Chapter 9: Immunity Mediated by B Cells and Antibodies
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
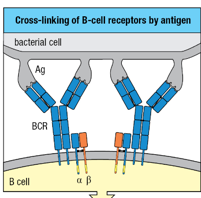
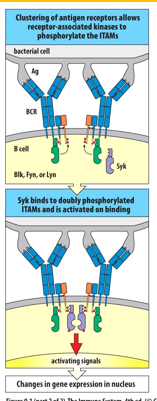
B-cell activation requires cross-linking of the _____________ (two or more receptors)
B-cell receptor
Receptor associated _____________ phosphorylate tyrosine residues in the ITAMs of cytoplasmic tails of Igα (blue) and Igβ (orange).
tyrosine kinases
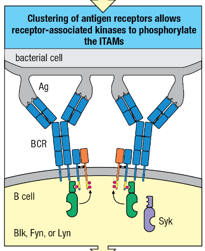
An _________________________________________________ is a conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated in the cytoplasmic tails of receptors.
immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)
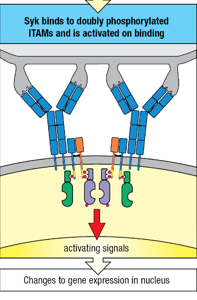
____ binds to the phosphorlated ITAMs of the B-cell receptor Igβ chains.
Syk
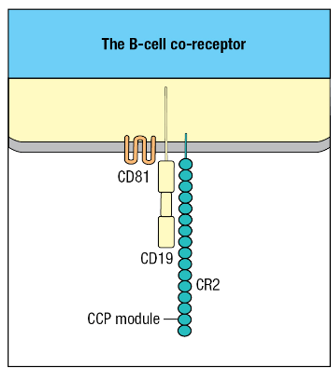
The B cell co-receptor is composed of _____, _____, and _____.
CR2; CD19; CD81
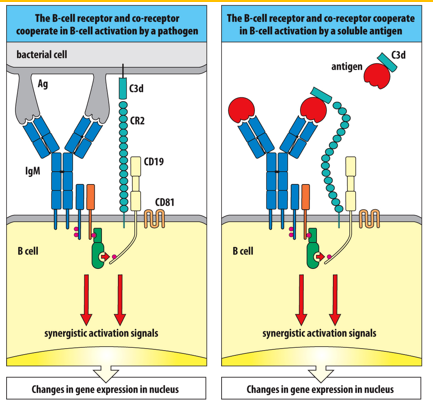
Phosphorylated ____ generates _____________that synergize with those generated by the B-cell receptor.
CD19; intracellular signals
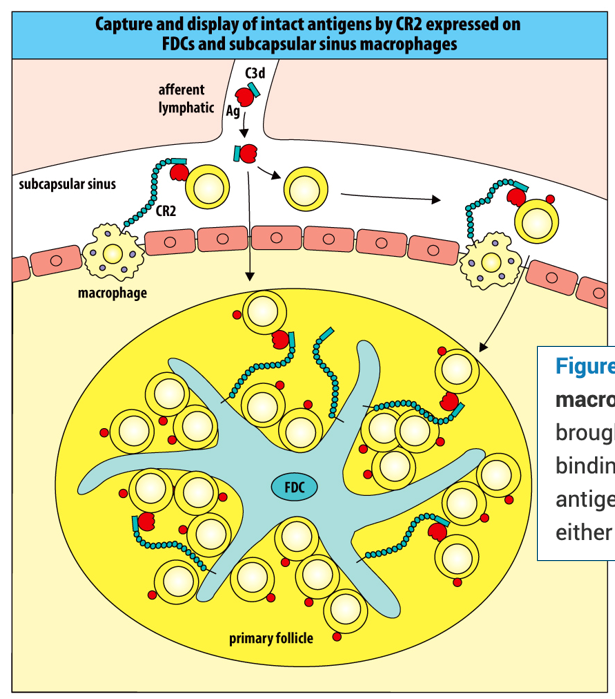
Naive B cells recognize antigens captured by subcapsular sinus macrophages and follicular dendritic cells.
