Social Psych Lecture 26 - Social Influence III
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Group Polarization
a group-produced exaggeration of members’ preexisting tendencies
3 features:
Refers to average tendency, not split in group
Whole group becomes more extreme in initial direction
Doesn’t work if a dissenter present
How Does Group Polarization Occur
Two processes:
Social comparison
extreme positions in favorable direction viewed as better (normative influence)
Mutual persuasion
members bring new, persuasive information and arguments (informational influence)
Groupthink
group members share such strong motivation to achieve consensus that they lose the ability to evaluate alternative points of view critically
Based on historical examples: Pearl Harbor, Bay of Pigs
Condition Leading to Groupthink
Highly cohesive group
Group isolated from contrary opinions
Group led by dominant leader who makes his/her wishes known
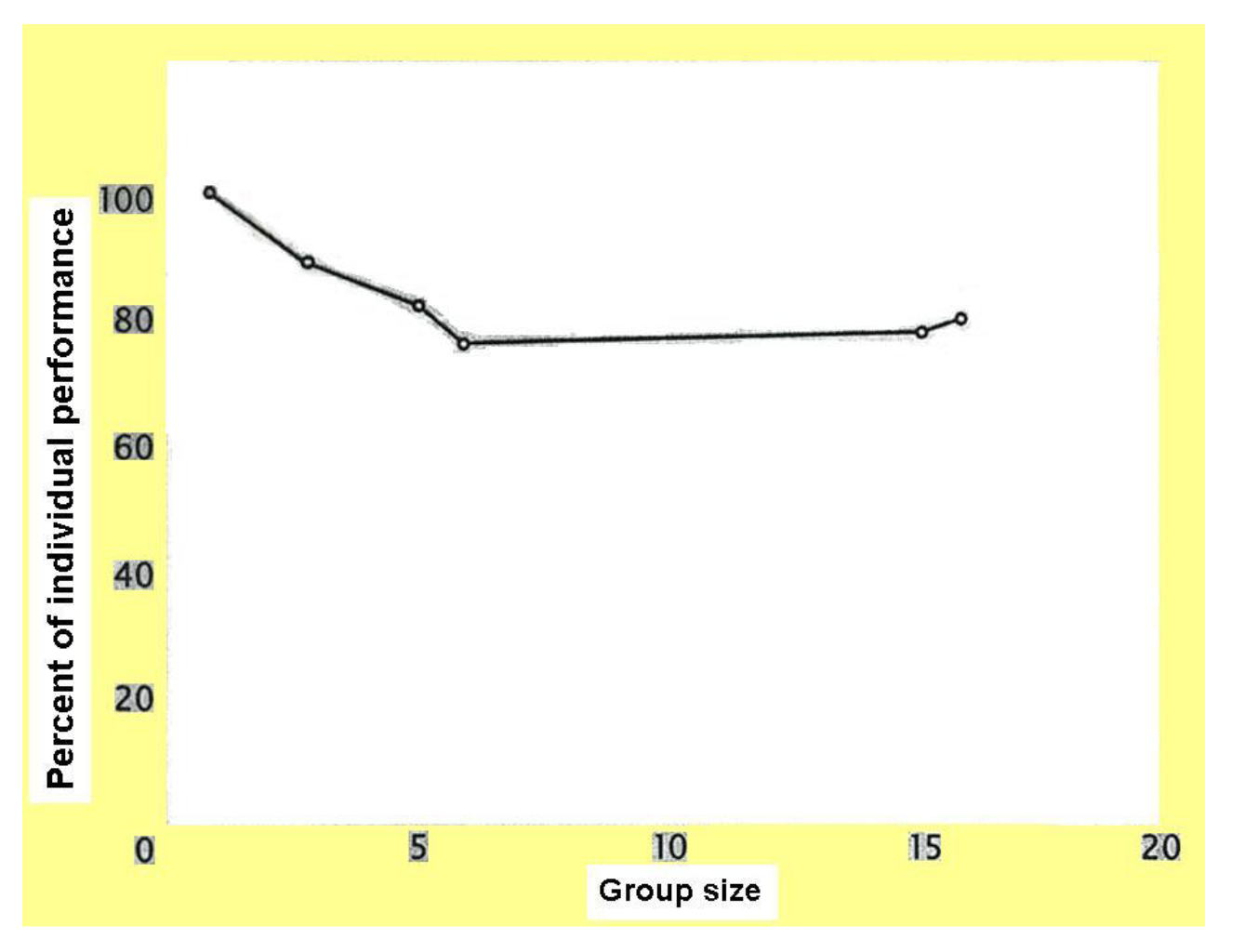
Social Loafing
-
Additive task
a task in which each member performs the same (or similar) duties and the final product is the sum of all contributions
Example: football team executing a play, factory workers making a product
Social loafing
tendency for people to exert less effort when they pool resources toward a common goal (than when they are individually accountable)
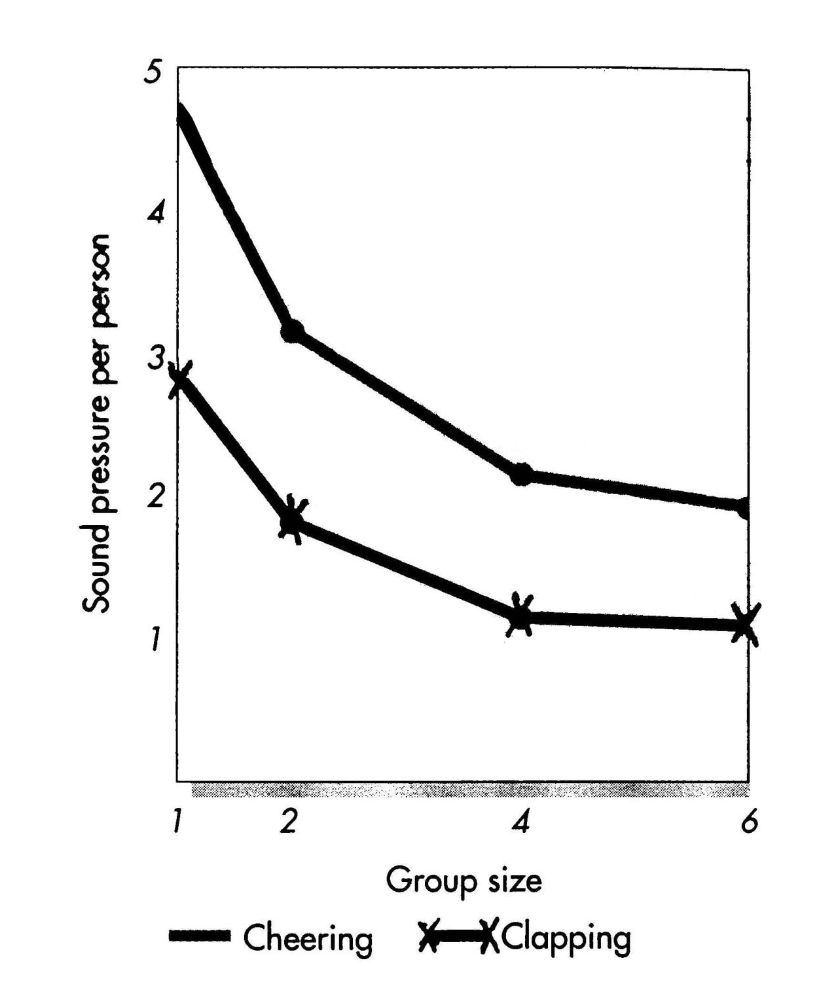
Latane et al (1979)
Subjects wore headphones and were blindfolded
Told would hear cheering/clapping; task was to make same noise as loudly as possible
