Chapter 2: The Periodic Table (10%)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
number of electron shells
(aka principal energy level, denoted by the principal quantum number n)
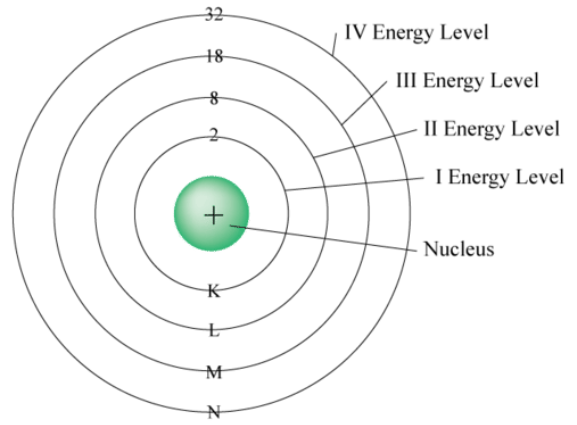
Elements in the same period/horizontal row all have the same WHAT?
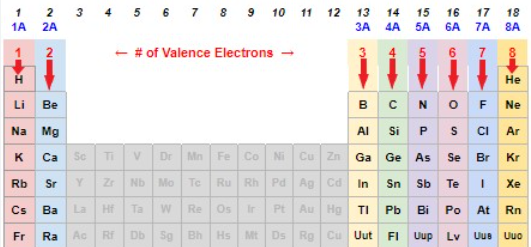
number of valence shell electrons
Elements in the same group/vertical column all have the same WHAT?
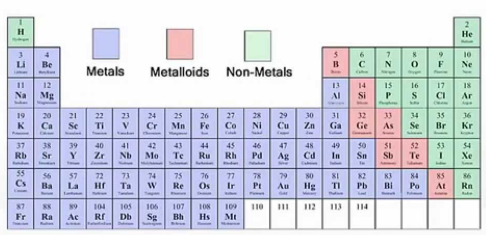
metals
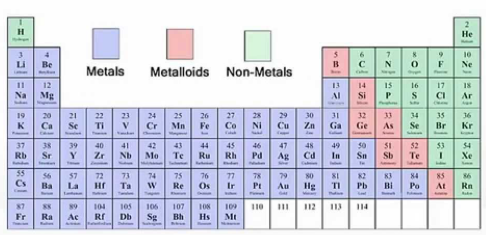
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Shiny (lustrous)
Conduct electricity well
Malleable
Ductile
metals
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Found on the left side and middle of the periodic table
high, Lithium, low
Metals
Metals generally have _____ boiling points and densities, but there are exceptions such as _________ which has a _____ density of about half of water’s density.

malleability
Metals
The ability of metals to be hammered into shapes
ductility
Metals
The ability of metals to be pulled or drawn into wires
low

Metals
Do metals have a HIGH or LOW effective nuclear charge (Zeff)?
low

Metals
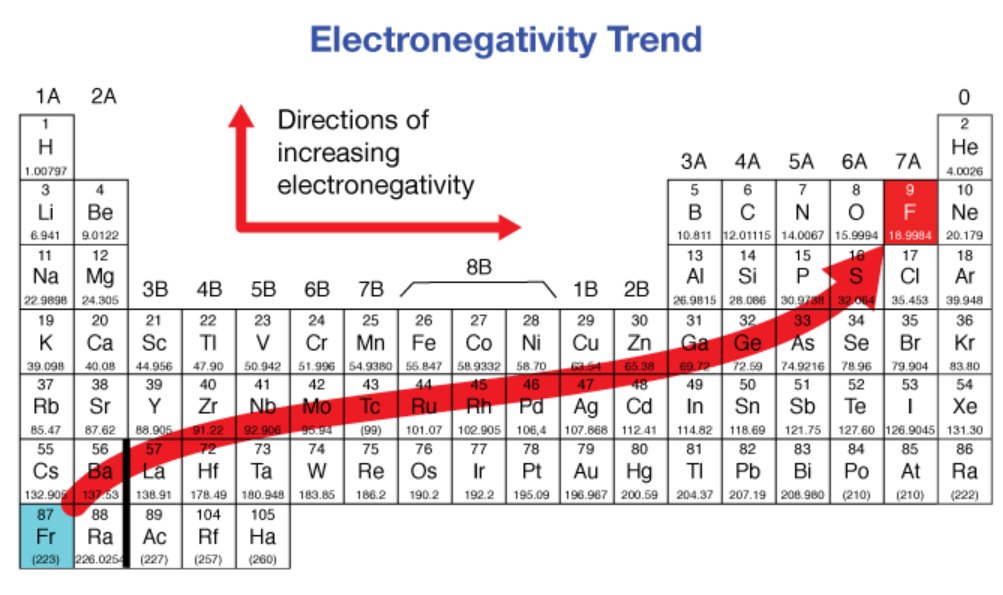
Do metals have a HIGH or LOW electronegativity?
large

Metals
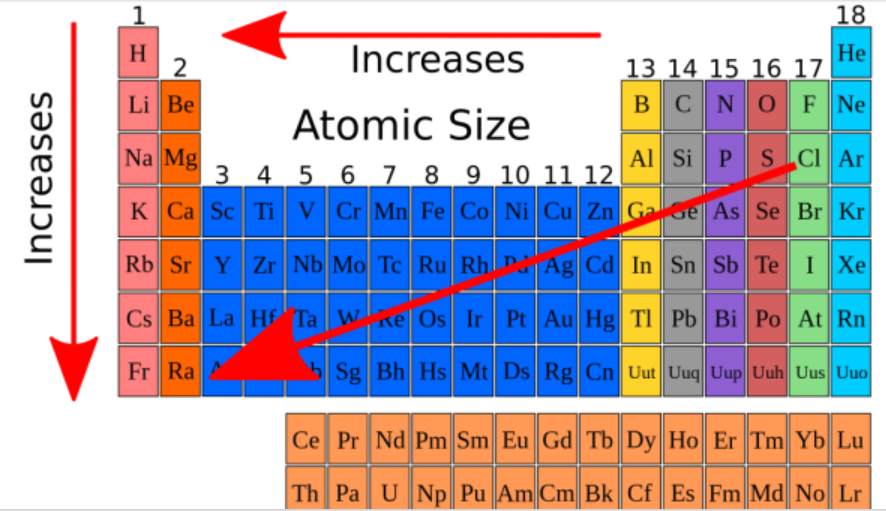
Do metals have a SMALL or LARGE atomic radius?
small