Antigens tagged with C3d are brought to the lymph node from the infected tissue via the afferent lymph. By binding to C3d, CR2 on subcapsular sinus macrophages and FDCs tethers the antigen to the cell surface, where it can be screened by naive B cells arriving either from the blood via a high endothelial venule or in the afferent lymph.
TFH cells help antigen-activated B cells through cell-surface interactions between ________________________ and by the targeted delivery of secreted cytokines to the B-cell surface.
CD40 ligand (TFH cell and CD40 (B cell)
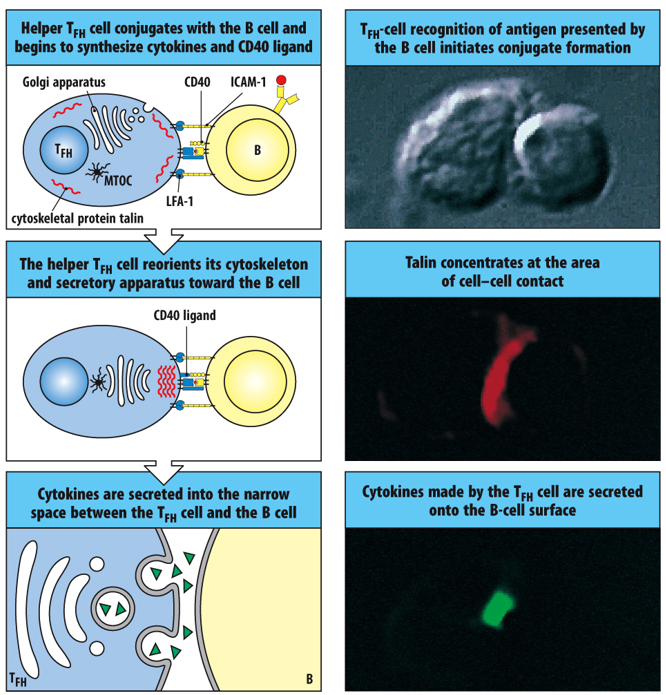
(MTOC) Microtubule-organizing center
Cellular structure responsible for the nucleation, stabilization, and organization of microtubules
Replication of B cells happens in the ________________. B cells start to produce ____ here as well.
medullary cord; IgM
B cells interact with TFH cells in the _____________- where the TFH cells release _________ for further B cell maturation.
boundary zone; cytokines
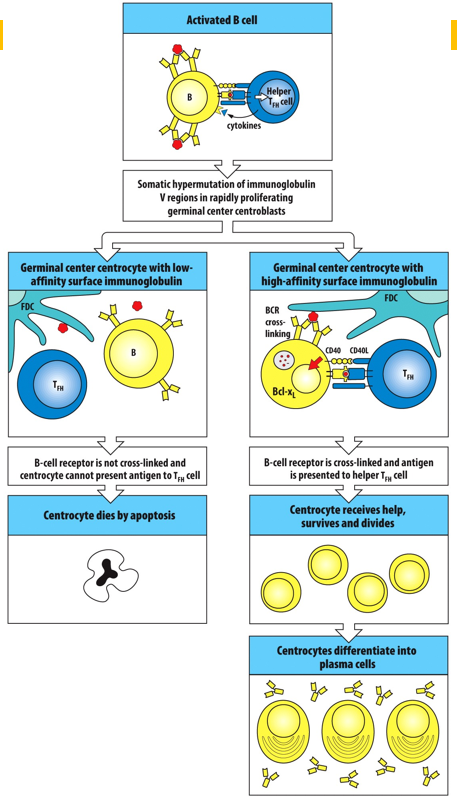
Expansion of antigen-activated B cells in the primary folicule creates the ___________________. This is where _________ and ________ occurs.
germinal center; affinity maturation; class switching
Class switching of B cells is based on ___________ release and interaction.
cytokine
A _____________ is a small, non-dividing B lymphocyte that is found in the germinal centers of secondary follicles.
