Atomic Structure, Spectra, and Quantum Mechanics in Chemistry
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Atomic Number
Number of Protons (I.D. of the Atom)-----Also # of Electrons in an uncharged atom.
Mass Number
Number of Protons AND Neutrons.
Isotopes
Atoms with different numbers of neutrons.
Sodium-23
The M.C.I (most common isotope).
Sodium-22
An isotope of Sodium with a different mass number.
Ions
*no charge written if neutral (protons and electrons equal each other).
Anion
Formed by gaining electron(s) ---> negative.
Cation
Formed by losing electron(s) ---> positive.
Number of Neutrons
Mass # - Atomic #.
Planck's Equation
E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is frequency.
Planck's Constant
6.626 x 10^-34 J s.
Energy
Expressed in joules or kilojoules.
1 kJ
1 x 10^3 J.
1 cal
4.184 J.
1 J
Equivalent to a 10 watt light bulb for 1/10 of a second.
180 Calorie glass of soda
Equivalent to 180,000 cal.
Energy of green light
What is the energy of green light that has a wavelength of 550nm?
Kinetic Energy (KE)
Energy possessed by an object due to its motion.
Potential Energy (PE)
Energy possessed by an object due to its position or state.
Chemical Potential Energy
Energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds.
180,000 cal = 753,120 J
This is the energy conversion for the soda.
Time to light bulb
75,312 sec to light a 10 watt bulb with energy from the soda.
Atomic spectra
Consist of discrete lines given off at specific wavelengths.
White light
Can be broken down into its color components by a prism or diffraction grating.
Sodium flame test
Has two distinct lines at 589.0 nm and 589.6 nm.
Qualitative TEST
Certain elements give off particular wavelengths of light.
Exciting electrons
Involves moving electrons from one energy level to another, which is quantized.
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an electron in an atom.
Copper flame
Produces a blue/green color.
Lithium flame
Produces a red color.
Rydberg Constant (RH)
2.180 x 10^-18 Joules (J).
Planck's constant (h)
6.626 x 10^-34 J s.
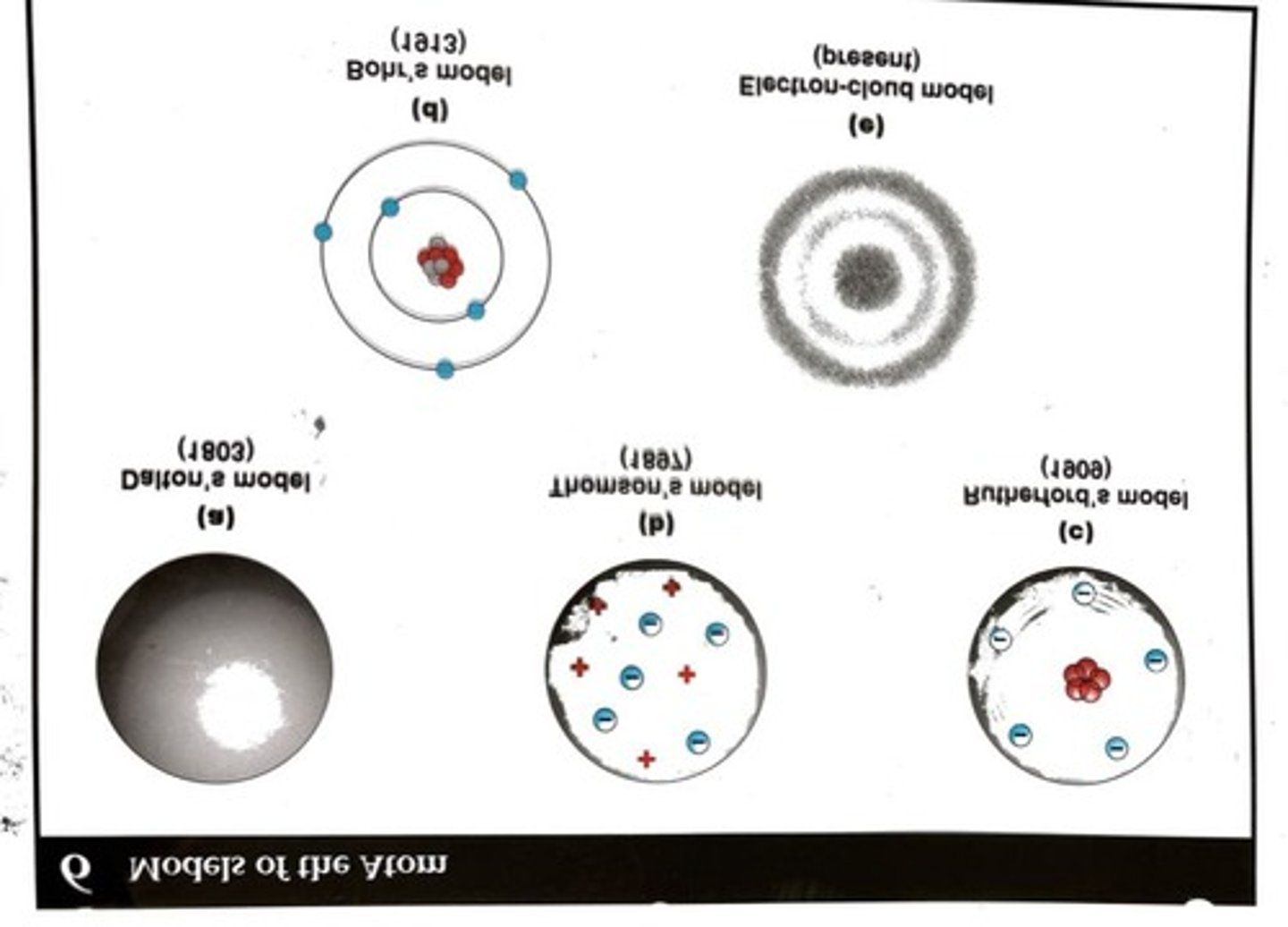
Bohr's model
Great for the hydrogen atom, but has limitations for more complex atoms.