Metals
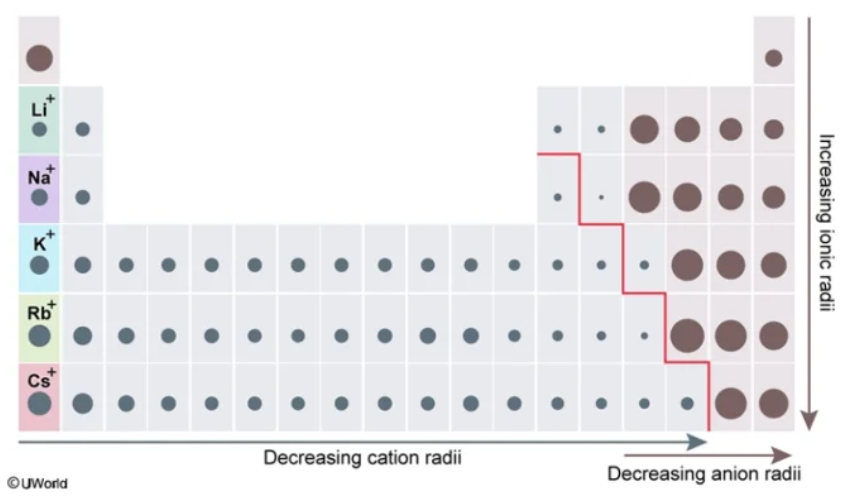
Do metals have a SMALL or LARGE ionic radius?
low

Metals
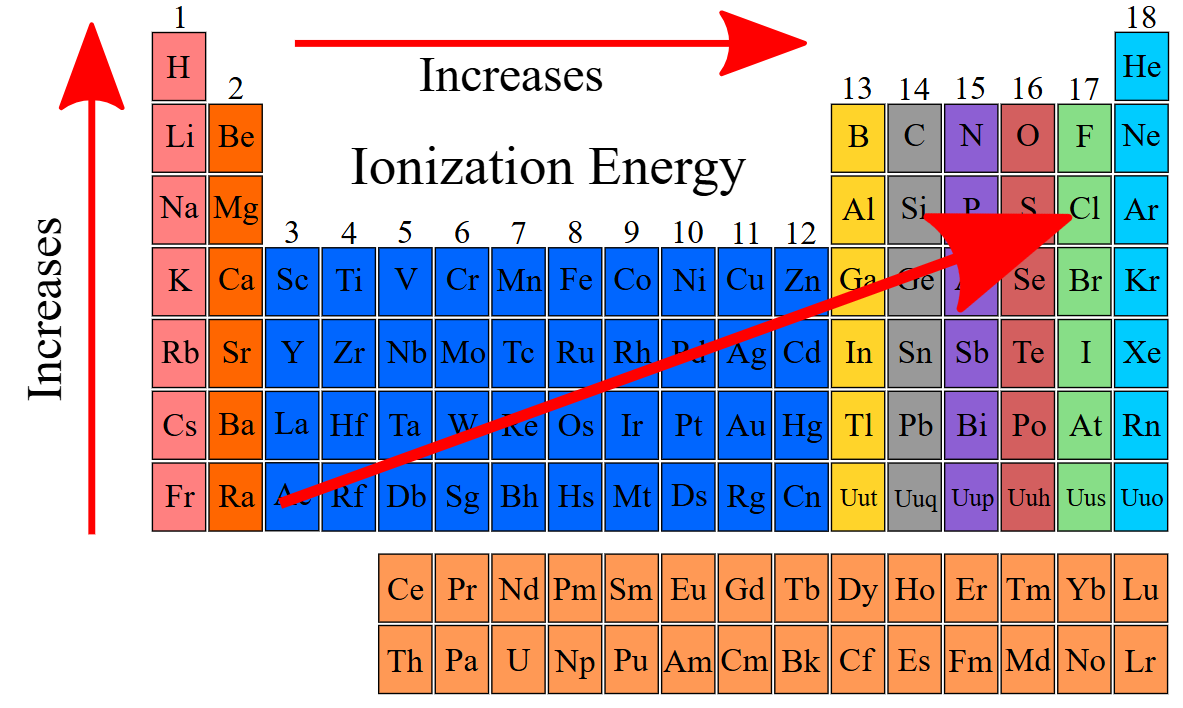
Do metals have a HIGH or LOW ionization energy?
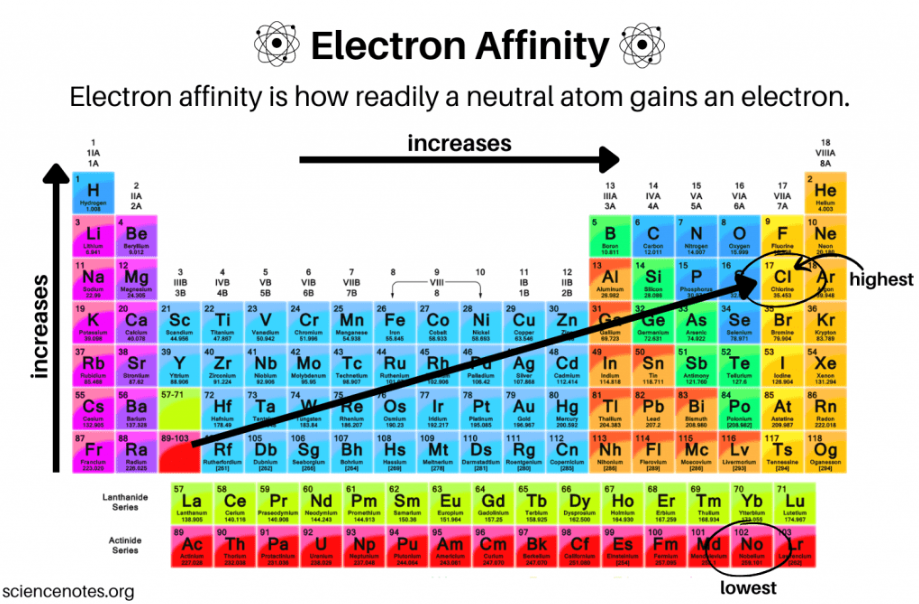
low

Metals
Do metals have a HIGH or LOW electron affinity?
nonmetals
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Dull
Poor conductors of electricity
Brittle
nonmetals
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Found on the right side of the periodic table
high

