final exam - virology (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes questions from all tests (that could be converted). Only half questions from ch 2 because there were missing questions on the key
Last updated 10:07 PM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
1
New cards
Which organisms can be infected by viruses?
All of them
2
New cards
True or False: Viruses are small enough to pass through a 0.2 micron filter
True
3
New cards
Do all viruses have envelopes?
No
4
New cards
What was a major advancement in virology that allowed us to examine the lifecycle of viruses?
Development of viral tissue culture
5
New cards
How far back in time did viruses originate
4 billion years ago
6
New cards
Viruses that are enveloped obtain this structure from which part or parts of the host cell?
Plasma Membrane
7
New cards
What proteinaceous structure connects the capsid to the envelope
Matrix
8
New cards
Highest to lowest order of the rank system
Realm, Order, Family, Genus, Species
9
New cards
Baltimore Classification System is based off of what viral component
Viral nucleic acid within the virion
10
New cards
What enzyme must all RNA viruses bring into the infected cell with them for the life cycle?
RNA-dependent RNA pol
11
New cards
In the Hershey-Chase Blender Experiments the S35-labled protein of the bacteriophage was found where in the progeny phages?
Not found
12
New cards
Strain
Genetically stable virus that differs from the parent strain phenotypically
13
New cards
Variant
Virus that contains mutations from the parental strain
14
New cards
Baltimore class that uses a reverse transcriptase
Class 6
15
New cards
Baltimore class that can immediately be translated by ribosomes
Class 4
16
New cards
Viral tropism
Types of cells that a virus can infect
17
New cards
Viral tropism is controlled by
Cell surface receptors
18
New cards
What percentage of the human genome consists of defunct endogenous retroviruses
10
19
New cards
What are some ways viruses resolve the competition between host mRNA and viral mRNA for translational machinery
degrading host mRNAs, contain elements in viral mRNA to increase affinity to ribosome, cleave and obtain host cell mRNA caps
20
New cards
What amendment did Fredricks and Relman make to Koch's and River's criteria for linking a virus to a particular disease
Detection of viral nucleic acids in diseased organs but not in unaffected organs
21
New cards
In a standard clinical virology laboratory setting, which techniques are routinely performed for rapid identification
elisa and pcr
22
New cards
Most antivirals are designed to impair which component of a virus
viral enzymes
23
New cards
What do cells do natural killer cells recognize
cells that show reduced expression of mhc I on their surface
24
New cards
What two major cell types can eliminate viral cells through apoptosis
Natural killer and CD8+ T-cells
25
New cards
Innate immunity
general non-specific defense against pathogens
26
New cards
secondary immune response
immunological memory
27
New cards
phagocytosis
uptake and killing of microbes
28
New cards
What do pathogen recognition receptors do
identify viral pathogens
29
New cards
What do Toll-like receptors do
they are sensors capable of detecting characteristics unique to a virus
30
New cards
Dendritic cells
Express high levels of mhc i and ii molecules and function as scouts to identify pathogens at the body's surfaces and mucosal sites
31
New cards
How do viruses evade host defense
mutate outer surface proteins, latency, inactivate cytokine signaling, inactivate immune cells
32
New cards
Major function of MHC II
presents peptides derived from engulfed viruses
33
New cards
What happens when ds-RNA-activated protein kinase (cellular altruism) is activated in a virally infected cell
Viral RNA degradation and host RNA degradation
34
New cards
Virally infected cell will present foreign antigens on where?
MHC I
35
New cards
Virally infected cells are recognized by which cell type?
