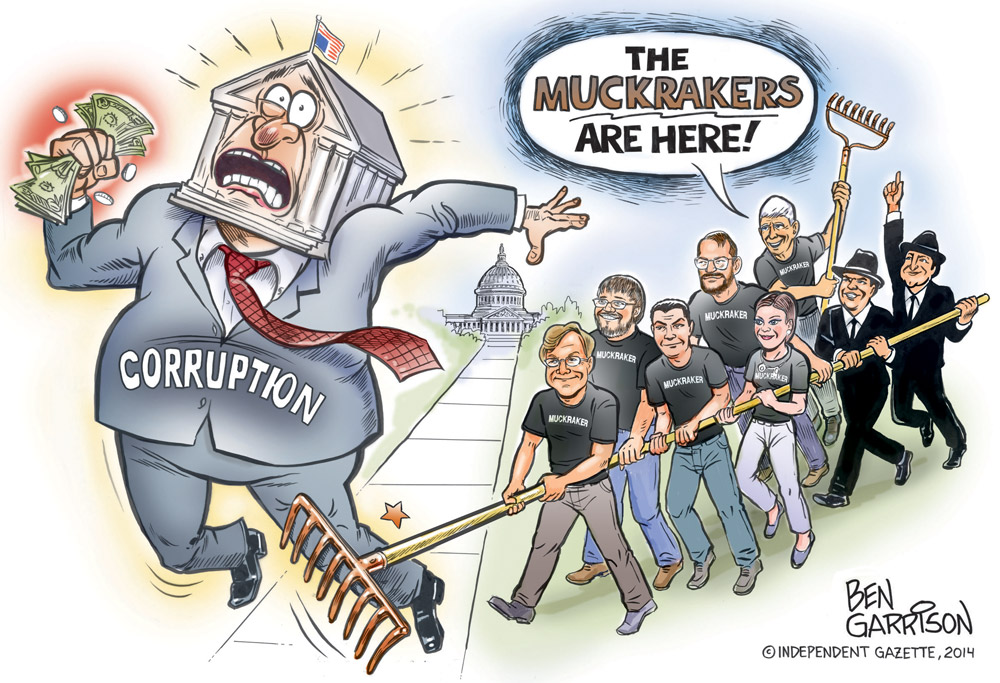
53
New cards
The goal of suffragettes like Susan B. Anthony, Carrie Chapman Catt, and Alice Paul was finally achieved when the ______________________ was ratified, granting women the right to vote in 1920.
19th amendment

54
New cards
An issue of importance to the Progressives was ____________________, and resulted in millions of acres of land being set preserved as national parks and forests.
Conservation

55
New cards
The ___________________ was created in 1913 and serves to stabilize the economy by controlling the amount of money in circulation and by setting interest rates.
Federal Reserve
56
New cards
The 18th amendment, which authorized ___________________ was a failure in the United States, and was eventually replaced by the 21st amendment.
Prohibition
57
New cards
America’s age of _________________ began with the Spanish-American War, and saw the United States become much more interested in establishing its influence in Latin America, Asia, and the Pacific Ocean.