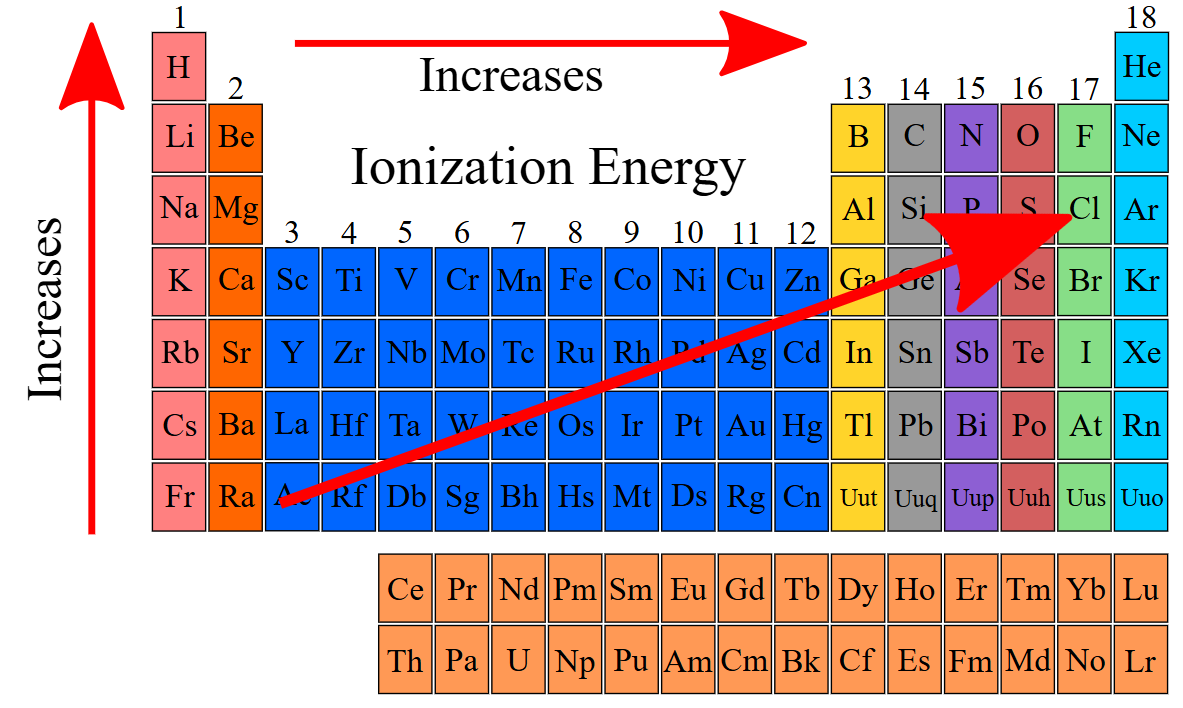
Nonmetals
Do nonmetals have a HIGH or LOW ionization energies?
high

Nonmetals
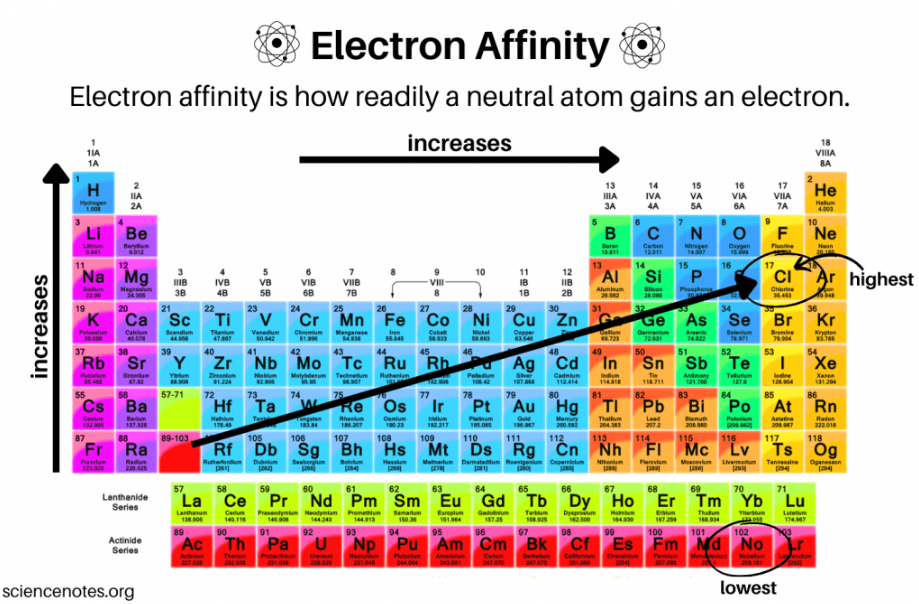
Do nonmetals have a HIGH or LOW electron affinities?
high

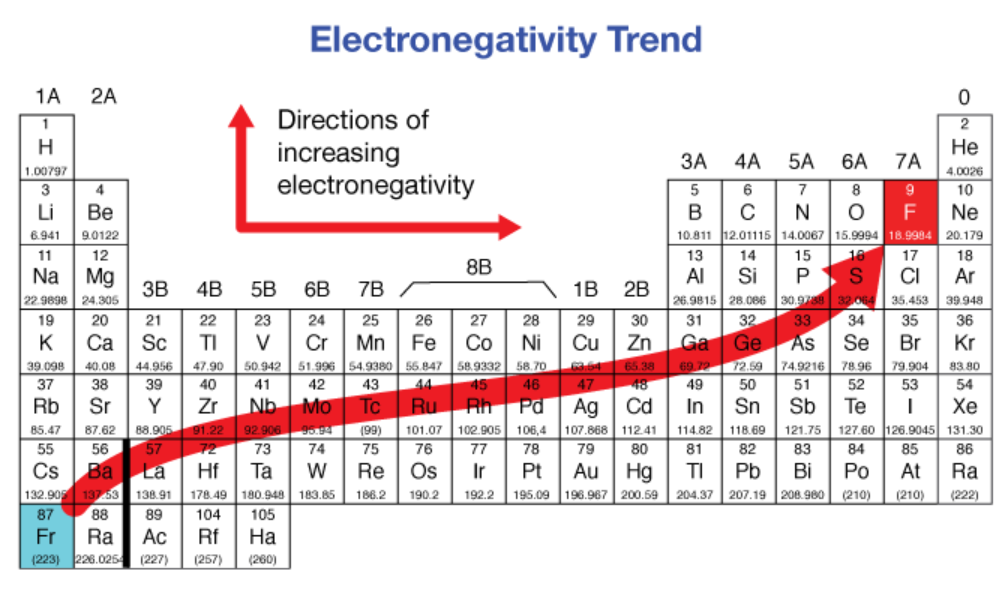
Nonmetals
Do nonmetals have a HIGH or LOW electronegativities?
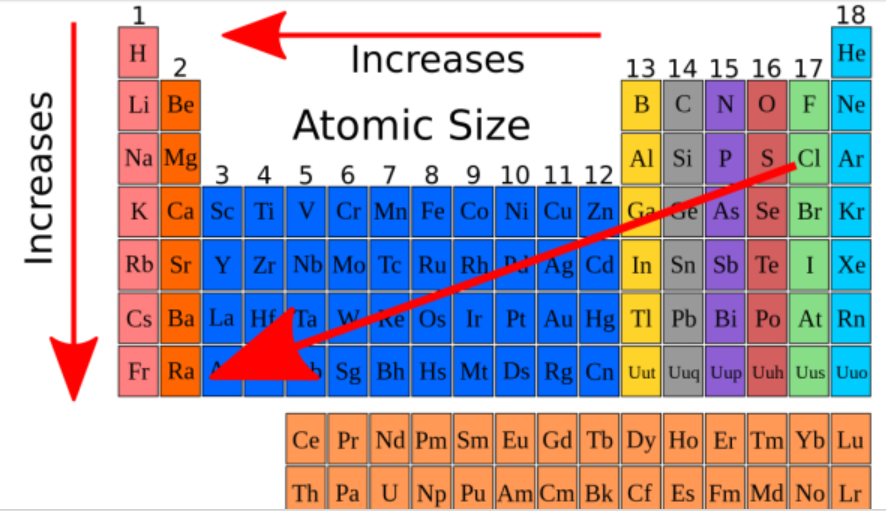
small

