Conjunctiva
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
conjunctival cyst
fluid-filled sac on the conjunctiva
also known as inclusion or retention cyst
conjunctival concretions
deposits of mucous and calcium rubbing against epithelial cells
what causes conjunctival nevus
benign proliferation of melanocytes on the conj
what is diagnostic for a conjunctival nevus
inclusion cysts within the lesion
what is PAM
primary acquired melanosis
unilateral acquired pigmentation with indistinct margins common in elderly white people
prognosis of PAM
can be benign but has malignant potential
30% progress to melanoma
biggest risk factors of PAM becoming malignant
increased vascularity
increased growth
what causes conjunctival melanoma
uncontrolled proliferation of melanocytes on the conj
who gets conjunctival melanoma
almost exclusively caucasians around 50+
where do conjunctival melanomas arise from
most (50-75%) arise from PAM
some arise from conjunctival nevi
most important risk factor for progression to malignant conjunctival melanoma
thickness of lesion
most common site of metastasis of conjunctival melanoma
liver
most common conjunctival neoplasia in the US
CIN (conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia)
is CIN malignant
CIN is premalignant
what can CIN progress to
squamous cell carcinoma
how does CIN present
elevated gelatinous mass with neo
10% are keratinized
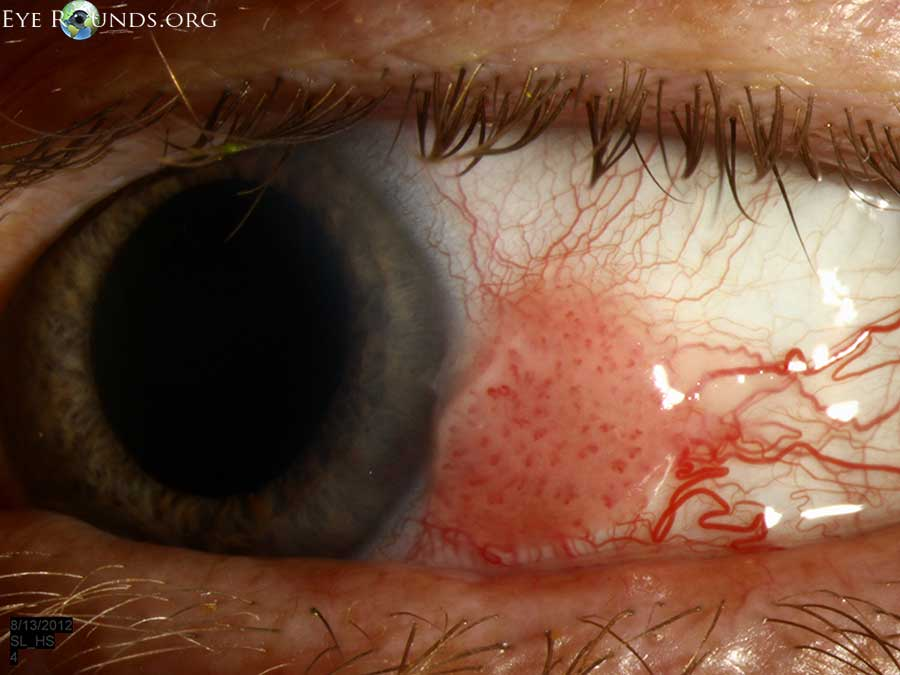
where are most CINs located
limbus
how does presentation of CIN differ from conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma
SCC usually has a feeder vessel

what is a pyogenic granuloma