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
It is impossible to define the precise position of an electron in an atom at a given instant.
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Also known as the Electron Cloud Model, where electrons occupy orbitals.
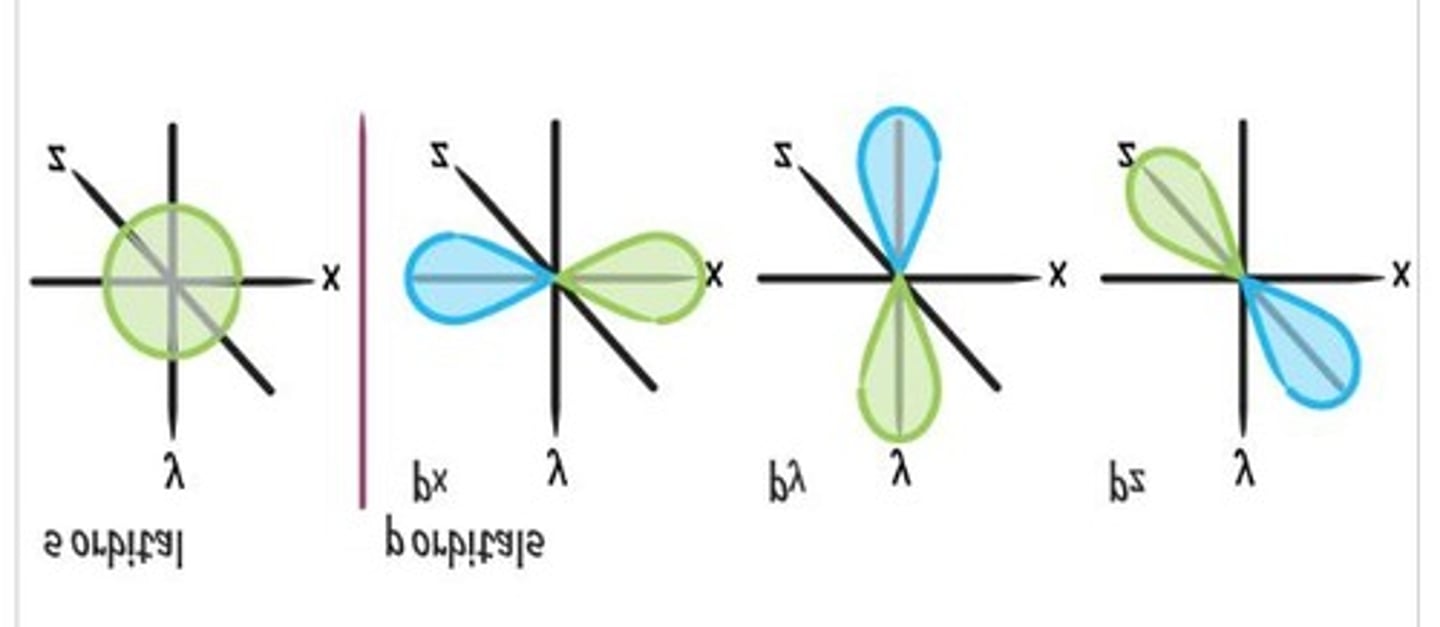
Orbitals
3D areas where electrons have the highest probability of existing.
Balmer Series
A series of spectral lines of hydrogen.
Energy levels (n)
Quantized states that electrons can occupy, such as n=1, n=2, n=3, etc.
Spectral lines
Result from electrons dropping back down to ground state and releasing absorbed energy.
Diffraction grating
Used to see atomic line spectra.
Flame Tests
Laboratory tests to identify elements based on the color of flame produced.
Louis deBroglie
Proposed that if light can behave as particles and waves, then electrons can too.
Error in Bohr's equation for Helium
Calculating energies results in a 5% error, compared to 0.1% for Hydrogen.