centrocyte
TFH cell cytokines _____ and _____ promote differentiation of antigen activated B cells into plasma cells (produces antibodies) or memory cells
IL-21; IL10
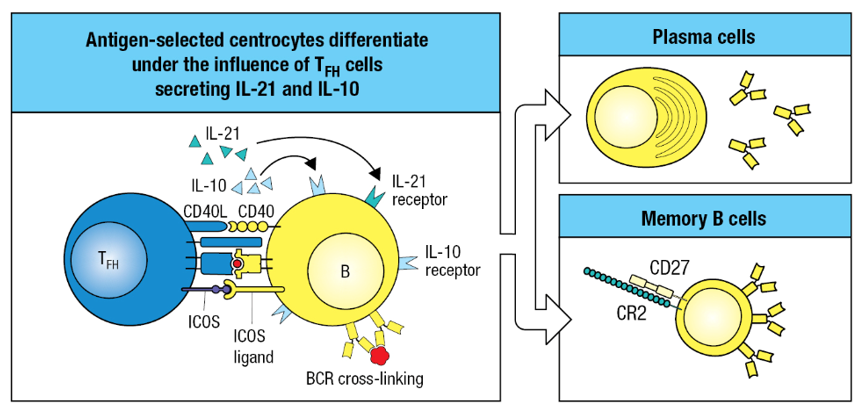
As infection subsides, _____________________ under the influence of the same cytokines into long-lived memory B cells
centrocytes differentiate
____, _______ and monomeric _____ protect the internal tissues of the body
IgM; IgG, IgA
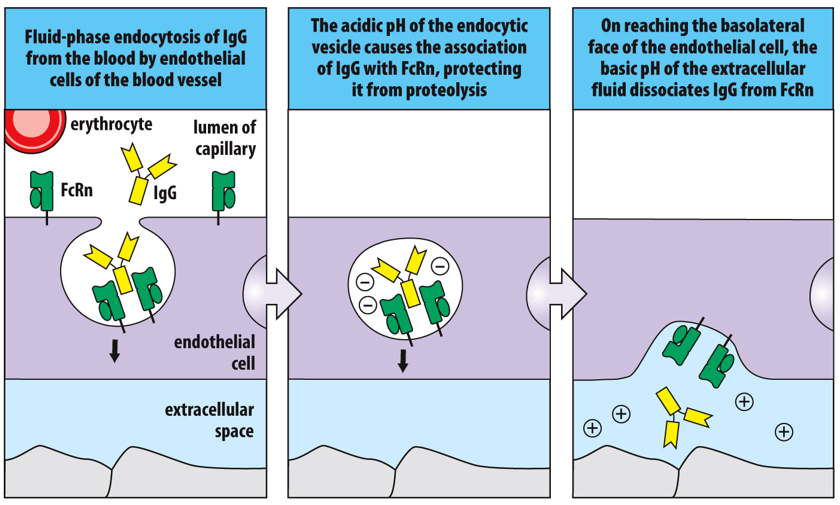
The receptor ___ transports ____ from the bloodstream into the extracellular spaces of the tissues
FcRn; IgG
IgM, IgG, and IgA bind and _________ any _____________ that enter the blood and tissues
neutralize; microorganisms
__________ IgA, and ___________ IgM protect __________________ of the body
Dimeric; pentameric; mucosal surfaces
Transcytosis
Transport of molecules from one side of the epithelium to the other. This involves endocytosis into vesicles
A _________ is made between one _______________________ of either one IgA dimer or one IgM pentamer
disulfide bond; poly-Ig receptor and the J chain
The receptor is called polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (or ____________) because _________________________
poly-Ig receptor; it specifically binds to IgA dimers or IgM pentamers
______ provides a mechanism for rapid killing of ________ and __________.
Functions as a cell-surface receptor of antigen not as a soluble antibody
IgE; parasites; pathogens
____________ contain large granules containing _______________________________________
Mast cells; histamine and inflammatory mediators
________________ that is present on the surface of____________________________________
Fc receptor called FcεRI; mast cells, basophils, and activated eosinophils
Two or more IgE/FcεRI ______________ causes _____________. Can also cause __________
crosslinked; degranulation; allergy
Before and after birth, mothers provide their children with protective _____________
antibodies
During pregnancy ___ from the maternal circulation is transported across the __________________ and delivered directly to the ______________
IgG; placenta by FcRn; fetal bloodstream
Transfer of IgG across placenta into fetal bloodstream by FcRn is so efficient that, at birth, human babies have a level of IgG in their plasma that is as ________________, and with as ______________ of antigen specificities.