benign, pedunculated, red, vascular lesion of palpebral conj from trauma or chronic irritation
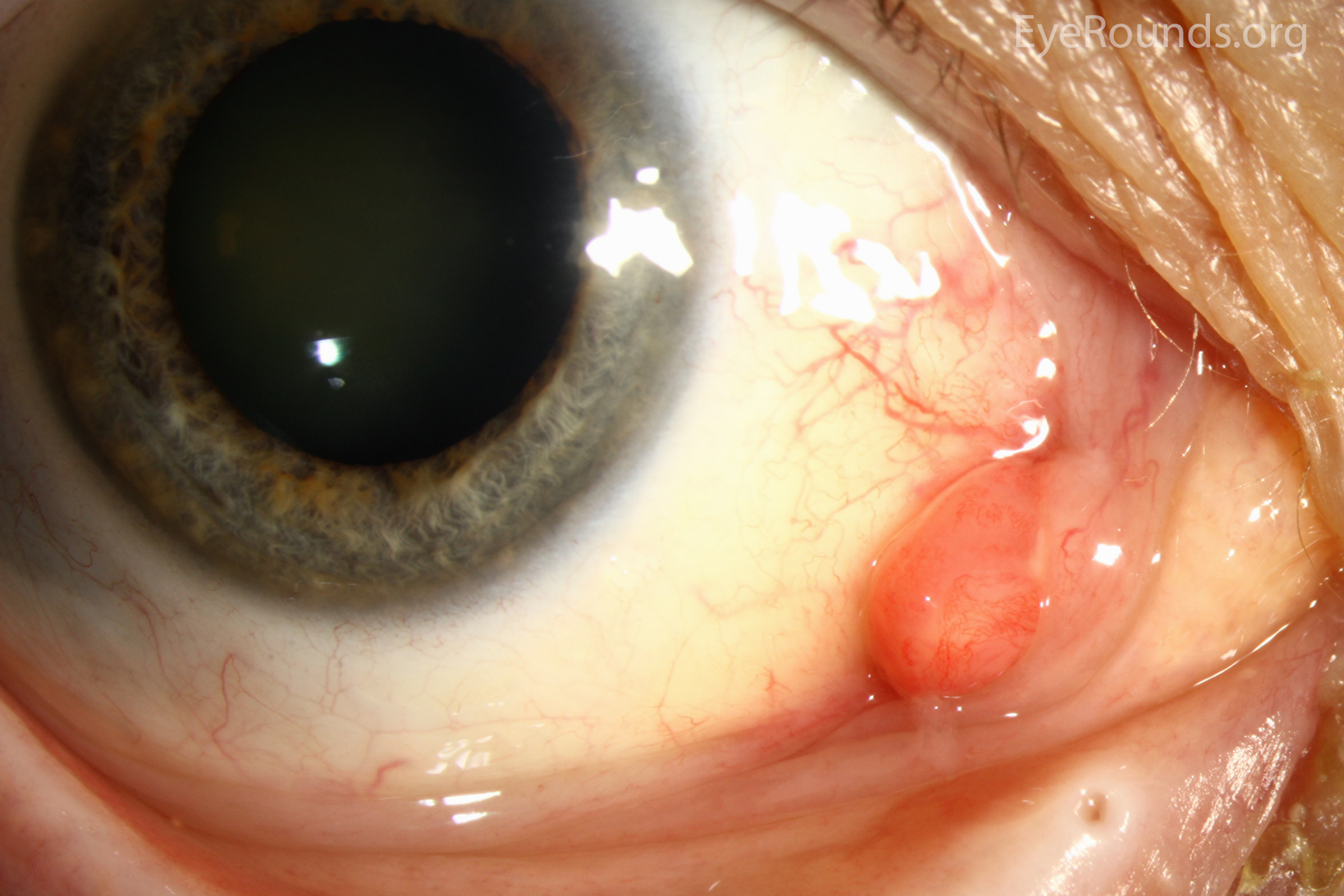
conjunctival granuloma
inflamed area on the conjunctival stromal tissue
can be from foreign bodies, trauma, infection, or systemic conditions
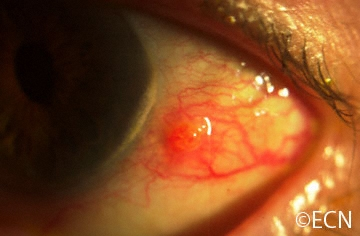
what age group most commonly gets bacterial conjunctivitis
kids
extremely rare in adults
what is the most common cause of bacterial conjunctivitis in kids
haemophilus influenzae
what is the most common cause of bacterial conjunctivitis in adults
staph aureus and s. epidermidis
s. aureus is catalase and coagulase positive
presentation of bacterial conjunctivitis
acute redness that starts in one eye and goes to both
FBS and lids stuck together
important that onset is acute
how long do symptoms last in bacterial conjunctivitis
can last up to 10-14 days
discharge in bacterial conjunctivitis
mucopurulent
can also be purulent
what is the most common cause of bacterial conjunctivitis and why
s. aureus
high association with blepharitis that can transfer to conjunctiva
what causes gonococcal conjunctivitis
neisseria gonorrhoeae
STD
what is used to diagnose gonococcal conjunctivitis
thayer-martin agar (chocolate agar)
what will a gram stain for gonococcal conjunctivitis look like
gram negative intracellular diplococci on chocolate agar (thayer-martin)
what is thayer-martin agar used to diagnose
chocolate agar
cultures for n. gonorrhoeae and h. influenzae
Hershey’s and Nestle chocolate
gonococcal conjunctivitis presentation
hyperacute onset of severe purulent discharge