CD8
36
New cards
If you were performing a Viral Detection ELISA, what would be coated on your 96-well dish
Antibody specific for viral pathogen
37
New cards
How are live-attenuated viruses produced
a virus is immediately repeatedly cultured in nonhuman cultured cells or animals
38
New cards
What results would indicate the highest viral levels in a RT-PCR
Ct of 10
39
New cards
Prevalence
total number of cases
40
New cards
Incidence
new cases
41
New cards
Toll-like receptors recognize viral
RNA or DNA
42
New cards
What proteins are secreted following the activation of TLRs
cytokines
43
New cards
Three corners of the epidemiological triangle
host, agent, environment
44
New cards
longitudinal study
study that examines individuals over time
45
New cards
Once ingested polioviruses initially invade which two tissues
peyers patchers or tonsils
46
New cards
what percentage of cases are asymptomatic in polio
95%
47
New cards
Where does the polio lifecycle occur
the cytoplasm (Remember, +ssRNA)
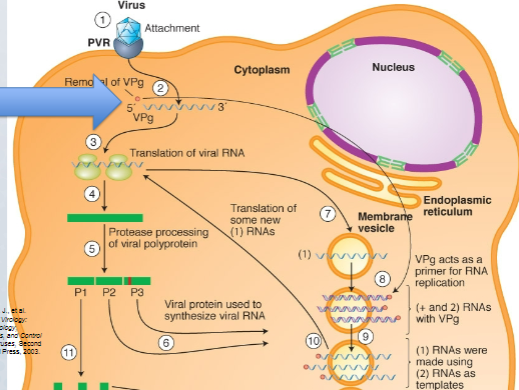
48
New cards
What would happen in the rna genome of poliovirus was transfected or delivered directly in to mouse cells
Rna genome would be translated by host ribosomes into a polyprotein
49
New cards
IRES stands for
Internal Ribosomal entry site
50
New cards
What does the IRES do