imperialism
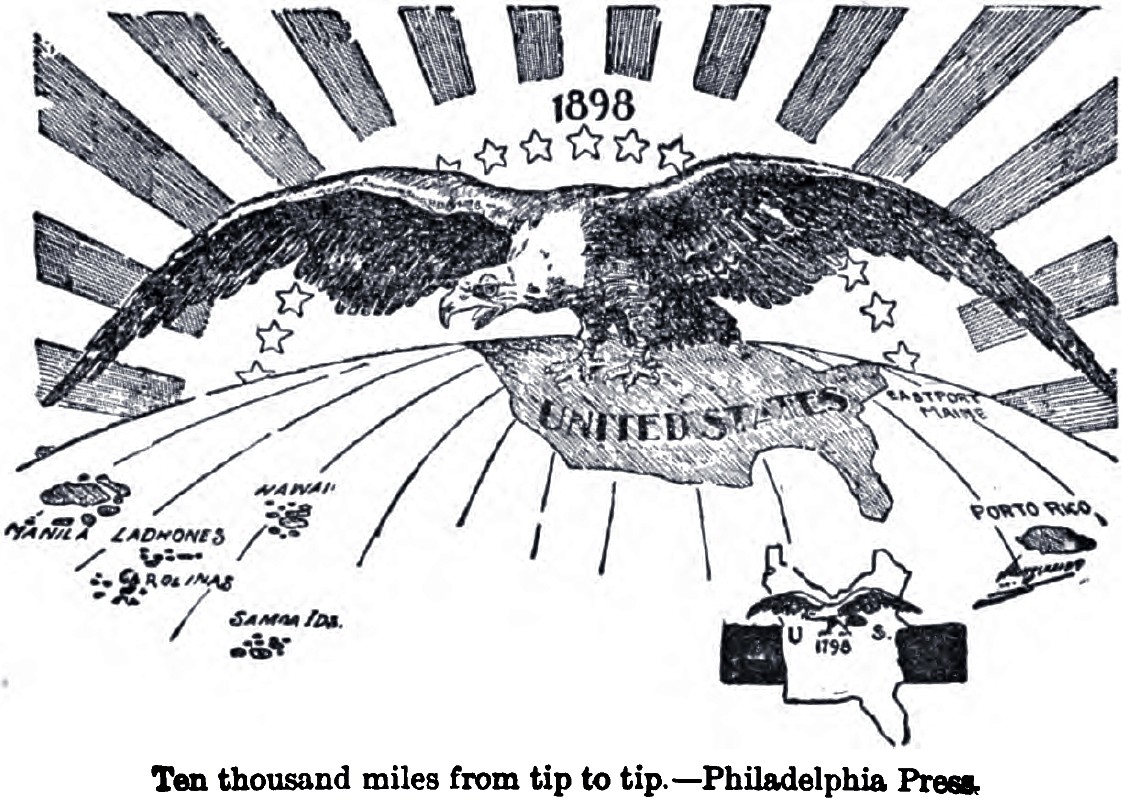
58
New cards
Denied access to the lucrative trading market in China by the European establishment of spheres of influence, the United States announced the __________________ in 1899, claiming that every nation had the right to trade equally in China.
Open Door Policy
59
New cards
A leading cause of U.S. entry into the Spanish-American War was ____________________, the practice of newspapers exaggerating events to increase their circulation.
yellow journalism
60
New cards
The United States constructed the ________________ across Central America to increase its ability to move warships between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Panama Canal
61
New cards
U.S. entry into World War I was influenced by a number of factors, like the Zimmerman Telegram, and also by Germany’s unrestricted use of submarines, which we believed violated the principle of ___________________.
Freedom of the seas
62
New cards
The “clear and present danger” rule towards free speech was established by the 1919 Supreme Court ruling in _______________________.
Schenck v. U.S.
63
New cards
President Wilson was unable to convince the United States Senate to ratify the _____________________ because a number of Senators were concerned about joining the League of Nations.
Treaty of Versailles
64
New cards
Assembly line production of the _______________ lowered costs to the point that most workers could purchase one in the 1920s, and led to the growth of suburbs.
Automobile
65
New cards
The conflict between Protestant fundamentalists and science over the teaching of evolution resulted in the ____________________ in Tennessee in 1925.
Scopes trial
66
New cards
Laws like the Emergency Quota Act and groups like the Ku Klux Klan are examples of _______________, the belief that native-born Americans are superior to immigrants.
nativism
67
New cards
The Great Migration of African-American to Northern cities during World War I led to the flourishing of African-American cultural achievement known as the _____________________ in the 1920s.
Harlem Renaissance
68
New cards
Risky practices like buying on margin helped lead to the ____________________ which many people consider the start of the Great Depression.
stock market crash
69
New cards
The economic catastrophe of the 1930s, known as the _____________________, was brought on by a growing gap between rich and poor and overproduction and underconsumption of goods.
Great Depression
70
New cards
President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s plan to fight the Great Depression was called the _______________, and led to creation of lasting programs like Social Security and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
New Deal
71
New cards
A major principle of the New Deal was the belief in _________________, which occurs when government spends more money than it makes in an attempt to stimulate the economy.
Deficit spending
72
New cards
After the NRA and AAA were declared to be unconstitutional, President Franklin D. Roosevelt announced his controversial _________________ plan, proposing to increase membership on the Supreme Court from 9 to 15.