Conditions:
Control (alone)
Two group
Four group
Six group
Results
More results
Factors that Reduce Social Loafing
Less likely when:
Contribution of each member is identifiable
Example: football film study
Task is challenging, interesting, or meaningful
Amish example
Group performance rewarded/punished
Other group members are one’s friends
Deindividualization
loosening of normal constraints on behavior when people in a crowd or their identity is concealed
Leads to increase in impulsive acts
Leads to increase in deviant acts
Conditions Promoting Deindividualization
Anonymity
Focusing attention away from self
Johnson & Downing (1979)
Told task was to recommend increase or decrease in shock level for another subject (confederate)
Clothing conditions:
KKK robe
Nurse outfit
Deindividuation conditions:
Deindividuation (face covered)
Control
Results
DV: increased or decreased shock (up to three levels in either direction)
Results:
KKK condition, no hood = +0.75
Nurse condition, no hood = -.30
KKK condition, hood = +0.97
Nurse condition, hood = -1.6
Gergen et al (1973)
Four male and four female subjects put in room for one hour
No rules; won’t see each other after study
Two conditions:
Control (lights on)
Deindividuation (lights off)
Results
Talking: Control condition talked more
Touching others: 0% touched others in control condition; 90% touched others in deindividuation condition
Hugging/kissing: 0% hugged or kissed in control condition; 50% hugged/kissed others in deindividuation condition