Permits translation of poliovirus RNA without the need for a 5' 7-methyl G cap
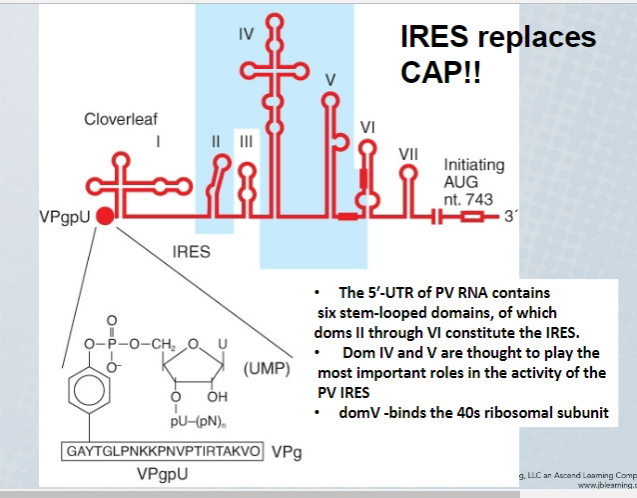
51
New cards
What attributes of the IRES facilitates and enhances its function
Contains extensive regions of secondary stem-loop structures binding to translation factors
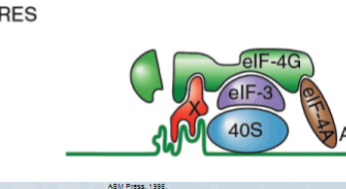
52
New cards
A poliovirus with a mutated VPg would be unable to
initiate replication
53
New cards
The poliovirus 2A protein has numerous functions that includes a role in
polyprotein processing and inhibiting host cell transcription
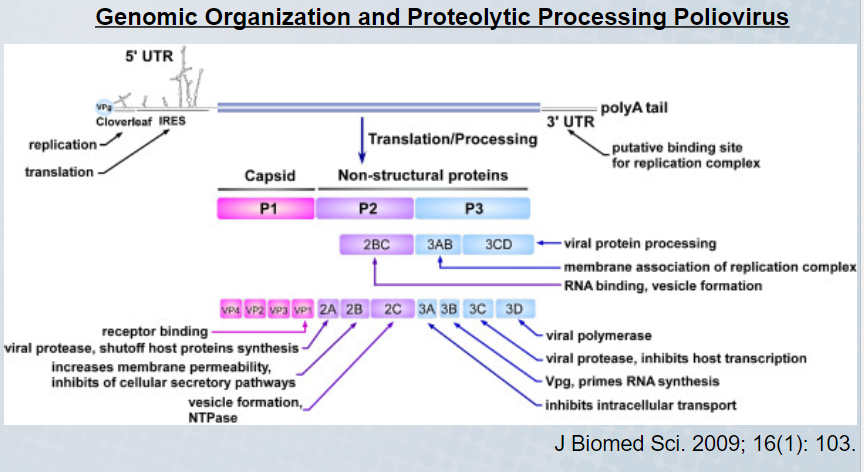
54
New cards
What poliovirus polypeptide is structural
VP4
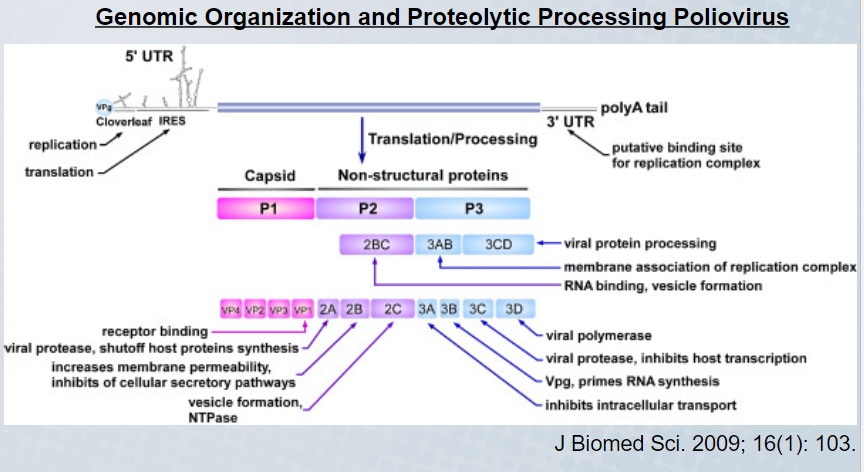
55
New cards
What poliovirus polypeptide is a polymerase
3D
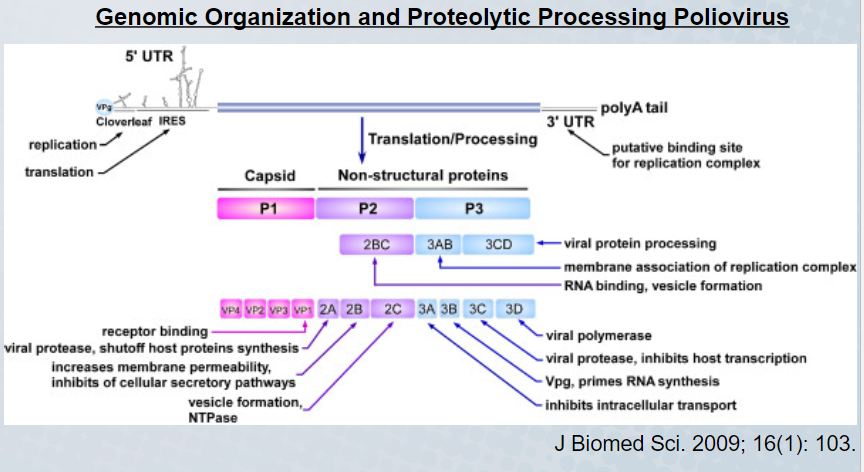
56
New cards
In poliovirus the cloverleaf structure at the 5' end is critical for binding what factors to initiate replication
VPg and 3D
57
New cards
Why is the Sabin vaccine no longer used in the US
potential risk of contracting paralytic polio
58
New cards
What receptor on the cellular surface is bound by the H glycoprotein of the influenza virus
sialic acid
59
New cards
Why do influenza viruses not need to code for or contain a protease
mRNA molecules are produced that code for a single protein
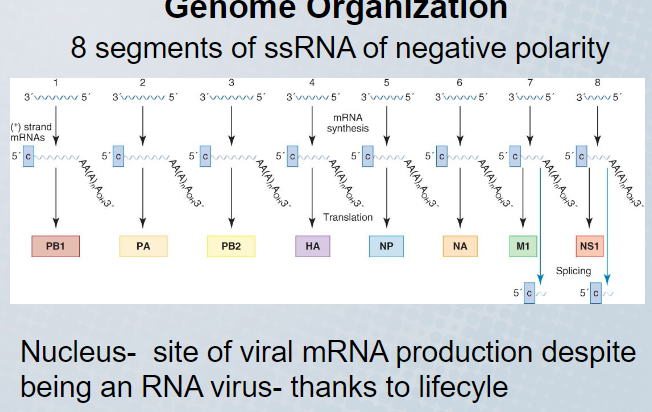
60
New cards
Influenza A host range
