Bio 211 Exam 1
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
The Scientific Method, Research Question, Hypothesis, Prediction
Referred to as "Trial and Error"
1) Problem - what grabbed your curiosity?
ex. box with unknown content, decades of observation; piecing together mechanisms, a metaphor for the atom
2) Research question - what am I trying to prove or better yet disprove?
3) Hypothesis and Prediction
ex. Smaller than the box? Is it one object? Multiple objects? Is it light, hard, papery, or noisy?
4) Test each hypothesis (What does this mean?)
ex. continuously disprove; is it a stuffed animal or perhaps a ball wrapped in paper?
5) Evaluate the results
a. The hypothesis is supported
b. The hypothesis isn't supported
6)Continuing tests until...
7)Theory
REALM
R) Repetition and repeatability
- Every condition is easily reached
- Repeated often
E) Experimental Control
- Constant that is measurably consistent
- Used as a constant to compare to
A) Adequate Sample Size
- Amount of participants in a study
- 30 is the magic number "minimum"
L) Limitation of factors
- Very difficult to limit factors
- Indirect causes
Ex. Physiology is a problem in drug studies
M) Measurable Results ( Qualitative or Quantitative )
ex. Pain Scale
Data
Observational DATA
Data is only as good as the experimental design
Theory
After thousands of experimental data correlate and remain cohesive, then does the information become theory
John Dalton
Gold Foil Experiment
1800s
Discovered the nucleus
Element
A atom that contains subatomic particles; protons, neutrons, and electrons; the type of element is determined the number of protons found in atomic nucleus
Atom
A singular particle of an element
Subatomic particles
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
Compound
a structure that contains more than one molecule
ex. Water (H2O)
Atomic Nucleus
consists of protons and neutrons and is located in the center of the atom
Atomic Symbol
the letter/letters that represent an element
Ex. H for Hydrogen
He for Helium
Au for Gold
Atomic Number
The # of protons found in an element
used to determine the order in which elements are arranged on the periodic table of elements
Mass Number
The number of protons and neutrons found in an element
Isotopes
A deviation in the number of neutrons in relation to protons
Ex. 39 protons and 40 neutrons is an isotope because there is one more neutron than there is protons
Atomic Shells
The electron cloud encompasses the nucleus with electrons
Orbitals
The flight pattern of an electron, essentially a 3d map of where the electron could be; S, P, D, and F orbitals are used to describe it’s particular shape.
Valence Shell
The outer most level in an atom’s shell; typically used as a means of determining the reactivity of an element, for example sodium is an extremely reactive element because it has a valence shell consisting of 1 electron which allows it to react to many elements.
Octet Rule
It is typical for valence shells to have a capacity of 8 electrons which would render it complete and lower it’s reactivity.
Covalent Bond
Covalent bonds are the sharing of electrons, typically consists of elements on the right side of periodic table.
the amount of bonds indicate the strength
h-h weakest (single)
o=o middle (double)
n-=n strongest (triple)
Hybrid orbital geometry
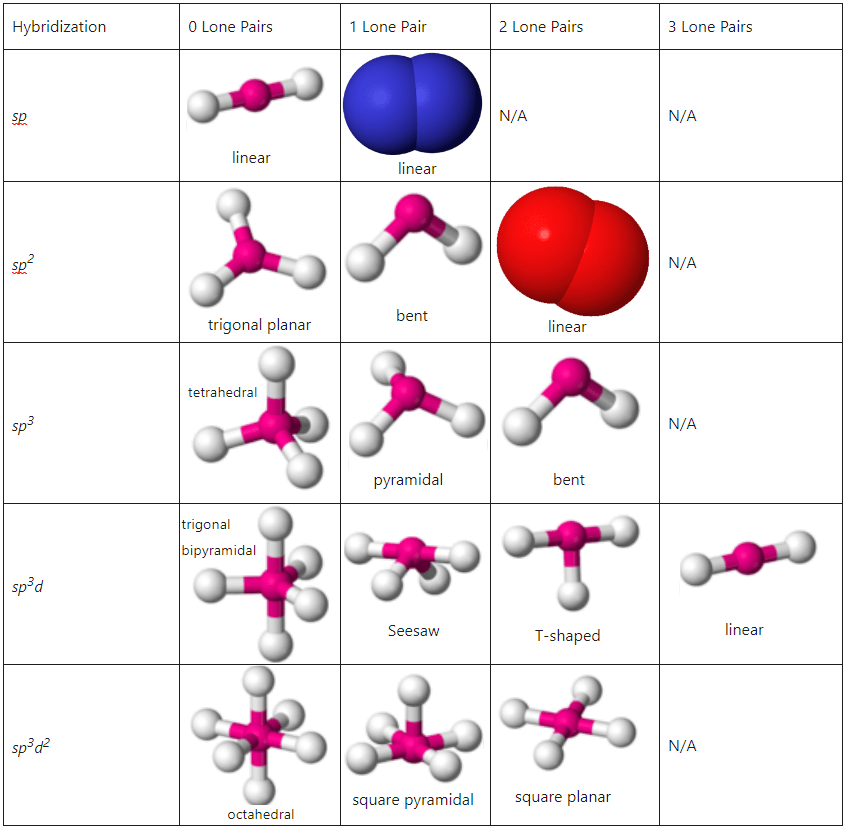
Tetrahedral
Ex. Carbon centers
Molecular Shape
Where on one atom another can bond is geothermic and specific
ex tetrahedral is a 4 sided pyramid
Ionic Bond
Electron Robbery, an electron(s) is taken from another element in order to complete it’s valence shell
ex. Sodium Chloride composes of Na and Cl in which the electron is taken from the sodium and put into the valence shell of the chlorine causing Na to become Na+1 (the +1 indicating a positive charge due to the number of protons being greater than electrons) and Cl to become Cl-1 (the -1 indicating a negative charge due to the number of electrons being greater than protons).