Nonmetals
Do nonmetals have a SMALL or LARGE atomic radii?
large

Nonmetals
Do nonmetals have a SMALL or LARGE ionic radii?
metals
Metals vs. Nonmetals
More likely to give up electrons during bonding
metalloids
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Possess characteristics of both metals and nonmetals
Shiny yet brittle
Semiconductors
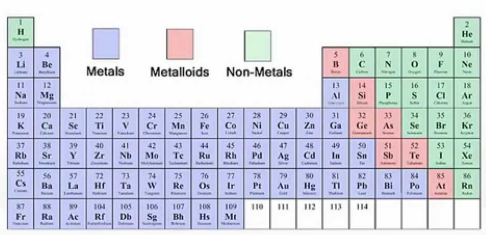
metalloids
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
Found in a stair-step pattern starting with boron (B)
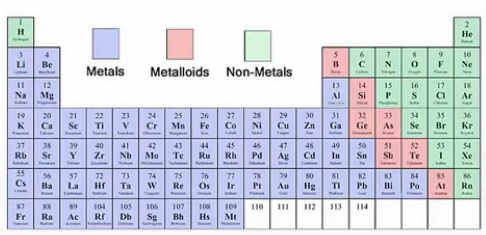
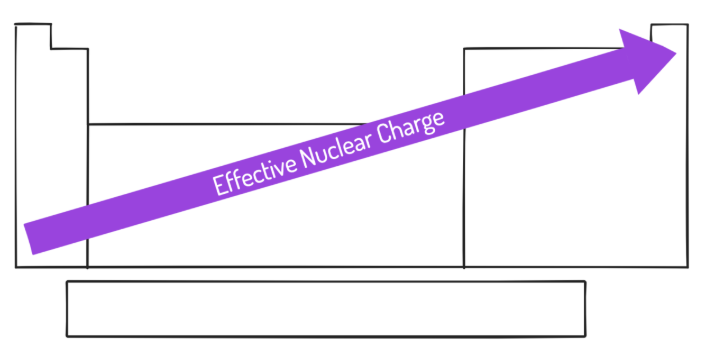
effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
The actual felt pull that the outermost electrons of an element “feel”
The net positive charge experienced by electrons in the valence shell
The electrostatic attraction between the valence shell electrons and the nucleus
Forms the foundation for all periodic trends
increases

Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff) __________ from left to right across a period, with little change in value from top to bottom in a group.
separated, increases, less, atomic radii, increases, reduces
Valence electrons become increasingly ___________ from the nucleus as the principal energy level (n) __________ from top to bottom in a group.
This means they are held _____ tightly by the nucleus.
This is because of the ________ _______ → the distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons _________, therefore _________ the force of attraction.
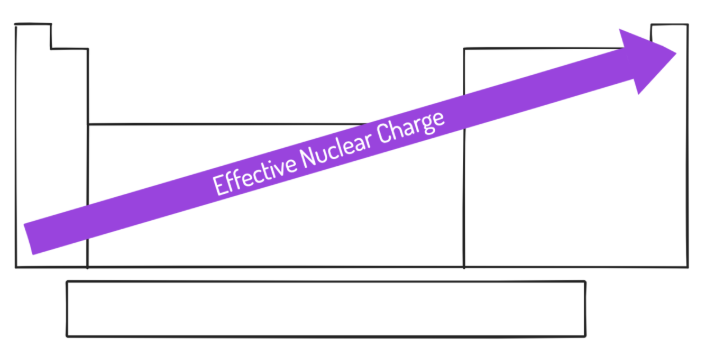
atomic radius
Think of an atom as a cloud of electrons surrounding a dense core of protons and neutrons.
The ________ ________ of an element is thus equal to ½ of the distance between the centers of two atoms of an element that are briefly in contact with each other.
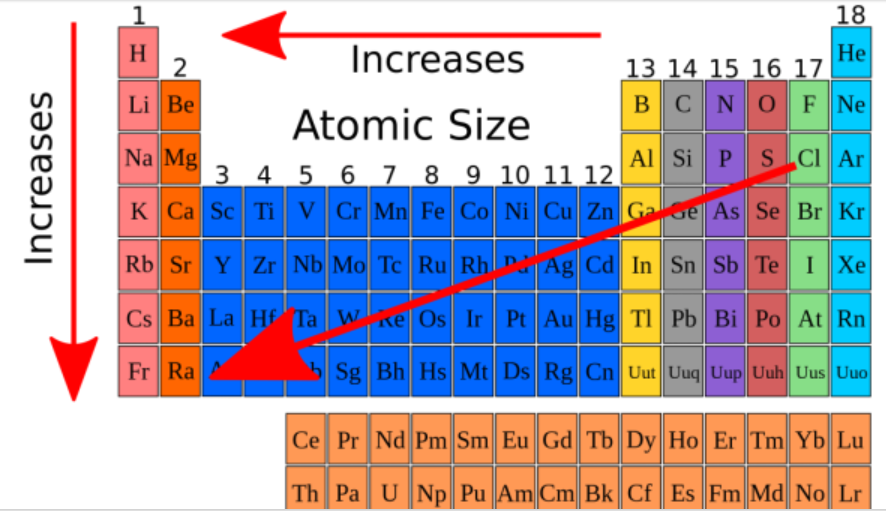
decreases, increases