high as that of their mothers; wide a range
The transfer of _________________________________________ is an example of the passive transfer of immunity
preformed IgA from mother to child in breast milk
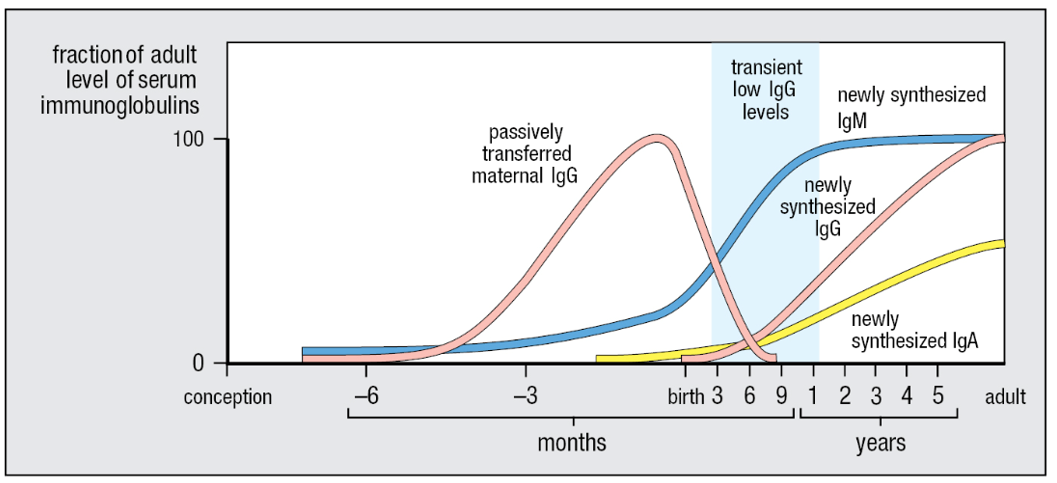
The first year of life is a period when infants have a limited supply of IgG and are particularly vulnerable to infections.
Before birth, high levels of IgG are provided by the mother; after birth, maternally derived IgG declines. Although infants produce IgM before birth, the production of IgG antibodies does not begin for about 6 months. The concentration of IgG in the blood reaches a minimum within the first year and then gradually increases until adulthood.
High-affinity ________________ prevent viruses and bacteria from infecting cells
neutralizing antibodies
Influenza infects ___________ of the respiratory track; IgA dimers are the effective antibody.
epithelial cells
Influenza Hemagglutinin
glycoprotein in the coat of the influenza virus that binds to certain carbohydrates on human cells, the first step in infection of cells with the virus. Changes in the hemagglutinin are the major source of the antigenic shift that heralds a major new influenza pandemic. The protein is called a hemagglutinin because it can agglutinate red blood cells.
Agglutinate
to clump together small particles to form larger particles. Usually refers to the action of an antibody or some other multivalent molecule that cross-links antigens on more than one particle. Such particles are said to be agglutinated. When the particles are red blood cells, the phenomenon is called hemagglutination.