humans, pigs, horses, birds, and marine mammals
61
New cards
Which influenza is responsible for pandemics
A
62
New cards
Who is the sole host of the influenza B virus
humans
63
New cards
Where does uncoating and membrane fusion of influenza take place
inside endosomes
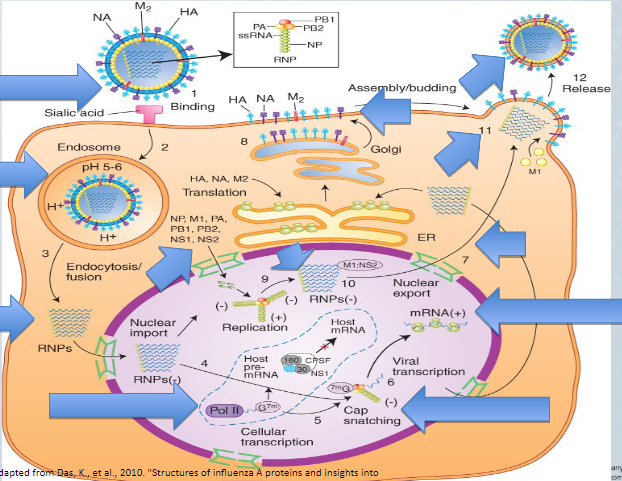
64
New cards
Which influenza viral protein is involved in viral shedding
Neuraminadase
65
New cards
Which influenza protein functions as an ion channel
M2
66
New cards
T or F; Antibodies against hemagglutinin function would reduce virion release from infected host cells
False
67
New cards
Hallmark clinical characteristic of rabies
hydrophobia
68
New cards
Standard and immediate post-exposure treatment of a recent bite wound from an animal with rabies virus can include the following
immunoglobulin treatment and vaccine administration
69
New cards
Rabies virus replicates within the ______ following transport from the ______
Cell body; axon
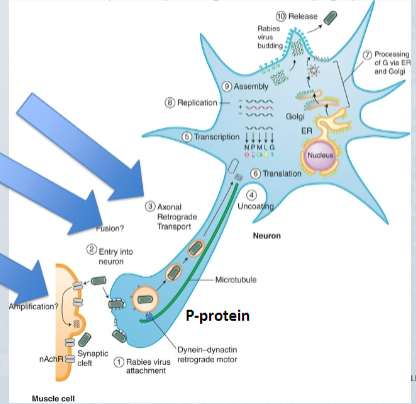
70
New cards
How does rabies virus escape detection from the immune system
RVP antagonizes IFN responses
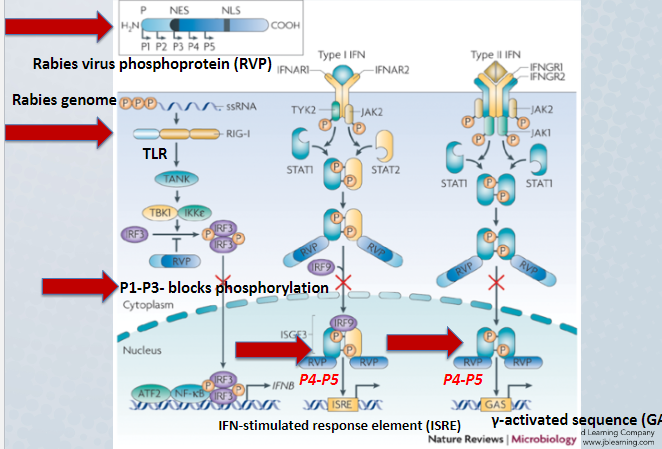
71
New cards
A rabies virus with a nonfunctional L protein would primarily be unable to
Cap or polyadenylate viral mRNA
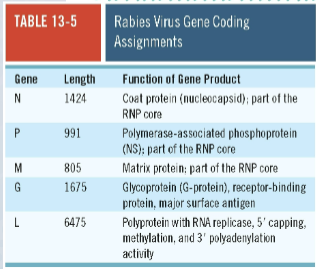
72
New cards