Atomic radius __________ from left to right across a period and __________ from top to bottom in a group.
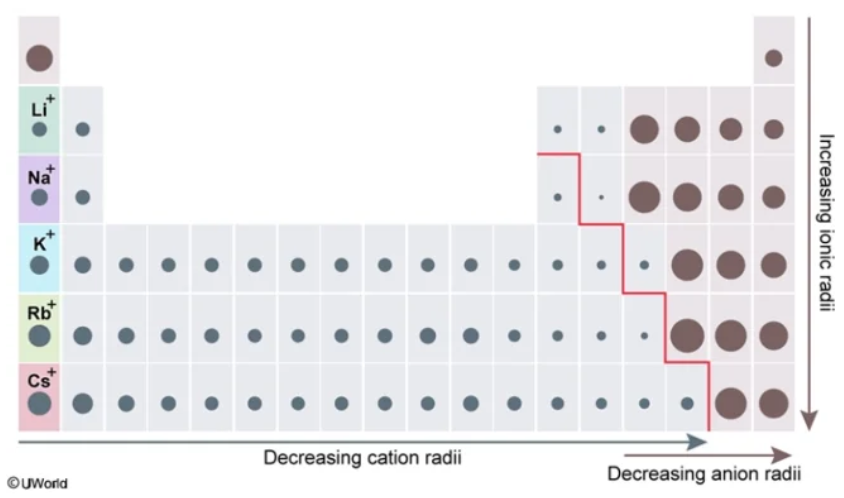
ionic radius
The size of a charged species (aka an ion)
The distance from its nucleus to the outermost electron shell
Typically determined within a crystal lattice
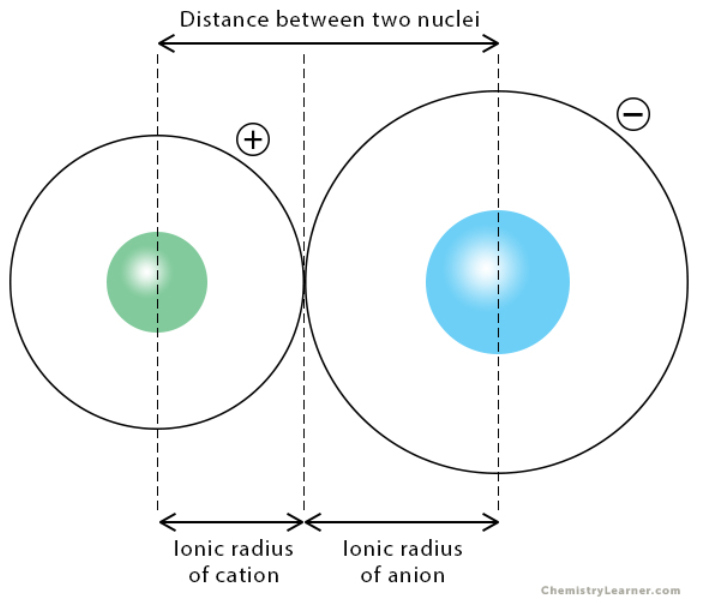
metals, cations, nonmetals, anions
Metals vs. Nonmetals
__________ lose electrons and become positive (aka they become _______) while __________ gain electrons and become negative (aka they become ________)
larger
Smaller vs. Larger
For nonmetals closer to the metalloid line, they have a ________ ionic radius than their counterparts closer to Group VIIIA
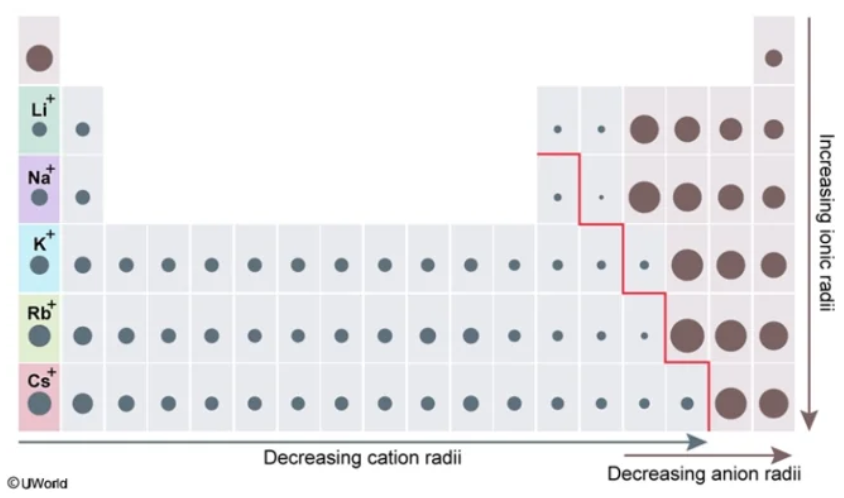
smaller
Smaller vs. Larger
For metals closer to the metalloid line, they have a ________ ionic radius than the other metals
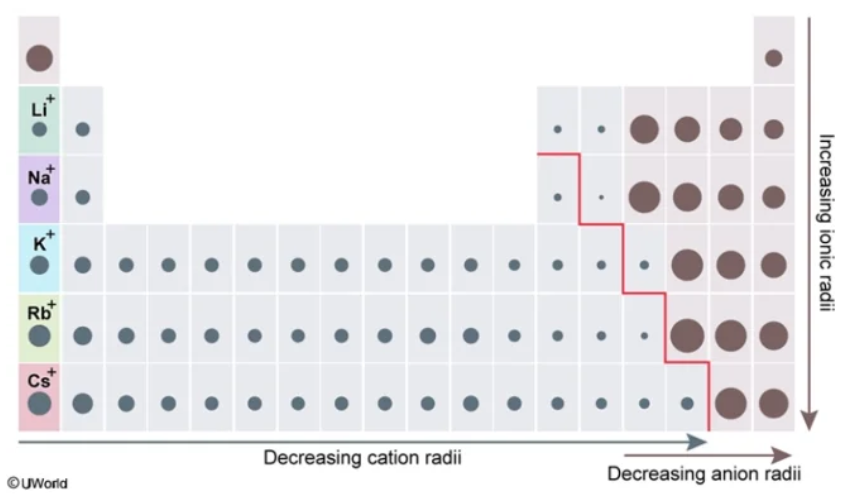
metalloid
The largest nonmetallic ionic radii and the smallest metallic ionic radii exist at the ___________ boundary
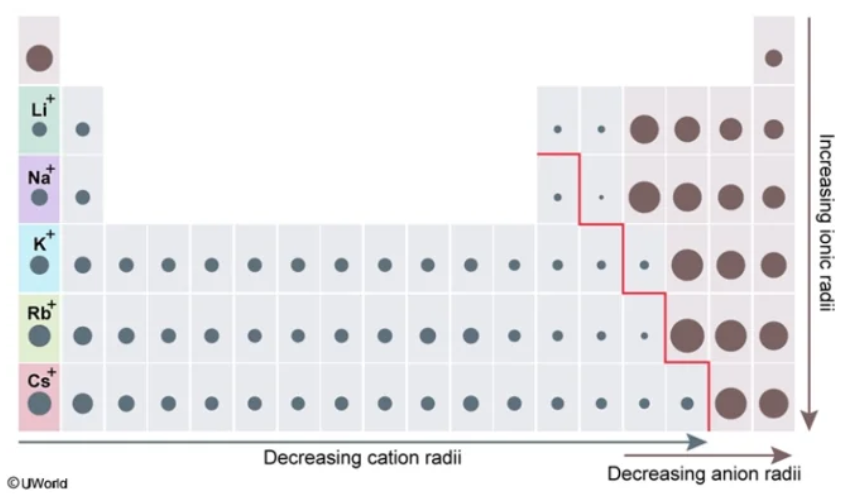
smaller