chemosis with pseudomembranes
papillary reaction
preauricular lymphadenopathy (rare in regular bacterial conjunctivitis)
what can occur in severe gonococcal conjunctivitis cases and why
corneal ulceration
n. gonorrhoeae can invade intact corneal epithelium
what are systemic gonorrhea symptoms of men and women
men: purulent urethral discharge after 3-5 day incubation period
women: discharge less common, 50% are asymptomatic
what 2 symptoms seen in gonococcal conjunctivitis are typically only seen in viral conjunctivitis
preauricular lymphadenopathy
pseudomembranes
gonococcal conjunctivitis is the only bacteria to cause these symptoms
most common co-existing infection with gonorrhea
chlamydia
who most commonly gets adenoviral conjunctivitis
adults
symptoms associated with all types of adenoviral conjunctivitis
follicles, pseudomembranes, diffuse conjunctival hyperemia, follow systemic viral infection
3 types of adenoviral conjunctivitis
acute nonspecific follicular conjunctivitis
pharyngoconjunctival fever (PCF)
epidemic keratoconjunctivitis (EKC)
most common adenoviral conjunctivitis
acute nonspecific folliclular conjunctivitis
what serotypes cause acute nonspecific folliclular conjunctivitis
1-11, 19
acute nonspecific folliclular conjunctivitis presentation
follicles, diffuse red eye, tearing, mild discomfort
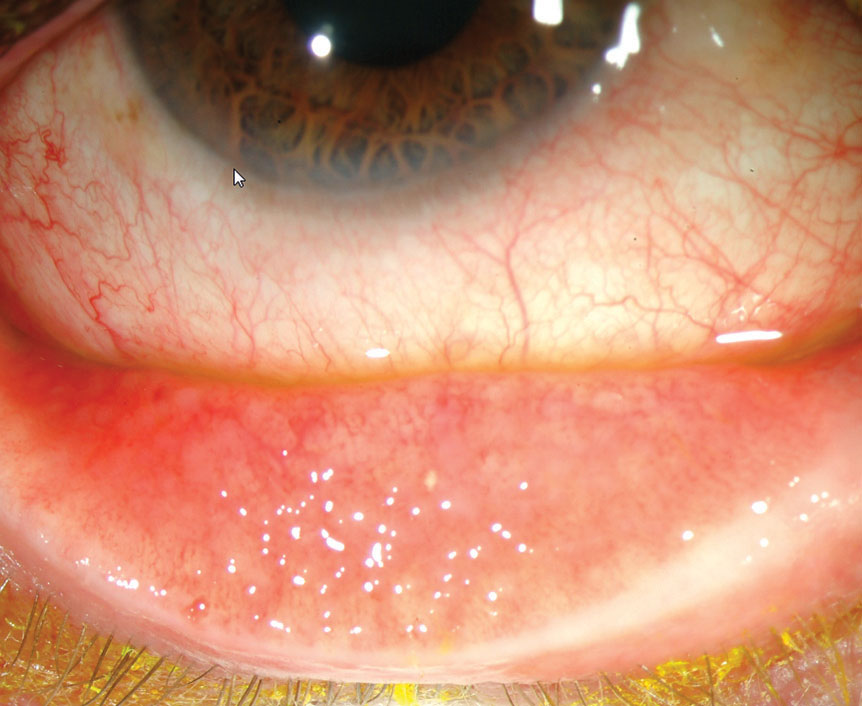
which viral conjunctivitis is most common in kids
PCF
aka swimming pool conjunctivitis
serotypes that cause PCF
3, 5, 7
PCF triad
follicles
low grade fever
pharyngitis (sore throat)
viral conjunctivitis that has corneal involvement
EKC
EKC serotypes
8, 19, 37