which of the following is a known receptor for rabies virus entry
nAch receptor
73
New cards
Where is the nAch receptor located in the neuromuscular junction
postsynaptic junction
74
New cards
Which animal propagates the most human rabies related deaths in Asia
dogs
75
New cards
Which animal propagates the most human rabies related deaths in the US
bats
76
New cards
Poxvirus genome
linear dsDNA, ITRs at the end of the genome, encodes at least 200 genes. dumbbell shaped core with nucleic acid, virion contains lateral bodies with various enzymes
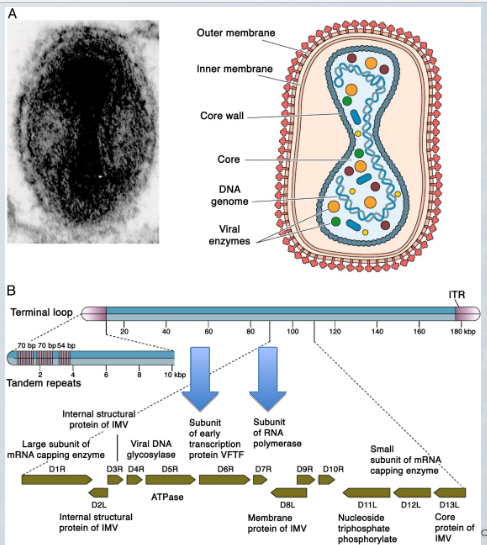
77
New cards
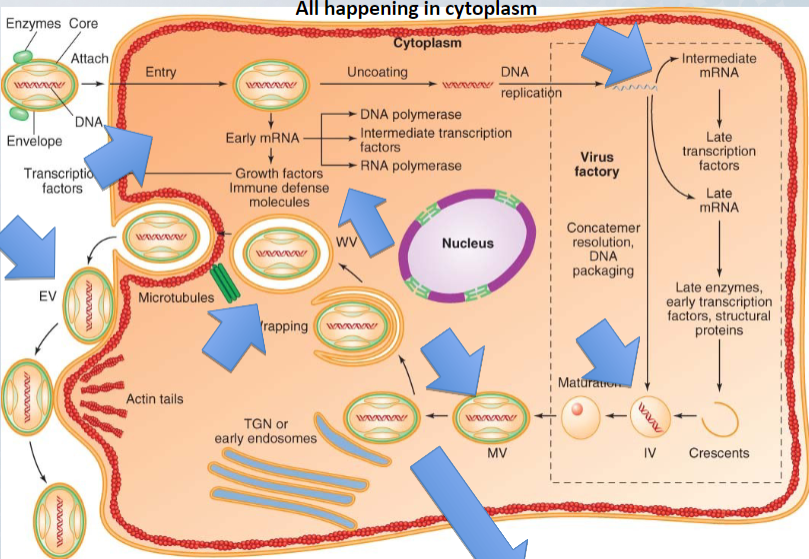
Where does the poxvirus replication occur
cytoplasm, dependent on viral pol
78
New cards
MV poxvirus
=Mature virion; 2 membranes
79
New cards
EV poxvirus
Extracellular virion; 1 membrane
80
New cards
Poxvirus genomes code for which enzymes
dna dependent rna pol
VETF
capping enzymes
methylating enzymes
VETF
capping enzymes
methylating enzymes
81
New cards
poxvirus gene is regulated by
viral promoter regions
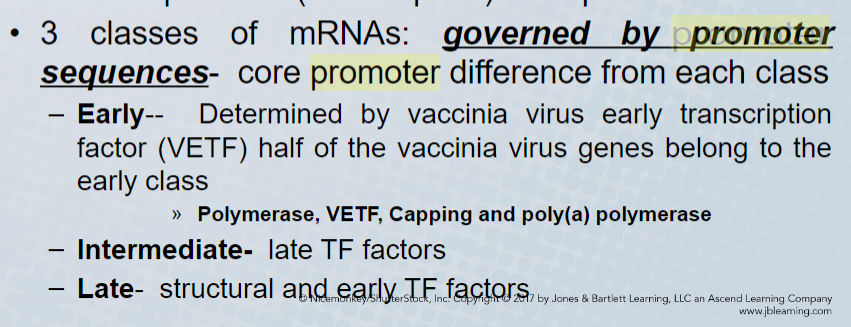
82
New cards
Early mRNAs of poxvirus code for
viroreceptors and virokines
83
New cards
late mRNAs of poxvirus code for
early transcription factors and structural proteins
84
New cards
poxvirus immune evasion
inhibit complement, inhibit cytokines, inhibit chemokines, and block cytokine receptors