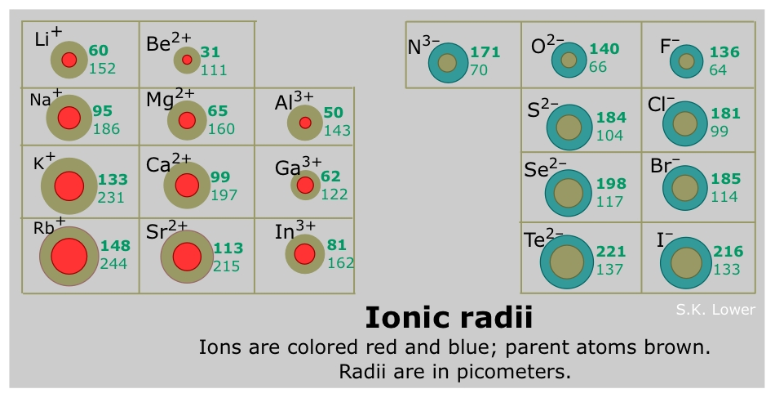
Smaller vs. Larger
The ionic radii of cations (aka metals) is generally ________ than the atomic radii of their corresponding neutral atom

larger

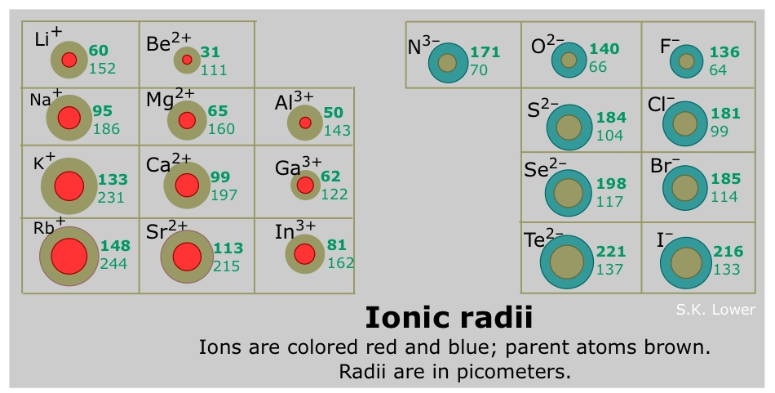
Smaller vs. Larger
The ionic radii of anions (aka nonmetals) is generally ________ than the atomic radii of their corresponding neutral atom

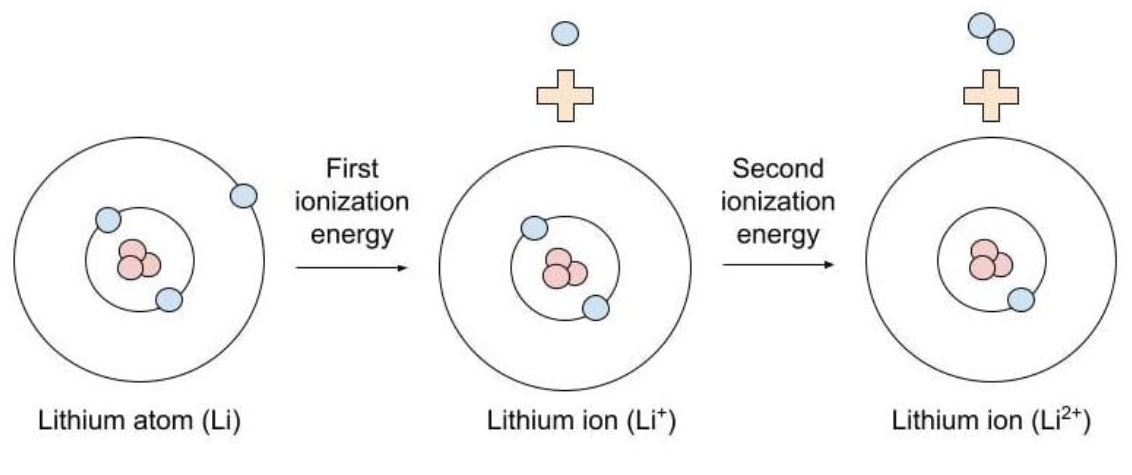
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from the valence shell of a gaseous species
Always requires an input of heat (is endothermic)
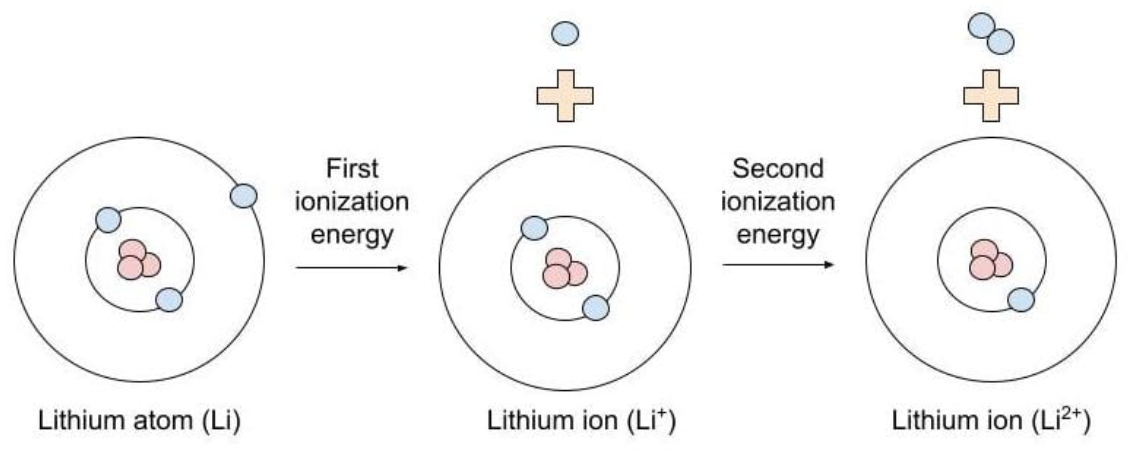
smaller, smaller
Smaller vs. Larger
The 1st ionization energy (IE) will always be _______ than the 2nd IE which will always be ________ than the 3rd IE and so on
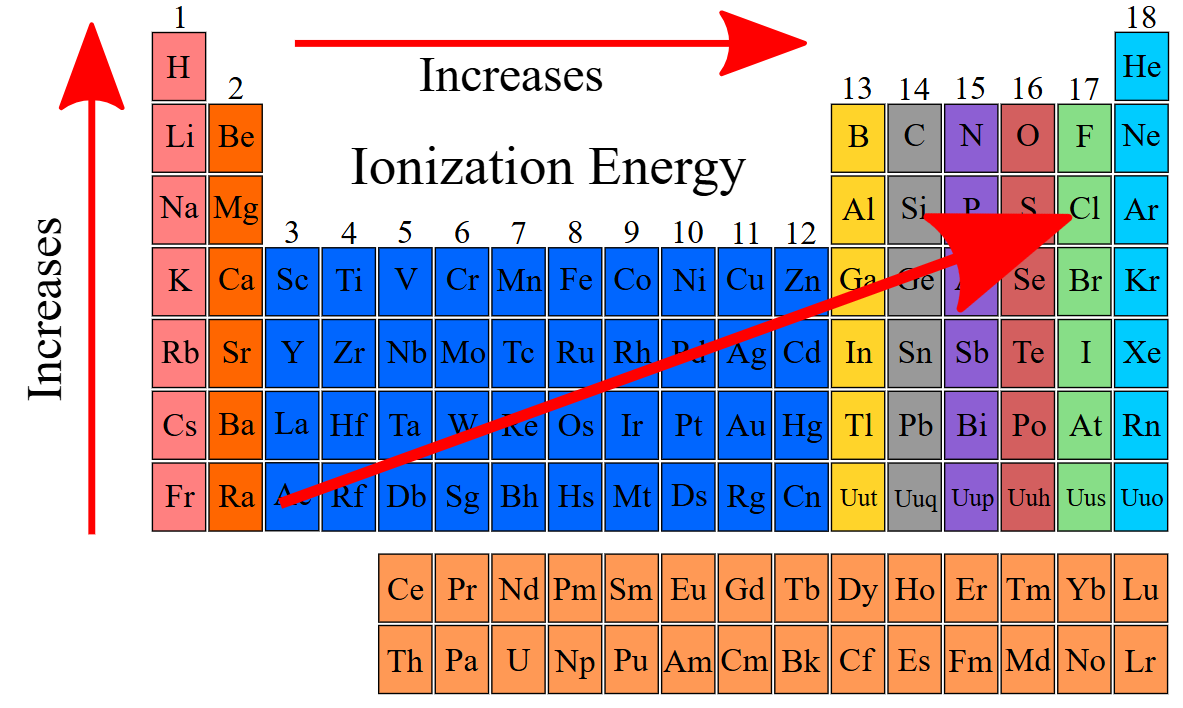
increases, decreases