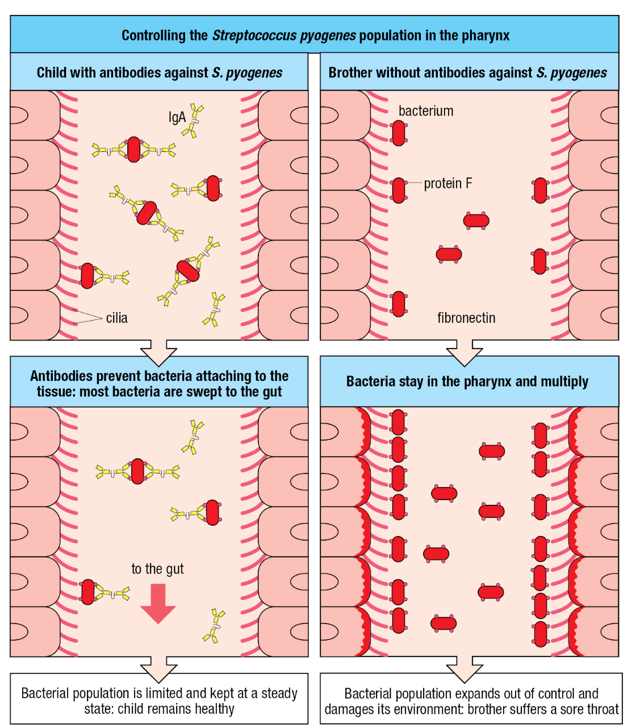
Protein-F binds ___________
fibronectin
Disease-causing bacterial infections at mucosal surfaces are prevented by neutralizing antibodies. The antibodies________________ and _______________________ to bind to the cilia or to attach to the fibronectin in the extracellular matrix, and so they prevent the bacteria from remaining in the pharynx.
coat the bacteria; impair the capacity of protein F of the bacteria
Toxoid
a toxin that has been deliberately inactivated by heat or chemical treatment so that it is no longer toxic but still provokes a protective immune response as a vaccine.
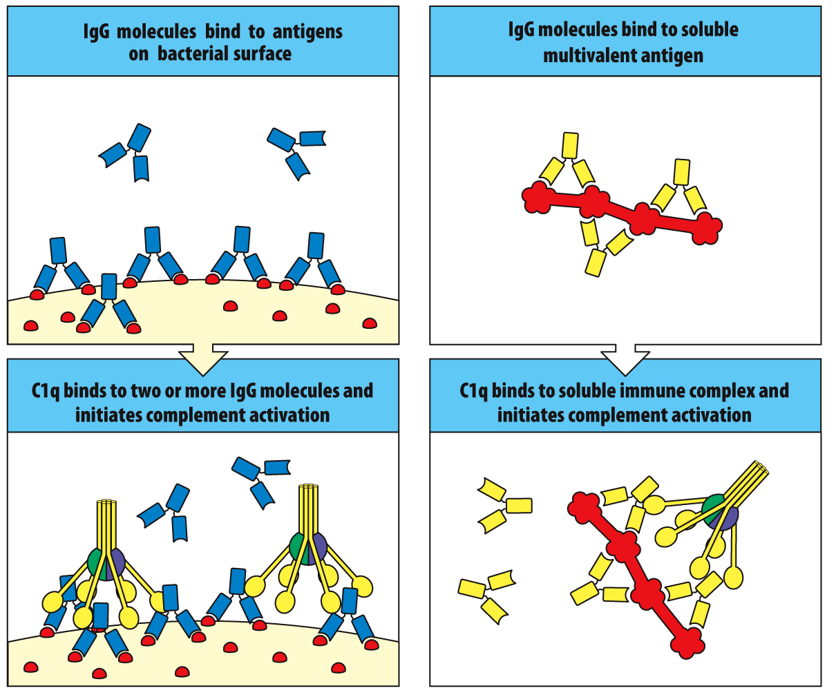
Binding of IgM and IgG (multiple) to antigen on a pathogen’s surface activates complement by the ____________
classical pathway
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
C5-C9 (polymerization of 18 C9 molecules
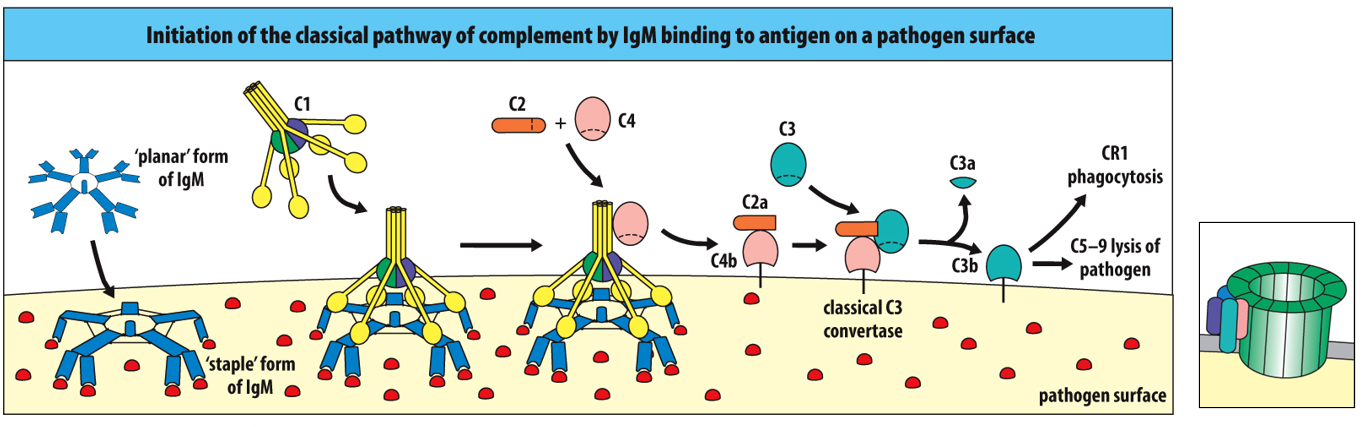
At least ______________ of IgG bound to pathogens or soluble antigens are required to activate the complement cascade.
two molecules
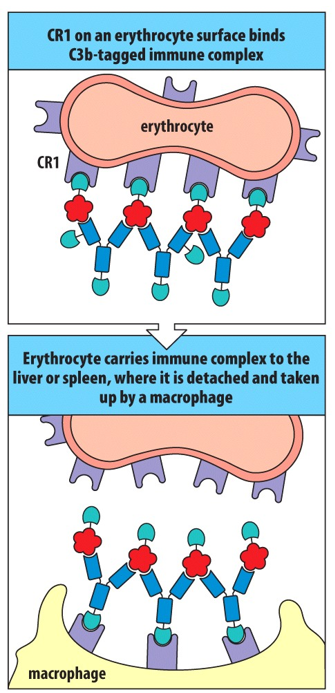
___________________ helps to clear immune complexes from the circulation.
Erythrocyte CR1
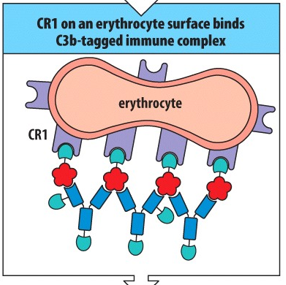
___________________________ can be bound by cells expressing the complement receptor CR1. Most numerous of the cells expressing CR1 is the erythrocyte, or ___________, which outnumbers the leukocytes by about 500 to 1. Thus, most immune complexes become bound to the surface of erythrocytes.
Immune complexes covered with C3b; red blood cell
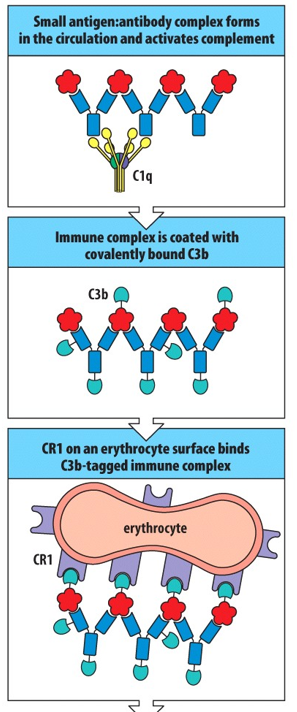
Erythrocytes _________________________ where tissue macrophages remove and degrade the complexes of ______________________ from the erythrocyte surface.
pass through the liver and spleen; complement, antibody, and antigen