85
New cards
why do pustules and vesicles appear in poxvirus
virus invades the capillary epithelium of the dermal layer of the skin
86
New cards
Where is the distribution of pustules and vesicles in poxvirus
arms and face
87
New cards
why was variola a good candidate for global eradication
narrow host range, genetically stable, surveillance of the disease was easy, disease is acute and self-limiting
88
New cards
Dryvax vaccine
vaccinia virus originally derived from horsepox, cultured on the skin of calves and freeze dried
89
New cards
TPOXX
blocks action of wrapping protein
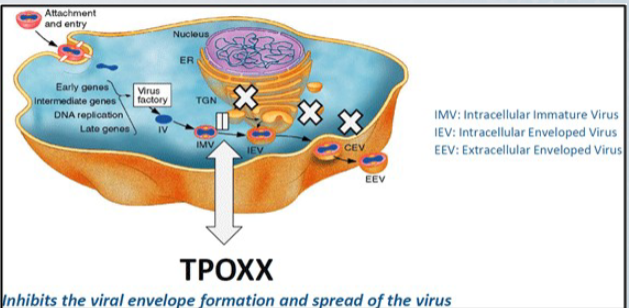
90
New cards
HHV2
genital herpes
91
New cards
HHV1
Mouth cold sores
92
New cards
HHV4
EBV
93
New cards
HHV5
CMV
94
New cards
herpesvirus lytic infection is in which cells
epithelial
95
New cards
herpes latent infection in which cells
neuronal
96
New cards
Herpesvirus establishes latency by:
LAT exon expression, microRNA species limit HSV early gene expression, virus persists as an episome
97
New cards
HSV-2 establishes latency where
sacral ganglia
98
New cards
HHV3 establishes latency where
spinal nerves
99
New cards
reactivation of herpesvirus is associated with
physical and emotional stress, UV exposure, pregnancy
100
New cards
Receptor for herpes
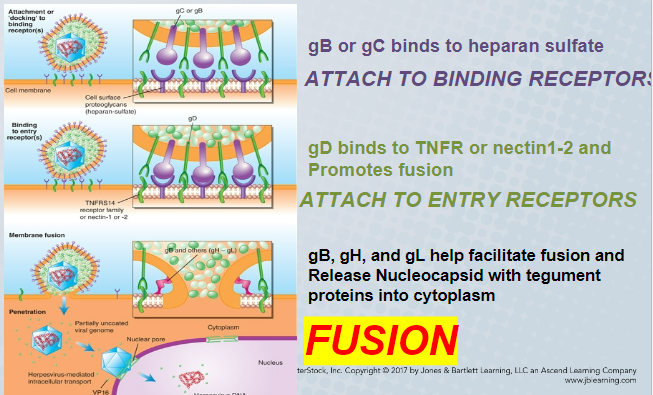
heparan sulfate