UNT Principles of Biochemistry Exam Two Review: Chapter 7 Flashcards
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Allosteric
Greek allo + steric, other shape
Allosteric Enzyme
A oligomer who’s biological activity is affected by the other substances binding to it
The substances specifically change the enzyme’s activity by altering the conformation of the 4” structure
Allosteric Effector
a substance modifying the behavior of an allosteric enzyme; can be :
allosteric inhibitor (or) activator
Aspartate Transcarbamoylase (ATCase)
Feedback Inhibition
Reaction Catalyzed by ATCase
leads to production of CTP
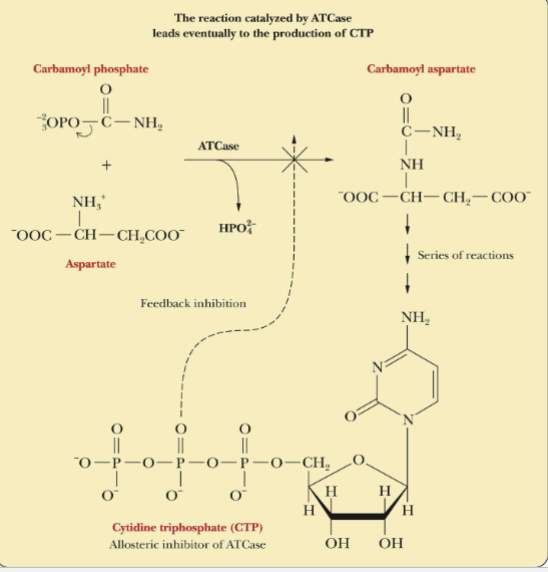
Feedback Inhibition
The feedback inhibition shown the in the reaction above, is a formation of products inhibits its continued production

ATCase
-The rate of ATCase Catalysis vs substrate concentration
