BIOL 2161 final exam
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
how did we measure things in physiology lab?
they were recorded from the surface or interior of the body and reflect underlying physiological processes
what is a finger pulse transducer?
accessory devices that convert a mechanical signal into an analog signal sent to the PowerLab hardware which sends a digital signal to the LabChart computer software
what does the finger pulse transducer specifically measure?
converts force applied to an active surface into an electric analog signal. When recorded over time results in a characteristic arterial pulse waveform
what did we measure for the somatic nervous system and skeletal muscle physiology lab?
EMG and grip strength
What is EMG?
electromyography
what does EMG measure?
electrical activity of muscles
what is an evoked contraction?
muscle contraction when a electrical stimulation was applied
what is conduction velocity?
action potential moves along nerve fiber
what is fatigue
inability to maintain power output or force during repeated muscle contractions
what is pseudo fatigue
feeling of fatigue not caused by a depletion pf physiological or biochemical energy
what is a motor unit?
A single neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
what is directly proportional to the number of motor units recruited during contraction?
contraction strength of a whole muscle
what is an example of motor units and muscle contraction correlation?
as the weight got heavier it required more force to hold the weight so more motor units were recruited
what is an EMG
electromyogram
what does an electromyogram measure?
records the summed electrical activity produced by active muscle cells during a contraction
what does an electromyogram use to measure muscle contraction?
surface electrodes
what are raw EMG signals?
the chaotic bursts of bipolar spikes with symmetric distribution of positive and negative amplitudes
what is root mean square?
a common processing method that first inverts the negative-going portions of the raw EMG and then smooths the signal
- does not change values just makes it easier to quantify data
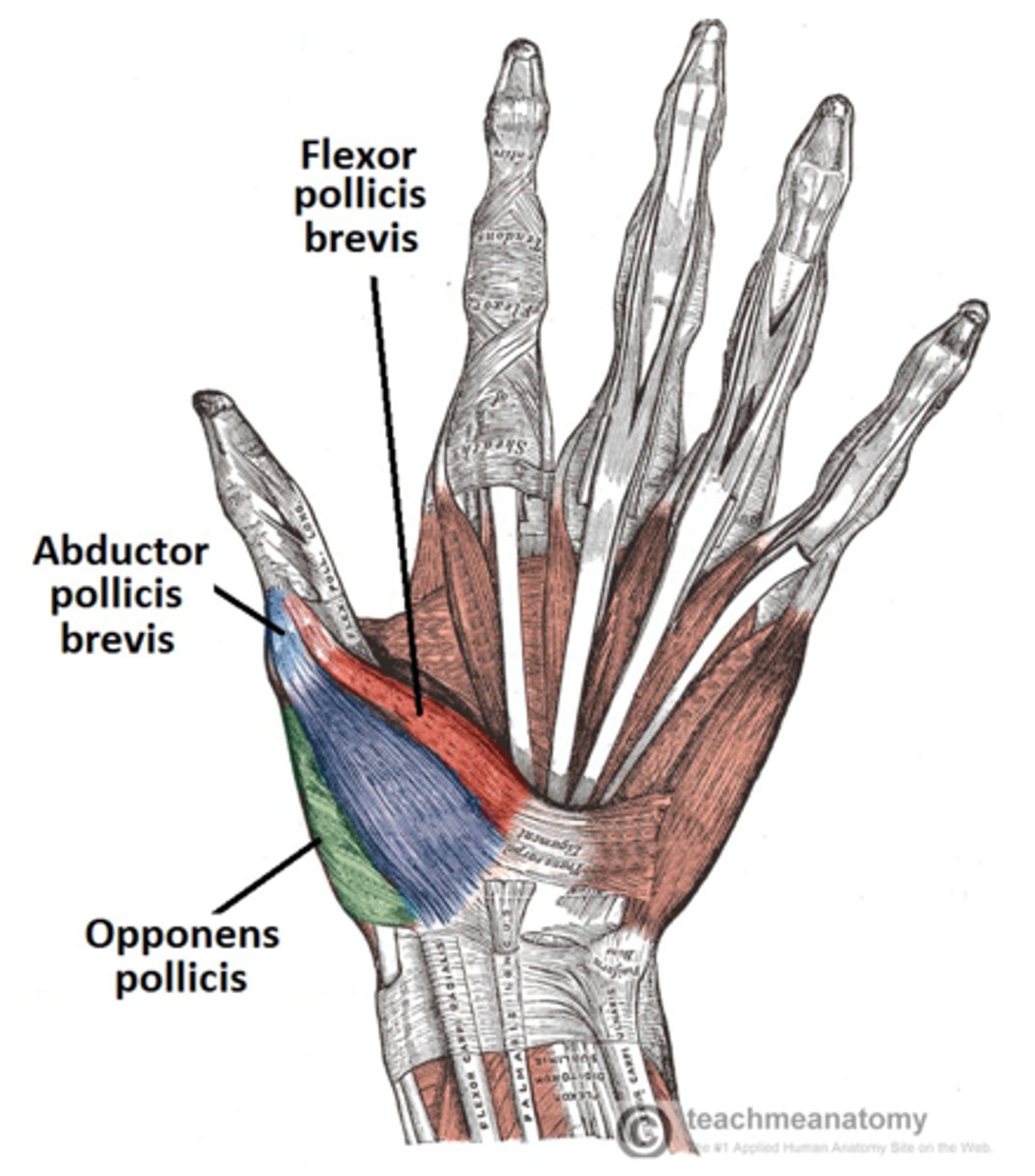
what muscle did we evoke contraction of?
abductor pollicis brevis
how did we evoke contraction of this muscle?
by stimulating the median nerve
where is the abductor pollicis brevis muscle located
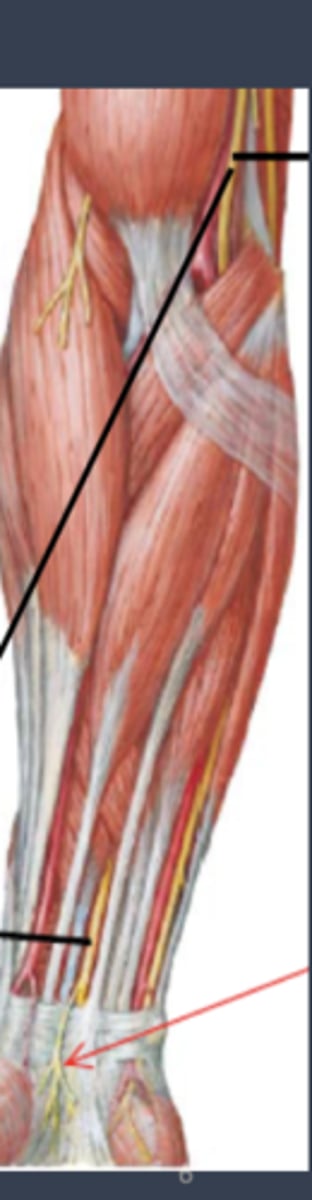
where is the median nerve located
what is latency?
the time to EMG onset
why does the stimulation of the median nerve at the elbow require more pressure?
because the nerve is not as close to the surface
What does ECG mean?
electrocardiogram
What is an element?
a record of cardiac electrical activity over time obtained with recording electrodes place on the body surface
what is normal sinus arrhythmia
electrical activity that occurs most of the time
what are the peaks of the normal ECG wave?