when do clinical symptoms occur in EKC
8 days after exposure
acute phase of EKC
1-2 weeks, superficial keratitis is common
what can be present after acute phase of EKC
subepithelial infiltrates
what viral conjunctivitis has preauricular lymphadenopathy most commonly
EKC
EKC rule of 8s
serotype 8
occurs 8 days after exposure
SEIs 8 days after onset of symptoms
presence of ____ in a patient with adenoviral infection is pathognomonic for EKC
palpable lymph node
what causes molluscum contagiosum
DNA pox virus spread through direct contact
what other disease needs to be considered if multiple molluscum nodules present
HIV or other immunodeficiency diseases
molluscum contagiosum presentation
1 or multiple waxy, umbilicated, dome-shaped nodules on lid
can have mild mucous discharge
what happens if molluscum nodules rupture
can cause follicular conjunctivitis or pannus
2 diseases that can present with unilateral follicular conjunctivitis and watery discharge
molluscum contagiosum
herpes simplex
what type of conjunctivitis is seasonal allergic conjunctivitis and what causes it
type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
usually caused by airborne allergens
what type of conjunctivitis is perennial allergic conjunctivitis and what causes it
type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
household allergies
who gets VKC and how long does it last
males under 10 in hot climates
often occurs in patients with atopic conditions (asthma, rhinitis)
lasts 2-10 years
when do seasonal outbreaks of VKC commonly occur
warm months
VKC discharge
thick mucus discharge
classic VKC sign