-The sigmoidal shape of curve describes allosteric behavior
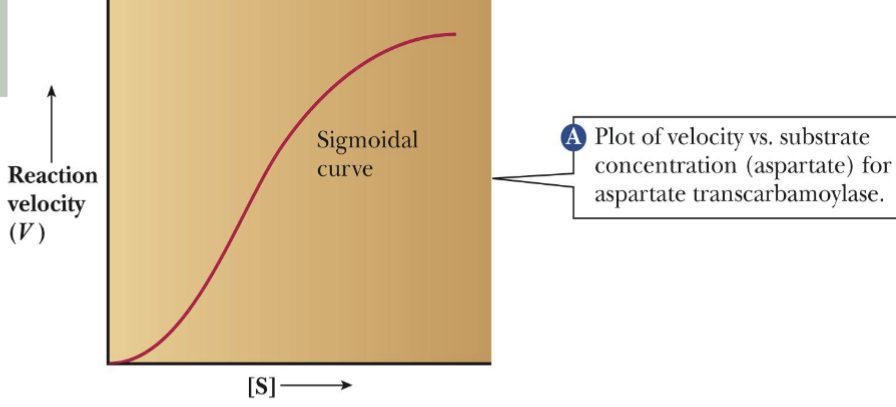
ATCase Catalysis curve
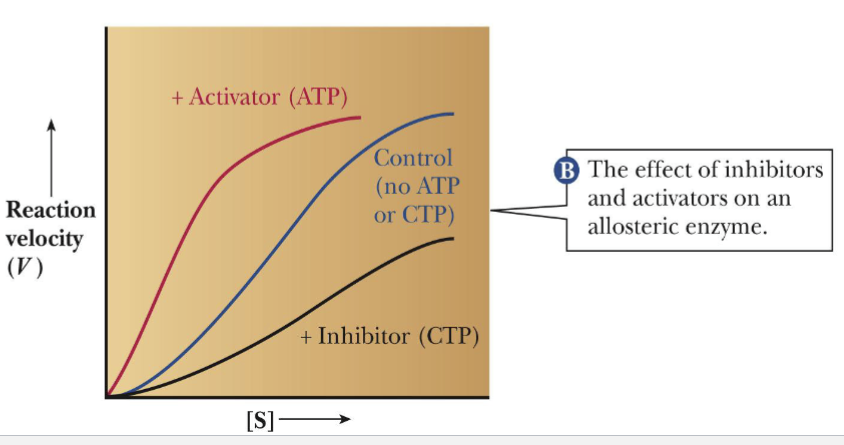
ATCase Catalysis in prescence of CTP; ATP
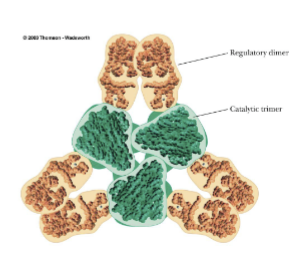
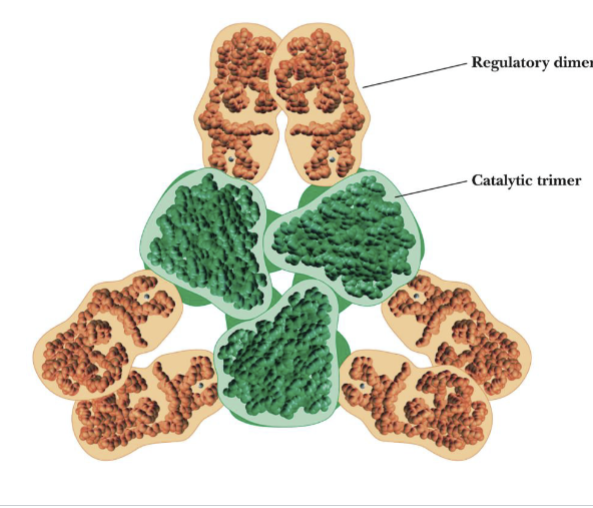
ATCase Organization
Catalytic unit: 6 subunits; organized into 2 trimers
Regulatory unit: 6 subunits; organized into 3 dimers
P-Hydroxymercuribenzoate
-A compound that reacts with cysteine
-This compound separates catalytic subunits from regulatory subunits, once it reacts with cysteine
Types of Allosteric Enzyme Systems (2)
-K-system: the enzyme for which a inhibitor or activators alters K0.5
-V-system: a enzyme for which a inhibitor or activator alters Vmax but not K0.5
*^^The substrate conc. for a allosteric enzyme at ½ Vmax is called K0.5