Ionization energy ____________ from left to right across a period and ___________ from top to bottom in a group
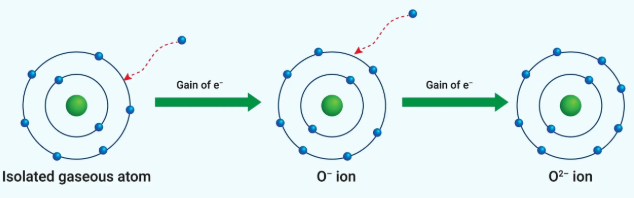
electron affinity
The amount of energy released when a gaseous species gains an electron in its valence shell
Exothermic process that expels energy as heat
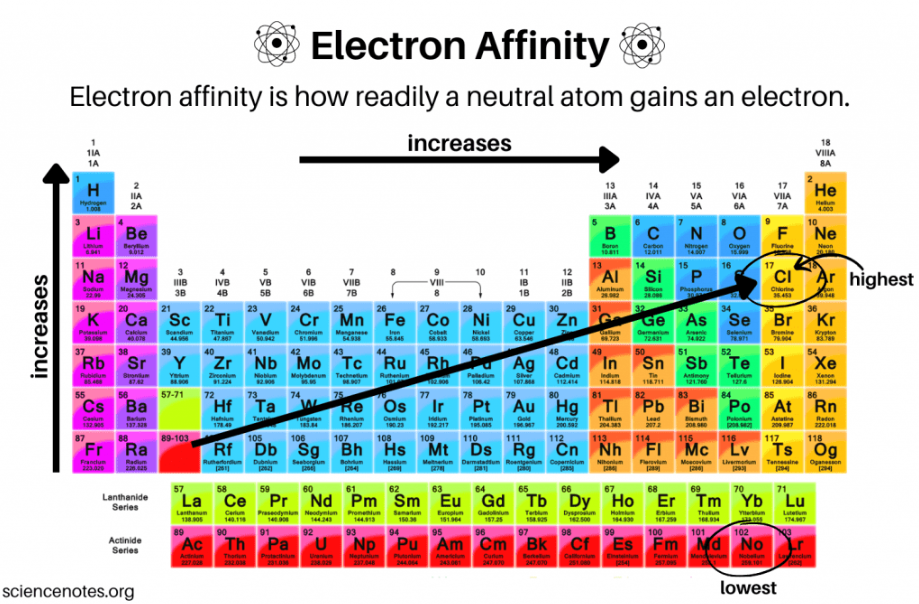
increases, decreases

Electron affinity ___________ from left to right across a period and ___________ from top to bottom in a group
greater, high
Lesser vs. Greater
The STRONGER the electrostatic pull (the higher the Zeff) between the nucleus and the valence shell electrons, the _________ the energy release will be when an atom gains the electron (aka the atom has a _____ electron affinity)
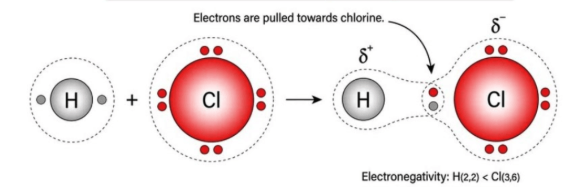
electronegativity
An atom's inherent ability to attract electrons towards its nucleus in a chemical bond
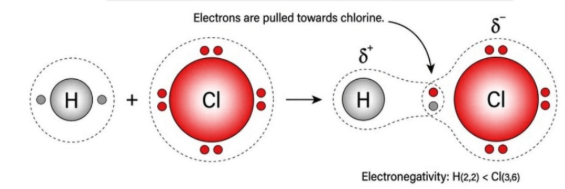
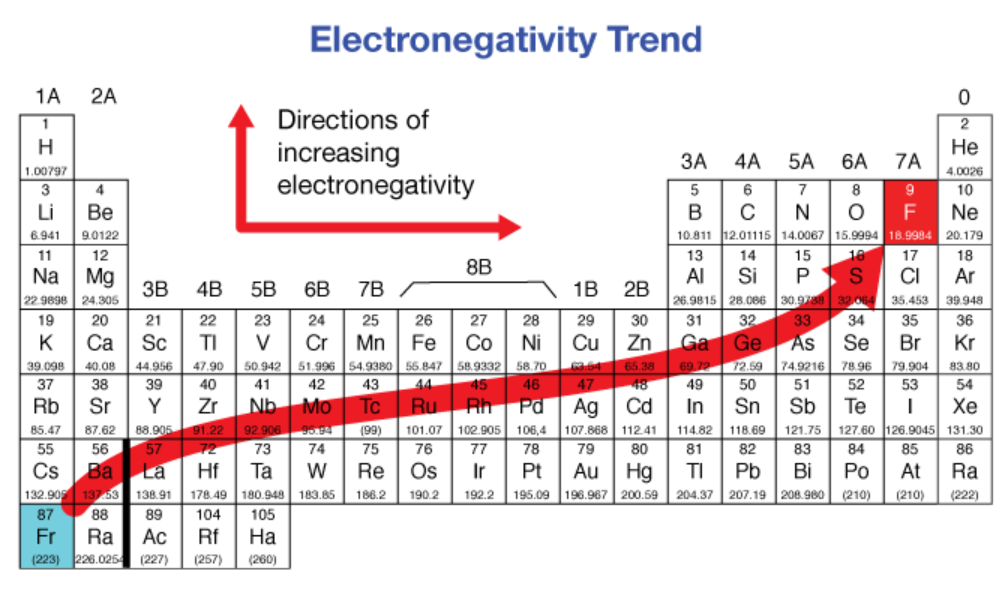
increases, decreases