Court packing
73
New cards
Residents of the Great Plains migrated to California in the 1930s because of the _____________.
Dust Bowl
74
New cards
President Franklin D. Roosevelt tried to improve relations with Latin America in the 1930s by adopting the _____________________, which rejected the right of the United States to intervene in another country’s internal politics.
Good Neighbor Policy
75
New cards
Passed in the 1930s, the _________________ attempted to keep the United States out of possible European conflicts by forbidding the U.S. to trade with any country at war.
Neutrality Acts
76
New cards
After World War II started in Europe, the United States became the arsenal of democracy, providing military equipment to Great Britain and the Soviet Union under the __________________, passed in 1941 replacing the previous policy of cash-and-carry.
Lend-Lease Act
77
New cards
The symbol of women doing their patriotic duty of working in homefront weapons factories during World War II was ____________________.
Rosie the Riveter
78
New cards
The limiting of consumer goods like gasoline, rubber, and butter during World War II is called _____________.
rationing
79
New cards
After World War II, the __________________ established the precedent that leaders were accountable for their wartime actions.
Nuremburg trials
80
New cards
Japanese internment was declared to be valid in the 1944 case ____________________.
*Korematsu v. U.S.*
81
New cards
By providing benefits like a free college education and low-interest mortgage loans, the ________________ changed the way that the United States rewards members of the military for their service.
G.I. Bill
82
New cards
An initial action of containment is the ____________________, in which the United States gave $400 million in aid to Greece and Turkey to aid their fight against Communist influence.
Truman Doctrine
83
New cards
The massive aid program from 1948-1952 in which the United States helped to rebuild Western Europe in order to keep it from falling under Communist influence is called the ______________________.
Marshall Plan
84
New cards
The United States broke its policy of avoiding peacetime military alliances when it helped to create _____________ in 1949, linking Western European countries against the Communist threat.
NATO
85
New cards
The Berlin Airlift, Korean War, and the formation of SEATO are all actions that were taken by the United States under the policy of ________________, or attempting to limit Communist expansion.
containment
86
New cards
The era known as __________________ refers to the anti-Communist hysteria of the United States in the 1950s.
McCarthyism
87
New cards
The largest federal works project in American history, begun in 1956, was the _____________________, designed to link together American cities and military bases.
Interstate Highway System
88
New cards
School desegregation was order by the Supreme Court in the 1954 case ________________, which overturned the *Plessy v. Ferguson* doctrine of “separate but equal.”
Brown v. Board
89
New cards
President Eisenhower was obligated to send federal troops to _______________, Arkansas in 1957 in order to protect 9 African-Americans attempting to desegregate the public school system.
Little Rock
90
New cards
President John F. Kennedy showed restraint in his handling of the ____________________, which was resolved by the Soviet Union withdrawing nuclear missiles from Cuba.
Cuban Missile Crisis
91
New cards
The humanitarian program established during the Kennedy administration that sent college-age Americans to developing nations is called the _____________________.
Peace Corps
92
New cards
President Lyndon Johnson’s ________________ was series of programs designed to use government programs to end poverty and racial discrimination in the United States.
Great Society
93
New cards
The 1963 Supreme Court ruling in _____________________ guaranteed the right to an attorney for all Americans accused of a crime.
Gideon v. Wainwright
94
New cards
The _____________________ case in 1966 established that a person accused of a crime must be read their rights at the time they are arrested.
Miranda v. Arizona
95
New cards
An important gain for the women’s rights movement was the passage of ___________, which guarantees that men’s and women’s programs in schools must be funded equally.
Title IX
96
New cards
Richard Nixon pursued the foreign policy of ______________, which represented easing the tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union, and featured a nuclear arms limitation treaty called SALT I.
Détente
97
New cards
The biggest political scandal in American history was the _______________ scandal, which led to President Nixon’s resignation rather than facing an impeachment trial.
Watergate
98
New cards
President Lyndon Johnson was given a “blank check” to escalate the Vietnam War when Congress passed the ________________________.
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution
99
New cards
The inflation of the 1970s was due in large part to the ____________________, in which Middle East countries placed an embargo on oil shipments to the United States.
OPEC oil crisis
100
New cards
President Jimmy Carter’s greatest foreign policy achievement was the signing of the ____________________, which brought about peace between Egypt and Israel.
Camp David Accords