Allosteric Effector
A substance that modifies the 4 degree structure of allosteric enzyme
Homotropic Effects
Allosteric Interactions that occur when several identical molecules are bound to a protein
*Ex. Binding of Aspartate to ATCase
Heterotropic Effects
allosteric interactions that occur when different substances are bound to the protein
*Ex. inhibition of ATCase by CTP and activation of ATP
The Concerted Model Enzymes
Wyman, Monod, & Changeux-1965 (Not highlighted but threw it in case 🤔 )
Two conformations of the enzyme:
-R (relaxed): binds substrate tightly; active form
-T(tight or taut): binds substrate less tight; inactive form
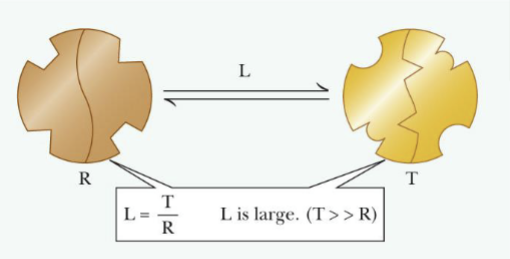
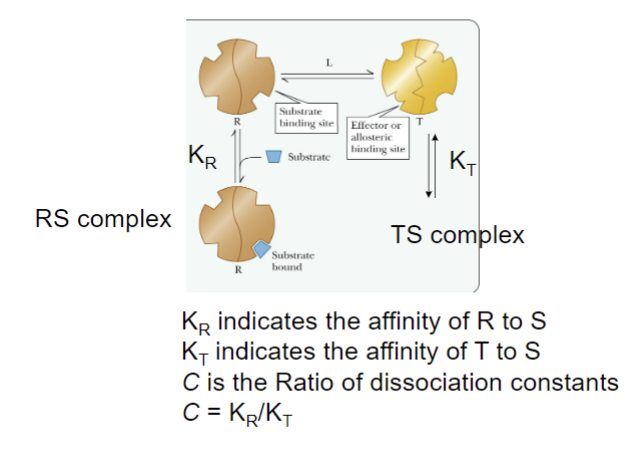
Concerted Model
The absence of substrate most enzymes molecules are in T (inactive) form