P wave, QRS complex, T wave
label ECG wave
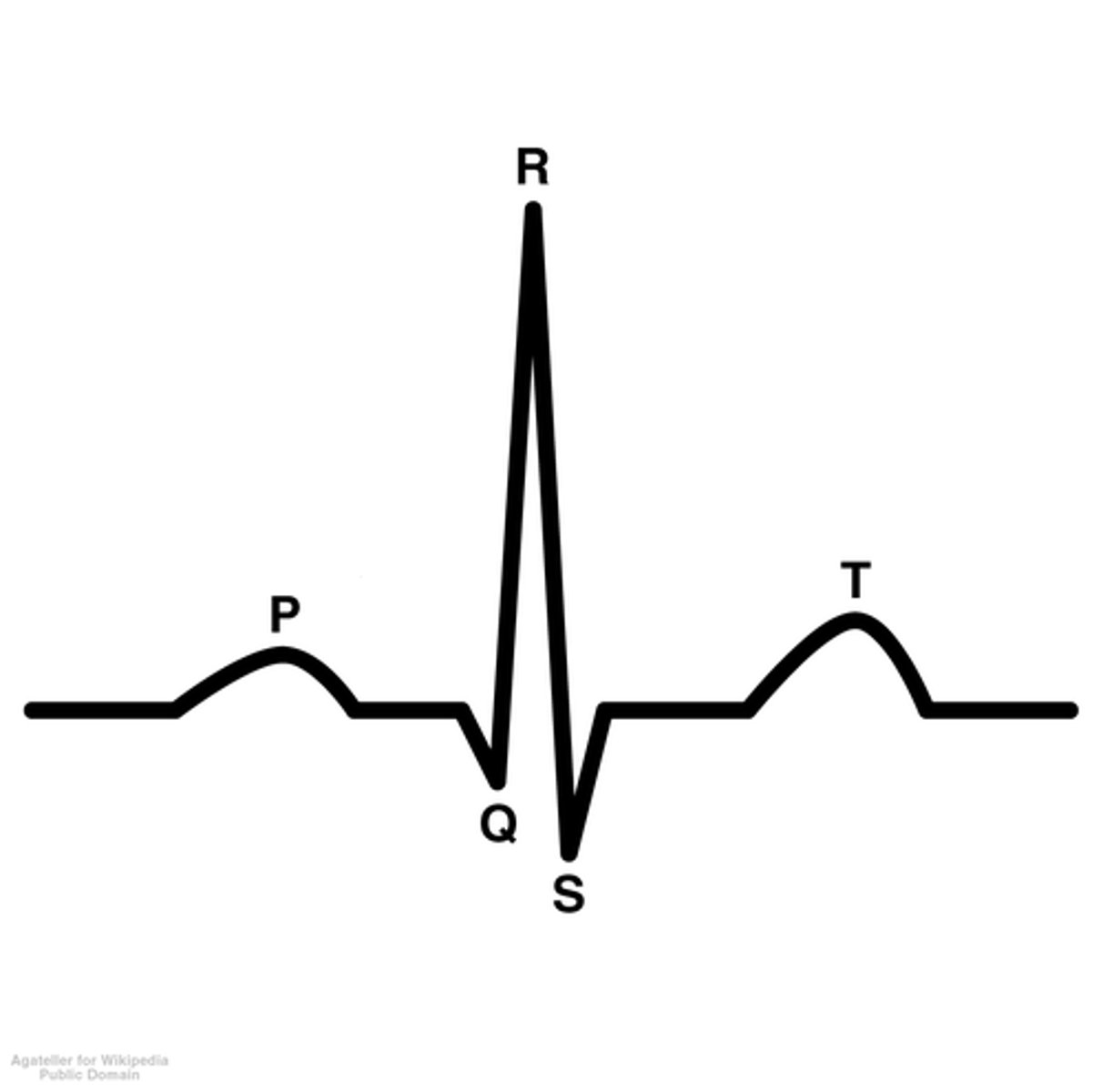
what is the p wave?
atrial depolarization (contraction)
what is the QRS complex?
ventricular depolarization (contraction)
what is the t wave?
ventricular repolarization
- ventricles start to relax
what is first heart sound lub stand for?
the av valve closing
what does the Av valve seperate?
the atria from the ventricles
when does the lub sound happen?
after atria contract and just before ventricles contracting
what is the second heart sound dub stand for
the semilunar valves closing
what does the semilunar valves seperate?
spearates ventricles from arteries
what happens when the semilunar valve closes?
at the end of ventricular systole when pressure in the ventricle decreases
where on the finger pulse wave form is the cardiac cycle?