bilateral severe papillae on limbus or superior palpebral conj
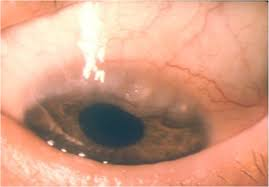
what are papillae on limbus called
trantas dots
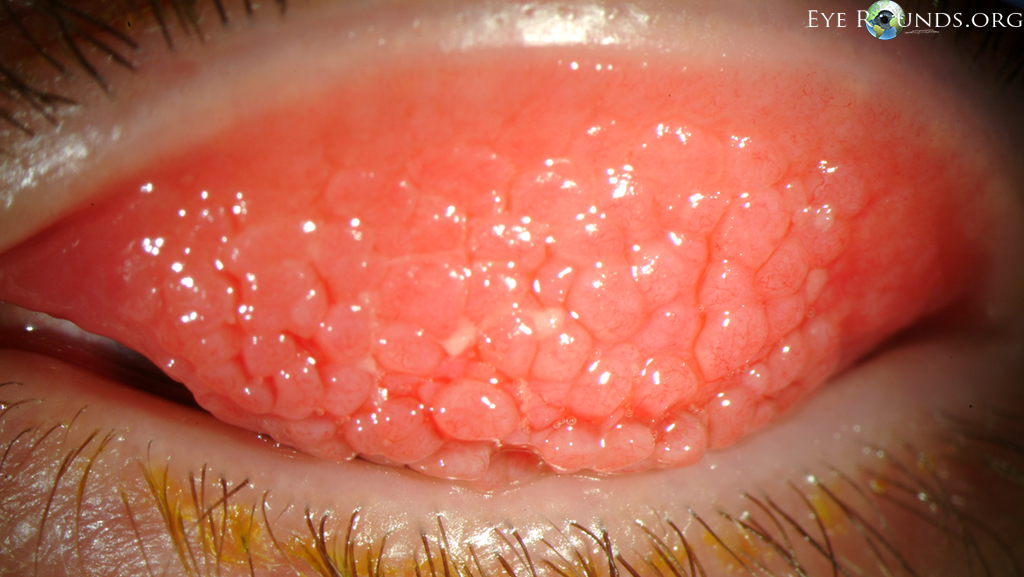
what are papillae on superior palpebral conj called
cobblestone papillae
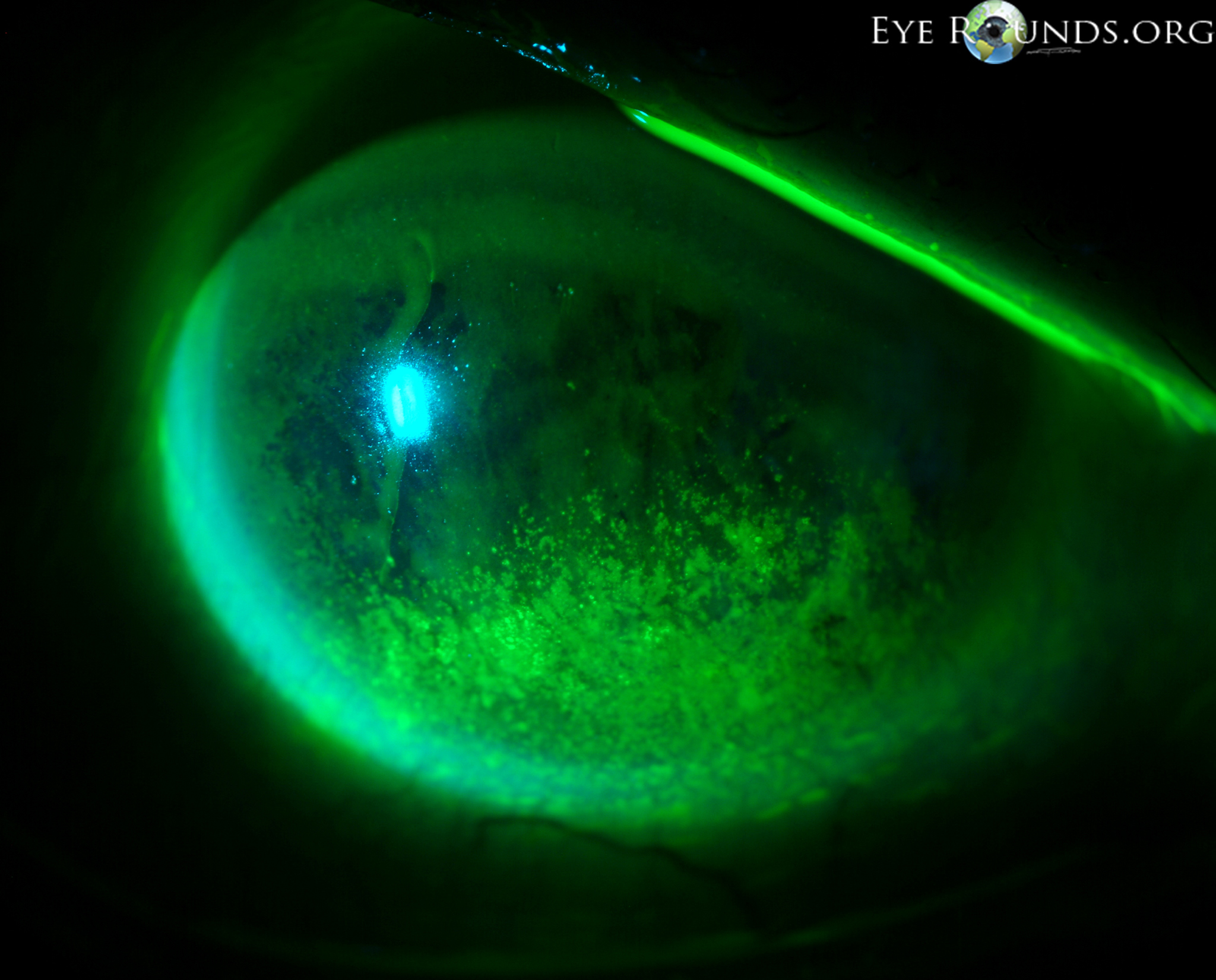
corneal involvement in VKC
begins with punctate epithelial keratitis and coalesces into large erosions
causes plaque formation and localized ulceration
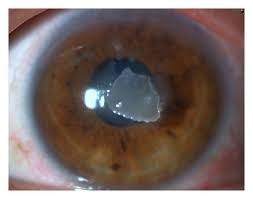
what is localized ulceration of the cornea called
shield ulcer
who gets AKC and what disease is it associated with
teens to middle aged adults
atopic dermatitis
what is atopic dermatitis
chronic eczema with itching and rash commonly diagnosed in babies
what ocular issue can be developed with severe atopic dermatitis
cataracts
what kind of reaction is AKC
type 1 and type 4 hypersensitivity
not seasonal
main symptom of AKC
bilateral itching of eyelids
AKC presentation
prominent outer lids, extra crease under eyes, atopic shiners, inferior papillae, corneal neo, cataracts
what ocular disease can develop with AKC
KCN from chronic eye rubbing
Dennie’s lines
extra crease under lid due to edema
what can be seen in severe AKC
formation of symblepharon
how does AKC differ from VKC
VKC has superior papillae while AKC has inferior papillae
VKC is seasonal
AKC has more lid involvement while VKC has more conj and cornea involvement
toxicity to medication causes (papillae/follicles)
follicles
what is a papillae
inflamed area of elevated conj with central vessel that is source of infiltration for eosinophils, mast cells, neutrophils, and lymphocytes