Presence of substrate shifts equilibrium from T (inactive) form to R (active) form
Changing from T to R and vice verse, the subunits change conformation simultaneously; all the changes are concerted
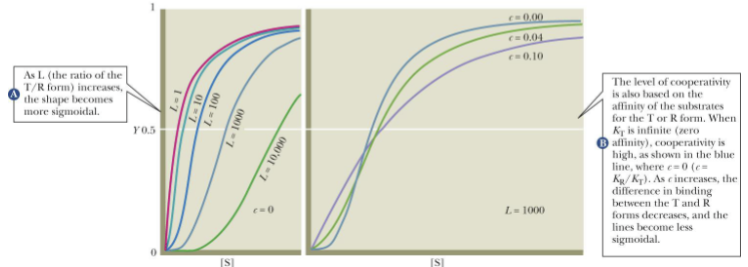
Concerted Model (Curve Graph)
-The model represents sigmoidal effects
-Higher L means favorability of free T form; also more sigmodial
-Higher C means higher affinity between S and R form less sigmoidal
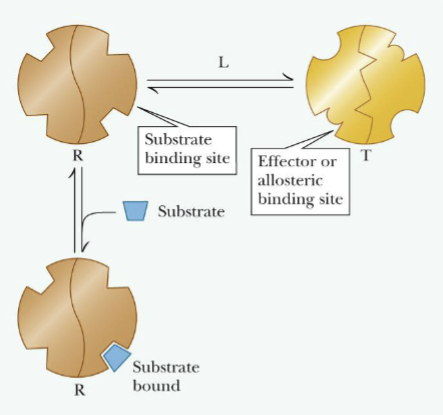
Concerted Model
(Effect of binding activators and inhibitors)
An allosteric activator (A) binds to and stabilizes the R (active) form
An allosteric inhibitor (I) binds to and stabilizes the T (inactive) form
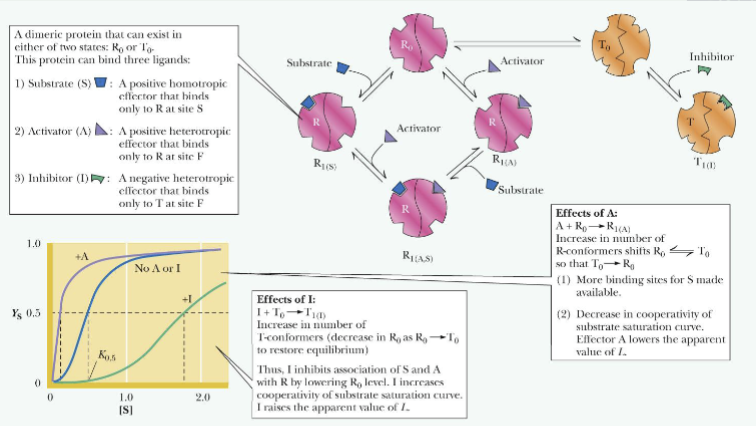
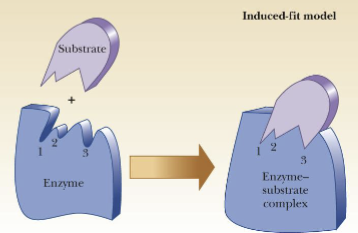
Sequential Model
(represents cooperativity)
-Main feature: binding of substrate induces a conformational change from T form to R form
-the change in conformation is induced by the fit of the substrate to the enzyme as per induced-fit model of substrate binding
Sequential model of Cooperative Binding
(substrate S to allosteric enzyme)
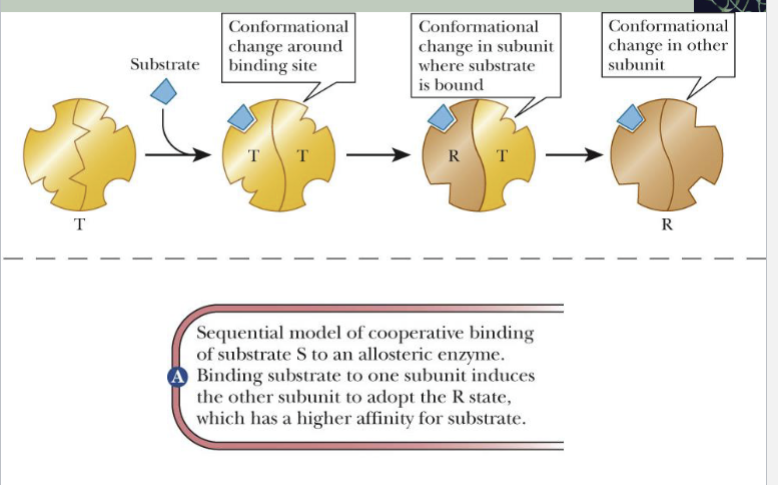
Sequential model of cooperative binding
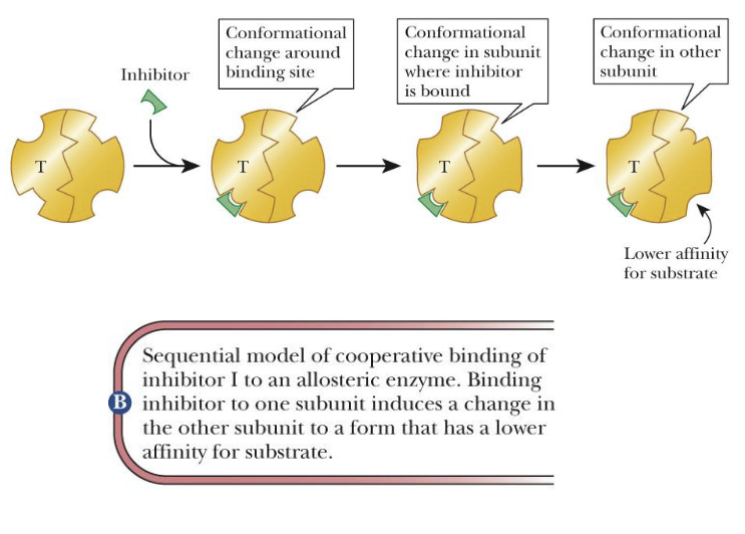
(inhibitor I to allosteric enzyme)
Conformational changes in substrate binding
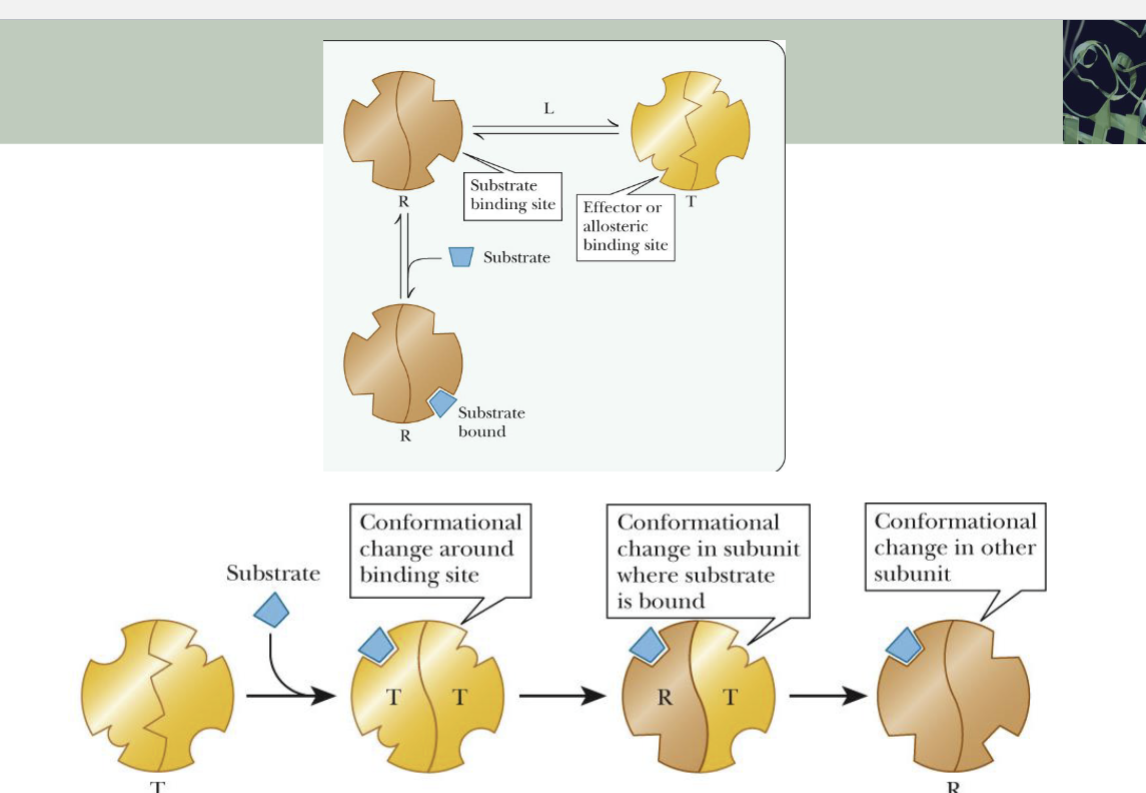
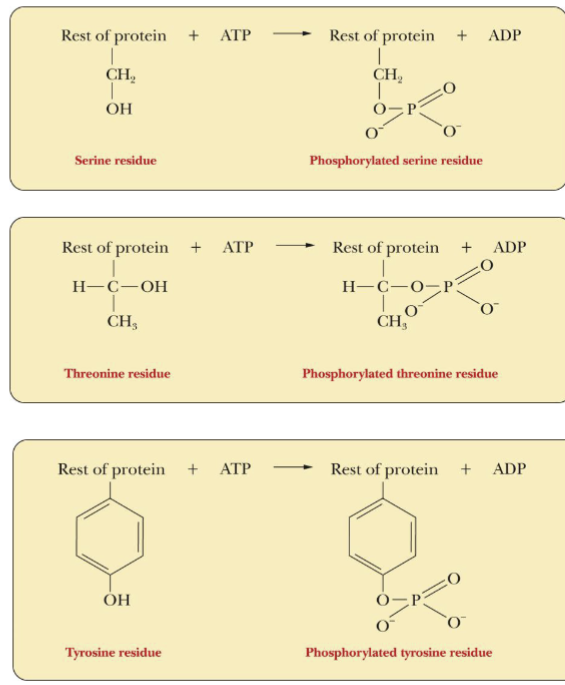
Control of Enzyme Activity via Phosphorylation
Side chain -OH groups: Ser, Thr, & Tyr can form phosphate esters
Phosphorylation by ATP can convert an inactive precursor into a active enzyme
Membrane transport is a common example
Membrane Transport
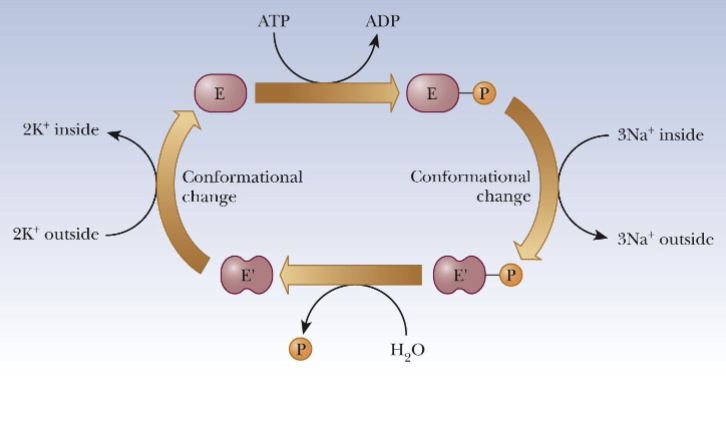
Zymogen
Inactive precursor of an enzyme where cleavage of one or more covalent bonds transforms to a active enzyme
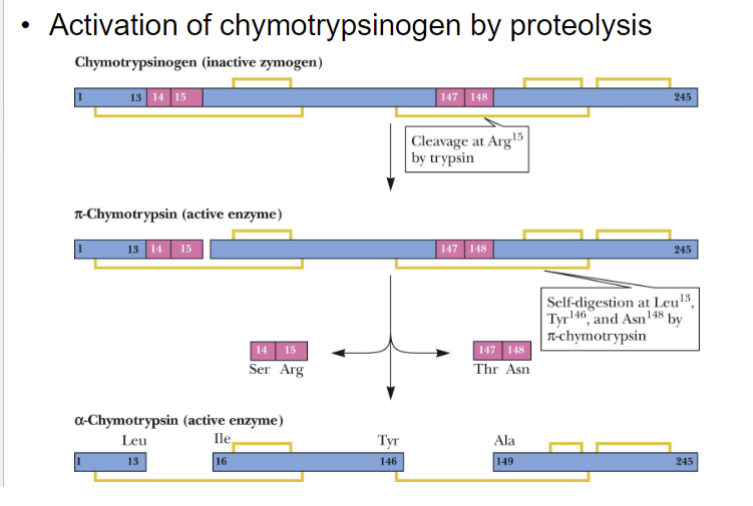
Chymotryspinogen
Synthesized and stored in the pancreas
Single polypeptide chain of 245 amino acid residues cross-linked by 5 disulfide (-S-S-) bonds
Only when secreted in the small intestine, the digestive enzyme trypsin cleaves a 15 unit polypeptide from the N-terminal end to give pi-chymotrypsin
*Chymotrypsin is an enzyme that catalyzes the selective hydrolysis of peptide bonds, where carboxyl group is contributed by Phe or Tyr
Chymotrypsin Reaction Model
Reaction with model substrate
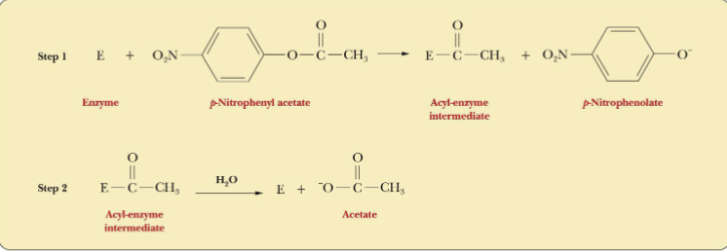
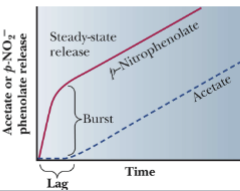
Kinetics of Chymotrypsin Reaction
p-nitrophenyl acetate (red line) is hydrolyzed by chymotrypsin in 2
stages.
• At the end of stage 1, the p-nitrophenolate ion is released.
• At stage 2, acyl-enzyme intermediate is hydrolyzed and acetate
(Product) is released free enzyme is regenerated
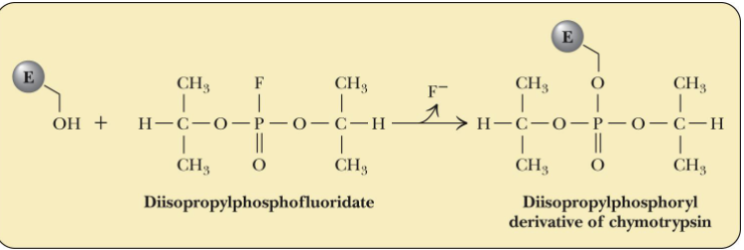
Chymotrypsin inactivated
Chymotrypsin is a serine protease
DIPF inactivates chymotrypsin by reacting with serine-195, verifying the residue is at the active site
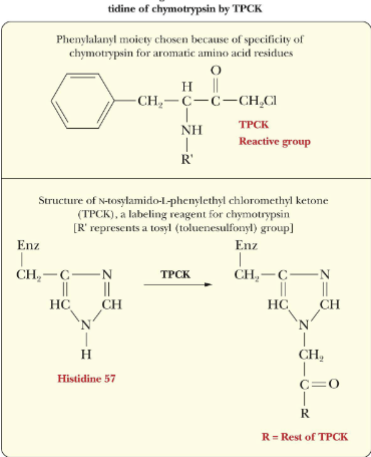
Chymotrypsin TPCK
-H57 is critical for activation of enzyme
-Can be chemically labelled by TPCK (reactive group)
-Ser-195 and H57 are required for activity so they must be close to each other in the active site
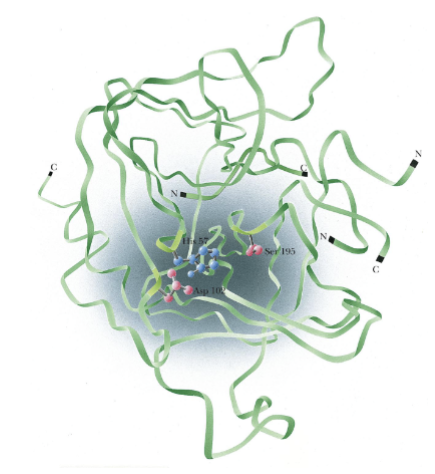
Chymotrypsin (background)
The active site of chymotrypsin shows proximity of 2 reactive a.a.
Results of x-ray crystallography show arrangement of amino acids at active site
Asp-102 is also involved in catalysis at the active site
Folding of chymotrypsin backbone, mostly anti-parallel pleated sheet array, positioning essential amino acids around active-site pocket
Coenzymes
-a non-protein substance that takes part in an enzymatic reaction and is regenerated for further reaction
-organic compounds, many of which are vitamins or metabolically related to vitamins
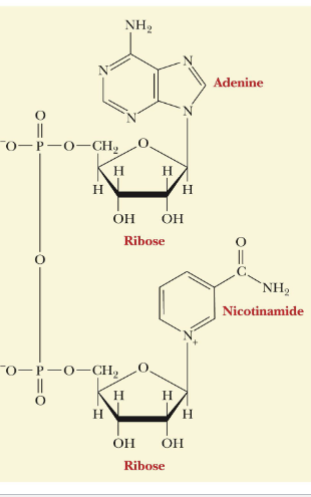
NAD+/NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is used in redox reactions in biology
Contains:
Nicotinamide ring
Adenine ring
2 sugar-phosphate groups
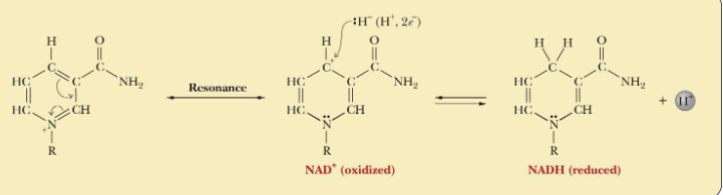
NAD+ to NADH
NAD+ is a two-electron oxidizing agent and is reduced to NADH
Nicotinamide ring is where reduction-oxidation occurs
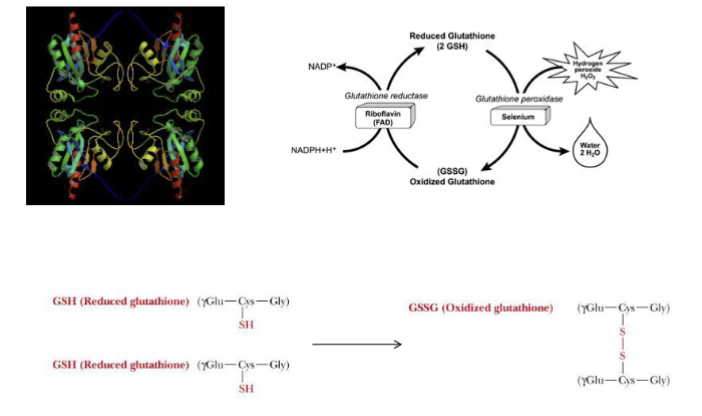
Glutathione Peroxidase