peak to peak
- one pulse amplitude to the next pulse amplitude
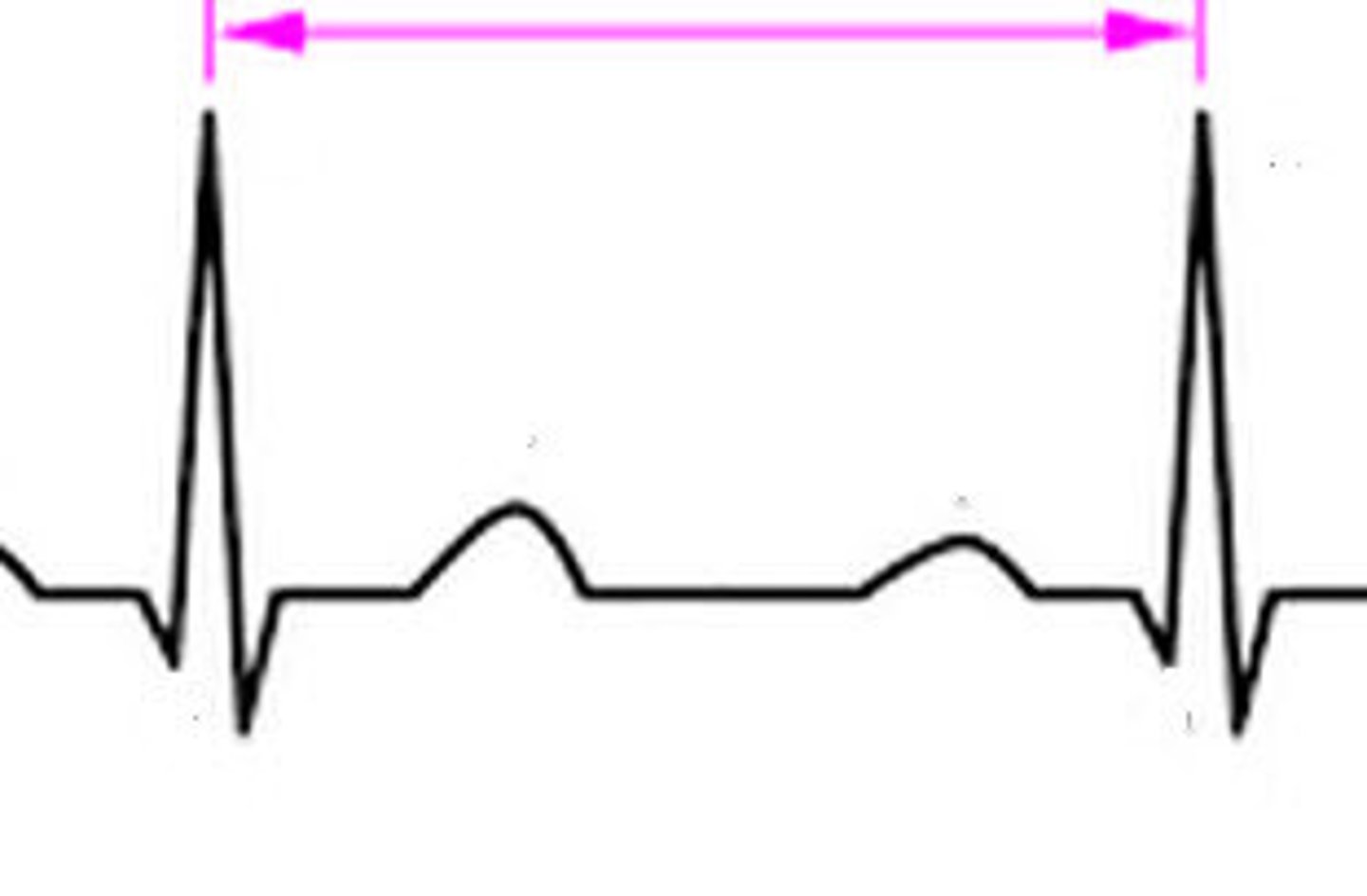
where do you measure pulse amplitude on a finger pulse wave?