Electronegativity ___________ from left to right across a period and ___________ from top to bottom in a group
more
Less vs. More
The GREATER the electronegativity of an atom, the ______ it attracts electrons within a bond
lower
The LOWER the ionization energy, the _________ the electronegativity
alkali metals
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Typically take on an oxidation state of +1
Prefer to lose an electron to achieve a noble gas-like configuration
Have only 1 loosely-bound electron in their valence shell
React readily with nonmetals, especially halogens
Group 1A/1
EX: Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na)
alkaline earth metals
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Take on an oxidation state of +2
Can lose 2 electrons to achieve noble gas-like configuration
Have 2 valence electrons
Group 2A/2
EX: Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca)
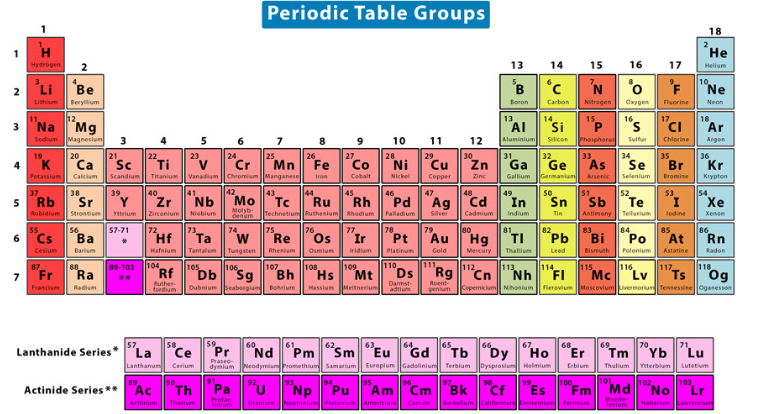
alkali metals, alkaline earth metals
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
The most reactive of all metals
Not naturally found in their elemental neutral state (2)
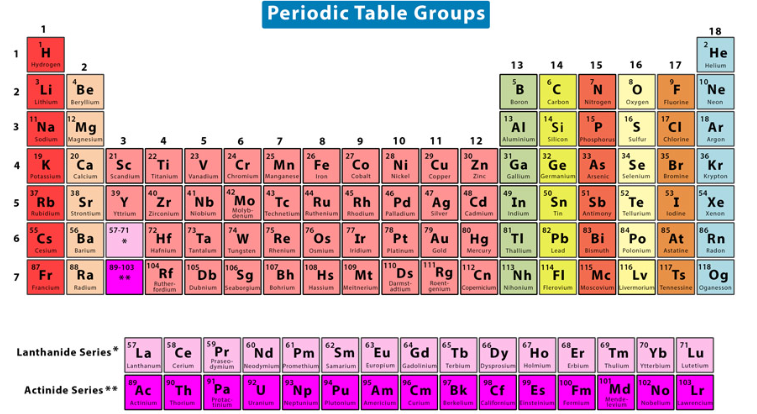
chalcogens
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Take on oxidation states of -2 or +6 (depending on whether they are nonmetals or metals, respectively) in order to achieve noble gas configuration
Each have 6 valence electrons
Extremely important for normal biological function
Group 6A/16
EX: Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S)
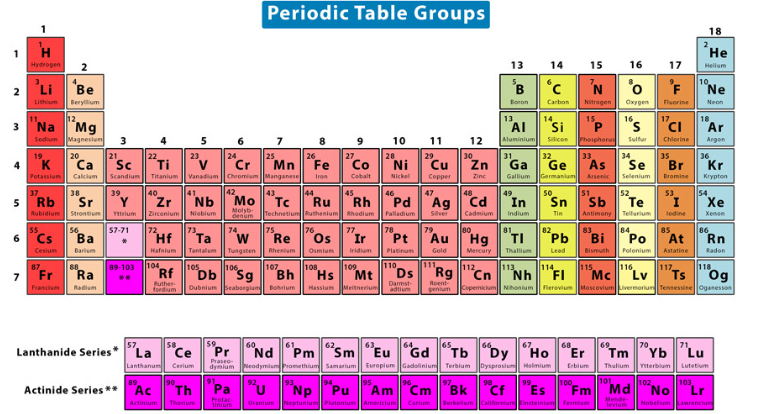
halogens
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Typically take on an oxidation state of -1
Prefer to gain an electron to achieve noble gas-like configuration
Have the highest electronegativities
Highly reactive especially towards alkali and alkaline earth metals
Not naturally found in their elemental neutral state but rather as ions
Group 7A/17
EX: Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl)
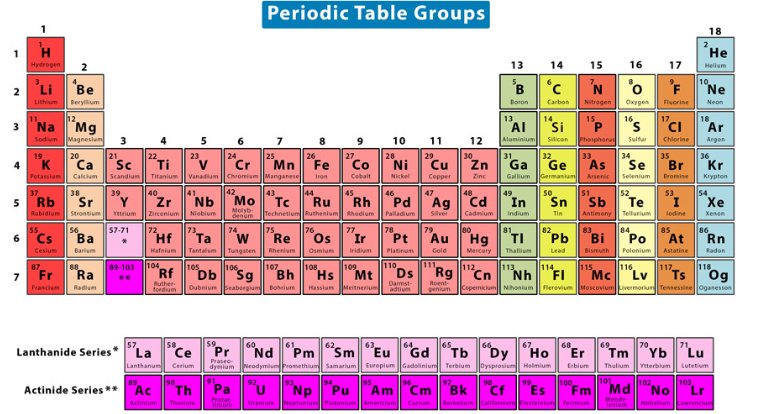
noble gases
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Have a fully filled valence shell in their standard state & prefer not to give up or take on additional electrons
Have very high ionization energies and virtually nonexistent electronegativities and electron affinities
Have extremely low boiling points and exist as gases at room temperature
Group 8A/18
EX: Neon (Ne), Helium (He)
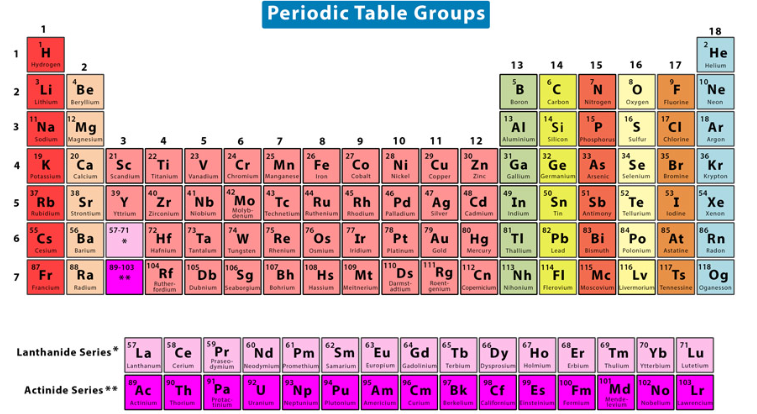
transition metals
Alkali Metals vs. Alkaline Earth Metals vs. Transition Metals vs. Chalcogens vs. Halogens vs. Noble Gases
Take on multiple oxidation states, which explains their ability to form colorful complexes with nonmetals in solution and their utility in certain biological systems
Groups 3-12
absorbed, subtraction frequencies, complementary color
When we perceive an object as a particular color, it is because the color is NOT __________.
If an object absorbs a given color of light and reflects all others, our brain mixes these _____________ _______________ and we perceive the ________________ _________ of the frequency that was absorbed.

atomic radius
The period trend that trends opposite of ALL the others