Hydrogen Bond
Colloquially referred to as FON bonds
1) Hydrogen is covalently bonded to F,O,N
2) That H becomes weakly attracted to another F,O,N
3) Polar covalent bonds - a result of partial
Van Der Waal Interactions
1) Long polymers - chains of carbon
2) temporary charges in regions, fluctuates
Potential Energy
the amount of energy stored in the bonds of molecules
PE = mgh
m= mass
g= gravity
h= height
Kinetic Energy
Energy associated with objects in motion; movement
KE=1/2MV²
Water
H2O, universal solvent
Hydrophilic
Attracts water
Hydrophobic
Repels water
Polar/Non-Polar
Polar is distinctly negative and positive (indicating polar ends, think north and south pole)
Nonpolar has no negative or positive ends, uniformly charged.
Ionic/Non-Ionic
Ionic - cation and anion, cation being positive and anion being negative; refer to ionic bonding.
Non-ionic - covalent bond
Cohesion
Waters ability to stick to itself
ex. surface tension
Adhesion
Waters ability to stick to surfaces
ex. capillary action
pH scale
amount of hydronium and hydroxide ions found in a solution
Acidic, Basic, Neutral
Acidic 1-6 (high hydrogen ion concentration)
Neutral 7 (equal amount)
Basic 7-14 (high hydroxide ion concentration)
Hydrogen Ion (H+)
Hydrolysis breaks water into H+ and OH- ions
Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
Hydrolysis breaks water into H+ and OH- Ions
Buffer
A solution that does not change in pH when adding an acid or base. Reverse acidity or reverse alkalinity.
Solution, Solvent, and Solute
Solution is a mixture of a solvent and solute ex. salt water
Solvent is what the solute is dissolved in ex. water
Solute is what is being dissolved, ex. salt
Dissolve
Solute → Solvent = Solution
Molecular Formula
The use of element symbols to write the composition of a molecule; h2o is the molecular formula for water
Structural Formula
A graphic of what a compound looks like
ex. H2O is the molecular formula
H-O-H is the structural formula
Organic Compounds
Only produced by living things
contains carbon atoms
typically composed of C,H,O,N,P, and S
highly variable in size and shape
Hydrocarbons
Typically referred to as the skeleton
made of carbon and hydrogen
it is the simplest of organic compounds
are hydrophobic
ex. H-C-C-H
Isomers
Constitutional isomers - also referred to as structural isomers; contain the same molecular formulae but different connectivity.
Ex. H-C-C-F vs C-F-C-H
Stereoisomers - Same type of bonding but different spatial positions.
a diastereomer is a change in one or more chiral centers but not all
R, R, R → R,S,R→D
R,R,R → S,S,S→EN
Meso compounds have complete changes but are identical in the molecular formula
forward, forward vs back, back
Ex. Enantiomers are mirrored over a chiral center
Configurational (Geometric) - bonds that are not easily interconverted, meaning they are stable; can only be changed via breaking bonds
“Cis” (Z) isomer
always diastereomers
same side
=
“Trans” (E) isomer
always diastereomers
opposing
/
Chiral Compounds
enantiomers, mirror image molecules
a chiral center
asymmetric carbon
Louis Pasteur
-tartaric acid salt test determined that there was enantiomers based off of optical activity
Optical Activity
“d” = “+” right form
“l” = “-” left form
racemic mix - no optical activity
Functional Groups
refer to worksheets, organic compounds
Polymer
a chain of repeating monomers
ex. starch is a chain of glucose, a monomer
Monomer
basic unit
ex. glucose
Dehydration Synthesis
H+ and OH- are attracted to each other at the ends of their chain, this leads to them bonding to form H2O which is separated from their respective chains causing them to merge
Hydrolysis
Water is constantly in motion as it is a liquid, as such hydrogen and hydroxide is constantly created as a result of water breaking apart.
Simple Carbohydrate
simple sugars
ex. glucose
Complex Carbohydrate
complex sugars
ex. starch
Glycosidic Linkage
Oxygen between monomers
Mono, Di, Oligo, Poly
Mono - One
Di - Two
Oligo - 2<x<10
Poly - more than x>10; massive numbers
Saccharides
fancy word for sugar
Lipids
macromolecule that encompasses triglycerides, sterols, and phospholipids; they do not contain a monomer thus making them NOT POLYMERS; their function revolves around moving and storing energy, hormones, and nutrient absorption.
Triglycerides
Consists of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains
Ester linkage
Carboxyl group in the fatty acid chain is attracted to the glycerol through the hydroxides along the side which results in dehydration synthesis
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
Glycerol is an alcohol 3-C
Fatty acid chains are hydrocarbons with a carboxyl end
Both combine to form triglycerides
Saturated vs Unsaturated Fats
Saturated means that the carbons are single bonded to one another meaning that their structure is linear
ex. butter
Unsaturated means that one or more carbons are double bonded to each other which causes their structure to become bent
ex. olive oil
Sterols
4-carbon ring structure
cholesterol
steroid hormones
function involves
1) cell membranes
2) chemical messengers aka hormones
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids
the most complex macromolecules
Amino Acids
structure is uniform
has an amino group NH2 and Carboxyl Acid group COOH
twenty different amino acids
10 essential/10 nonessential
Each amino acid has a specific side chain which changes its purpose
Peptide Bonds
C-OH + H-N → C-N + H2O (DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS)
Nucleic Acids
RNA and DNA
Ribonucleic Acid
and Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Nucleotides
Monomer of nucleic acids
consists of sugar
phosphate functional group
nitrogenous base (4 different molecules)
phosphodiester bonds
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
Phosphodiester Bonds
Phosphoric Acid bonding with Hydroxyl group
Phospholipids
Major component of cell membrane
Hydrophilic which means it is not a true lipid
Spontaneously assembles into bubbles or sheets
a phospholipid bilayer is a long sheet with water on both sides
Cell/Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane consists of a phospholipid that contains the cell components, and regulates what can enter or leave; this directly correlates to control over metabolic reactions.
Fluid-Mosaic
the cell membrane consists of integral proteins, fats, and other structure that increase the selective permeability
Integral Proteins
the channel through both layers of the bilayer for transport
Peripheral Proteins
the channel through one layer of the bilayer for transport
Cholesterol
A sterol, hormone
Lipid
function is to decrease the permeability of animal cell membranes
retain more water
only found in animals (excluding fish) due to exposure to the sun which causes dehydration
Transport Proteins
Acts as a channel or pore for material to enter or leave; integrated into phospholipid bilayers
ex. lock and key analogy
Membrane Permeability factors
Transport proteins can increase permeability
fatty acids that are unsaturated within the bilayer cause more permeability as there’s more space to enter
fatty acids that are saturated within the bilayer causes less permeability as there’s no gaps
Length is also a deciding factor as it is easier to cross a narrow river than a wide one
the more cholesterol the more gaps are filled which decreases permeability
Passive and Active Transport
Passive transport requires no energy; solutes move through cell membranes by themselves
Diffusion
a) diffusion is the movement from high concentration to low concentration
dialysis - solute through a membrane
hypertonic → hypotonic
osmosis - water through a membrane
hypotonic → hypertonic
b) facilitated diffusion
-solutes
-travels through a membrane transport protein
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Endocytosis is absorbance of material outside of the cell through the cell membrane
Exocytosis is the secretion of material found within the cell through the cell membrane
Robert Hooke
1665 oldest
discovered 1cm lens
the double lens method
etymology of cell was a result of thinking they looked like monk rooms (cells)
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
Made a better version of Hooke’s lens
made early microscope
looked at sperm
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Cell Theory
all living things are composed of cells
cells are the basic unit of life
cells can only reproduce from themselves
Prokaryotic
no nucleus
usually small
constitutes bacteria, unicellular
no organelles
Eukaryotic
contain a nucleus
usually the biggest
found in animals, plants, and fungi
organelles
little organ
Archaean
similar to bacteria
extremophiles
similar to eukaryotic genetic characteristics
Nucleus
the control center of the cell
contains the DNA
in the nucleus envelope is chromatin which then forms into chromosomes
nucleolus is where ribosomes are made
Rough ER
has ribosomes attached to it
transporting material such as proteins
Smooth ER
no ribosomes attached to it
transporting material such as proteins
Ribosomes
sourced from the nucleus
function is to synthesis proteins
Golgi Apparatus
referred to as the Golgi body
proteins are moved into it to be customized into usable shapes, adding lipids, or carbohydrates
Vesicles and Vacuoles
A vesicle is used to transport material such as protein
A vacuole are sac-like structure that stores different materials
Lysosomes
Garbage collectors
Filled with enzymes that break down faulty components
Peroxisomes
found free in the cytoplasm
play a role in metabolism
oxidation reactions
where cholesterol is made
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Cellular respiration creates ATP that provides energy
Cytoskeleton
What keeps the shape of the cell, includes microfilaments