trough to peak
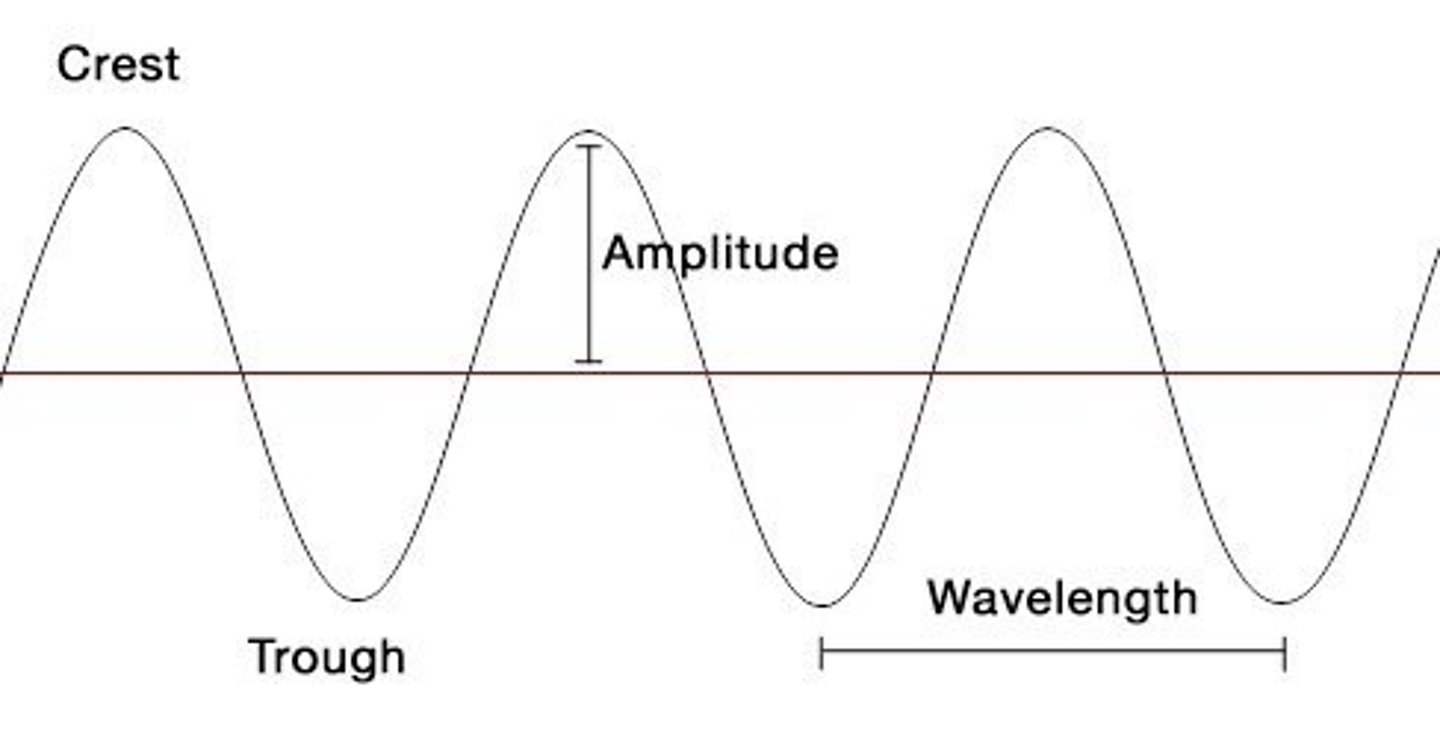
how would you measure pulse duration on a finger wave from?
trough to trough
what does the thoracic cavity house?
heart, lungs, esophagus, and thymus
why does blood pressure in the large arteries vary?
due to intermittent pumping action of the heart
what is systolic pressure?
the highest arterial blood pressure recorded during a cardiac cycle
what is diastolic pressure?
the lowest arterial blood pressure recorded during a cardiac cycle
what produces kortokoff sounds?
turbulent blood flow
what estimates systolic pressure?
when korotkoff sounds are first heard
what estimates diastolic pressure?
when korotkoff sounds are not heard anymore
what are baroreceptors?
pressure receptors
what do arterial baroreceptors do?
short-term regulatory mechanism that reduces minute-to-minute variation of arterial pressure
does someone with high blood pressure mean their baroreceptors are not working?
NO
is the baroreceptor mechanism strong long term?
NO
what is the baroreceptor reflex?
detects a drop in arterial pressure which triggers mass sympathetic discharged upon which effectors act to restore arterial pressure
during exercise what happens to the blood flow?
blood flow to the skeletal muscles are increased
how fast will the heart pump?
as fast as it needs to
- increases during exercise and decreases during relaxing
what does every graph need?
- label of x and y axis with appropriate unites
- figure legend that explains what is being shown in the figure
when do you use a bar graph?
when there are independent measures that are unrelated from one another; where time is not an issue
when do you use a line graph?
when time is a factor --> this means all measurements are related to one another
What is the amplitude of a wave?
maximum vertical distance of a periodic wave
what does the pulse amplitude correspond to
the magnitude or strength of a recorded signal
what is an independent variable?
variable that is manipulated by the experimenter
what is the dependent variable?
variable that is affected by changes in the independent variable
how do you calculate heart rate?
60/ cardiac cycle
what are the units for pulse amplitude?
millivolt (mV)
what are the units for cardiac cycle?
seconds
what are the units for heart rate
beats per minute
what is a cardiac cycle?
The period from the end of one ventricular contraction to the end of the next ventricular contraction.
what side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circulation?
right
what side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation?
left
what is responsible for the normal sinus rhythm?
pacemaker cells of the SA node
what happens when you stand up from laying spine?
gravity causes blood to pool in the lower extremities
what happens when blood pools in the lower extremities?
cardiac output decreases and so does blood pressure
what is cardiac output?
the volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (L/min)
why is CO regulated
to match blood flow rate (perfusion) with metabolic demand of the tissues
what happens to the heart rate during deep breathing?
it fluctuates
when is the heart rate increased during deep breathing?
during inspiration
- lungs expand and there is decrease pressure in the thoracic cavity. This inhibits the vagus nerve
when does the heart rate decrease during deep breathing?
during exhalation
- there is increase pressure inside the thoracic cavity and the receptors pick up this change and activates vagus activity
would cardiac output vary during respiration?
yes
- the heart rate and pulse amplitude fluctuates during breathing
- increase in heart rate means increase in cardiac out put --> the faster the heart beats, the more blood pumped out
-increase in pulse amplitude means strong contracts of the heart
what happens when you stand up from laying down to blood pressure and heart rate?
blood pressure decreases due to pooling in legs. Baroreceptors activate the sympathetic nervous system when increases the heart rate. The increase in heart rate makes sure blood reaches other place like the brain and organs.
when does pseudo fatigue happen?
when the individual's eyes were closed when asked to maintain 40% grip strength
- when eyes are open they can maintain this grip strength
the skeletal muscle contraction is dependent on what?
on input from somatic nervous system
whole skeletal muscles are bundles of
elongated muscle fibers packaged together by layers of connective tissue
skin preparation for electrode attachment
- use abrasive gel to gently remove dead skin
- alcohol swab to clean away dead skin cells and dirt
- allow skin to dry
what does electrode cream do?
improve electrode contact
what is independent variable of voluntary muscle contraction of increasing weights
weight that is being added
what is the dependent variable of voluntary muscle contraction of increasing weights
RMS amplitude
what is the threshold mean in evoked EMG stimulus
the lowest stimulus amplitude able to evoke a noticeable contraction
what is the independent variable of the condition velocity of the median nerve
stimulus location
what is the dependent variable of the condition velocity of the median nerve
latency (time of EMG onset)
how do you calculate conduction velocity
distance between stimulation sites / difference between latencies
what were the different stimulation sites on the arm for the location of median nerve stimulation?
wrist and elbow
what does EMG amplitude measure and how does it relate to motor unit recruitment
EMG amplitude is the relative amount of contractile force
if there is a higher amplitude this means the muscle has a strong contraction and needs to recruit motor units
what is the PR interval?
the interval of time between the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex
why is there a delay between the P wave and the QRS complex
the AV node delays its signal to the ventricles to allow all the blood from the atria to flow into the ventricles before contracting
described how blood pressure change throughout the cardiac cycle?
- the blood pressure increases when ventricles eject blood into the arteries ; there is more blood in the arteries
- blood pressure decreases when ventricles relax because there is no blood in the arteries and there is constant outflow
what is the only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles
Av node
what is isovolumic ventricular contraction?
when there is an increase in ventricular pressure but no change in ventricular volume
-begins when AV valves close
what is isovolumic ventricular relaxation?
decrease in ventricular pressure but no change in ventricular volume
- begins when semilunar valves close
what physiological event occurs during the latency from the beginning of the QRS complex to the beginning of the finger pulse
QRS complex represents ventricular contraction, when the ventricles contract blood is ejected into the arteries and blood pressure is increased
- this can be felt as a pulse in the finger
stroke volume
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction.